Abstract
We theoretically investigate the electronic and magnetic structure of FeHf. The density functional theory calculations are shown to produce the negative, easy-plane, magnetic anisotropy in the hexagonal FeHf. Antimony substitution suppresses the planar magnetization direction and favors the uniaxial magnetic anisotropy, in agreement with experimental observations. Our study suggests the possibility of the chemical control of the magnetic anisotropy in FeHf by Sb substitution, and illustrates the potential of (Fe,Sb)Hf Laves phase alloys for the permanent magnet applications.
1. Introduction
Permanent magnets are an indispensable part of the modern technology [1]. They are mainly used for data storage and energy conversion, and are present in smartphones; laptops; audio and video devices; and industrial applications, such as electrical motors and wind turbines. There is a high demand for permanent magnets (PMs) with high performance for efficient renewable energy production and conversion [2]. Research targeting new PMs is driven by both technological and economical factors, to keep costs low and ensure supply stability.
A good PM has to have a high Curie temperature, large magnetization density, and coercivity. The large coercivity is required to resist demagnetization, and advanced PM should achieve a coercivity T [3]. It is determined by the magneto-crystalline anisotropy energy (MAE), the energy to rotate the magnetization from the easy to the hard direction. This large coercivity can be provided by uniaxial magnetic phases with hexagonal, rhombohedral, or tetragonal crystal structures with the high MAE MJ/m.
The best known PMs are based on NdFeB with the most superior PM properties [4], and SmCo [5] which is used for the high temperature PM applications. These materials belong to the class of the rare-earth (RE)-transitional metal (3d) intermetallics. In these materials, the RE element provides high value of the MAE, and the 3d metal component yields a high magnetization density and a high Curie temperature.
In recent years, major effort has been made to search for the RE-free PM materials [6]. The reason is a growing concern for the RE elements’ (Nd, Sm, Dy) sustainability, together with growing demand from the industry for cheap and stable high-temperature PMs [2]. So far, the research has followed two routes: (i) to search directly for the transition metal based intermetallics in hexagonal, rhombohedral, or tetragonal crystal structures with the high MAE; (ii) to find a modification of already known ferromagnets by substitutional and interstitial alloying to increase the MAE.
Great prospects in the second direction were demonstrated by Coey and Sun [7] who have observed strong MAE increase in the iron-based RE intermetalics with substitution of the interstitial nitrogen. Furthermore, recently it was proposed experimentally and theoretically that alloying 6.25% of Sb into the hexagonal ferromagnet FeSn changes the MAE and turns the magnetization direction from the easy-plane to the easy axis [8]. Another successful example of the chemical engineering of the MAE is the recent experimental observation of a large uniaxial MAE in FeHf with Sb substitution [9].
The Fe-based Laves phases with 1:2 stoichiometry were never considered as candidates for magnetically hard materials. They usually crystallize in the cubic C15 structure with the small MAE, and posses superior magnetostrictive properties (e.g., giant magnetostriction in rare-earth-Fe [10]). Experimentally for the stoichiometric HfFe, the cubic C15 phase is slightly more stable than the hexagonal C14 phase at the low temperatures [11], and both phases were reported to co-exist for high temperatures [12].
It was shown experimentally [9] that the Sb substitution stabilizes Fe-Hf-Sb alloy in hexagonal C14 phase, and leads to the large positive MAE of ∼1.5 MJ/m for (Fe,Sb)Hf alloy with 13.5% of Sb. Together with saturation magnetic polarization of ∼0.8 MA/m (1 T), and the Curie temperature of 470 K, these properties make the alloy a promising candidate for the PM applications.
In this work, we aim to investigate the MAE in the hexagonal FeHf compound, and the Fe-Hf-Sb alloy making use of the density functional theory (DFT) implemented in the projector augmented-wave VASP [13], the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FLAPW) [14], and the Korringa–Kohn–Rostokker (KKR) [15] methods.
We show theoretically that the Sb substitution in hexagonal FeHf leads to the strong uniaxial MAE in good quantitative agreement with the experimental data. We demonstrate that the role of Sb substitution is not limited by stabilization of the FeHf in hexagonal C14 structure. The large uniaxial MAE occurs due to the presence of the Sb atoms in the crystalline matrix. Apart from the electronic mechanism, the structure relaxation plays an essential role in the MAE increase. In addition, we evaluate the inter-atomic exchange interactions in FeHf, and make an estimate for the Curie temperature.
