Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation
Abstract
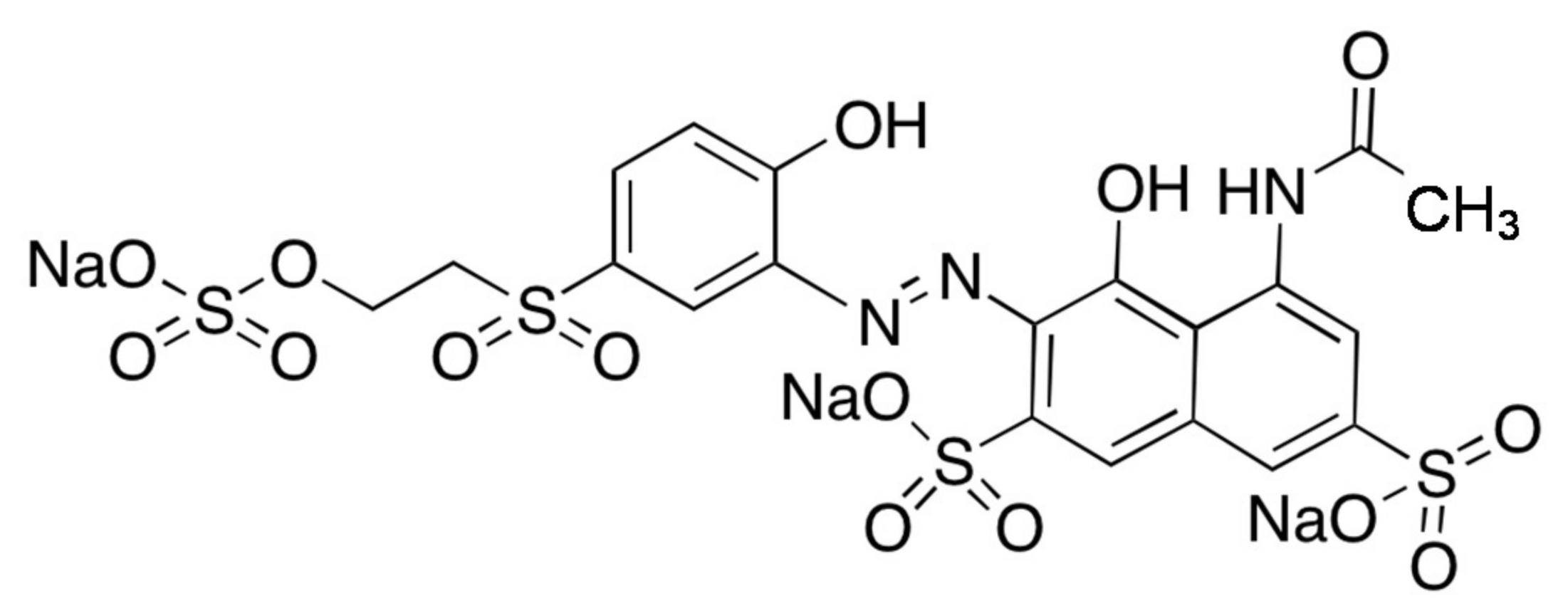
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. Catalyst Screening and Selection
- P-25 resulted in a color removal close to 23% at the end of the treatment;
- 100Fe-TiO2 showed a final decolorization degree close to 42%;
- 10Fe-TiO2 exhibited an intermediate behavior and decolorized the dye solution to about 35%;
- 50Fe-TiO2 was the most effective catalyst, with a color removal efficiency of 47.6%.
