Mn-doped CeO2 Nanorod Supported Au Catalysts for Dehydrogenation of Ethane with CO2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. TPR Studies
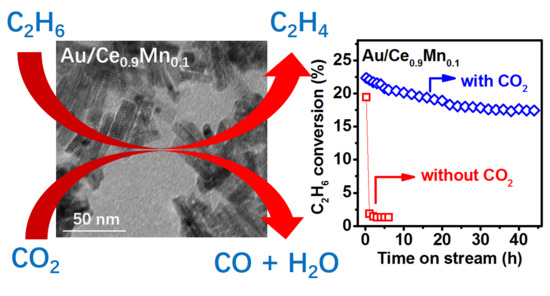
2.3. Catalytic Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterizations
3.3. Catalyst Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nawaz, Z. Light alkane dehydrogenation to light olefin technologies: A comprehensive review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2015, 31, 413–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, J.J.H.B.; Ruiz-Martinez, J.; Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Catalytic dehydrogenation of light alkanes on metals and metal oxides. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10613–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.B.; Zhu, Z.H. Catalytic conversion of alkanes to olefins by carbon dioxide oxidative dehydrogenation. Energy Fuel 2004, 18, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.B.; Park, S.E. Carbon dioxide utilization as a soft oxidant and promoter in catalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9419–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Park, S.E.; Reddy, B.M. CO2 as a soft oxidant for oxidative dehydrogenation reaction: An eco benign process for industry. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 16, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanga, M.A.; Rezaei, F.; Jawad, A.; Fitch, M.; Rownaghi, A.A. Oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propylene with carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 220, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Okamura, M.; Ikenaga, N.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, T. Dehydrogenation of ethane over gallium oxide in the presence of carbon dioxide. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Kajita, C.; Okumura, K.; Ikenaga, N.; Nishitani-Gamo, M.; Ando, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Suzuki, T. Role of carbon dioxide in the dehydrogenation of ethane over gallium-loaded catalysts. J. Catal. 2001, 203, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Lei, T.Q.; Miao, C.X.; Hua, W.M.; Yue, Y.H.; Gao, Z. Ga2O3/NaZSM-5 for C2H6 dehydrogenation in the presence of CO2: Conjugated effect of silanol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Miao, C.X.; Hua, W.M.; Yue, Y.H.; Gao, Z. Cr/ZSM-5 for ethane dehydrogenation: Enhanced catalytic activity through surface silanol. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 532, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.Q.; Miao, C.X.; Hua, W.M.; Yue, Y.H.; Gao, Z. Silica-doped TiO2 as support of gallium oxide for dehydrogenation of ethane with CO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 177, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Halasi, G.; Solymosi, F. Reactions of ethane with CO2 over supported Au. J. Catal. 2015, 330, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Halasi, G.; Bánsagi, T.; Solymosi, F. Reactions of propane with CO2 over Au catalysts. J. Catal. 2016, 337, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.Q.; Miao, C.X.; Hua, W.M.; Yue, Y.H.; Gao, Z. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane with CO2 over Au/CeO2 Nanorod catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Nelson, N.C.; Sadow, A.D.; Slowing, I.I.; Overbury, S.H. Role of CO2 as a soft oxidant for dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene over a high-surface-area ceria catalyst. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6426–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.C.; Yao, Y.F.Y. Ceria in automotive exhaust catalysts: I. Oxygen storage. J. Catal. 1984, 86, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Gao, H.J.; Shaikhutdinov, S.; Freund, H.J. Gold supported on well-ordered ceria films: Nucleation, growth and morphologh in CO Oxidation reaction. Catal. Lett. 2007, 114, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. The role of Au, Cu & CeO2 and their interactions for an enhanced WGS performance. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 187, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H. Co3O4@CeO2 Core@Shell Cubes: Designed synthesis and optimization of catalytic properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 4469–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhu, B.; Cao, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wu, S. Comparative study on catalytic performances for low-temperature CO oxidation of Cu-Ce-O and Cu-Co-Ce-O catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2008, 124, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.S.; Yang, R.T.; Chang, R. MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 51, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delimaris, D.; Loannides, T. VOC oxidation over MnOx-CeO2 catalysts prepared by a combustion method. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataswamy, P.; Jampaiah, D.; Mukherjee, D.; Aniz, C.U.; Reddy, B.M. Mn-doped ceria solid solutions for CO oxidation at lower temperatures. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Sayai, A.; Adnot, A.; Larahi, F. Composition-activity effects of Mn-Ce-O composites on phenol catalytic wet oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 32, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2884–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.S.