2. Results
2.1. Hexagonal FeHf
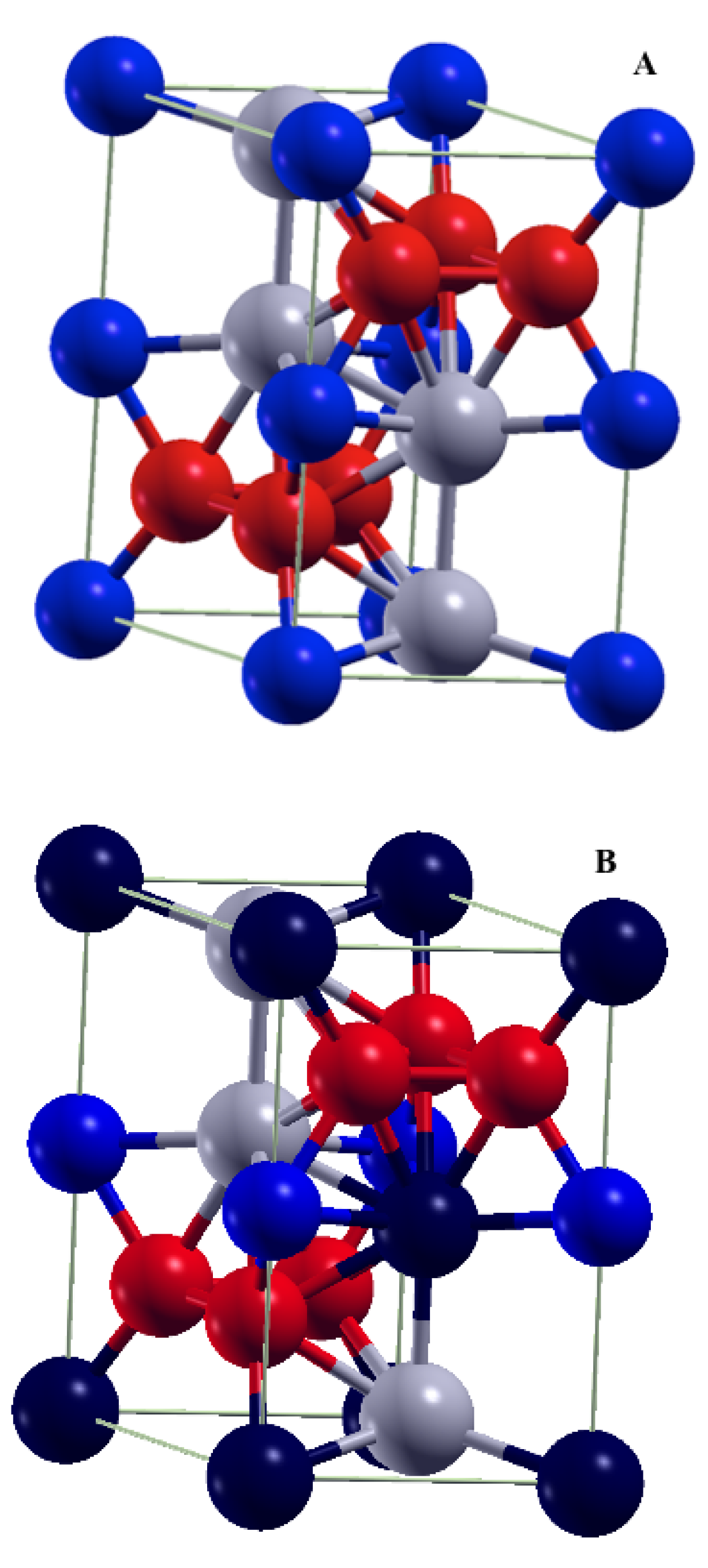
The FeHf has hexagonal C14 crystal structure with P6/mmc (number 194) space group and contains twelve atoms per unit cell (see Figure 1A). There are four formula units in the unit cell. The Fe atoms occupy (2a) and (6h) Wyckoff positions, and Hf is in (4f) Wyckoff position (see Table 1). First, we performed the scalar-relativistic VASP, KKR, and FLAPW calculations without spin-orbit coupling (SOC). The experimental lattice constants and , and internal positions [16] shown in Table 1 were used in the calculations. The FLAPW calculated magnetic moments inside “muffin-tin” (MT) spheres for different Fe and Hf atoms in the unit cell together with the total magnetic moment per cell are shown in Table 1. The VASP and KKR calculations yield very similar results. Note that the magnetic moments are aligned in the same direction for the both Fe-sublattices, and the Hf moments are pointed in the opposite direction.
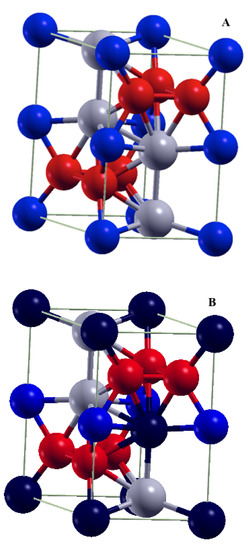
Figure 1.
Crystal structure (hexagonal C14) for pristine FeHf (A). Iron atoms in (2a) Wyckoff positions are represented by red-colored balls, iron atoms in (6h) Wyckoff positions are represented by blue-colored balls, and hafnium atoms in (4f) Wyckoff positions are represented by gray balls. (B) The unit cell of Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy in the lowest energy configuration. Antimony atoms are shown by dark-blue-colored balls.

Table 1.
The calculated magnetic moments (in ) inside the MT-spheres of different atoms in pristine FeHf and Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy unit cell, together with the total magnetic moment per cell. The Wyckoff positions and internal coordinates of different atoms in the unit cell are shown.
