Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts
Abstract
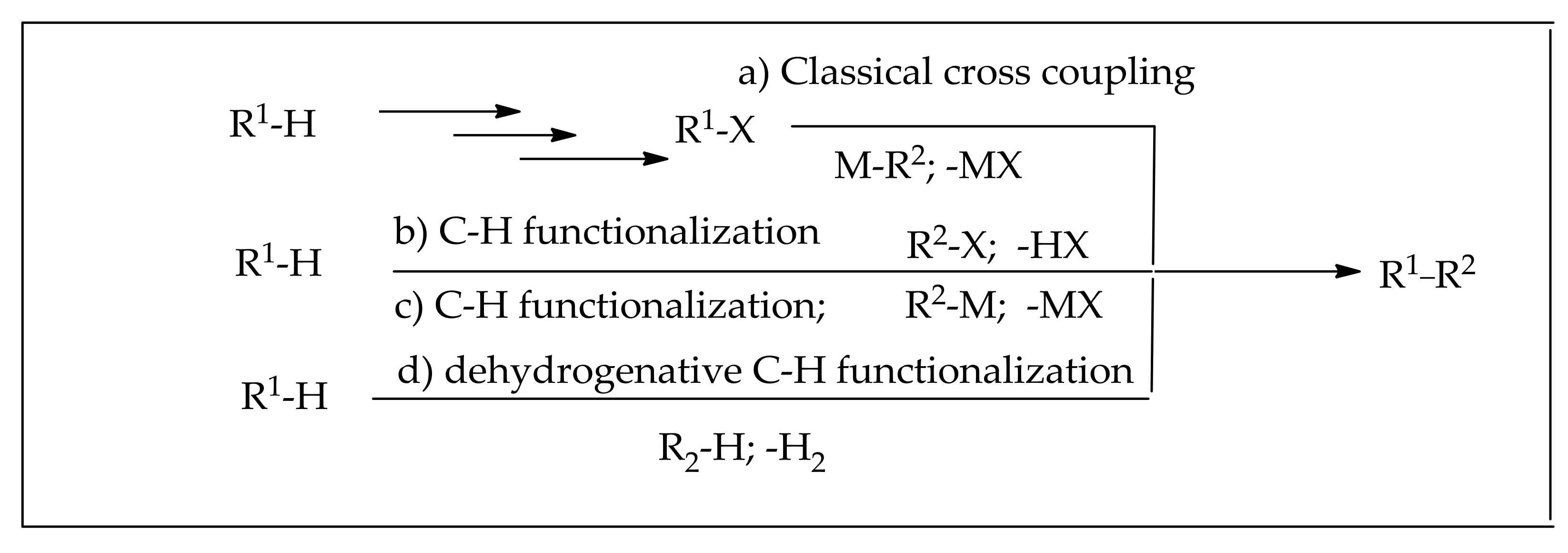
:1. Introduction
2. Ruthenium-Catalysed C–H Bond Arylation
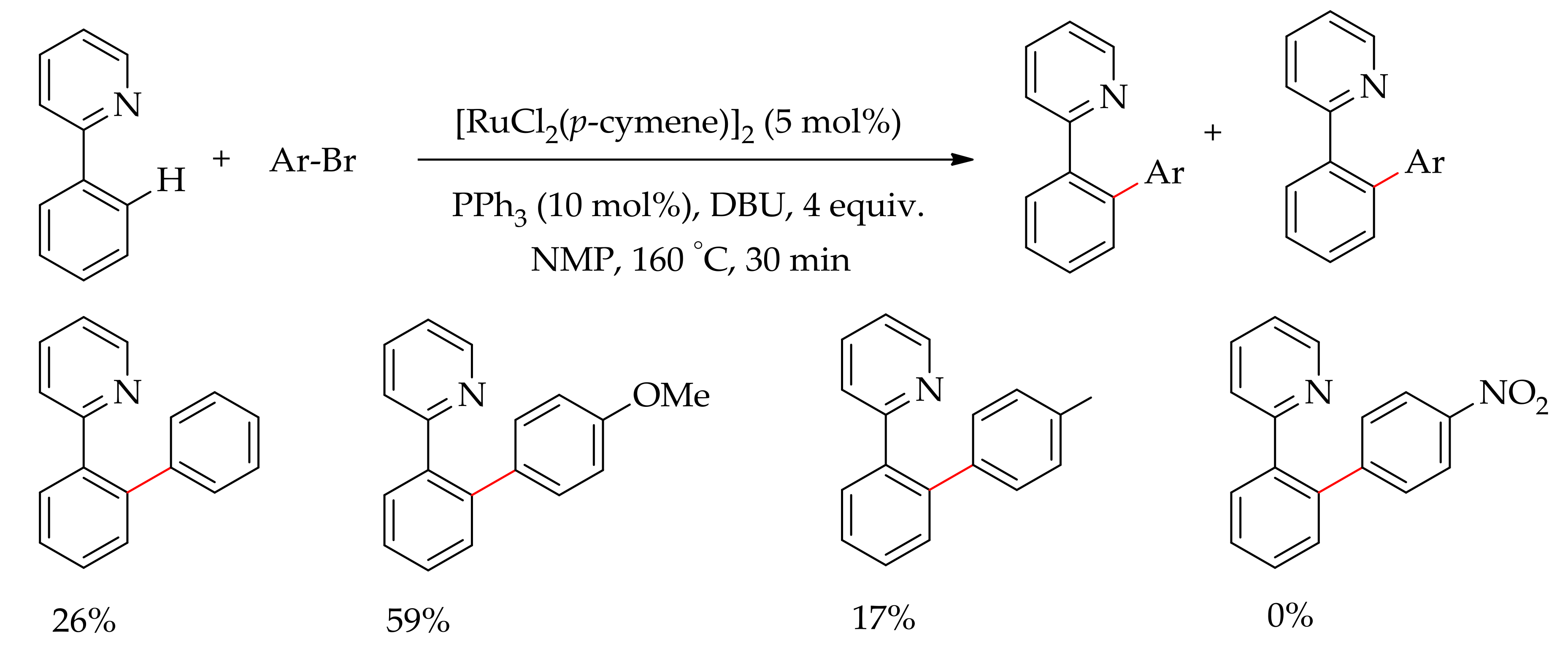
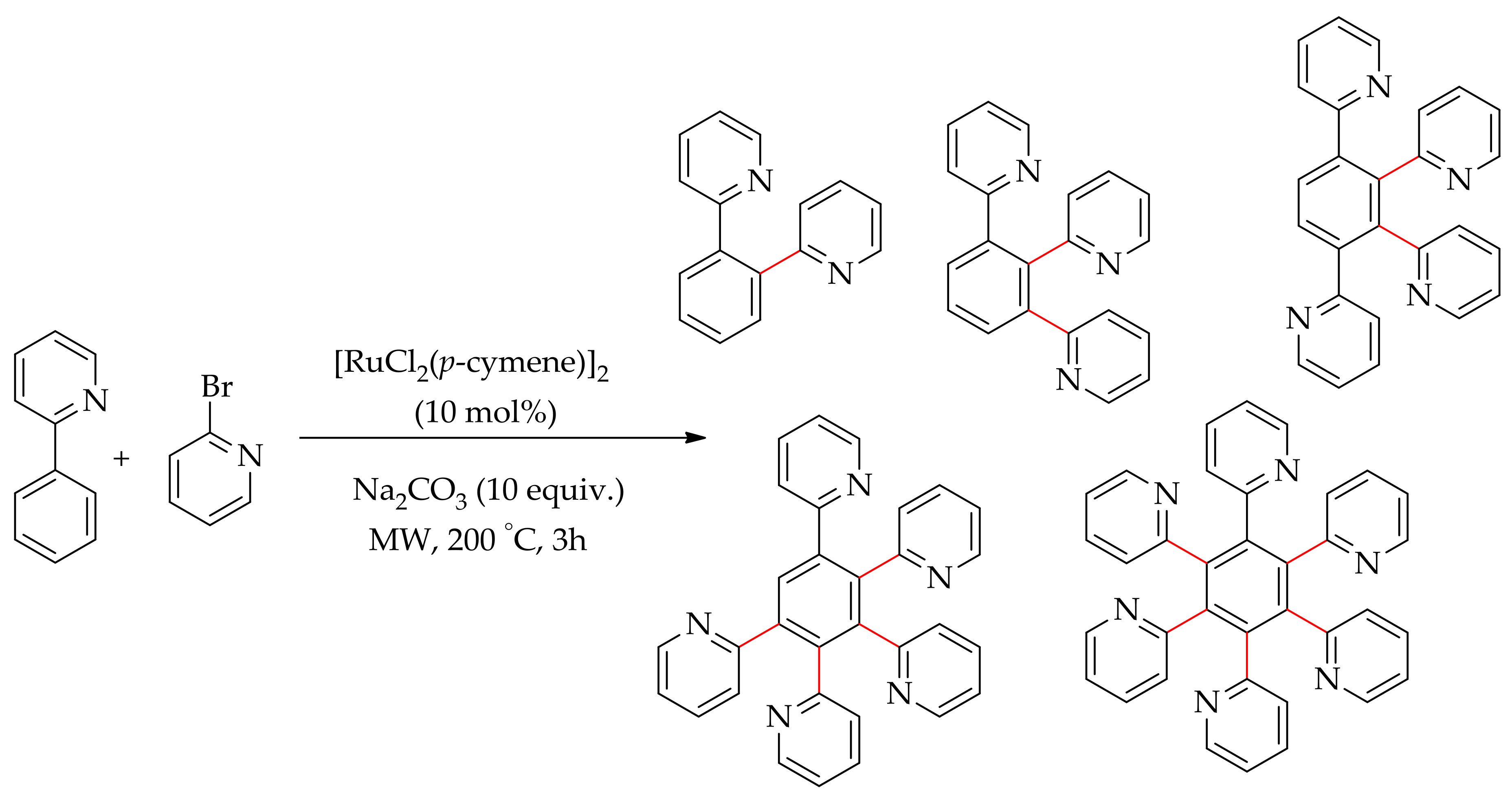
2.1. C–H Bond Arylation Directed by N–Heteroarenes
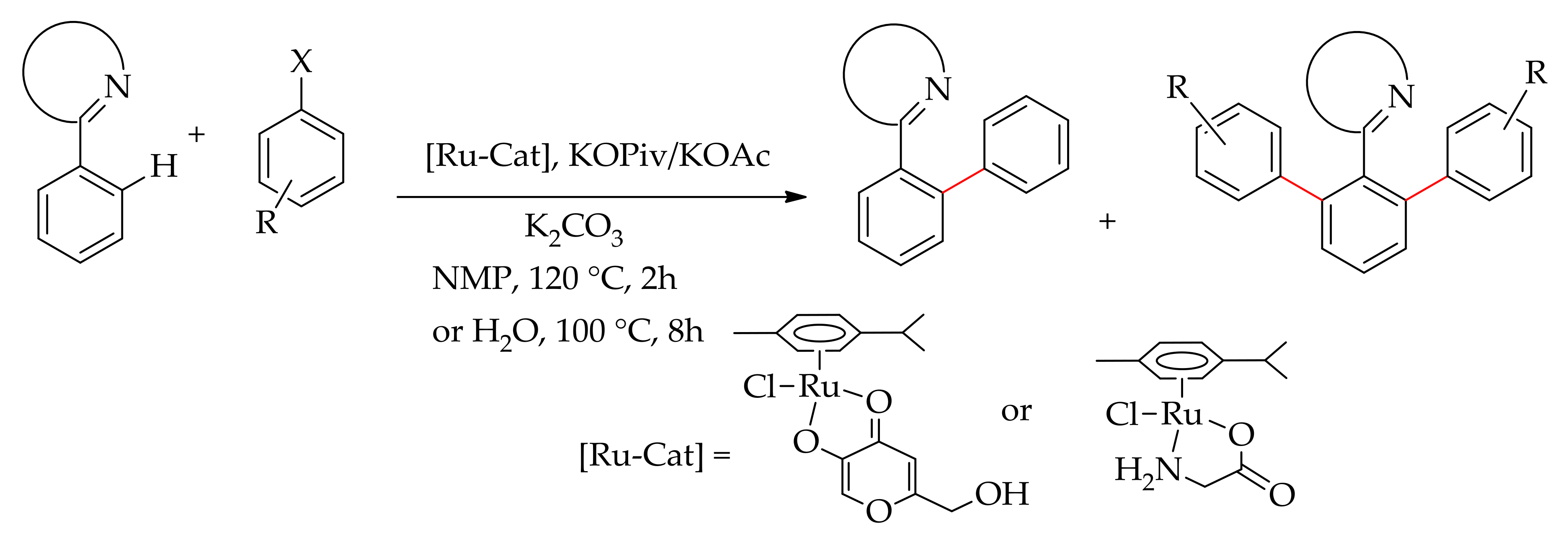
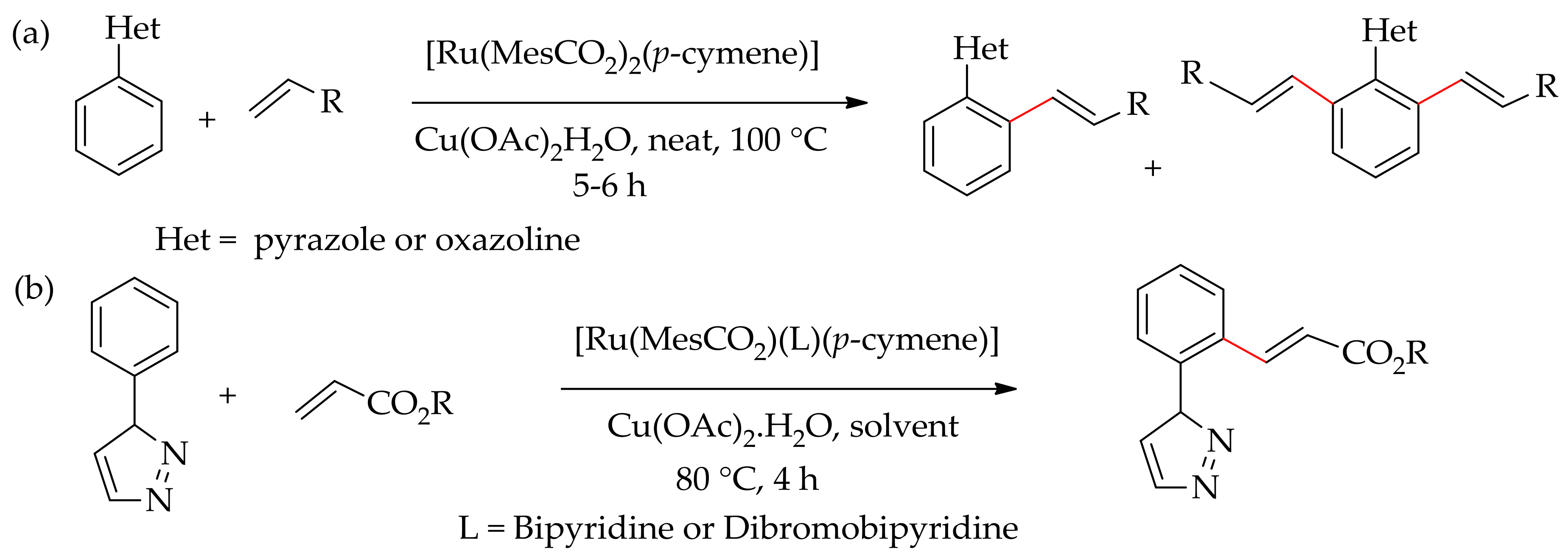
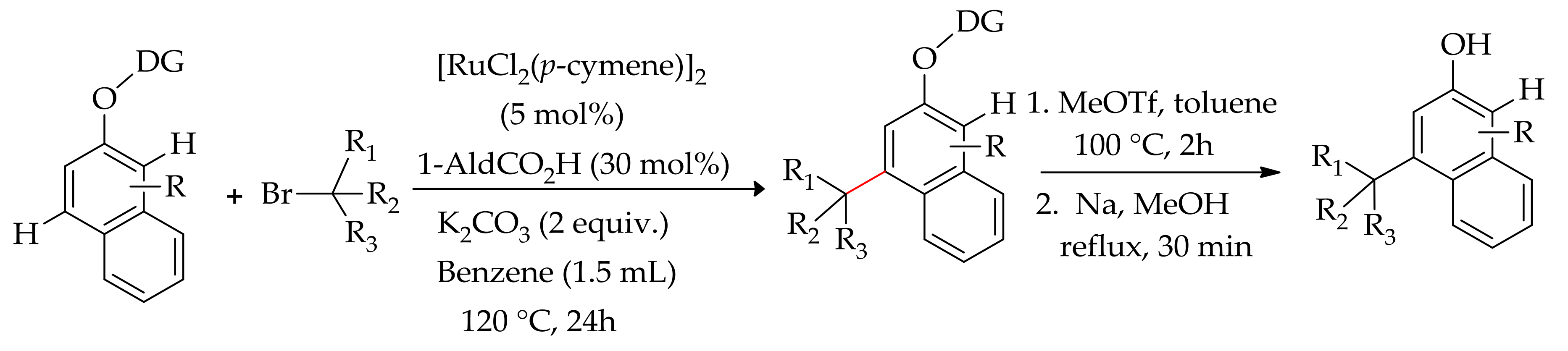
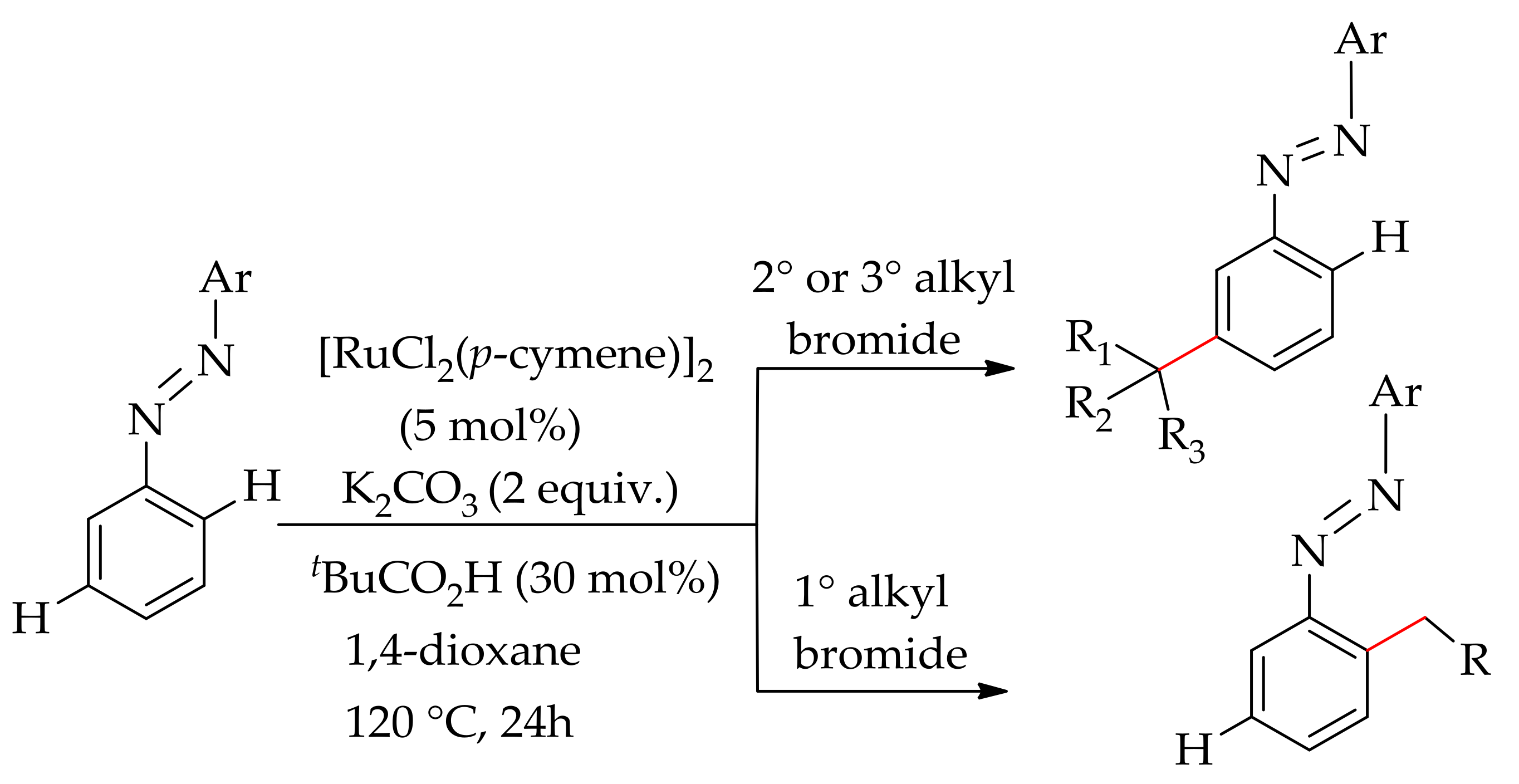
2.2. Ruthenium-Catalysed Selective Monoarylation
2.3. Arylation of Arenes with Imine and Diazine as Directing Groups
2.4. Arylation Involving Dehydrative, Oxidative and Weakly Coordinated Directing Groups
2.5. Arylation of C–H Bond without a Directing Group
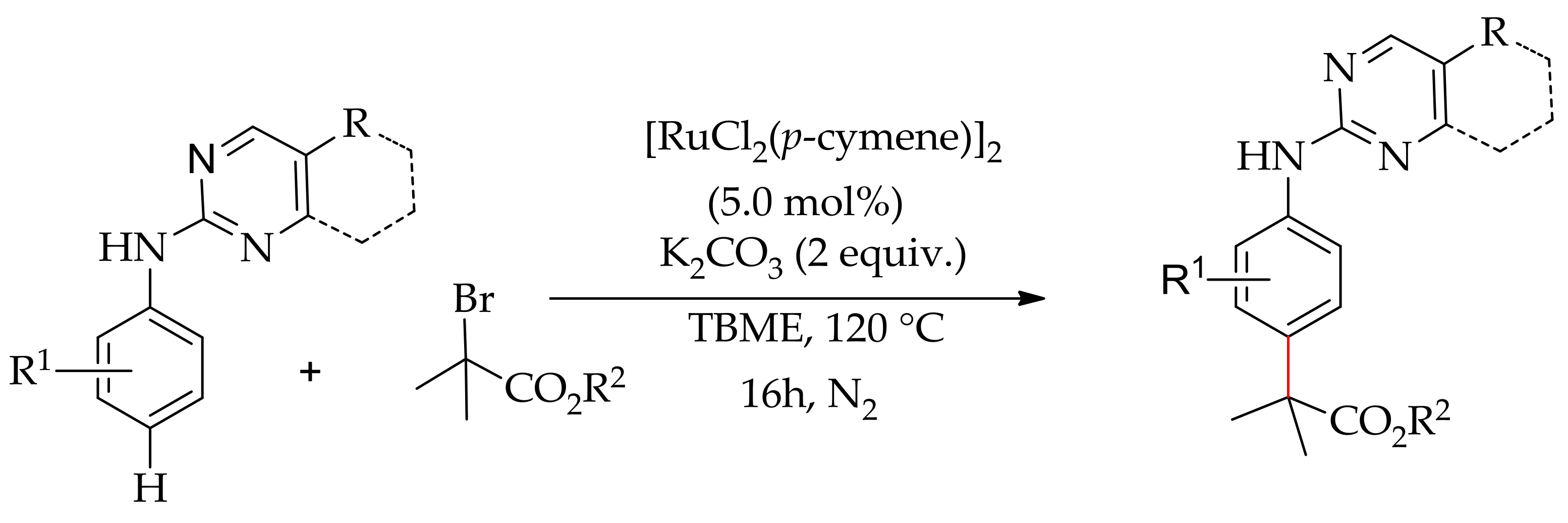
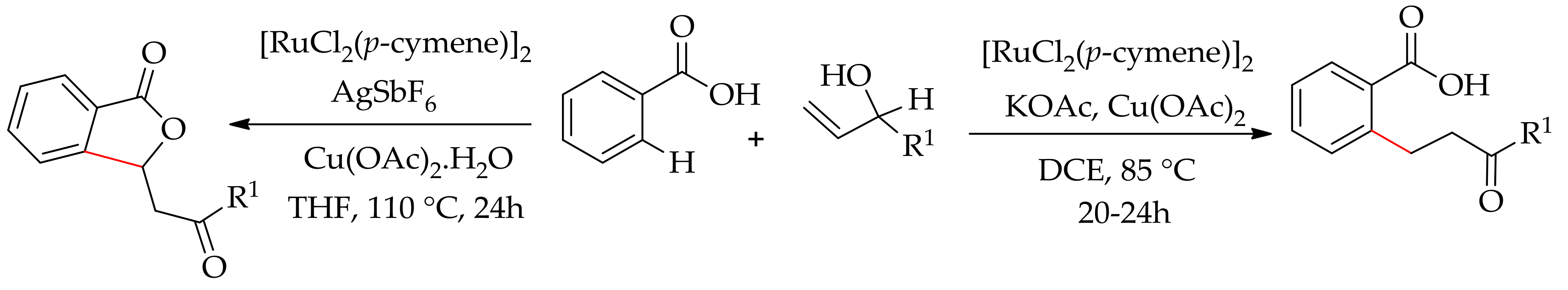
2.6. Arylation Involving Decarboxylative and sp3 C–H Bond Functionalization
3. Ruthenium-Catalysed C–H Bond Alkenylation
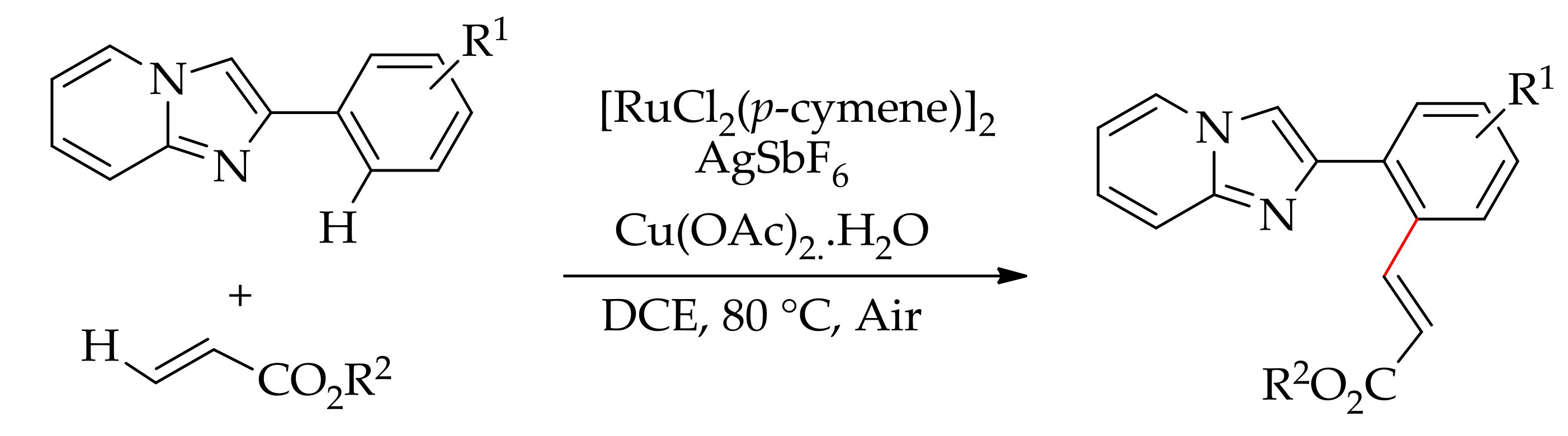
3.1. Alkenylation Involving sp2C–H Bond Directed by Nitrogen-Containing Hetroaryl Ring
3.2. Alkenylation with Carboxylic Acids and Sulfonic Acids
3.3. Alkenylation Involving Weakly Coordinated Directing Group and Dehydrogenative Coupling
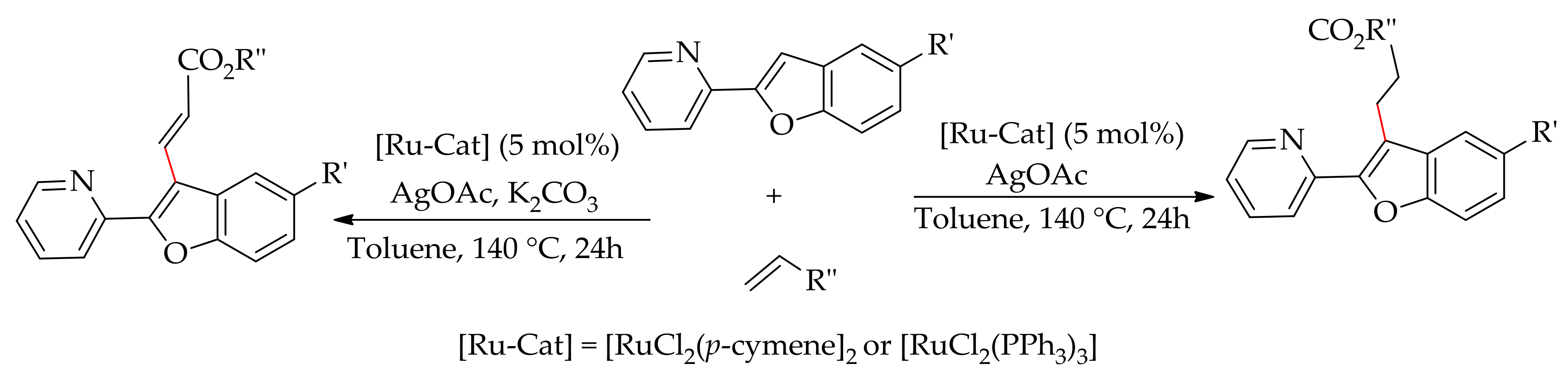
3.4. Alkenylation through Hydroarylation with Alkynes
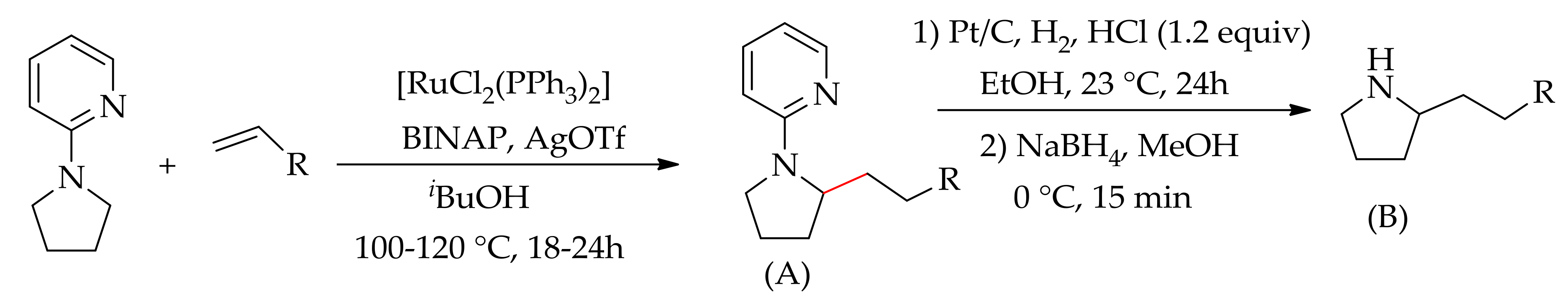
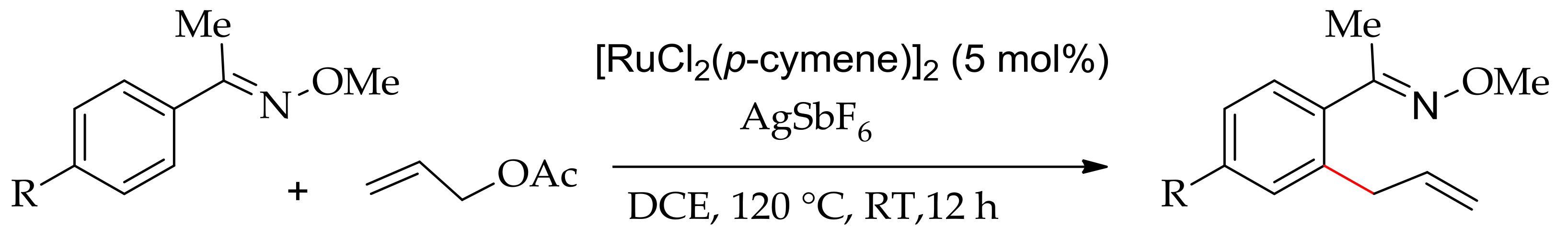
4. Ruthenium-Catalysed C–H Bond Alkylation and Allylation
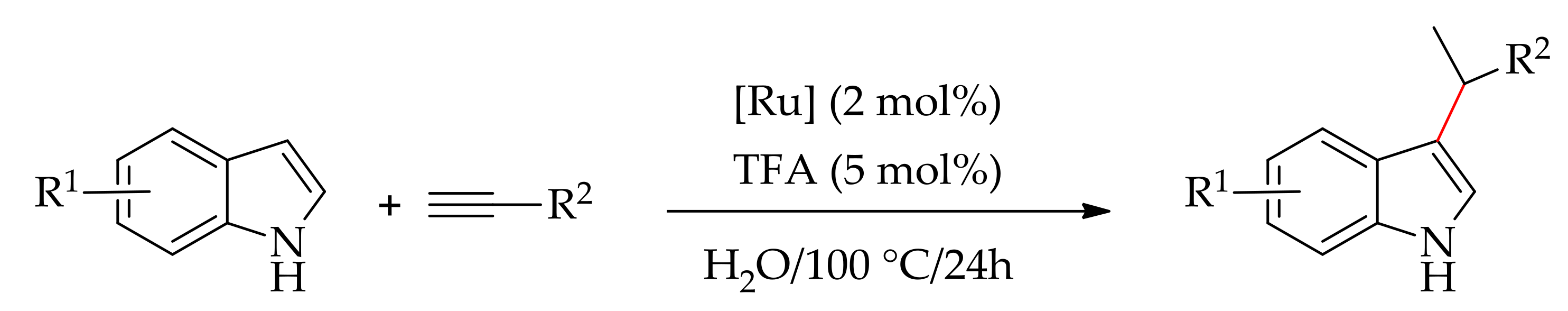
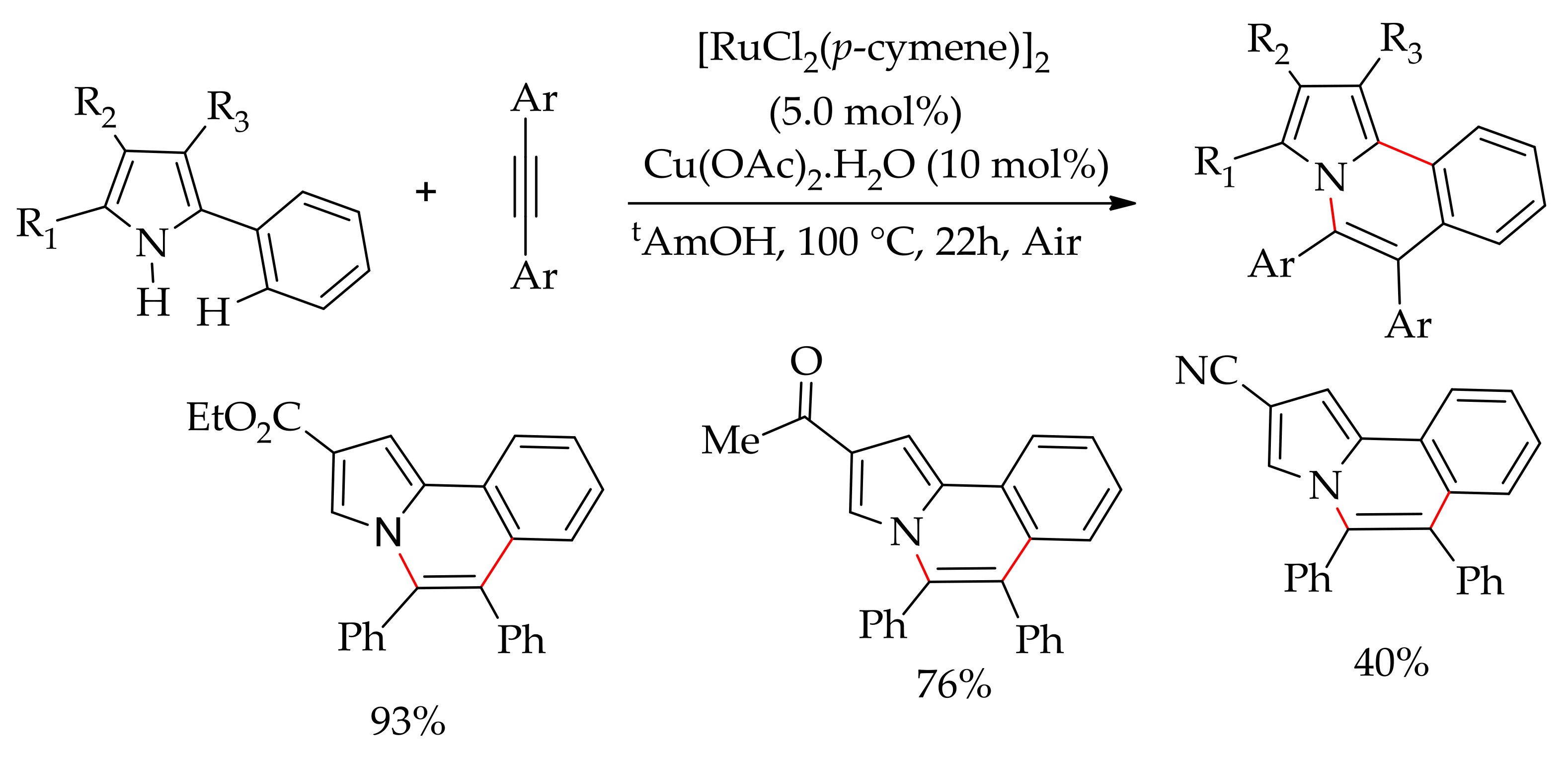
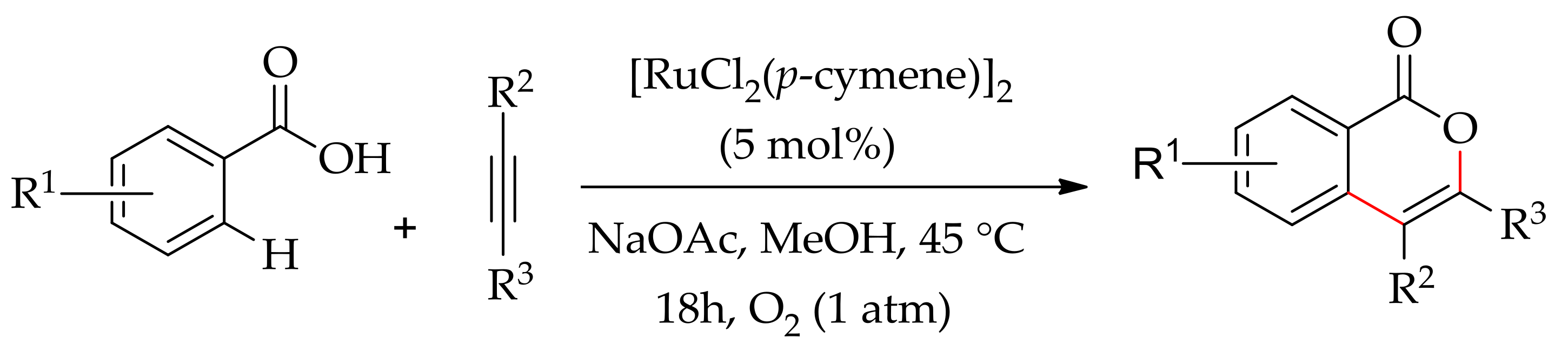
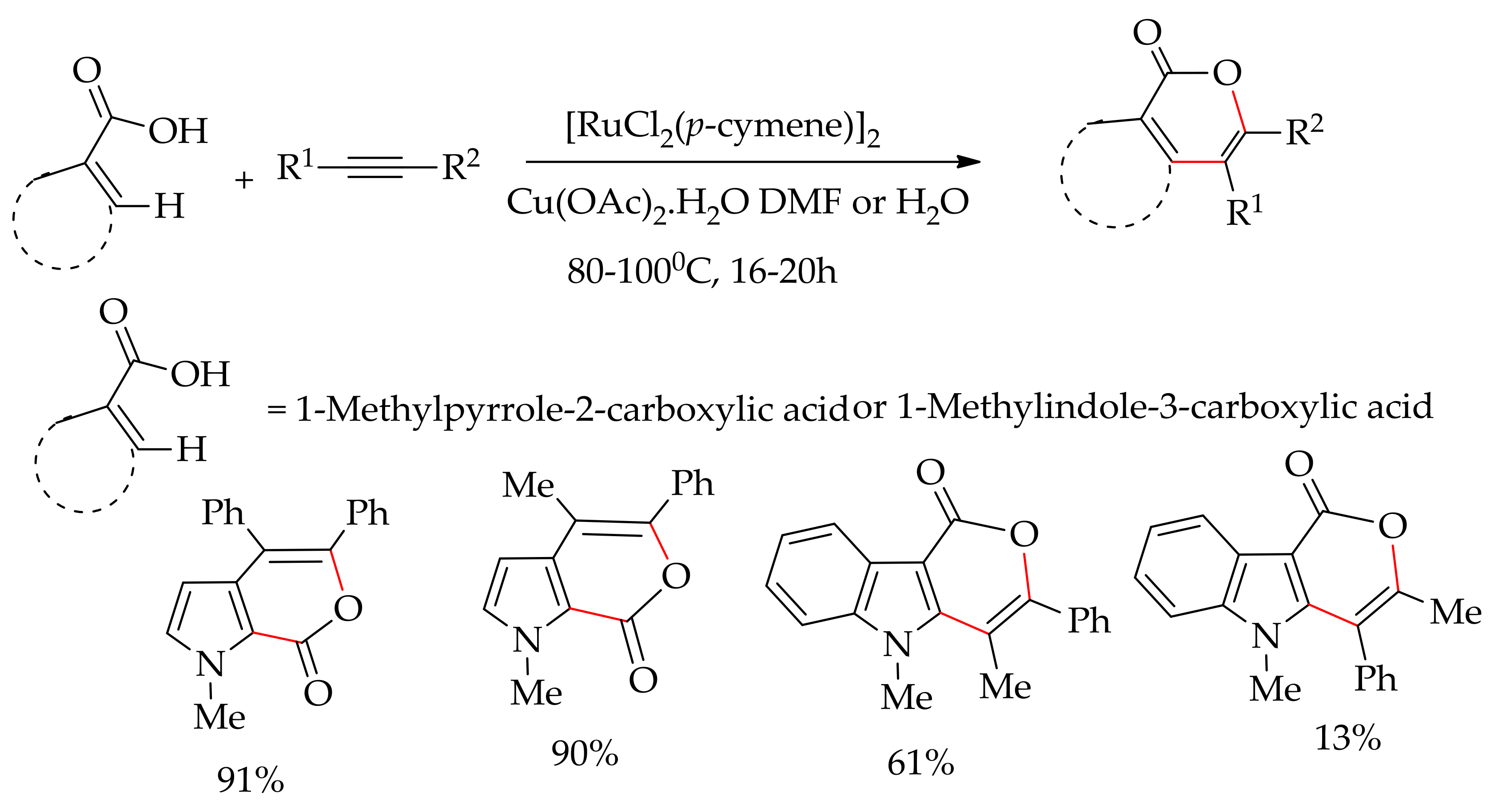
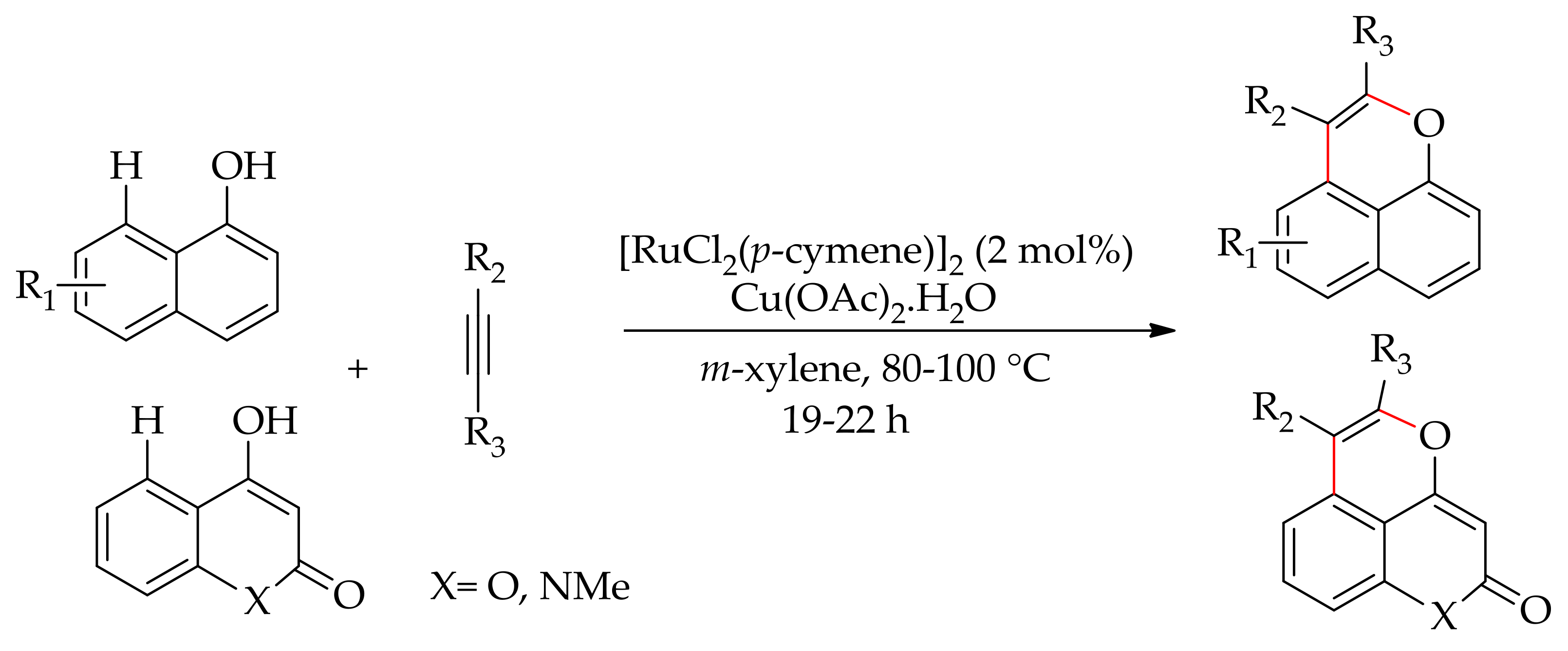
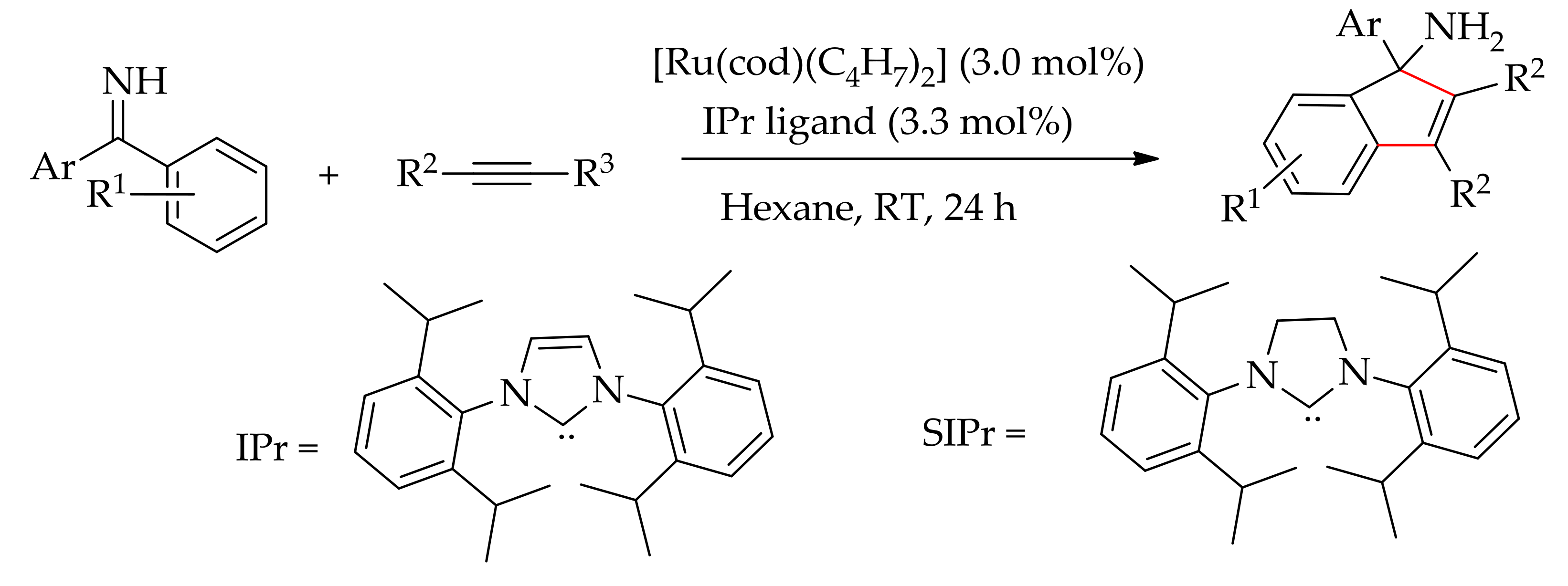
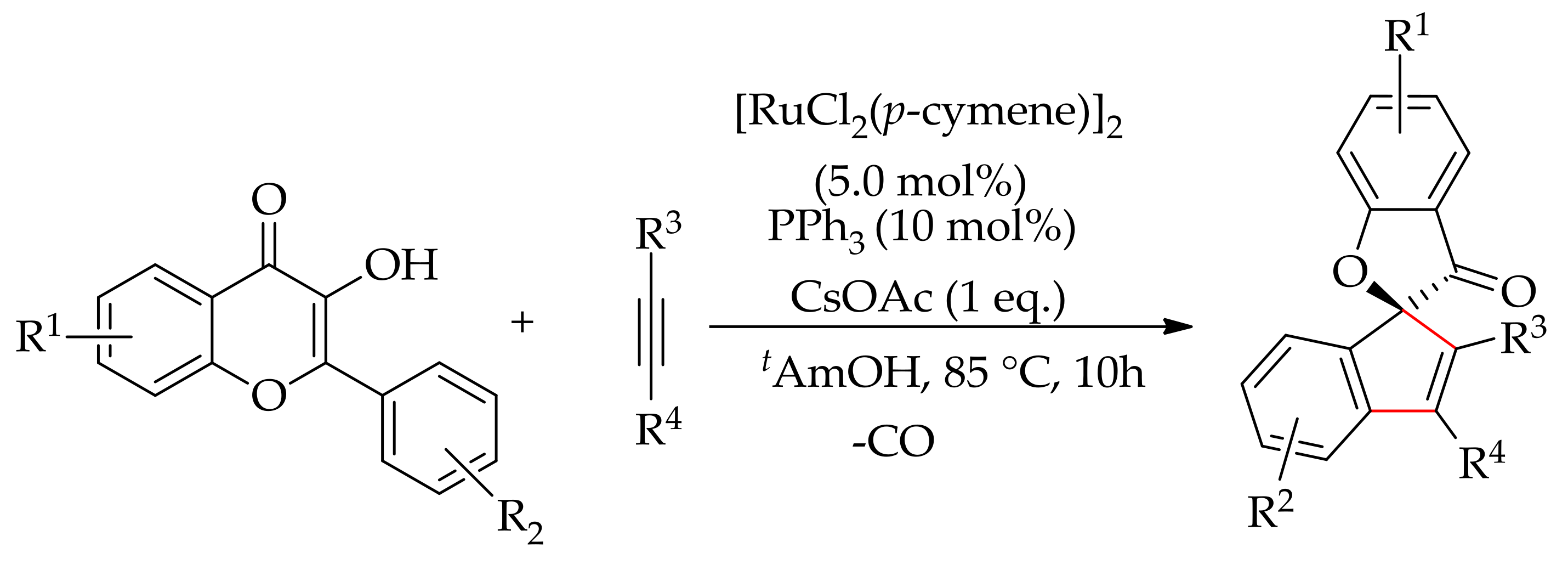
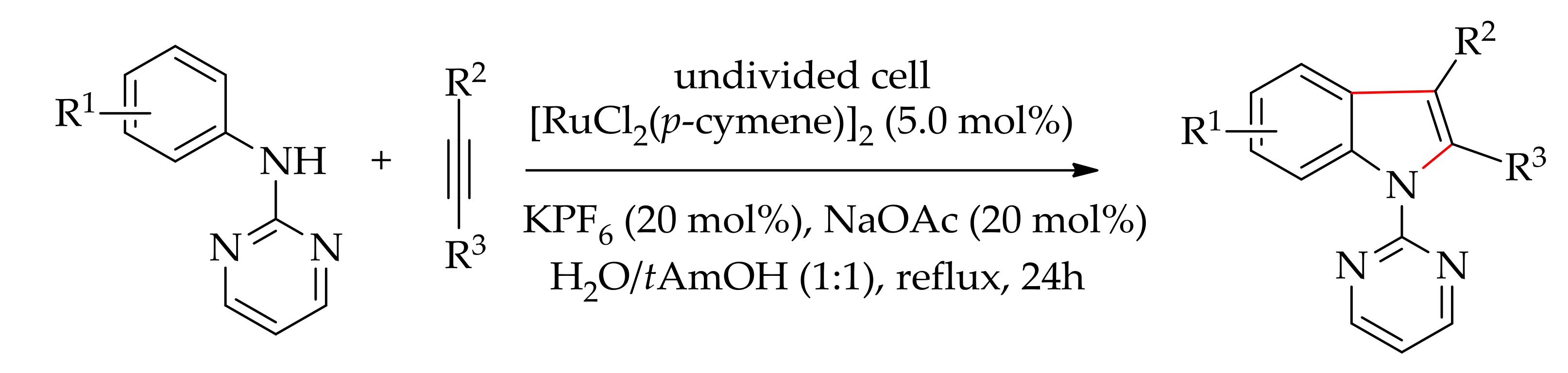
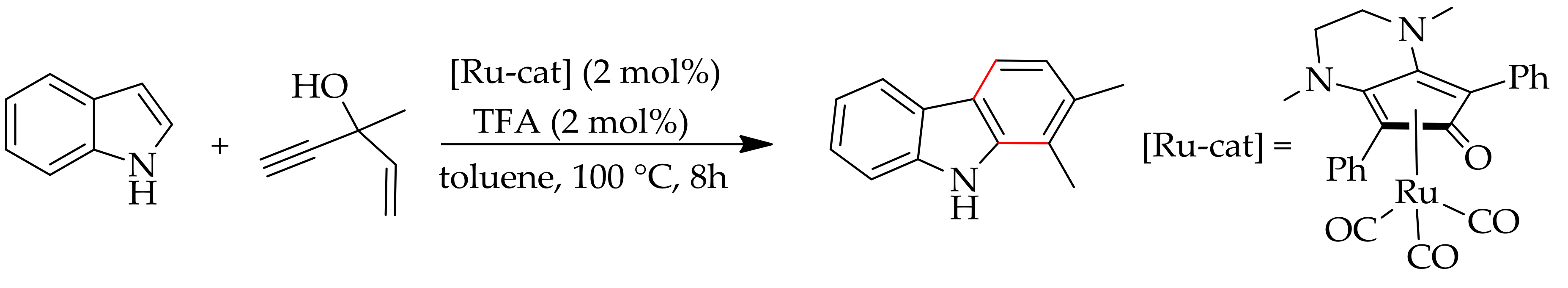
5. Ruthenium-Catalysed Annulation Reaction of Arenes with Alkynes
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Fang, K.; Dong, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Miao, Z.; Yao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, C. Scaffold Diversity Inspired by the Natural Product Evodiamine: Discovery of Highly Potent and Multitargeting Antitumor Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6678–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathula, C.; Dangi, P.; Hati, S.; Agarwal, R.; Munshi, P.; Singh, A.; Singh, S.; Sen, S. Diverse synthesis of natural product inspired fused and spiro-heterocyclic scaffolds via ring distortion and ring construction strategies. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 9281–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamao, K.; Sumitani, K.; Kumada, M. Selective carbon-carbon bond formation by cross-coupling of Grignard reagents with organic halides. Catalysis by nickel-phosphine complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 4374–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriu, R.J.P.; Masse, J.P. Activation of Grignard reagents by transition-metal complexes. A new and simple synthesis of trans-stilbenes and polyphenyls. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1972, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Villuendas, P.; Urriolabeitia, E.P. Ru-catalysed C–H functionalisations as a tool for selective organic synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 3413–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, M.; Cannas, D.M.; Baringo, X.J.; Vitorica-Yrezabal, I.J.; Larrosa, I. Cyclometallated ruthenium catalyst enables late-stage directed arylation of pharmaceuticals. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, J.; Yamaguchi, A.D.; Itami, K. C-H bond functionalization: emerging synthetic tools for natural products and pharmaceuticals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8960–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Bulger, P.G.; Sarlah, D. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions in total synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4442–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Vicente, R.; Kapdi, A.R. Transition-metal-catalyzed direct arylation of (hetero)arenes by C-H bond cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9792–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.M.L.; Bois, J.D.; Yu, J.Q. C-H functionalization in organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1855–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, B.J.; Shi, Z.J. From C(sp2)-H to C(sp3)-H: systematic studies on transition metal-catalyzed oxidative C-C formation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5588–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.W.; Sanford, M.S. Palladium-catalyzed ligand-directed C–H functionalization reactions. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.C.; Bergman, R.G.; Ellman, J.A. Direct functionalization of nitrogen heterocycles via Rh-catalyzed C–H bond activation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.C.; Wiedemann, S.H.; Bergman, R.G.; Ellman, J.A. Arylation of heterocycles via rhodium-catalyzed C-H bond functionalization. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arockiam, P.B.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C-H bond activation and functionalization. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5879–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Jeganmohan, M. Recent advances in the ruthenium(II)-catalyzed chelation-assisted C–H olefination of substituted aromatics, alkenes and heteroaromatics with alkenes via the deprotonation pathway. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8931–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Akiba, N.; Kochi, T.; Kakiuchi, F. Ruthenium-catalyzed monoalkenylation of aromatic ketones by cleavage of carbon–heteroatom bonds with unconventional chemoselectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9293–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padala, K.; Pimparkar, S.; Madasamy, P.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed regioselective oxidative coupling of aromatic and heteroaromatic esters with alkenes underan open atmosphere. Chem Commun. 2012, 48, 7140–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Ortloff, Y.; Hirano, K.; Satoh, T.; Bolm, C.; Miura, M. Ru/Ag-catalyzed oxidative alkenylation of benzamides and phenylazoles through regioselective CH bond cleavage. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Zhang, S.K.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H alkynylation of weakly coordinating benzoic acids. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 3171–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, P.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative ortho-benzoxylation of acetanilides with aromatic acids. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9651–9653. [Google Scholar]
- Pimparkar, S.; Padala, K.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed ortho C-O bond formation of substituted aromatics with oxygen nucleophiles throughC-H bond activation. Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.D.; Liu, W.; Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. Weakly coordinating directing groups for ruthenium(II)- catalyzed C-H activation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Kumar, G.S.; Kapur, M. Amides as weak coordinating groups in proximal C-H bond activation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 5439–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L. Carboxylate-assisted transition-metal-catalyzed C-H bond functionalizations: Mechanism and scope. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1315–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L. Carboxylate-assisted ruthenium-catalyzed alkyne annulations by C-H/Het-H bond functionalizations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Hofmann, N.; Vicente, R. Carboxylate-assisted ruthenium-catalyzed direct alkylations of ketimines. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1875–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenbo, L.; Arockiam, P.B.; Fischmeister, C.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. C–H bond functionalisation with [RuH(codyl)2]BF4 catalyst precursor. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, A.; Tsybizova, A.; Roithova, J. Carboxylate-assisted C–H activation of phenylpyridines with copper, palladium and ruthenium: a mass spectrometry and DFT study. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5544–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dixneuf, P.H. sp2 C–H bond activation in water and catalytic cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5744–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Fenner, S. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–H/N–O bond functionalization: Green isoquinolone syntheses in water. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6548–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, K.; Jeganmohan, M. ortho-benzoxylation of N-alkyl benzamides with aromatic acids catalyzed by ruthenium(II) complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 4092–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Abdukader, A.; Han, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C. Ruthenium-catalyzed C7 amidation of indoline C-H Bonds with sulfonyl azides. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 3606–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Zeng, S.H.; Sun, S.Z.; Dai, H.X.; Yu, J.Q. Ru(II)-catalyzed ortho-C–H amination of arenes and heteroarenes at room temperature. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5286–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ackermann, L. Versatile ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H cyanations of benzamides. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teskey, C.J.; Lui, A.Y.W.; Greaney, M.F. Ruthenium-catalyzed meta-selective C-H bromination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11677–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Fan, Z.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, A. Ru(II)-catalyzed direct C(sp2)–H activation/selenylation of arenes with selenyl chlorides. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 5263–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalysed sp2 C-H bond functionalization by C–C bond formation. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 48, 119–194. [Google Scholar]
