Influence of High-Concentration LLDPE on the Manufacturing Process and Morphology of Pitch/LLDPE Fibres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
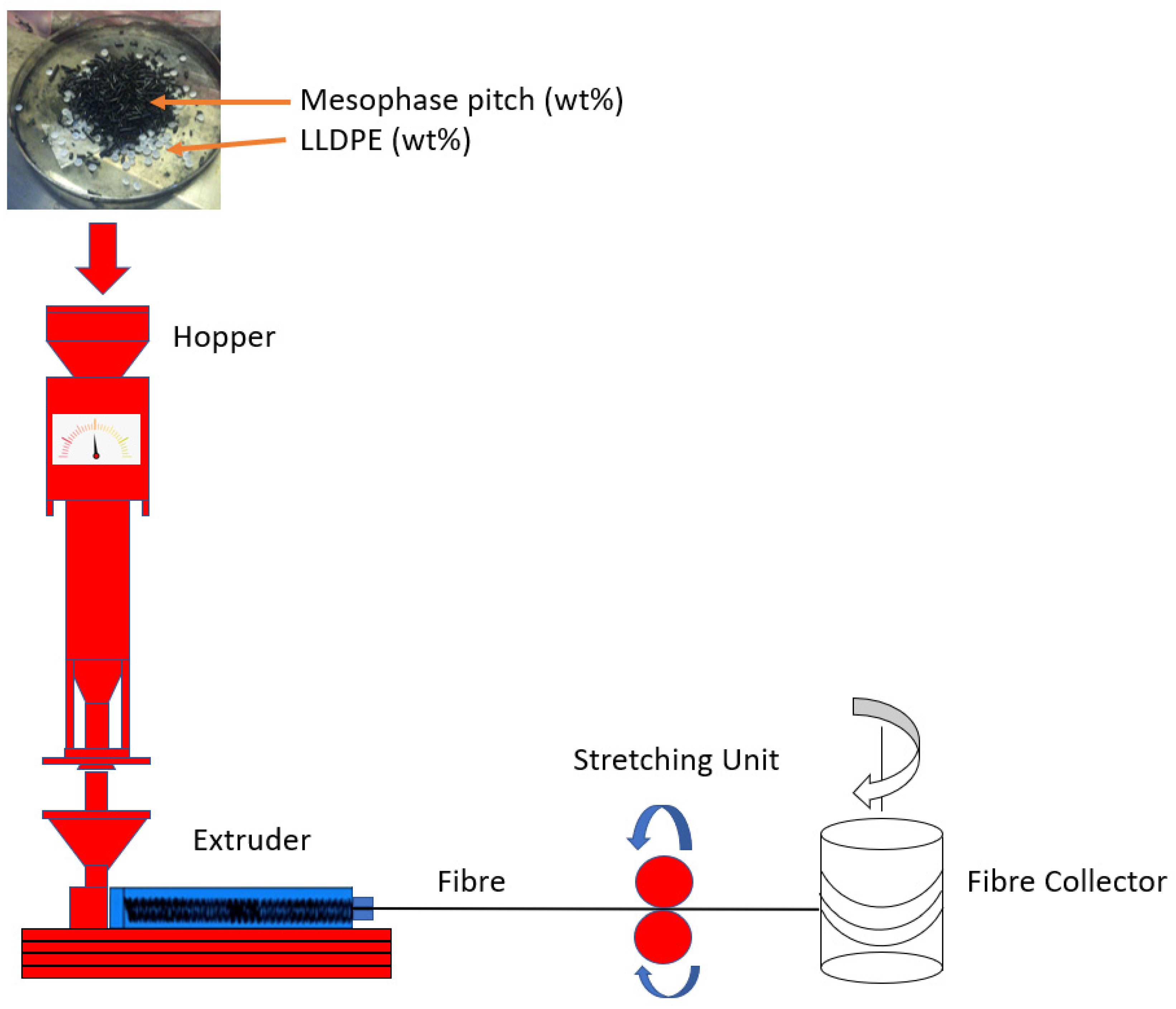
