Abstract
A series of molecular sieve catalysts (Cu–Mn/SAPO-34) with different loadings of Cu and Mn components were prepared by the impregnation method. The deNOx activity of the catalyst was investigated during the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 in the temperature range of 120 °C to 330 °C, including the effects of H2O vapors and SO2. In order to understand the poisoning mechanism by the injection of H2O and/or SO2 into the feeding gas, the characteristics of the fresh and spent catalyst were identified by means of Brunner−Emmet−Teller (BET), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM) and Thermal Gravity- Differential Thermal Gravity (TG-DTG). The conversion of NO by the catalyst can achieve at 72% under the reaction temperature of 120 °C, while the value reached more than 90% under the temperature between 180 °C and 330 °C. The deNOx activity test shows that the H2O has a reversible negative effect on NO conversion, which is mainly due to the competitive adsorption of H2O and NH3 on Lewis acid sites. When the reaction temperature increases to 300 °C, the poisoning effect of H2O can be negligible. The poisoning effect of SO2 on deNOx activity is dependent on the reaction temperature. At low temperature, the poisoning effect of SO2 is permanent with no recovery of deNOx activity after the elimination of SO2. The formation of (NH4)2SO4, which results in the plug of active sites and a decrease of surface area, and the competitive adsorption of SO2 and NO should be responsible for the loss of deNOx activity over Cu/SAPO-34.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen oxides were estimated as one of the major air pollutants released from the combustion of fossil fuels (especially coal), being hazardous for the ecological and environmental system [1,2,3,4]. Currently, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) was regarded as a widely-used deNOx technology for the purification of flue gas, where the performance of the catalyst plays a significant role in the process [5]. Most of the commercial catalysts (e.g., V-W-Ti system) exhibited the effective activity with temperature located in a narrow and relatively high window as 300–400 °C, accelerating the deactivation of catalyst through sintering and occlusion of salts produced from H2O or SO2. The high deNOx activity of SCR catalyst at relatively low temperature is highly required without the formation of salts from H2O and SO2 in the flue gas. The stability of the air-preheating system can be improved along with the secure low-temperature SCR system, leading to a full-time deNOx for the power plant under different power loadings. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop efficient and stable low-temperature SCR catalyst [6].
Among all these catalysts, transition metal loaded on zeolite materials with CHA structure have been widely focused due to the broad operating temperature range and the high deNOx activity [7,8,9]. A number of research works have been conducted on the deNOx performance of molecular sieve catalysts, such as the ZSM-5, BEA, USY, SSZ-13 and so on [10,11,12]. Kim [13] prepared Mn–Fe/ZSM-5 by the impregnation method, exhibiting the NOx conversion ratio as high as 95% at 175 °C, and the conversion of NOx nearly to 100% during the temperature between 200 and 350 °C. SAPO-34 possesses pear-shaped cages with 8-membered ring (8MR) openings, and double 6-membered ring (D6MR) units linked by 4-membered ring (4MR) units, while most of the P is replaced by Si to generate a Si–O–Al linkage, resulting in remarkable SCR performance. Compared with Fe-zeolites and vanadia-zeolites, Cu-zeolites exhibited a superior deNOx activity and high N2 selectivity [14,15]. Wang [16,17], Ye [18] and Deka [19] prepared Cu/SAPO-34 by different methods, exhibiting an excellent low-temperature SCR activity in the temperature range from 150 °C to 500 °C. Among all these researches, Cu-SAPO-34 based catalysts showed a remarkable deNOx activity compared to other zeolites [8,20].
However, Cu-SAPO-34 catalyst is proved to be sensitive to SO2 poisoning due to the strong chemical binding strength and the oxidative conditions in the gas and the deactivation effect is more pronounced at low temperatures [21]. Zhang et al. [7] have used DRIFT and Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD) method to study the poisoning effect of SO2 over Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst, they reported that low-temperature deactivation is caused by the formation of ammonium sulfates. Shen et al. [22] observed no obvious sulfur species on the Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst and they concluded that the reduction of the number of isolated Cu2+ caused by SO2 might induce the loss of SCR activity. Wijayanti et al. [23] studied the SO2 poisoning effects and found that the main reason for the deactivation is the formation of copper sulfates, resulting in the loss of redox properties. Jangjou et al. [24] reported the S species formed on Cu2+ at 6MR by DRIFT study. On the basis of such observations, the formation of ammonium sulfates in a complex with Cu is claimed as the main mechanism for the loss of low-temperature deNOx activity. In general, different SO2 poisoning mechanisms have been proposed by different researchers.
In addition, H2O is also one of the main components in the flue gas and often causes the loss of low-temperature deNOx activity [3]. In this work, for a better and specific understanding of the SO2 poisoning mechanism and the synergistic effect of H2O and SO2 over Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst, the influence of SO2 or/and H2O with different concentrations at different reaction temperatures on deNOx activity and physicochemical properties over Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst was studied. A series of Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalysts were prepared through the impregnation method. The low-temperature deNOx activity of the catalysts was estimated by means of a self-designed apparatus, where the effects of H2O and SO2 on the reaction activity were also investigated. BET, XRD, SEM and TG-DTG were employed to determine the characteristics of the fresh and spent catalyst, in order to understand the poisoning mechanism of the catalyst by H2O and SO2 during the low-temperature SCR process.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. DeNOx Activity of the Catalysts Without H2O and SO2
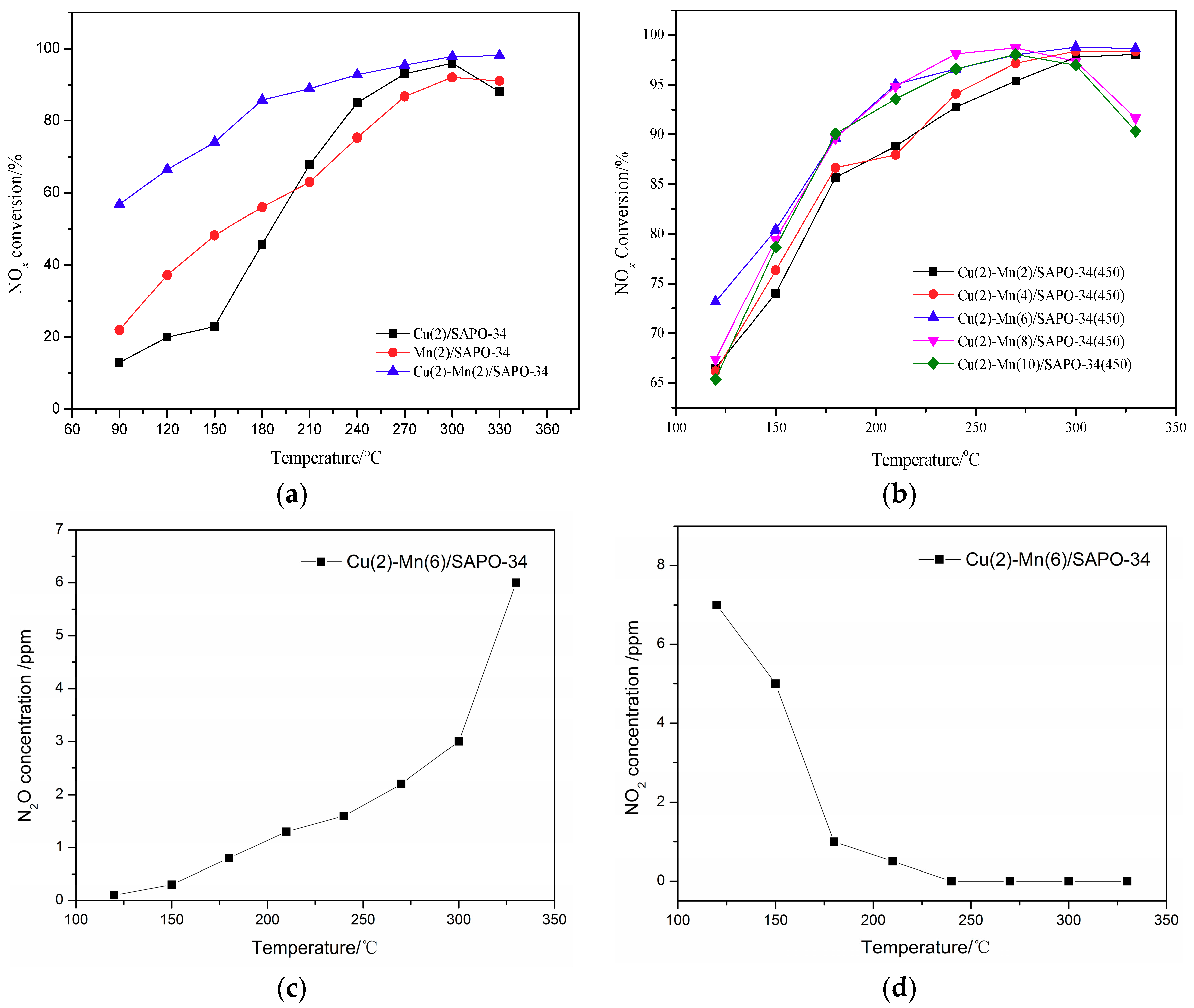
Figure 1a illustrates the deNOx activity of Cu/SAPO-34, Mn/SAPO-34, Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 catalysts under different temperatures without H2O and SO2. The deNOx activity of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst (bimetallic composite molecular sieve) was much higher than that of Cu/SAPO-34 and Mn/SAPO-34 catalysts (monomeric molecular sieve). Even when the reaction temperature is lower than 100 °C the NO conversion by Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst can be achieved at about 60%, while for the other two catalysts was around 20%.