- Thirunavukkarasu, V.S.; Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. C–H nitrogenation and oxygenation by ruthenium catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Xia, Y. Recent progress in Ru(II)-catalyzed C–H activations with oxidizing directing groups. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Zhu, L.; Qu, L.B.; Bai, R.; Lan, Y. Mechanistic view of Ru-catalyzed C–H bond activation and functionalization: Computational advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7552–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcintyre, J.; Mayoral-Soler, I.; Salvador, P.; Poater, A.; Nelson, D.J. Insights into mechanism and selectivity in ruthenium(II)-catalysed ortho-arylation reactions directed by Lewis basic groups. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3174–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, S.; Fukita, S.; Hirata, N.; Watanuki, N.; Miyano, S.; Inoue, Y. Ruthenium complex-catalyzed direct ortho arylation and alkenylation of 2-arylpyridines with organic halides. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2579–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, S.; Sakai, K.; Inoue, Y. Ruthenium-catalyzed arylation of 2-alkenylpyridines with aryl bromides: Alternative E, Z-selectivity to Mizoroki−Heck reaction. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4009–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Vicente, R.; Althammer, A. Assisted ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond activation: Carboxylic acids as cocatalysts for generally applicable direct arylations in apolar solvents. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2299–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakakou, M.; Schön, M.; Schnürch, M.; Mihovilovic, M.D. Arylation of pyridines via Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling and pyridine- directed C–H activation using a continuous-flow approach. Synlett 2013, 24, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drev, M.; Grošelj, U.; Ledinek, B.; Perdih, F.; Svete, J.; Štefane, B.; Požgan, F. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed microwave-promoted multiple C–H activation in synthesis of hexa(heteroaryl)benzenes in water. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5268–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Devaraj, K.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Catalytic C-H bond arylation of aryl imines and oxazolines in water with ruthenium(II)-acetate catalyst. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 5179–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Vicente, R.; Potukuchi, H.K.; Pirovano, V. Mechanistic insight into direct arylations with ruthenium(II) carboxylate catalysts. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5032–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požgan, F.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II) acetate catalyst for direct functionalisation of sp2-C-H bonds with aryl chlorides and access to tris-heterocyclic molecules. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiam, P.B.; Fischmeister, C.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. C-H bond functionalization in water catalyzed by carboxylato ruthenium(II) systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6629–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arockiam, P.; Poirier, V.; Fischmeister, C.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Diethyl carbonate as a solvent for ruthenium catalysed C–H bond functionalisation. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Dixneuf, P.H. Direct C-H bond arylation in water promoted by (O,O)-and (O,N)-chelate ruthenium(II) catalysts. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnani, C.; Rai, R.K.; Tyagi, D.; Mobin, S.M.; Singh, S.K. Ligand-tuned C–H bond activation/arylation of 2-arylpyridines over pyridine-based N,O/N,N ligated ruthenium–arene complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.; Knight, J.G.; Addyman, C.R.; Smyth, C.H.; Ward, N.A.B.; Harrington, R.W. Ruthenium complexes of κ(P)- and κ(P)-η6-coordinated KITPHOS monophosphines: Efficient catalysts for the direct ortho arylation of 2-phenylpyridine and N-phenylpyrazole with aryl chlorides. Organometallics 2011, 30, 6010–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiam, P.B.; Fischmeister, C.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed selective monoarylation in water and sequential functionalisations of C–H bonds. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.S.; Castro, L.C.M.; Aihara, Y.; Tobisu, M.; Chatani, N. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed chelation-assisted arylation of C-H bonds with diaryliodonium salts. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2014, 3, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.M.; Rao, N.S.S.; Satyanarayana, P.; Maheswaran, H. PhI(OCOCF3)2-mediated ruthenium catalyzed highly site-selective direct ortho-C–H monoarylation of 2-phenylpyridine and 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole and their derivatives by arylboronic acids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105347–105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnani, C.; Tyagi, D.; Rai, R.K.; Mobin, S.M.; Singh, S.K. C-H bond activation/arylation catalyzed by arene-ruthenium-aniline complexes in water. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 3022–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M. Highly efficient catalytic system for C–H activation: A practical approach to angiotensin II receptor blockers. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, R.R.; Greenlee, W.J.; Irvin, J.D.; Goldberg, M.R.; Prendergast, K.; Smith, R.D.; Timmermans, P.B.M.W.M. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: The next generation in antihypertensive therapy. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 625–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubrich, J.; Ackermann, L. Amino Acid Ligands for Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Arylation of Aryltetrazoles with Chlorides: Expedient Access to Antihypertension Drugs. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 3700–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Diers, E.; Manvar, A. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond arylations of arenes bearing removable directing groups via six-membered ruthenacycles. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalysed functionalisation of C-H bonds via a six-membered cyclometallate: monoarylation of aryl 2-pyridyl ketones. ChemCatChem. 2014, 6, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloğlu, N.; Özdemir, I.; Gürbüz, I.N.; Arslan, H.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(η6,η1-arene-CH2-NHC) catalysts for direct arylation of 2-phenylpyridine with (hetero)aryl chlorides in water. Molecules 2018, 23, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Vicente, R. Catalytic direct arylations in polyethylene glycol (PEG): Recyclable Palladium(0) catalyst for C-H bond cleavages in the presence of air. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4922–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Yu, Z. RuCl3⋅x H2O-Catalyzed direct arylation of arenes with aryl chlorides in the presence of triphenylphosphine. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrio, L.A.; Gimeno, J.; Vicent, C. One-pot direct C–H arylation of arenes in water catalysed by RuCl3·nH2O–NaOAc in the presence of Zn. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8320–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, R.G.; Achelle, S.; Bruneau, C.; Guen, F.R.; Dorcet, V.; Roisnel, T. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H (hetero)arylation of alkenylic 1,n-diazines (n = 2, 3, and 4): Scope, mechanism, and application in tandem hydrogenations. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1462–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siopa, F.; Cladera, V.A.R.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Oble, J.; Poli, G. Ruthenium-catalyzed C-H arylation and alkenylation of furfural imines with boronates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 6101–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Mulzer, M. Dehydrative direct arylations of arenes with phenols via ruthenium-catalyzed C–H and C−OH bond functionalizations. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5043–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Pospech, J.; Potukuchi, H.K. Well-defined ruthenium(II) carboxylate as catalyst for direct C–H/C–O bond arylations with phenols in water. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2146–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, J.; Hierso, J.C. Phenol derivatives in ruthenium-catalyzed C–H arylation: A general synthetic access to azole-based congested polyaromatics. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 4953–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Lygin, A.V. Ruthenium-catalyzed direct C-H bond arylations of heteroarenes. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3331–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollert, C.; Devaraj, K.; Orthaber, A.; Gates, P.J.; Pilarski, L.T. Ru-catalysed C-H arylation of indoles and pyrroles with boronic acids: Scope and mechanistic Studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnagolla, R.K.; Jeganmohan, M. Regioselective ortho-arylation and alkenylation of N-alkyl benzamides with boronic acids via ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond activation: An easy route to fluorenones synthesis. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5246–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareddy, P.; Jordan, F.; Szostak, M. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed ortho-C–H arylation of diverse N-heterocycles with aryl silanes by exploiting solvent-controlled N-coordination. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 4783–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareddy, P.; Jordan, F.; Brenner-Moyer, S.E.; Szostak, M. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed regioselective C–H arylation of cyclic and N,N-dialkyl benzamides with boronic acids by weak coordination. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4755–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareddy, P.; Jordan, F.; Szostak, M. Highly chemoselective ruthenium(II)-catalyzed direct arylation of cyclic and N,N-dialkyl benzamides with aryl silanes. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 3204–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareddy, P.; Jordan, F.; Szostak, M. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed direct C–H arylation of indoles with arylsilanes in water. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norinder, J.; Matsumoto, A.; Yoshikai, N.; Nakamura, E. Iron-catalyzed direct arylation through directed C–H bond activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5858–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chen, C.; Chen, W. Ortho-functionalization of 2-phenoxypyrimidines via Palladium-catalyzed C–H bond activation. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 7203–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xie, C. Peroxide-promoted regioselective arylation of 2-phenylpyridines and related substrates with aryl iodides. Synlett 2008, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefane, B.; Fabris, J.; Pozgan, F. C–H bond functionalization of arylpyrimidines catalyzed by an in situ generated ruthenium(II) carboxylate system and the construction of tris(heteroaryl)-substituted benzenes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefane, B.; Žugelj, H.B.; Grošelj, U.; Kuzman, P.; Svete, J.; Požgan, F. Quinazoline-Directed C–H Bond Functionalization Catalyzed by Ruthenium(II) Carboxylate—Construction of Polyconjugated Aryl-Heteroaryl Systems. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Snieckus, V. Quinazoline-directed C–H bond functionalization catalyzed by ruthenium(II) carboxylate – construction of polyconjugated aryl-heteroaryl systems. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamari, H.H.; Diers, E.; Ackermann, L. Triazole-assisted ruthenium-catalyzed C-H arylation of aromatic amides. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9739–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamakawa, T. Ruthenium/base-catalyzed ortho-selective C–H arylation of acylarenes with halogenated arylboronates. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105829–105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, Y.; Kitazawa, K.; Miyake, M.; Kochi, T.; Kakiuchi, F. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho C–H arylation of aromatic nitriles with arylboronates and observation of partial para arylation. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 6503–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Weix, D.J. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–H arylation of diverse aryl carboxylic acids with aryl and heteroaryl halides. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5432–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, M.; Perry, G.J.P.; Cambeiro, X.C.; Hernández, F.J.; Arokianathar, J.N.; Larrosa, I. Ru-catalyzed C–H arylation of fluoroarenes with aryl halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegeau, E.F.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H.; Jutand, A. Autocatalysis for C–H bond activation by ruthenium(II) complexes in catalytic arylation of functional arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10161–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, M.; Cannas, D.M.; Panigrahi, A.; Kujawa, S.; Kryjewski, M.; Xie, P.; Larrosa, I. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–H arylation of benzoic acids and indole carboxylic acids with aryl halides. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastine, S.J.; Gribkov, D.V.; Sames, D. sp3 C–H bond arylation directed by amidine protecting group: α-arylation of pyrrolidines and piperidines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14220–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschiulli, A.; Smout, V.; Storr, T.E.; Mitchell, E.A.; Eliáš, Z.; Herrebout, W.; Berthelot, D.; Meerpoel, L.; Maes, B.U.W. Ruthenium-catalyzed a-(hetero)arylation of saturated cyclic amines: Reaction scope and mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10378–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastbaravardeh, N.; Schnürch, M.; Mihovilovic, M.D. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed sp3 C–H bond arylation of benzylic amines using aryl halides. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3792–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.Y.P.; Jeyachandran, R.; Ackermann, L. C(sp3)–H bond arylations catalyzed by well-defined [Ru(O2CMes)2(p-cymene)]. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 4145–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribkov, D.V.; Pastine, S.J.; Schnürch, M.; Sames, D. Ruthenium catalyzed decarbonylative arylation at sp3 carbon centers in pyrrolidine and piperidine heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11750–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moselage, M.; Li, J.; Kramm, F.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C-C arylations and alkylations: Decarbamoylative C-C functionalizations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5341–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, H.; Song, X.; Milstein, D. Ru-catalyzed oxidative coupling of arenes with olefins using O2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.S.; Lee, D.W. Intermolecular dehydrative coupling reaction of aryl ketones with cyclic alkenes catalyzed by a well-defined cationic ruthenium−hydride complex: A novel ketone olefination method via vinyl C–H bond activation. Organometallics 2010, 29, 1883–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, T.; Mochida, S.; Fukutani, T.; Hirano, K.; Satoh, T.; Miura, M. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidative Vinylation of Heteroarene Carboxylic Acids with Alkenes via Regioselective C–H Bond Cleavage. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium-catalyzed direct oxidative alkenylation of arenes through twofold C–H bond functionalization. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiam, P.B.; Fischmeister, C.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium diacetate-catalysed oxidative alkenylation of C–H bonds in air: Synthesis of alkenyl N-arylpyrazoles. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, Y.; Kochi, T.; Kakiuchi, F. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho-selective aromatic CH alkenylation with alkenyl carbonates. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommagalla, Y.; Mullapudi, V.B.; Francis, F.; Ramana, C.V. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed switchable C3-alkylation versus alkenylation with acrylates of 2-pyridylbenzofurans via C–H bond activation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Devaraj, K.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II) catalysed synthesis of unsaturated oxazolines via arene C–H bond alkenylation. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2706–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Ogiwara, Y.; Tamura, M.; Kochi, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Chatani, N.; Kakiuchi, F. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho-selective C–H alkenylation of aromatic compounds with alkenyl esters and ethers. Organometallics 2014, 33, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C-H alkenylations of phenols with removable directing groups. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 13925–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, D.; Singh, I.; Tulsyan, G.; Abbagani, K.; Pardasani, R.T. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative C–H bond alkenylation of 2-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine. Synlett 2015, 26, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, S.; Singh, S.P. Solvent-free ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H activation: Synthesis of alkenylarylpyrazole derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 6025–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, S.; Singh, S.P. Ruthenium-bipyridine complex catalyzed C–H alkenylation of arylpyrazole derivatives. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, M.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, C.M. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H alkenylation/annulation cascade for the rapid synthesis of benzoimidazoisoindoles. Org. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseyni, M.; Kianmehr, E. A ruthenium-catalyzed alkenylation–annulation approach for the synthesis of indazole derivatives via C–H bond activation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5973–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Pospech, J. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative C–H bond alkenylations in water: Expedient synthesis of annulated lactones. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4153–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.Y.P.; Bechtoldt, A.; Raghuvanshi, K.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed decarboxylative C–H activation: Versatile routes to meta-alkenylated arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6929–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.Y.; Xie, L.J.; Cheng, H.P.; Liu, A.D.; Li, X.D.; Wang, D.; Cheng, L.; Liu, L. Ruthenium-catalyzed decarboxylative C–H alkenylation in aqueous media: Synthesis of tetrahydropyridoindoles. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 7514–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, S.; Mandal, A.; Sahoo, H.; Mallik, S.; Grandhi, G.S.; Baidya, M. Ru(II)-catalyzed oxidative Heck-type olefination of aromatic carboxylic acids with styrenes through carboxylate-assisted C–H bond activation. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Mei, R.; Tenti, G.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed oxidative C-H alkenylations of sulfonic acids, sulfonyl chlorides and sulfonamides. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 15248–15251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, S.; Kakiuchi, F.; Sekine, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kamatani, A.; Sonoda, M.; Chatani, N. Efficient catalytic addition of aromatic carbon-hydrogen bonds to olefins. Nature 1993, 366, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.; Genet, J.P.; Darses, S. Anti-Markovnikov hydroarylation of styrenes catalyzed by an in situ generated ruthenium complex. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3855–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.O.; Genet, J.-P.; Darses, S. Ruthenium chloride as an efficient catalytic precursor for hydroarylation reactions via C-H bond activation. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3038–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiuchi, F.; Kochi, T.; Mizushima, E.; Murai, S. Room-Temperature regioselective C-H/olefin coupling of aromatic ketones using an activated ruthenium catalyst with a carbonyl ligand and structural elucidation of key intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17741–17750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, K.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho-alkenylation of aromatic ketones with alkenes by C -H bond activation. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6144–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.S.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed alkenylation of ferrocenyl ketones via C–H bond activation. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7320–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padala, K.; Jeganmohan, M. Highly regio- and stereoselective ruthenium(II)-catalyzed direct ortho-alkenylation of aromatic and heteroaromatic aldehydes with activated alkenes under open atmosphere. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.C.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho alkenylation of aromatic nitriles with activated alkenes via C–H bond activation. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10738–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Wang, L.; Wolfram, R.; Lygin, A.V. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative C–H alkenylations of anilides and benzamides in water. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ma, J.; Xie, W.; Song, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Ruthenium-catalyzed regioselective C2 alkenylation of indoles and pyrroles via C–H bond functionalization. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 9345–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Kapur, M. Fujiwara–Moritani reaction of Weinreb amides using a ruthenium-catalyzed C–H functionalization reaction. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtoldt, A.; Tirler, C.; Raghuvanshi, K.; Warratz, S.; Kornhaaß, C.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium oxidase catalysis for site-selective C-H alkenylations with ambient O2 as the sole oxidant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Yao, B.B.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhang, Y.H. RuCl3-catalyzed alkenylation of aromatic C–H bonds with terminal alkynes. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5309–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.G.; Liu, K.; Zou, G.; Liu, P.N. Ruthenium-catalyzed alkenylation of arenes with alkynes or alkenes by 1,2,3-triazole-directed C–H activation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 7878–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed hydroarylation of anilides with alkynes: An efficient route to ortho-alkenylated anilines. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, M.; Marek, I.; Ackermann, L. Carboxylate-assisted ruthenium(II)-catalyzed hydroarylations of unactivated alkenes through C-H cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, M.; Wang, L.; Bielefeld, K.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C(sp3)–H α-alkylation of pyrrolidines. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadierno, V.; Francos, J.; Gimeno, J. Ruthenium/TFA-catalyzed regioselective C-3-alkylation of indoles with terminal alkynes in water: Efficient and unprecedented access to 3-(1-methylalkyl)-1H-indoles. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4175–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Hirano, K.; Satoh, T.; Miura, M. Palladium- and Nickel-catalyzed direct alkylation of azoles with unactivated alkyl bromides and chlorides. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 12307–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Punji, B.; Song, W. User-Friendly [(Diglyme)NiBr2]-catalyzed direct alkylations of heteroarenes with unactivated alkyl halides through C-H bond cleavages. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 3325–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Novák, P.; Vicente, R.; Hofmann, N. Ruthenium-catalyzed regioselective direct alkylation of arenes with unactivated alkyl halides through C-H bond cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6045–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, N.; Ackermann, L. meta-Selective C–H Bond Alkylation with Secondary Alkyl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5877–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Gao, P.; Lv, X.; Qu, C.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Synthesis of m-alkylphenols via a ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond functionalization of phenol derivatives. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2682–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, X.; Jia, C.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, S. Ruthenium-catalyzed meta/ortho-selective C–H alkylation of azoarenes using alkyl bromides. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Korvorapun, K.; Sarkar, S.D.; Rogge, T.; Burns, D.J.; Warratz, S.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalysed remote C–H alkylations as a versatile platform to meta-decorated arenes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, J.A.; McMullin, C.L.; Paterson, A.J.; Mahon, M.F.; Bhonoah, Y.; Frost, C.G. Ruthenium-catalyzed para-selective C-H alkylation of aniline derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15131–15135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, J.A.; McMullin, C.L.; Mahon, M.F.; Bhonoah, Y.; Frost, C.G. Remote C6-selective ruthenium-catalyzed C–H alkylation of indole derivatives via σ-activation. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Chand, T.; Singh, D.; Kapur, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–H functionalization of benzoic acids with allyl alcohols: A controlled reactivity switch between C–H alkenylation and C–H alkylation pathways. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4934–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed dehydrogenative β-benzylation of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines with aryl aldehydes: Access to functionalized quinolines. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3174–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, Y. Ortho-selective allylation of 2-pyridylarenes with allyl acetates catalyzed by ruthenium complexes. Organometallics 2006, 25, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriya, Y.; Ramana, C.V. Ruthenium-catalyzed C6-propenylation reactions of substituted pyridine derivatives: Directed and direct C-H activation. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13288–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Madasamy, P.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidant-free allylation of aromatic ketoximes with allylic acetates at room temperature. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13934–13938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ji, H. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed rgio- and stereoselective C–H allylation of indoles with allyl alcohols. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.X. Synthesis of isocoumarin derivatives by copper-catalyzed addition of o-halobenzoic acids to active internal alkynes. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 1660–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, L.; Wu, W.; Jiang, H. Palladium-catalyzed oxidative annulation of acrylic acid and amide with alkynes: A practical route to synthesize α-pyrones and pyridones. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2146–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Chen, D.; Song, G.; Han, K.; Li, X. Palladium-catalyzed cascade cyclization–Oxidative olefination of tert-butyl 2-alkynylbenozates. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; John, M.; Ackermann, L. Amidines for versatile ruthenium(II)-catalyzed oxidative C-H activations with internal alkynes and acrylates. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 5403–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midya, S.P.; Sahoo, M.K.; Landge, V.G.; Rajamohanan, P.R.; Balaraman, E. Reversed reactivity of anilines with alkynes in the rhodium-catalysed C–H activation/carbonylation tandem. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamoto, M.; Yamauchi, D.; Nishimura, T. Iridium-catalyzed asymmetric [3+2] annulation of aromatic ketimines with alkynes via C–H activation: Unexpected inversion of the enantioselectivity induced by protic acids. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5876–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ackermann, L. Versatile pyrrole synthesis through ruthenium(II)-catalyzed alkene C–H bond functionalization on enamines. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, N.; Liang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Ruthenium-catalyzed pyrrole synthesis via oxidative annulation of enamides and alkynes. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.S.; Dong, L. Synthesis of indoles and polycyclic amides via ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C–H activation and annulations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 11228–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villuendas, P.; Urriolabeitia, E.P. Primary amines as directing groups in the Ru-catalyzed synthesis of isoquinolines, benzoisoquinolines, and thienopyridines. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 5254–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaishap, P.P.; Sarma, B.; Gogoi, S. The amide C–N bond of isatins as the directing group and the internal oxidant in Ru-catalyzed C–H activation and annulation reactions: Access to 8-amido isocoumarins. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9809–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Graczyk, K.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium-catalyzed alkyne annulations with substituted 1H-pyrazoles by C–H/N–H bond functionalizations. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 6318–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, D.; Shi, F.; Wu, C. Cu-Catalyzed alkynylation–cyclization cascade for the construction of the pyrazolo[5,1-a]isoquinoline skeleton. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10434–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Lygin, A.V. Cationic Ruthenium(II) catalysts for oxidative C–H/N–H bond functionalizations of anilines with removable directing group: Synthesis of indoles in water. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Wang, L.; Lygin, A.V. Ruthenium-catalyzed aerobic oxidative coupling of alkynes with 2-aryl-substituted pyrroles. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnagolla, R.K.; Jeganmohan, M. Regioselective synthesis of isocoumarins by ruthenium-catalyzed aerobic oxidative cyclization of aromatic acids with alkynes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2030–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Pospech, J.; Graczyk, K.; Rauch, K. Versatile synthesis of isocoumarins and α-pyrones by ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative C–H/O–H bond cleavages. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warratz, S.; Kornhaaß, C.; Cajaraville, A.; Niepçtter, B.; Stalke, D.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C-H activation/alkyne annulation by weak coordination with O2 as the sole oxidant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5513–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Sawant, S.G.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed synthesis of pyrrole- and indole fused isocoumarins by C-H bond activation in DMF and water. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Sawant, S.G.; Kaminsky, W. Regioselective synthesis of pyrrole and indole-fused isocoumarins catalysed by N∧O chelate ruthenium(II) complex. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnagolla, R.K.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed regioselective cyclization of aromatic ketones with alkynes: An efficient route to indenols and benzofulvenes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.C.; Manikandan, R.; Jeganmohan, M. Ruthenium-catalyzed aerobic oxidative cyclization of aromatic and heteroaromatic nitriles with alkynes: a new route to isoquinolones. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6060–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirunavukkarasu, V.S.; Donati, M.; Ackermann, L. Hydroxyl-directed ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond functionalization: Versatile access to fluorescent pyrans. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3416–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, F.; Han, K.; Li, X. Ruthenium- and sulfonamide-catalyzed cyclization between N-sulfonyl imines and alkynes. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5506–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ugrinov, A.; Zhao, P. Ruthenium(II)/N-heterocyclic carbene catalyzed [3+2] carbocyclization with aromatic N-H ketimines and internal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6681–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, N.; Sukumar, G.; Kumar, V.P.; Mainkar, P.S.; Chandrasekhar, S. Ruthenium-catalyzed benzimidazoisoquinoline synthesis via oxidative coupling of 2-arylbenzimidazoles with alkynes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 4198–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Villuendas, P.; Ortuño, M.A.; Lledós, A.; Urriolabeitia, E.P. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative coupling of primary amines with internal alkynes through C-H bond activation: Scope and mechanistic studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 8626–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allu, S.; Kumara Swamy, K.C. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative annulation of 6-anilinopurines with alkynes via C-H activation: Synthesis of indole-substituted purines/purine nucleosides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2665–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Kumari, A.; Sawant, D.M.; Pardasani, R.T. Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative annulation of anilines using benzothiazole as a removable directing group. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2017, 6, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaishap, P.P.; Duarah, G.; Sarma, B.; Chetia, D.; Gogoi, S. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed synthesis of spirobenzofuranones by a decarbonylative annulation reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Santra, S.K.; Mohanta, P.R.; Patel, B.K. Ruthenium(II) catalyzed regiospecific C–H/O−H annulations of directing arenes via weak coordination. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5678–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Xu, H.C. Ruthenium-catalyzed electrochemical dehydrogenative alkyne annulation. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3820–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.; Jäckel, E.; Haak, E. Ruthenium-catalyzed cascade annulation of indole with propargyl alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5908–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





