Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4 Nanorods Supported on Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane
Abstract
1. Introduction
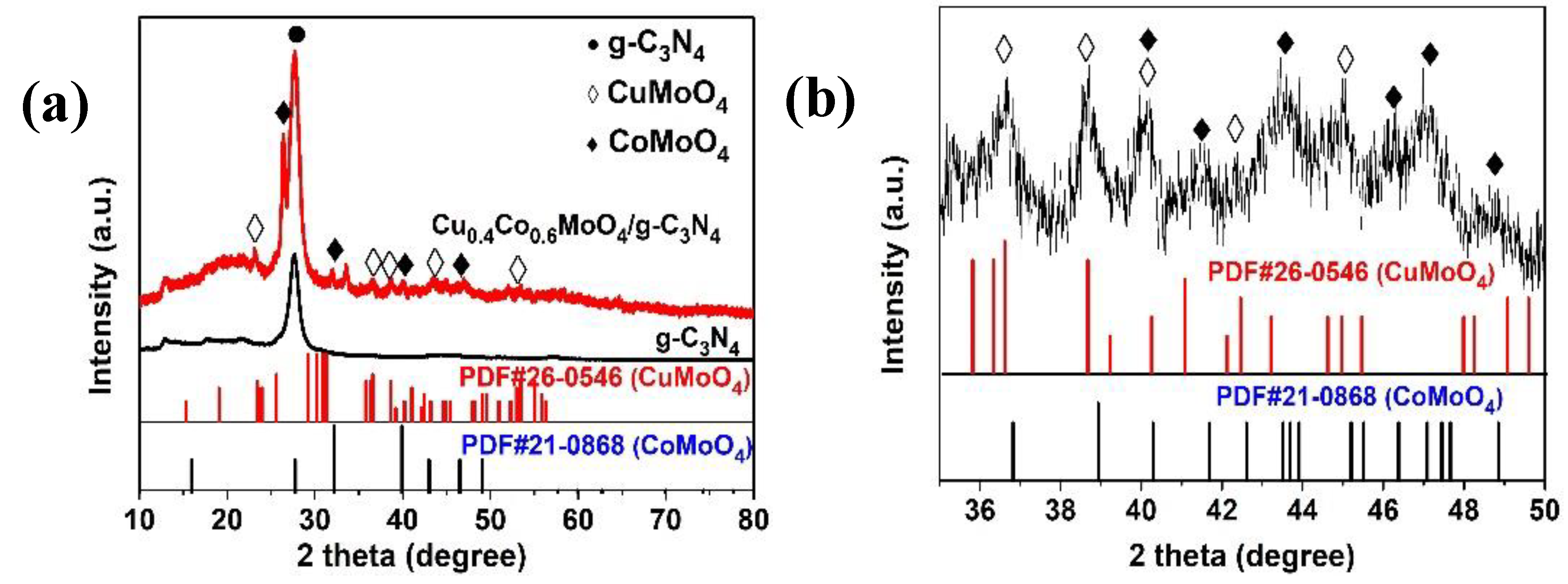
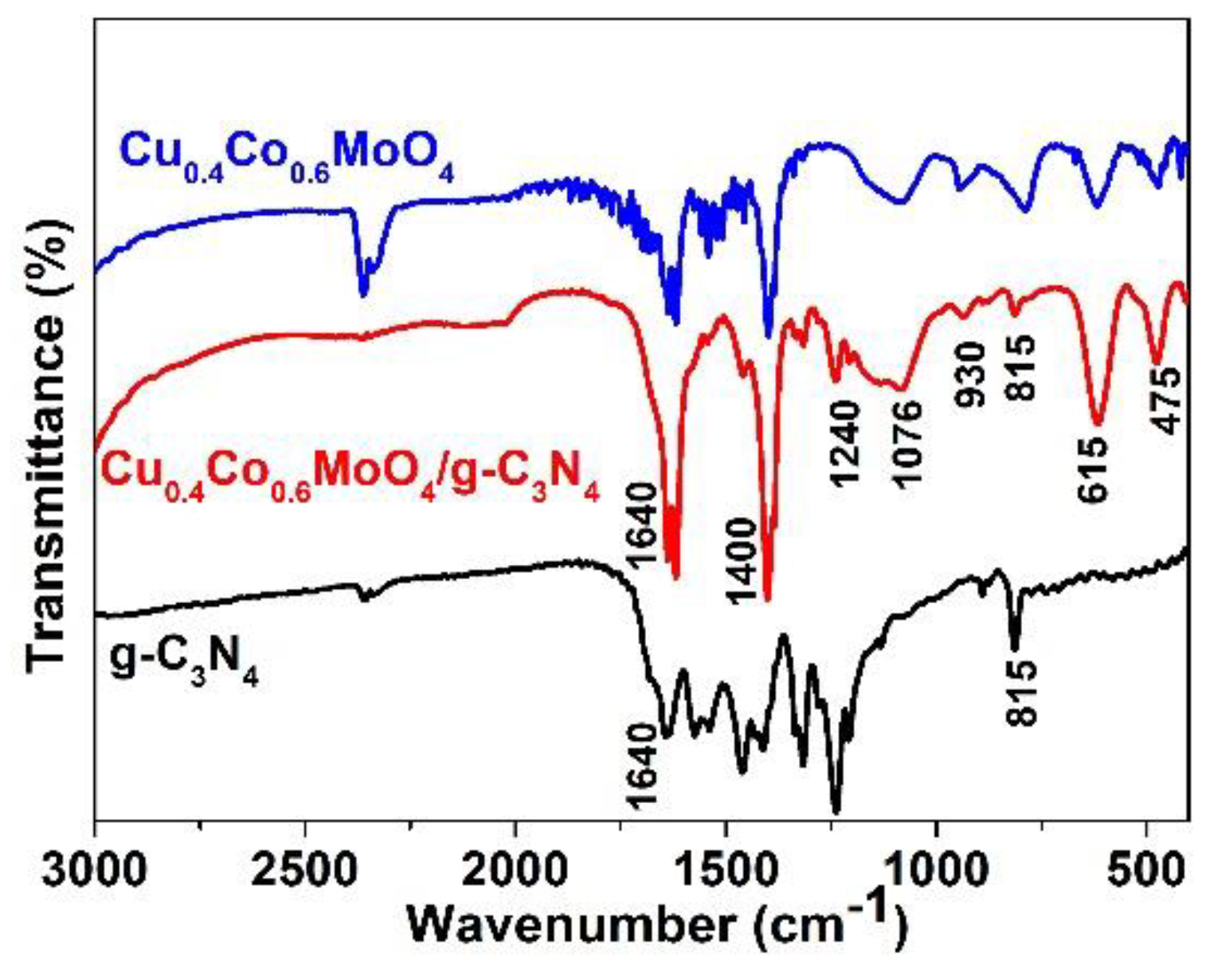
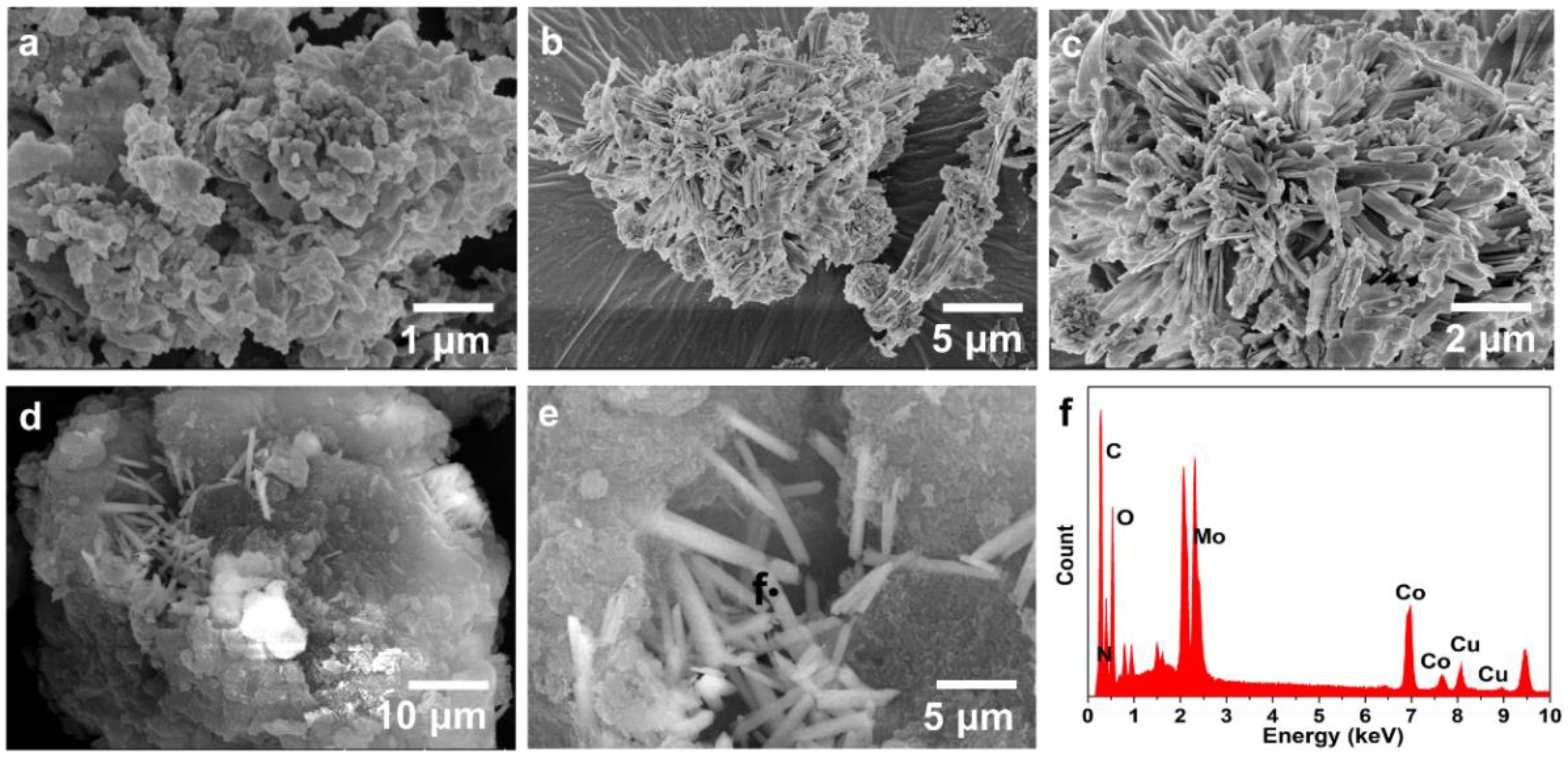
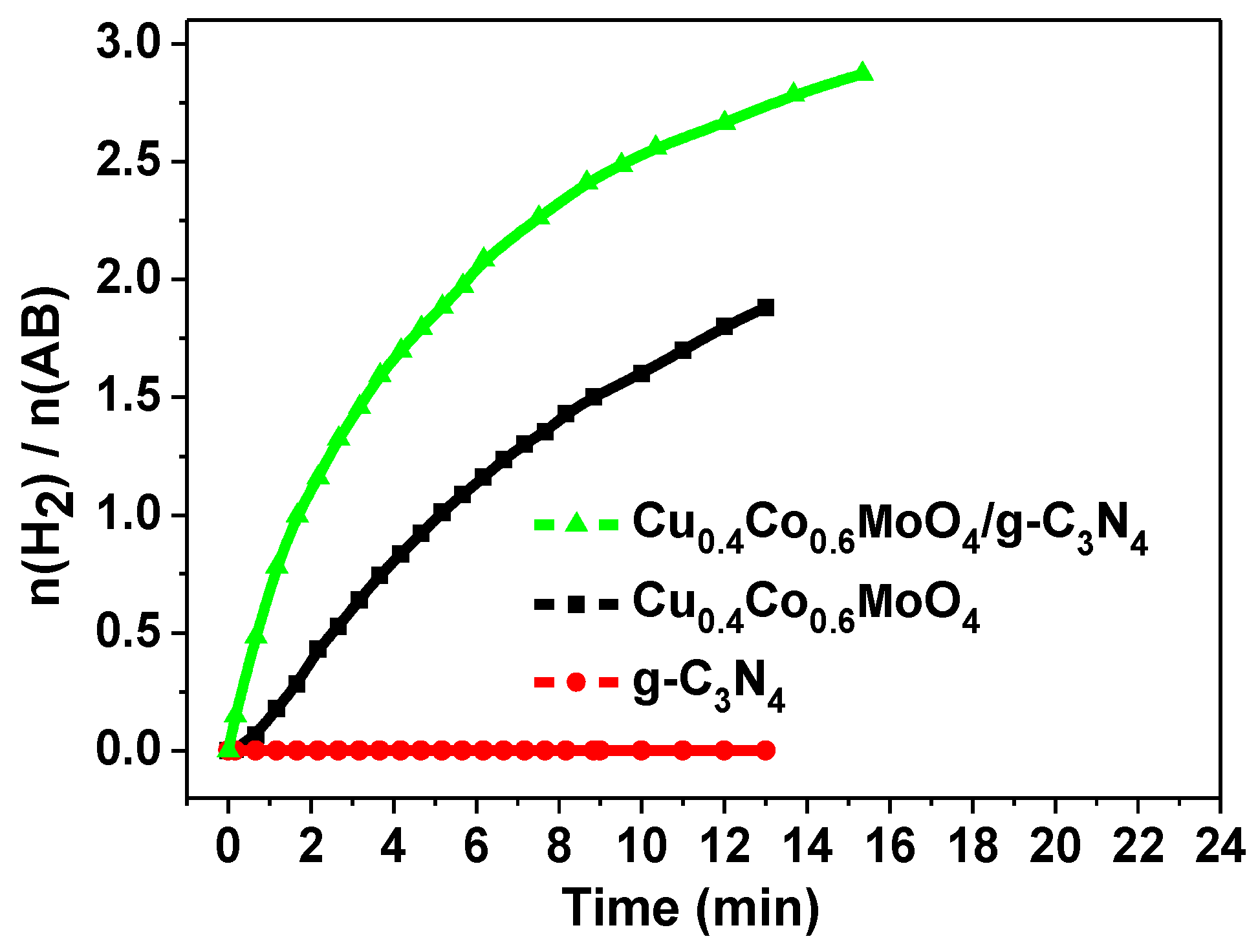
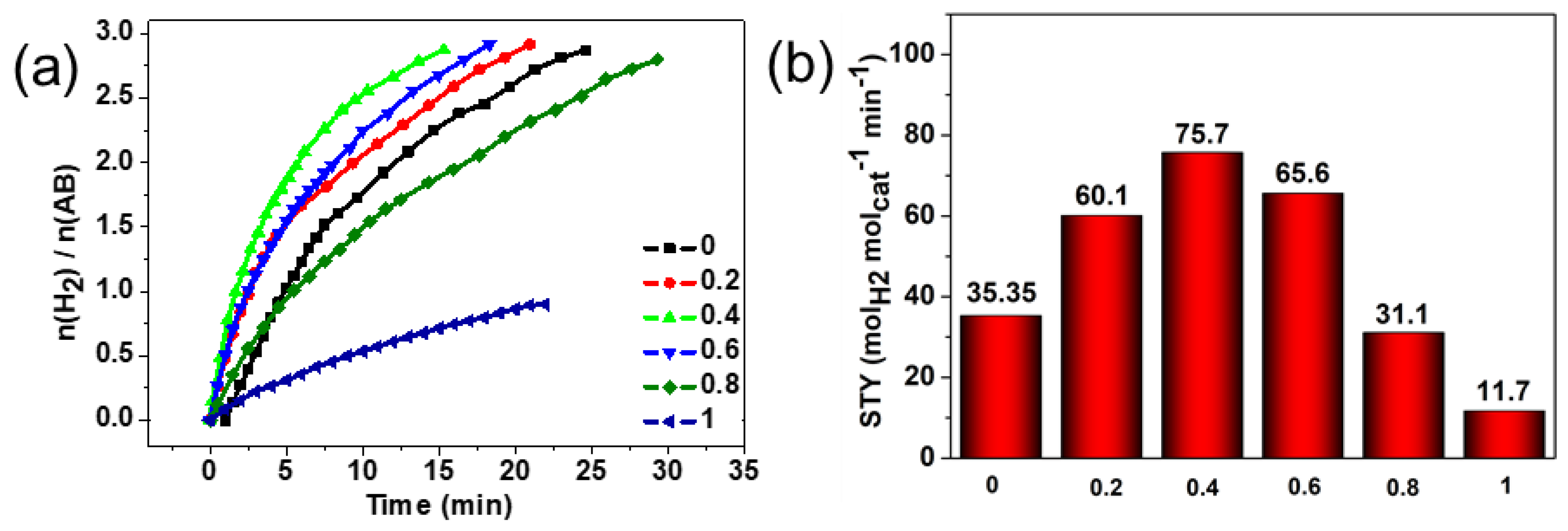
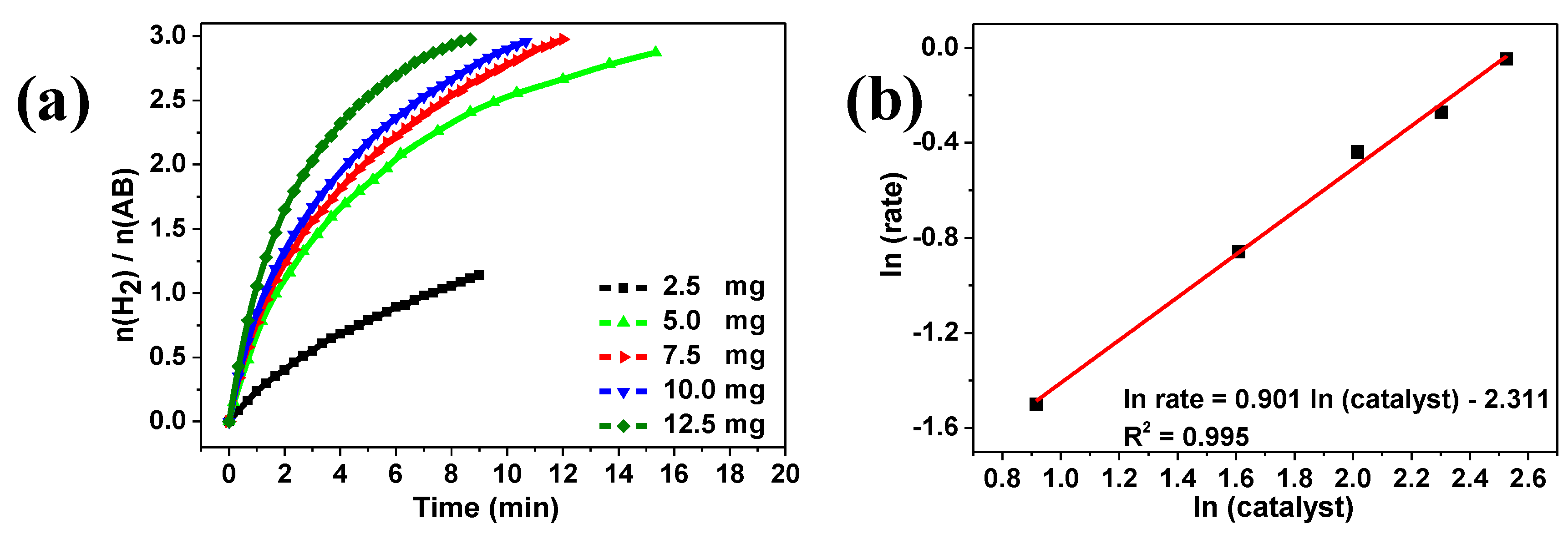
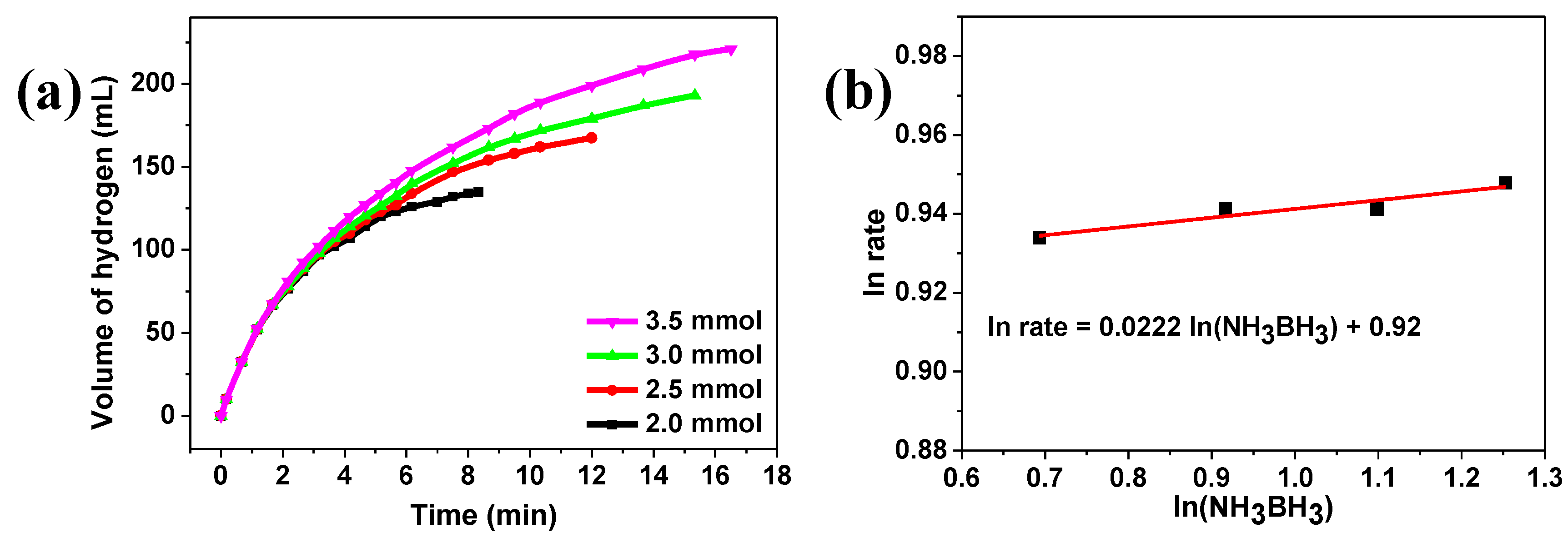
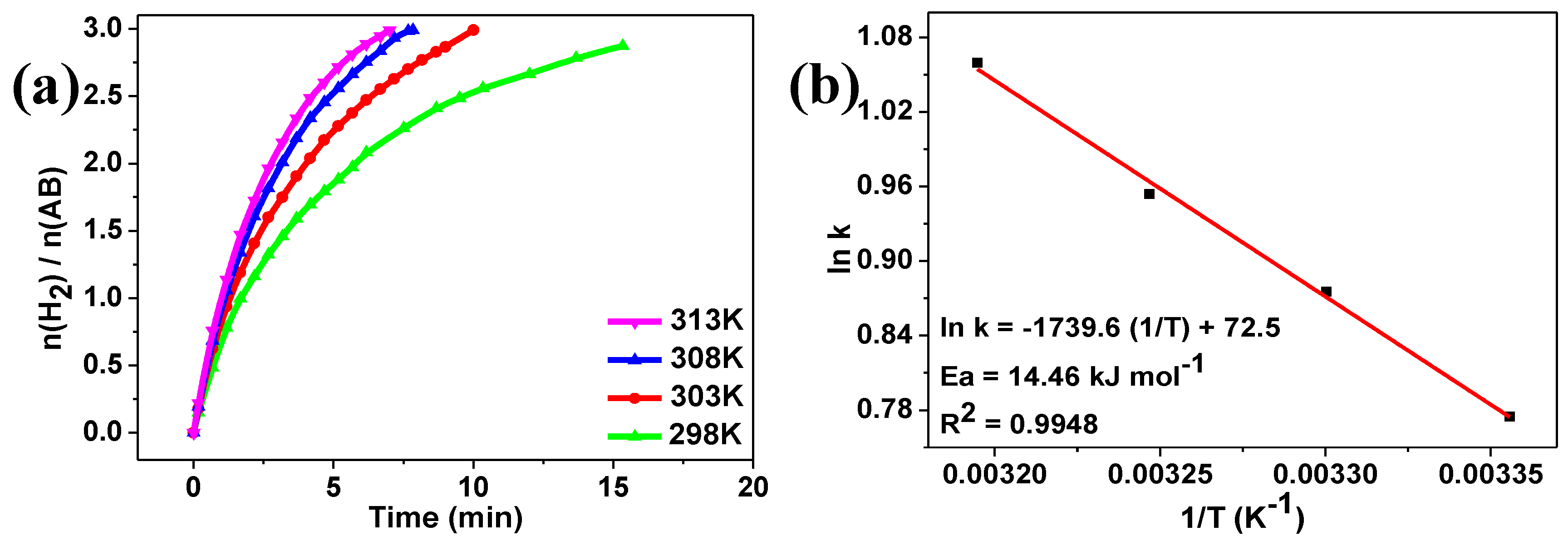
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Catalysts
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Catalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartbaeva, A.; Kuznetsov, V.L.; Wells, S.A.; Edwards, P.P. Hydrogen nexus in a sustainable energy future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Colella, W.G.; Golden, D.M. Cleaning the air and improving health with hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles. Science 2005, 308, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fan, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Cong, H.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Hydrogen Storage in Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes at Room Temperature. Science 1999, 286, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Kang, L.; Cao, S.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.S.; Fu, W.F. Nanostructured Ni2P as a Robust Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia-Borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 15725–15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Feng, M.; Li, H. Ni