Identification and Characterization of New Laccase Biocatalysts from Pseudomonas Species Suitable for Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening for Laccase Activity Using Guaiacol Agar Plates and ABTS Assay
2.2. Primer Design Based on UniProt Data Analysis
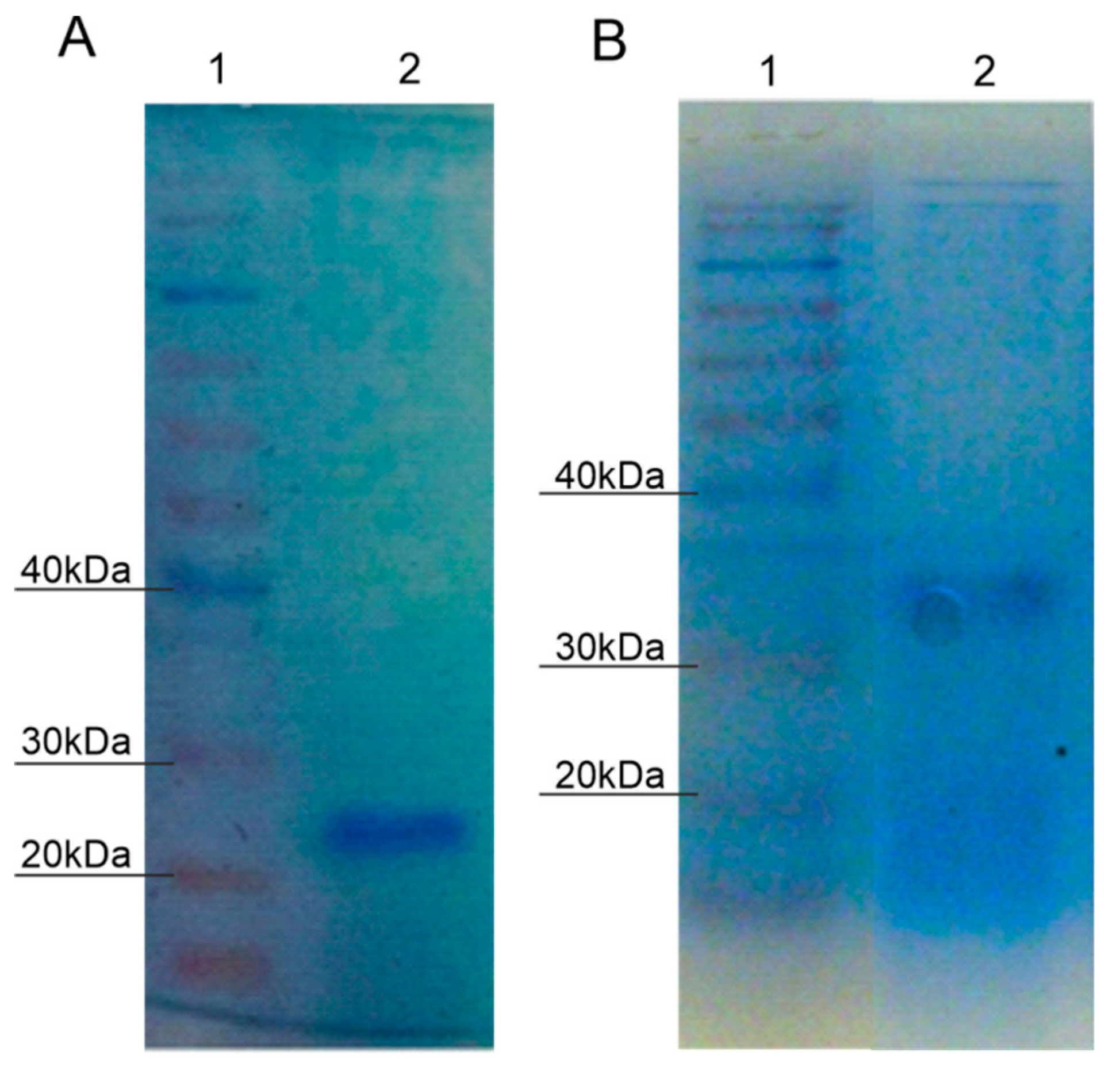
2.3. Purification of Protein with Laccase Activity from P. putida F6
2.4. N-Terminal Lacc1 Protein and P. putida F6 Genome Sequencing
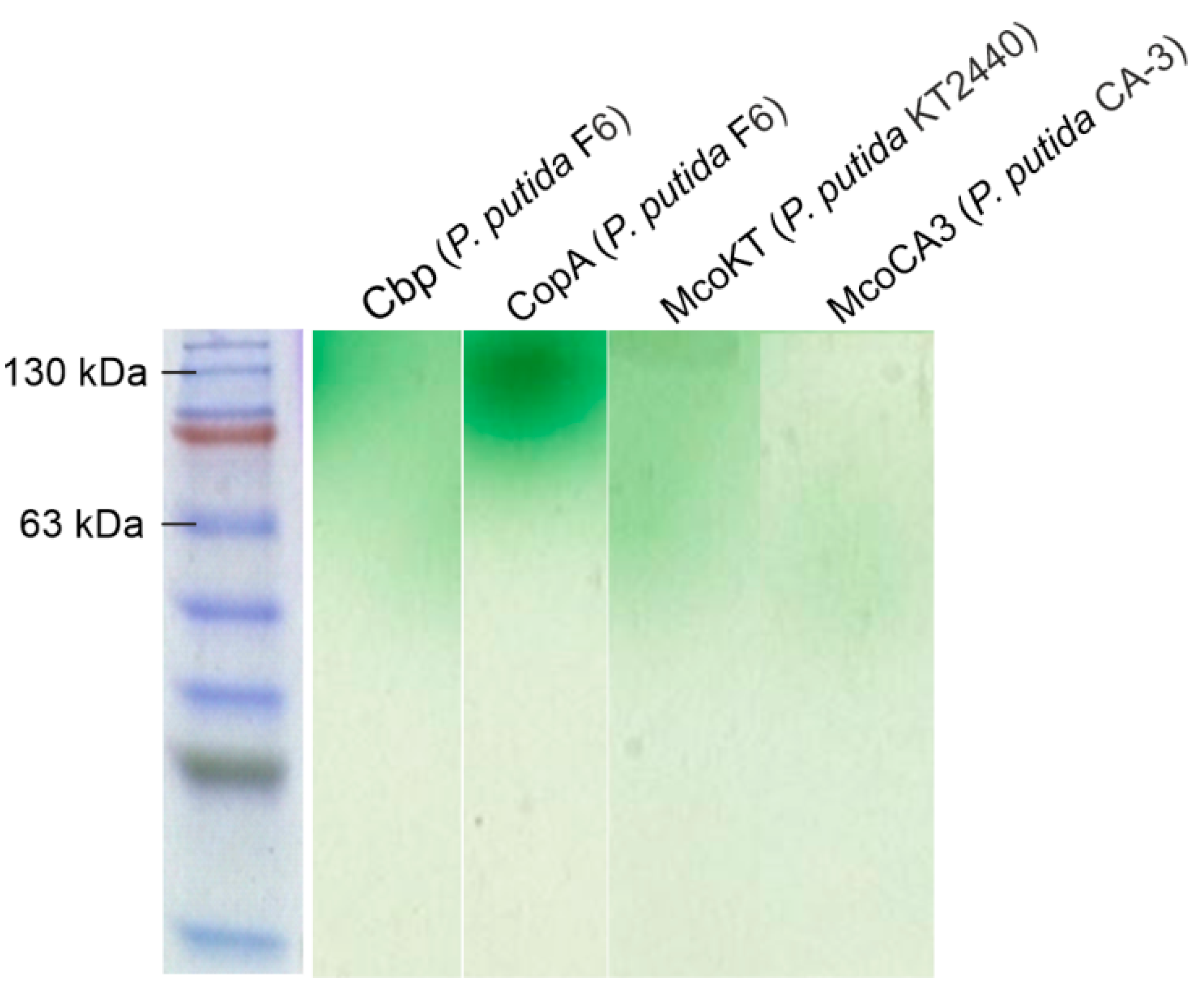
2.5. Cloning and Expression of Enzymes with Laccase Activity from Pseudomonas Species
2.6. Characterization of Recombinantly Expressed Laccases from Pseudomonas species
2.7. Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes Using Laccases from Pseudomonas Species
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Bacterial Strains
3.3. Media
3.4. Screen for Laccase Activity on Guaiacol Agar and in ABTS Assay
3.5. Primer Design, Gene Amplification and Cloning
3.6. Protein Purification from P. putida F6
3.7. N-Terminal and Genome Sequencing
3.8. Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
3.9. Temperature and pH Optimum of Purified Laccases
3.10. Textile Dyes Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaropolov, A.I.; Skorobogat’Ko, O.V.; Vartanov, S.S.; Varfolomeyev, S.D. Laccase: Properties, catalytic mechanism, and applicability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1994, 49, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, O.V.; Shumakovich, G.P.; Gorbacheva, M.A.; Shleev, S.V.; Yaropolov, A.I. “Blue” laccases. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2007, 72, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lončar, N.; Božić, N.; Vujičić, Z. Expression and characterization of a thermostable organic solvent-tolerant laccase from Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 9945a. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 134, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ece, S.; Lambertz, C.; Fischer, R.; Commandeur, U. Heterologous expression of a Streptomyces cyaneus laccase for biomass modification applications. AMB Express 2017, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granja-Travez, R.S.; Bugg, T.D.H. Characterisation of multicopper oxidase CopA from Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5: Involvement in bacterial lignin oxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 660, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brijwani, K.; Rigdon, A.; Vadlani, P.V. Fungal laccases: Production, function, and applications in food processing. Enzyme. Res. 2010, 2010, 149748–149758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerva, A.; Koutroufini, E.; Kostopoulou, I.; Detsi, A.; Topakas, E. A novel thermophilic laccase-like multicopper oxidase from Thermothelomyces thermophila and its application in the oxidative cyclization of 2′,3,4-trihydroxychalcone. New Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, A.C.; Jawdy, S.; Gunter, L.; Gjersing, E.; Sykes, R.; Hinchee, M.A.; Winkeler, K.A.; Collins, C.M.; Engle, N.; Tschaplinski, T.J.; et al. Knockdown of a laccase in Populus deltoides confers altered cell wall chemistry and increased sugar release. