Microbial Phosphotriesterase: Structure, Function, and Biotechnological Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Function
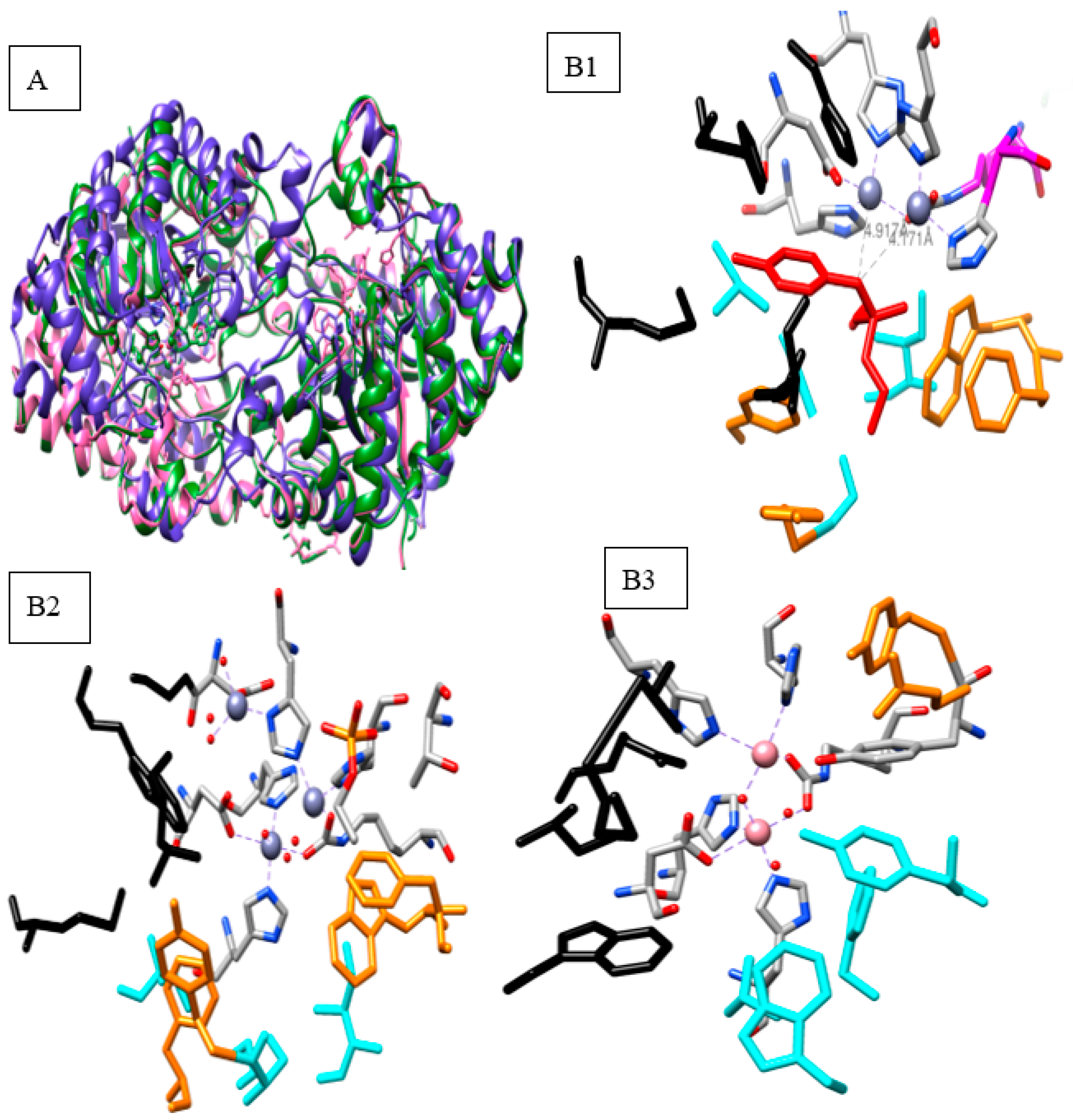
2.1. Bacterial Phosphotriesterase 3D Structures
2.2. Mechanism of Hydrolysis and Stereoselectivity of PTE
2.3. Industrial Application of Bacterial Phosphotriesterase
2.3.1. Biosensors
2.3.2. Bioremediation and Detoxification
2.3.3. Enzyme Therapy
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, B.K. Organophosphorus-degrading bacteria: Ecology and industrial applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, A.R.S.; Pande, A.H. Organophosphate-Hydrolyzing Enzymes as First-Line of Defence Against Nerve Agent-Poisoning: Perspectives and the Road Ahead. Protein J. 2016, 35, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alejo-González, K.; Hanson-Viana, E.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Enzymatic detoxification of organophosphorus pesticides and related toxicants. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Castro, A.A.; Caetano, M.S.; Silva, T.C.; Mancini, D.T.; Rocha, E.P.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Ramalho, T.C. Molecular Docking, Metal Substitution and Hydrolysis Reaction of Chiral Substrates of Phosphotriesterase. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2016, 19, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benning, M.M.; Kuo, J.M.; Raushel, F.M.; Holden, H.M. Three-Dimensional Structure of Phosphotriesterase: An Enzyme Capable of Detoxifying Organophosphate Nerve Agents. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 15001–15007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, N.B.; Raushel, F.M. Catalytic Mechanism for phosphotriesterases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1834, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Manco, G.; Porzio, E.; Suzumoto, Y. Enzymatic detoxification: A sustainable means of degrading toxic organophosphate pesticides and chemical warfare nerve agents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2064–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriot, C.M.; Grunden, A.M. Hydrolysis of organophosphorus compounds by microbial enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.C.; Fox, N.; Bigley, A.N.; Harvey, S.P.; Barondeau, D.P.; Raushel, F.M. Enzymes for the homeland defense: Optimizing phosphotriesterase for the hydrolysis of organophosphate nerve agents. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6463–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.B.; Dawson, A.; Ollis, D. University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA, 2 South Asian Clinical Toxicology Research Collaboration (SACTRC), Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka and School of Population and Health, Univers. Front. Biosci. 2010, S2, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigley, A.N.; Mabanglo, M.F.; Harvey, S.P.; Raushel, F.M. Variants of Phosphotriesterase for the Enhanced Detoxification of the Chemical Warfare Agent VR. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5502–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.Y.; Wu, N.F.; Deng, M.J.; Tian, J.; Yao, B.; Fan, Y.L. Expression of organophosphorus hydrolase OPHC2 in Pichia pastoris: Purification and characterization. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 49, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkar, R.S. Enzyme-Mediated Bioremediation of Organophosphates Using Stable Yeast Biocatalysts. J. Bioremed. Biodeg. 2013, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merone, L.; Mandrich, L.; Rossi, M.; Manco, G. Enzymes with Phosphotriesterase and Lactonase Activities in Archaea Enzymes with Phosphotriesterase and Lactonase Activities in Archaea. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2008, 2, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, G.; Dar, M.A.; Nimesh, S.; LÓpez-chuken, U.J.; Villarreal-chiu, J.F. Microbial Degradation of Organophosphate Pesticides: A Review. