Spin-Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted 2,6-Bis(Pyrazol-3-yl)Pyridines: An Effect of a Distal Substituent in the 2,6-Dibromophenyl Group
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
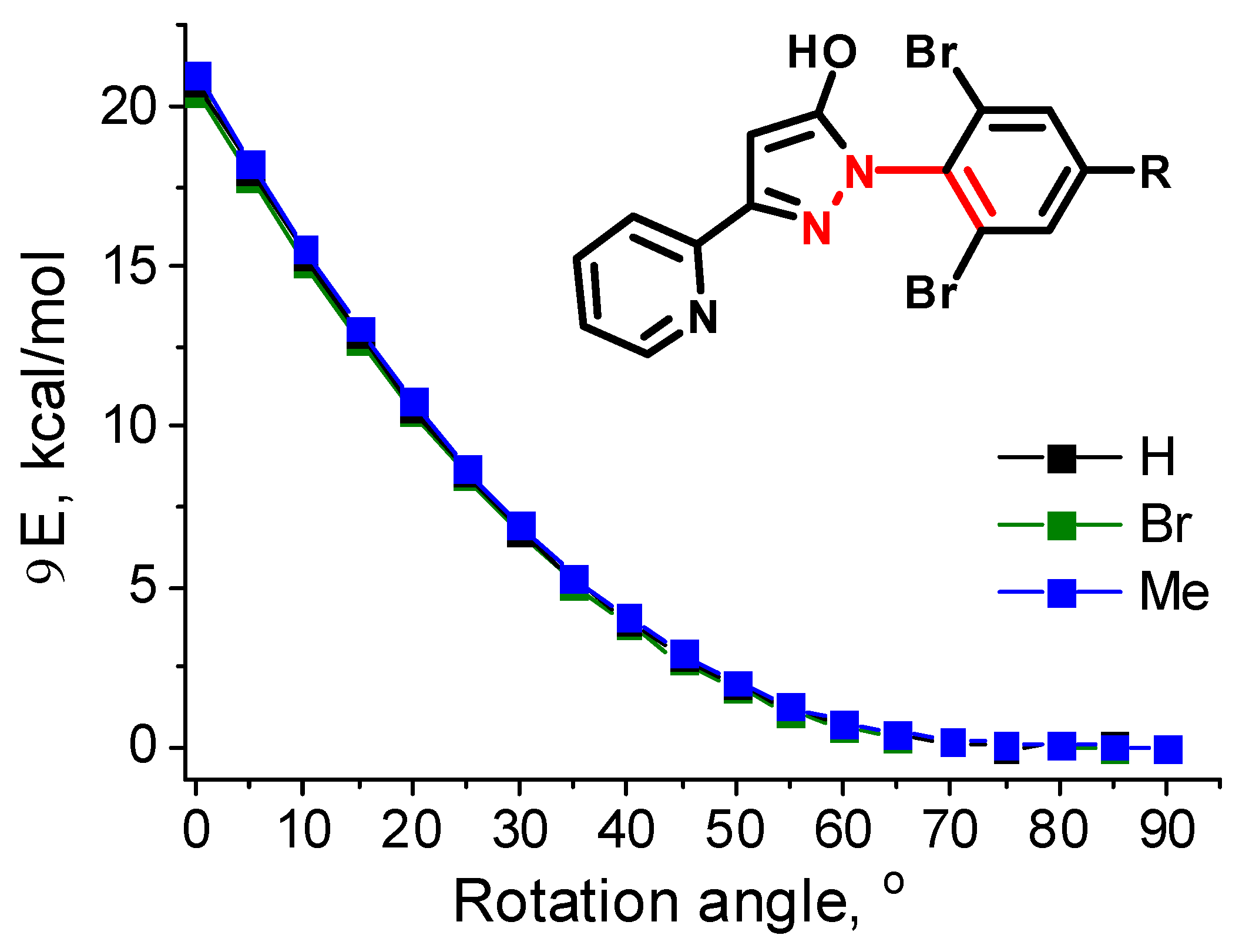
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin-Crossover Materials: Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.; Rat, S.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W.; Bousseksou, A. Spin Crossover Nanomaterials: From Fundamental Concepts to Devices. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1703862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, K.; Ruben, M. Emerging trends in spin crossover (SCO) based functional materials and devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 176–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Kröber, J.; Jay, C. Spin Transition Molecular Materials for displays and data recording. Adv. Mater. 1992, 4, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resines-Urien, E.; Burzurí, E.; Fernandez-Bartolome, E.; García García-Tuñón, M.Á.; de la Presa, P.; Poloni, R.; Teat, S.J.; Costa, J.S. A switchable iron-based coordination polymer toward reversible acetonitrile electro-optical readout. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6612–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linares, J.; Codjovi, E.; Garcia, Y. Pressure and Temperature Spin Crossover Sensors with Optical Detection. Sensors 2012, 12, 4479–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalva, J.; Develioglu, A.; Montenegro-Pohlhammer, N.; Sánchez-de-Armas, R.; Gamonal, A.; Rial, E.; García-Hernández, M.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, L.; Costa, J.S.; Calzado, C.J.; et al. Spin-state-dependent electrical conductivity in single-walled carbon nanotubes encapsulating spin-crossover molecules. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, A.E.; Gaudette, A.I.; Harris, T.D. Spin-crossover and high-spin iron(ii) complexes as chemical shift (19)F magnetic resonance thermometers. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukiashi, A.; Min, K.S.; Kitayama, H.; Terasawa, H.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takeda, M.; Lindoy, L.F.; Hayami, S. Application of spin-crossover water soluble nanoparticles for use as MRI contrast agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P.; Le Gac, F.; Kaiba, A.; Costa, J.S.; Chasseau, D.; Létard, J.-F. A reversible metal–ligand bond break associated to a spin-crossover. Chem. Commun. 2007, 36, 3723–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guionneau, P.; Costa, J.S.; Létard, J.F. Revisited crystal symmetry of the high-spin form of the iron(II) spin-crossover complex dicyano[2,13-dimethyl-6,9-dioxa-3,12,18-triazabicyclo[12.3.1]octadeca-1(18),2,12,14,16-pentaene]iron(II) monohydrate. Acta Cryst. C 2004, 60, m587–m589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halcrow, M.A. The Effect of Ligand Design on Metal Ion Spin State—Lessons from Spin Crossover Complexes. Crystals 2016, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Hrudka, J.J.; Igimbayeva, D.; Lawson Daku, L.M.; Shatruk, M. A Simple Approach for Predicting the Spin State of