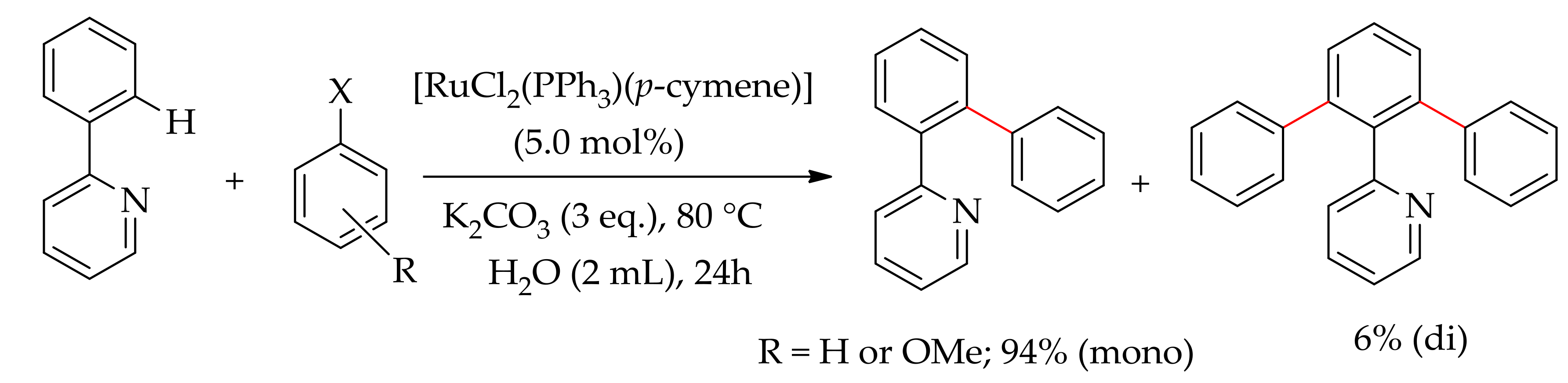

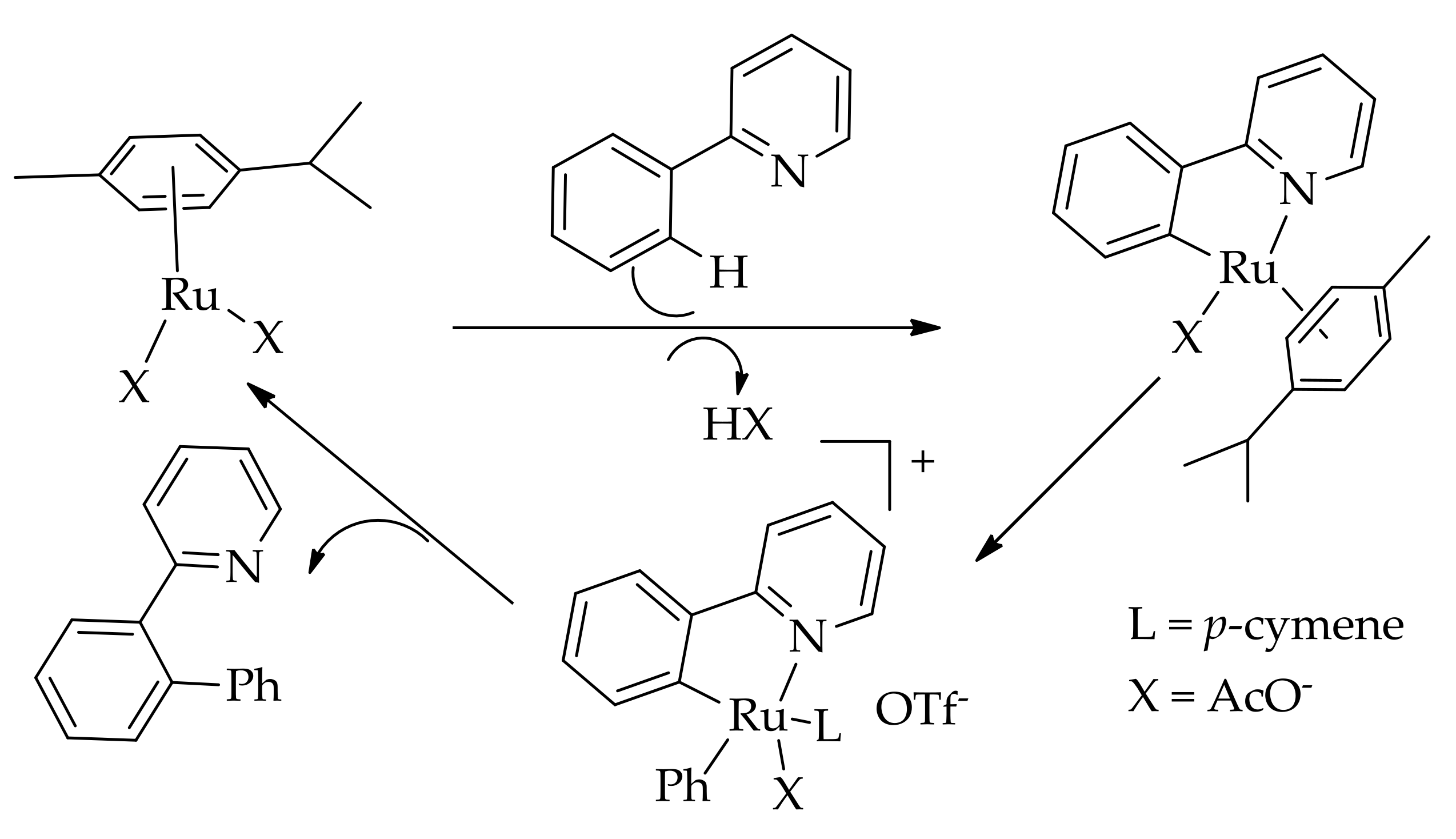
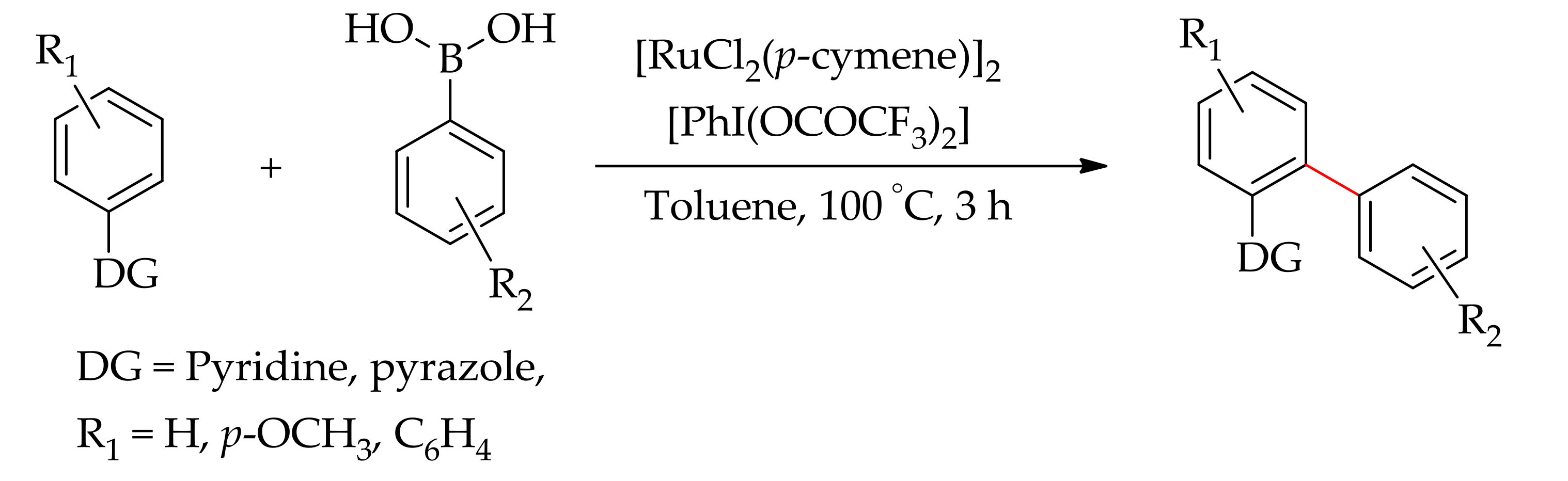

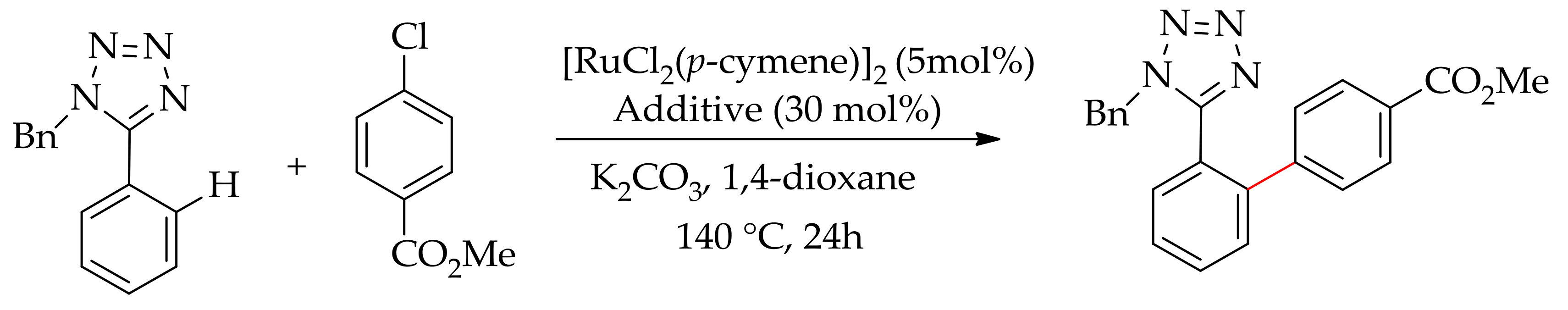
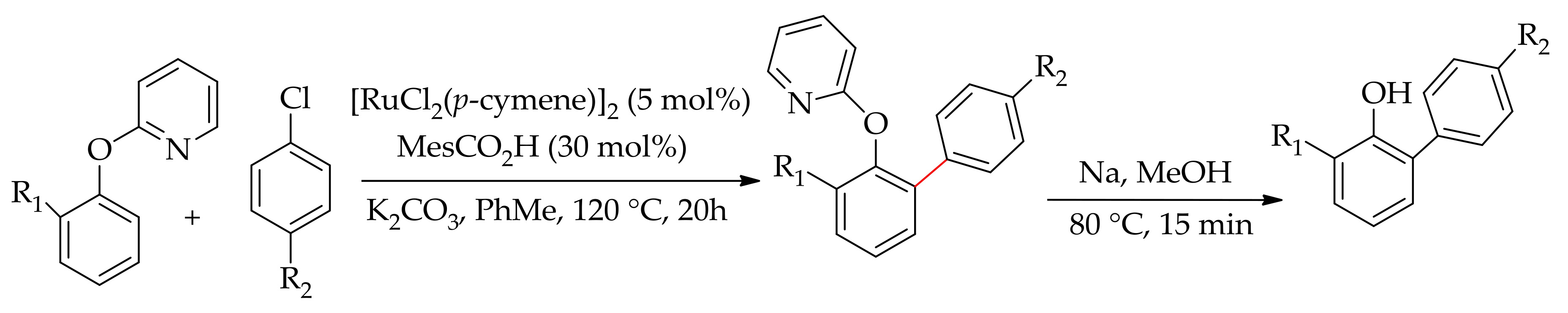
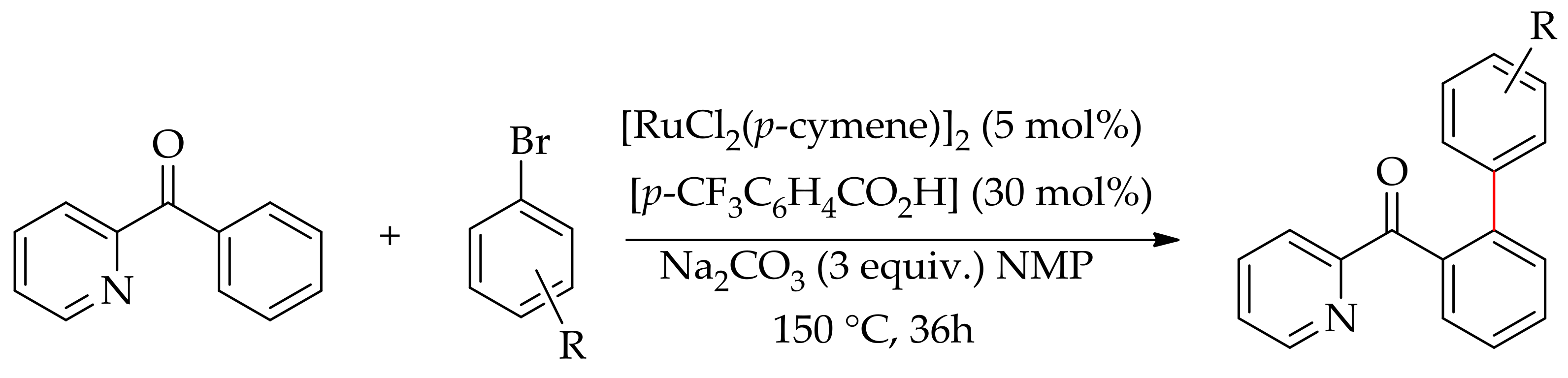
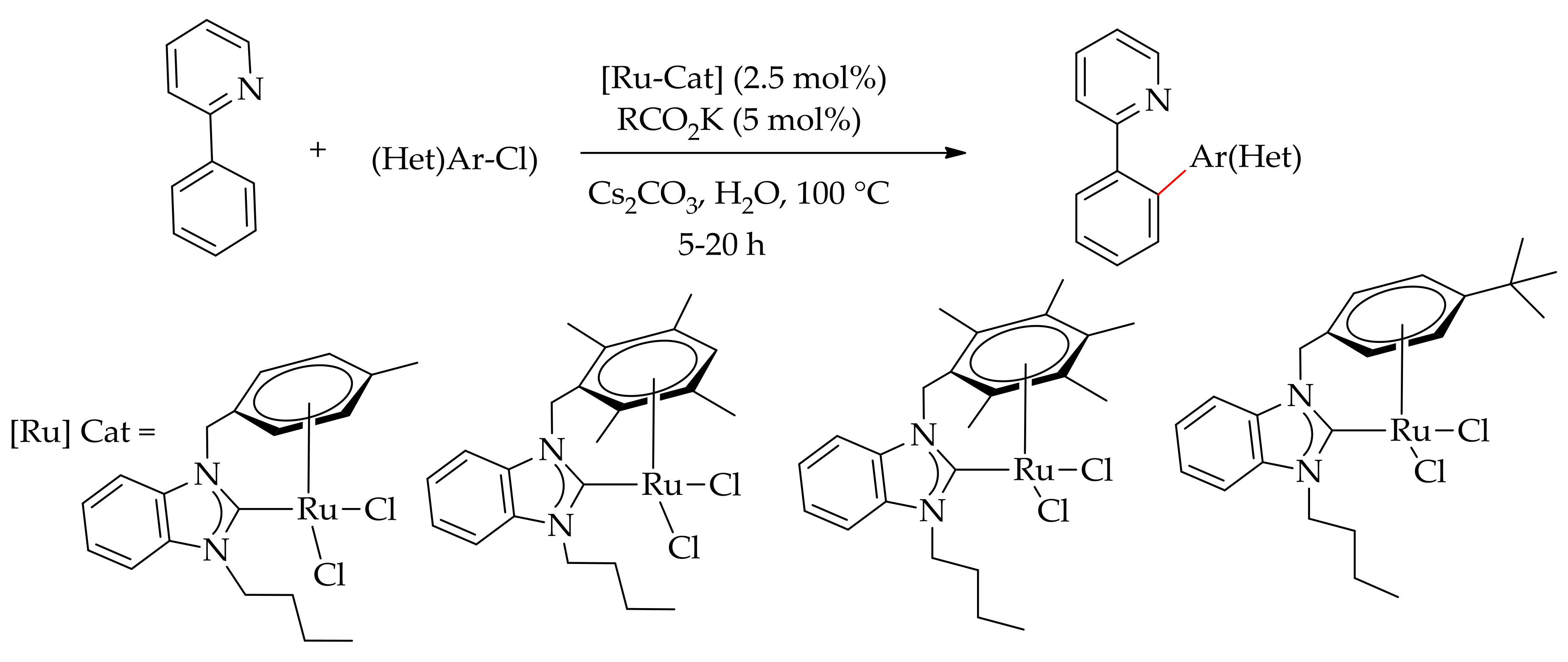
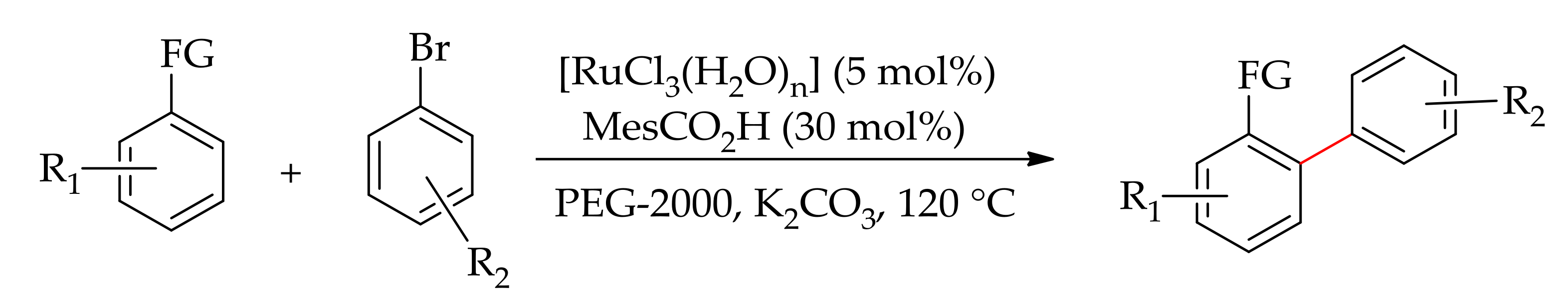


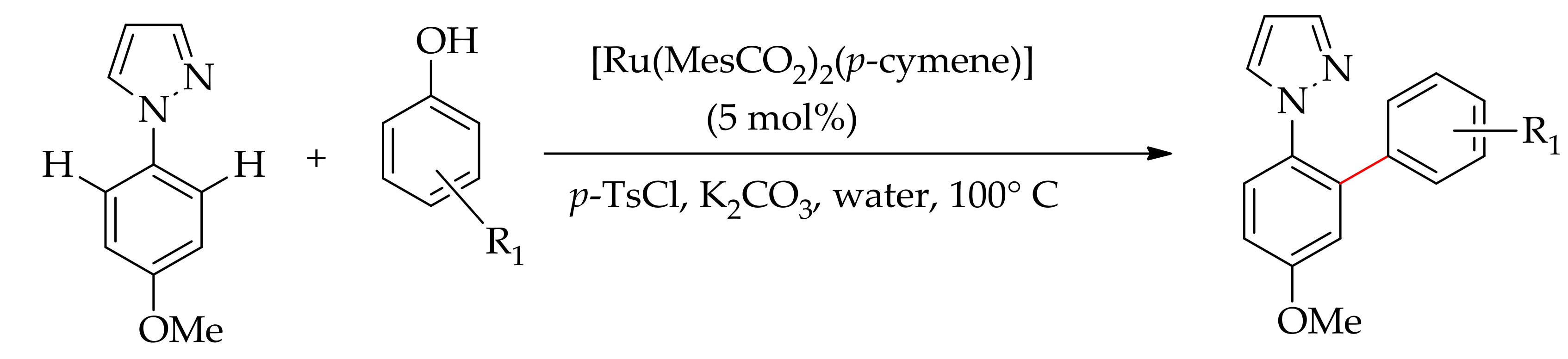
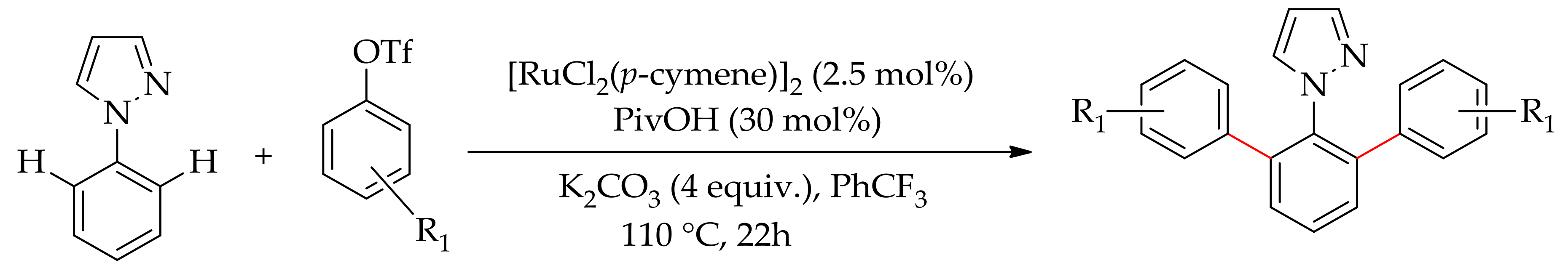
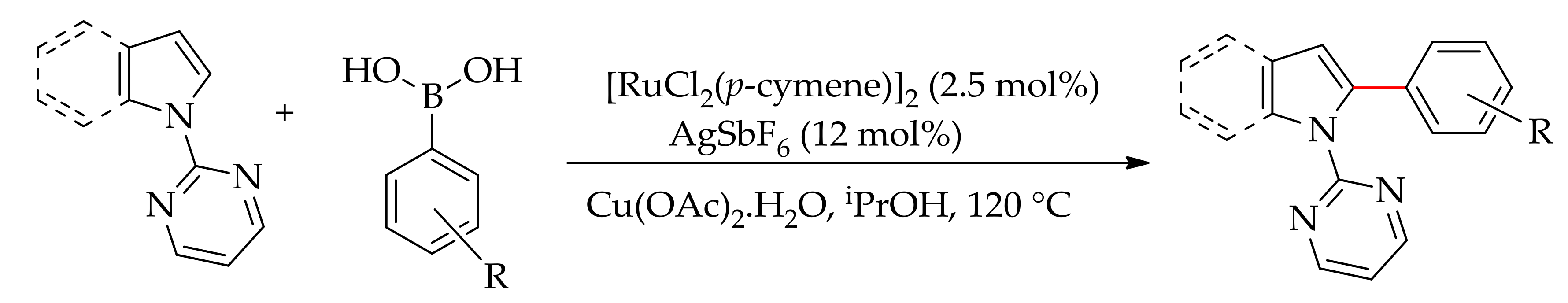