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2010–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, L. Comprehensive analysis of rice laccase gene (OsLAC) family and ectopic expression of OsLAC10 enhances tolerance to copper stress in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, Z.; Beckett, R.P.; Minibayeva, F.V.; Lüthje, S.; Böttger, M. Diversity of laccases from lichens in suborder Peltigerineae. Bryologist 2009, 112, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Korzhev, M.; Schröder, H.C.; Link, T.; Tahir, M.N.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Müller, W.E. Potential biological role of laccase from the sponge Suberites domuncula as an antibacterial defense component. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, H.; Ni, A.; Zhang, Y. The second conserved motif in bacterial laccase regulates catalysis and robustness. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4039–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumarasamy, N.P.; Jackson, B.; Raj, A.J.; Sevanan, M. Production of extracellular laccase from Bacillus subtilis MTCC 2414 using agroresidues as a potential substrate. Biochem. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 765190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscitelli, A.; Pezzella, C.; Giardina, P.; Faraco, V.; Giovanni, S. Heterologous laccase production and its role in industrial applications. Bioengineered 2010, 1, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouraris, D.; Zerva, A.; Topakas, E.; Karantonis, A. Kinetic and amperometric study of the MtPerII peroxidase isolated from the ascomycete fungus Myceliophthora thermophila. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 118, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Guido, C.; Baez, A.; Torres, E. Dioxygen activation by laccases: Green chemistry for fine chemical synthesis. Catalysts 2018, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blánquez, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Brissos, V.; Mendes, S.; Martins, L.O.; Ball, A.S.; Arias, M.E.; Hernández, M. Decolorization and detoxification of textile dyes using a versatile Streptomyces laccase-natural mediator system. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 26, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Couto, S.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Lacasses in the textile industry. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 1, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Legerska, B.; Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M. Degradation of synthetic dyes by laccases—A mini-review. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2016, 15, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Domingo-Espín, J.; Corchero, J.L.; Vázquez, E.; Villaverde, A. Microbial factories for recombinant pharmaceuticals. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 24, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, S.R.; Herrera, J.L.T. Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.J.; Blanford, C.F.; Giddens, S.R.; Skamnioti, P.; Armstrong, F.A.; Gurr, S.J. Designer laccases: A vogue for high-potential fungal enzymes? Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.A.R.; Silveira, W.B.; Passos, F.M.L.; Zucchi, T.D. Laccases from actinobacteria—What we have and what to expect. Postepy Mikrobiol. 2014, 4, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.B.; Shui, Y.; Song, C.M.; Zhang, N.; Cai, Y.J.; Liao, X.R. Efficient secretory production of CotA-laccase and its application in the decolorization and detoxification of industrial textile wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9515–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.O.; Soares, C.M.; Pereira, M.M.; Teixeira, M.; Costa, T.; Jones, G.H.; Henriques, A.O. Molecular and biochemical characterization of a highly stable bacterial laccase that occurs as a structural component of the Bacillus subtilis endospore coat. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18849–18859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihssen, J.; Reiss, R.; Luchsinger, R.; Thöny-Meyer, L.; Richter, M. Biochemical properties and yields of diverse bacterial laccase-like multicopper oxidases expressed in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherif, M.; Waung, D.; Korbeci, B.; Mavisakalyan, V.; Flick, R.; Brown, G.; Abouzaid, M.; Yakunin, A.F.; Master, E.R. Biochemical studies of the multicopper oxidase (small laccase) from Streptomyces coelicolor using bioactive phytochemicals and site directed mutagenesis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.E.; Arenas, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Soliveri, J.; Ball, A.S.; Hernández, M. Kraft pulp biobleaching and mediated oxidation of a nonphenolic substrate by laccase from Streptomyces cyaneus CECT 3335. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Devi, P.; Chendrayan Uthandi, S. Laccase producing Streptomyces bikiniensis CSC12 isolated from compost. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food. Sci. 2017, 6, 794–798. [Google Scholar]
- Eugenio, M.E.; Hrenández, M.; Moya, R.; Martínsampedro, R. Evaluation of a new laccase produced by Streptomyces ipomoea on biobleaching and ageing of kraft pulps. BioResources 2011, 6, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar]
- Kuddus, M.; Joseph, B.; Ramteke, P.V. Production of laccase from newly isolated Pseudomonas putida and its application in bioremediation of synthetic dyes and industrial effluents. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.K.; Vandana, P. Congo red dye decolourization by partially purified laccases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Arunkumar, T.; Anand, A.D.; Narendrakumar, G. Production and partial purification of laccase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa ADN04. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 727–731. [Google Scholar]