Homoleptic Fe(II) Tris-diimine Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6437–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Jiménez, S.; Yang, M.; Stewart, I.; Garden, A.L.; Brooker, S. A Simple Method of Predicting Spin State in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18392–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Ishida, T. Spin-Crossover Temperature Predictable from DFT Calculation for Iron(II) Complexes with 4-Substituted Pybox and Related Heteroaromatic Ligands. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6737–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw Cook, L.J.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Mohammed, R.; Dudley, S.; Barrett, S.A.; Little, M.A.; Deeth, R.; Halcrow, M.A. A Unified Treatment of the Relationship Between Ligand Substituents and Spin State in a Family of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4327–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaïk, J.; Evans, D.J.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. A structural, magnetic and Mössbauer spectroscopic study of an unusual angular Jahn–Teller distortion in a series of high-spin iron(ii) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2005, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, J.N.; Elton, T.E.; Colbran, S.B. A Strain-Deformation Nexus within Pincer Ligands: Application to the Spin States of Iron(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12312–12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Kershaw Cook, L.J.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Barrett, S.A.; Cespedes, O.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) Complexes of Tridentate Indazolylpyridine Ligands: Enhanced Spin-Crossover Hysteresis and Ligand-Based Fluorescence. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Suemura, N.; Yoneda, K.; Kawata, S.; Kaizaki, S. Substituent effect of the coordinated pyridine in a series of pyrazolato bridged dinuclear diiron(ii) complexes on the spin-crossover behavior. Dalton Trans. 2005, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, J.A.; Olguín, J.; Kulmaczewski, R.; White, N.G.; Milway, V.A.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Tallon, J.L.; Brooker, S. Effect of N4-Substituent Choice on Spin Crossover in Dinuclear Iron(II) Complexes of Bis-Terdentate 1,2,4-Triazole-Based Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 11185–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoselton, M.A.; Wilson, L.J.; Drago, R.S. Substituent effects on the spin equilibrium observed with hexadentate ligands on iron(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw Cook, L.; Mohammed, R.; Sherborne, G.; Roberts, T.D.; Alvarez, S.; Halcrow, M.A. Spin state behavior of iron(II)/dipyrazolylpyridine complexes. New insights from crystallographic and solution measurements. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.A.; Costa, J.S.; Roubeau, O.; Teat, S.J.; Aromí, G. Local Coordination Geometry and Spin State in Novel FeII Complexes with 2,6-Bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-Type Ligands as Controlled by Packing Forces: Structural Correlations. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 11703–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, S.; Zhang, X.; Mu, S.; Naim, A.; Rosa, P.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.F.; Liu, J.; Sterbinsky, G.E.; Arena, D.A.; et al. Surface-induced spin state locking of the [Fe(H2B(pz)2)2(bipy)] spin crossover complex. J. Phys. Condensed Mat. 2016, 28, 206002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, D.; Liscio, F.; Demitri, N.; Schäfer, B.; Borgatti, F.; Torelli, P.; Gobaut, B.; Panaccione, G.; Rossi, G.; Degli Esposti, A.; et al. Surface induces different crystal structures in a room temperature switchable spin crossover compound. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikovskiy, I.; Polezhaev, A.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Aleshin, D.; Pavlov, A.A.; Saffiulina, E.; Aysin, R.R.; Dorovatovskii, P.; Nodaraki, L.; Tuna, F.; et al. Towards molecular design of spin-crossover complexes of 2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridines. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 5629–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.A.; Roubeau, O.; Aromí, G. Spin state switching in 2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine (3-bpp) based Fe(II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 269, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudder, M.L.; Craig, D.C.; Goodwin, H.A. Hydrogen bonding influences on the properties of heavily hydrated chloride salts of iron(ii) and ruthenium(ii) complexes of 2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine, 2,6-bis(1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine and 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine. CrystEngComm 2005, 7, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; Giménez-López, M.C.; Romero, F.M. Structural, Thermal, and Magnetic Study of Solvation Processes in Spin-Crossover [Fe(bpp)2][Cr(L)(ox)2]2·nH2O Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 11266–11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Gimenez-Lopez, M.C.; Gimenez-Saiz, C.; Romero, F.M. Spin crossover complexes as building units of hydrogen-bonded nanoporous structures. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 2198–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartual-Murgui, C.; Codina, C.; Roubeau, O.; Aromí, G. A Sequential Method to Prepare Polymorphs and Solvatomorphs of [Fe(1,3-bpp)2](ClO4)2⋅nH2O (n = 0, 1, 2) with Varying Spin-Crossover Behaviour. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12767–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jornet-Molla, V.; Gimenez-Saiz, C.; Romero, F.M. Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions. Crystals 2018, 8, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, S.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Anion-dependent spin crossover in solution for an iron(ii) complex of a 1H-pyrazolyl ligand. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 11240–11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.A.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Spin-crossover in [Fe(3-bpp)2][BF4]2 in different solvents—A dramatic stabilisation of the low-spin state in water. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 12021–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.D.; Little, M.A.; Kershaw Cook, L.J.; Barrett, S.A.; Tuna, F.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) complexes of 2,6-di(1-alkylpyrazol-3-yl)pyridine derivatives—The influence of distal substituents on the spin state of the iron centre. Polyhedron 2013, 64, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelyubina, Y.V.; Polezhaev, A.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Aleshin, D.; Savkina, S.A.; Efimov, N.N.; Aliev, T.; Novikov, V.V. Intramolecular Spin State Locking in Iron(II) 2,6-Di(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine Complexes by Phenyl Groups: An Experimental Study. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argent, S.P.; Adams, H.; Harding, L.P.; Riis-Johannessen, T.; Jeffery, J.C.; Ward, M.D. Homo- and heteropolynuclear helicates with a ‘2 + 3 + 2′-dentate compartmental ligand. New J. Chem. 2005, 29, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, L.A.; Bartual-Murgui, C.; Peyrecave-Lleixa, E.; Le Guennic, B.; Teat, S.J.; Roubeau, O.; Aromi, G. Homoleptic versus Heteroleptic Formation of Mononuclear Fe(II) Complexes with Tris-Imine Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratova, Y.; Aleshin, D.; Nikovskiy, I.; Novikov, V.; Nelyubina, Y. In Situ NMR Search for Spin-Crossover in Heteroleptic Cobalt(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 7700–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polezhaev, A.V.; Chen, C.-H.; Kinne, A.S.; Cabelof, A.C.; Lord, R.L.; Caulton, K.G. Ligand Design toward Multifunctional Substrate Reductive Transformations. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 9505–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yan, W.; Cao, L.-L.; Ye, Y.-H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzimidazole Phenylhydrazone Derivatives as Antifungal Agents against Phytopathogenic Fungi. Molecules 2016, 21, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.H.; Hong, J.S.; Hunter, R.N.; Orr, G.F.; Cowan, J.R.; Sherman, D.B.; Sparks, S.M.; Reitter, B.E.; Andrews, C.W.; Hazen, R.J.; et al. 2-Amino-6-arylsulfonylbenzonitriles as Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors of HIV-1. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1866–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delany, E.G.; Connon, S.J. Highly chemoselective intermolecular cross-benzoin reactions using an ad hoc designed novel N-heterocyclic carbene catalyst. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhead, M.; Shen, D.; Chan, L.K.M.; Lowe, E.D.; Donohoe, T.J.; Howarth, M. Love–Hate ligands for high resolution analysis of strain in ultra-stable protein/small molecule interaction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT–Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bain, G.A.; Berry, J.F. Diamagnetic Corrections and Pascal’s Constants. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, N.F.; Anderson, R.P.; Turner, L.D.; Soncini, A.; Murray, K.S. Phi: A Powerful New Program for the Analysis of Anisotropic Monomeric and Exchange-Coupled Polynuclear D- and F-Block Complexes. J. Comp. Chem. 2013, 34, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F. The determination of the paramagnetic susceptibility of substances in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Chem. Soc. 1959, 2003–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, C. Paramagnetic Susceptibility by NMR: The “Solvent Correction” Removed for Large Paramagnetic Molecules. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.A.; Nehrkorn, J.; Pankratova, Y.A.; Ozerov, M.; Mikhalyova, E.A.; Polezhaev, A.V.; Nelyubina, Y.V.; Novikov, V.V. Detailed electronic structure of a high-spin cobalt(ii) complex determined from NMR and THz-EPR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8201–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Walker, F.A. Solution NMR studies of iron(II) spin-crossover complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 6794–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutz, S.E.; Peters, J.C. Spin-State Tuning at Pseudo-tetrahedral d6 Ions: Spin Crossover in [BP3]FeII–X Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 3894–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system, version 4.0. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Perdew, J.P.; Staroverov, V.N.; Scuseria, G.E. Climbing the Density Functional Ladder: Nonempirical Meta--Generalized Gradient Approximation Designed for Molecules and Solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 146401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staroverov, V.N.; Scuseria, G.E.; Tao, J.; Perdew, J.P. Comparative assessment of a new nonempirical density functional: Molecules and hydrogen-bonded complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 12129–12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroverov, V.N.; Scuseria, G.E.; Tao, J.; Perdew, J.P. Erratum: “Comparative assessment of a new nonempirical density functional: Molecules and hydrogen-bonded complexes” [J. Chem. Phys. 119, 12129 (2003)]. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirera, J.; Via-Nadal, M.; Ruiz, E. Benchmarking Density Functional Methods for Calculation of State Energies of First Row Spin-Crossover Molecules. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 14097–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neese, F. An improvement of the resolution of the identity approximation for the formation of the Coulomb matrix. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.A.; Aleshin, D.Y.; Nikovskiy, I.A.; Polezhaev, A.V.; Efimov, N.N.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Novikov, V.V.; Nelyubina, Y.V. New Spin-Crossover Complexes of Substituted 2,6-Bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridines. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2819–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, H.; Djomgoue, P.; Hörner, G.; Lochenie, C.; Weber, B.; Rüffer, T. Bis-meridional Fe2+ spincrossover complexes of phenyl and pyridyl substituted 2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,10-phenanthrolines. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.A.; Denisov, G.L.; Kiskin, M.A.; Nelyubina, Y.V.; Novikov, V.V. Probing Spin Crossover in a Solution by Paramagnetic NMR Spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 14759–14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadzhun, I.