nanoparticles supported on graphitic carbon nitride as visible light catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Chen, J. Ammonia borane as an efficient and lightweight hydrogen storage medium. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Cui, Y.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Non-Noble-Metal Nanoparticle Supported on Metal-Organic Framework as an Efficient and Durable Catalyst for Promoting H2 Production from Ammonia Borane under Visible Light Irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21278–21284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liao, J.; Zhong, S.; Leng, Y.; Ji, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Li, H. Cu0.6Ni0.4Co2O4 nanowires, a novel noble-metal-free catalyst with ultrahigh catalytic activity towards the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 5541–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-García, M.; Mori, K.; Nozaki, A.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Highly efficient Ru/carbon catalysts prepared by pyrolysis of supported Ru complex towards the hydrogen production from ammonia borane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 527, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. Room temperature hydrogen generation from aqueous ammonia-borane using noble metal nano-clusters as highly active catalysts. J. Power Sources 2007, 168, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Umegaki, T.; Akita, T.; Zhang, X.B.; Haruta, M.; Xu, Q. Bimetallic Au–Ni nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 nanospheres: Synergetic catalysis in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Desinan, S.; Rosei, R.; Rosei, F.; Ma, D. Synthesis of Ni–Ru alloy nanoparticles and their high catalytic activity in dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 7925–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Vasileff, A.; Li, L.H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S. Molecule-level g-C3N4 coordinated transition metals as a new class of electrocatalysts for oxygen electrode reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3336–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Antonietti, M. Solvent-free and metal-free oxidation of toluene using O2 and g-C3N4 with nanopores: Nanostructure boosts the catalytic selectivity. ACS Catal. 2012, 10, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Mousavi, M.; Nakata, K. Boosting visible-light photocatalytic performance of g-C3N4/Fe3O4 anchored with CoMoO4 nanoparticles: Novel magnetically recoverable photocatalysts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 368, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cai, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, L.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Ren, Q.; Su, J.; Chen, J. Multifunctional Au-Co@CN Nanocatalyst for Highly Efficient Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Hu, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Gao, D.; Bi, J.; Fan, G. Hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by Rh/g-C3N4 