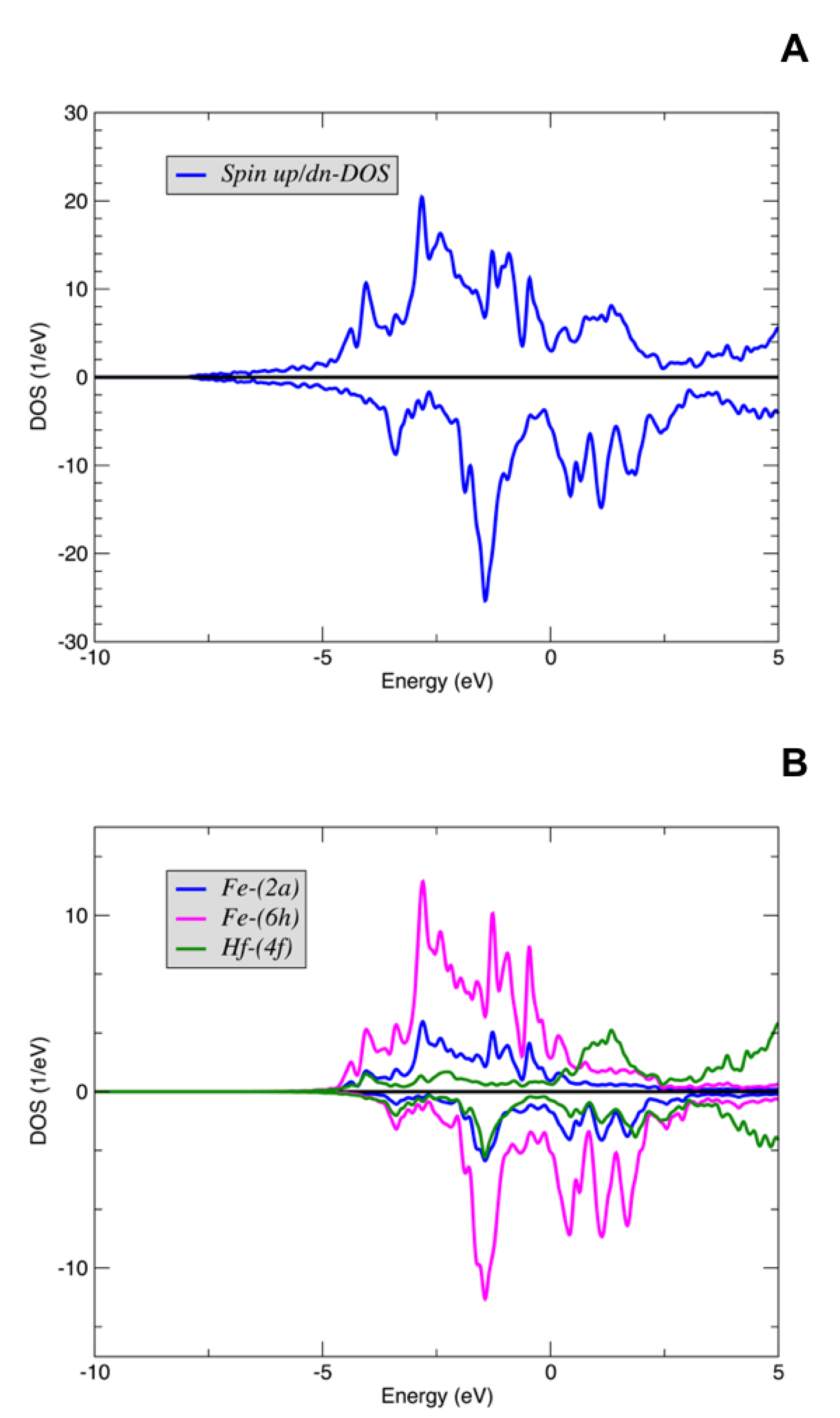
The spin-projected total density of states (DOS), as a result of FLAPW calculations without spin-orbit coupling (SOC), is shown in Figure 2A, and the d-states projected DOS for Fe and Hf atoms in different Wyckoff positions are shown in Figure 2B. Since the magnetic moments of Fe and Hf are anti-aligned, the exchange splitting of Fe and Hf is opposite. Virtually all the DOS character near is from Fe d-states. Both Fe and Hf-projected DOS illustrate itinerant character of the d-states. The calculated total (spin-up plus spin-down) DOS() for FeHf of 1.075 1/eV per Fe atom is close to the corresponding DOS value of 1.11 1/eV for the -Fe. Since the Fe-atom moments in FeHf (see Table 1) are smaller than 2.2 moment for -Fe, the moment formation in FeHf is weaker.
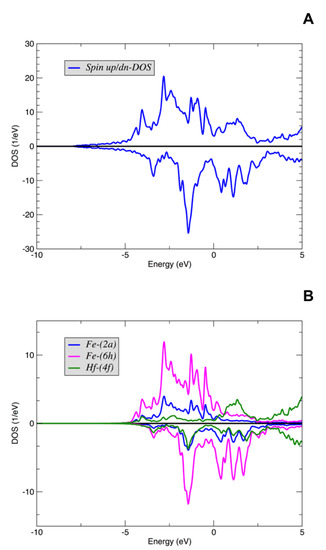
Figure 2.
Density of states (DOS) of the FeHf: (A) Spin-projected total DOS. (B) Spin-projected DOS for the d-states of Fe and Hf atoms in different Wyckoff positions. The Fermi level is set to .
In order to estimate the Curie temperature we calculate the inter-site pair exchange interactions of the classical Heisenberg Hamiltonian,
where and mark the unit directional vectors of the magnetic moments at i and j different Fe lattice sites for FeHf. The calculations were performed making use of the magnetic force theorem [17] implemented in the bulk KKR formalism [18]. Since the magnetic ordering happens out of high temperature paramagnetic state, the exchange interactions were evaluated in the disordered local moment (DLM) [19] model, used to treat the thermal magnetic disorder. The importance of using the DLM reference state for estimation of the Curie temperature is demonstrated in [20].