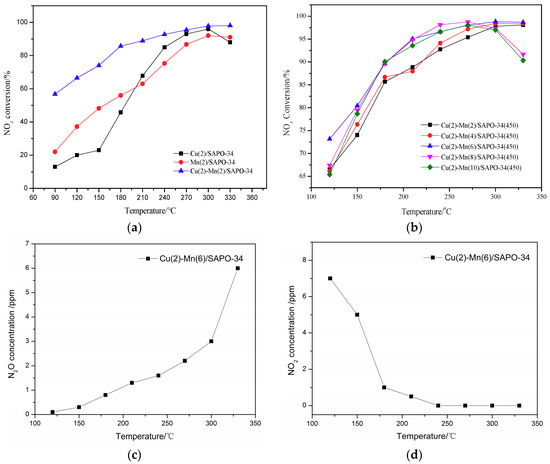
Figure 1.
DeNOx performance of mono-component and multi-component catalysts (a); deNOx performance of molecular catalysts with different Mn loadings (b); outlet N2O concentration over Cu(2)-Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst (c); outlet NO2 concentration over Cu(2)-Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst (d).
The NO conversion over Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst could reach 90% at around 180 °C, compared to that of 220 °C for Cu/SAPO-34 and 270 °C for Mn/SAPO-34. It can be concluded that the Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst gives a better deNOx performance under the relatively low-temperature range from 100 to 200 °C. This can be attributed to the promotion of NH3 adsorption on the surface of the catalyst by the bimetallic system on SAPO-34 [25,26,27]. In addition, the deNOx reaction energy might be declined by the bimetallic interaction on the catalyst, improving the low-temperature activity of the catalyst and broadening its SCR temperature range.
The effect of metal loading on the activity of Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst is shown in Figure 1b. The deNOx activity of Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 performed as the best one among the catalysts at the temperature from 120 to 210 °C and from 270 to 330 °C, while Cu(2)–Mn(8)/SAPO-34 performs the best one at the temperature from 210 to 270 °C. It needs to be noted that the NO conversion over Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 with the Mn content more than 8% was notably declined when the reaction temperature is higher than 270 °C. Under high temperatures, the oxidation of the catalyst can be enhanced with the increased loading of Mn [28]. This leads to the oxidation of NH3 to NO and then the decline of the NO conversion (Figure 1b). In addition, the nonselective catalytic reduction (NSCR) reaction and catalytic oxidation reaction (i.e., the C–O reaction) happens simultaneously during the NH3-SCR reaction. The outlet N2O and NO2 concentration over Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst are shown in Figure 1c,d. It can be seen that the N2O concentration increases with the increase of reaction temperature, which may contribute to the decrease of deNOx activity over Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst at 330 °C. With the increase of reaction temperature, the NO2 concentration decreases. These results demonstrate that N2 is the main product of NH3-SCR reaction over Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst according to the “standard SCR ” reaction [29].
2.2. Effect of H2O on the deNOx Activity of the Catalyst
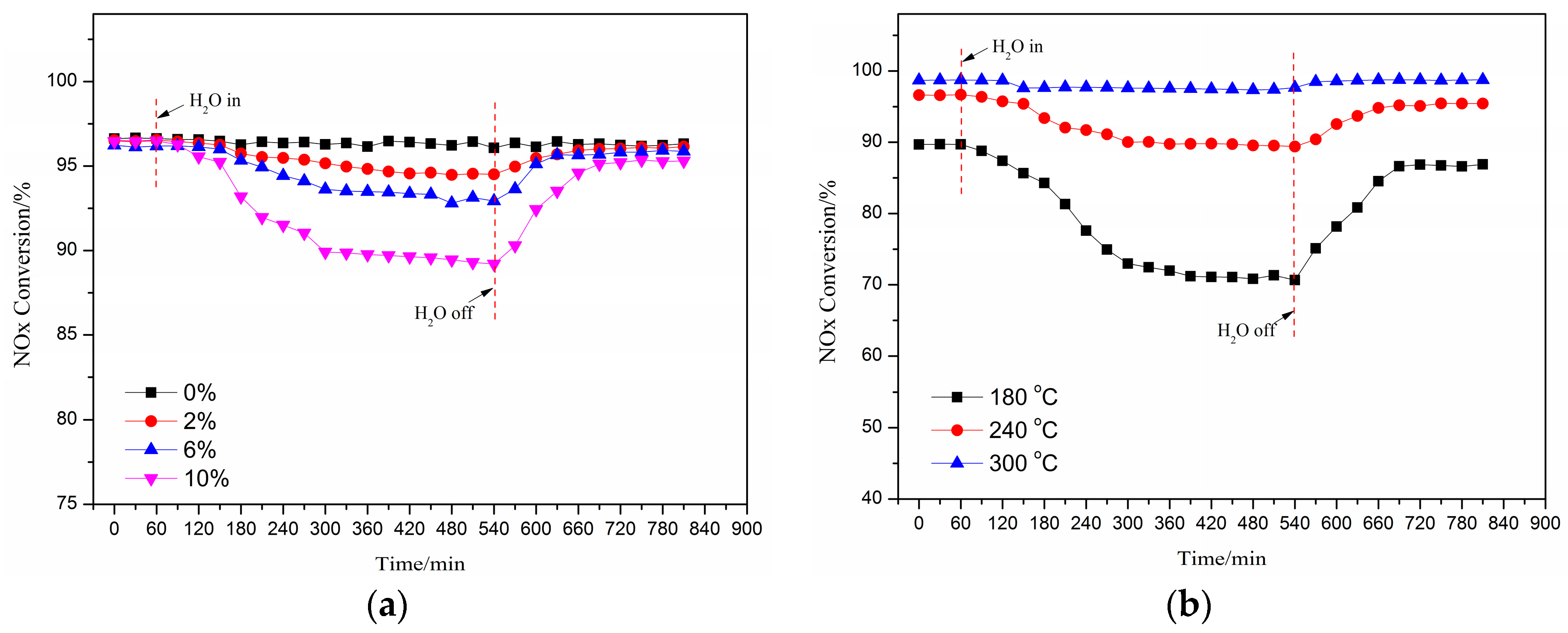
The effect of the injected H2O concentration into feeding gas on the deNOx activity of Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst at a reaction temperature of 240 °C was shown in Figure 2a. The NO conversion decreased with an increased H2O concentration. When the volume concentration of 2% water vapor was injected into the original feeding gas after 8 h, the deNOx activity of the catalyst was declined from 93% to 91%. While the volume concentration of the vapor injected into the feeding gas was increased to 10%, after 8 h, the activity of the catalyst decreased to 86%. It needs to be noted that the activity of catalyst after the 8-hour injection of vapor was recovered to its original level after a while of the vapor cut-off in spite of the concentration of vapor. This indicates that the poisoning of the catalyst by the water is due to the competitive adsorption between H2O vapor and NH3 or NO, which is reversible. When the water vapor concentration was increased, the activity of the spent catalyst (after the cut-off of vapor) was a little bit lower than that of the original catalyst. It is demonstrated that the hydroxyl may be created due to the adsorption and decomposition of H2O on the surface of Cu/SAPO-34 with the increase of H2O concentration, resulting in the irreversible loss of deNOx activity [3].