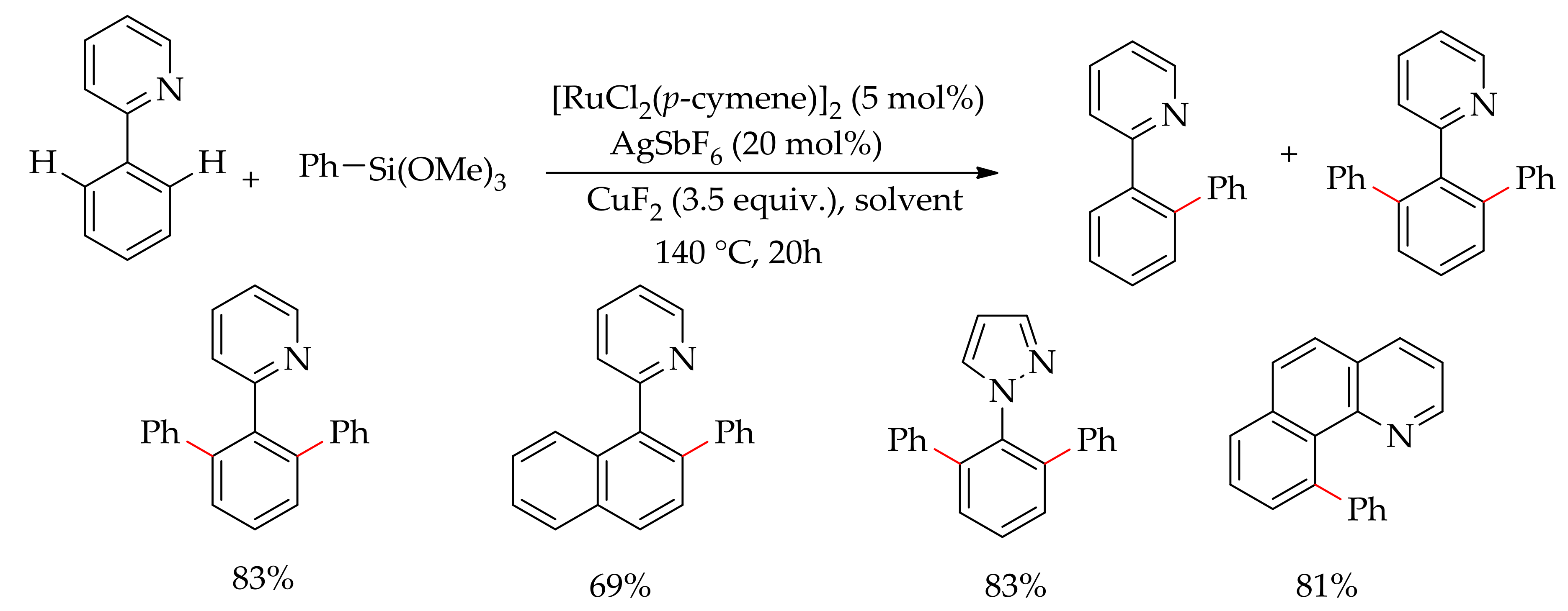
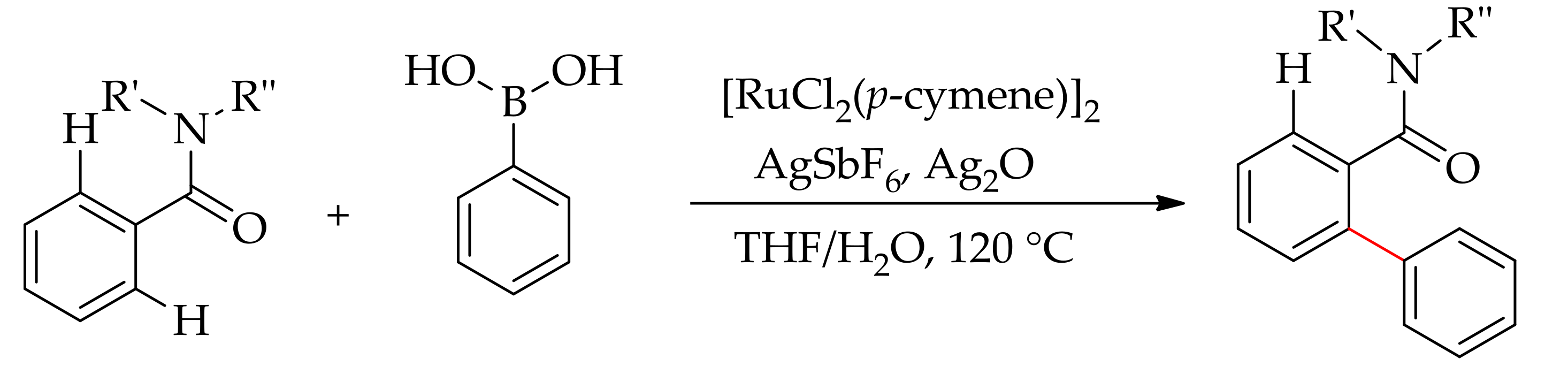
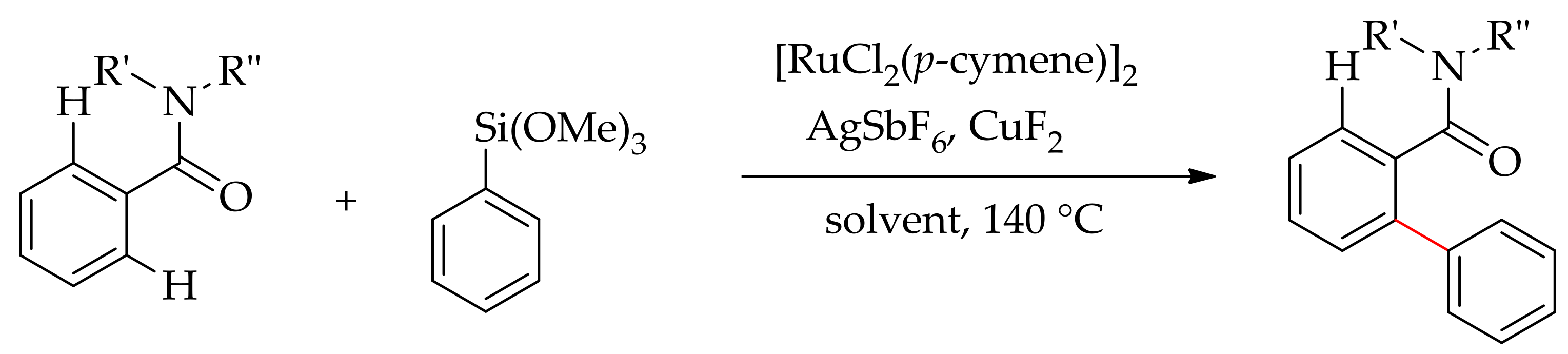

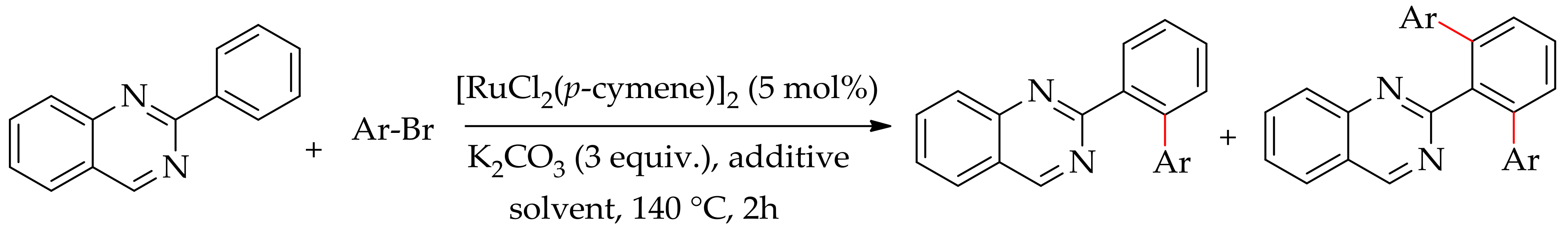
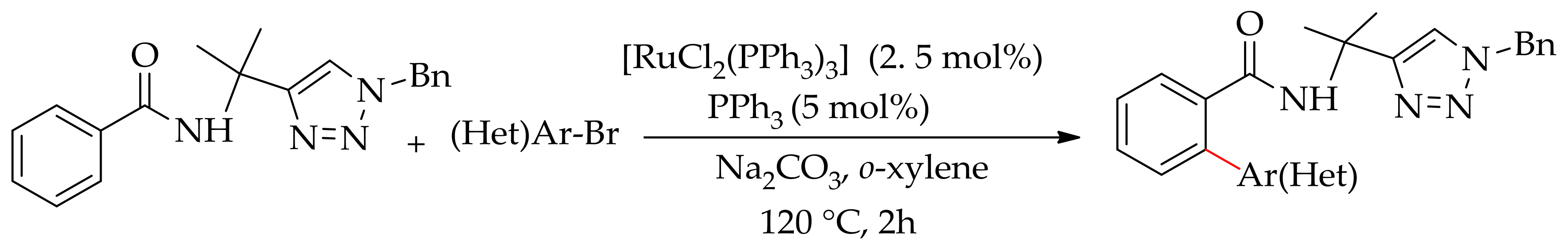
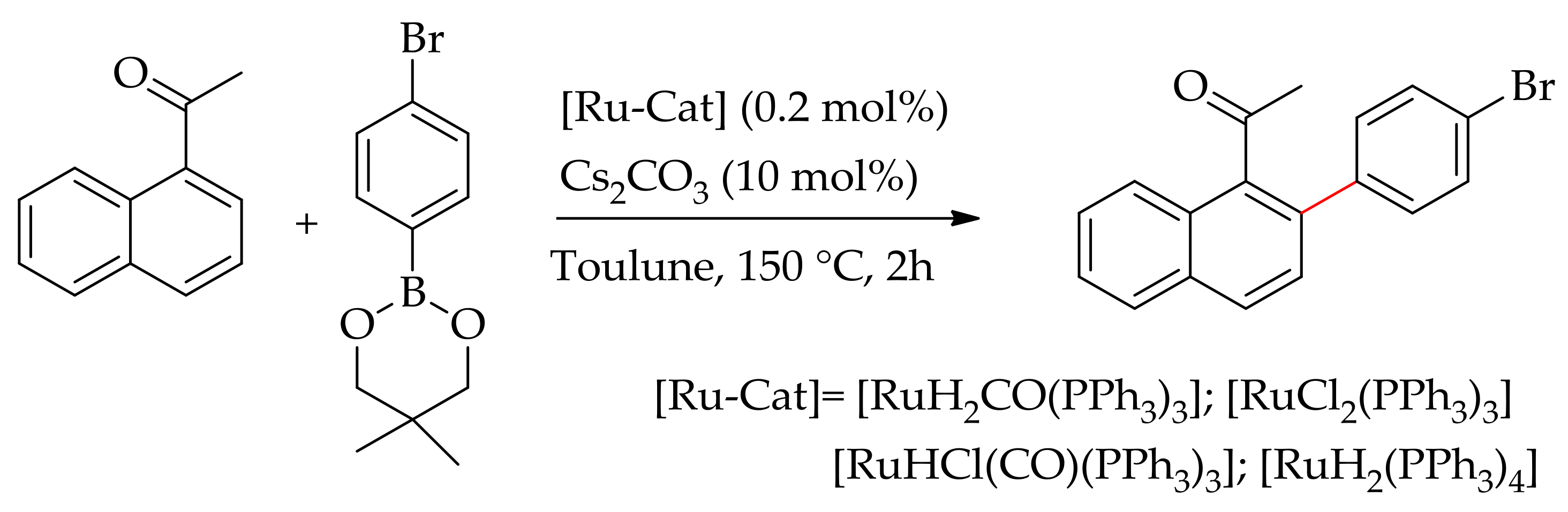


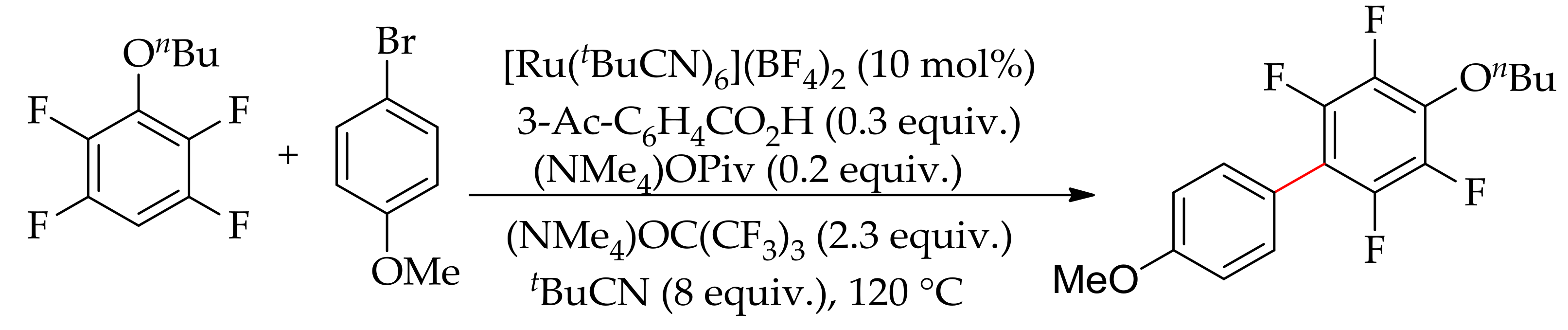
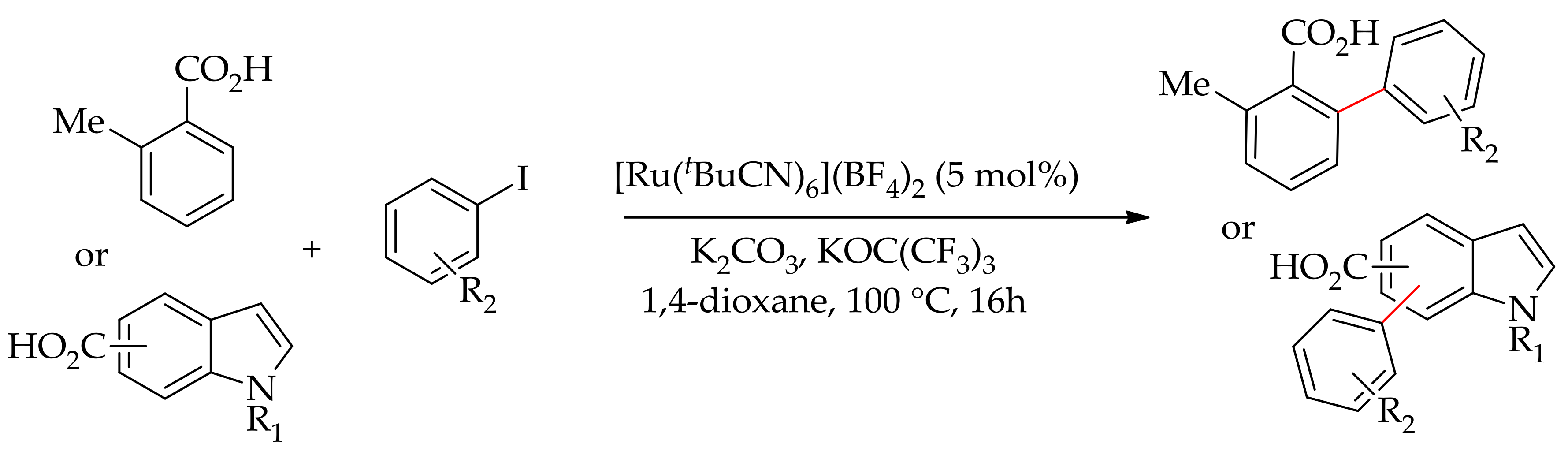
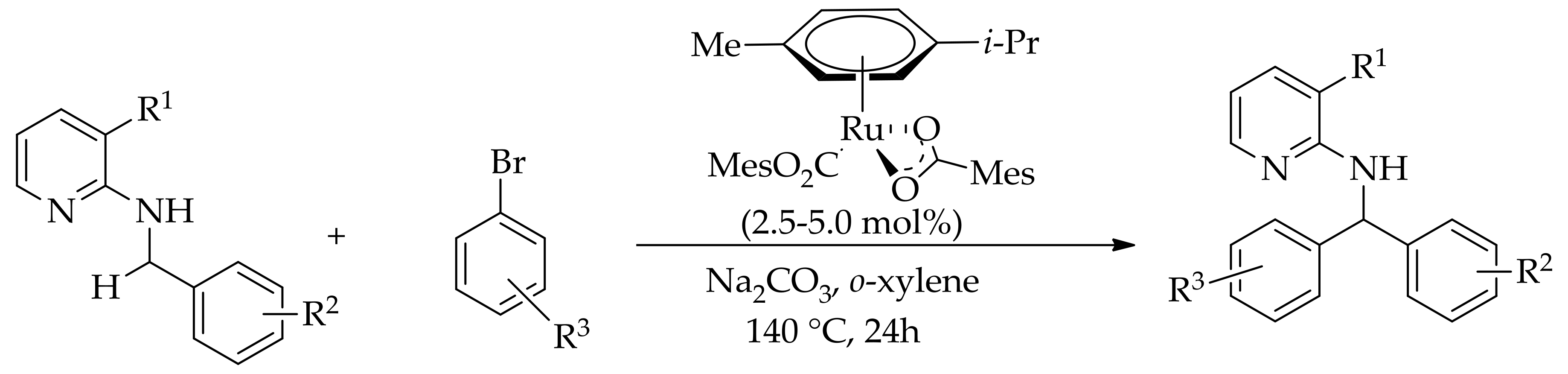
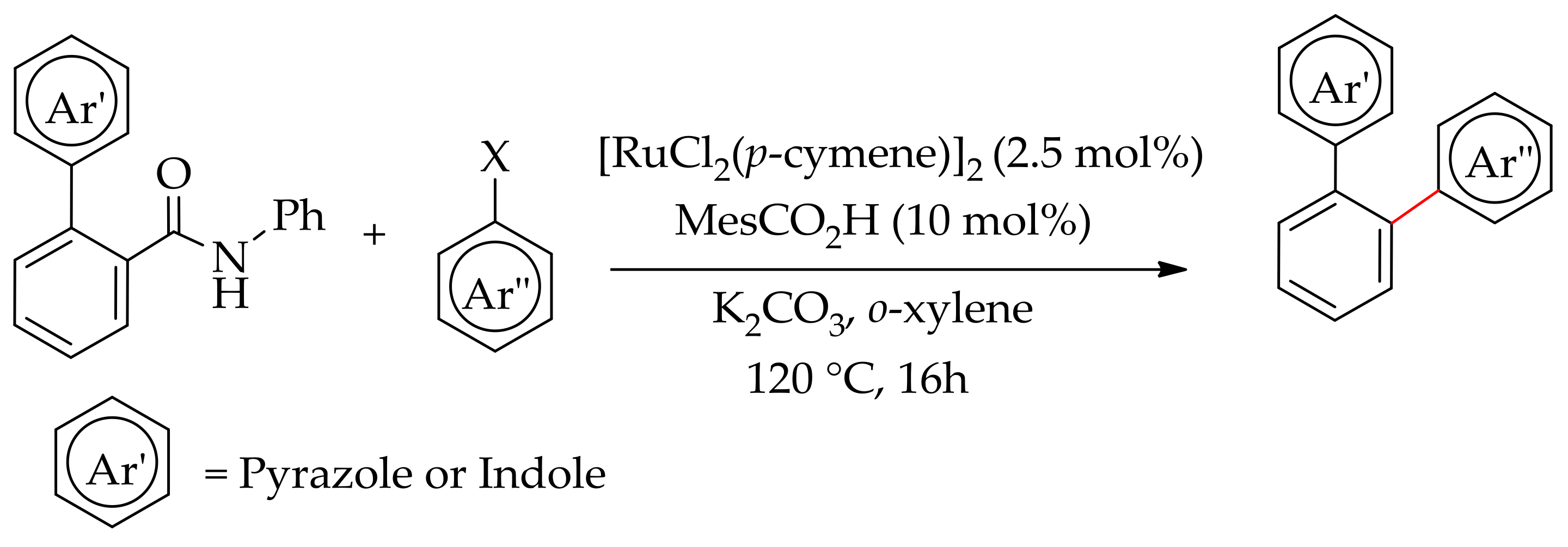