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotthard, G.; Hiblot, J.; Gonzalez, D.; Elias, M.; Chabriere, E. Structural and enzymatic characterization of the phosphotriesterase OPHC2 from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, S.D.; Li, Y.; Raushel, F.M. Mechanism for the Hydrolysis of Organophosphates by the Bacterial Phosphotriesterase. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 5707–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Chen, D.C.; Hu, D.X.; Su, X.F.; Tang, X.M. Cloning, Expression, Purification, and Characterization of an Organophosphate-Degrading Enzyme in Escherichia Coli. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 610, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, E.; Raushel, F.M. Detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents by bacterial phosphotriesterase. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 207, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.I.; Miller, C.E.; Wild, J.R. Characterization of organophosphorus hydrolases and the genetic manipulation of the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1993, 87, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, I.; Coppolecchia, R.; Merone, L.; Porzio, E.; Carusone, T.M.; Mandrich, L.; Worek, F.; Manco, G. An efficient thermostable organophosphate hydrolase and its application in pesticide decontamination. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, E.; Jacquamet, L.; Loiodice, M.; Rochu, D.; Masson, P.; Nachon, F. Update on biochemical properties of recombinant Pseudomonas diminuta phosphotriesterase. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodveldt, C.; Tawfik, D.S. Directed evolution of phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta for heterologous expression in Escherichia coli results in stabilization of the metal-free state. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2005, 18, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchbinder, J.; Stephenson, R.; Dresser, M.; Pitera, J.; Scanlan, T.; Fletterick, R. Biochemical characterization and crystallographic structure of an Escherichia coli protein from the phosphotriesterase gene family. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 5096–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Goodspeed, M.; Sogorb, M.A.; Wu, F.; Raushel, F.M. Enhancement, Relaxation, and Reversal of the Stereoselectivity for Phosphotriesterase by Rational Evolution of Active Site Residues† Misty. Biochemistry 2004, 40, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuscript, A.; Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J.; Sommer, M.A.; Wurtz, R.H. NIH Public Access. Changes 2010, 38, 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, H.; Hong, S.B.; Raushel, F.M. Hydrolysis of phosphodiesters through transformation of the bacterial phosphotriesterase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 17445–17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroso, M.M.; Ely, F.; Mitić, N.; Carpenter, M.C.; Gahan, L.R.; Wilcox, D.E.; Larrabee, J.L.; Ollis, D.L.; Schenk, G. Comparative investigation of the reaction mechanisms of the organophosphate-degrading phosphotriesterases from Agrobacterium radiobacter (OpdA) and Pseudomonas diminuta (OPH). J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, P.; Hiblot, J.; Daudé, D.; Bergonzi, C.; Gotthard, G.; Armstrong, N.; Chabrière, E.; Elias, M. Rational engineering of a native hyperthermostable lactonase into a broad spectrum phosphotriesterase. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawwa, R.; Aikens, J.; Turner, R.J.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Andrew, D.; Brook, O. Structural basis for thermostability revealed through the identification and characterization of a highly thermostable phosphotriesterase-like lactonase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 488, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, R.J. Enzyme-Based Detoxification of Organophosphorus Neurotoxic Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Agents. Ph. D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bigley, A.N.; Xiang, D.F.; Ren, Z.; Xue, H.; Hull, K.G.; Romo, D.; Raushel, F.M. Chemical Mechanism of the Phosphotriesterase from Sphingobium sp. Strain TCM1, an Enzyme Capable of Hydrolyzing Organophosphate Flame Retardants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2921–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Choi, J.M.; Kyeong, H.