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Cespedes, O.; Yamada, M.; Yoshinari, N.; Konno, T.; Halcrow, M.A. 2,6-Bis(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine-4-carboxylate Esters with Alkyl Chain Substituents and Their Iron(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 13761–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, H.L. New Atom/Functional Group Volume Additivity Data Bases for the Calculation of the Crystal Densities of C-, H-, N-, O-, F-, S-, P-, Cl-, and Br-Containing Compounds. Struct. Chem. 2001, 12, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartual-Murgui, C.; Vela, S.; Roubeau, O.; Aromi, G. Designed intramolecular blocking of the spin crossover of an Fe(ii) complex. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 14058–14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, S. Distortion Pathways of Transition Metal Coordination Polyhedra Induced by Chelating Topology. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13447–13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, S.E. Understanding Substituent Effects in Noncovalent Interactions Involving Aromatic Rings. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) complexes of 2,6-di(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridines—A versatile system for spin-crossover research. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2493–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudder, M.L.; Goodwin, H.A.; Dance, I.G. Crystal supramolecular motifs: Two-dimensional grids of terpy embraces in [ML2] complexes (L = terpy or aromatic N3-tridentate ligand). New J. Chem. 1999, 23, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, R.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(ii) complexes with a terpyridine embrace packing motif show remarkably consistent cooperative spin-transitions. Chem. Commun. 2007, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. The Halogen Bond. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinnon, J.J.; Mitchell, A.S.; Spackman, M.A. Hirshfeld Surfaces: A New Tool for Visualising and Exploring Molecular Crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A.; Jayatilaka, D. Hirshfeld surface analysis. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A.; McKinnon, J.J. Fingerprinting intermolecular interactions in molecular crystals. CrystEngComm 2002, 4, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Turner, M.J.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. CrystalExplorer (Version 3.1); University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berdiell, I.C.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Shahid, N.; Cespedes, O.; Halcrow, M.A. The number and shape of lattice solvent molecules controls spin-crossover in an isomorphous series of crystalline solvate salts. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 6566–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw Cook, L.J.; Thorp-Greenwood, F.L.; Comyn, T.P.; Cespedes, O.; Chastanet, G.; Halcrow, M.A. Unexpected Spin-Crossover and a Low-Pressure Phase Change in an Iron(II)/Dipyrazolylpyridine Complex Exhibiting a High-Spin Jahn–Teller Distortion. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 6319–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kamihata, H.; Lee, Y.H. Spin-crossover in cobalt(II) compounds containing terpyridine and its derivatives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbow, T.J.; Fettinger, J.C.; Berben, L.A. Control of Ligand pKa Values Tunes the Electrocatalytic Dihydrogen Evolution Mechanism in a Redox-Active Aluminum(III) Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8651–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabel, D.; Schubert, A.; Wolmershäuser, G.; Jones Jr, R.L.; Thiel, W.R. Iron and Cobalt Complexes of Tridentate N-Donor Ligands in Ethylene Polymerization: Efficient Shielding of the Active Sites by Simple Phenyl Groups. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 3648–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.J.; Chen, C.-H.; Pink, M.; Lord, R.L.; Caulton, K.G. Coordination and electronic characteristics of a nitrogen heterocycle pincer ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 451, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.M.; Barrett, S.A.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Control of the spin state of Fe(II) 2,6-di(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine complexes by distal ligand substitution. Inorg. Chem. Comm. 2002, 5, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, R.J.; Halcrow, M.A.; Kershaw Cook, L.J.; Raithby, P.R. Ab Initio Ligand Field Molecular Mechanics and the Nature of Metal-Ligand π-Bonding in Fe(II) 2,6-di(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine Spin Crossover Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 5204–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
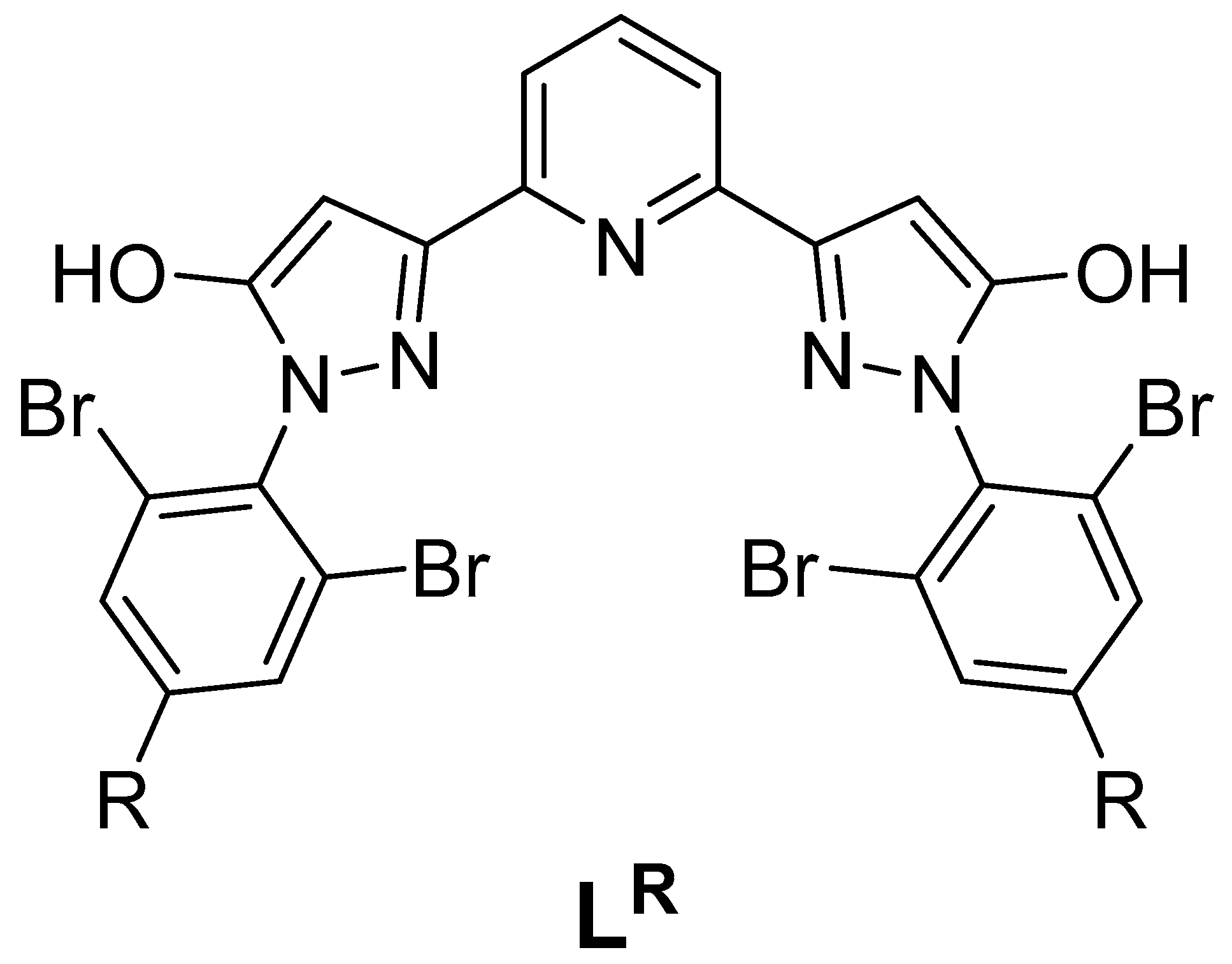
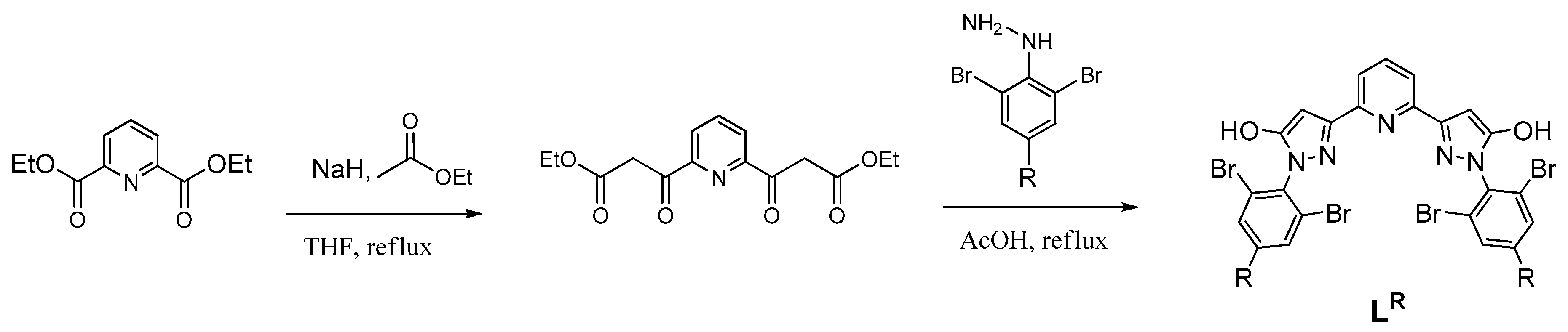


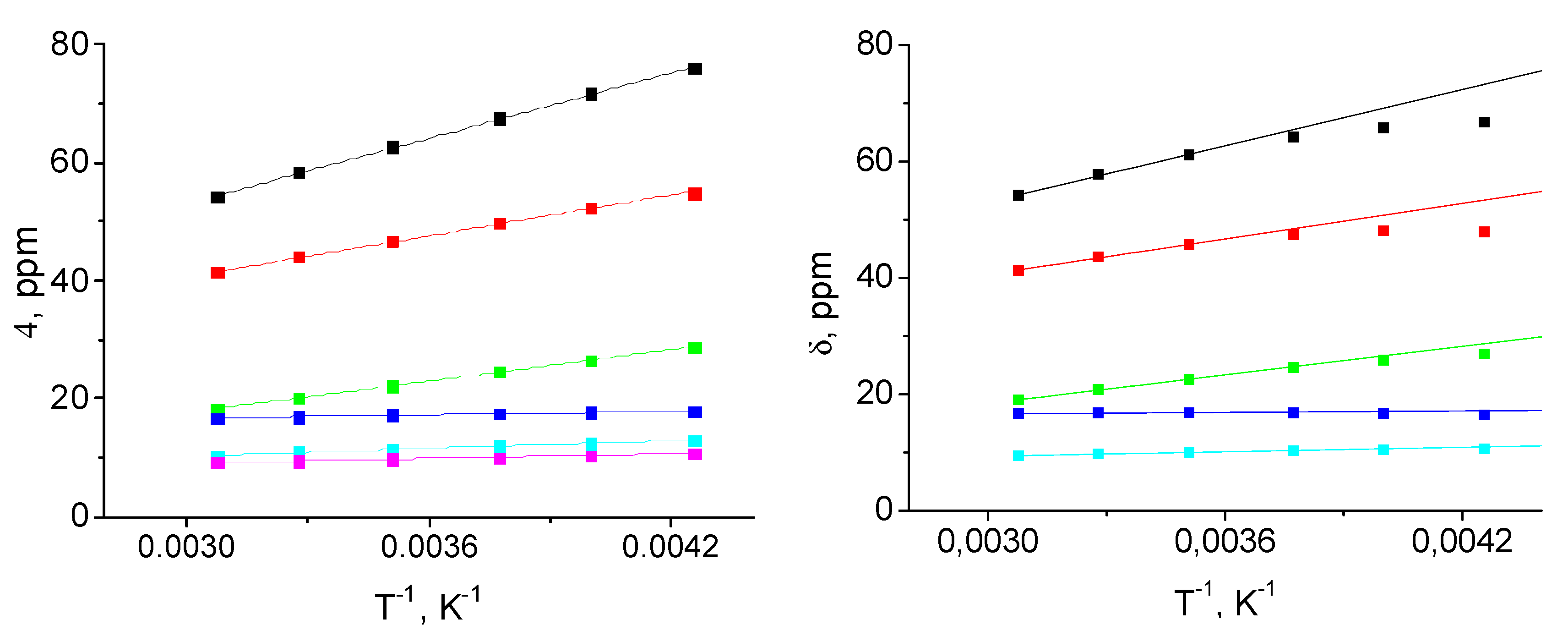
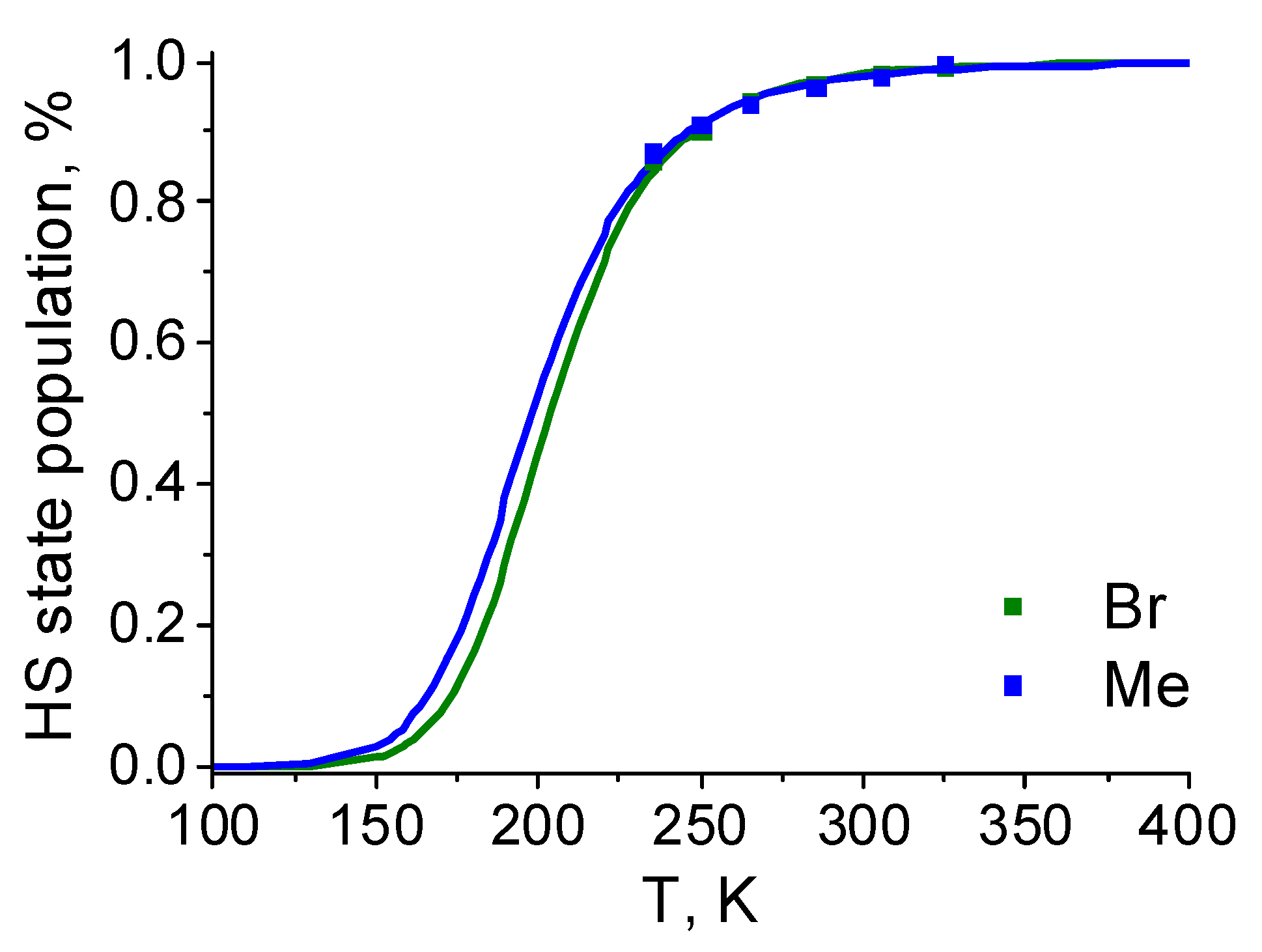



| Parameter | [Fe(LH)2](ClO4)2 | [Fe(LBr)2](ClO4)2 | [Fe(LMe)2](ClO4)2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula unit | 2C46H26Br8FeN10O4, 4ClO4, 11C4H8O | 2C46H22Br12FeN10O4, 4ClO4, 11C4H8O, 4H2O | C50H34Br8FeN10O4, 4ClO4, 2C4H10O, 2CH3CN |
| Formula weight | 4146.70 | 4850.01 | 1963.25 |
| T, K | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | C2/c | P21/c | P21/c |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| a, Å | 34.797(3) | 15.914(2) | 15.4750(3) |
| b, Å | 12.9466(10) | 17.779(2) | 18.6741(4) |
| c, Å | 23.6896(18) | 30.696(4) | 24.7555(5) |
| β, ° | 131.9720(10) | 102.245(2) | 90.3160(10) |
| V, Å3 | 7934.5(11) | 8487.4(18) | 7153.8(3) |
| Dcalc (g cm−1) | 1.736 | 1.898 | 1.823 |
| Linear absorption, μ (cm−1) | 43.57 | 59.62 | 82.10 |
| F(000) | 4108 | 4736 | 3872 |
| 2Θmax, ° | 58 | 54 | 135 |
| Reflections measured | 89,248 | 89,299 | 100,303 |
| Independent reflections | 10,553 | 18,529 | 12,778 |
| Observed reflections [I > 2σ(I)] | 8445 | 8377 | 11,985 |
| Parameters | 504 | 1026 | 952 |
| R1 | 0.0749 | 0.1152 | 0.0437 |
| wR2 | 0.1667 | 0.3278 | 0.1086 |
| GOF | 1.044 | 1.083 | 1.055 |
| Δρmax/Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.760/−1.551 | 1.822/−1.055 | 0.868/−0.673 |
| Parameter | [Fe(LBr)2](ClO4)2 | [Fe(LMe)2](ClO4)2 |