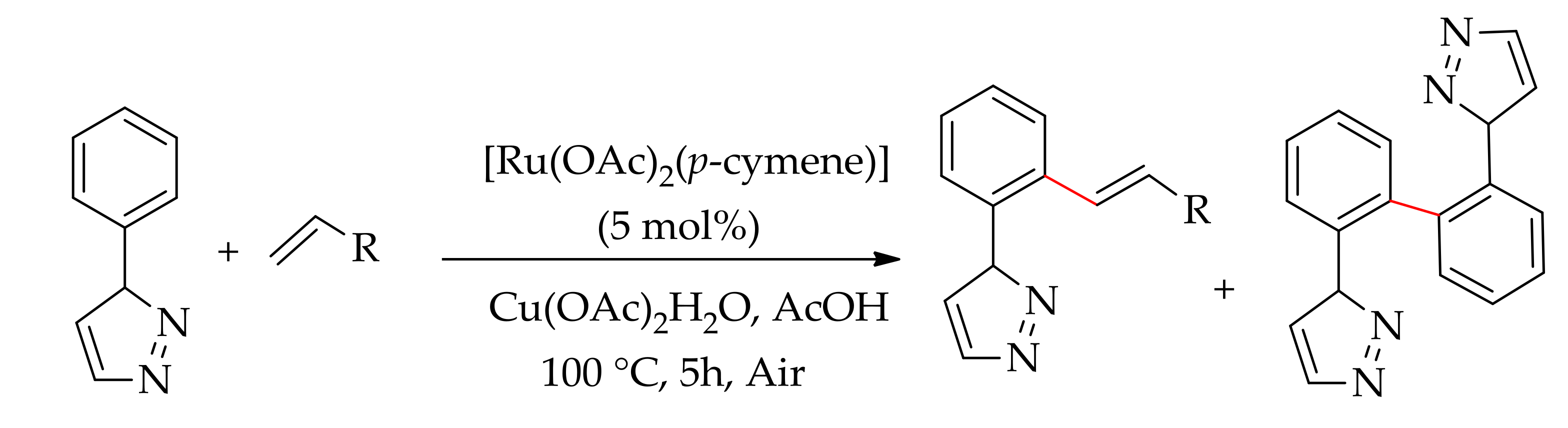
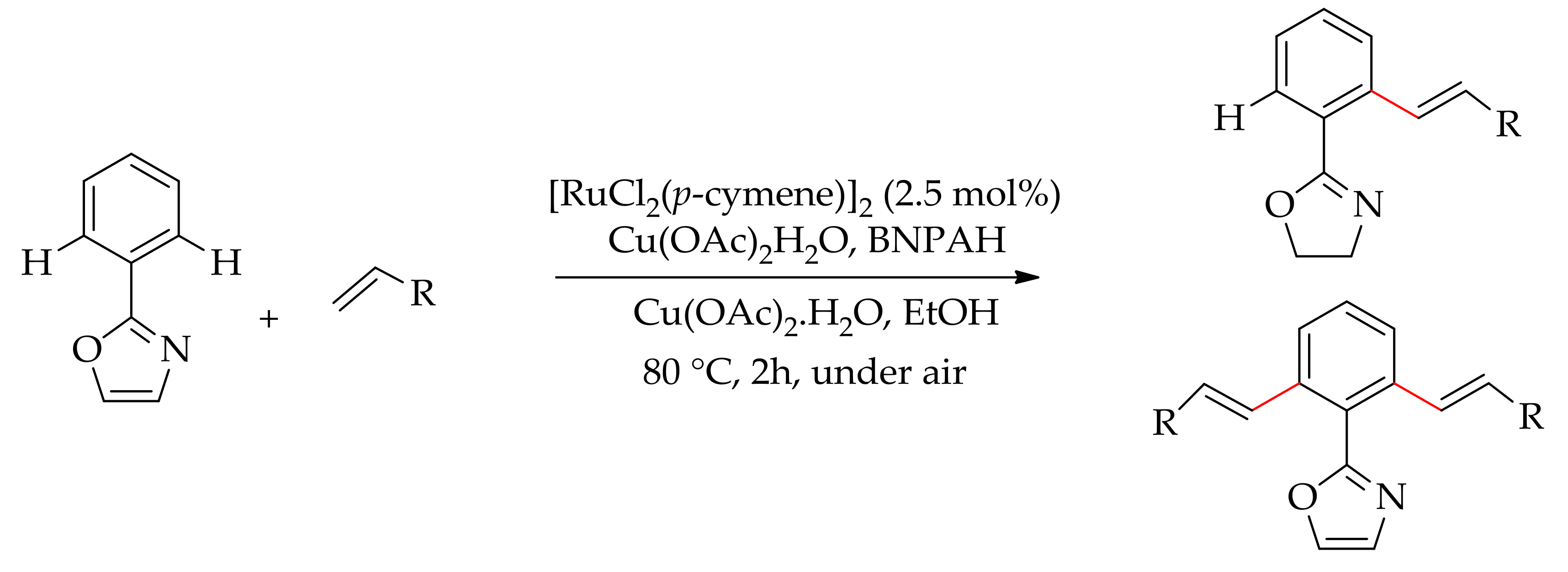
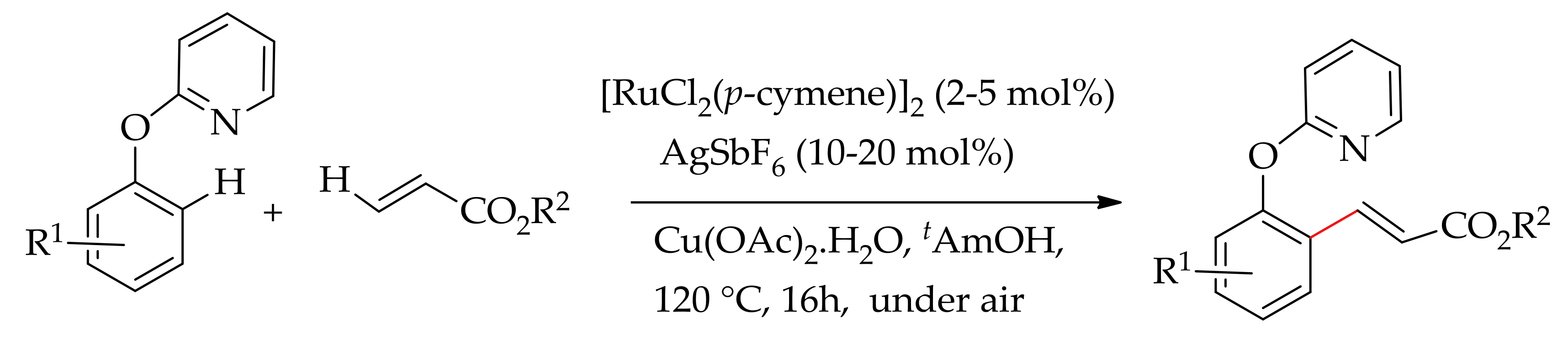
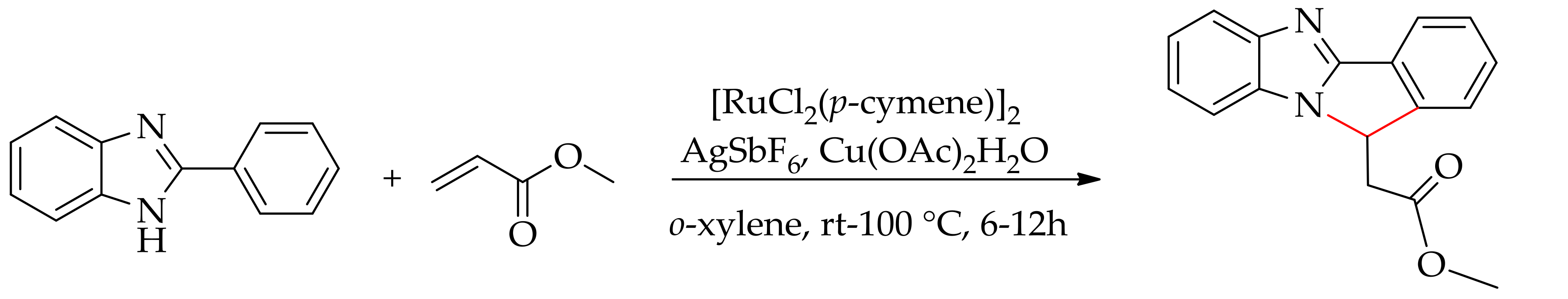
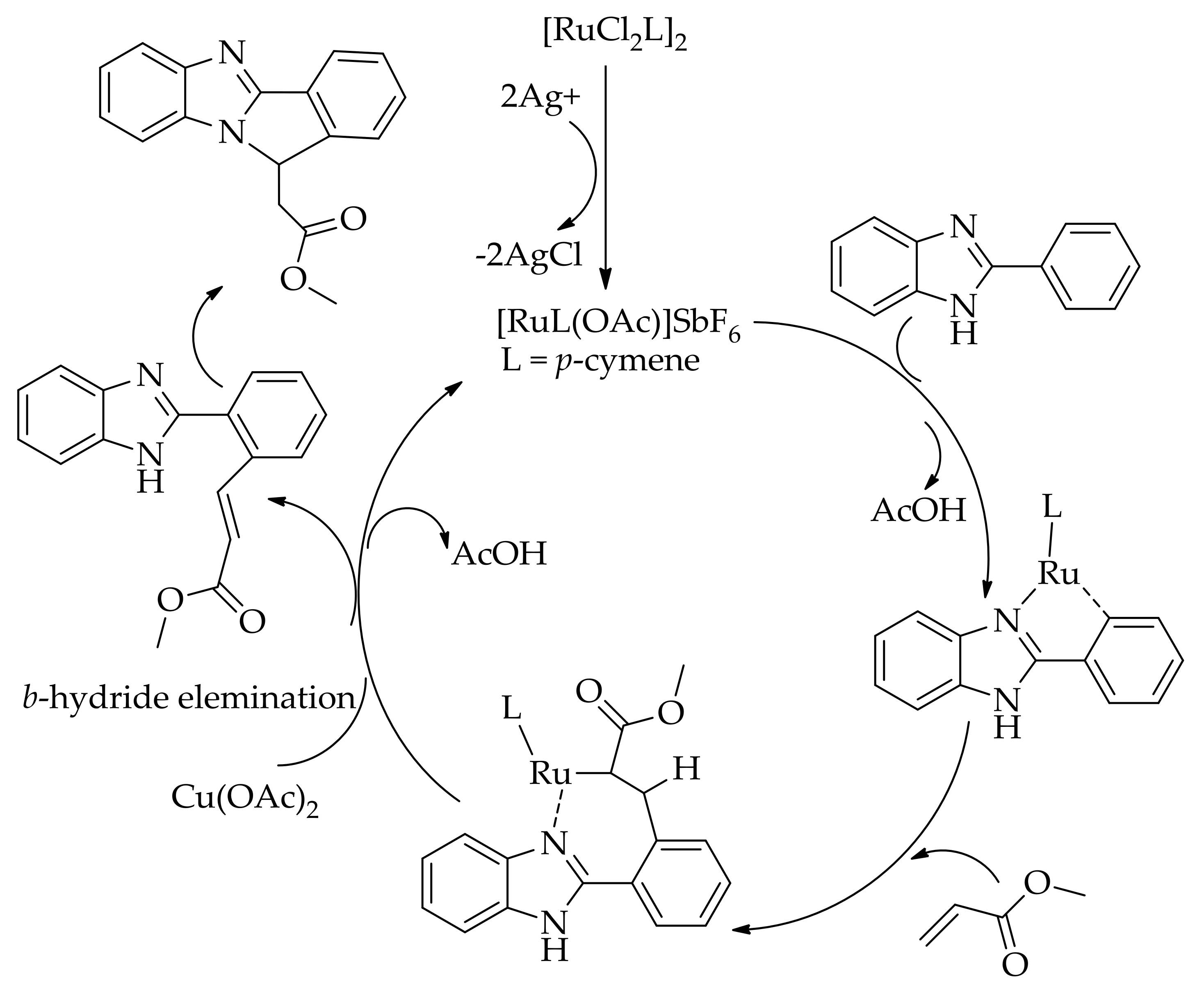

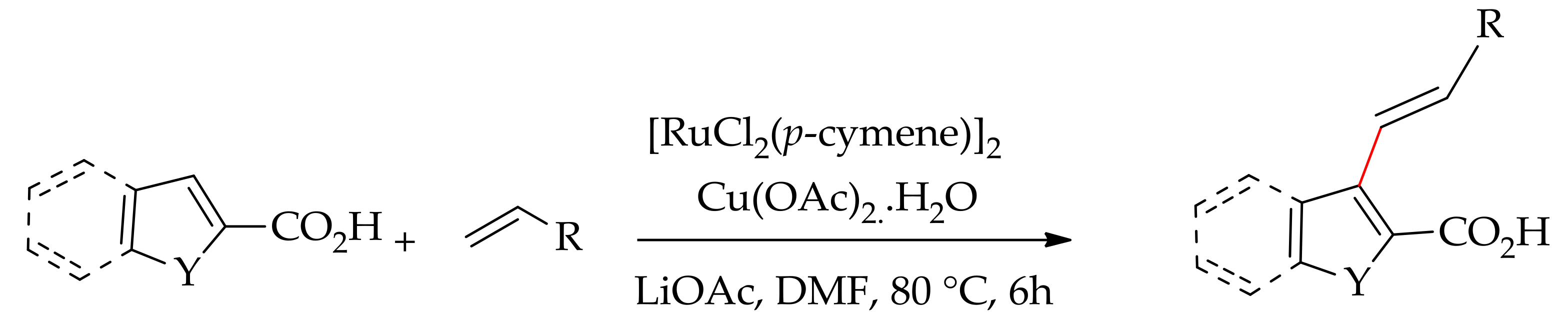

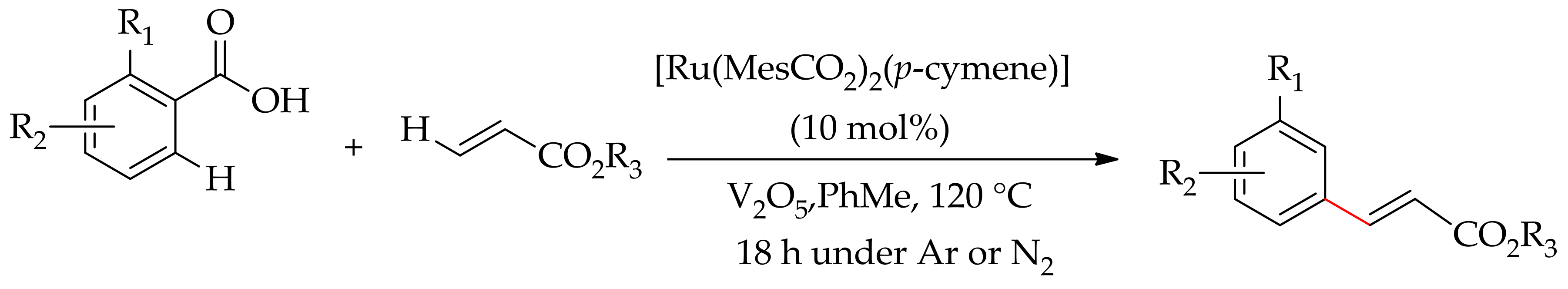
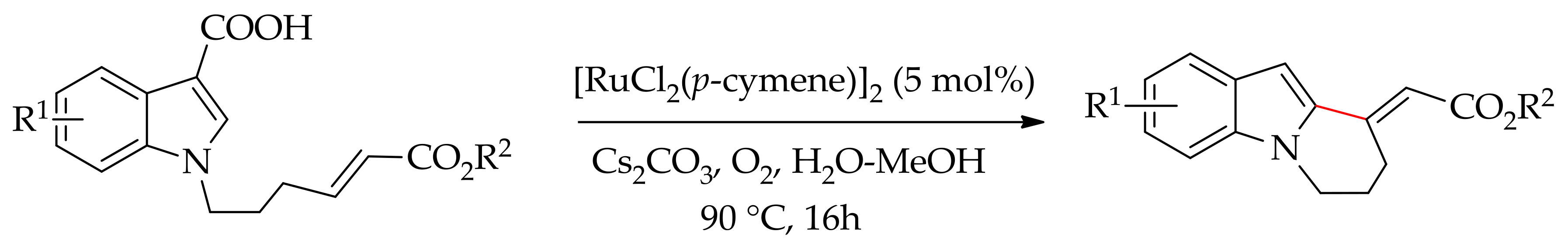
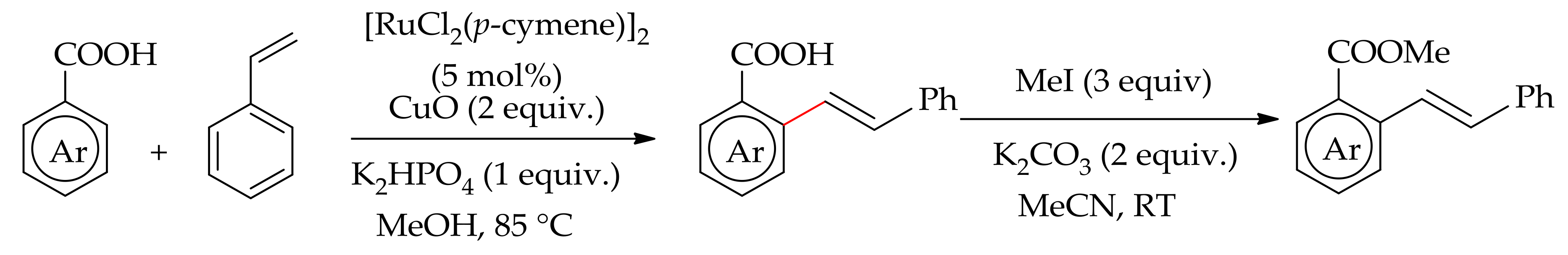
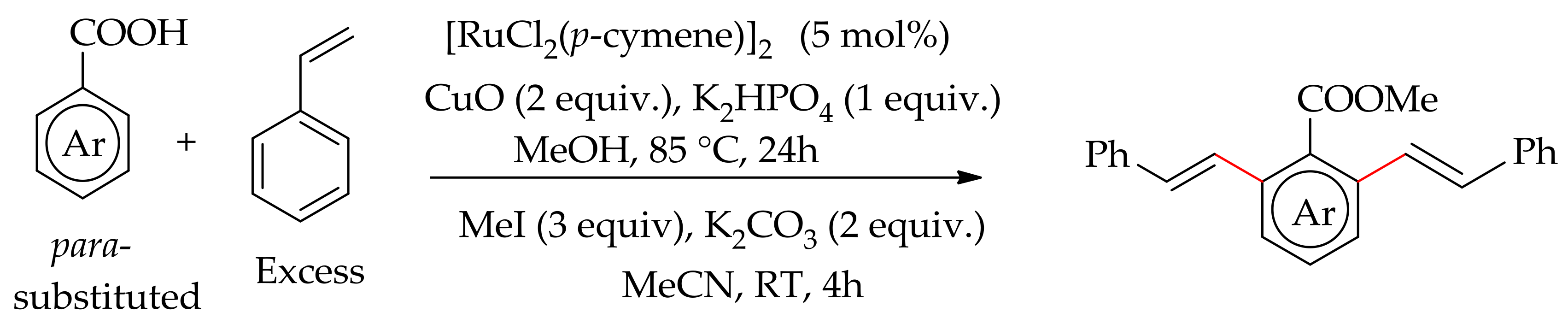
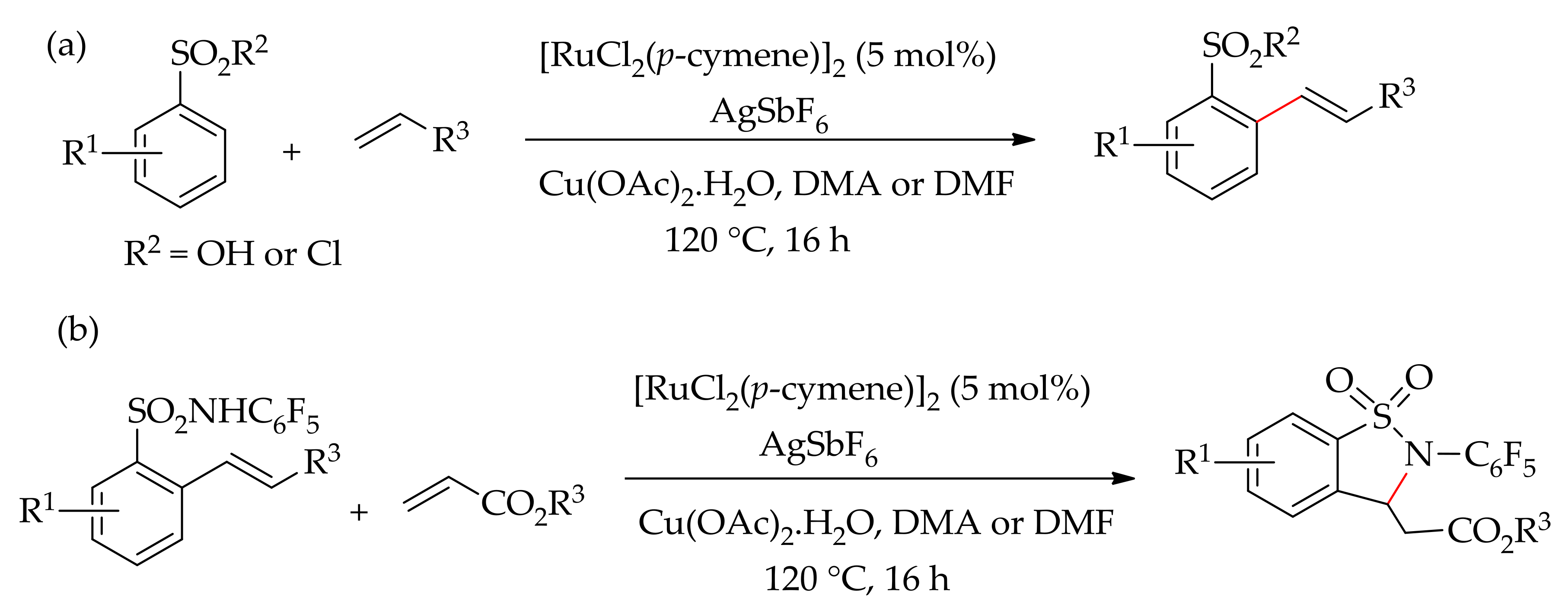