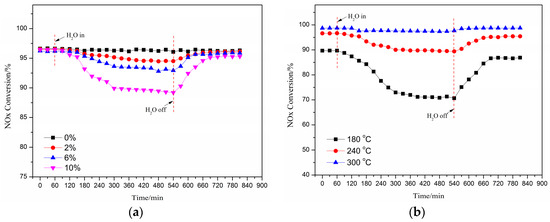
Figure 2.
Effect of the injected H2O concentration on the deNOx activity of the catalyst (240 °C) (a); effect of H2O on the deNOx activity of catalyst under different temperatures (10% H2O) (b).
Figure 2b shows the effect of H2O on the deNOx activity of the catalyst Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 under different temperatures with the concentration of water vapor as 10%. The deNOx activity of the catalyst was significantly influenced at low reaction temperature with the presence of H2O. A sharp decline of the deNOx activity of catalyst (from 86% to 68%) can be observed under the reaction temperature of 180 °C after the 4-hour injection of vapor into the feeding gas. However, no significant change in the activity of the catalyst can be found for the reaction under 300 °C in the presence of vapor. After 8 h injection of the vapor under 180 °C, the activity of the catalyst was all recovered to its original level in 2 h, while the activity recovery duration for the catalyst was decreased with the increased reaction temperature after the cut-off of vapor. The adsorption capacity of H2O on the surface of the catalyst can be enhanced under the lower temperatures, occupying more active sites than that of NH3, NO and other reaction gases [30]. It can be also concluded that poisoning performance of water on the activity of the catalyst can be ignored while the reaction temperature is increased over 300 °C.
2.3. Effect of SO2 on the deNOx Activity of the Catalyst
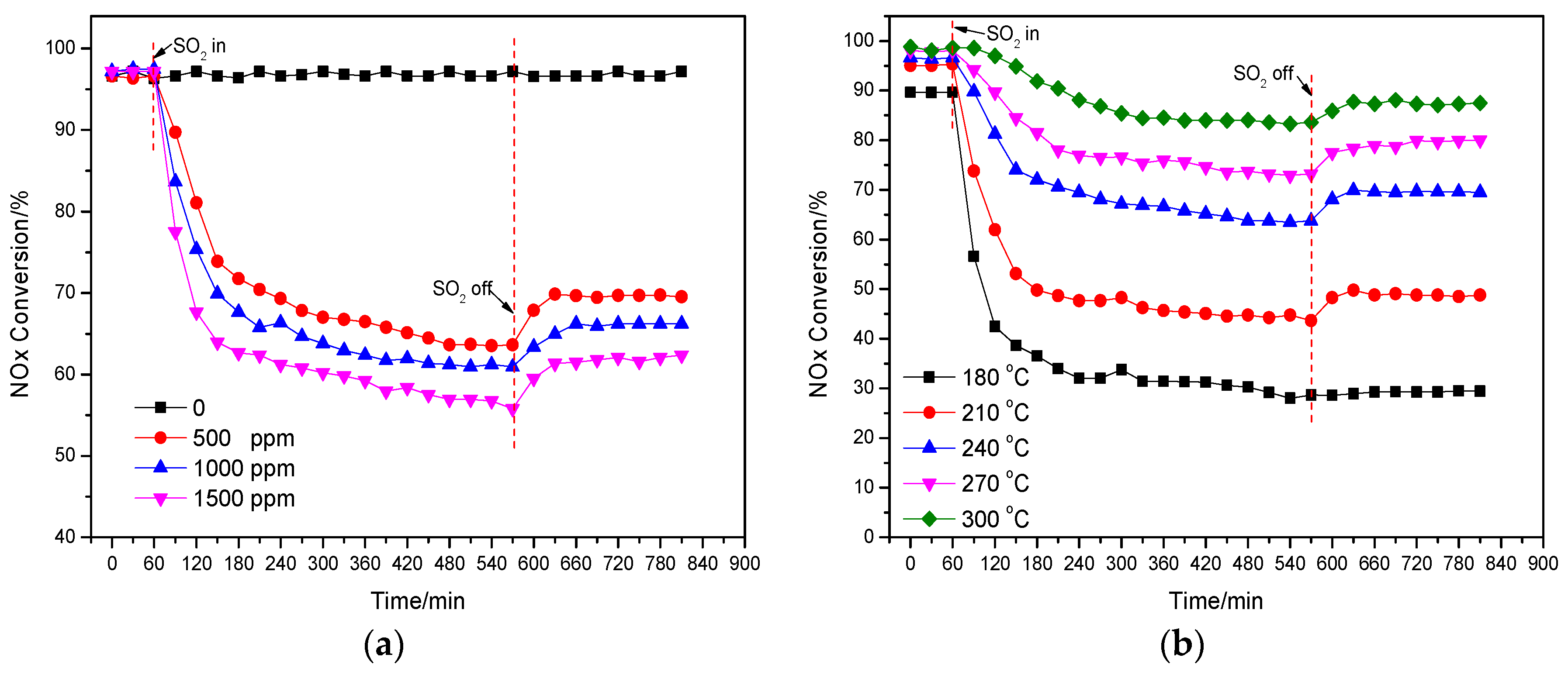
The effect of the injected SO2 concentration (from 500 ppm to 1500 ppm) on the deNOx activity of the catalyst Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 under the reaction temperature of 240 °C was shown in Figure 3a. It is obvious that the deNOx activity of the catalyst was remarkably and abruptly decreased with the injection of SO2 for the three different concentrations. After 2 h injection of SO2, the deNOx activity of catalyst was reduced from 97% to 72%, 68%, 63% for the SO2 concentration of 500, 1000 and 1500 ppm. Compared to that of the injected H2O, the high concentration of the injected SO2 could accelerate the decline of the activity of the catalyst. The formation of SO3 can be promoted by the high concentration of the injected SO2, consequently enhancing the formation of ammonium sulfate with NH3 covering the catalyst active sites on the surface. After the cut-off (8 h) of the injected SO2, the activity of the catalyst was increased, but much lower than its initial activity. It is indicated that the competitive adsorption between SO2 and NH3 or NO is not the main reason for the loss of deNOx activity in the presence of SO2. Part of active sites on the catalyst was occupied by SO2 over NH3 and NO leading to the temporary poisoning, while a great number of active sites was covered by the formed sulfate salts (such as ammonium sulfate) for the permanent deactivation of the catalyst [31,32].
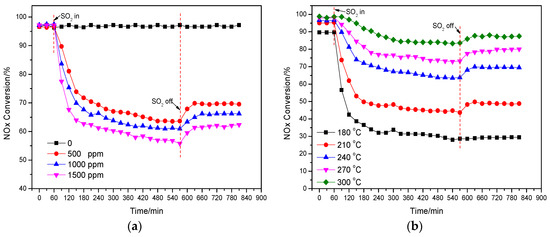
Figure 3.
Effect of the injected SO2 concentration of on deNOx activity of catalyst (240 °C) (a); Effect of the injected SO2 (500 ppm) on deNOx activity of catalyst under different temperatures (b).
The effect of the injected SO2 on the deNOx activity of the catalyst Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 under different reaction temperatures was shown in Figure 3b. The effect of the injected SO2 on the activity of the catalyst was greatly influenced by the reaction temperature. It needs to be noted that the activity of the catalyst was decreased from 90% to 29% after 8-hour injection of 500 ppm SO2 under 180 °C. Comparatively, under the reaction temperature of 300 °C, the activity of the catalyst was reduced from 99% to 88% after 8-hour injection of 500 ppm SO2. This result demonstrates that the effect of SO2 on deNOx activity is greatly related to the reaction temperature and a much more rapid decrease of deNOx activity happened with the addition of SO2 at a lower temperature. It should be noted that no obvious recovery of deNOx activity at the reaction temperature of 180 °C can be observed. The more detailed mechanism of SO2 poisoning over Cu/SAPO-34 at different reaction temperatures will be further discussed.