- Bugg, T.D.; Ahmad, M.; Hardiman, E.H.; Singh, R. The emerging role for bacteria in lignin degradation and bio-product formation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 3, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Laccase: A green catalyst for the biosynthesis of poly-phenols. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Kataoka, K. Basic and applied features of multicopper oxidases, CueO, bilirubin oxidase, and laccase. Chem. Rec. 2007, 7, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miñambres, B.; Martínez-Blanco, H.; Olivera, E.R.; García, B.; Díez, B.; Barredo, J.L.; Moreno, M.A.; Schleissner, C.; Salto, F.; Luengo, J.M. Molecular cloning and expression in different microbes of the DNA encoding Pseudomonas putida U phenylacetyl-CoA ligase. Use of this gene to improve the rate of benzylpenicillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33531–33538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Goel, R.; Capalash, N. Bacterial laccases. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, J.; Bennati-Granier, C.; Maillard, J.; Blánquez, P.; Barry, D.A.; Holliger, C. Bacterial versus fungal laccase: Potential for micropollutant degradation. AMB Express 2013, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, S.; Cowley, A.; Lee, J.; Foix, A.; Lopez, R. Programmatic access to bioinformatics tools from EMBL-EBI update: 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, A.M.; Doyle, E.M.; Brooksa, S.; O’Connor, K.E. Biochemical characterization of the coexisting tyrosinase and laccase in the soil bacterium Pseudomonas putida F6. Enzm. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, T. PROKKA: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architecture. Nucleic Acid Res. 2017, 45, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, N.; Vivanco, J.M.; Decker, S.R.; Reardon, K.F. Expression of industrially relevant laccases: Prokaryotic style. Trends. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tony, B.D.; Goyal, D.; Khanna, S. Decolorization of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial consortium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Coelho, A.V.; Viegas, C.A.; Correia dos Santos, M.M.; Robalo, M.P.; Martins, L.O. Enzymatic biotransformation of the azo dye Sudan Orange G with bacterial CotA-laccase. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.K.; Sharma, H. Decolourization of textile azo dyes by Bacillus spp. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Traditional and Technical Textiles, Jalandhar, India, 11–12 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, H.G.; Kaltwasser, H.; Gottschalk, G. A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: Growth physiological studies. Arch. Mikrobiol. 1961, 38, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primers with Restriction Enzyme Sites | Annealing T | Strain | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS_LACF | ATGAGTGRCCTGRCBCAG | 50 °C | Pseudomonas spp. |
| PS_LACR | GCGGNTCCAGCCASACCARSGA | ||
| CA3F | TAACAGGATCCGAGTGGCCTGACTCAGG (Bam HI) | 55 °C | P. putida CA-3 |
| CA3R | TAATTAAGCTTTTGCGGTTCCAGCCAGAC (Hind III) | ||
| KTF | TAACAGGATCCGAGTGACCTGACGCAGG (Bam HI) | 59 °C | P. putida KT2440 |
| KTR | TAATTAAGCTTGCGCGGGTCCAGCCAGAC (Hind III) | ||
| CopAF | TAACAGCTAGCATGTCGCATGATGATTTTCGT (Nhe I) | 55 °C | P. putida F6 |
| CopAR | TAATTAAGCTTTTCGTCGACCCTCACCGTGCG (Hind III) | ||
| CbpF | TAACAGCTAGCATGACTCACCATTCCGAAGAC (Nhe I) | 58 °C | P. putida F6 |
| CbpR | TAATTAAGCTTAGCCGCCATGGCGCTGCAGCT (Hind III) | ||