2.2. Materials Processing
3. Characterisation Methods
3.1. Microscopy: Optical and SEM
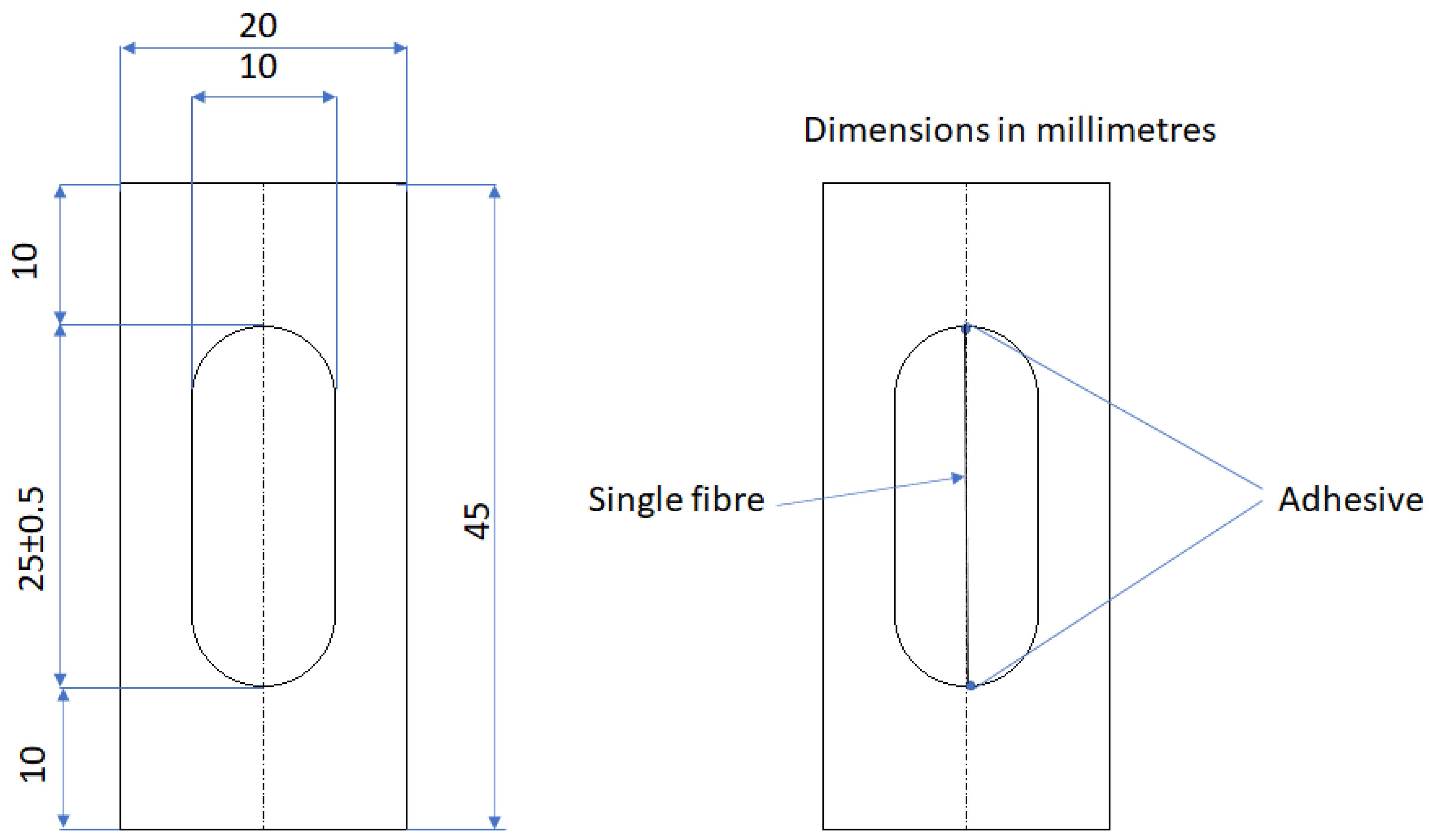