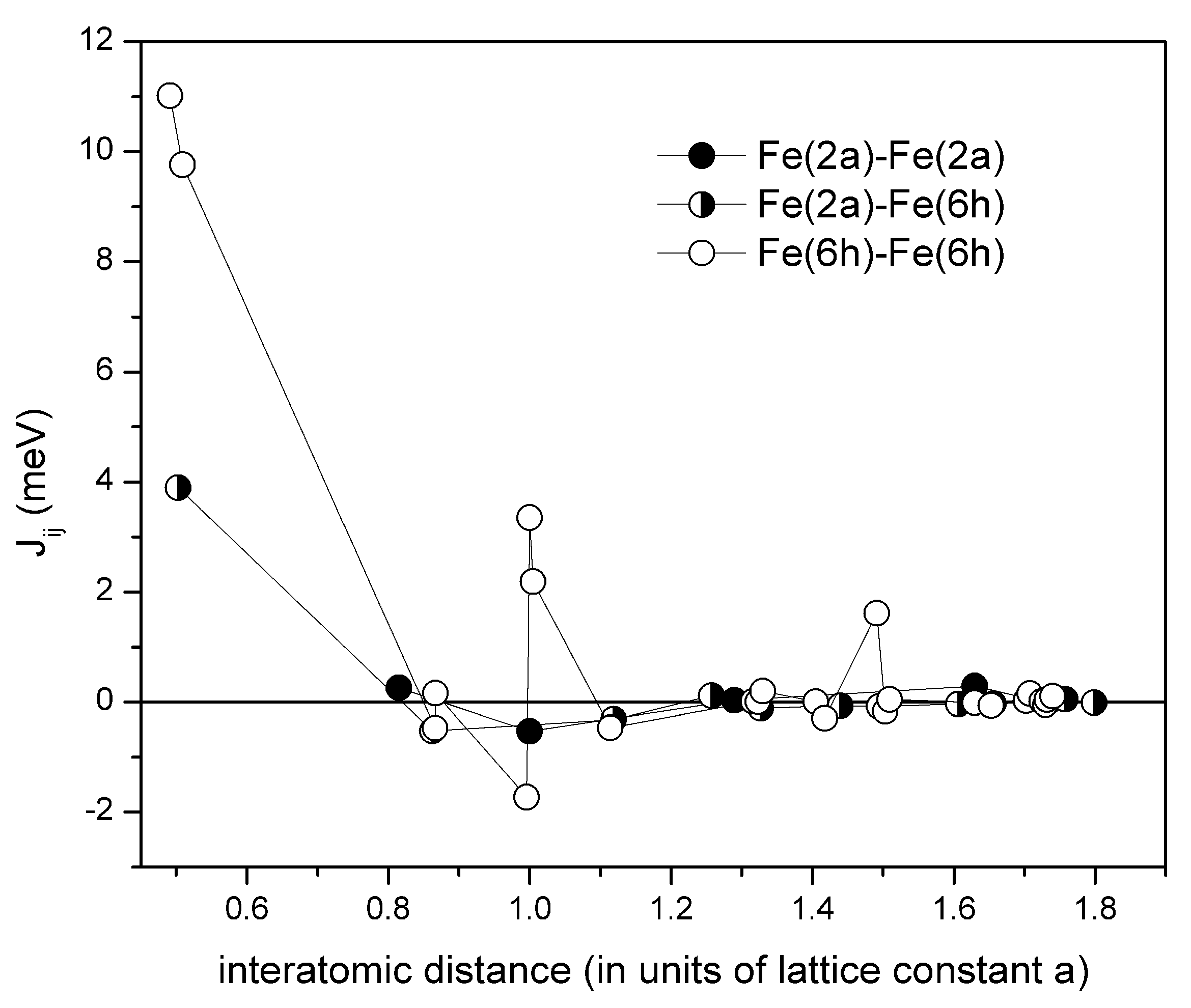
The calculated exchange constants are shown in the Figure 3. There are three types of the inter-site exchange interactions: intra-sublattice interactions between Fe moments on (2a)–(2a) sites and (6h)–(6h) sites, and inter-sublattice (2a)–(6h) exchange coupling. It is seen from the Figure 3 that the exchange interactions have a long range, as expected for the metallic magnet. The (6h)–(6h) intra-sublattice exchange couplings are the strongest, and provide main contribution to the Curie temperature. The inter-sublattice exchange coupling between the (2a) and (6h) first nearest neighbors is also strong. Thus, it is expected that the magnetization of (2a) sublattice will have similar temperature behavior to the magnetization of (6h) sublattice. The mean-field theory estimate yields 445 K for the Curie temperature. This value is in fair agreement with the value of 470 K experimentally determined for Fe-Hf-Sb alloys [9].
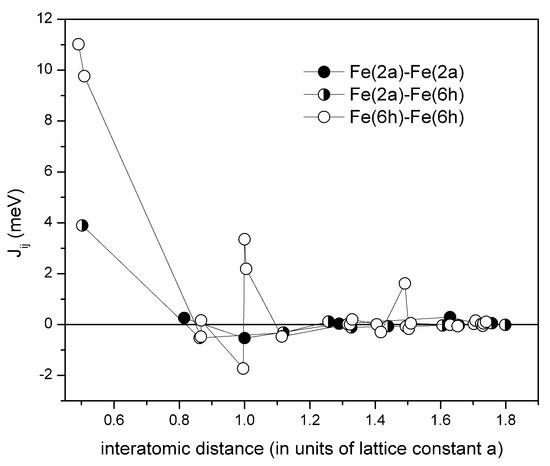
Figure 3.
