European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definitions and Fundamentals of Gasoline Engines and Filters
2.1. Gasoline Engine Fundamentals
2.2. GPF Performance
2.2.1. Durability and Ash Accumulation
2.2.2. Regeneration
3. Regulations
3.1. Emission Standards
3.2. Test Cycles and Procedures
- Road load setting.
- Laboratory test set up and conditions.
- Post-processing of the test results.
- Declaration of CO2 results.
3.3. Real-Driving Emissions (RDE)
3.4. SPN-PEMS
3.5. Market Surveillance
4. Results
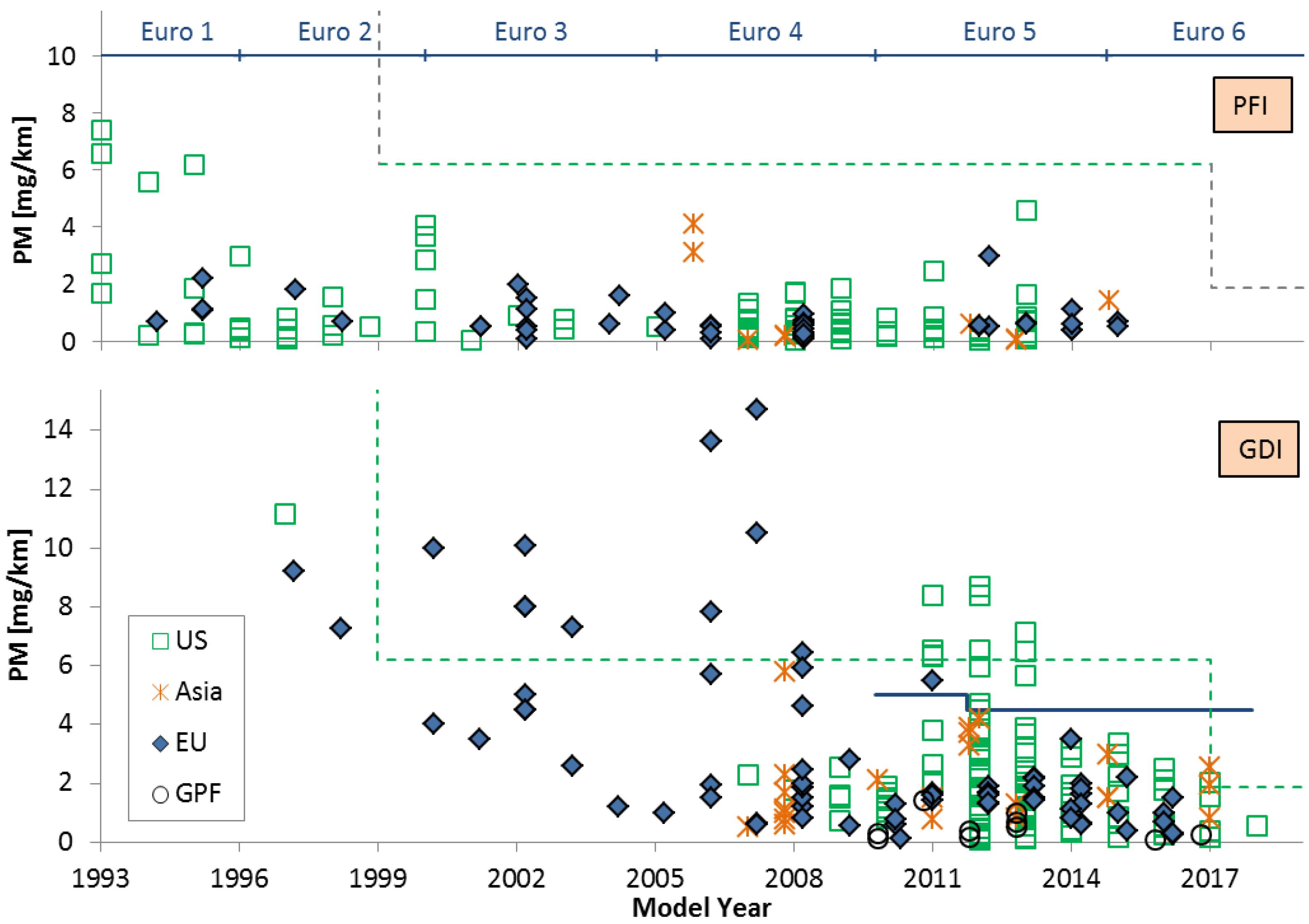
4.1. PM Mass Emissions
4.2. Chemical Composition
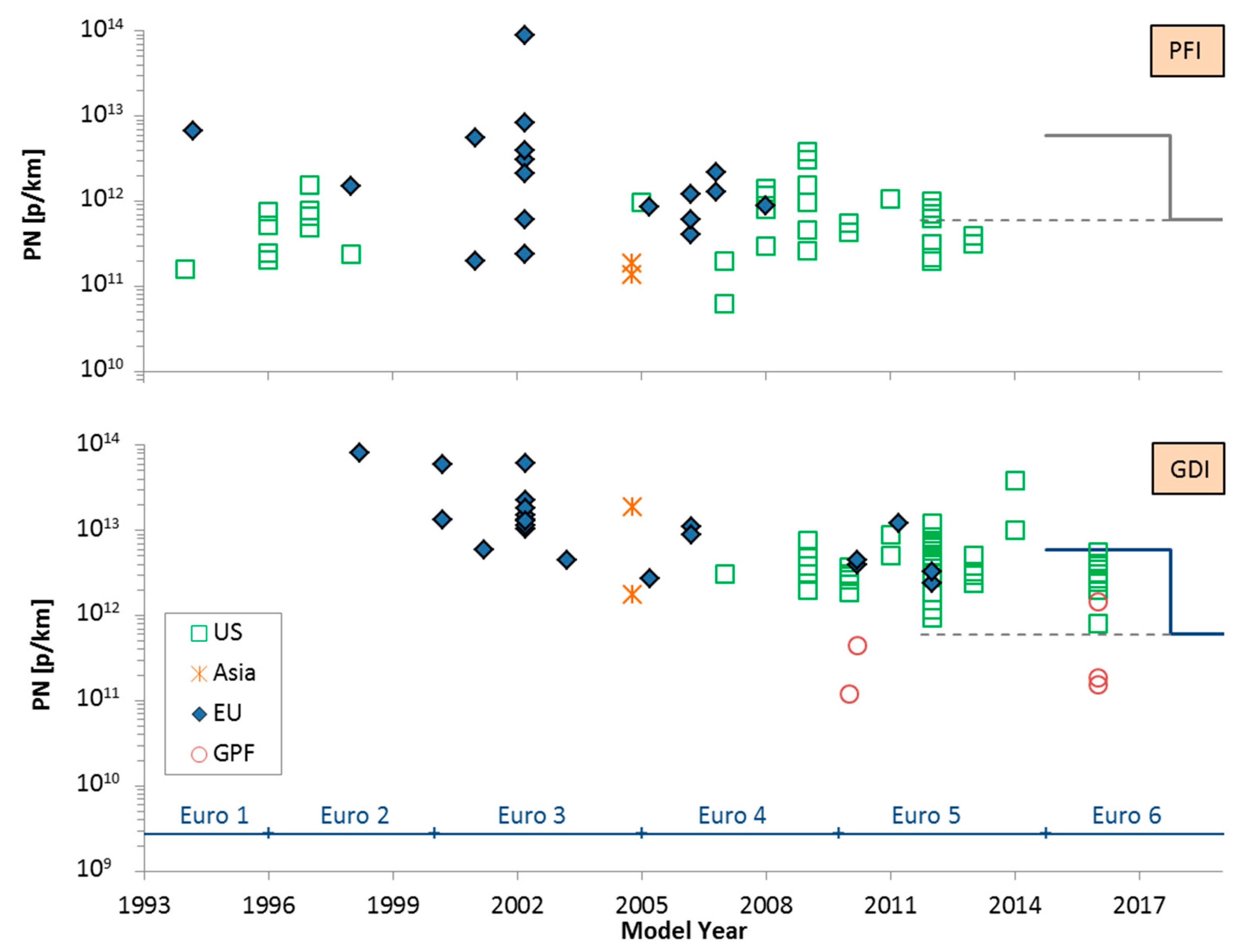
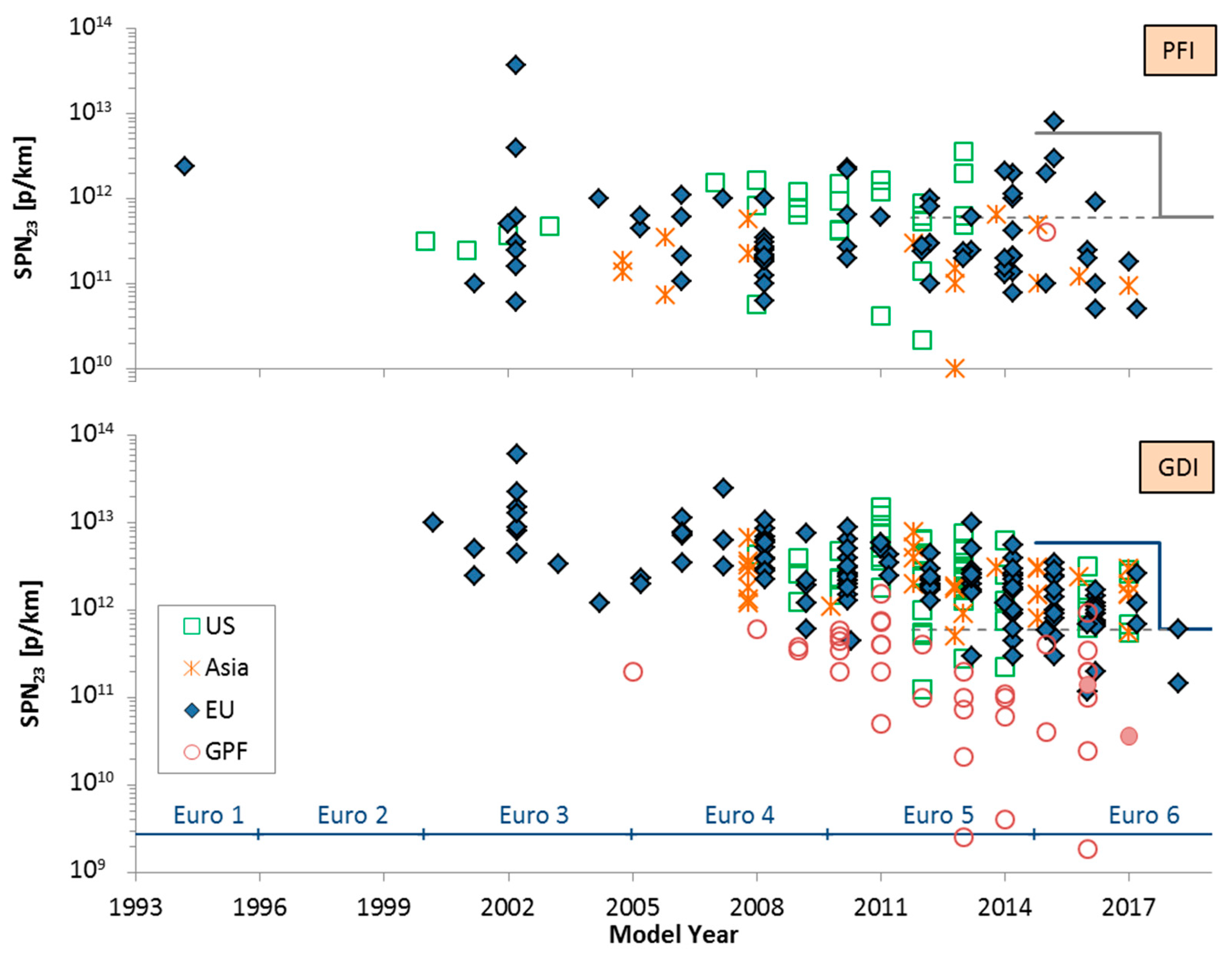
4.3. SPN Emissions
4.4. Size Distributions
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Studies
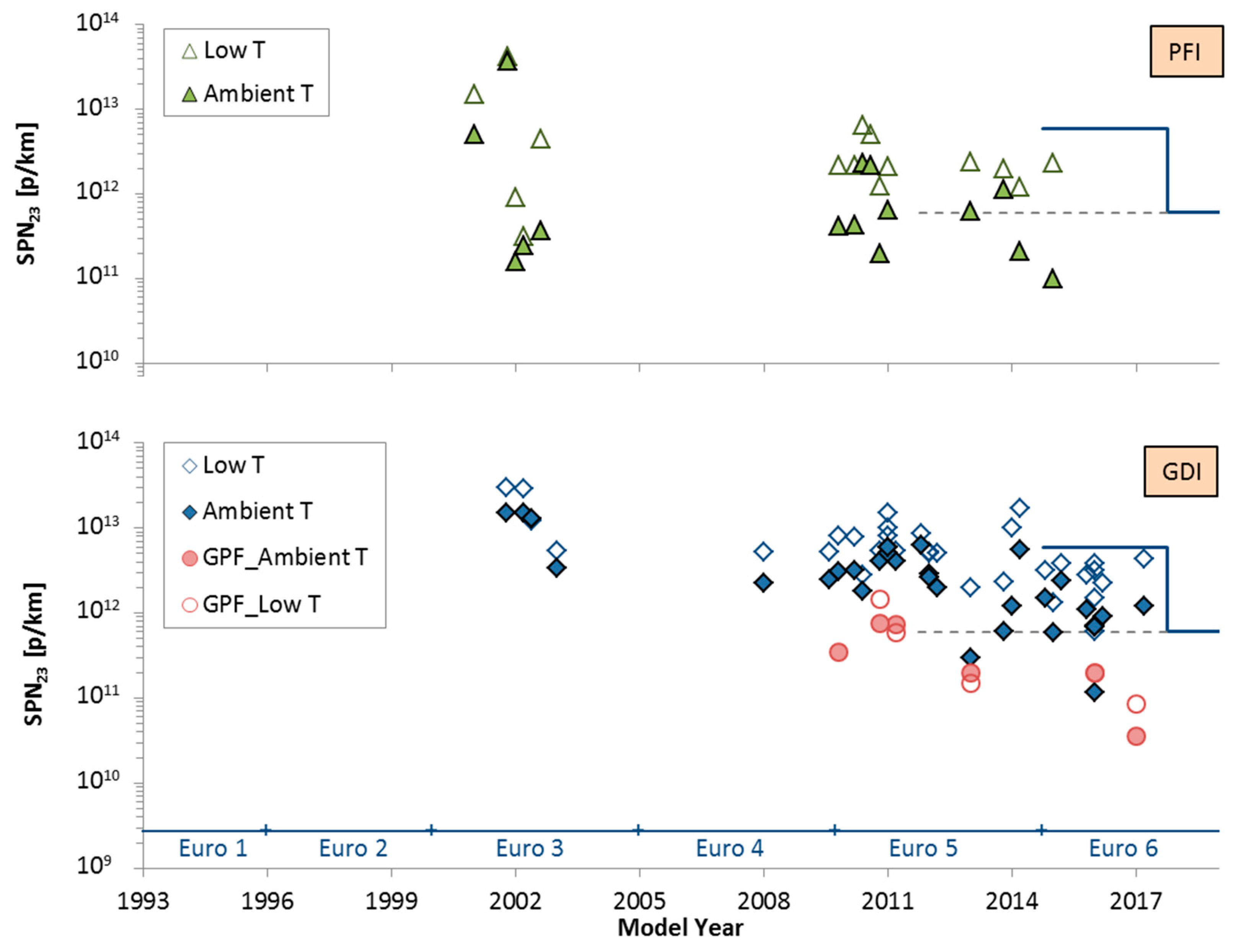
4.6. Low Ambient Temperature
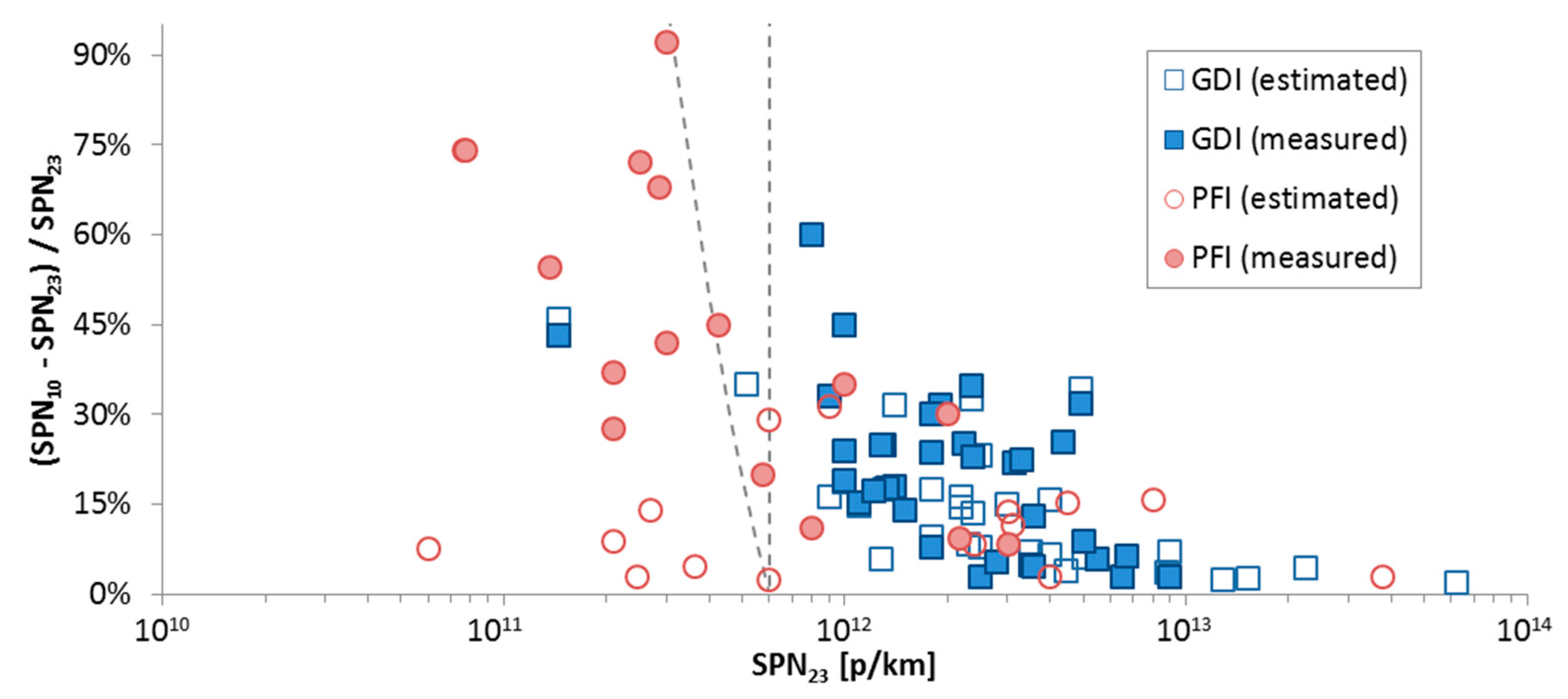
4.7. Sub-23 nm Fraction
5. Materials and Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- European Commission. A Roadmap for Moving to a Competitive Low Carbon Economy in 2050; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- European Commission. Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area—Towards a Competitive and Resource Efficient Transport System; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Javid, R.; Nejat, A.; Hayhoe, K. Selection of CO2 mitigation strategies for road transportation in the United States using a multi-criteria approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambhir, A.; Tse, L.K.C.; Tong, D.; Martinez-Botas, R. Reducing China’s road transport sector CO2 emissions to 2050: Technologies, costs and decomposition analysis. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkidas, A.C. Combustion advancements in gasoline engines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinig, U. One hundred years of gasoline direct injection: Part 1. MTZ Worldw. 2016, 77, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinig, U. One hundred years of gasoline direct injection: Part 2. MTZ Worldw. 2016, 77, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, P. Particulate Emissions from Vehicles; Wiley-Professional engineering publishing series; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-470-72455-2. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, Y.; Noma, K.; Nakayama, O.; Yamauchi, T.; Ando, H. Development of gasoline direct injection engine. SAE Trans. 1997, 106, 970541. [Google Scholar]
- Mock, P. European Vehicle Market Statistics: Pocketbook 2018/19; International Council on Clean Transportation Europe: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.C.; Williams, S.E.; Boundy, R.G.; Moore, S.A. 2016 Vehicle Technologies Market Report; Oak Ridge National Lab.: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2017.