2.4. Effect of Both H2O and SO2 Injection on the deNOx Activity of the Catalyst
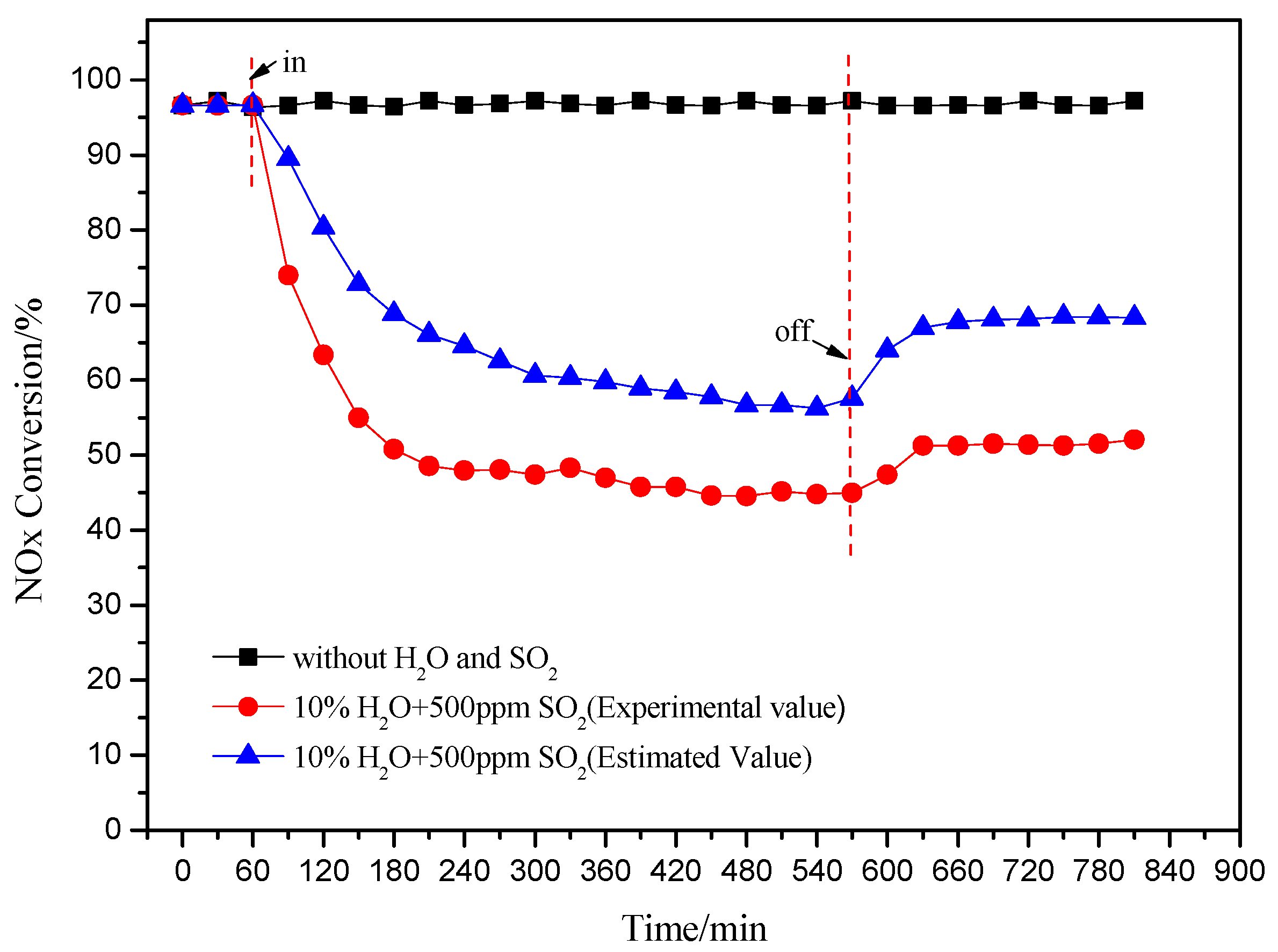
Figure 4 shows the effect of injection of H2O and SO2 on the catalytic activity of Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34. NO conversion was decreased at the presence of H2O and SO2, compared to the performance the individual injection of H2O or SO2. Moreover, the co-existence of H2O and SO2 in the feeding gas gave a much more serious decline on the deNOx activity of the catalyst compared to the sum of the effect of H2O and SO2 respectively, which is labeled as the estimated value as shown in Figure 4. The existence of H2O could enhance the deactivation of the catalyst by SO2 through two ways: (1) SO2 in gas phase reacted with the H2O adsorbed on active site of catalyst to generate sulfuric acid or sulfurous acid which is easily reacted with NH3; (2) the thermal decomposition of the formed ammonium sulfate on the active sites was confined at the presence of H2O.
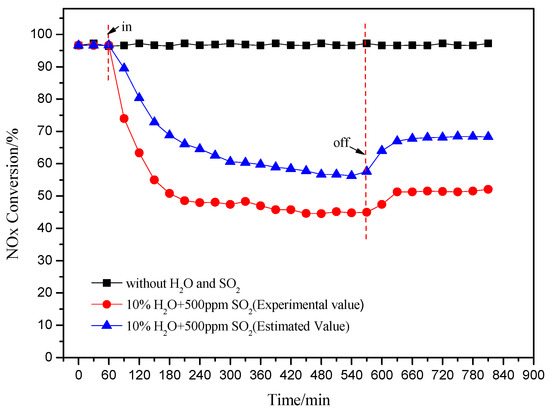
Figure 4.
Effect of the injected H2O and SO2 on the deNOx activity of catalyst (240 °C).
2.5. Mechanism of the Catalyst Poisoning by H2O and/or SO2
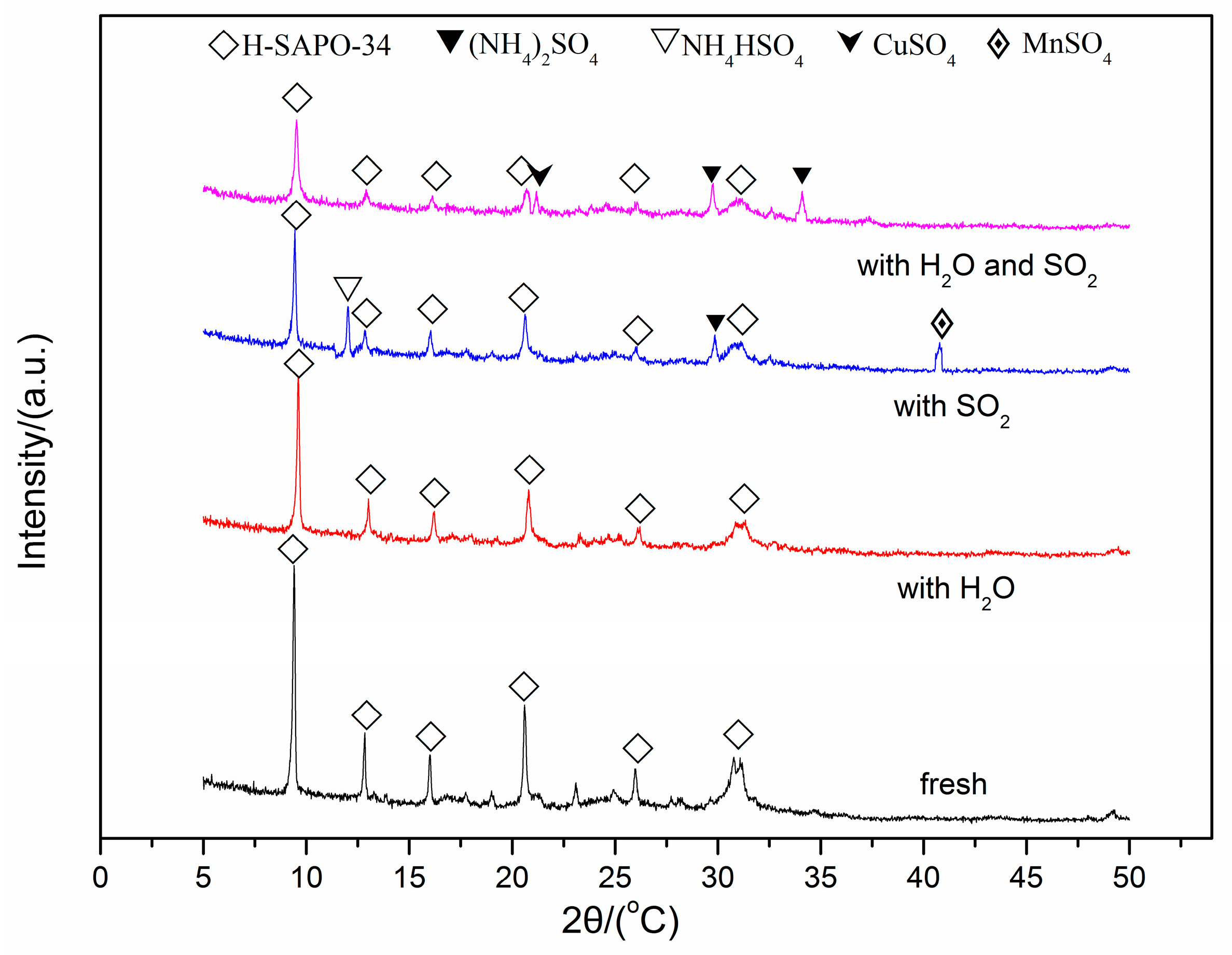
In order to identify the change of crystalline phases for the fresh and spent Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst after SO2 and/or H2O poisoning. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were carried out and the patterns are shown in Figure 5. For the fresh Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst, sharp diffraction peaks corresponding to CHA phases are obtained. After poisoned with SO2 or H2O, the intensity of each peak decreases, especially for the catalyst after SO2 + H2O treatment, indicating the obvious skeleton damage of SAPO-34 after adding SO2 + H2O for 8 h [33]. No obvious crystalline change can be observed in the presence of 10% H2O, this indicates that the phase poisoned by H2O existed either in amorphous form or in the particle beyond the limited size of XRD detection [34]. For the catalyst after SO2 poisoning for 8 h, A number of new diffraction peaks at 2θ = 11.9°, 29.8°and 40.7° can be observed. The peaks at 11.9° and 29.8° can be attributed to NH4HSO4 and (NH4)2SO4, while the latter peak at 40.7° is assigned to MnSO4. For the catalyst after SO2 + H2O poisoning for 8h, new diffraction peaks at 2θ = 29.8° and 34.1° can be observed, which can be assigned to (NH4)2SO4. In addition, the new peak at 2θ = 21.1° can be assigned to the formation of CuSO4. It can be deduced that the newly formed NH4HSO4, (NH4)2SO4 and MnSO4 result in the loss of deNOx activity in the presence of SO2. When H2O and SO2 were added simultaneously, SO2 in gas phase may react with adsorbed H2O to generate sulfuric acid or sulfurous acid, which is easily reacted with NH3 to form (NH4)2SO4. Thus, the formation of (NH4)2SO4 and CuSO4 may cause the loss of deNOx activity in the presence of SO2 + H2O.
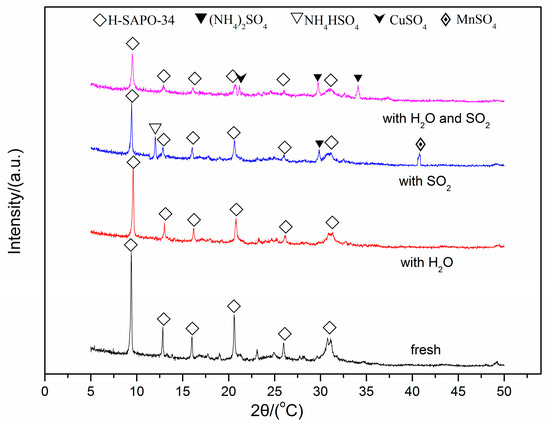
Figure 5.
X-ray diffraction spectra of the fresh and spent Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34.
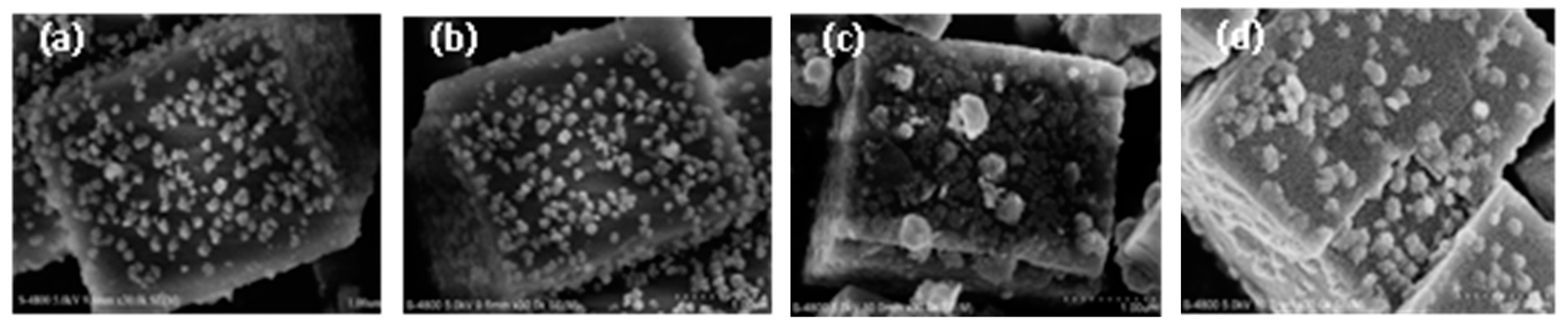
In order to determine the morphology before and after SO2 or/and H2O poisoning, the fresh Cu/SAPO-34 and poisoned catalyst by SO2 or/and H2O were characterized by SEM method shown in Figure 6. No significant change of the surface morphology can be found between the catalysts before and after the H2O poisoning. The active particles on the surface of fresh catalyst were replaced by the bulks of ammonium sulfate after the poisoning by individual SO2, inhibiting the deNOx activity of the catalyst. Similar phenomena can be observed for the spent catalyst in presence of H2O and SO2, where the agglomeration of ammonium sulfate lead to the decline in the surface active sites of the catalyst and thus the activity of the catalyst.
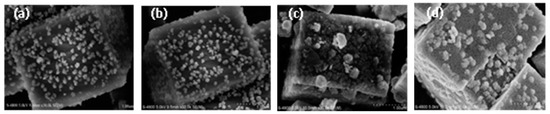
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of fresh and spent Cu(2)-Mn(6)/SAPO-34: (a) fresh; (b) 10% H2O 240 °C 8 h; (c) 500 ppm SO2 240 °C 8 h; (d) 10% H2O and 500 ppm SO2 240 °C 8 h.