The inter-site exchange interactions in hexagonal FeHf compound calculated in the disordered local moment (DLM) state. Open symbols are for the (2a)–(2a) Fe intra-sublattice interactions, closed symbols are for (6h)–(6h) intra-sublattice interactions, and semi-closed symbols denote the inter-sublattice (2a)–(6h) interactions. The calculations are presented for up to 50 nearest-neighbor shells.
The energy penalty of changing the orientation of the magnetization from in-plane to out-of-plane is called the magnetic anisotropy energy (MAE). Note that for a hexagonal crystal symmetry, the leading term in the MAE angular dependence is , with the angle between the magnetization and crystallographic c-axis. The MAE is then computed as the total energy difference when magnetization is oriented along [1100] and [0001] crystal axes, MAE = .
Starting from the scalar-relativistic calculations, we perform the self-consistent total energy calculations with the SOC included, making use of a relativistic version of FLAPW [21]. The conventional local spin density approximation (von Barth–Hedin) is adopted, which we expect to be valid for itinerant metallic systems. In these calculations, the magnetization is fixed along [1100] and [0001] axes. The special k-points method is used for the Brillouin zone (BZ) integration with the Gaussian smearing of 1 mRy for k-points weighting, and the equivalent to about 3200 k-points in the full BZ are used. Importantly, the same set of k-points must be used for different directions of the magnetization, in order to achieve accurate MAE results. The calculated MAE = −0.57 meV per unit cell (−0.54 MJ m) indicates the "in-plane" preferential direction of the magnetization in pristine FeHf. Although hexagonal FeHf has a saturation magnetic moment and the Curie temperature desirable for a permanent magnet applications, the magnetization lies in the hexagonal plane, which is detrimental for PM material.
2.2. Fe–Hf–Sb Alloy
The MAE can be altered by alloying. Experimentally, Goll et al. [9] observed that off-stoichiometric (Fe,Sb)Hf compounds have the uniaxial MAE of ∼1.5 MJ m. In order to examine the effect of Sb substitutional alloying as a possible tuning for positive MAE, we consider substitution of Fe and Hf atoms by Sb atoms in the FeHf unit cell. To stay close to the experimental composition Fe60.0-Hf26.5-Sb13.5 [9], we substitute simultaneously one Fe and one Hf in the 12 atoms FeHf unit cell. This yields Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 composition (FeHfSb unit cell) which we model considering 32 different ordered configurations of the Sb dopant.
We make use of the VASP code to evaluate the total energy. The total energies for different configurations of the Sb dopant are shown in Appendix A Table A1. We identify the four lowest energy ordered configurations where the Sb dopants substitute the pairs of [Fe (1)–Hf (4)] (see Table 1), and [Fe (1)–Hf (1)], [Fe (2)–Hf (2)], and [Fe (2)–Hf (3)]. All of these configurations in which Sb substitutes the Fe atoms in (2a) Wyckoff positions, are energetically equivalent. The alloy configuration where Sb dopants substitute the pair [Fe (1)–Hf (4)]) is shown in Figure 1B.
Additionally, we estimate stability of the lowest energy configurations calculating the enthalpy of formation H.
where E is the DFT total energy of the alloy, is the chemical potential of element i, and is the quantity of element i in the compound. The standard convention is to take the chemical potential of each species to be the DFT total energy of the elemental Fe, Hf, and Sb ground state. The enthalpy of formation is found H = −0.724 eV/f.u., which has somewhat smaller magnitude than the H = −1.165 eV/f.u. for pristine FeHf. Negative sign of H supports the thermodynamic stability of Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy.
Moreover, we estimate the enthalpy of formation for Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy formed from pristine FeHf. In this case, the is calculated from the alloy total energy subtracting the total energy of FeHf, and taking into account excess of Fe and incorporation of two Sb atoms into the unit cell. This results in = 0.15 eV/f.u., and indicates the potential of Sb incorporation in already existing FeHf at finite temperatures.
Next, we perform the FLAPW calculations for the alloy configuration shown in Figure 1B. The calculated magnetic moments inside MT-spheres for different Fe and Hf atoms in the unit cell together with the total magnetic moment per cell are shown in Table 1. It is seen that the magnetic moment is increased for the Fe atom in (2a) position, and is decreased for the (6h) Fe atoms. Additionally, magnitude of the moment on Hf atom is smaller than in the pristine FeHf. The Sb dopant yields almost no contribution to the magnetic moment, and the total moment per FeHfSb unit cell is decreased by 3 .
Starting from the scalar-relativistic calculations, we perform the calculations with the SOC included, making use of a relativistic version of FLAPW [21]. In these calculations, the magnetization is fixed along [1100] and [0001] axes, as it was done for FeHf described above, with the same set of the special k-points for the BZ-integration. The MAE of 0.88 meV per unit cell (0.82 MJ m, see Table 2) is calculated. This significant positive MAE indicates the "out-of-plane" preferential direction of the magnetization, and is crucial for PM applications.

Table 2.
Magnetic moment (, MA/m), and the uniaxial magnetocrystalline anisotropy (MAE, MJ/m).
