Thermal Convection in the Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
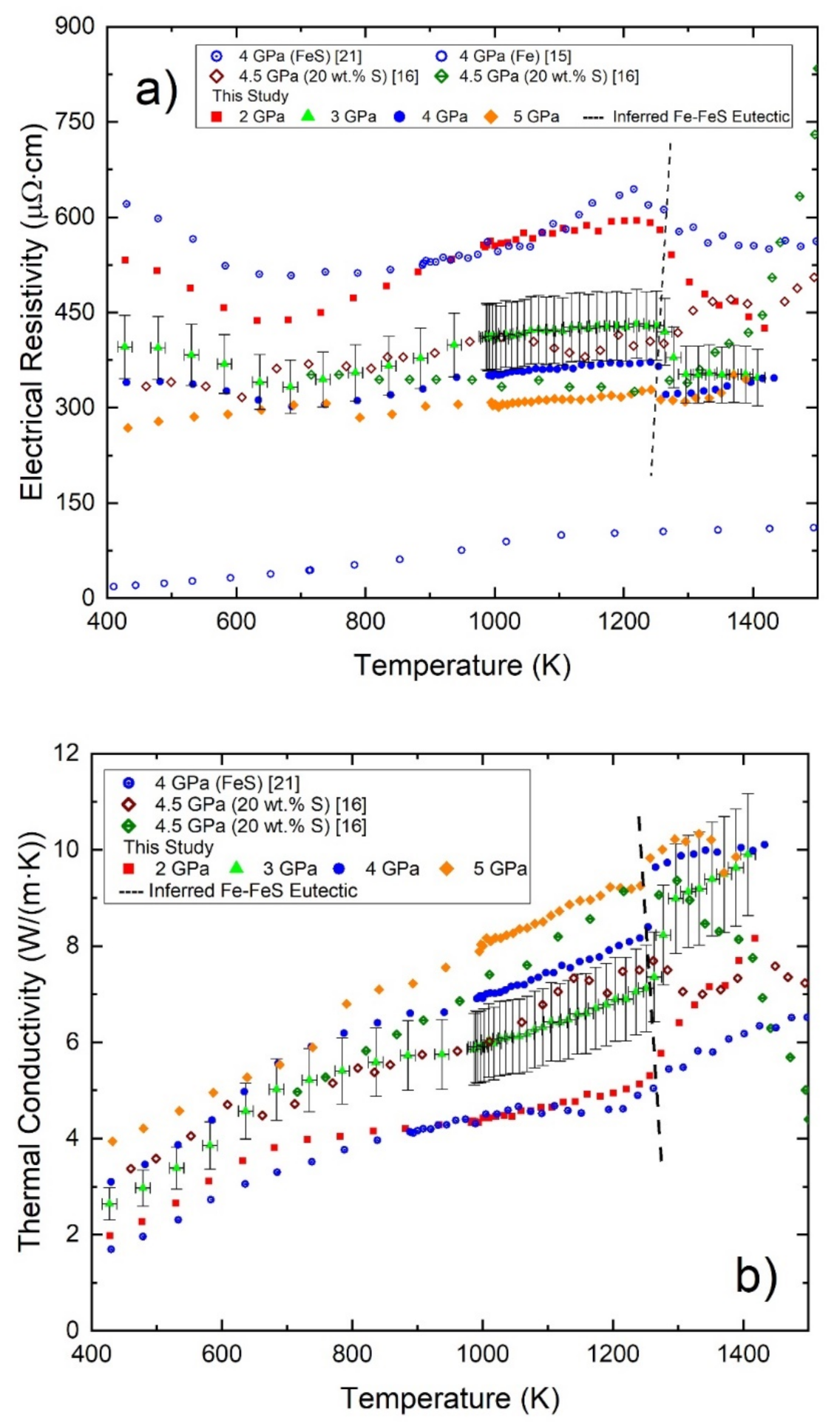
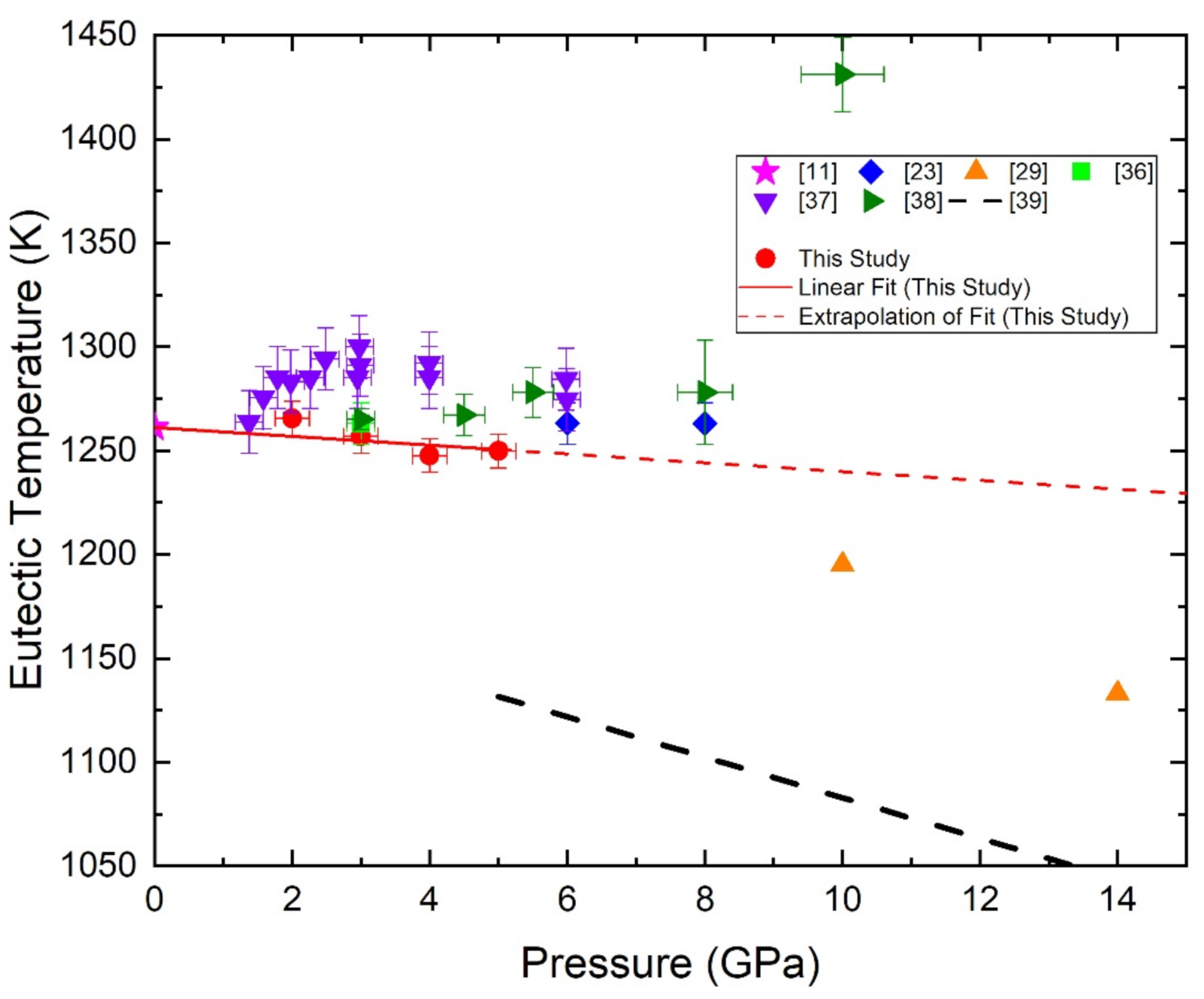
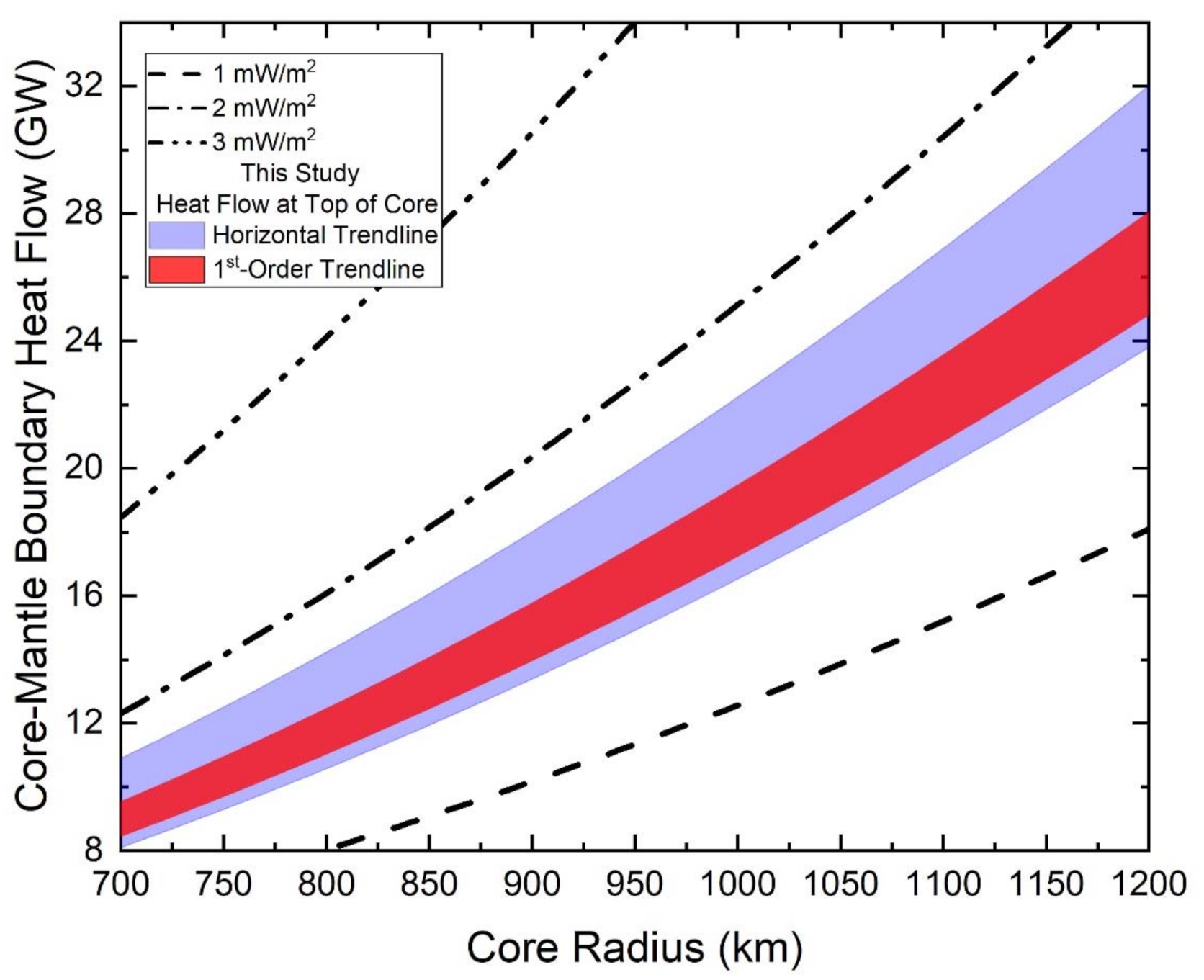
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Connerney, J.E.P. Planetary Magnetism. In Treatise on Geophysics, 1st ed.; Spohn, T., Schubert, G., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdamn, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 10, pp. 243–280. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, P. Mantle control of the geodynamo: Consequences of top-down regulation. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 1935–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauck II, S.A.; Aurnou, J.M.; Dombard, A.J. Sulfur’s impact on core evolution and magnetic field generation on Ganymede. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 2006, 111, E09008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rückriemen, T.; Breuer, D.; Spohn, T. The Fe snow regime in Ganymede’s core: A deep-seated dynamo below a stable snow zone. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 2015, 120, 1095–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rückriemen, T.; Breuer, D.; Spohn, T. Top-down freezing in a Fe-FeS core and Ganymede’s present-day magnetic field. Icarus 2018, 307, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G.; Zhang, K.; Kivelson, M.G.; Anderson, J.D. The magnetic field and internal structure of Ganymede. Nature 1996, 384, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, F.; Spohn, T.; Breuer, D.; Nagel, K. Implications from Galileo observations on the interior structure and chemistry of the Galilean satellites. Icarus 2002, 157, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.P.; Williams, Q.; Ryerson, F.J. Experimental constraints on the chemical evolution of