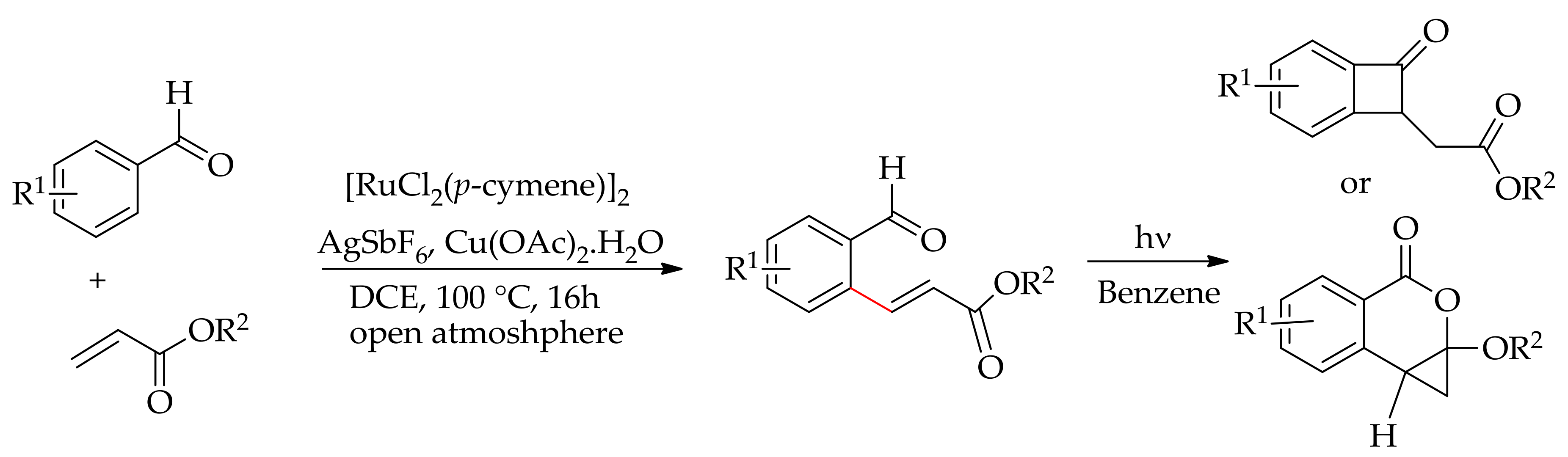



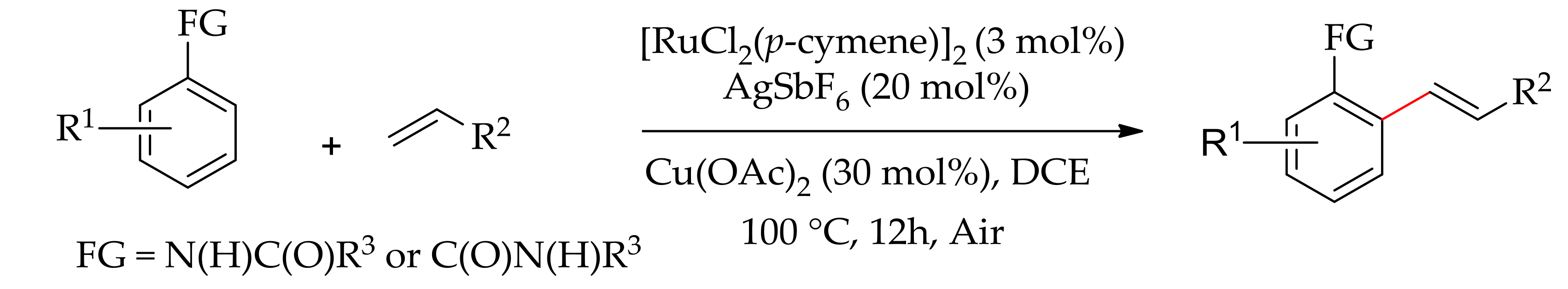

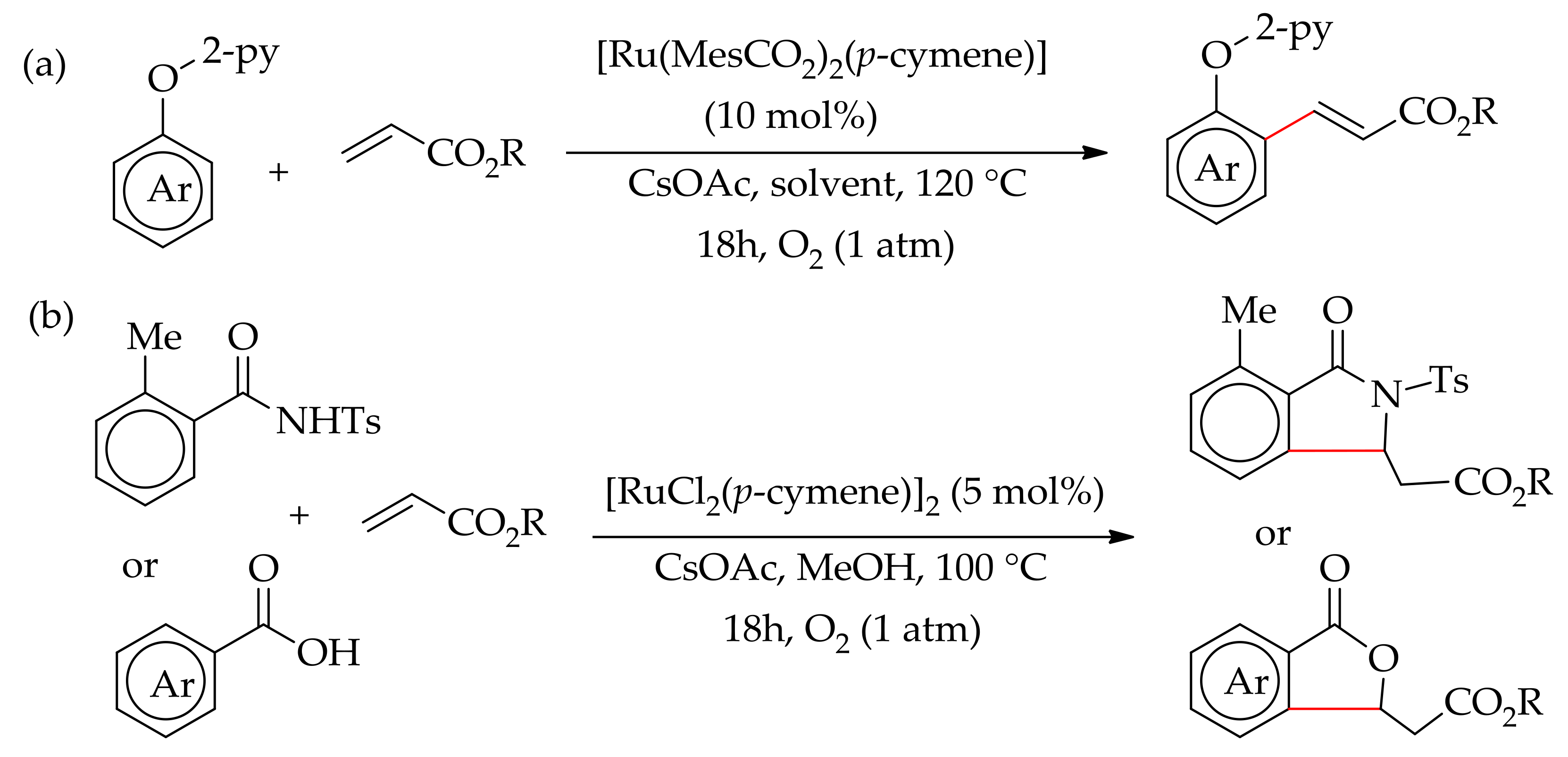

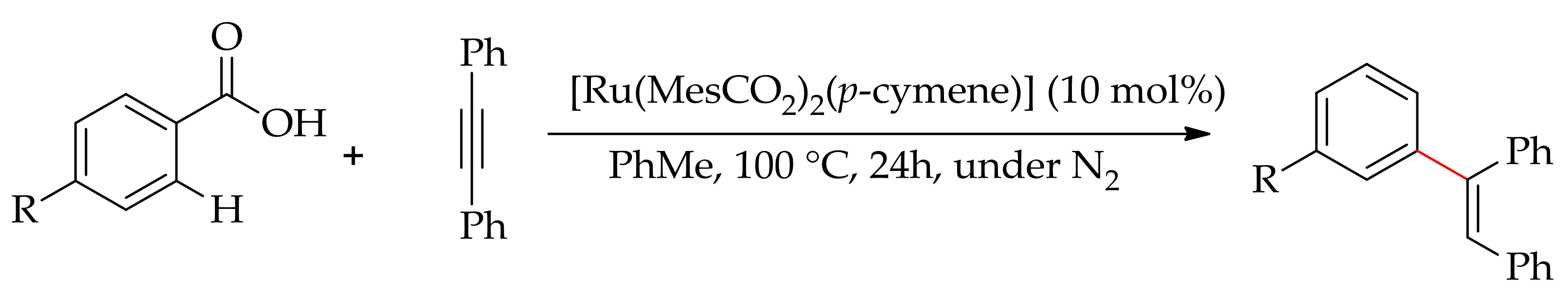
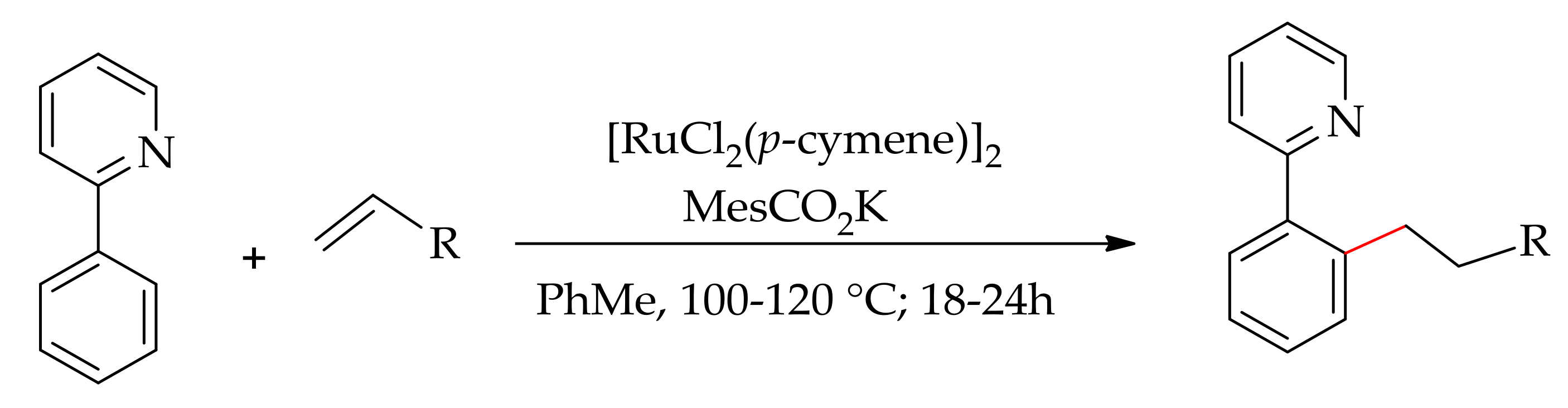

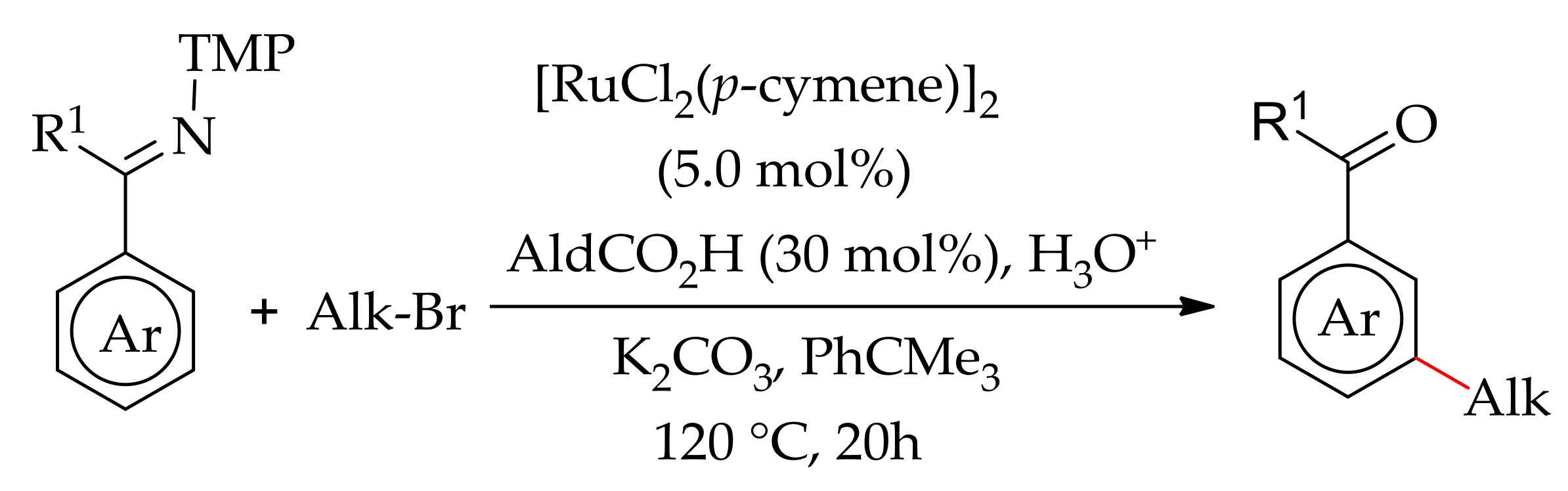

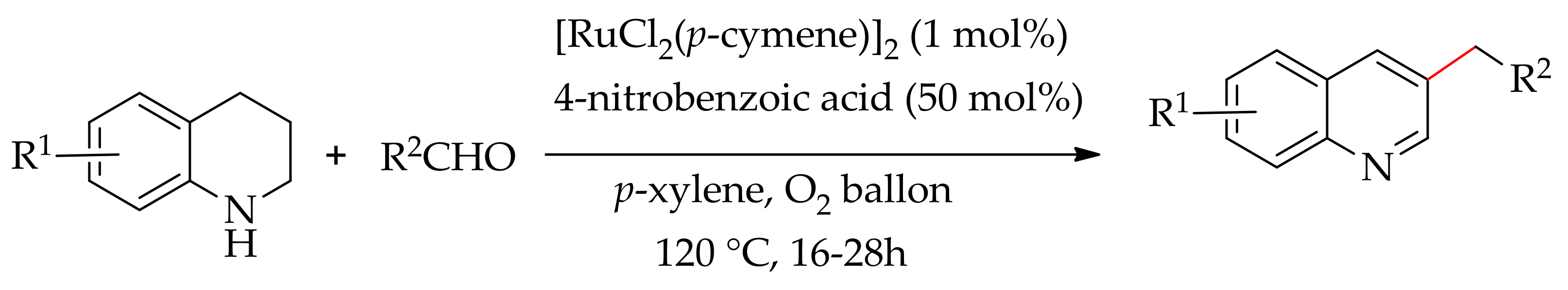


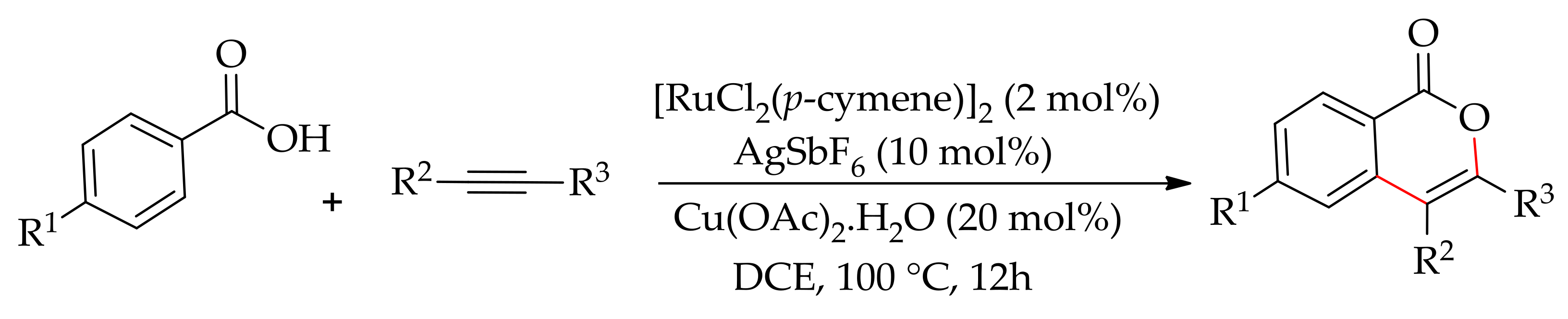
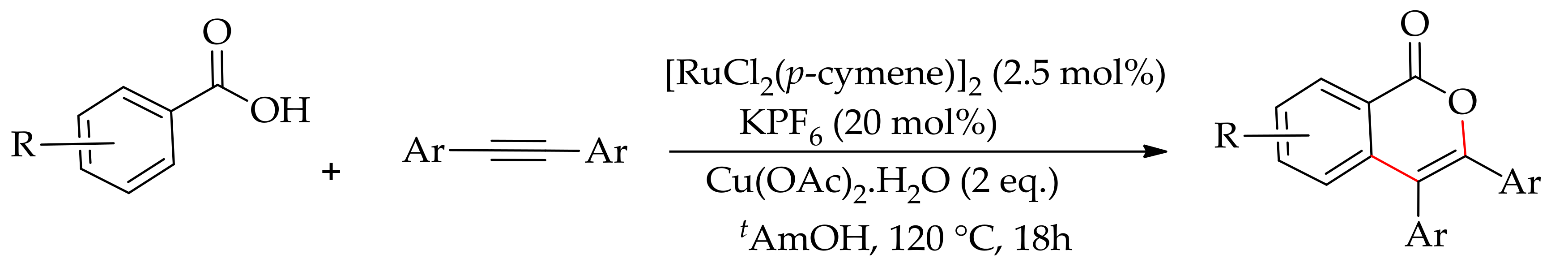


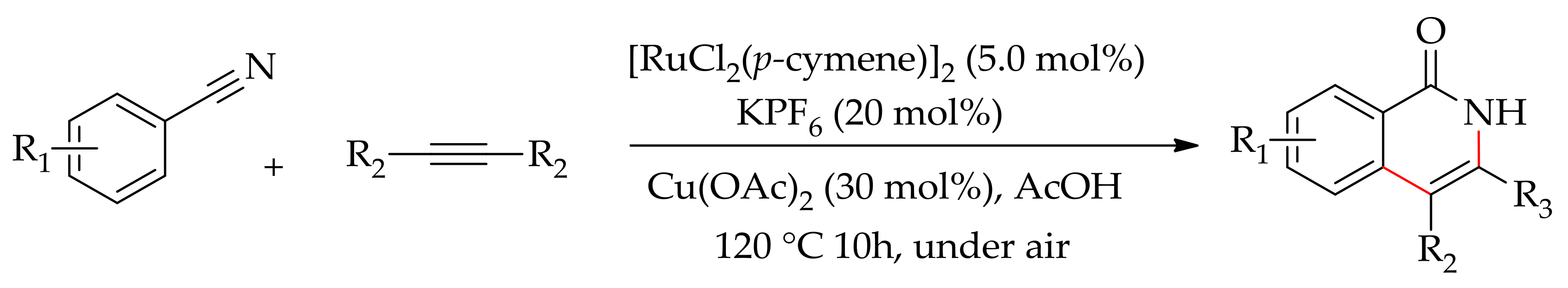
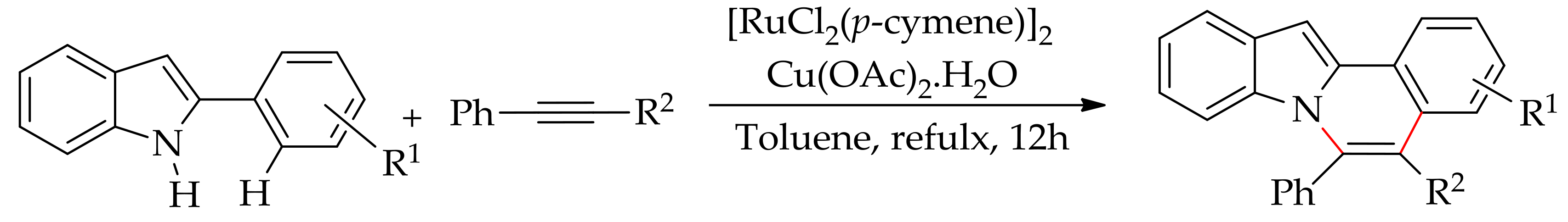




| Additive | Oxidant | Solvent | Mono/Di | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuF2 | − | DEC | 6:94 | >95 |
| CuF2 | − | Toluene | 69:31 | >95 |
| CuF2 | − | THF | 75:25 | >95 |
| CuF2 | − | NMP | − | <2 |
| CuF2 | AgF | DCE | − | <2 |
| CuF2 | Ag2O | DCE | 95:5 | 40 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, K.S. Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020173
Singh KS. Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts. Catalysts. 2019; 9(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Keisham S. 2019. "Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts" Catalysts 9, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020173
APA StyleSingh, K. S. (2019). Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts. Catalysts, 9(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020173