- Hula, A.; French, R.; Maguire, A.; Bunker, A.; Rojeck, T. The 2018 EPA Automot. Trends Report: Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Fuel Economy, and Technol. since 1975; EPA-420-R-19-002; The Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Basshuysen, R.; Spicher, U. (Eds.) Gasoline Engine with Direct Injection: Processes, Systems, Development, Potential, 1st ed.; MTZ; Vieweg + Teubner: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-8348-0670-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. (Ed.) Gasoline and Gas Engines; Advanced Direct Injection Combustion Engine Technologies and Development; Woodhead: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-84569-389-3. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Dhar, A.; Sharma, N.; Shukla, P.C. Engine Exhaust Particulates; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 9789811332999. [Google Scholar]
- Boger, T.; Cutler, W. Reducing Particulate Emissions in Gasoline Engines; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-7680-9417-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Lai, M.-C.; Harrington, D.L. Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 437–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Manfredi, U.; Martini, G. Engine exhaust solid sub-23 nm particles: I. literature survey. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubric. 2014, 7, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, C.L.; Ko, A.; Park, S. Review on characterization of nano-particle emissions and PM morphology from internal combustion engines: Part 1. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Zhan, R.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z. Review of the state-of-the-art of exhaust particulate filter technology in internal combustion engines. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Überall, A.; Otte, R.; Eilts, P.; Krahl, J. A literature research about particle emissions from engines with direct gasoline injection and the potential to reduce these emissions. Fuel 2015, 147, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Particulate matter emissions from gasoline direct injection engines: Research review. J. Automot. Saf. Energy 2017, 8, 226–238. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Johnson, T. Gasoline particulate filters—A review. Emiss. Contr. Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Chen, L.; Leach, F.; Ding, S. A review of particulate number (PN) emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines and their control techniques. Energies 2018, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xu, H. Recent progress in automotive gasoline direct injection engine technology. Automot. Innov. 2018, 1, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duleep, K.G. The Impact of Gasoline Direct Injection System Design on PM Emissions; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Review of the state-of-the-art of particulate matter emissions from modern gasoline fueled engines. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1269–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. Vehicular emissions in review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. Vehicular emissions in review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. Vehicular emissions in review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2014, 7, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. Review of vehicular emissions trends. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1152–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T. Vehicular emissions in review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Joshi, A. Review of Vehicle Engine Efficiency and Emissions; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.; Joshi, A. Review of Vehicle Engine Efficiency and Emissions; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A. Review of Vehicle Engine Efficiency and Emissions; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ikoma, T.; Abe, S.; Sonoda, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Basaki, M. Development of V-6 3.5-Liter Engine Adopting New Direct Injection System; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fanick, R.; Kroll, S.; Swarts, A.; Quarderer, S. Effects of Dual Port Injection and Direct-Injection Technology on Combustion Emissions from Light-Duty Gasoline Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, N.; Jeon, J.; Kittelson, D.; Northrop, W.F. Solid Particle Number and Mass Emissions from Lean and Stoichiometric Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Operation; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, S.; Hoyer, R.; Adam, F.; Eckhoff, S.; Wunsch, R.; Schoen, C.; Vent, G. Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment for Lean Gasoline Direct Injection Engines—Potential for Future Applications; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, J.E.; Storey, J.M.E.; Prikhodko, V.Y.; Debusk, M.M.; Lewis, S.A. Filter-Based Control of Particulate Matter from a Lean Gasoline Direct Injection Engine; AE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shelef, M.; McCabe, R.W. Twenty-five years after introduction of automotive catalysts: What next? Catal. Today 2000, 62, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piock, W.; Hoffmann, G.; Berndorfer, A.; Salemi, P.; Fusshoeller, B. Strategies towards meeting future particulate matter emission requirements in homogeneous gasoline direct injection engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velji, A.; Yeom, K.; Wagner, U.; Spicher, U.; Rossbach, M.; Suntz, R.; Bockhorn, H. Investigations of the Formation and Oxidation of Soot Inside a Direct Injection Spark Ignition Engine Using Advanced Laser-Techniques; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, R.B.; Heywood, J.B. Piston Fuel Film Observations in an Optical Access GDI Engine; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, N.; Jeon, J.; Kittelson, D.; Northrop, W. Effects of Fuel Properties on Particle Number and Particle Mass Emissions from Lean and Stoichiometric Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Operation; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berndorfer, A.; Breuer, S.; Piock, W.; Von Bacho, P. Diffusion Combustion Phenomena in GDi Engines Caused by Injection Process; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, X.; Sarangi, A.K.; Weall, A.; Krueger-Venus, J. Fuel injector deposits in direct-injection spark-ignition engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 50, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xu, H.; Srivastava, D.; Ma, X.; Dearn, K.; Cracknell, R.; Krueger-Venus, J. Effect of fuel injector deposit on spray characteristics, gaseous emissions and particulate matter in a gasoline direct injection engine. Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, T.; Stenlaas, O.; Erlandsson, A. Future Fuels for DISI Engines: A Review on Oxygenated, Liquid Biofuels; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Karavalakis, G.; Durbin, T.D.; Yang, J.; Ventura, L.; Xu, K. Fuel Effects on PM Emissions from Different Vehicle/Engine Configurations: A Literature Review; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.W.; Meloche, E.; Kubsh, J.; Rosenblatt, D.; Brezny, R.; Rideout, G. Evaluation of a gasoline particulate filter to reduce particle emissions from a gasoline direct injection vehicle. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2012, 5, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Eakle, S.T.; Weber, P. Simultaneous Reduction of PM, HC, CO and NOx Emissions from a GDI Engine; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, A.; Warkins, J.; Aravelli, K.; Moser, D.; Yang, L.; Ball, D.; Tao, T.; Ross, D. Low cost LEV-III, Tier-III emission solutions with particulate control using advanced catalysts and substrates. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Siani, A.; Chen, F.; Chen, B. On Developing Advanced Catalysts Systems to Meet China New Regulations; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, C.; Nakatani, T.; Miyairi, Y.; Yuuki, K.; Makino, M.; Kurachi, H.; Heuss, W.; Kuki, T.; Furuta, Y.; Kattouah, P.; et al. New Particulate Filter Concept to Reduce Particle Number Emissions; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, S. Reduction of particle emissions from gasoline vehicles with direct fuel injection systems using a gasoline particulate filter. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiess, S.; Wong, K.-F.; Richter, J.-M.; Klingmann, R. Investigations of emission control systems for gasoline direct injection engines with a focus on removal of particulate emissions. Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.M.; Klingmann, R.; Spiess, S.; Wong, K.-F. Application of catalyzed gasoline particulate filters to GDI vehicles. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C. Platinum group metal and washcoat chemistry effects on coated gasoline particulate filter design. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 2015, 59, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Shimoda, T.; Aoki, T.; Yuuki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Kato, K.; Thier, D.; Kattouah, P.; Ohara, E.; Vogt, C. Next Generation of Ceramic Wall Flow Gasoline Particulate Filter with Integrated Three Way Catalyst; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Zheng, Y.; He, X.; Yang, D.; Shao, H.; Remias, J.; Roos, J.; Wang, Y. Catalyzed Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF) Performance: Effect of Driving Cycle, Fuel, Catalyst Coating; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.; Carpentier, G.; Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Remias, J.; Roos, J.; Xia, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yang, D.; et al. Engine Accelerated Aging Method Developed to Study the Effect of Lubricant Formulations on Catalyzed Gasoline Particulate Filter Durability; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, B.; Spiess, S.; Richter, J.M. Comprehensive Gasoline Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment, an Effective Measure to Minimize the Contribution of Modern Direct Injection Engines to Fine Dust and Soot Emisions? SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maricq, M.M.; Szente, J.J.; Adams, J.; Tennison, P.; Rumpsa, T. Influence of mileage accumulation on the particle mass and number emissions of two gasoline direct injection vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11890–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.K.; Bumbaroska, M.; Dobson, D.; Hangas, J.; Pakko, J.; Tennison, P. Analysis of high mileage gasoline exhaust particle filters. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijiiwa, R.; Rose, D.; Nicolin, P.; Coulet, B.; Jung, F.; Glasson, T.; Lv, Z.; Bachurina, A.; Shimizu, M.; Boger, T. Ash Accumulation in Advanced Gasoline Particulate Filter Technologies; JSAE: Yokohama, Japan, 2018; p. 20185404. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chanko, T.; Lambert, C.; Maricq, M. Gasoline Particulate Filter Efficiency and Backpressure at Very Low Mileage; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Howard, K.; Kirkman, P.; Browne, D.; Lu, Z.; He, S.; Boger, T. A Study into the Impact of Engine Oil on Gasoline Particulate Filter Performance through a Real-World Fleet Test; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Szente, J.; Pakko, J.; Lambert, C.; Maricq, M. Using Artificial Ash to Improve GPF Performance at Zero Mileage; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolin, P.; Rose, D.; Kunath, F.; Boger, T. Modeling of the soot oxidation in gasoline particulate filters. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easter, J.E.; Fiano, A.; Bohac, S.; Premchand, K.; Hoard, J. Evaluation of Low Mileage GPF Filtration and Regeneration as Influenced by Soot Morphology, Reactivity, and GPF Loading; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nieuwstadt, M.; Shah, A.; Serban, E.; Martin, D. Regeneration Strategies for Gasoline Particulate Filters; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boger, T.; Rose, D.; Nicolin, P.; Coulet, B.; Bachurina, A. Severe Soot Oxidations in Gasoline Particulate Filter Applications; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.W.; Saffaripour, M.; Liu, F.; Hendren, J.; Thomson, K.A.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R.; Rideout, G. Characterization of real-time particle emissions from a gasoline direct injection vehicle equipped with a catalyzed gasoline particulate filter during filter regeneration. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Clairotte, M.; Grigoratos, T.; Zardini, A.; Perujo, A.; Martini, G. Particle number measurements in the European legislation and future JRC activities. Combust. Engines 2018, 174, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B. Differences between tailpipe and dilution tunnel sub-23 nm non-volatile (solid) particle number measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 1–13, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W. Legislation for the reduction of exhaust gas emissions. In Traffic and Environment; Gruden, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 175–253. ISBN 978-3-540-00050-1. [Google Scholar]
- Truex, T.J. Interaction of Sulfur with Automotive Catalysts and the Impact on Vehicle Emissions—A Review; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dardiotis, C.; Wang, X.; Axmann, H.; Bergmann, A.; Schindler, W. Review of motor vehicle particulate emissions sampling and measurement: From smoke and filter mass to particle number. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Andersson, J.; Dilara, P.; Martini, G.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of automotive nonvolatile particle number emissions within the European legislative framework: A review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Dilara, P.; Sandbach, E.; Andersson, J. Particle measurement programme (PMP) light-duty inter-laboratory exercise: Comparison of different particle number measurement systems. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 095401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, J.; Ciuffo, B.; Fontaras, G.; Valverde, V.; Marotta, A. How much difference in type-approval CO2 emissions from passenger cars in Europe can be expected from changing to the new test procedure (NEDC vs. WLTP)? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 111, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Bonnel, P.; Hummel, R.; Provenza, A.; Manfredi, U. On-road emissions of light-duty vehicles in europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8575–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Rhys-Tyler, G. New insights from comprehensive on-road measurements of NOx, NO2 and NH3 from vehicle emission remote sensing in London, UK. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Clairotte, M.; Valverde-Morales, V.; Bonnel, P.; Kregar, Z.; Franco, V.; Dilara, P. Framework for the assessment of PEMS (Portable Emissions Measurement Systems) uncertainty. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Fuc, P.; Lijewski, P.; Bielaczyc, P. The Comparison of the Emissions from Light Duty Vehicle in On-Road and NEDC Tests; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Real-World Emissions in China: A Meta-Study of PEMS Emissions Data from China 0 to China5/V light- and Heavy-Duty Vehicles; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Bonnel, P. Feasibility Study on the Extension of the Real Driving Emissions (RDE) Procedure to Particle Number (PN): Experimental Evaluation of Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS) with Diffusion Chargers (DCs) to Measure Particle Number (PN) Concentration; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Bonnel, P. Feasibility Study on the Extension of the Real Driving Emissions (RDE) Procedure to Particle Number (PN): Chassis Dynamometer Evaluation of Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS) to Measure Particle Number (PN) Concentration: Phase II; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-51003-8. [Google Scholar]
- Riccobono, F.; Giechaskiel, B.; Mendoza Villafuerte, P. Particle Number PEMS Inter-Laboratory Comparison Exercise; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag, D.B.; Baldauf, R.W.; Yanca, C.A.; Fulper, C.R. Particulate matter speciation profiles for light-duty gasoline vehicles in the United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, E.; Kishan, S.; Baldauf, R.W.; Fulper, C.R.; Sabisch, M.; Warila, J. Temperature effects on particulate matter emissions from light-duty, gasoline-powered motor vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4672–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Lehmann, U.; Margaria, G. ACEA Programme on the Emissions of Fine Particulates from Passenger Cars(2) Part1: Particle Characterisation of a Wide Range of Engine Technologies; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi, A.; Kondo, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Fujitani, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Takami, A.; Tanabe, K. Chemical composition and source of fine and nanoparticles from recent direct injection gasoline passenger cars: Effects of fuel and ambient temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.D.; Wedekind, B.G.A.; Hall, D.; Stradling, R.; Wilson, G. DETR/SMMT/CONCAWE Particulate Research Programme: Light Duty Results; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bosteels, D.; May, J.; Karlsson, H.; de Serves, C. ‘Regulated’ and ‘Non-Regulated’ Emissions from Modern European Passenger Cars; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Shao, L.; Zheng, R.; Peng, J.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shuai, S.; Hu, M. Individual particles emitted from gasoline engines: Impact of engine types, engine loads and fuel components. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Shuai, S.-J.; Qin, Y.; Peng, J.; Niu, H.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Lu, S.; Hu, M. The Impact of Fuel Properties from Chinese Market on the Particulate and VOCs Emissions of a PFI and a DIG Engine; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.J.; Christensen, C.G.; Kittelson, D.B.; Johnson, J.P.; Watts, W.F. Impact of ambient temperatures and driving conditions on the chemical composition of particulate matter emissions from non-smoking gasoline-powered motor vehicles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Vu, D.; Russell, R.; Hajbabaei, M.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Durbin, T.D. Evaluating the effects of aromatics content in gasoline on gaseous and particulate matter emissions from SI-PFI and SIDI vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7021–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, B.; Sagebiel, J.; McDonald, J.D.; Whitney, K.; Lawson, D.R. Emissions rates and comparative chemical composition from selected in-use diesel and gasoline-fueled vehicles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, H.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Saarikoski, S.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Simonen, P.; Murtonen, T.; Dal Maso, M.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Bloss, M.; et al. Influence of fuel ethanol content on primary emissions and secondary aerosol formation potential for a modern flex-fuel gasoline vehicle. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5311–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Ruehl, C.R.; Shafer, M.M.; Antkiewicz, D.S.; Durbin, T.D.; Cocker, D.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Karavalakis, G. Physical, chemical, and toxicological characteristics of particulate emissions from current technology gasoline direct injection vehicles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Chen, V.; Espinoza, C.; Berte, T.; Durbin, T.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Jung, H.; Ntziachristos, L.; Amanatidis, S.; et al. Evaluating Particulate Emissions from a Flexible Fuel Vehicle with Direct Injection when Operated on Ethanol and Iso-Butanol Blends; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khalek, I.A.; Bougher, T.; Jetter, J.J. Particle emissions from a 2009 gasoline direct injection engine using different commercially available fuels. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M. Monitoring motor vehicle PM emissions: An evaluation of three portable low-cost aerosol instruments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Szente, J.J.; Harwell, A.L.; Loos, M.J. Impact of aggressive drive cycles on motor vehicle exhaust PM emissions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Szente, J.J.; Jahr, K. The impact of ethanol fuel blends on PM emissions from a light-duty GDI vehicle. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Zhu, H.; Durbin, T.D.; Karavalakis, G. Impacts of gasoline aromatic and ethanol levels on the emissions from GDI vehicles: Part 2. Influence on particulate matter, black carbon, and nanoparticle emissions. Fuel 2019, 252, 212–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Seong, H. Oxidation characteristics of gasoline direct-injection (GDI) engine soot: Catalytic effects of ash and modified kinetic correlation. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2371–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, P.; Stone, R.; OudeNijeweme, D.; Chen, X. Cold Start Particulate Emissions from a Second Generation DI Gasoline Engine; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Herreros, J.M.; Lattimore, T.; Shuai, S. Fuel effect on particulate matter composition and soot oxidation in a direct-injection spark ignition (DISI) engine. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenyuk, A.; Wilson, J.; Imre, D.; Stewart, M.; Muntean, G.; Storey, J.; Prikhodko, V.; Lewis, S.; Eibl, M.; Parks, J. Detailed characterization of particulate matter emitted by lean-burn gasoline direct injection engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 2017, 18, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, L.; Thier, D.; Schumann, T.; Guettler, S.; Russ, G. Fundamental Study of GPF Performance on Soot and ash Accumulation Over Artemis Urban and Motorway Cycles—Comparison of Engine Bench Results with GPF Durability Study on Road; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Haag, R.; Zeyer, K.; Mohn, J.