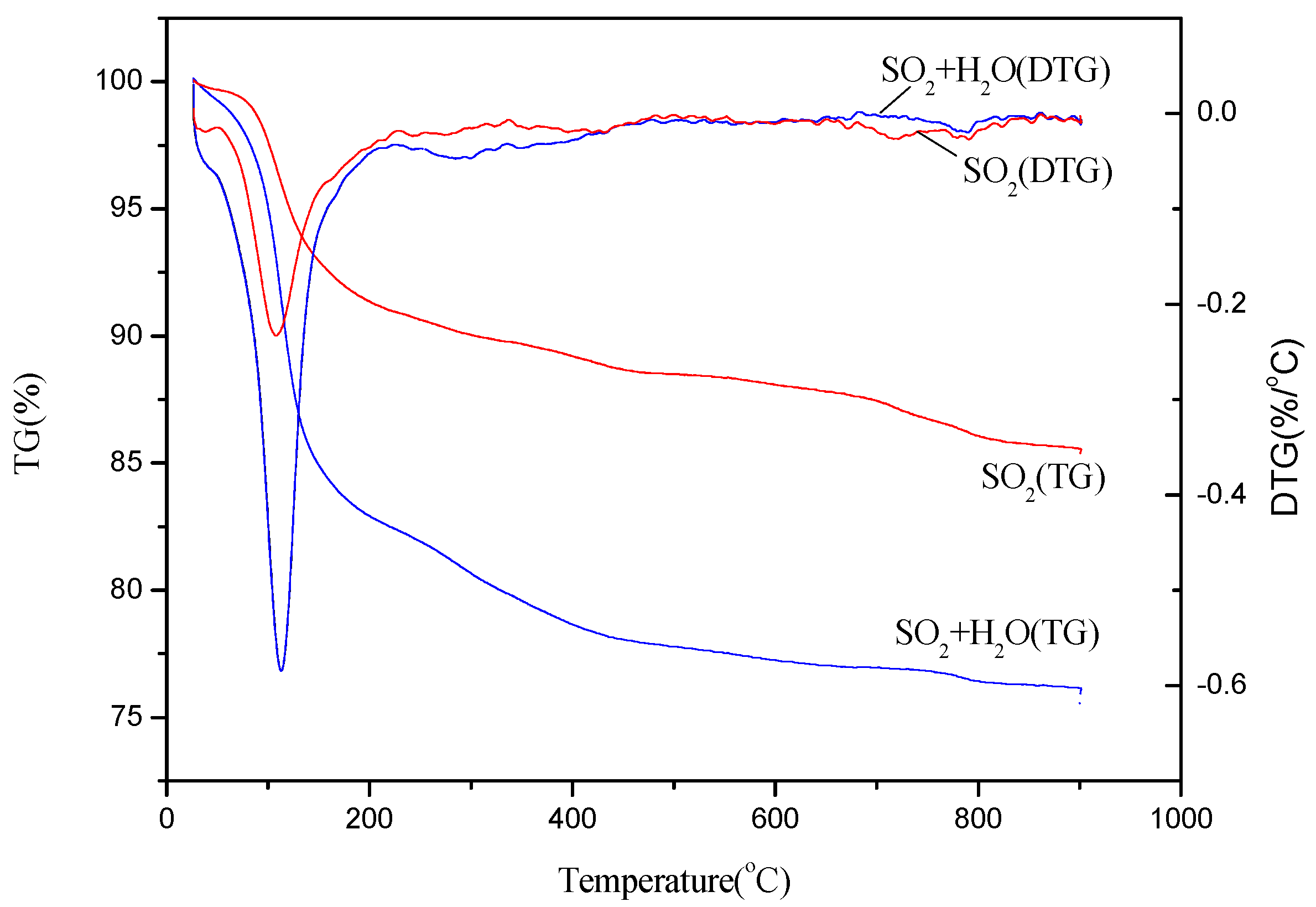
The TG curves of the poisoned catalyst in the presence of individual SO2 and both H2O and SO2 were shown in Figure 7. Three mass loss stages can be observed for the two kinds of the poisoned catalyst: the first mass loss in the temperature between 50 °C and 100 °C was attributed to the dehydration of the catalyst; the second stage between 200 °C and 400 °C can be designated to the thermal decomposition of NH4HSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 is 200 °C [35]; the third stage between 600 °C and 800 °C can be attributed to the decomposition of the sulfate metal salts [36]. The peak value of the second mass loss stage of the poisoned catalyst in the presence of H2O and SO2 is notably higher than that of the poisoned catalyst in presence of individual SO2, indicating that more content of (NH4)SO4 deposited on the surface of the catalyst. This confirms that the formation of ammonium sulfate can be facilitated and promoted with the injection of H2O in the feeding gas, which is consistent with the XRD and TG-DTG analysis. While the peak value of the third mass loss stage of the poisoned catalyst in the presence of H2O and SO2 is lower than that in the presence of SO2. It might be because the formation of (NH4)SO4 can inhibit the formation of sulfate metal salts due to the consumption of SO2.
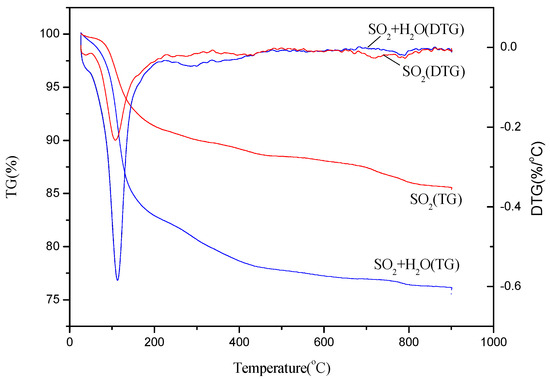
Figure 7.
TG-DTG curves of the thermal decomposition for the Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst after 8 h poisoning in presence of 500 ppm SO2 and/or 10% H2O.
The specific surface area, pore volume and pore size of fresh and spent Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 were determined by N2 adsorption and summarized in Table 1. The specific surface area and pore volume of Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst was decreased after the all different NO reduction experiments with or without the injection of H2O and/or SO2. It can be seen that the damage of the surface area is related to the concentration of SO2 or H2O and the reaction temperature. With the increase of reaction temperature, the damage of the surface area caused by SO2 is lightening. The low reaction temperature could confine the thermal decomposition of the formed NH4HSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 on the surface, resulting in a decline in surface area and the blockage of pore channel [37]. With the increase of the concentration of SO2, a change of which (from 331 m2/g to 320 m2/g) can be observed for different SO2 concentrations (from 500 ppm to 1500 ppm) under the temperature of 240 °C. For the poisoning effect of H2O, with the increase of reaction temperature, the existence of H2O has a more severe effect on the surface area of Cu/SAPO-34, which may result from the inhibited adsorption capacity of H2O. With the increase of the concentration of H2O, the surface area decreases from 425 m2/g to 408 m2/g as the concentration of H2O increased from 2% to 10% as well as the pore volume of catalyst. When H2O and SO2 added into the gas stream simultaneously for 8 h, the surface area decreases from 457 m2/g to 276 m2/g, which is a dramatically decrease compared to the injection of SO2 for 8 h at 240 °C (from 457 m2/g to 331 m2/g) and the injection of H2O for 8 h at 240 °C (from 457 m2/g to 408 m2/g). It is demonstrated that the synergistic poisoning effect of SO2 and H2O is enhanced, ascribed to the large amount of deposited (NH4)2SO4 on the pore channel of Cu/SAPO-34, which is consistent with the TG-DTG results.

Table 1.
Brunner−Emmet−Teller (BET) analysis of the fresh and spent Cu(2)–Mn(6)/SAPO-34 catalyst.
Based on the activity tests and characterizations, the poisoning effect of SO2 or/and H2O can be described as follows. The poisoning effect of H2O, especially at low temperatures, can be ascribed to the competitive adsorption between H2O and NH3 on Lewis acid sites by occupying the metal sits [38], which can be recovered to nearly the original activity after H2O was removed. The XRD patterns of the catalyst after H2O poisoning did not show ant obvious changes, indicating no change with the active metal sites.
While for the poisoning effect of SO2 over Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst, the deNOx activity decreases from 90% to 29% at 180 °C in a short time of SO2 injection. In addition, the deNOx activity could not be recovered after the elimination of SO2, indicating the permanent deactivation of SO2 on Cu/SAPO-34 at 180 °C. The poisoning mechanism could be summarized as three aspects. Firstly, SO2 in the gas may be oxidized to SO3 and further react with NH3 to form NH4HSO4, which is a drying powdery decomposed at 280 °C [39]. The formation of NH4HSO4 causes the plug of active sites of the catalyst and the decline in surface area. Ammonium sulfate crystallite is observed on the XRD spectra and the weight loss peak ascribed to the decomposition of ammonium sulfates is also observed from the TG curves. Secondly, the active sites (i.e., MnO2 or CuO species) may react with SO2 or SO3 to form MnSO4 or CuSO4, which inhibited the redox properties [23]. The diffraction peaks assigned to MnSO4 and CuSO4 are observed in XRD spectra. Thirdly, the competitive adsorption of SO2 and NO on metal sites may be a part of the reason for the loss of deNOx activity at the reaction temperature of above 180 °C [40]. With regards to the synergistic effect of SO2 + H2O, the deNOx activity tests and characterizations show that the existence of H2O could enhance the deactivation of the catalyst by SO2 through two ways: (1) SO2 in gas phase reacted with the H2O adsorbed on active site of catalyst to generate sulfuric acid or sulfurous acid which is easily reacted with NH3 to form large amount of (NH4)2SO4; (2) the thermal decomposition of the formed ammonium sulfate on the active sites was confined at the presence of H2O. Both of the two explanations can be assigned to the deposition of (NH4)2SO4, which further plug the pore channel of catalyst and cause the rapid decrease of surface area as shown in Table 1.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
The molecular sieve was modified by impregnation method. A certain amount of zeolite molecular sieve H-SAPO-34 (n(P2O5):n(SiO2):n(Al2O3) = 1:1:1), provided by the catalyst factory of Nankai University, was weighed and dried in a drying oven at 105 °C for 30 min. A certain amount of Cu(NO3)2•3H2O powder was mixed with manganese nitrate solution with the 50 wt.% in the beaker of 200 mL, and then added 50 mL of deionized water into the immersion liquid. The beaker with a magnetic stirrer inside was immersed in a water bath at a constant temperature of 40 °C. After 12 h of immersion, the solution was thoroughly mixed and heated until the moisture was completely evaporated. The powder was then put into a dry oven at about 100 °C for 12 h. The dried powder was ground and sieved by the 40 to 60 mesh. The obtained powders were placed in a tube furnace and calcined at 450 °C for 6 h to obtain the catalyst sample for the experiment. The catalyst sample Cu(2)-Mn(6)/SAPO-34(450) indicated that the 2 wt.% Cu and 6 wt.% Mn were loaded on the molecular sieve SAPO-34 with the calcination temperature of 450 °C.
