Development of Red Clay Ultrafiltration Membranes for Oil-Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Characterization of Ceramic Membrane
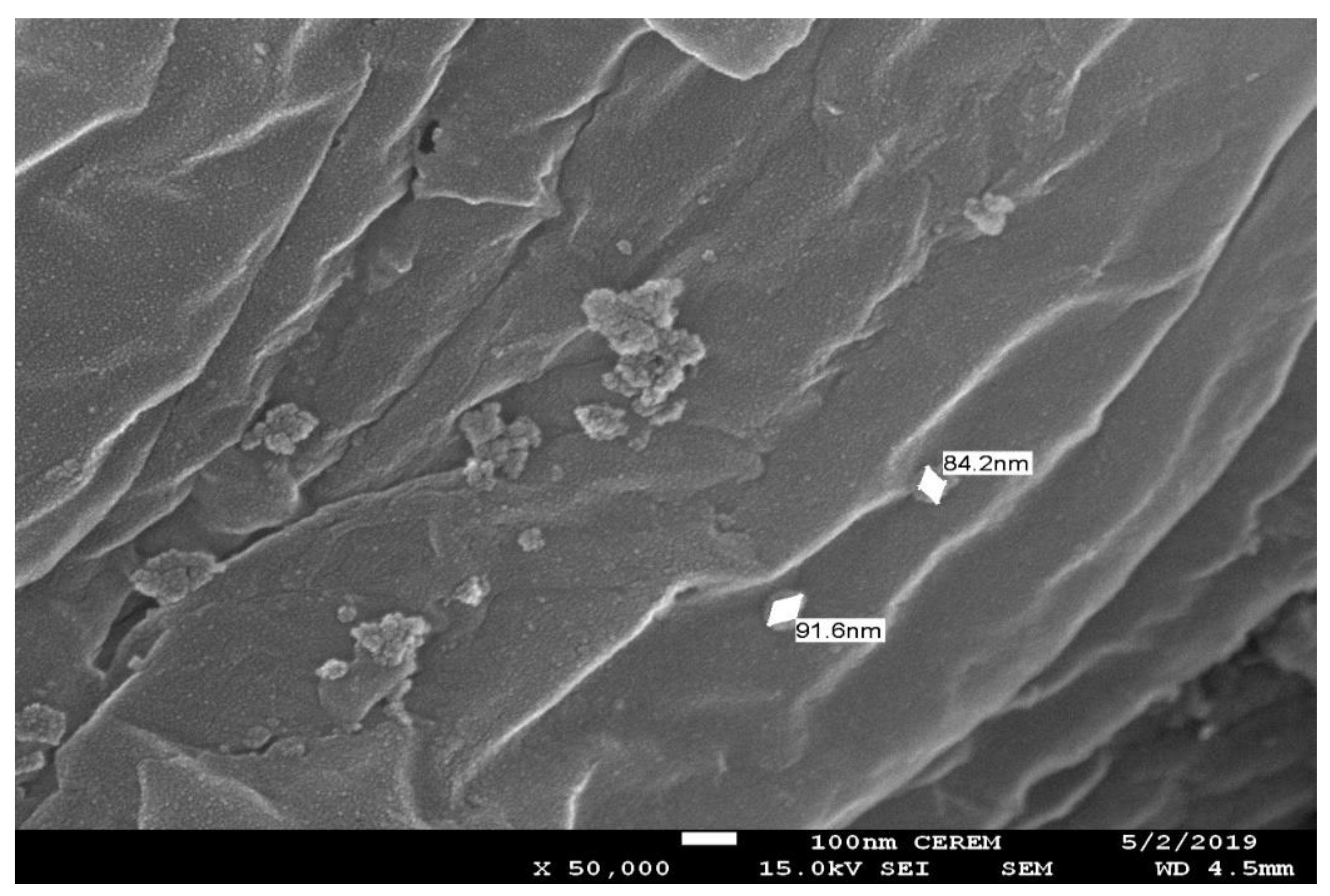
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Apparent Porosity
2.3.3. Contact Angle Measurements
2.3.4. Mechanical Test
2.3.5. X-Ray Diffraction
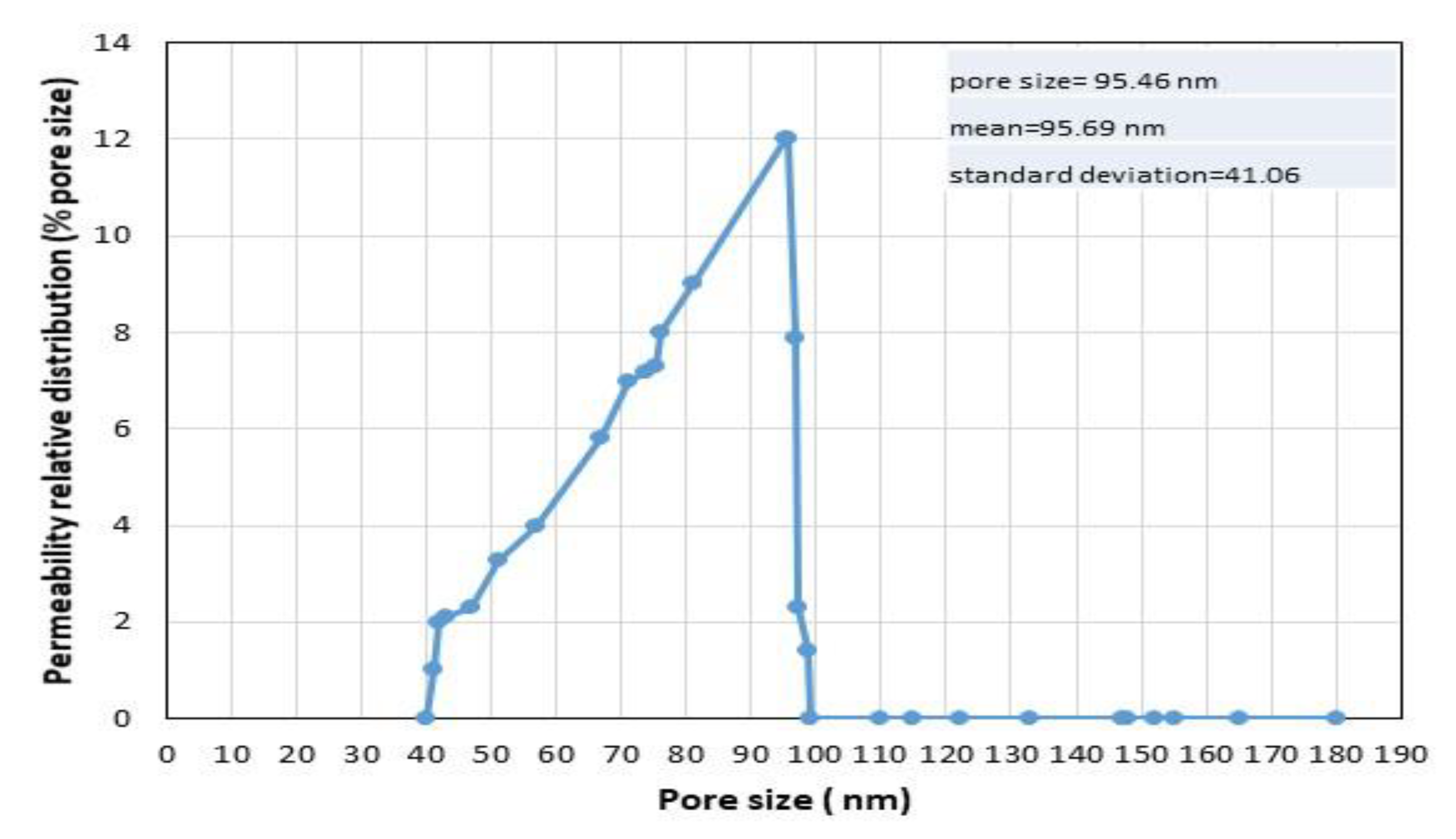
2.3.6. Pore size Distribution Measurements
2.4. Oil Emulsion Characterization
2.5. Ultrafiltration Testing
3. Results and Discussion
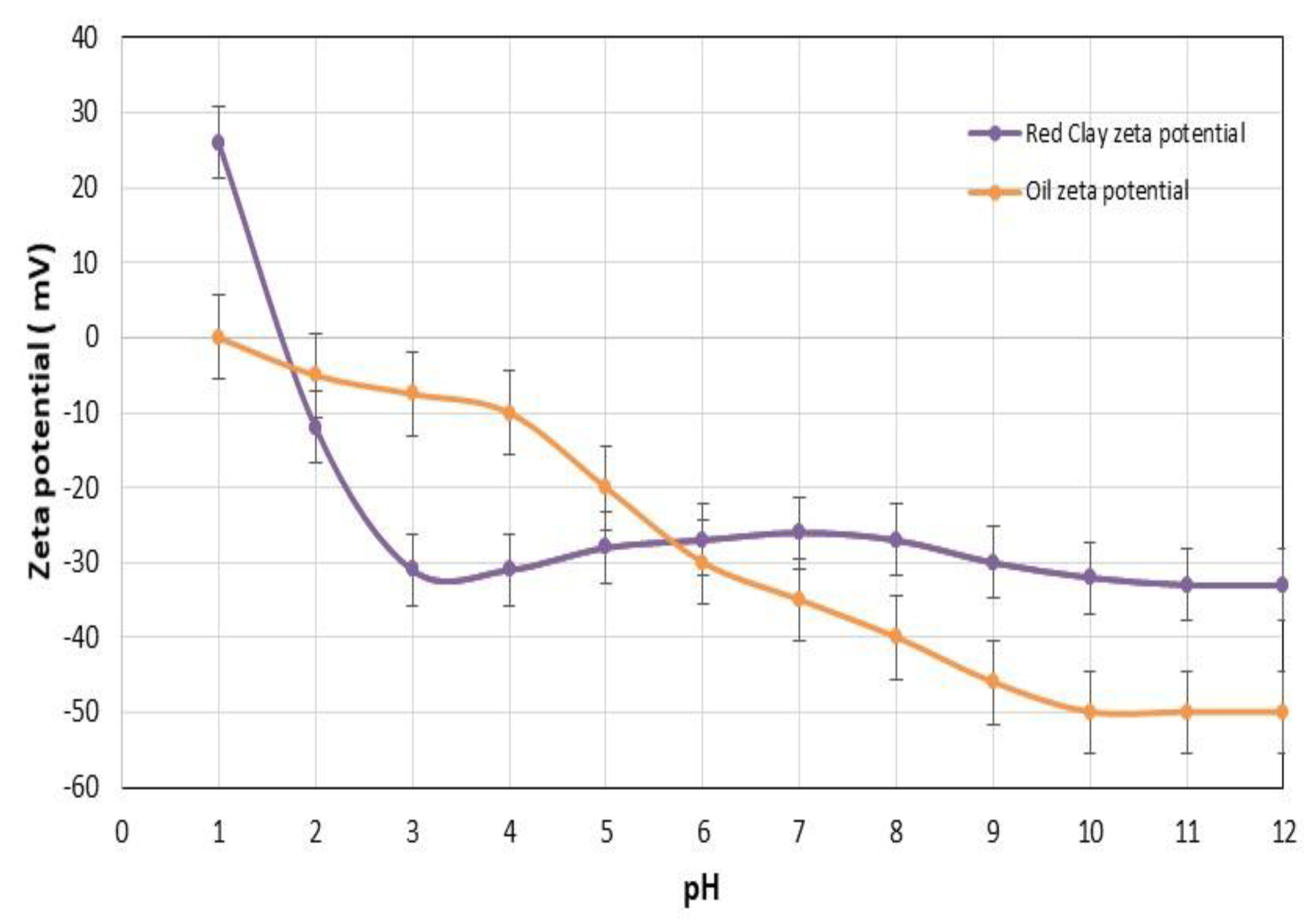
3.1. Characterizations
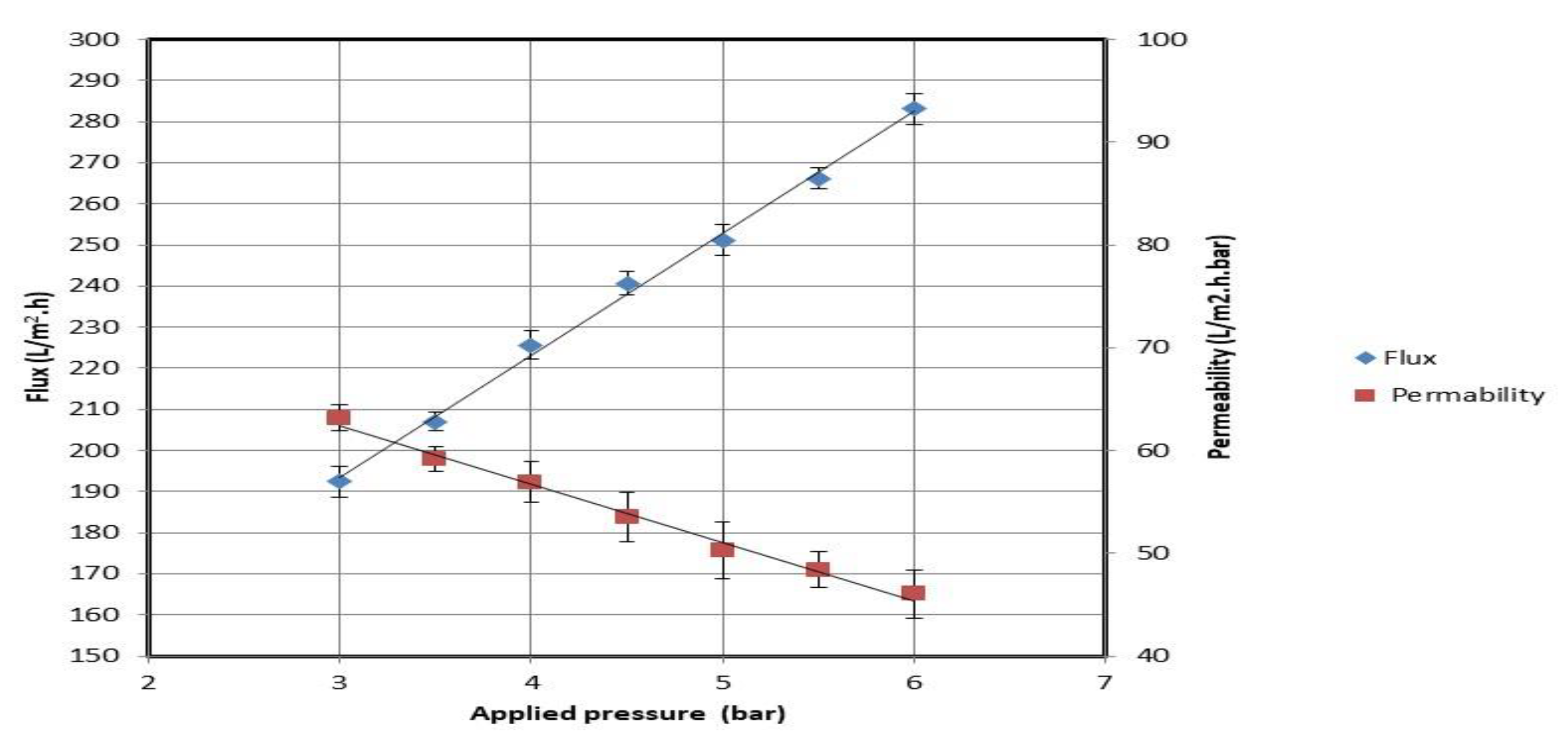
3.2. Evaluation of Fabricated Membrane
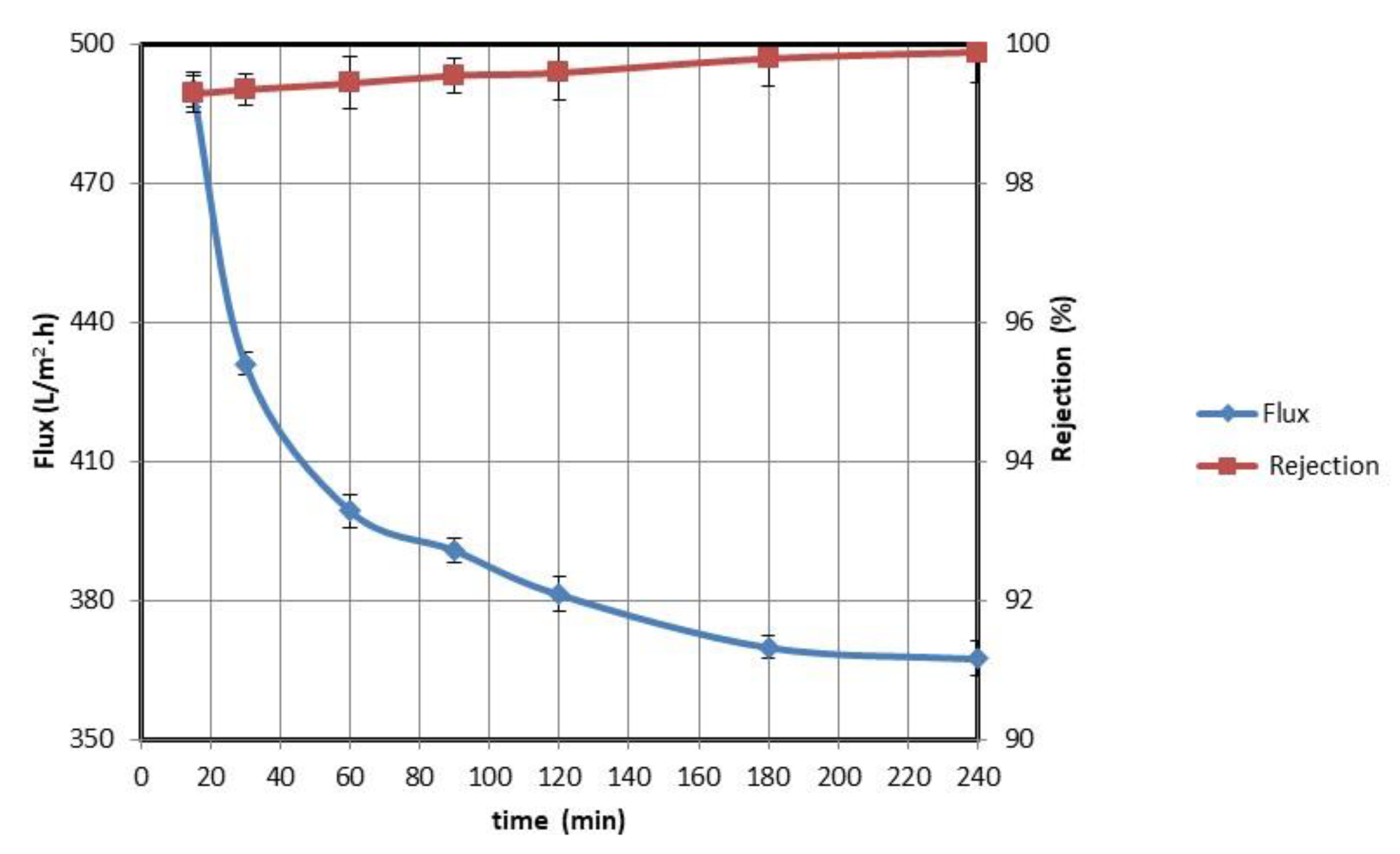
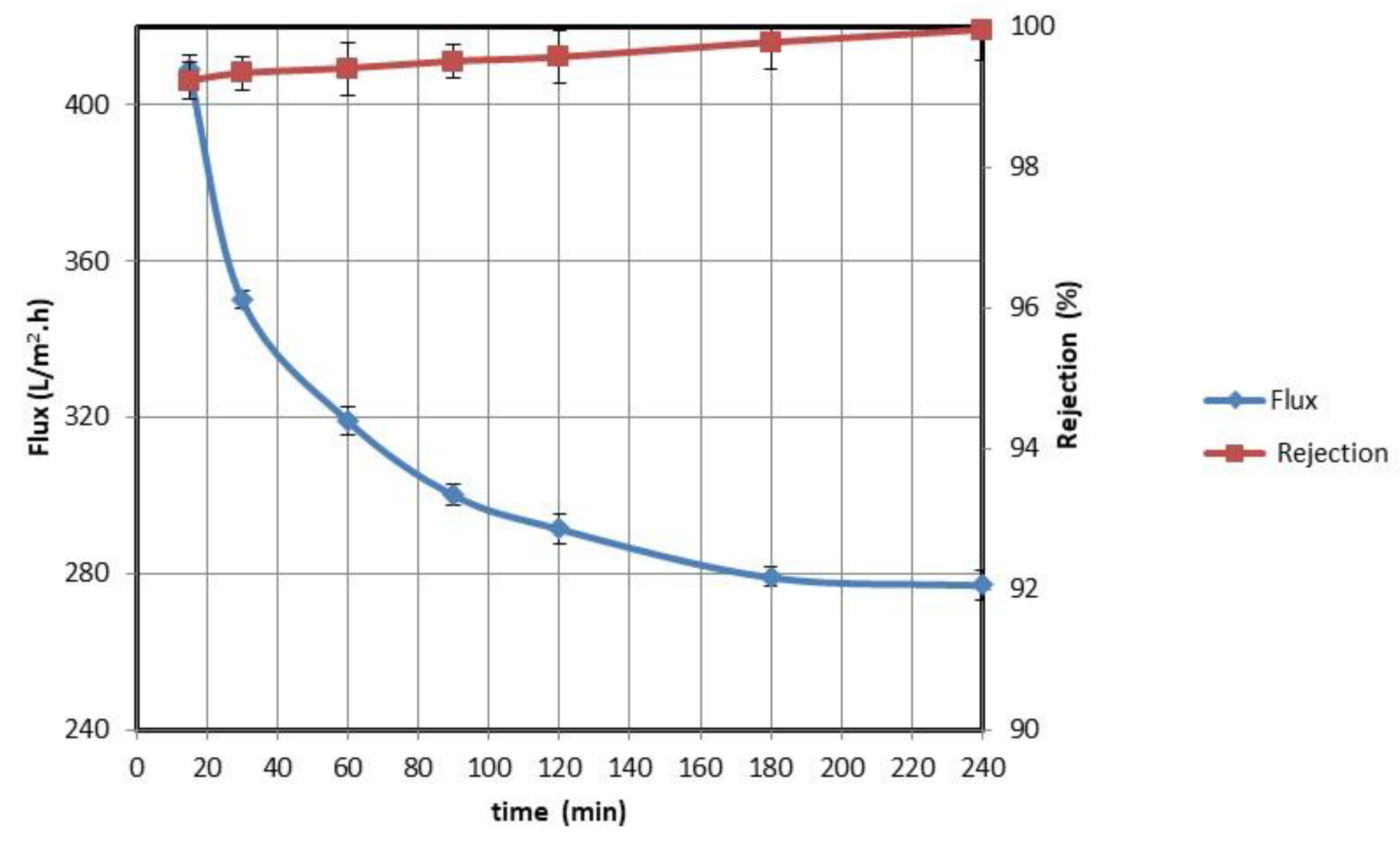
3.2.1. Evaluation with Synthetic Oil Emulsion
3.2.2. Evaluation with Aramco Oil-Contaminated Water
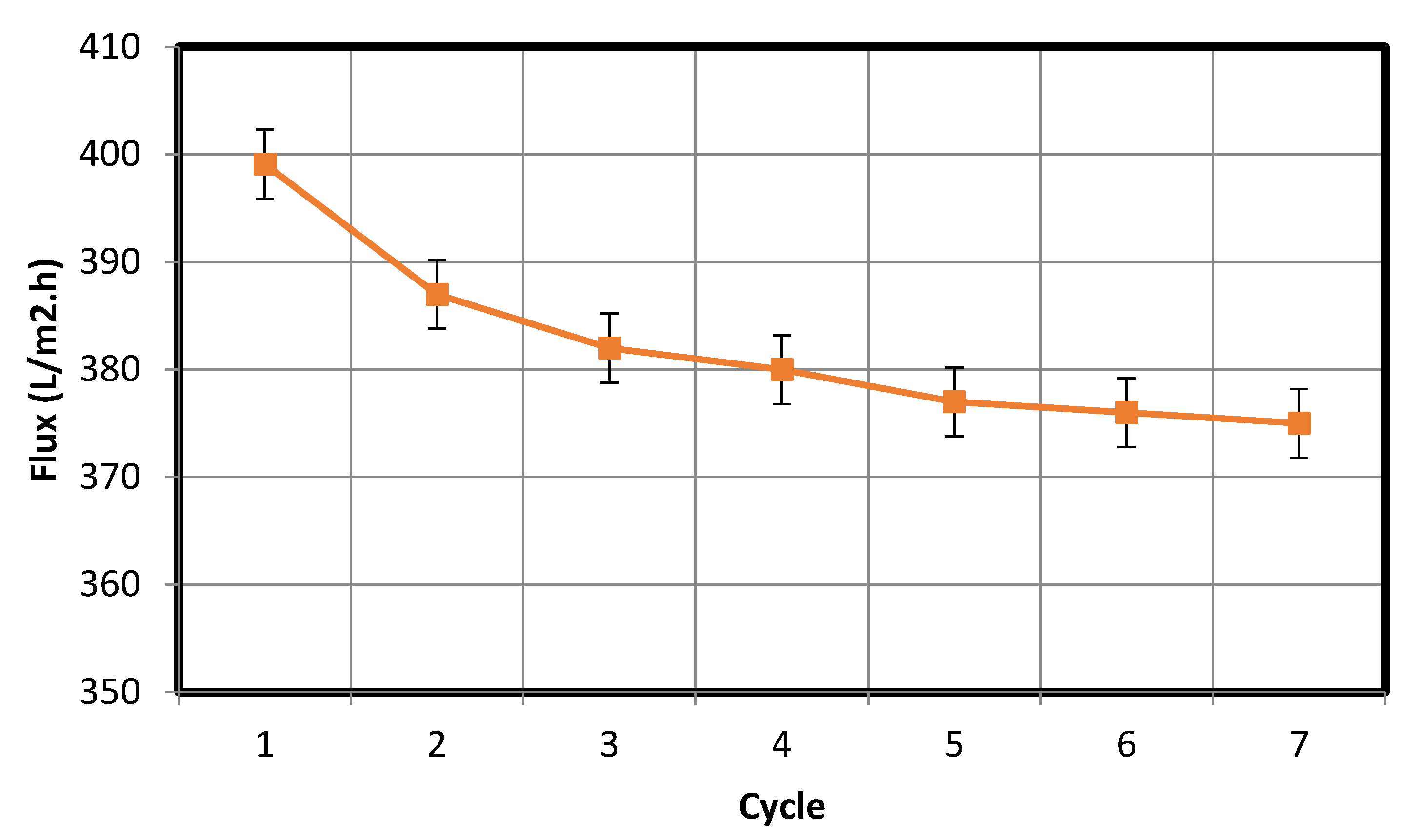
3.3. Cleaning Mechanism of a Fouled Membrane and Cyclic Filtering Test
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mercado, M.; Acuna, J.C.; Vasquez, J.E.; Caballero, C.; Soriano, J.E. Successful field application of a high temperature conformance polymer in Mexico. SPE Int. Symp. Oilfield Chem. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, B.; Jianhua, Z.; Xing, W.; Zongli, X. A review on current development of membranes for oil removal from wastewaters. Membranes 2020, 65, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padaki, M.; Surya Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4-Hakami, M.W.; Alkhudhiri, A.; Al-Batty, S.; Zacharof, M.P.; Maddy, J.; Hilal, N. Ceramic microfiltration membranes in wastewater treatment: Filtration behavior, fouling and prevention. Membranes 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xing, W. Clarification of raw rice wine by ceramic microfiltration membranes and membrane fouling analysis. Desalination 2010, 256, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, N.P.; Lu, N.; Hilal, N. Enhanced removal of heavy metal ions bound to humic acid by polyelectrolyte flocculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.; Jefferson, B. Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, B.M.; Yeh, H.H. Removal of giardia and cryptosporidium in drinking water treatment: A pilot-scale study. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Yeung, K.L. Preparation and application of zeolite/ceramic microfiltration membranes for treatment of oil contaminated water. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, G.; Huang, M.; Liang, J.; Zeng, B.; Fu, C.; Wu, H. Ultrarobust and biomimetic hierarchically macroporous ceramic membrane for oil–water separation templated by emulsion-assisted self-assembly method. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35555–35562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongwei, L.; Zhang, T.; Gutierrez, L.; Ma, J.; Croué, J.P. Influence of surface properties of filtration-layer metal oxide on ceramic membrane fouling during ultrafiltration of oil/water emulsion. Env. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4668–4674. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, A.; Cambiella, Á.; Benito, J.M.; Pazos, C.; Coca, J. Ultrafiltration of oil-in-water emulsions with ceramic membranes: Influence of pH and crossflow velocity. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 278, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Gang, H.; Chung, T.