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Heeb, N.V. Effects of four prototype gasoline particle filters (GPFs) on nanoparticle and genotoxic PAH emissions of a gasoline direct injection (GDI) vehicle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10709–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fang, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Guan, C.; Xia, C.; Xie, X.; Huang, Z. Size distribution, chemical composition and oxidation reactivity of particulate matter from gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine fueled with ethanol-gasoline fuel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 89, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xie, F.; Hong, W.; Li, X.; Hu, T. Experimental study of particulate emission characteristics from a gasoline direct injection engine during starting process. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2019, 20, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Yuan, C.; Xie, F.; Su, Y.; Chen, J. Particulate matter and particle-bound PAHs emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine with methanol-gasoline blended fuel during start. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2018, 19, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E.; Brown, R.J.C. A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Cocker, D.R.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Brezny, R.; Geller, M.; Karavalakis, G. Gasoline particulate filters as an effective tool to reduce particulate and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) vehicles: A case study with two GDI vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braisher, M.; Stone, R.; Price, P. Particle Number Emissions from a Range of European Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, P.; Kapus, P.; Ogris, M.; Hollerer, P. Measures to reduce particulate emissions from gasoline DI engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.; Smith, S.; Kapus, P.; Vidmar, K.; Hochnetz, A. EU6c particle number on a full Size SUV—Engine out or GPF? SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Pielecha, J.; Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J. Analysis of Emission Factors in RDE Tests as Well as in NEDC and WLTC Chassis Dynamometer Tests; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pielecha, J.; Merkisz, J.; Markowski, J.; Jasiński, R. Analysis of passenger car emission factors in RDE tests. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 10, 00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Vlachos, T.; Mendoza-Villafuerte, P.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Fontaras, G.; Bonnel, P.; Weiss, M. Vehicle emission factors of solid nanoparticles in the laboratory and on the road using portable emission measurement systems (PEMS). Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Drossinos, Y. Regulating particle number measurements from the tailpipe of light-duty vehicles: The next step? Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Bielaczyc, P.; Pielecha, J.; Woodburn, J. RDE Testing of Passenger Cars: The Effect of the Cold Start on the Emissions Results; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, F.; Dornoff, J. Beyond NOx: Emissions of Unregulated Pollutants from a Modern Gasoline Car; ICCT: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Deng, W.; Zhan, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, H.; Shuai, S. The Impact of Injector Deposits on Spray and Particulate Emission of Advanced Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicle; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, C.K.; Chanko, T.; Jagner, M.; Hangas, J.; Liu, X.; Pakko, J.; Kamp, C.J. Analysis of ash in low mileage, rapid aged, and high mileage gasoline exhaust particle filters. SAE Int. J. Engines 2017, 10, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosteels, D. Real driving emissions of a GPF-equipped production car 2015. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Real Driving Emissions, Berlin, Germany, 27–29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ACEA. RDE 3 Data from European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA). Available online: https://www.acea.be/publications/article/access-to-euro-6-rde-monitoring-data (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- JAMA. RDE 3 Data from Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA). Available online: http://www.jama-english.jp/europe/publications/rde.html (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- Merkisz, J.; Pielecha, J. Observations from PEMS testing of combustion engines of different applications. Combust. Engines 2018, 174, 40–55. [Google Scholar]
- Merkisz, J.; Brzezinski, L.; Magdziak, A.; Skobiej, K. Analysis of particle emissions of passenger cars in RDE tests. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 44, 00108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valverde, V.; Mora, B.A.; Clairotte, M.; Pavlovic, J.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Giechaskiel, B.; Astorga-LLorens, C.; Fontaras, G. Emissions factors derived from 13 Euro 6b light-duty vehicles based on laboratory and on-road measurements. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alföldy, B.; Giechaskiel, B.; Hofmann, W.; Drossinos, Y. Size-distribution dependent lung deposition of diesel exhaust particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.J.; Maricq, M.M. Signature size distributions for diesel and gasoline engine exhaust particulate matter. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, U.; Kaegi, R.; Mohr, M.; Zenobi, R. TEM analysis of volatile nanoparticles from particle trap equipped diesel and direct-injection spark-ignition vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4347–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, T.L.; Storey, J.M.E.; Youngquist, A.D.; Szybist, J.P. An analysis of direct-injection spark-ignition (DISI) soot morphology. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Kondo, Y.; Fushimi, A.; Takami, A.; Tanabe, K.; Kobayashi, S. Characterization of structure of single particles from various automobile engines under steady-state conditions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.O.; Seong, H.; Sakai, S.; Hageman, M.; Rothamer, D. Detailed Morphological Properties of Nanoparticles from Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Combustion of Ethanol Blends; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gaddam, C.K.; Vander Wal, R.L. Physical and chemical characterization of SIDI engine particulates. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Choi, S.; Lee, K. Examination of nanoparticles from gasoline direct-injection (GDI) engines using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, D.; Ford, M.A.; Jayne, D.T.; O’Neill, A.E.; Haack, L.P.; Hangas, J.; Jagner, M.J.; Sammut, A.; Gangopadhyay, A.K. Characterization of gasoline soot and comparison to diesel soot: Morphology, chemistry, and wear. Tribol. Int. 2014, 80, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffaripour, M.; Chan, T.W.; Liu, F.; Thomson, K.A.; Smallwood, G.J.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Effect of drive cycle and gasoline particulate filter on the size and morphology of soot particles emitted from a gasoline-direct-injection vehicle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11950–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liati, A.; Schreiber, D.; Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler, P.; Arroyo Rojas Dasilva, Y.; Spiteri, A.C. Electron microscopic characterization of soot particulate matter emitted by modern direct injection gasoline engines. Combust. Flame 2016, 166, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liati, A.; Schreiber, D.; Arroyo Rojas Dasilva, Y.; Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler, P. Ultrafine particle emissions from modern gasoline and diesel vehicles: An electron microscopic perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, P.; Pirjola, L.; Heikkilä, J.; Lähde, T.; Tzamkiozis, T.; Ntziachristos, L.; Keskinen, J.; Rönkkö, T. Exhaust particles of modern gasoline vehicles: A laboratory and an on-road study. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkkö, T.; Pirjola, L.; Ntziachristos, L.; Heikkilä, J.; Karjalainen, P.; Hillamo, R.; Keskinen, J. Vehicle engines produce exhaust nanoparticles even when not fueled. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J.; Szczotka, A. Low ambient temperature cold start emissions of gaseous and solid pollutants from Euro 5 vehicles featuring direct and indirect injection spark-ignition engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2013, 6, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Arndt, M.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A.; Silvis, W.; Drossinos, Y. Sampling of non-volatile vehicle exhaust particles: A simplified guide. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Pistikopoulos, P.; Samaras, Z.; Mathis, U.; Mohr, M.; Ristimäki, J.; Keskinen, J.; Mikkanen, P.; Casati, R.; et al. Performance Evaluation of a Novel Sampling and Measurement System for Exhaust Particle Characterization; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mamakos, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Comparability of particle emission measurements between vehicle testing laboratories: A long way to go. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, J.; Rönkkö, T. Can real-world diesel exhaust particle size distribution be reproduced in the laboratory? A critical review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, M.; Forss, A.-M.; Steffen, D. Particulate Emissions of Gasoline Vehicles and Influence of the Sampling Procedure; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Mamakos, A.; Samaras, Z.; Mathis, U.; Mohr, M.; Thompson, N.; Stradling, R.; Forti, L.; De Serves, C. Overview of the European “Particulates” Project on the Characterization of Exhaust Particulate Emissions from Road Vehicles: Results for Light-Duty Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, M.; Forss, A.-M.; Lehmann, U. Particle emissions from diesel passenger cars equipped with a particle trap in comparison to other technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.; Giechaskiel, B.; Munoz-Bueno, R.; Sandbach, E.; Dilara, P. Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Light-Duty Inter-Laboratory Correlation Exercise (ILCE_LD) Final Report; European Communities: Luxembourg, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, D.; Forss, A.-M.; Mohr, M.; Dimopoulos, P. Particle Characterisation of Modern CNG, Gasoline and Diesel Passenger Cars; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson, P.; Holmström, M.; Amberntsson-Carlsson, A.; Ohlson, C.; Skoglundh, M.; Andersson, B.; Carlsson, P.-A. Characterization of Particulate Emissions and Methodology for Oxidation of Particulates from Non-Diesel Combustion Systems; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mamakos, A.; Martini, G.; Marotta, A.; Manfredi, U. Assessment of different technical options in reducing particle emissions from gasoline direct injection vehicles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 63, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Ge, Y.; Tan, J.; Han, X.; Gao, L.; Hao, L.; Ye, W.; Dai, P. Comparison of PM emissions from a gasoline direct injected (GDI) vehicle and a port fuel injected (PFI) vehicle measured by electrical low pressure impactor (ELPI) with two fuels: Gasoline and M15 methanol gasoline. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J.; Szczotka, A. Particulate emissions from European vehicles featuring direct injection spark ignition engines tested under laboratory conditions. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Podsiadlik, D.H.; Chase, R.E. Examination of the size-resolved and transient nature of motor vehicle particle emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Podsiadlik, D.H.; Chase, R.E. Gasoline vehicle particle size distributions: Comparison of steady state, FTP, and US06 measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Pistikopoulos, P.; Fysikas, E.; Samaras, Z. Particle Emissions Characteristics of Different On-Road Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.W.; Meloche, E.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R.; Rosenblatt, D.; Rideout, G. Impact of ambient temperature on gaseous and particle emissions from a direct injection gasoline vehicle and its implications on particle filtration. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2013, 6, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; McMahon, W. Particulate emissions for LEV II light-duty gasoline direct injection vehicles. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2012, 5, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, K.; Myung, C.-L.; Lee, Y.; Park, S. Comparative investigation of regulated emissions and nano-particle characteristics of light duty vehicles using various fuels for the FTP-75 and the NEDC mode. Fuel 2013, 106, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Chase, R.E.; Xu, N.; Podsiadlik, D.H. The effects of the catalytic converter and fuel sulfur level on motor vehicle particulate matter emissions: Gasoline vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.O.; Shields, J.E. Evaluation of solid particle number and black carbon for very low particulate matter emissions standards in light-duty vehicles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Jeong, Y.I.; Jung, M.W.; Cha, K.O.; Kwon, S.I.; Kim, J.C.; Park, S. Experimental investigation and comparison of nanoparticle emission characteristics in light-duty vehicles for two different fuels. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2008, 9, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Shuai, S.-J. Impacts of COLD-start and Gasoline RON on Particulate Emission from Vehicles Powered by GDI and PFI Engines; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Lai, Y.; Zu, L.; Li, Y.; Su, S. Tailpipe emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicles at both low and high ambient temperatures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Inomata, S.; Tanimoto, H. Particle and VOC emissions from stoichiometric gasoline direct injection vehicles and correlation between particle number and mass emissions. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Comparisons of the nanoparticle emission characteristics between GDI and PFI vehicles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J. An overview of particulate matter emissions from modern light duty vehicles. Combust. Engines 2013, 2, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J. The impact of fuel ethanol content on particulate emissions from light-duty vehicles featuring spark ignition engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczyk, M.; Hejny, B.; Bielaczyc, P. An overview of particle number emission from direct injection SI engine in scope of new legislation rules. Combust. Engines 2015, 163, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J. Regulated and unregulated exhaust emissions from CNG fueled vehicles in light of Euro 6 regulations and the new WLTP/GTR 15 test procedure. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J.; Szczotka, A. Exhaust Emissions of Gaseous and Solid Pollutants Measured Over the NEDC, FTP-75 and WLTC Chassis Dynamometer Driving Cycles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Johnson, K.; Durbin, T.; Villela, M.; Pham, L.; Hosseini, S.; Zheng, Z.; Short, D.; Karavalakis, G.; et al. Determination of Suspended Exhaust PM Mass for Light-Duty Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fulper, C.R.; Kishan, S.; Baldauf, R.W.; Sabisch, M.; Warila, J.; Fujita, E.M.; Scarbro, C.; Crews, W.S.; Snow, R.; Gabele, P.; et al. Methods of characterizing the distribution of exhaust emissions from light-duty, gasoline-powered motor vehicles in the U.S. fleet. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros, D.C.; Zhang, S.; Sardar, S.; Kamboures, M.A.; Eiges, D.; Zhang, M.; Jung, H.S.; Mccarthy, M.J.; Chang, M.-C.O.; Ayala, A.; et al. Measuring particulate emissions of light duty passenger vehicles using integrated particle size distribution (IPSD). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5618–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.A.; VanBergen, S.; Kleeman, M.J.; Jakober, C.A. Size and composition distributions of particulate matter emissions: Part 1—light-duty gasoline vehicles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, D.; Vu, D.; Chen, V.; Espinoza, C.; Berte, T.; Karavalakis, G.; Durbin, T.D.; Asa-Awuku, A. Understanding particles emitted from spray and wall-guided gasoline direct injection and flex fuel vehicles operating on ethanol and iso-butanol gasoline blends. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, G.; Saleh, R.; Zhao, Y.; Presto, A.A.; Lambe, A.T.; Frodin, B.; Sardar, S.; Maldonado, H.; Maddox, C.; May, A.A.; et al. Comparison of gasoline direct-injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicle emissions: Emission certification standards, cold-start, secondary organic aerosol formation potential, and potential climate impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6542–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stradling, R.; Bazzani, R.; Bjordal, S.; Martinez, P.; Rickeard, D.J.; Schmelzle, P.; Scorletti, P.; Wolff, G.; Zemroch, P.J.; Thompson, N. Fuel Effects on Emissions from Modern Gasoline Vehicles. Part. 2—Aromatics, Olefins and Volatility Effects; Report 2/04; Concawe: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. The Effects of Ultra-Low Sulfur Gasoline on Emissions from Tier 2 Vehicles in the In-Use Fleet: Final Study Report. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/moves/ultra-low-sulfur-gasoline-emissions-study (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- Ahlvik, P.; Erlandsson, L.; Laveskog, A. The Influence of Block Heaters on the Emissions from Gasoline Fueled Cars with Varying Emission Control Technology at Low Ambient Temperatures; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1997; p. 970747. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, J.C. Emission Rates and Elemental Composition of Particles Collected from 1995 Ford Vehicles Using the Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule, the Highway Fuel Economy Test, and the USO6 Driving Cycle; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1997; p. 972914. [Google Scholar]
- Vuk, C.; Vander Griend, S.J. Fuel Property Effects on Particulates in Spark Ignition Engines; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.E.; Dickens, C.J. Measurement of the Number and Size Distribution of Particles Emitted from a Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicle; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Aakko, P.; Nylund, N.-O. Particle Emissions at Moderate and Cold Temperatures Using Different Fuels; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Peckham, M.S.; Finch, A.; Campbell, B.; Price, P.; Davies, M.T. Study of Particle Number Emissions from a Turbocharged Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engine Including Data from a Fast-Response Particle Size Spectrometer; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Kim, J.; Myung, C.-L.; Lee, M.; Kwon, S.; Lee, Y.; Park, S. Effect of the mixture preparation on the nanoparticle characteristics of gasoline direct-injection vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2012, 226, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Kim, J.; Ko, A.; Myung, C.-L.; Park, S.; Lee, J. Size-resolved engine exhaust aerosol characteristics in a metal foam particulate filter for GDI light-duty vehicle. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J. Exhaust emissions of particulate matter from light-duty vehicles—An overview and the current situation. Combust. Engines 2017, 171, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Demuynck, J.; Favre, C.; Bosteels, D.; Hamje, H.; Andersson, J. Real-World Emissions Measurements of a Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicle Without and with a Gasoline Particulate Filter; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, T.; Makino, M.; Aoki, T.; Shimoda, T.; Kato, K.; Nakatani, T.; Nagata, K.; Vogt, C.D.; Ito, Y.; Thier, D. Particle Number Emission Reduction for GDI Engines with gasoline Particulate Filters; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ge, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, Z.; Hao, L.; Yin, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J. Evaluation on toxic reduction and fuel economy of a gasoline direct injection- (GDI-) powered passenger car fueled with methanol–gasoline blends with various substitution ratios. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Vu, D.; Villela, M.; Russell, R.; Jung, H.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Durbin, T. Regulated emissions, air toxics, and particle emissions from SI-DI light-duty vehicles operating on different iso-butanol and ethanol blends. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, V.; Khalek, I.; Morgan, P.; Michlberger, A.; Sutton, M.; Vincent, P. Effect of Lubricant Oil on Particle Emissions from a Gasoline Direct Injection Light-Duty Vehicle; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Myung, C.-L.; Kim, J.; Choi, K.; Hwang, I.G.; Park, S. Comparative study of engine control strategies for particulate emissions from direct injection light-duty vehicle fueled with gasoline and liquid phase liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Fuel 2012, 94, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Choi, K.; Myung, C.-L.; Lim, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S. The impact of various ethanol-gasoline blends on particulates and unregulated gaseous emissions characteristics from a spark ignition direct injection (SIDI) passenger vehicle. Fuel 2017, 209, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Zu, L. Effects of aromatics, olefins and distillation temperatures (T50 & T90) on particle mass and number emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) vehicles. Energy Policy 2017, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, F. Testing of Particulate Emissions from Positive Ignition Vehicles with Direct Fuel Injection System; TUV Nord: Hanover, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Vu, D.; Russell, R.L.