3.2. DeNOx Activity Measurements
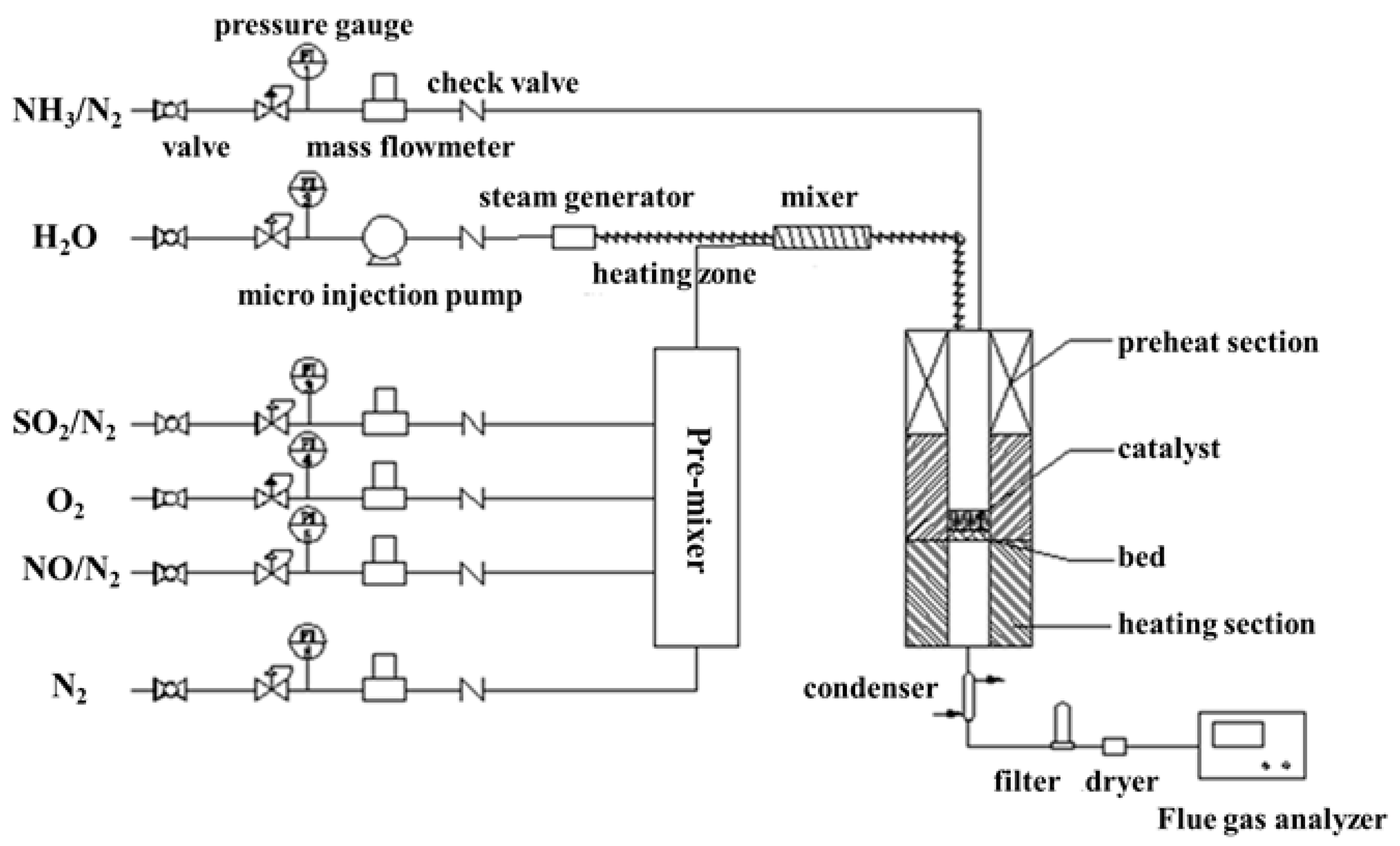
DeNOx activity measurements using NH3 were carried out in a fixed-bed stainless steel tubular flow reactor (Inner diameter: 16 mm) (Figure 8). The tube furnace of the reactor can be heated from the room temperature to 800 °C The gas feeding system was composed of five gas feeding pipes controlled by the mass flow meter (0–1.5 L) and one liquid feeder a microinjection pump (0.001 μL/min–127 mL/min), equipped with the reactor for adjusting the composition of the feeding gas. The reaction temperature in the experiments was set to be changed from 90 to 330 °C.
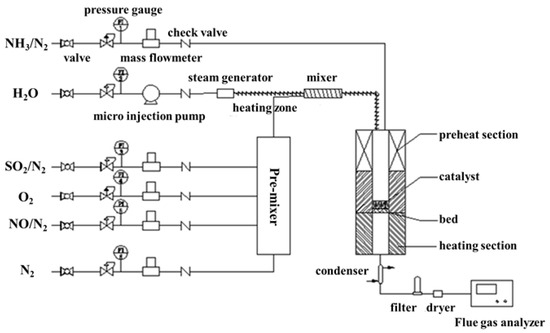
Figure 8.
Schematics for the fixed-bed tubular flow reactor.
Two milliliter catalyst was placed on the holder of the reactor, and the feeding gas consisted of 350 ppm NO, 350 ppm NH3, 3 vol.% O2 and N2 as balanced. H2O (0–10 vol.%) and/or 500–1500 ppm SO2 would be injected into the feeding gas for investigating the effect of H2O and/or SO2 on the catalyst poisoning. The GHSV was set to be 15,000h−1. The NO and NO2 concentration of the reactor inlet and outlet was collected by an airbag and analyzed by the flue gas analyzer (Testo 350, Testo, Inc., Lenzkirch, Germany). The outlet N2O concentration is collected by the N2O analyzer (Medi-Gas G200, Bedfont Scientific Ltd., Bedfont, United Kingdom). The NO conversion was obtained from the equation as follows:
Where η, , represented the NO conversion, inlet and outlet NO concentration.
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
A micromeritics ASAP 2010M micropore size analyzer was used to measure the N2 adsorption isotherms of the catalyst sample at liquid N2 temperature (−196 °C. Specific surface area, pore volume and pore diameter can be determined by N2 adsorption using the BET and BJH methods.
The XRD measurement for the catalyst was carried out on a Rigaku D/Smartlab(Ⅲ) system (Rigaku, Neu-Isenburg, Germany) with Cu Ka radiation. The X-ray source was operated at 40kV and 40mA. The diffraction patterns were taken in the 2θ range of 5–50° at a scan speed of 10° min−1 and a resolution of 0.02°.
SEM was performed using a SIRION-50 scanning electron microscope from Field Electron and Ion Company, the Netherlands, with a resolution of 150 eV.
Thermal gravimetric analysis of the catalyst samples was performed using TGA-101 type produced by the Nanjing Exhibition Electrical and Mechanical Technology Company (Nanjing, China). The accuracy of the instrument is 0.2 μg. For the TG experiments, the spent catalyst samples were measured under the temperature from room temperature to 900 °C at the heating rate of 15 °C min−1.