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Oil/water separation via ultrafiltration by novel triangle-shape tri-bore hollow fibre membranes from sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, C.; Mortazavi, S.; Tremblay, A.; Doiron, A. In-process steam cleaning of ceramic membranes used in the treatment of oil sands produced water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 33, 15232–15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaoui, M.; Lionel, L. Low-cost ceramic membranes: Synthesis, classifications, and applications. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Jana, S.; Mohanty, K. Synthesis of low-cost hydrophilic ceramic–polymeric composite membrane for treatment of oily wastewater. Desalination 2011, 282, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, M.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Huang, A.; Li, L. A low-cost mullite-titania composite ceramic hollow fiber microfiltration membrane for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsion. Water Res. 2016, 90, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; McPherson, B.J.; Li, L.; Lee, R.L. Factors determining the reverse-osmosis performance of zeolite membranes on produced-water purification. Int. Symp. Oil Field Chem. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, B.K.; Moparthi, A.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Treatment of oily wastewater using low cost ceramic membrane: Comparative assessment of pore blocking and artificial neural network models. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.P.; Pugazhenthi, G. Credibility of polymeric and ceramic membrane filtration in the removal of bacteria and virus from water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amar, R.; Khemakhem, M.; Oun, A.; Cerneaux, S.; Cretin, M.; Khemakhem, S. Decolorization of dyeing effluent by novel ultrafiltration ceramic membrane from low cost natural material. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2018, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hubadillah, S.K.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahman, M.A.; Harun, Z.; Jaafar, J.; Nomura, M. Fabrications and applications of low cost ceramic membrane from kaolin: A comprehensive review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4538–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.; Bram, M.; Pedersen, S.; Yang, Z. Membrane fouling