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, Y.M.; Fan, K.N.; Cao, Y. Morphology effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.J.; Iwamoto, S.; Hosokawa, S.; Wada, K.; Kanai, H.; Inoue, M. Effects of Mn content on physical properties of CeOx-MnOy support and BaO-CeOx-MnOy catalysts for direct NO decomposition. J. Catal. 2011, 277, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, A.D.; Perera, S.D.; Tan, K.; Chabal, Y.; Balkus, K.J. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of Y-doped CeO2 nanorods. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Norby, P.; Krumeich, F.; Okamoto, H.; Nesper, R.; Fjellvag, H. Synthesis and properties of layered-structured Mn5O8 nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larachi, F.; Pierre, J.; Adnot, A.; Bernis, A. Ce 3d XPS study of composite CexMn1−xO2−y wet oxidation catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 195, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.D.; Lee, J.S. Effects of pretreatment conditions on CO oxidation over supported Au catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.F.; Chen, J.L.; Li, Y.G.; Xu, Y.D.; Shen, W.J. Complete oxidation of formaldehyde over Ag/MnOx-CeO2 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, A.M.; Pantaleo, G.; Longo, A.; Carlo, G.D.; Casaletto, M.P.; Liotta, F.L.; Deganello, G. Relationship between structure and CO oxidation activity of ceria-supported gold catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Muratsugu, S.; Ishiguro, N.; Tada, M. Ceria-doped Ni/SBA-16 catalysts for dry reforming of methane. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.J.; Tang, H.D.; Zhou, Y.P.; Han, W.F.; Liu, H.Z.; Li, X.N.; Li, Y. Direct synthesis of ruthenium-containing ordered mesoporous carbon with tunable embedding degrees by using a boric acid-assisted approach. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.X.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Si, R.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H.P.; Liu, H.C.; Yan, C.H. Shape-selective synthesis and oxygen storage behavior of ceria nanopolyhedra, nanorods, and nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24380–24385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Catalysts | SBET (m2/g) | Ce3+ Percent | Surface Ce/Mn Ratio | Mn2+ in Total Mn (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au/CeO2 | 66 | 28.0 | - | - |
| Au/Ce0.95Mn0.05 | 65 | 16.7 | 15.8 | - |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 | 67 | 16.5 | 9.8 | - |
| Au/Ce0.8Mn0.2 | 62 | 7.9 | 4.6 | 8.0 |
| Au/Ce0.7Mn0.3 | 59 | 6.6 | 3.3 | 5.3 |
| Au/Ce0.6Mn0.4 | 62 | 6.3 | 1.9 | 3.4 |
| Au/Mn2O3 | 3 | - | - | 1.8 |
| Catalysts | Total Reducible Species | Cerium Species | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | H2 Consumption (mmol/g) | H2 Consumption (mmol/g) | |
| Au/CeO2 | 50–220 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Au/Ce0.95Mn0.05 | 50–210 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 | 50–270 | 0.52 | 0.33 |
| Au/Ce0.8Mn0.2 | 50–340 | 0.73 | 0.28 |
| Au/Ce0.7Mn0.3 | 50–350 | 1.02 | 0.26 |
| Au/Ce0.6Mn0.4 | 50–350 | 1.42 | 0.24 |
| Au/Mn2O3 | 200–430 | 5.50 | - |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 1 | 50–270 | 0.24 | 0.12 |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 2 | 50–270 | 0.23 | 0.12 |
| Catalysts | Conversion (%) 2 | Selectivity (%) 2 | C2H4 Yield (%) 2 | TOF 4 (h−1) | Carbon Balance (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2H4 | |||||
| Blank | 0.9(0.9) | 26.5(25.7) | 73.5(74.4) | 0.7(0.7) | − | 99.3 |
| Au/CeO2 [14] | 17.2(17.1) | 2.4(2.1) | 97.6(97.9) | 16.8(16.7) | 40.8 | 94.0 |
| Au/Ce0.95Mn0.05 | 20.4(19.9) | 2.0(1.8) | 98.0(98.2) | 20.0(19.5) | 48.4 | 93.0 |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 | 22.7(20.6) | 2.0(1.7) | 98.0(98.3) | 22.2(20.3) | 53.9 | 92.7 |
| Au/Ce0.8Mn0.2 | 22.4(19.6) | 2.3(1.9) | 97.7(98.1) | 21.9(19.2) | 53.2 | 95.7 |
| Au/Ce0.7Mn0.3 | 20.2(16.9) | 2.1(1.9) | 97.9(98.1) | 19.8(16.5) | 48.0 | 95.7 |
| Au/Ce0.6Mn0.4 | 17.3(14.4) | 2.2(2.2) | 97.8(97.8) | 16.9(14.1) | 41.1 | 95.5 |
| Au/Mn2O3 | 16.4(4.2) | 1.8(5.5) | 98.2(94.5) | 16.1(4.0) | 38.9 | 94.2 |
| Ce0.9Mn0.1 | 10.2(8.8) | 3.8(3.3) | 96.2(96.7) | 9.8(8.5) | − | 93.0 |
| Au/CeO2 3 [14] | 14.1(1.5) | 5.9(19.8) | 94.1(80.2) | 13.2(1.2) | 33.5 | 95.0 |
| Au/Ce0.9Mn0.1 3 | 19.4(1.3) | 29.8(20.0) | 70.2(80.0) | 13.6(1.0) | 46.1 | 92.4 |
| Ga2O3/ZSM-5 [9] | 25.3(14.6) | 6.1(5.4) | 91.7(92.0) | 23.2(13.4) | 5.3 | − |
| Cr2O3/ZSM-5 [10] | 65.5(61.3) | 24.3(20.9) | 75.4(78.9) | 49.4(48.4) | 20.0 | − |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, T.; Guo, H.; Miao, C.; Hua, W.; Yue, Y.; Gao, Z. Mn-doped CeO2 Nanorod Supported Au Catalysts for Dehydrogenation of Ethane with CO2. Catalysts 2019, 9, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020119
Lei T, Guo H, Miao C, Hua W, Yue Y, Gao Z. Mn-doped CeO2 Nanorod Supported Au Catalysts for Dehydrogenation of Ethane with CO2. Catalysts. 2019; 9(2):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020119
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Tianqi, Hongyao Guo, Changxi Miao, Weiming Hua, Yinghong Yue, and Zi Gao. 2019. "Mn-doped CeO2 Nanorod Supported Au Catalysts for Dehydrogenation of Ethane with CO2" Catalysts 9, no. 2: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020119
APA StyleLei, T., Guo, H., Miao, C., Hua, W., Yue, Y., & Gao, Z. (2019). Mn-doped CeO2 Nanorod Supported Au Catalysts for Dehydrogenation of Ethane with CO2. Catalysts, 9(2), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020119