The calculations which are presented above were done assuming the experimental unit cell volume and internal positions of FeHf [16]. The structure optimization can play important role, and we examined the effect of structural relaxation on the electronic structure, magnetism, and MAE of Fe-Hf-Sb alloy. In these calculations, the unit cell volume, c/a-ratio, and internal coordinates were optimized making use of the VASP method. Internal positions were relaxed until residual forces were less than 0.1 meV/Å. The relaxed volume of 179 Å and c/a-ratio of 1.64 for Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy are bigger than the volume of 173 Å and c/a-ratio of 1.63 for unrelaxed unit cell. The saturated magnetization of 10.93 (0.57 MA m, see Table 2) slightly exceeds the unrelaxed value of 10.48 (0.55 MA m). This slight increase of the magnetization is consistent with an increase of equilibrium volume.
Importantly, the MAE is increased with relaxation from 0.88 meV per unit cell (0.82 MJ m) to 1.37 meV per unit cell (1.27 MJ m), as shown in Table 2. The MAE calculations require special care to converge energy differences of often less than 0.1 meV per unit cell from the total energy, which may be ten orders of magnitude larger. This is an involved endeavor and about 5200 special k-points in the full BZ were used in order to achieve the accuracy better than 0.05 meV per unit cell in the MAE calculations.
Comparison between calculated relaxed Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 and experimental Fe60.0-Hf26.5-Sb13.5 [9] alloy is shown in Table 2. There is a fair agreement for the saturation magnetization . The calculated value of is somewhat smaller since there is a deficiency of Fe and Hf, and excess of Sb in the model supercell as compared with the experiment. Agreement between the uniaxial MAE is good. Significantly positive MAE and corresponding anisotropy field of 3.58 MA/m ( = 4.5 T), together with saturation magnetization of 0.72 T and reasonably high Curie temperature of 470 K, allow us to suggest that Fe-Hf-Sb alloys with the optimal amount of Sb dopant can be a suitable candidates for a magnetically hard material.
3. Discussion
The MAE strength depends on the value of the SOC constant [22]. In Fe-Hf-Sb alloy, the SOC for p-states of Sb, and d-states of Fe and Hf play a role for the MAE. The strongest = 0.978 eV is for the 5p-states of Sb, while the values for 3d-states of Fe and 5d-states Hf are of 0.065 eV and 0.188 eV respectively. Bruno [22] has shown that the MAE is proportional to the anisotropy of the orbital moment ,
when the exchange splitting . For the Fe-Hf-Sb alloy, the exchange splitting = 0.654 eV, and we can use this approach to estimate contributions to the MAE of Fe-Hf-Sb alloy from Fe and Hf atoms. Making use of the calculated values, we obtain the negative Fe-atoms MAE of −1.14 meV per unit cell, and the positive Hf-atoms MAE of 0.28 meV per unit cell. The total contribution to the MAE = −0.88 meV due to the SOC of Fe and Hf d-states is semi-quantitatively consistent with the negative MAE = −0.57 meV per unit cell for pristine FeHf.
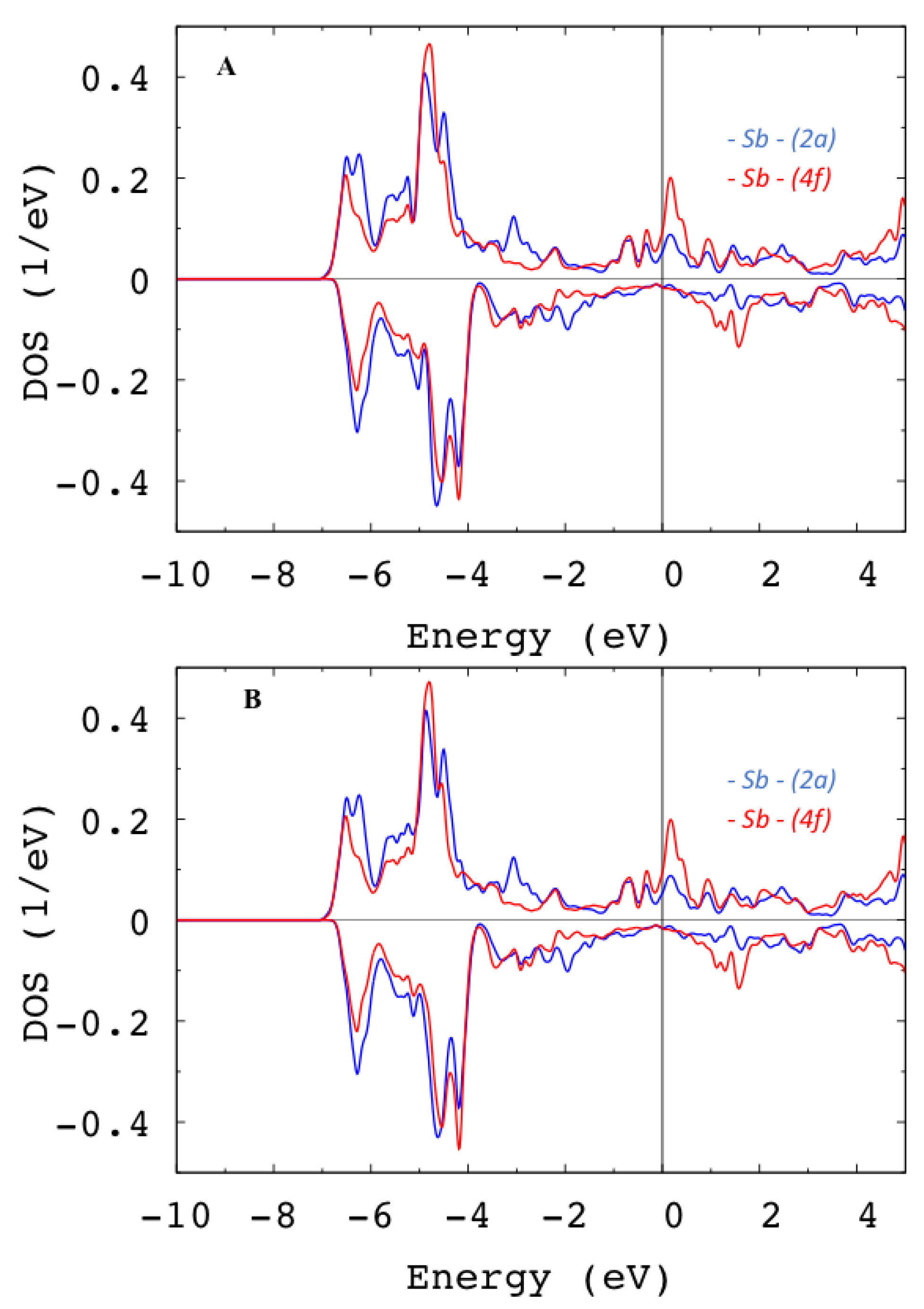
Since the Sb-p-states’ SOC is bigger than , no perturbation theory is expected to be valid for their contribution to the MAE. At first, we show in Figure 4 the p-projected Sb-atoms’ DOS for different directions of the magnetization. While they look alike, closer examination shows small p-DOS anisotropy of 0.02 states/eV at the Fermi level. This DOS anisotropy is usually related to the MAE [23].
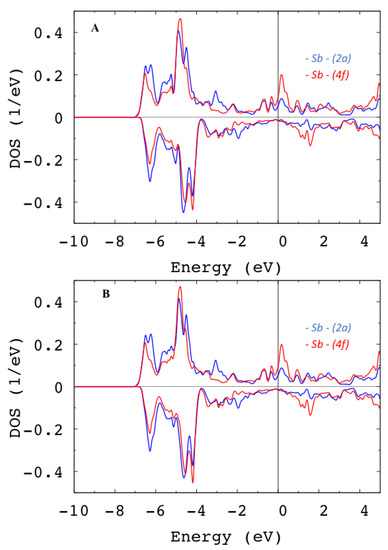
Figure 4.