3.2. Tensile Mechanical Test
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
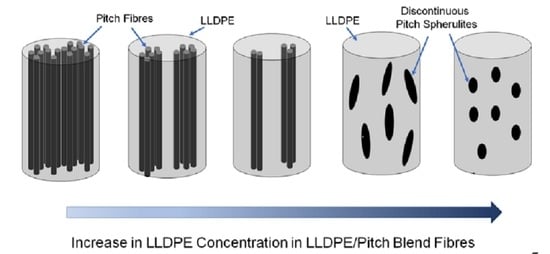
4.1. Optical Microscopy
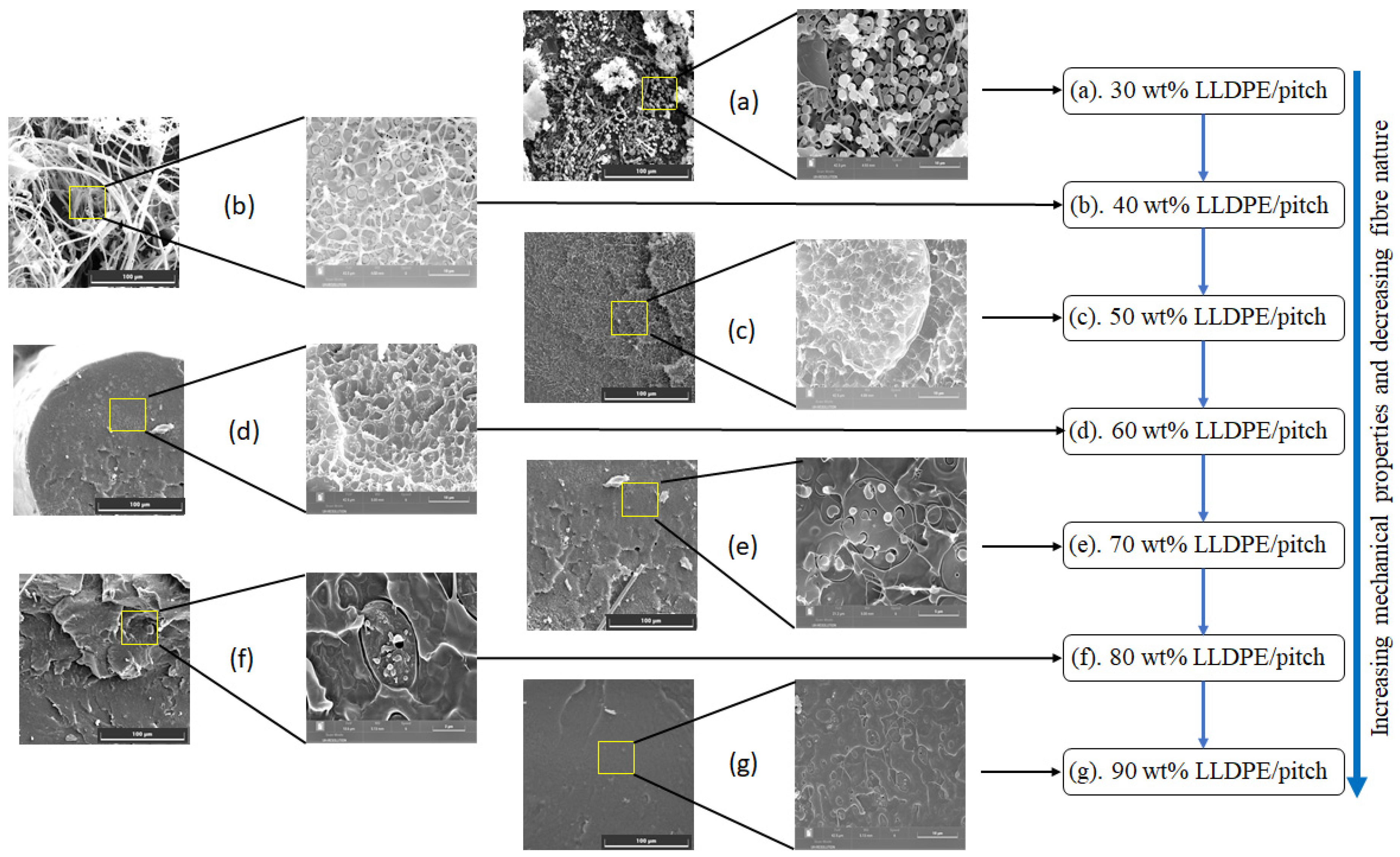