under mild conditions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 7038–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahri, H.; Sevim, M.; Metin, Ö. Enhanced catalytic activity of monodispersed AgPd alloy nanoparticles assembled on mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane under sunlight. Nano Res. 2016, 10, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Zheng, X.; Guan, X.; Liu, P. Graphitic carbon nitride-chitosan composites–anchored palladium nanoparticles as high-performance catalyst for ammonia borane hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 43, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, C.; Ming, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Fan, G. In Situ Formation of AgCo Stabilized on Graphitic Carbon Nitride and Concomitant Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane to Hydrogen. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, J.; Lin, C.; Liao, J.; Feng, Y.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. A Simple and Scalable Route to Synthesize CoxCu1- xCo2O4@CoyCu1- yCo2O4 Yolk-Shell Microspheres, A High-Performance Catalyst to Hydrolyze Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production. Small 2019, 15, e1805460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, D.; Sun, C.; Yang, S.; Guan, Y.; He, H. Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4/Ag3VO4 composites with significantly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for triphenylmethane dye degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, W. Effect of cobalt (nickel) content on the catalytic performance of molybdenum carbides in dry-methane reforming. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanulla, A.M.; Shahina, S.K.J.; Sundaram, R.; Magdalane, C.M.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Letsholathebe, D.; Mohamed, S.B.; Kennedy, J.; Maaza, M. Antibacterial, magnetic, optical and humidity sensor studies of beta-CoMoO4-Co3O4 nanocomposites and its synthesis and characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, A.; Wang, E. Two diphosphonate-functionalized asymmetric polyoxomolybdates with catalytic activity for oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 8414–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, D.; Yin, S.; Tu, W.; Chen, Z.; Kraft, M.; Chen, G.; Xu, R. Unique P–Co–N Surface Bonding States Constructed on g-C3N4 Nanosheets for Drastically Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of H2 Evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, C.; Tao, K.; Liu, R.; Han, L. Ultrathin nanosheet-assembled hollow microplate CoMoO4 array derived from metal-organic framework for supercapacitor with ultrahigh areal capacitance. J. Power Sources 2019, 430, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.Q.; Jiang, L.X.; Yang, H.G. Ultrathin nanosheets constructed CoMoO4 porous flowers with high activity for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14361–14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Jiang, G.; Xu, W.