(A) Spin-projected p-DOS for [0001]; (B) spin-projected p-DOS for [1100] for Sb atoms in (2a) and (4f) Wyckoff positions. The Fermi level is set to .
In order to evaluate effect of the Sb-p-states SOC on the MAE, we performed the total energy calculations, where we set = 0 for the p-states of the Sb atoms; i.e., explicitly removed the Sb p-state’s contribution to the MAE. The calculated MAE = 0.13 meV per unit cell (0.12 MJ/m) is positive. It is substantially smaller than the full MAE of 1.37 meV per unit cell (1.27 MJ/m) shown in Table 2, where the Sb-p-states SOC is included. These calculations show explicitly and quantitatively that the p-states of Sb play a key role in the positive MAE of Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy.
4. Conclusions
To summarize, we have investigated the electronic structure and magnetic character of FeHf hexagonal C14 phase. The negative MAE was found, and determined the "in-plane" preferential direction of the magnetization in the pristine material. The first-principles calculations demonstrate that Sb substitution changes the MAE from planar to uniaxial, in agreement with experimental observations. We emphasize the essential contribution of the structural relaxation to the MAE of Fe-Hf-Sb alloy. Our results suggest that the chemical substitution of the p-elements to the Fe-based hexagonal Laves phases can be a promising way for positive MAE control in the rare-earth free permanent magnets for technological applications.
Author Contributions
L.K. and M.T. performed the total energy VASP calculations for the electronic structure, crystal structure optimization, and enthalpy of formation; A.B.S. performed the total energy FLAPW calculations of the DOS, spin and orbital magnetic moments, and magnetic anisotropy energy; S.K. performed the KKR calculations of exchange coupling constants and Curie-temperature; D.L. performed the project administration, supervision, and analysis of the results. All authors contributed in writing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by Operational Program Research, Development and Education financed by European Structural and Investment Funds and the Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports (project number SOLID21-CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16019/0000760), European Regional Development Fund in the IT4Innovations national supercomputing center—path to exascale project, project number CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16013/0001791 within the Operational Program Research, Development and Education, mobility grant number 8J18AT004, and by the Czech Science Foundation grant number 18-06240S. D.L. was supported by the Czech Science Foundation grant number 17-23964S.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The total energies relative to the lowest energy configuration for thirty two different configurations where the Sb dopants substitute the pairs of [Fe–Hf ] are shown in Table A1. We identify four different groups of the ordered configurations with the same energy. Inside of the each group, different configurations are connected by the symmetry operations.
Note that we made a comparison between the enthalpy of formation for Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 alloy eV/f.u. (one Fe and one Hf atoms are substituted by Sb), and two alloys where either Fe (Fe50-Hf33-Sb17) or Hf (Fe66-Hf17-Sb17) sites are replaced by Sb. We found eV/f.u., and eV/f.u. Thus, the configuration with two Hf sites substituted by Sb may be energetically preferable to the 1:1 Fe58-Hf25-Sb17 substitution. One has to take this comparison with some cautiousness since it is done for T = 0 K and without phonon contribution.