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.S. Rational design of organophosphorus hydrolase with high catalytic efficiency for detoxifying a V-type nerve agent. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnecke, D.M. Enzymatic hydrolysis of organophosphate insecticides, a possible pesticide disposal method. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 32, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nachon, F.; Brazzolotto, X.; Trovaslet, M.; Masson, P. Progress in the development of enzyme-based nerve agent bioscavengers. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 206, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Gao, J. The reaction mechanism of paraoxon hydrolysis by phosphotriesterase from combined QM/MM simulations. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 13352–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, I.; Sutherland, T.D.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Russell, R.J. Cloning and expression of the phosphotriesterase gene hocA from Pseudomonas monteilii C11. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-C.; Fan, Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, L.; Almo, S.C.; Gao, Y.Q.; Raushel, F.M. Structural Determinants for the Stereoselective Hydrolysis of Chiral Substrates by Phosphotriesterase. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 7988–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, T.E.; Wales, M.E.; Grimsley, J.K.; Li, P.; Cerasoli, D.M.; Wild, J.R. Balancing the stability and the catalytic specificities of OP hydrolases with enhanced V-agent activities. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2008, 21, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigley, A.N.; Xu, C.; Henderson, T.J.; Harvey, S.P.; Raushel, F.M. Enzymatic neutralization of the chemical warfare agent VX: Evolution of phosphotriesterase for phosphorothiolate hydrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10426–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondred, J.A.; Breger, J.C.; Alves, N.J.; Trammell, S.A.; Walper, S.A.; Medintz, I.L.; Claussen, J.C. Printed Graphene Electrochemical Biosensors Fabricated by Inkjet Maskless Lithography for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Organophosphates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11125–11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, D.H.; Cheunrungsikul, K.; Wichitwechkarn, J.; Surareungchai, W. A colorimetric assay for determination of methyl parathion using recombinant methyl parathion hydrolase. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianova, M.S.; Gubanova, O.V.; Komarova, N.V.; Kuznetsov, E.V.; Kuznetsov, A.E. Development of a Biosensor Based on Phosphotriesterase and n-Channel ISFET for Detection of Pesticides. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurulain, S.M. Different approaches to acute organophosphorus poison treatment. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2012, 62, 712–717. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Krause, R.; Block, K.; Musameh, M.; Mulchandani, A.; Mulchandani, P.; Chen, W.; Schöning, M.J. Dual amperometric-potentiometric biosensor detection system for monitoring organophosphorus neurotoxins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 469, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latip, W.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.; Leow, A.T.C.; Mohd Shariff, F.; Kamarudin, N.H.A.; Mohamad Ali, M.S. The effect of N-terminal domain removal towards the biochemical and structural features of a thermotolerant lipase from an antarctic Pseudomonas sp. Strain AMS3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Krause, R.; Block, K.; Musameh, M.; Mulchandani, A.; Schöning, M.J. Flow injection amperometric detection of OP nerve agents based on an organophosphorus-hydrolase biosensor detector. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 18, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Mulchandani, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Highly sensitive and selective amperometric microbial biosensor for direct determination of p-nitrophenyl-substituted organophosphate nerve agents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8853–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzio, E.; Bettazzi, F.; Mandrich, L.; Del Giudice, I.; Restaino, O.F.; Laschi, S.; Febbraio, F.; De Luca, V.; Borzacchiello, M.G.; Carusone, T.M.; et al. Innovative Biocatalysts as Tools to Detect and Inactivate Nerve Agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.; Peregudov, A.; Kildeeva, N.; Perminov, P.; Varfolomeyev, S. New enzymatic immobilized biocatalysts for detoxification of organophosphorus compounds. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2005, 23, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, A.; Mulchandani, P.; Chen, W. Enzyme Biosensor for Determination of Organophosphates. Field Anal. Chem. Technol. Chem. Technol. 1998, 2, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Alexander, M. Microbial cleavage of various organophosphorus insecticides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.K.; Walker, A.; Morgan, J.A.W.; Wright, D.J. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by Enterobacter strain B-14 and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4855–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, A.A.; Prandi, I.G.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C. Organophosphorus degrading enzymes: Molecular basis and perspectives for enzymatic bioremediation of agrochemicals. Cienc. Agrotecnologia 2017, 41, 471–482. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, N.K.; Nickitenko, A.; Rastogi, V.K.; Shah, S.S.; Quiocho, F.A. Structural insights into the dual activities of the nerve agent degrading organophosphate anhydrolase/prolidase. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, T.; Neumaier, K.; Koller, M.; Ehinger, C.; Aggarwal, N.; Ashani, Y.; Goldsmith, M.; Sussman, J.L.; Tawfik, D.S.; Thiermann, H.; et al. Single treatment of VX poisoned guinea pigs with the phosphotriesterase mutant C23AL: Intraosseous versus intravenous injection. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 258, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istamboulie, G.; Durbiano, R.; Fournier, D.; Marty, J.L.; Noguer, T. Biosensor-controlled degradation of chlorpyrifos and chlorfenvinfos using a phosphotriesterase-based detoxification column. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Chung, Y.C.; Xiong, Y. Purification and Characterization of a Dimethoate-Degrading Enzyme of Aspergillus niger ZHY256, Isolated from Sewage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3746–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latip, W.; Knight, V.F.; Abdul Halim, N.; Ong, K.K.; Mohd Kassim, N.A.; Wan Yunus, W.M.Z.; Mohd Noor, S.A.; Mohamad Ali, M.S. Microbial Phosphotriesterase: Structure, Function, and Biotechnological Applications. Catalysts 2019, 9, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080671
Latip W, Knight VF, Abdul Halim N, Ong KK, Mohd Kassim NA, Wan Yunus WMZ, Mohd Noor SA, Mohamad Ali MS. Microbial Phosphotriesterase: Structure, Function, and Biotechnological Applications. Catalysts. 2019; 9(8):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080671
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatip, Wahhida, Victor Feizal Knight, Norhana Abdul Halim, Keat Khim Ong, Noor Azilah Mohd Kassim, Wan Md Zin Wan Yunus, Siti Aminah Mohd Noor, and Mohd Shukuri Mohamad Ali. 2019. "Microbial Phosphotriesterase: Structure, Function, and Biotechnological Applications" Catalysts 9, no. 8: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080671
APA StyleLatip, W., Knight, V. F., Abdul Halim, N., Ong, K. K., Mohd Kassim, N. A., Wan Yunus, W. M. Z., Mohd Noor, S. A., & Mohamad Ali, M. S. (2019). Microbial Phosphotriesterase: Structure, Function, and Biotechnological Applications. Catalysts, 9(8), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080671