large icy satellites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 203, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, M.T.; Showman, A.P.; Tobie, B. The production of Ganymede’s magnetic field. Icarus 2008, 198, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Nakagawa, T.; Kurita, K. Size and compositional constraints of Ganymede’s metallic core for driving an active dynamo. Icarus 2009, 202, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaschewski, I. Iron-Sulphur. In IRON—Binary Phase Diagrams; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Düsseldorf, Germany, 1982; pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, H.; Yoshino, T. Impurity resistivity of fcc and hcp Fe-based alloys: Thermal stratification at the top of the core of super-Earths. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konôpková, Z.; McWilliams, R.S.; Gómez-Pérez, N.; Goncharov, A.F. Direct measurement of thermal conductivity of solid iron at planetary core conditions. Nature 2016, 534, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Kuwayama, Y.; Hirose, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohishi, Y. Experimental determination of the electrical resistivity of iron at Earth’s core conditions. Nature 2016, 534, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, R.E.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W.; Littleton, J.A.H. Electrical resistivity of liquid Fe to 12 GPa: Implications for heat flow in cores of terrestrial bodies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommier, A. Influence of sulfur on the electrical resistivity of a crystallizing core in small terrestrial bodies. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 496, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Secco, R.A.; Littleton, J.A.H.; Silber, R.E. The iron invariance: Implications for thermal convection in Earth’s core. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11065–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.-P.; Goncharov, A.F.; Labrosse, S.; Holtgrewe, N.; Lobanov, S.S.; Chuvashova, I.; Deschamps, F.; Lin, J.-F. Low thermal conductivity of iron-silicon alloys at Earth’s core conditions with implications for the geodynamo. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezenwa, I.C.; Yoshino, T. Martian core heat flux: Electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of liquid Fe at Martian core P-T conditions. Icarus 2021, 360, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthilake, G.; Chantel, J.; Monteux, J.; Andrault, D.; Bouhifd, M.A.; Casanova, N.B.; Boulard, E.; Guignot, N.; King, A.; Itie, J.P. Thermal conductivity of FeS and its implications for Mercury’s long-sustaining magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 2019, 124, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleton, J.A.H.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W. Electrical resistivity of FeS at high pressures and temperatures: Implications of thermal transport in the core of Ganymede. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 2021, 126, e2020JE006793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskov, O.L.; Kronrod, V.A. Core sizes and internal structure of Earth’s and Jupiter’s satellites. Icarus 2001, 151, 204–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, A.S.; Walker, D. H, not O or pressures, causes eutectic T depression in the Fe-FeS system to 8 GPa. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2015, 50, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secco, R.A. High p,T physical property studies of Earth’s interior: Thermoelectric power of solid and liquid Fe up to 6.4 GPa. Can. J. Phys. 1995, 73, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleton, J.A.H.