for produced water treatment: A review study from a process control perspective. Water 2018, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franks, R.; Chilekar, S.; Bartels, C.R. The unexpected performance of highly permeable SWRO membranes at high temperatures. IDA J. Desalin. Water Reuse 2012, 4, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, H. Dairy product processing equipment. Handb. Farm Dairy Food Mach. 2007, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, B.K.; Das, B.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Microfiltration of mosambi juice using low cost ceramic membrane. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; HuHong, M.; NiuXian, L.; ChenHua, Z. Natural cellulose microfiltration membranes for oil/waternanoemulsions separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 564, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Liang, Z. Super-wetting, photoactive TiO2 coating on amino-silane modified PAN nanofiber membranes for high efficient oil-water emulsion separation application. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiang, Z.W. Treating oilfield wastewater: Technology review. Filtr. Sep. 2008, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabode, Y.; Othman, M.; Nordin, N.; Tai, Z.; Usman, J.; Mamah, S.; Ismail, A.; Rahman, M.; Jaafar, J. Fabrication of magnesium bentonite hollow fibre ceramic membrane for oil-water separation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5996–6008. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Miller, D.J.; Kasemset, S.; Wang, L.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Fouling propensity of a poly(vinylidene fluoride) microfiltration membrane to several model oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Oxides | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Loss on Ignition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 47.63 | 24.03 | 9.57 | 0.23 | 2.08 | 1.29 | 1.28 | 11.55 |
| Ref | Membrane Type | Solution | Pressure (bar) | Permeation Flux (L/m2 h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | cellulose microfiltration membranes | Synthetic produced water | 3 | 200 |
| [28] | PAN nanofiber membrane | Synthetic produced water | 0.1 | 810 |
| [29] | a-Al2O3 ceramic membrane | Synthetic produced water | 1.37 | 66 |
| [30] | Magnesium bentonite hollow fiber ceramic membrane | Synthetic produced water | 1 | 224 |
| [31] | Tubular UF module equipped with polyvinylidene fluoride and inorganic nano-sized Al2O3 | Oilfield | 1 | 170 |
| [9] | NaA zeolite/α- Al2O3 tubular ceramic membrane | Synthetic produced water | 0.5 | 85 |
| This work | Red clay tubular ceramic membrane | Synthetic produced water | 5 | 367.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljlil, S.A. Development of Red Clay Ultrafiltration Membranes for Oil-Water Separation. Crystals 2021, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030248
Aljlil SA. Development of Red Clay Ultrafiltration Membranes for Oil-Water Separation. Crystals. 2021; 11(3):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030248
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljlil, Saad A. 2021. "Development of Red Clay Ultrafiltration Membranes for Oil-Water Separation" Crystals 11, no. 3: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030248
APA StyleAljlil, S. A. (2021). Development of Red Clay Ultrafiltration Membranes for Oil-Water Separation. Crystals, 11(3), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030248