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Jung, H.; Johnson, K.C.; Durbin, T.D. The impact of ethanol and iso-butanol blends on gaseous and particulate emissions from two passenger cars equipped with spray-guided and wall-guided direct injection SI (spark ignition) engines. Energy 2015, 82, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J.; Szczotka, A. Particulate emissions from passenger cars with DISI engines tested at sub-zero temperatures 2014. In Proceedings of the 18th ETH Conference on Combustion Generated Nanoparticles, Zurich, Switzerland, 22–25 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, J.M.; Barone, T.; Norman, K.; Lewis, S. Ethanol blend effects on direct injection spark-ignition gasoline vehicle particulate matter emissions. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.M.E.; Barone, T.L.; Thomas, J.F.; Huff, S.P. Exhaust Particle Characterization for Lean and Stoichiometric DI Vehicles Operating on Ethanol-Gasoline Blends; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 2012–010437. [Google Scholar]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J. Investigations into Exhaust Particulate Emissions from Multiple Vehicle Types Running on Two Chassis Dynamometer Driving Cycles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Q.; Maricq, M.M.; Pakko, J.; Chanko, T.B.; Pui, D.Y.H. Design and evaluation of a sintered metal fiber filter for gasoline direct injection engine exhaust aftertreatment. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 133, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.; Roth, P.; Berte, T.; Yang, J.; Cocker, D.; Durbin, T.D.; Karavalakis, G.; Asa-Awuku, A. Using a new mobile atmospheric chamber (MACh) to investigate the formation of secondary aerosols from mobile sources: The case of gasoline direct injection vehicles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.E. Particulate Matter (PM) Emissions from Low Greenhouse Gas Engine Technologies. Presentation at the Advanced Clean Cars Symposium. Available online: https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/advanced-clean-cars-symposium-september-2016 (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- Ligterink, N. Emissions of Three Common GDI Vehicles; TNO: Hague, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, J.M.; Moses-DeBusk, M.; Huff, S.; Thomas, J.; Eibl, M.; Li, F. Characterization of GDI PM During Vehicle Start-Stop Operation; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chambon, P.; Huff, S.; Norman, K.; Edwards, K.D.; Thomas, J.; Prikhodko, V. European Lean Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicle Benchmark; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koczak, J.; Boehman, A.; Brusstar, M. Particulate Emissions in GDI Vehicle Transients: An Examination of FTP, HWFET, and US06 Measurements; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, S.; Ma, C. Effects of the particulate matter index and particulate evaluation index of the primary reference fuel on particulate emissions from gasoline direct injection vehicles. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Lax, D.; Gunter, G.C.; Hendren, J.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Assessment of the fuel composition impact on black carbon mass, particle number size distributions, solid particle number, organic materials, and regulated gaseous emissions from a light-duty gasoline direct injection truck and passenger car. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10452–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, C.; Bosteels, D.; May, J. Exhaust Emissions from European Market-Available Passenger Cars Evaluated on Various Drive Cycles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.; Sundvor, I.; Figenbaum, E. Comparison of regulated emission factors of Euro 6 LDV in Nordic temperatures and cold start conditions: Diesel- and gasoline direct-injection. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristimäki, J.; Keskinen, J.; Virtanen, A.; Maricq, M.; Aakko, P. Cold temperature PM emissions measurement: Method evaluation and application to light duty vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9424–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikawa, K.; Sakurai, T.; Jetter, J.J. Development of a predictive model for gasoline vehicle particulate matter emissions. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Wichser, A.; Mayer, A.; Lemaire, J. Experiences from Nanoparticle Research on Four Gasoline Cars; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Engelmann, D.; Heeb, N.; Muñoz, M.; Bonsack, P.; Hensel, V.; Mayer, A. PN-Emissions of Gasoline Cars MPI and Potentials of GPF; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hensel, V.; Mayer, A.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Engelmann, D. Nanoparticle emissions and GPF for MPI gasoline cars. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 421, 042027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, S. Characterizing particulate matter emissions from GDI and PFI vehicles under transient and cold start conditions. Fuel 2017, 189, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairotte, M.; Valverde, V.; Bonnel, P.; Giechaskiel, P.; Carriero, M.; Otura, M.; Fontaras, G.; Pavlovic, J.; Martini, G.; Krasenbrink, A. Joint Res. Centre 2017 Light-Duty Vehicles Emissions Testing Contribution to the EU Market Surveillance: Testing Protocols and Vehicle Emissions Performance; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 978-92-79-90600-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, G.; Song, C.; Pan, S.; Gao, J.; Cao, X. Comparison of number, surface area and volume distributions of particles emitted from a multipoint port fuel injection car and a gasoline direct injection car. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, T.W.; Meloche, E.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Black carbon emissions in gasoline exhaust and a reduction alternative with a gasoline particulate filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6027–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Li, Y.; Quiros, D.; Hu, S.; Huai, T.; Ayala, A.; Jung, H.S. Investigation of alternative metrics to quantify PM mass emissions from light duty vehicles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 113, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sogawa, Y.; Hattori, H.; Yanagisawa, N.; Hosoya, M.; Shoji, T.; Iwakiri, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Ikeda, T.; Tanaka, S.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Nano Particle Emission Evaluation of State of the Art Diesel Aftertreatment Technologies (DPF, Urea-SCR and DOC), Gasoline Combustion Systems (Lean Burn/Stoichiometric DISI and MPI) and Fuel Qualities Effects (EtOH, ETBE, FAME, Aromatics and Distillation); SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.; Cha, G. Impact of fuel, injection type and after-treatment system on particulate emissions of light-duty vehicles using different fuels on FTP-75 and HWFET test cycles. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2015, 16, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zu, L.; Bao, X.; Lai, Y.; Su, S. The impact from the direct injection and multi-port fuel injection technologies for gasoline vehicles on solid particle number and black carbon emissions. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bernard, Y.; Posada, F.; German, J. Laboratory and on-road testing of exhaust emissions of two modern China 5 light-duty gasoline vehicles; ICCT: Hamburg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Astorga, C. Impact of cold temperature on Euro 6 passenger car emissions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Thomas, D.; Wang, X.; Su, S.; Li, H.; He, H. Real driving particle number (PN) emissions from China-6 compliant PFI and GDI hybrid electrical vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Casadei, S.; Mazzini, M.; Sammarco, M.; Montabone, G.; Tonelli, R.; Deana, M.; Costi, G.; Di Tanno, F.; Prati, M.; et al. Inter-laboratory correlation exercise with portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) on chassis dynamometers. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Shimoda, T.; Aoki, T.; Shibagaki, Y.; Yuuki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Vogt, C.; Matsumoto, T.; Heuss, W.; Kattouah, P.; et al. Advanced Ceramic Wall Flow Filter for Reduction of Particulate Number Emission of Direct Injection Gasoline Engines; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gallus, J.; Kirchner, U.; Vogt, R.; Börensen, C.; Benter, T. On-road particle number measurements using a portable emission measurement system (PEMS). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Heeb, N.; Mayer, A.; Hensel, V. Nanoparticle Emissions of DI Gasoline Cars with/without GPF; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Keller, A.; Kumar, N.; Muñoz, M.; Pieber, S.; Prévôt, A.; Wichser, A.; Heeb, N. GASOMEP: Current Status and New Concepts of Gasoline Vehicle Emission Control for Organic, Metallic and Particulate Non-Legislative Pollutants; EMPA: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Vanhanen, J.; Väkevä, M.; Martini, G. Investigation of vehicle exhaust sub-23 nm particle emissions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Amanatidis, S.; Samaras, Z.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A. Use of a catalytic stripper as an alternative to the original PMP measurement protocol. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2013, 6, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Kim, K.; Chung, W.; Myung, C.-L.; Park, S. Characteristics of on-road particle number (PN) emissions from a GDI vehicle depending on a catalytic stripper (CS) and a metal-foam gasoline particulate filter (GPF). Fuel 2019, 238, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Lai, Y.; Zu, L.; Li, Y.; Su, S. Investigation of tailpipe and evaporative emissions from China IV and Tier 2 passenger vehicles with different gasolines. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 50, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happonen, M.; Matilainen, P.; Kanniainen, K.; Kinnunen, T.; Karjalainen, P.; Heikkilä, J.; Ronkko, T.; Keskinen, J.; Lähde, T.; Malinen, A.; et al. The Effect of a Particle Oxidation Catalyst (POC®) on Particle Emissions of a GDI car During Transient Engine Operation; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OudeNijeweme, D.; Freeland, P.; Behringer, M.; Aleiferis, P. Developing Low Gasoline Particulate Emission Engines through Improved Fuel Delivery; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zinola, S.; Raux, S.; Leblanc, M. Persistent Particle Number Emissions Sources at the Tailpipe of Combustion Engines; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa, K.; Jetter, J.J. Impact of gasoline composition on particulate matter emissions from a direct-injection gasoline engine: Applicability of the particulate matter index. Int. J. Engine Res. 2014, 15, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, Z.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Oleksiak, S. Nanoparticle and non-legislated gaseous emissions from a gasoline direct-injection car with ethanol blend fuels and detergent additives. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7268–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Yuan, X.; Yang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; He, X.; Shao, H.; Carpentier, G.; Remias, J.; et al. Design of Catalyzed Gasoline Particulate Filter (cGPF) and Investigation of Its Durability Performance Using Accelerated Engine Aging; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Pavlovic, J.; Trentadue, G.; Otura-Garcia, M.; Tansini, A.; Ciuffo, B.; Astorga, C. Effect of low ambient temperature on emissions and electric range of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3159–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Cocker, D.R.; Karavalakis, G. Investigation of the effect of mid- and high-level ethanol blends on the particulate and the mobile source air toxic emissions from a gasoline direct injection flex fuel vehicle. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, U.; Mohr, M.; Forss, A. Comprehensive particle characterization of modern gasoline and diesel passenger cars at low ambient temperatures. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Czerwinski, J.; Kasper, M.; Ulrich, A.; Mooney, J.J. Metal Oxide Particle Emissions from Diesel and Petrol Engines; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guse, D.; Roehrich, H.; Lenz, M.; Pischinger, S. Influence of Vehicle Operators and Fuel Grades on Particulate Emissions of an SI Engine in Dynamic Cycles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.K.; Holmén, B.A. Onboard, real-world second-by-second particle number emissions from 2010 hybrid and comparable conventional vehicles. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2233, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graskow, B.R.; Kittelson, D.B.; Ahmadi, M.R.; Morris, J.E. Exhaust Particulate Emissions from a Direct Injection Spark Ignition Engine; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Karavalakis, G.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Villela, M.; Quiros, D.; Hu, S.; et al. Comparison of vehicle exhaust particle size distributions measured by SMPS and EEPS during steady-state conditions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.E.; Goodfellow, C.L.; Heinze, P.; Rickeard, D.J.; Nancekievill, G.; Martini, G.; Hevesi, J.; Rantanen, L.; Merino, P.M.; Morgan, T.D.B.; et al. A Study of the Size, Number and Mass Distribution of the Automotive Particulate Emissions from European Light Duty Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998; p. 982600. [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola, M.A.; Prati, M.V.; Mariani, A.; Unich, A.; Morrone, B. Gaseous and particulate exhaust emissions of hybrid and conventional cars over legislative and real driving cycles. Energy Power Eng. 2015, 7, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Hu, M.; Peng, J.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Gu, F.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Comparison of primary aerosol emission and secondary aerosol formation from gasoline direct injection and port fuel injection vehicles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9011–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Lou, D.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Tan, P.; Yao, D. A PEMS study of the emissions of gaseous pollutants and ultrafine particles from gasoline- and diesel-fueled vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, C.-L.; Kim, J.; Jang, W.; Jin, D.; Park, S.; Lee, J. Nanoparticle filtration characteristics of advanced metal foam media for a spark ignition direct injection engine in steady engine operating conditions and vehicle test modes. Energies 2015, 8, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Wang, J.M.; Jeong, C.-H.; Ramos, M.; Hilker, N.; Healy, R.M.; Sabaliauskas, K.; Wallace, J.S.; Evans, G.J. Field measurements of gasoline direct injection emission factors: Spatial and seasonal variability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.; Liu, Y.; Tassel, P.; Perret, P.; Chaumond, A.; André, M. PAH, BTEX, carbonyl compound, black-carbon, NO2 and ultrafine particle dynamometer bench emissions for Euro 4 and Euro 5 diesel and gasoline passenger cars. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cédric, L.; Goriaux, M.; Tassel, P.; Perret, P.; André, M.; Liu, Y. Impact of aftertreatment device and driving conditions on black carbon, ultrafine particle and NOx emissions for Euro 5 diesel and gasoline vehicles. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.; Clairotte, M.; Adam, T.W.; Giechaskiel, B.; Heringa, M.F.; Elsasser, M.; Martini, G.; Manfredi, U.; Streibel, T.; Sklorz, M.; et al. Emissions of organic aerosol mass, black carbon, particle number, and regulated and unregulated gases from scooters and light and heavy duty vehicles with different fuels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 16591–16639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Vu, D.; Villela, M.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Durbin, T.D. Evaluating the regulated emissions, air toxics, ultrafine particles, and black carbon from SI-PFI and SI-DI vehicles operating on different ethanol and iso-butanol blends. Fuel 2014, 128, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Review | Health | Engine | Fuel | Aftertreatment | PM/SPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Book 2009 [13] | - | Y | Y | (Y) | - |
| Book 2010 [14] | - | Y | Y | (Y) | - |
| Book 2019 [15] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Book 2019 [16] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Paper 1999 [17] | - | Y | - | - | - |
| Paper 2007 [5] | - | Y | - | - | - |
| Paper 2014 [18] | Y | - | - | - | Y |
| Paper 2014 [19] | - | Y | - | Y | Y |
| Paper 2015 [20] | - | - | - | Y | Y |
| Paper 2015 [21] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Paper 2017 [22] | - | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Paper 2018 [23] | - | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Paper 2018 [24] | - | Y | Y | - | Y |
| Paper 2018 [25] | - | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Paper 2019 [26] | - | Y | - | Y | Y |
| Paper 2019 [27] | - | Y | Y | - | Y |
| Annual reviews [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] | - | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Euro | Class | Cycle | NM | AM | CO | HC | NOx | CFNOx | PM 1 | SPN 1 | CFSPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M1, M2 | EDC | 07/‘92 | 01/‘93 | 2.72 | 970 | - | - | - | - | - |
| N1-I | 10/‘93 | 10/‘94 | 2.72 | 970 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 10/‘93 | 10/‘94 | 5.17 | 1400 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-III | 10/‘93 | 10/‘94 | 6.90 | 1700 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2 | M1, M2 | 01/‘96 | 01/‘97 | 2.20 | 500 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| N1-I | 01/’97 | 10/’97 | 2.20 | 500 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 01/‘98 | 10/‘98 | 4.00 | 600 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-III | 01/‘98 | 10/‘99 | 5.00 | 700 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3 | M1, M2 | NEDC | 01/‘00 | 01/’01 | 2.30 | 200 | 150 | - | - | - | - |
| N1-I | 01/‘00 | 01/’01 | 2.30 | 200 | 150 | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 01/’01 | 01/‘02 | 4.17 | 250 | 180 | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-III | 01/’01 | 01/‘02 | 5.22 | 290 | 210 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 4 | M1, M2 | 01/‘05 | 01/‘06 | 1.00 | 100 | 80 | - | - | - | - | |
| N1-I | 01/‘05 | 01/‘06 | 1.00 | 100 | 80 | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 01/‘06 | 01/‘07 | 1.81 | 130 | 100 | - | - | - | - | ||
| N1-III | 01/‘06 | 01/‘07 | 2.27 | 160 | 110 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 5a | M1, M2 | 09/’09 | 09/‘11 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 5.0 | - | - | |
| N1-I | 09/’09 | 09/‘11 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 5.0 | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 09/‘10 | 01/‘12 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | - | 5.0 | - | - | ||
| N1-III, N2 | 09/‘10 | 01/‘12 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | - | 5.0 | - | - | ||
| 5b | M1, M2 | 09/‘11 | 01/‘13 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | - | - | |
| N1-I | 09/‘11 | 01/‘13 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | - | - | ||
| N1-II | 09/‘11 | 01/‘13 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | - | 4.5 | - | - | ||
| N1-III, N2 | 09/‘11 | 01/‘13 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | - | 4.5 | - | - | ||
| 6 | M1, M2 | 09/‘14 | 09/‘15 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1012 | - | |
| N1-I | 09/‘14 | 09/‘15 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1012 | - | ||
| N1-II | 09/‘15 | 09/‘16 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1012 | - | ||
| N1-III, N2 | 09/‘15 | 09/‘16 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1012 | - | ||
| 6c | M1, M2 | WLTC | - | 09/‘18 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | - |
| N1-I | - | 09/‘18 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | - | ||
| N1-II | - | 09/‘19 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | - | ||
| N1-III, N2 | - | 09/‘19 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | - | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | - | ||
| 6d- | M1, M2 | 09/‘17 | 09/‘19 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | |
| temp | N1-I | 09/‘17 | 09/‘19 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | |
| N1-II | 09/‘18 | 09/‘20 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | ||
| N1-III, N2 | 09/‘18 | 09/‘20 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | ||
| 6d | M1, M2 | 01/‘20 | 01/‘21 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | 1.43 2 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | |
| N1-I | 01/‘20 | 01/‘21 | 1.00 | 100 | 60 | 1.43 2 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | ||
| N1-II | 01/‘20 | 01/‘22 | 1.81 | 130 | 75 | 1.43 2 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 | ||
| N1-III, N2 | 01/‘20 | 01/‘22 | 2.27 | 160 | 82 | 1.43 2 | 4.5 | 6 × 1011 | 1.5 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giechaskiel, B.; Joshi, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dilara, P. European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070586
Giechaskiel B, Joshi A, Ntziachristos L, Dilara P. European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review. Catalysts. 2019; 9(7):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070586
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiechaskiel, Barouch, Ameya Joshi, Leonidas Ntziachristos, and Panagiota Dilara. 2019. "European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review" Catalysts 9, no. 7: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070586
APA StyleGiechaskiel, B., Joshi, A., Ntziachristos, L., & Dilara, P. (2019). European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review. Catalysts, 9(7), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070586





