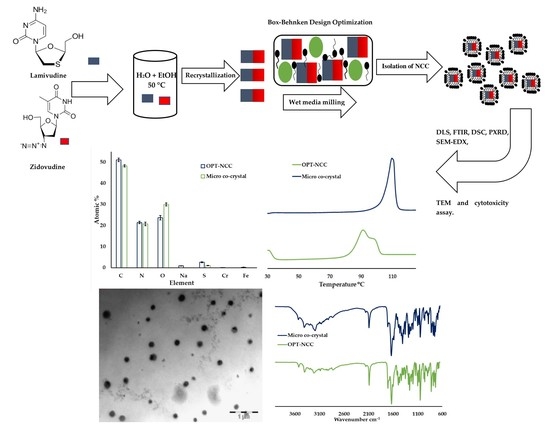
Top-Down Synthesis of a Lamivudine-Zidovudine Nano Co-Crystal
Abstract
Share and Cite
Witika, B.A.; Smith, V.J.; Walker, R.B. Top-Down Synthesis of a Lamivudine-Zidovudine Nano Co-Crystal. Crystals 2021, 11, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11010033
Witika BA, Smith VJ, Walker RB. Top-Down Synthesis of a Lamivudine-Zidovudine Nano Co-Crystal. Crystals. 2021; 11(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitika, Bwalya A., Vincent J. Smith, and Roderick B. Walker. 2021. "Top-Down Synthesis of a Lamivudine-Zidovudine Nano Co-Crystal" Crystals 11, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11010033
APA StyleWitika, B. A., Smith, V. J., & Walker, R. B. (2021). Top-Down Synthesis of a Lamivudine-Zidovudine Nano Co-Crystal. Crystals, 11(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11010033