2.3. Analysis of the UV–Vis Absorption Spectrum of RV5 During Degradation
2.4. Effect of pH
2.5. Effect of Catalyst Load
2.6. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide
2.7. Comparison with the Results of Other Published Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
3.3. Photocatalytic Apparatus
3.4. Photodegradation Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunger, K. Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M. Handbook of Textile and Industrial Dyeing – Volume 1: Principles, Processes and Types of Dyes; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 428–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zuorro, A.; Maffei, G.; Lavecchia, R. Kinetic modeling of azo dye adsorption on non-living cells of Nannochloropsis oceanica. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4121–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, E.; Di Palma, L.; Lavecchia, R.; Zuorro, A. Treatment of diazo dye Reactive Green 19 by anodic oxidation on a boron-doped diamond electrode. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Camargo, B.C.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Azo dyes: Characterization and toxicity—A review. Text. Light Ind. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 85–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.-T. Azo dyes and human health: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Pt. C-Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2016, 34, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathi, C.; Maruthavanan, T.; Sivamani, S.; Prakash, C. Removal of dyes from textile wet processing industry: A review. J. Text. Assoc. 2011, 71, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Arora, S. Removal of synthetic textile dyes from wastewaters: A critical review on present treatment technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 807–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelpohl, A.; Kim, S.M. Advanced oxidation processes AOPs in wastewater treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2004, 10, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Oturan, M.A.; Aaron, J.-J. Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: Principles and applications. A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, S.; Moyet, M.A.; Arthur, R.B.; Patterson, H.H. Recent advances on TiO2-based photocatalysts toward the degradation of pesticides and major organic pollutants from water bodies. Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade Atul, V.; Gaikwad, G.S.; Dhonde, M.G.; Khaty, N.T.; Thakare, S.R. Removal of organic pollutant from water by heterogenous photocatalysis: A review. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2013, 17, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.-G.; Liao, S.-J.; Liu, J.-M.; Dang, Z.; Petrik, L. Preparation of visible-light responsive N-F-codoped TiO2 photocatalyst by a sol-gel-solvothermal method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2006, 184, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, T.J.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsieh, M.T.; Chen, J.J. Laser-induced silver nanoparticles on titanium oxide for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4707–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ma, F.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, W.; Huo, M.; Guo, Y. Mixed phase titania nanocomposite codoped with metallic silver and vanadium oxide: New efficient photocatalyst for dye degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 175, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zou, W.; Qu, W.; Zhang, J. Photocatalytic performance of a visible light TiO2 photocatalyst prepared by a surface chemical modification process. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, J. Photocatalytic discolorization of methyl orange solution by Pt modified TiO2 loaded on natural zeolite. Dyes Pigment. 2008, 77, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.G.; Devi, L.G. Review on modified TiO2 photocatalysis under UV/visible light: Selected results and related mechanisms on interfacial charge carrier transfer dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 13211–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Shin, M.; Lee, M.; Hwang, Y.J. Photo-oxidation activities on Pd-doped TiO2 nanoparticles: Critical PdO formation effect. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 165, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rady, A.A.; Abd El-Sadek, M.S.; El-Sayed Breky, M.M.; Assaf, F.H. Characterization and photocatalytic efficiency of palladium doped-TiO2 nanoparticles. Adv. Nanopart. 2013, 2, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K.; Kansal, S.K. Highly effective Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles photocatalysts for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic compounds. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Ganguly, P.; Rhatigan, S.; Kumaravel, V.; Byrne, C.; Hinder, S.; Bartlett, J.; Nolan, M.; Pillai, S.C. Cu doped TiO2: Visible light assisted photocatalytic antimicrobial activity and high temperature anatase stability. ChemRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, V.; Jun, M.B.G.; Blackburn, A.; Herring, R.A. Significant improvement in visible light photocatalytic activity of Fe doped TiO2 using an acid treatment process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Bechstein, R.; Kibsgaard, J.; Vang, R.T.; Besenbacher, F. High-quality Fe-doped TiO2 films with superior visible-light performance. J. Mat. Chem. 2012, 22, 23755–23758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iervolino, G.; Vaiano, V.; Rizzo, L. Visible light active Fe-doped TiO2 for the oxidation of arsenite to arsenate in drinking water. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 70, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y. Degradation of azo dye reactive violet 5 by TiO2 photocatalysis. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabansag, J.L.J.; Dumelod, J.C.; Alfaro, J.C.O.; Arsenal, J.D.; Sambot, J.C.; Enerva, L.T.; Leaño, J.L., Jr. Photocatalytic degradation of aqueous C.I. Reactive Violet 5 using bulk zinc oxide (ZnO) slurry. Philipp. J. Sci. 2013, 142, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kunal, J.; Varun, S.; Digantkumar, C.; Datta, M. Decolorization and degradation of azo dye—Reactive Violet 5R by an acclimatized indigenous bacterial mixed cultures-SB4 isolated from anthropogenic dye contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mat. 2012, 213–214, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Bheemaraddi, M.C.; Patil, S.; Shivannavar, C.T.; Gaddad, S.M. Isolation and characterization of Paracoccus sp. GSM2 capable of degrading textile azo dye Reactive Violet 5. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 410704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; Bekir, K.; Achour, S.; Cheref, A.; Bakhrouf, A. Exploring bioaugmentation strategies for azo dye CI Reactive Violet 5 decolourization using bacterial mixture: Dye response surface methodology. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidaleo, M.; Lavecchia, R.; Petrucci, E.; Zuorro, A. Application of a novel definitive screening design to decolorization of an azo dye on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaiano, V.; Iervolino, G.; Sannino, D.; Rizzo, L.; Sarno, G. MoOx/TiO2 immobilized on quartz support as structured catalyst for the photocatalytic oxidation of As(III) to As(V) in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongwan, P.; Inceesungvorn, B.; Wetchakun, K.; Phanichphant, S.; Wetchakun, N. Highly efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Eng. J. 2012, 16, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, W.; He, W.; Zu, X. Effect of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticle derived from modified hydrothermal process on the photocatalytic degradation performance on methylene blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhai, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, H. Study of homologous elements: Fe, Co, and Ni dopant effects on the photoreactivity of TiO2 nanosheets. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, W.; Cao, Y. Doping and transformation mechanisms of Fe3+ ions in Fe-doped TiO2. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marami, M.B.; Farahmandjou, M.; Khoshnevisan, B. Sol–gel synthesis of Fe-doped TiO2 nanocrystals. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yu, J.; Cheng, B. Effects of Fe-doping on the photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 powders prepared by an ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Luan, T.; LÜ, T.; Cheng, K.; Xu, H. Performance of V2O5-WO3-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, B.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, A.K. Investigation of the physical properties of Fe:TiO2-diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 425–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tadé, M.O.; Shao, Z. Research progress of perovskite materials in photocatalysis and photovoltaics-related energy conversion and environmental treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5371–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Tripathi, P.; Azam, A.; Raza, W.; Ahmed, A.S.; Ahmed, A.; Muneer, M. Photocatalytic performance of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under visible-light irradiation. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, aa576d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navio, J.A.; Testa, J.J.; Djedjeian, P.; Padron, J.R.; Rodriguez, D. Iron-doped titania powders prepared by a sol–gel method. Part II: Photocatalytic properties. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 1999, 178, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpone, N.; Lawless, D.; Disdier, D. Spectroscopic, photoconductivity, and photocatalytic studies of TiO2 colloids: Naked and with the lattice doped with Cr3+, Fe3+, and V5+ cations. Langmuir 1994, 10, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, E.; Di Palma, L.; Lavecchia, R.; Zuorro, A. Modeling and optimization of Reactive Green 19 oxidation on a BDD thin-film electrode. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Ashraf, S.S. Fundamental principles and application of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of dyes in solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, A.; Majeed, I.; Malik, R.N.; Idriss, H.; Nadeem, M.A. Principles and mechanisms of photocatalytic dye degradation on TiO2 based photocatalysts: A comparative overview. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37003–37026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.; Saquib, M.; Muneer, M. Photocatalytic degradation of two selected dye derivatives, chromotrope 2B and amido black 10B, in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide. Dyes Pigment. 2005, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Modirshahla, N.; Shokri, M. Photodestruction of acid orange 7 (AO7) in aqueous solutions by UV/H2O2: Influence of operational parameters. Chemosphere 2005, 55, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Shetty K, V. Solar photocatalysis for treatment of Acid Yellow-17 (AY-17) dye contaminated water using Ag@TiO2 core-shell structured nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5692–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H. Photodegradation of C.I. Reactive Red 2 in UV/TiO2-based systems: Effects of ultrasound irradiation. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 167, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandham, M.; Swaminathan, M. Solar photocatalytic degradation of a reactive azo dye in TiO2-suspension. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 81, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandham, M.; Sobana, N.; Swaminathan, M. Solar assisted photocatalytic and photochemical degradation of Reactive Black 5. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.A.; Dulay, M.T. Heterogeneous photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, E.M.; Goh, S.N.; Wu, T.Y.; Ling, T.T.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Juan, J.C. Evaluation on the photocatalytic degradation activity of Reactive Blue 4 using pure anatase nano-TiO2. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.S.T.; Pinto, E.M.S.; Nkeonye, P.; Oliveira-Campos, A.M.F. Degradation of C.I. Reactive Orange 4 and its simulated dyebath wastewater by heterogeneous photocatalysis. Dyes Pigment. 2005, 64, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavitha, S.K.K.; Palanisamy, P.N. Photocatalytic and sonophotocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red 120 using dye sensitized TiO2 under visible light. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saquib, M.; Muneer, M. Semiconductor mediated photocatalysed degradation of an anthraquinone dye, Remazol Brilliant Blue R under sunlight and artificial light source. Dyes Pigment. 2002, 53, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamaraiselvi, K.; Sivakumar, T. Photocatalytic activities of novel SrTiO3–BiOBr heterojunction catalysts towards the degradation of reactive dyes. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 207, 218–232. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, R.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Zeng, G. Principle and application of hydrogen peroxide based advanced oxidation processes in activated sludge treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, F.S.; Freitas, T.K.F.D.S.; de Almeida, C.A.; de Souza, R.P.; Ambrosio, E.; Palácio, S.M.; Garcia, J.C. Hydrogen peroxide-assisted photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater using titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, A.; Hammedi, T.; Najjar, W.; Ksibi, Z.; Sayadi, S. Photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater in presence of hydrogen peroxide: Effect of cerium doping titania. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, D.-H.; Juang, L.-C.; Huang, H.-H. Effect of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide on the photocatalytic degradation of monochlorobenzene in TiO2 aqueous suspension. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 328526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhu, R.; Song, K.; Ouyang, F.; Cao, G. Synergistic photocatalytic degradation of phenol using precious metal supported titanium dioxide with hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppolian, B.; Choi, H.C.; Sakthivel, S.; Arabindoo, B.; Murugesan, V. Solar light induced and TiO2 assisted degradation of textile dye reactive blue 4. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Dung, N.; Van Khoa, N.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic degradation of reactive dye RED-3BA in aqueous TiO2 suspension under UV-visible light. Int. J. Photoenergy 2005, 7, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, I.; Tsachpinis, I. Photodegradation of the textile dye Reactive Black 5 in the presence of semiconducting oxides. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Maffei, G.; Lavecchia, R. Effect of solvent type and extraction conditions on the recovery of Phenolic compounds from artichoke waste. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 39, 463–468. [Google Scholar]











| Photocatalysts | Crystalline Size [nm] | Specific Surface Area [m2/g] | Band Gap Energy [eV] |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 8.4 | 169 | 3.20 |
| 10Fe-TiO2 | 8.3 | 171 | 3.12 |
| 50Fe-TiO2 | 7.9 | 179 | 2.90 |
| 100Fe-TiO2 | 7.9 | 179 | 2.63 |
| Photocatalysts | Fe(C5H7O2)3 Amount [mg] | Titanium Isopropoxide [mL] | Distilled Water [mL] | Fe/Ti Molar Ratio [mol/mol] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 0 | 25 | 100 | 0 |
| 10Fe-TiO2 | 10 | 25 | 100 | 0.00033 |
| 50Fe-TiO2 | 50 | 25 | 100 | 0.0017 |
| 100Fe-TiO2 | 100 | 25 | 100 | 0.0033 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Monaco, M.M.; Iervolino, G.; Vaiano, V. Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080645
Zuorro A, Lavecchia R, Monaco MM, Iervolino G, Vaiano V. Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation. Catalysts. 2019; 9(8):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080645
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuorro, Antonio, Roberto Lavecchia, Marika Michela Monaco, Giuseppina Iervolino, and Vincenzo Vaiano. 2019. "Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation" Catalysts 9, no. 8: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080645
APA StyleZuorro, A., Lavecchia, R., Monaco, M. M., Iervolino, G., & Vaiano, V. (2019). Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Violet 5 on Fe-Doped Titania Catalysts under Visible Light Irradiation. Catalysts, 9(8), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080645