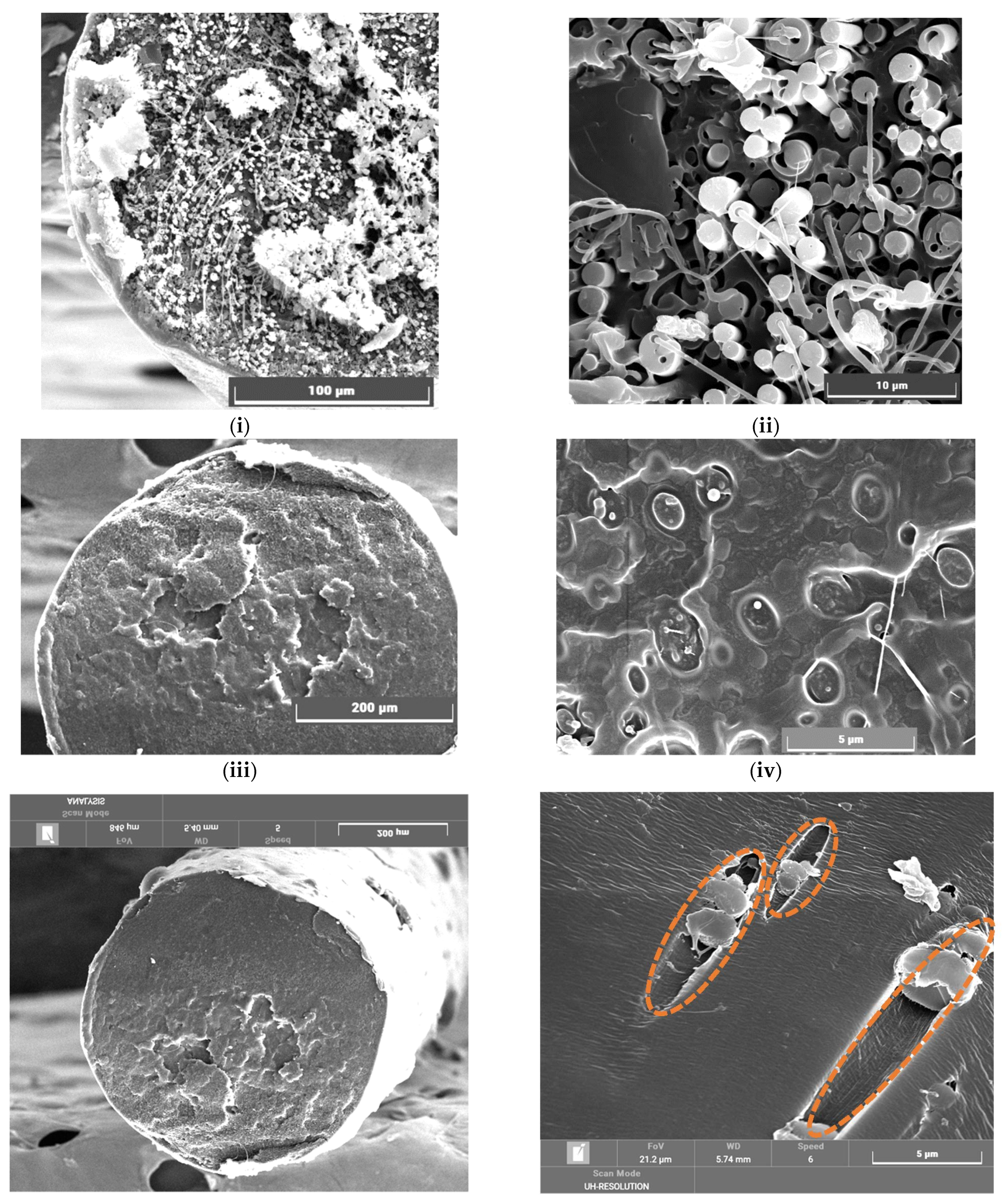
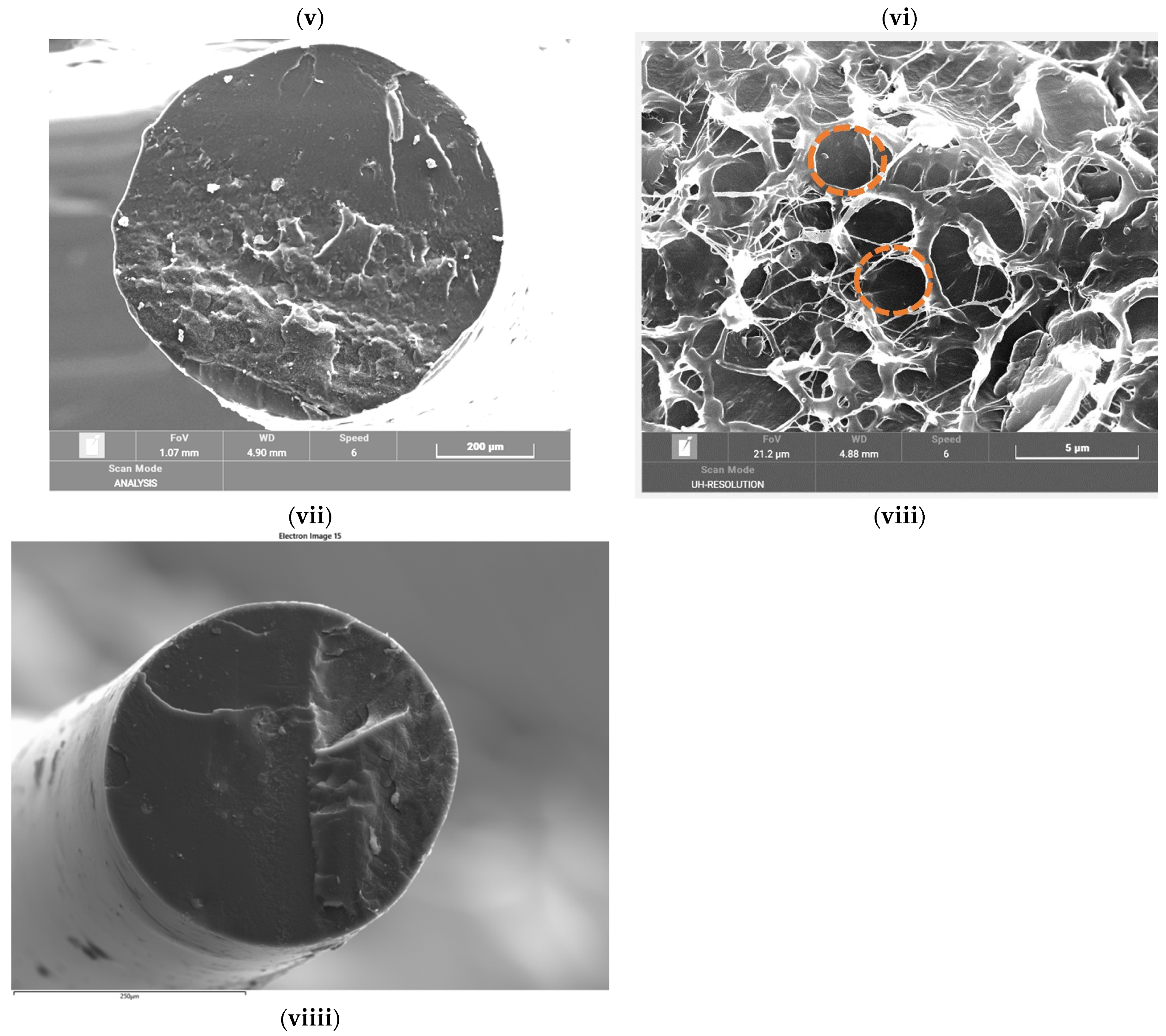
4.2. SEM of Fibres