|---|---|---|
| T1/2, K | 198 | 205 |
| ∆H, kJ/mol | 18.7 | 21.1 |
| ∆S, J/mol | 94.3 | 103.8 |
| Parameter | [Fe(LH)2](ClO4)2 | [Fe(LBr)2](ClO4)2 | [Fe(LMe)2](ClO4)2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-NPy, Å | 2.098(5) | 2.071(13)–2.123(12) | 2.105(5)–2.109(5) |
| Fe-NPz, Å | 2.242(5), 2.262(5) | 2.208(12)–2.277(13) | 2.225(5)–2.266(5) |
| Npz…Npz, Å | 4.340(9) | 4.303(18), 4.38(2) | 4.311(6), 4.417(7) |
| NpzNpyNpz, ° | 110.6(3) | 109.4(6), 112.5(6) | 110.5(2), 111.9(2) |
| θ,° | 82.43(10) | 81.64(13) | 81.58(10) |
| φ,° | 166.5(3) | 167.0(5) | 166.31(18) |
| γ,° | 82.9(3), 83.4(4) av. 83.1 | 82.8(6), 82.2(7), 78.0(7), 81.8(7) av. 81.2 | 79.8(2), 81.2(2), 77.1(2), 77.2(2) av. 78.8 |
| β,° | 15.0(3), 2.3(3) | 11.8(6), 2.4(7), 12.8(6), 3.1(6) | 14.7(2), 3.2(2), 8.5(2), 4.3(2) |
| S(Oh) | 5.473 | 5.534 | 5.840 |
| S(ebcT) | 10.379 | 10.264 | 10.192 |
| Br…Br, Å | 3.615(2), 3.690(4), 3.904(19), 3.7094(13) | 3.808(3), 3.579(3), 3.804(3), 3.630(3) | 3.5644(9), 3.8028(10), 3.6351(11), 3.7500(11) |
| Parameter | LH | LBr | LMe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-NPy, Å | 4.794 | 5.085 | 5.002 |
| Fe-NPz, Å | 2.795/2.771 | 2.811/2.902 | 2.763/2.893 |
| Npz…Npz, Å | 118.9 | 125.7 | 124.4 |
| Npy…Npz, Å | −0.22 | −0.22 | −0.22 |
| NpzNpyNpz, ° | −0.37 | −0.38 | −0.37 |
| q(NPz), e | 81.1/88.9 | 84.7/75.7 | 80.8/81.2 |
| q(NPy), e | 4.5/19.2 | 15.5/36.0 | 12.2/39.8 |
| γ,° | 4.794 | 5.085 | 5.002 |
| β,° | 2.795/2.771 | 2.811/2.902 | 2.763/2.893 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikovskiy, I.A.; Polezhaev, A.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Aleshin, D.Y.; Aysin, R.R.; Melnikova, E.K.; Carrella, L.M.; Rentschler, E.; Nelyubina, Y.V. Spin-Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted 2,6-Bis(Pyrazol-3-yl)Pyridines: An Effect of a Distal Substituent in the 2,6-Dibromophenyl Group. Crystals 2021, 11, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080922
Nikovskiy IA, Polezhaev AV, Novikov VV, Aleshin DY, Aysin RR, Melnikova EK, Carrella LM, Rentschler E, Nelyubina YV. Spin-Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted 2,6-Bis(Pyrazol-3-yl)Pyridines: An Effect of a Distal Substituent in the 2,6-Dibromophenyl Group. Crystals. 2021; 11(8):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080922
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikovskiy, Igor A., Alexander V. Polezhaev, Valentin V. Novikov, Dmitry Yu. Aleshin, Rinat R. Aysin, Elizaveta K. Melnikova, Luca M. Carrella, Eva Rentschler, and Yulia V. Nelyubina. 2021. "Spin-Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted 2,6-Bis(Pyrazol-3-yl)Pyridines: An Effect of a Distal Substituent in the 2,6-Dibromophenyl Group" Crystals 11, no. 8: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080922
APA StyleNikovskiy, I. A., Polezhaev, A. V., Novikov, V. V., Aleshin, D. Y., Aysin, R. R., Melnikova, E. K., Carrella, L. M., Rentschler, E., & Nelyubina, Y. V. (2021). Spin-Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted 2,6-Bis(Pyrazol-3-yl)Pyridines: An Effect of a Distal Substituent in the 2,6-Dibromophenyl Group. Crystals, 11(8), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080922







