Magnetocaloric Effect, Magnetoresistance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2, and Phase Diagrams of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2−xTx Alloys with T = Mn or Co
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
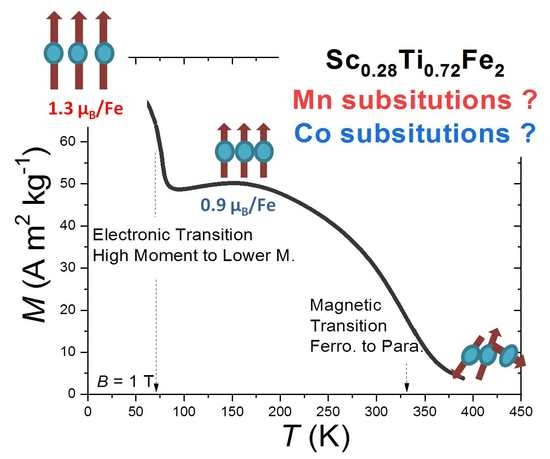
3.1. Magnetocaloric and Magnetoresitance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2 Ternary Alloy
3.2. Co for Fe Substitution in Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2
3.3. Mn for Fe Substitution in Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishida, S.; Asano, S.; Ishida, J. Electronic structures of the C14 laves phase compounds AFe2 (A = Mo, Hf, Ta, W). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 54, 4695–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K. Binary rare earth Laves phases—An overview. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 2006, 221, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Magnetic phase transitions in itinerant electron magnets Hf1−xTaxFe2. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 52, 3630–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, J.F.; Fuerst, C.D.; McMichael, R.D. Structural, magnetic, and magnetocaloric properties of (Hf0.83Ta0.17)Fe2+x materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 5998–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Hagii, T.; Yashiro, S.; Samata, H.; Abe, S. Magnetism and transport properties of Hf1−xTaxFe2 and Mn2−xCrxSb. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 292, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechenberg, H.R.; Morellon, L.; Algarabel, P.A.; Ibarra, M.R. Magnetic moment at highly frustrated sites of antiferromagnetic Laves phase structure. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, L.V.B.; Kastil, J.; Isnard, O.; Arnold, Z.; Kamarad, J. Collapse of ferromagnetism in itinerant-electron system: A magnetic, transport properties, and high pressure study of (Hf,Ta)Fe2 compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 163907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, L.V.B.; Benea, D.; Mankovsky, S.; Isnard, O. Crossover between ferro and antiferromagnetic order in Fe itinerant electron magnetism: An experimental and theoretical study of the model (Hf,Ta)Fe2 Laves phases. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 643, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luo, X.H.; Wang, H.; Ren, W.J.; Yano, S.; Wang, C.W.; Gardner, J.S.; Liss, K.D.; Miao, P.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Colossal Negative Thermal Expansion Induced by Magnetic Phase Competition on Frustrated Lattices in Laves Phase Compound (Hf,Ta)Fe2. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 224405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bag, P.; Rawat, R.; Chaddah, P.; Babu, P.D.; Siruguri, V. Unconventional thermal effects across first-order magnetic transition in the Ta-doped HfFe2 intermetallic. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 014416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yibole, H.; Pathak, A.K.; Mudryk, Y.; Guillou, F.; Zarkevich, N.; Gupta, S.; Balema, V.; Pecharsky, V.K. Manipulating the stability of crystallographic and magnetic sublattices: A first-order magnetoelastic transformation in transition metal based Laves phase. Acta Mater. 2018, 154, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.D.; Wang, D.H.; Huang, S.L.; Su, Z.H.; Tang, S.L.; Du, Y.W. Low-field magnetic entropy changes in Hf1−xTaxFe2. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 377, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Magnetic Structures in the Sc1−xTixFe2 System—Magnetic Phase Transitions in Itinerant Electron Systems. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 54, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Ferromagnetic Transition in the Itinerant Electron Magnet (Sc0.35Ti0.65Fe2). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 54, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Negishi, A. Magneto-volume of the Ferro- to Antiferromagnetic Transition in (Sc0.35Ti0.65)Fe2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1986, 54–57, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Magnetic Properties of the (Sc1−xTix)Fe2 System Having Two Magnetic States with Different Degrees of Localization. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 55, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi, M.; Desportes, J.; Ouladdiaf, B. Magnetic Ground State of Ti1−xScxFe2 System. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 231, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, M.E.; Keune, W.; Roldan Cuenya, B.; Weis, C.; Landers, J.; Makarov, S.I.; Klar, D.; Hu, M.Y.; Alp, E.E.; Zhao, J.; et al. Element-Resolved Thermodynamics of Magnetocaloric LaFe13−xSix. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 057202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dung, N.H.; Ou, Z.; Caron, L.; Zhang, L.; Thanh, D.T.C.; de Wijs, G.A.; de Groot, R.A.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Brück, E. Mixed Magnetism for Refrigeration and Energy Conversion. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, H.; Shimamura, N.; Shiga, M. Thermal and Transport Properties of Sc1−xTixFe2. J. Phys. Soc. Japn. 1994, 63, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanomata, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kaneko, T.; Nishihara, Y. Pressure Effect on the Magnetic Transition Temperatures of Sc1−xTixFe1.95 (x = 0.60, 0.70 and 0.85). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 104–107, 2063–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, G.