4. Conclusions
Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 with the loading of 2 wt.% Cu and 6 wt.% Mn exhibited remarkable low-temperature NO reduction activity among the prepared Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalysts. The NO conversion could achieve as high as 72% under the reaction temperature of 120 °C, while the value reached more than 90% under the temperature between 180 °C and 330 °C. The reversibly poisoning effect of H2O is mainly due to the competitive adsorption between H2O and NH3 on Lewis acid sites by occupying the metal sits. With the increase of reaction temperature, the poisoning effect is less important. The poisoning effect of SO2 on deNOx activity is dependent on the reaction temperature. At low temperature, the poisoning effect of SO2 is permanent with no recovery of deNOx activity after the elimination of SO2. XRD, SEM and BET analysis suggested that the deposition of (NH4)2SO4 on active sites may be the main reason for the loss of deNOx activity. TG-DTG analysis shows that some metal sulfates are formed on the surface of Cu/SAPO-34 catalyst, which may inhibit the redox properties and cut off the redox cycle during the low-temperature SCR reaction. The addition of H2O into the SO2-containing atmosphere promotes the formation of (NH4)2SO4 on the surface of the catalyst, causing the damage of surface area and the rapid decrease of deNOx activity. At a higher reaction temperature, the formation of ammonium sulfate might be inhibited by the high reaction temperature, or the formed ammonium sulfate from SO2 and NH3 can be easily decomposed under the high temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, D.S.; Investigation, S.G., B.Y., R.L. and Y.S.; Methodology, G.L., W.Z., P.H., S.G., B.Y., R.L., Y.S. and D.S.; Supervision, D.S.; Writing–original draft, G.L., W.Z. and P.H.; Writing–review & editing, G.L., W.Z. and P.H.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 51676047], the international collaboration project from Department of Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province [grant number BZ2017014], Key Technology R and D Program of Jiangsu Province [grant number BE2015677], and the Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Power Design Institute Co., Ltd. [grant number 32-JK-2019-017].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tie, X.; Huang, R.-J.; Dai, W.; Cao, J.; Long, X.; Su, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, G. Effect of heavy haze and aerosol pollution on rice and wheat productions in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D.A.; Foulds, P.G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D.M.A.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 10797–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—A review. Catal. Today. 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzatti, P.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E.; Kustov, A.; Thøgersen, J.R. Effect of operating variables on the enhanced SCR reaction over a commercial V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for stationary applications. Catal. Today 2012, 184, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Shen, B.X.; Chen, J.H.; Cai, J.; He, C.; Wang, K. Mn0·4/Co0·1Ce0·45Zr0·45OX, high performance catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO by ammonia. J. Energy Inst. 2013, 86, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Kamasamudram, K.; Li, L.; Epling, W. SO2 poisoning impact on the NH3-SCR reaction over a commercial Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 156–157, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, Y.; Cavataio, G.; McCabe, R.W.; Fu, L.; Li, L. Characterization of commercial Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts with hydrothermal treatment for NH3-SCR of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeman, P.G.; Burkholder, E.M.; Chen, H.-Y.; Collier, J.E.; Fedeyko, J.M.; Jobson, H.; Rajaram, R.R. The role of pore size on the thermal stability of zeolite supported Cu SCR catalysts. Catal. Today 2014, 231, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.A.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H.; Miller, J.T.; Gounder, R. Methods for NH3 titration of Brønsted acid sites in Cu-zeolites that catalyze the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Catal. 2014, 312, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.A.; Verma, A.A.; Paolucci, C.; Parekh, A.A.; Anggara, T.; Yezerets, A.; Schneider, W.F.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Identification of the active Cu site in standard selective catalytic reduction with ammonia on Cu-SSZ-13. J. Catal. 2014, 312, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettireddy, P.R.; Kotrba, A.; Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P. Low temperature SCR catalysts optimized for cold-start and low-load engine exhaust conditions. SAE Technical Paper 2015, 01, 1026. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Heo, I.; Nam, I.S.; Cho, B.K.; Jin, W.C.; Cha, M.S.; Yeo, G.K. Mn–Fe/ZSM5 as a low-temperature SCR catalyst to remove NOx from diesel engine exhaust. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 126, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. Urea-SCR Technology for deNOx after Treatment of Diesel Exhausts; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Wei, Z.; Kollar, M.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H. A comparative study of N2O formation during the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 on zeolite supported Cu catalysts. J. Catal. 2015, 329, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Qi, G.; Xue, J.; Shen, M.; Li, W. The influence of silicon on the catalytic properties of Cu/SAPO-34 for NOx reduction by ammonia-SCR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 127, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, X.; Qi, G.; Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Li, W. Characterization of copper species over Cu/SAPO-34 in selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia: Relationships between active Cu sites and de-NOx performance at low temperature. J. Catal. 2013, 297, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.T. Activity, propene poisoning resistance and hydrothermal stability of copper exchanged chabazite-like zeolite catalysts for SCR of NO with ammonia in comparison to Cu/ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 427–428, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, U.; Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Warrender, S.J.; Picone, A.L.; Wright, P.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Beale, A.M. Changing active sites in Cu–CHA catalysts: deNOx selectivity as a function of the preparation method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Kwak, J.H.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H. Current Understanding of Cu-Exchanged Chabazite Molecular Sieves for Use as Commercial Diesel Engine DeNOx Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 1441–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Weng, D.; Si, Z.; Ran, R. Migration, reactivity, and sulfur tolerance of copper species in SAPO-34 zeolite toward NOx reduction with ammonia. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37787–37796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wen, H.; Hao, T.; Yu, T.; Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, J. Deactivation mechanism of SO2 on Cu/SAPO-34 NH3-SCR catalysts: structure and active Cu2+. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, K.; Andonova, S.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.M.; Yezerets, A.; Olsson, L. Impact of sulfur oxide on NH3-SCR over Cu-SAPO-34. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2015, 166–167, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangjou, Y.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Epling, W.S. SO2 Poisoning of the NH3-SCR Reaction over Cu-SAPO-34: Effect of Ammonium Sulfate versus Other S-Containing Species. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6612–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, R.; Ying, M. Characteristics and performance of SAPO-34 catalyst for methanol-to-olefin conversion. Appl. Catal. 1990, 64, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Du, A.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Synthesis of SAPO-34 with only Si(4Al) species: Effect of Si contents on Si incorporation mechanism and Si coordination environment of SAPO-34. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, A.; Wang, W.; Xu, M.; Arnold, A.; Hunger, M. Thermal stability and dehydroxylation of Brønsted acid sites in silicoaluminophosphates H-SAPO-11, H-SAPO-18, H-SAPO-31, and H-SAPO-34 investigated by multi-nuclear solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 56, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhu, S.; Shen, M.; Li, W.; Wang, J. The migration of Cu species over Cu–SAPO-34 and its effect on NH3 oxidation at high temperature. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. Inhibition effect of H2O on V2O5/AC catalyst for catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 63, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, T. A comparative study of Mn/CeO2, Mn/ZrO2 and Mn/Ce-ZrO2 for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 in the presence of SO2 and H2O. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notoya, F.; Su, C.; Sasaoka, E.; Nojima, S. Effect of SO2 on the Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide with Ammonia over TiO2, ZrO2, and Al2O3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3732–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S. The role of isolated Cu2+ location in structural stability of Cu-modified SAPO-34 in NH3-SCR of NO. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Alamdari, H.; Kaliaguine, S. SO2 poisoning of LaFe0.8Cu0.2O3 perovskite prepared by reactive grinding during NO reduction by C3H6. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 340, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Cao, F.H. Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Ammonium Sulfate. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2011, 25, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.X.; Liu, T. Deactivation of MnOx-CeOx/ACF Catalysts for Low-Temperature NH3-SCR in the Presence of SO2. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica 2010, 26, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; He, H.; Yu, Y. Deactivation of a Ce/TiO2 catalyst by SO2 in the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4426–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Luo, H.; Li, L.; Wei, Z.; Huang, B. H2O and SO2 deactivation mechanism of MnOx/MWCNTs for low-temperature SCR of NOx with NH3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 377, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoura, R.; Urano, K. Mechanism, Kinetics, and Equilibrium of Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Dev. 1970, 9, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.Q.; Wu, Z.B.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, W.K. DRIFT Study of the SO2 Effect on Low-Temperature SCR Reaction over Fe−Mn/TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4961–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).