Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Chlorobenzenes Catalyzed by Goethite and Promoted by Hydroxylamine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Blank Experiments
2.2. CWPO Experiments
2.2.1. Study of pH Effect
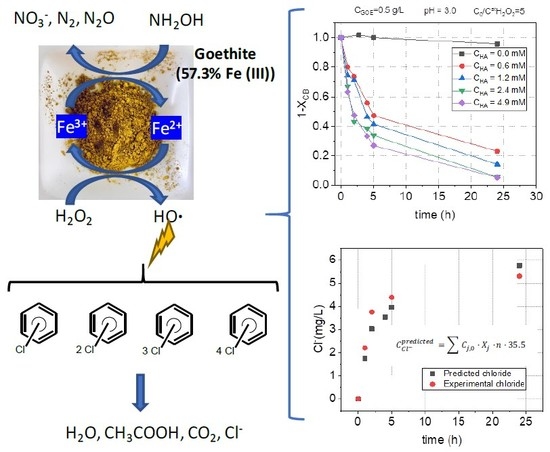
2.2.2. HA Concentration Effect
2.2.3. Hydrogen Peroxide Concentration Effect
2.2.4. Effect of Goethite Concentration
3. Methods
3.1. Reagents and Catalyst
3.2. Blank Experiments
3.3. CWPO Experiments
3.4. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Notation
References
- Weber, R.; Watson, A.; Forter, M.; Oliaei, F. Persistent organic pollutants and landfills—A review of past experiences and future challenges. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, S.; Zahn, D.; Montes, R.; Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Knepper, T.P.; Reemtsma, T.; Berger, U. Occurrence of emerging persistent and mobile organic contaminants in European water samples. Water Res. 2019, 153, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Jennings, A. Worldwide Regulations of Standard Values of Pesticides for Human Health Risk Control: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Mukherji, S. Threat Posed by Persistent Organochlorine Pesticides and their Mobility in the Environment. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 954–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Gaus, C.; Tysklind, M.; Johnston, P.; Forter, M.; Hollert, H.; Heinisch, E.; Holoubek, I.; Lloyd-Smith, M.; Masunaga, S.; et al. Dioxin- and POP-contaminated sites-contemporary and future relevance and challenges. Enviro. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2008, 15, 363–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeck, C.; Radny, D.; Huggenberger, P.; Affolter, A.; Auckenthaler, A.; Hollender, J.; Berg, M.; Schirmer, M. Spatial distribution of anthropogenic inputs into groundwater: A case study. Grundwasser 2018, 23, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Hossini, H.; Asadi, F.; Janjani, H. A systematic review on organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides content in water resources. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Jones, K.C. Behavior and fate of chlorobenzenes (cbs) introduced into soil-plant systems by sewage-sludge application—A review. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 1325–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, D.; Cohet, E.; Gard, A.; Caspers, N.; van Ginkel, C.; Thompson, R.; de Rooij, C.; Garny, V.; Lecloux, A. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene marine risk assessment with special emphasis on the Osparcom region North Sea. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djohan, D.; Yu, Q.; Connell, D.W. Partition isotherms of chlorobenzenes in a sediment-water system. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 161, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecloux, A.J. Scientific activities of Euro Chlor in monitoring and assessing naturally and man-made organohalogens. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, D.; Thompson, R.S.; De Rooij, C.; Garny, V.; Lecloux, A.; Kanne, R. 1,2-Dichlorobenzene marine risk assessment with special reference to the OSPARCOM region: North Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 97, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutonnet, J.C.; Thompson, R.S.; De Rooij, C.; Garny, V.; Lecloux, A.; Van Wijk, D. 1,4-Dichlorobenzene marine risk assessment with special reference to the OSPARCOM region: North Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 97, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wijk, D.; Thompson, R.S.; De Rooij, C.; Garny, V.; Lecloux, A.; Kanne, R. Monochlorobenzene Marine Risk Assessment with Special Reference to the Osparcom Region: North Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 97, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroll, R.; Brahushi, F.; Dörfler, U.; Kühn, S.; Fekete, J.; Munch, J.C. Biomineralisation of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene in soils by an adapted microbial population. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Sun, X.-F.; Yao, Z.-T.; Zhao, X.-Y. Remediation of 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene contaminated soil using a combined thermal desorption–molten salt oxidation reactor system. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Min, X.; Fang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, P. Acute toxicity of chlorobenzenes in Tetrahymena: Estimated by microcalorimetry and mechanism. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Fernandez, J.; Guadaño, J.; Lorenzo, D.; Romero, A. Chlorinated organic compounds in liquid wastes (DNAPL) from lindane production dumped in landfills in Sabiñanigo (Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, D.F.; Weiss, R.G. Polydimethylsiloxane as a Matrix for the Stabilization and Immobilization of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles. Applications to Dehalogenation of Environmentally Deleterious Molecules. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chai, X.-S.; Li, Y.; Guo, C. A quint-wavelength UV spectroscopy for simultaneous determination of dichlorobenzene, chlorobenzene, and benzene in simulated water reduced by nanoscale zero-valent Fe/Ni bimetal. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2017, 181, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.Q. Application of coupled zero-valent iron/biochar system for degradation of chlorobenzene-contaminated groundwater. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, C.M.; Romero, A.; Fernandez, J.; Santos, A. In situ chemical reduction of chlorinated organic compounds from lindane production wastes by zero valent iron microparticles. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhotský, O.; Krákorová, E.; Mašín, P.; Žebrák, R.; Linhartová, L.; Křesinová, Z.; Kašlík, J.; Steinová, J.; Rødsand, T.; Filipová, A.; et al. Pharmaceuticals, benzene, toluene and chlorobenzene removal from contaminated groundwater by combined UV/H2O2 photo-oxidation and aeration. Water Res. 2017, 120, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharan, V.K.; Pinjari, D.V.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. Chapter 3—Advanced Oxidation Technologies for Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. In Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse; Ranade, V.V., Bhandari, V.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 141–191. [Google Scholar]
- Dilmeghani, M.; Zahir, K.O. Kinetics and mechanism of chlorobenzene degradation in aqueous samples using advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Fernandez, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Dominguez, C.M.; Lominchar, M.A.; Lorenzo, D.; Romero, A. Abatement of chlorinated compounds in groundwater contaminated by HCH wastes using ISCO with alkali activated persulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlak, D.L.; Andren, A.W. Oxidation of chlorobenzene with Fenton’s reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Volpe, A.; Lopez, A.; Mascolo, G.; Ciannarella, R. Degradation of chlorobenzene by Fenton-like processes using zero-valent iron in the presence of Fe3+ and Cu2+. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of monochlorobenzene using green synthesis of iron nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 410, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Pardo, F.; Romero, A. Use of Fenton reagent combined with humic acids for the removal of PFOA from contaminated water. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Boopathy, R.; Gupta, V.K.; Sekaran, G. Preparation, characterizations and its application of heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the treatment of synthetic phenol solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 177, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Huang, X.; Jia, F.; Ai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. Hydroxylamine Promoted Goethite Surface Fenton Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5118–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Domínguez, P.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Naturally-occurring iron minerals as inexpensive catalysts for CWPO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baloyi, J.; Ntho, T.; Moma, J. Synthesis and application of pillared clay heterogeneous catalysts for wastewater treatment: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5197–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Qian, X.F.; Fang, M.Y.; Yue, D.T.; Zhao, Y.X. Ferric (hydr)oxide/mesoporous carbon composites as Fenton-like catalysts for degradation of phenol. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4103–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Shi, W.B.; He, J.C.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.M. Fe3O4-MWCNT magnetic nanocomposites as efficient peroxidase mimic catalysts in a Fenton-like reaction for water purification without pH limitation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45809–45815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Jones, A.P.; Chen, P.H.; Kenny, A. Mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like oxidation of sorbed chlorobenzenes. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, W.P.; Voelker, B.M. Rates of hydroxyl radical generation and organic compound oxidation in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Huang, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.C.; Wang, P. Enhancement on Fenton system by N-substituted hydroxylamines. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 252, 1155. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Guan, Y.H. Effect of common cations, anions and organics on the Fenton-hydroxylamine system. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 243, 1155. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.Y.; Guan, Y.H.; Xie, P.C. Strong Enhancement on Fenton Oxidation by Addition of Hydroxylamine to Accelerate the Ferric and Ferrous Iron Cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayazi, M.; Taher, M.A.; Afzali, D.; Mostafavi, A. Enhanced Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue by magnetically activated carbon/hydrogen peroxide with hydroxylamine as Fenton enhancer. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.B.; Huang, W.; Ding, Z.Q.; Nie, G.; Tang, H.Q. Dramatically enhanced Fenton oxidation of carbamazepine with easily recyclable microscaled CuFeO2 by hydroxylamine: Kinetic and mechanism study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 168, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Fronæus, S.; Bengtsson-Kloo, L. The kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of hydroxylamine by iron(iii). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 2548–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, C.M.; Oturan, N.; Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Oturan, M.A. Lindane degradation by electrooxidation process: effect of electrode materials on oxidation and mineralization kinetics. Water Res. 2018, 35, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.H.; Wan, J.Q.; Ma, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, D.Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Li, Y. Enhanced decolorization of Orange G in a Fe(II)-EDDS activated persulfate process by accelerating the regeneration of ferrous iron with hydroxylamine. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, C.M.; Romero, A.; Santos, A. Improved Etherification of Glycerol with Tert-Butyl Alcohol by the Addition of Dibutyl Ether as Solvent. Catalysts 2019, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Arjol, M.; Cacho, C. POP-contaminated sites from HCH production in Sabiñánigo, Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1937–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Goethite as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of methyl orange. Catal. Today 2015, 252, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Chen, T.H.; Frost, R.L. An overview of the role of goethite surfaces in the environment. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| pH0 | ∑COCs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 a–g* | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 1–7 | 0 |
| B2 | 2.4 | 0 | 0.5 | 3 | |
| B3 | 2.4 | 5 | 0 | 3 | |
| B4 | 2.4 | 5 | 0.5 | 3 | |
| S1 a, b, c | 2.4 | 5 | 0.5 | 7, 5, 2 | 31.73 |
| S2 | 0 | 5 | 0.5 | 3 | |
| S3 | 0.6 | 31.73 | |||
| S4 | 1.2 | ||||
| S5 | 2.4 | ||||
| S6 | 4.9 | ||||
| S7 | 2.4 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 | 31.73 |
| S8 | 10 | ||||
| S9 | 2.4 | 5 | 0.25 | 3 | 31.73 |
| S10 | 1 |
| COCs | Chemical | Acronym | Initial Concentration | Initial Concentration | (mM) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | (mg L−1) | (mM) | |||
| chlorobenzene | C6H5Cl | CB | 16.29 | 0.145 | 2.030 |
| 1,3-dichlorobenzene | C6H4Cl2 | 1,3 DCB | 0.33 | 0.002 | 0.026 |
| 1,4-dichlorobenzene | C6H4Cl2 | 1,4 DCB | 4.77 | 0.032 | 0.416 |
| 1,2-dichlorobenzene | C6H4Cl2 | 1,2 DCB | 4.64 | 0.032 | 0.416 |
| 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene | C6H3Cl3 | 1,2,4 TCB | 3.86 | 0.021 | 0.252 |
| 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene | C6H3Cl3 | 1,2,3 TCB | 0.75 | 0.004 | 0.048 |
| 1,2,4,5 tetrachlorobenzene | C6H2Cl4 | TetraCB-a | 0.41 | 0.002 | 0.020 |
| 1,2,3,4 tetrachlorobenzene | C6H2Cl4 | TetraCB-b | 0.68 | 0.003 | 0.030 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenzo, D.; Dominguez, C.M.; Romero, A.; Santos, A. Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Chlorobenzenes Catalyzed by Goethite and Promoted by Hydroxylamine. Catalysts 2019, 9, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060553
Lorenzo D, Dominguez CM, Romero A, Santos A. Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Chlorobenzenes Catalyzed by Goethite and Promoted by Hydroxylamine. Catalysts. 2019; 9(6):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenzo, David, Carmen M. Dominguez, Arturo Romero, and Aurora Santos. 2019. "Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Chlorobenzenes Catalyzed by Goethite and Promoted by Hydroxylamine" Catalysts 9, no. 6: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060553
APA StyleLorenzo, D., Dominguez, C. M., Romero, A., & Santos, A. (2019). Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Chlorobenzenes Catalyzed by Goethite and Promoted by Hydroxylamine. Catalysts, 9(6), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060553