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nishihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Ferromagnetic to Ferromagnetic Phase Transition in Sc0.25Ti0.75Fe2 Under Pulsed High Magnetic Field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 70, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 1993, 192, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol, A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Porcari, G.; Yibole, H.; van Dijk, N.; Brück, E. Taming the First-Order Transition in Giant Magnetocaloric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2671–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillou, F.; Yibole, H.; Porcari, G.; van Dijk, N.; Brück, E. Magnetocaloric effect, cyclability and coefficient of refrigerant performance in the MnFe(P, Si, B) system. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 063903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Fujita, A.; Fukamichi, K. Large magnetocaloric effect in La(FexSi1−x)13 itinerant-electron metamagnetic compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Feng, L.; Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H.; et al. Stable magnetostructural coupling with tunable magnetoresponsive effects in hexagonal ferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taubel, A.; Gottschall, T.; Fries, M.; Faske, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. nfluence of magnetic field, chemical pressure and hydrostatic pressure on the structural and magnetocaloric properties of the Mn–Ni–Ge system. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 464005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biwas, A.; Pathak, A.K.; Zarkevich, N.A.; Liu, X.; Mudryk, Y.; Balema, V.; Johnson, D.D.; Pecharsky, V.K. Designed materials with the giant magnetocaloric effect near room temperature. Acta Mater. 2019, 180, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanggai, W.; Tegus, O.; Yibole, H.; Guillou, F. Structural and magnetic phase diagrams of MnFe0.6Ni0.4(Si,Ge) alloys and their giant magnetocaloric effect probed by heat capacity measurements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 494, 165785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valdés, C.F.; Gimaev, R.R.; López-Cruz, M.; Sánchez Llamazares, J.L.; Zverev, V.I.; Tishin, A.M.; Carvalho, A.M.G.; Aguiar, D.J.M.; Mudryk, Y.; Pecharsky, V.K. The effect of cooling rate on magnetothermal properties of Fe49Rh51. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 498, 166130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Maňosa, L.; Acet, M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2009, 21, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Luo, H.Z.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, G.H. Realization of multifunctional shape-memory ferromagnets in all-d-metal Heusler phases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 022406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Han, X.; Yu, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Ma, S.; Zeng, H.; Chen, C.; Luo, X.; et al. Magnetic-field-induced metamagnetic reverse martensitic transformation and magnetocaloric effect in all-d-metal Ni36.0Co14.0Mn35.7Ti14.3 alloy ribbons. Intermetallics 2019, 110, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Bez, H.; Pathak, A.K.; Biswas, A.; Zarkevich, N.; Balema, V.; Mudryk, Y.; Johnson, D.D.; Pecharsky, V.K. Giant enhancement of the magnetocaloric response in Ni-Co-Mn-Ti rapid solidification. Acta Mater. 2019, 173, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.W.; Craig, R.S. Magnetic and structural characteristics of TiCr2, ZrCr2, HfCr2 and the TiCo2-ZrCo2 and YFe2-YCo2 alloy systems. J. Less-common Met. 1968, 16, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, K.; Shinogi, A.; Endo, K. Exchange Enhanced Pauli Paramagnetism of ScCo2. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1984, 53, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Obara, G.; Nakamura, T. Magnetic Properties of C14 Laves Phase Ti(Fe1−xTx)2 with T = Mn, Co and Ni (x ≤ 0.6). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 285, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempelmann, R.; Hilscher, G. Ferromagnetism in Ti-Mn ternary hydrides. J. Less Common Met. 1980, 74, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpa, M.; Talik, E.; Winiarski, A.; Mydlarz, T.; Gilewski, A.; Kusz, J.; Böhm, H.; Suski, W. Electronic structure and magnetic examination of ScMn2 single crystal. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 386, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Yibole, H.; Tegus, O.; Guillou, F. Magnetocaloric Effect, Magnetoresistance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2, and Phase Diagrams of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2−xTx Alloys with T = Mn or Co. Crystals 2020, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050410
Sun L, Yibole H, Tegus O, Guillou F. Magnetocaloric Effect, Magnetoresistance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2, and Phase Diagrams of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2−xTx Alloys with T = Mn or Co. Crystals. 2020; 10(5):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050410
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Liting, Hargen Yibole, Ojiyed Tegus, and Francois Guillou. 2020. "Magnetocaloric Effect, Magnetoresistance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2, and Phase Diagrams of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2−xTx Alloys with T = Mn or Co" Crystals 10, no. 5: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050410
APA StyleSun, L., Yibole, H., Tegus, O., & Guillou, F. (2020). Magnetocaloric Effect, Magnetoresistance of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2, and Phase Diagrams of Sc0.28Ti0.72Fe2−xTx Alloys with T = Mn or Co. Crystals, 10(5), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050410