Table A1.
The total energy difference (eV/f.u.) relative to the lowest energy configuration for 32 ordered configurations of FeHfSb.
Table A1.
The total energy difference (eV/f.u.) relative to the lowest energy configuration for 32 ordered configurations of FeHfSb.
| Group | Sb Substitution Sites | (eV/f.u) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Fe(1)–Hf(1)] | 0 |
| [Fe(2)–Hf(2)] | 0 | |
| [Fe(2)–Hf(3)] | 0 | |
| [Fe(1)–Hf(4)] | 0 | |
| 2 | [Fe(3)–Hf(1)] | 0.137 |
| [Fe(4)–Hf(1)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(7)–Hf(1)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(5)–Hf(2)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(6)–Hf(2)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(8)–Hf(2)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(3)–Hf(3)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(4)–Hf(3)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(7)–Hf(3)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(5)–Hf(4)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(6)–Hf(4)] | 0.137 | |
| [Fe(8)–Hf(4)] | 0.137 | |
| 3 | [Fe(5)–Hf(1)] | 0.215 |
| [Fe(6)–Hf(1)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(8)–Hf(1)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(3)–Hf(2)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(4)–Hf(2)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(7)–Hf(2)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(5)–Hf(3)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(6)–Hf(3)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(8)–Hf(3)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(3)–Hf(4)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(4)–Hf(4)] | 0.215 | |
| [Fe(7)–Hf(4)] | 0.215 | |
| 4 | [Fe(2)–Hf(1)] | 0.258 |
| [Fe(1)–Hf(2)] | 0.258 | |
| [Fe(1)–Hf(3)] | 0.258 | |
| [Fe(2)–Hf(4)] | 0.258 |
References
- Skomski, R.; Coey, J.M.D. Permanent Magnetism; Institute of Physics: Bristol, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Willard, M.; Bruck, E.; Chen, C.; Sankar, S.; Liu, J. Magnetic Materials and Devices for the 21st Century: Stronger, Lighter, and More Energy Efficient. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Heavy rare earth free, free rare earth and rare earth free magnets-Vision and reality. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, J.M. R2Fe14B Materials-Intrinsic Properties and Technological Applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1991, 63, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K. RETM5 and RE2TM17 Permanent Magnets Development. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dirba, I.; Helbig, T.; Alff, L.; Gutfleisch, O. Engineering perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in Fe via interstitial nitrogenation: N choose K. APL Mater. 2016, 4, 116104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Sun, H. Improved magnetic properties by treatment of iron-based rare earth intermetallic compounds in ammonia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1990, 87, L251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekilova, O.Y.; Fayyazi, B.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O.; Echevarria-Bonet, C.; Barandiaron, J.M.; Kovacs, A.; Fischbacher, J.; Schrefl, T.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Tuning the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Fe3Sn by alloying. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 024421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, D.; Gross, T.; Loeffler, R.; Pflanz, U.; Vogel, T.; Kopp, A.; Grubesa, T.; Schneider, G. Hard Magnetic Off-Stoichiometric (Fe,Sb)2+xHf1−x Intermetallic Phase. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2017, 11, 1700184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, G. Handbook of Giant Magnetostrictive Materials; Engdahl, G., Ed.; Academic Press: San-Diego, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 264. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, O.; Hard, G.L.W.; Curtarolo, S. Hafnium binary alloys from experiments and first principles. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villars, P.; Berndt, M.; Brandenburg, K.; Cenzual, K.; Daams, J.; Hulliger, F.; Massalski, T.; Okamoto, H.; Osaki, K.; Prince, A.; et al. The Pauling File. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 367, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, E.; Krakauer, H.; Weinert, M.; Freeman, A.J. Full-potential self-consistent linearized-augmented-plane-wave method for calculating the electronic structure of molecules and surfaces: O2 molecule. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 24, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.V.; Skriver, H.L. Calculated surface segregation in transition metal alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1999, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; van Engen, P.G.; Jongebreur, R. Magneto-optical properties of metallic ferromagnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1983, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechtenstein, A.I.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Antropov, V.P.; Gubanov, V.A. Local spin density functional approach to the theory of exchange interactions in ferromagnetic metals and alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 67, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.V.; Simak, S.I.; Shallcross, S.; Skriver, H.L. Local lattice relaxations in random metallic alloys: Effective tetrahedron model and supercell approach. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 214302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorffy, B.L.; Pindor, A.J.; Staunton, J.; Stocks, G.M.; Winter, H. A first-principles theory of ferromagnetic phase transitions in metals. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1985, 15, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelevskyi, S.; Ruban, A.V.; Mohn, P. Magnetic ordering and exchange interactions in structural modifications of Mn3Ga alloys: Interplay of frustration, atomic order, and off-stoichiometry. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 184404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shick, A.B.; Novikov, L.D.; Freeman, J.A. Relativistic spin-polarized theory of magnetoelastic coupling and magnetic anisotropy strain dependence: Application to Co/Cu (001). Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, R14259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P. Tight-binding approach to the orbital magnetic moment and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of transition-metal monolayers. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shick, A.B.; Maca, F.; Masek, J.; Jungwirth, T. Prospect for room temperature tunneling anisotropic magnetoresistance effect: Density of states anisotropies in CoPt systems. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 024418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).