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W.; Berrada, M. Electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of W and Re up to 5 GPa and 2300 K. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 135901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, A. Experimental investigations of the effect of nickel on the electrical resistivity of Fe-Ni and Fe-Ni-S alloys under pressure. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, R.E.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W.; Littleton, J.A.H. Heat Flow in Earth’s Core From Invariant Electrical Resistivity of Fe-Si on the Melting Boundary to 9 GPa: Do Light Elements Matter? J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 5521–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada, M.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W.; Littleton, J.A.H. Electrical resistivity measurements of Fe-Si with implications for the early lunar dynamo. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 2020, 125, e2020JE006380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Bertka, C.M.; Finger, L.W. High-Pressure Iron-Sulfur Compound, Fe3S, and Melting Relations in the Fe-FeS System. Science 1997, 275, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Li, J.; Bertka, C.M.; Prewitt, C.T. Structure type and bulk modulus of Fe3S, a new iron-sulfur compound. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 1830–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fei, Y.; Mao, H.K.; Hirose, K.; Shieh, S.R. Sulfur in the Earth’s inner core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 193, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.J.; Schmidt, M.W.; van Westrenen, W.; Liebske, C. Mars: A new core-crystallization regime. Science 2007, 316, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morard, G.; Andrault, D.; Guignot, N.; Sanloup, C.; Mezouar, M.; Petitgirard, S.; Fiquet, G. In situ determination of Fe-Fe3S phase diagram and liquid structural properties up to 65 GPa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 272, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, S.; Terasaki, H.; Ohtani, E.; Sakai, T.; Kikegawa, T.; Ohishi, Y.; Hirao, N.; Sata, N.; Kondo, T. Phase relationships of the Fe-FeS system in conditions up to the Earth’s outer core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 293, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, A.; Leinenweber, K.; Tran, T. Mercury’s thermal evolution controlled by an insulating liquid outermost core? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 517, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, R.; Bell, P.M. Melting relations in the Fe-rich portion of the system Fe-FeS at 30 kb pressure. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1969, 6, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhenko, B.; Kennedy, G.C. The effect of pressure on the eutectic in the system Fe-FeS. Am. J. Sci. 1973, 273, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usselman, T.M. Experimental approach to the state of the core: Part, I. The liquidus relations of the Fe-rich portion of the Fe-Ni-S system from 30 to 100 kb. Am. J. Sci. 1975, 275, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morard, G.; Sanloup, C.; Fiquet, G.; Mezouar, M.; Rey, N.; Poloni, R.; Beck, P. Structure of eutectic Fe-FeS melts to pressures up to 17 GPa: Implications for planetary cores. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 262, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, D.; Rückriemen, T.; Spohn, T. Iron snow, crystal floats, and inner-core growth: Modes of core solidification and implications for dynamos in terrestrial planets and moons. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehler, R. Fe-FeS eutectic temperatures to 620 kbar. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1996, 96, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleton, J.A.H.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W. Thermal Convection in The Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures; [dataset]; Mendeley Data; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Version 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
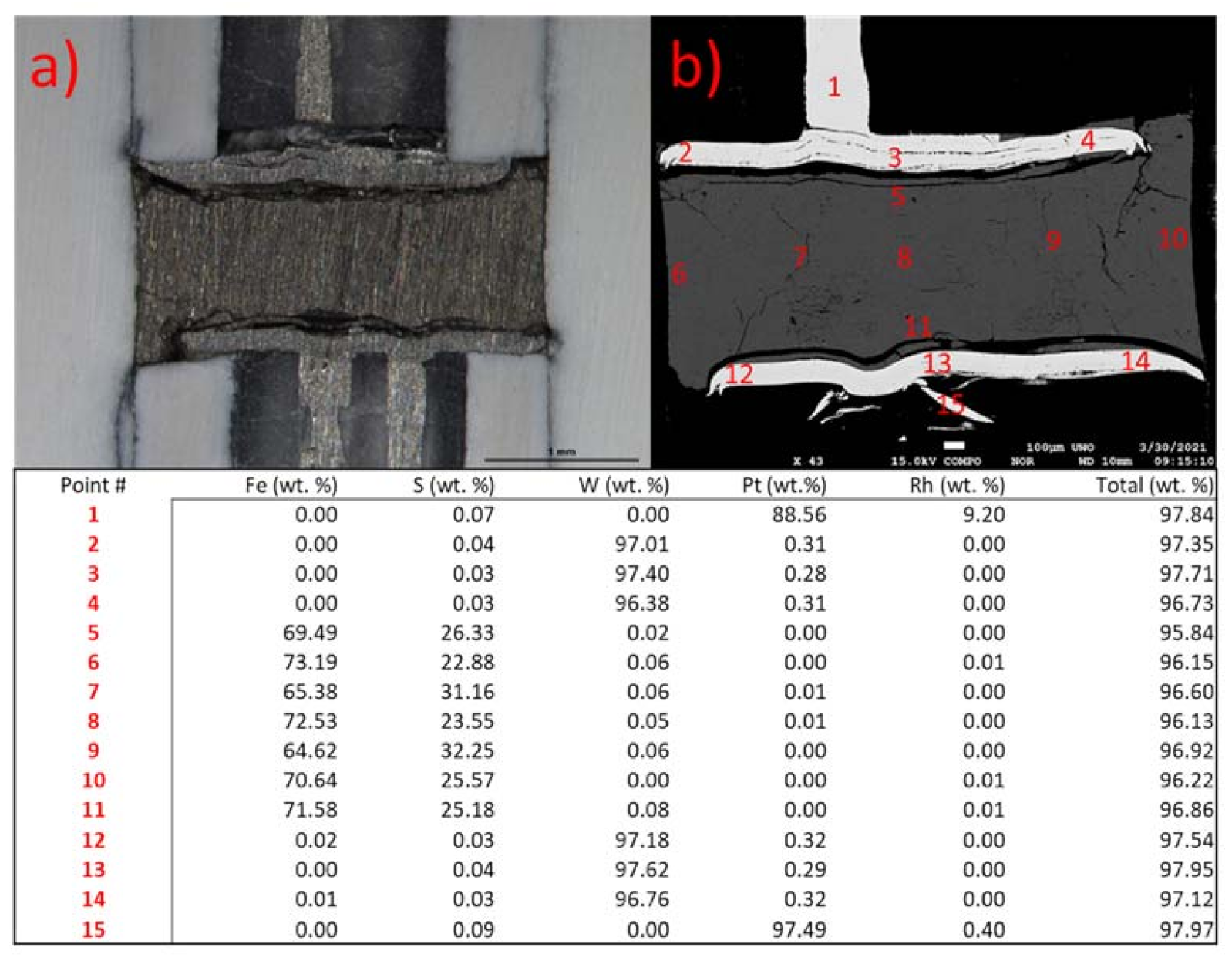

| Pressure (GPa) | Target Eutectic Composition (wt.% S) | Sample Composition (Post-Experiment) (wt.% S) | Relative Location Adjacent to Eutectic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 28.0 | 29.56 ± 0.05 | FeS-rich |
| 3 | 26.5 | 26.17 ± 0.05 | Fe-rich |
| 4 | 25.1 | 25.68 ± 0.07 | FeS-rich |
| 5 | 23.8 | 23.76 ± 0.06 | Fe-rich |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Littleton, J.A.H.; Secco, R.A.; Yong, W. Thermal Convection in the Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures. Crystals 2021, 11, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080875
Littleton JAH, Secco RA, Yong W. Thermal Convection in the Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures. Crystals. 2021; 11(8):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080875
Chicago/Turabian StyleLittleton, Joshua A. H., Richard A. Secco, and Wenjun Yong. 2021. "Thermal Convection in the Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures" Crystals 11, no. 8: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080875
APA StyleLittleton, J. A. H., Secco, R. A., & Yong, W. (2021). Thermal Convection in the Core of Ganymede Inferred from Liquid Eutectic Fe-FeS Electrical Resistivity at High Pressures. Crystals, 11(8), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080875