| Gene Name | Protein Size (AA) | GeneBank Match | GeneBank Acc No | Identity (%) | Discovered with |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative cysteine-rich protein YhjQ | 116 | Four-helix bundle copper-binding protein (Cbp) from Pseudomonas putida | WP_026070601 | 100 | MTHHSED motif search |
| Not annotated | 623 | Copper resistance system multicopper oxidase (CopA) from Xantomonadaceae | WP_017354985 | 100 | Conserved Domains tool |
| Copper resistance protein B | 425 | Copper resistance protein B (CopB) from Xantomonadaceae | WP_017354984 | 100 | Genome annotation |
| Copper resistance protein C | 127 | Copper homeostasis periplasmic binding protein (CopC) from Xanthomonadaceae | WP_017354979 | 100 | Genome annotation |
| Laccase domain protein YfiH | 246 | Multi-copper polyphenol oxidoreductase laccase from Pseudomonas putida | WP_075804457 | 96.3 | Genome annotation |
| Laccase domain protein YfiH | 256 | Multi-copper polyphenol oxidoreductase laccase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | WP_099560244 | 99.2 | Genome annotation |
| Multicopper oxidase mco | 460 | Multicopper oxidase from Pseudomonas putida | WP_075806698 | 97.4 | Genome annotation |
| Blue copper oxidase CueO | 675 | Multicopper oxidase protein from Pseudomonas | WP_075804455 | 79.9 | Genome annotation |
| Bacterial Strain | Reference |
|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | ATCC 15,692 |
| Pseudomonas putida CA-3 | NCIMB 41,162 |
| Pseudomonas putida F6 | [33] |
| Pseudomonas putida KT2440 | ATCC 47,054 |
| Pseudomonas putida mt-2 | NCIMB 10,432 |
| Pseudomonas putida S12 | ATCC 70,0801 |
| Pseudomonas chlororaphis B561 | ATCC 19,523 |
| Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) | Merck, Darmstadt, Germany |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandic, M.; Djokic, L.; Nikolaivits, E.; Prodanovic, R.; O’Connor, K.; Jeremic, S.; Topakas, E.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Identification and Characterization of New Laccase Biocatalysts from Pseudomonas Species Suitable for Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes. Catalysts 2019, 9, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070629
Mandic M, Djokic L, Nikolaivits E, Prodanovic R, O’Connor K, Jeremic S, Topakas E, Nikodinovic-Runic J. Identification and Characterization of New Laccase Biocatalysts from Pseudomonas Species Suitable for Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes. Catalysts. 2019; 9(7):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070629
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandic, Mina, Lidija Djokic, Efstratios Nikolaivits, Radivoje Prodanovic, Kevin O’Connor, Sanja Jeremic, Evangelos Topakas, and Jasmina Nikodinovic-Runic. 2019. "Identification and Characterization of New Laccase Biocatalysts from Pseudomonas Species Suitable for Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes" Catalysts 9, no. 7: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070629
APA StyleMandic, M., Djokic, L., Nikolaivits, E., Prodanovic, R., O’Connor, K., Jeremic, S., Topakas, E., & Nikodinovic-Runic, J. (2019). Identification and Characterization of New Laccase Biocatalysts from Pseudomonas Species Suitable for Degradation of Synthetic Textile Dyes. Catalysts, 9(7), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070629