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y.; Lei, N.; Evariste, U.; Ma, P. Construction of NiMoO4/CoMoO4 nanorod arrays wrapped by Ni-Co-S nanosheets on carbon cloth as high performance electrode for supercapacitor. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 799, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Patel, N.; Miotello, A.; Calliar, L. Co–Mo–B–P Alloy with Enhanced Catalytic Properties for H2 Production by Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Top. Catal. 2012, 55, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Lu, D.; Diao, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, H. Co0.8Cu0.2MoO4 Microspheres Composed of Nanoplatelets as a Robust Catalyst for the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5843–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tuninetti, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ciganda, R.; Salmon, L.; Moya, S.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Hydrolysis of ammonia-borane over Ni/ZIF-8 nanocatalyst: High efficiency, mechanism and controlled hydrogen release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Feng, K.; Shang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhong, J. Cube-Like CuCoO Nanostructures on Reduced Graphene Oxide for H2 Generation from Ammonia Borane. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.C.; Xu, Y.; Chan, S.L.; Wang, W.W.; Li, F.; Liang, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.S.; Fu, W.F.; Che, C.M. Highly efficient hydrolysis of ammonia borane by anion (−OH, F−, Cl−)-tuned interactions between reactant molecules and CoP nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.T. CuxCo1–xO Nanoparticles on Graphene Oxide as A Synergistic Catalyst for High-Efficiency Hydrolysis of Ammonia–Borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 11950–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. High Pt-like activity of the Ni–Mo/graphene catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 8579–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, A.; Yurderi, M.; Ertas, İ.E.; Celebi, M.; Kaya, M.; Zahmakiran, M. Carbon dispersed copper-cobalt alloy nanoparticles: A cost-effective heterogeneous catalyst with exceptional performance in the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia-borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mi, G. Porously hierarchical Cu@Ni cubic-cage microstructure: Very active and durable catalyst for hydrolytically liberating H2 gas from ammonia borane. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Zhu, Q.L.; Yang, X.C.; Xu, Q. Monodispersed CuCo Nanoparticles Supported on DiamineFunctionalized Graphene as a Non-noble Metal Catalyst for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Yang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.; Luo, W. Amorphous NiP supported on rGO for superior hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 14181–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalysts | STY (molH2 molcat−1 min−1) | STY without support (molH2 molcat−1 min−1) | Ea (kJ mol−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni/ZIF-8 | 85.7 | / | 28 | [33] |
| Cu0.5Co0.5O-rGO | 81.7 | / | −45.26 | [34] |
| Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4/g-C3N4 | 75.7 | 17.6 | 14.46 | This work |
| CoP | 72.2 | / | / | [35] |
| Cu0.8Co0.2O-GO | 70.0 | / | 45.53 | [36] |
| Ni0.9Mo0.1/graphene | 66.7 | 2.3 | / | [37] |
| Co0.8Cu0.2MoO4 | 55 | / | / | [32] |
| Cu0.49Co0.51/C | 45 | / | 51.9 | [38] |
| Cu0.8Ni0.2 | 41.9 | / | 40.53 | [39] |
| CuCo/graphene | 41 | 12 | 54.89 | [40] |
| NiP | 40.4 | / | 44.6 | [5] |
| Ni91P9/rGO | 13.3 | / | 34.7 | [41] |
| Ni/g-C3N4 | 18.7 | / | 36 | [6] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, F.; Liao, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4 Nanorods Supported on Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts 2019, 9, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9090714
Li J, Li F, Liao J, Liu Q, Li H. Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4 Nanorods Supported on Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts. 2019; 9(9):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9090714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junhao, Fangyuan Li, Jinyun Liao, Quanbing Liu, and Hao Li. 2019. "Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4 Nanorods Supported on Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane" Catalysts 9, no. 9: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9090714
APA StyleLi, J., Li, F., Liao, J., Liu, Q., & Li, H. (2019). Cu0.4Co0.6MoO4 Nanorods Supported on Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts, 9(9), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9090714