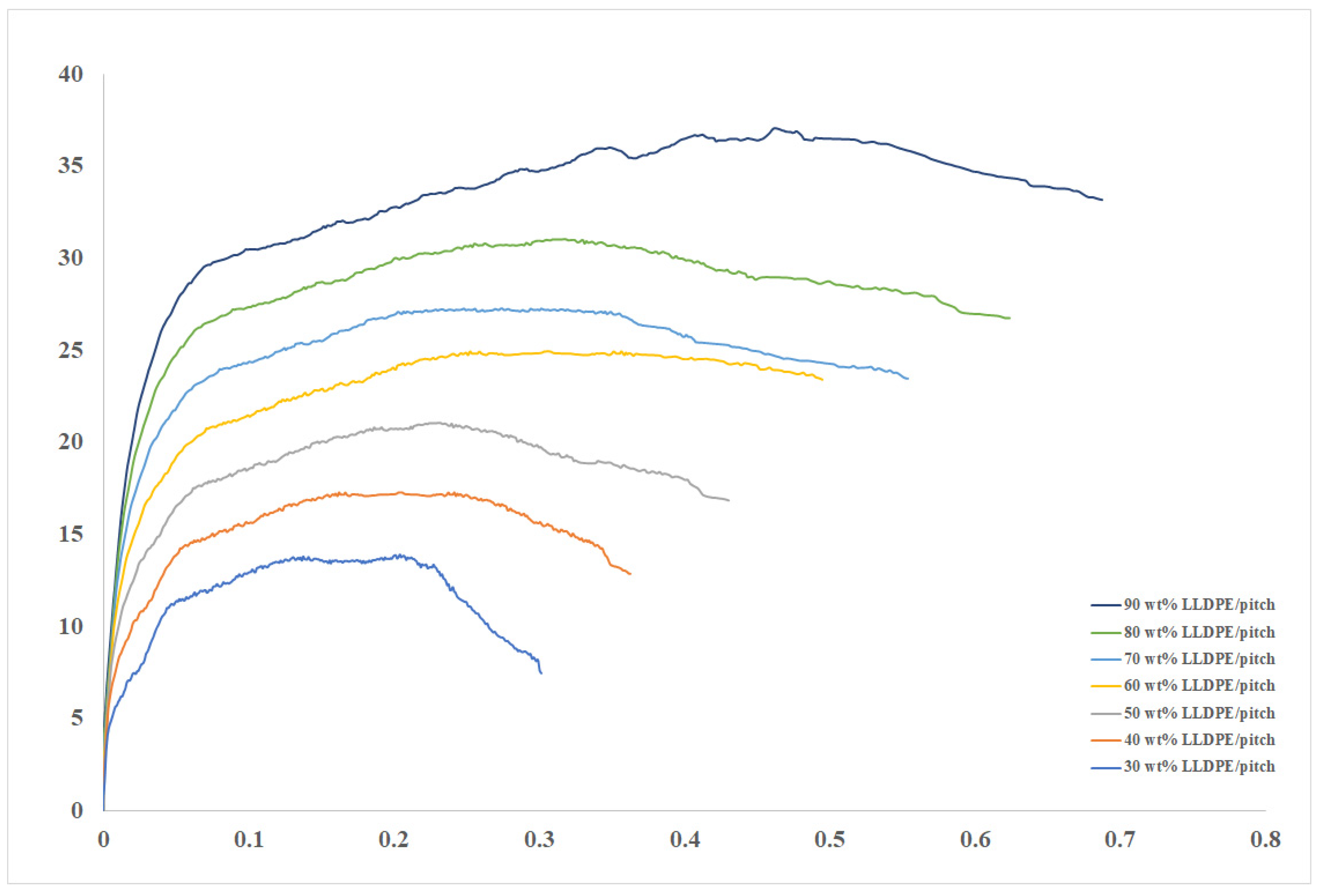
4.3. Tensile Tests of Pitch Blends
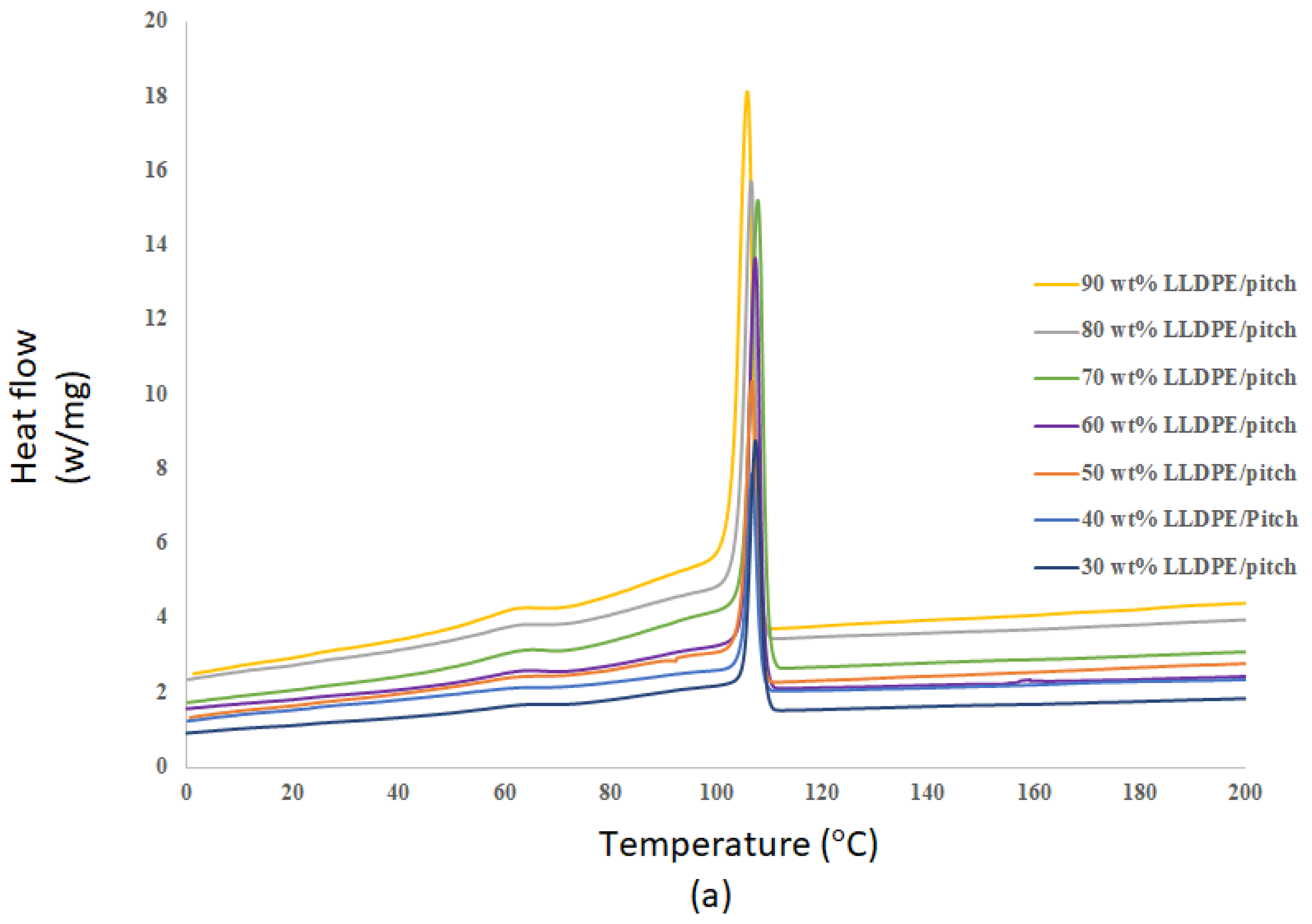
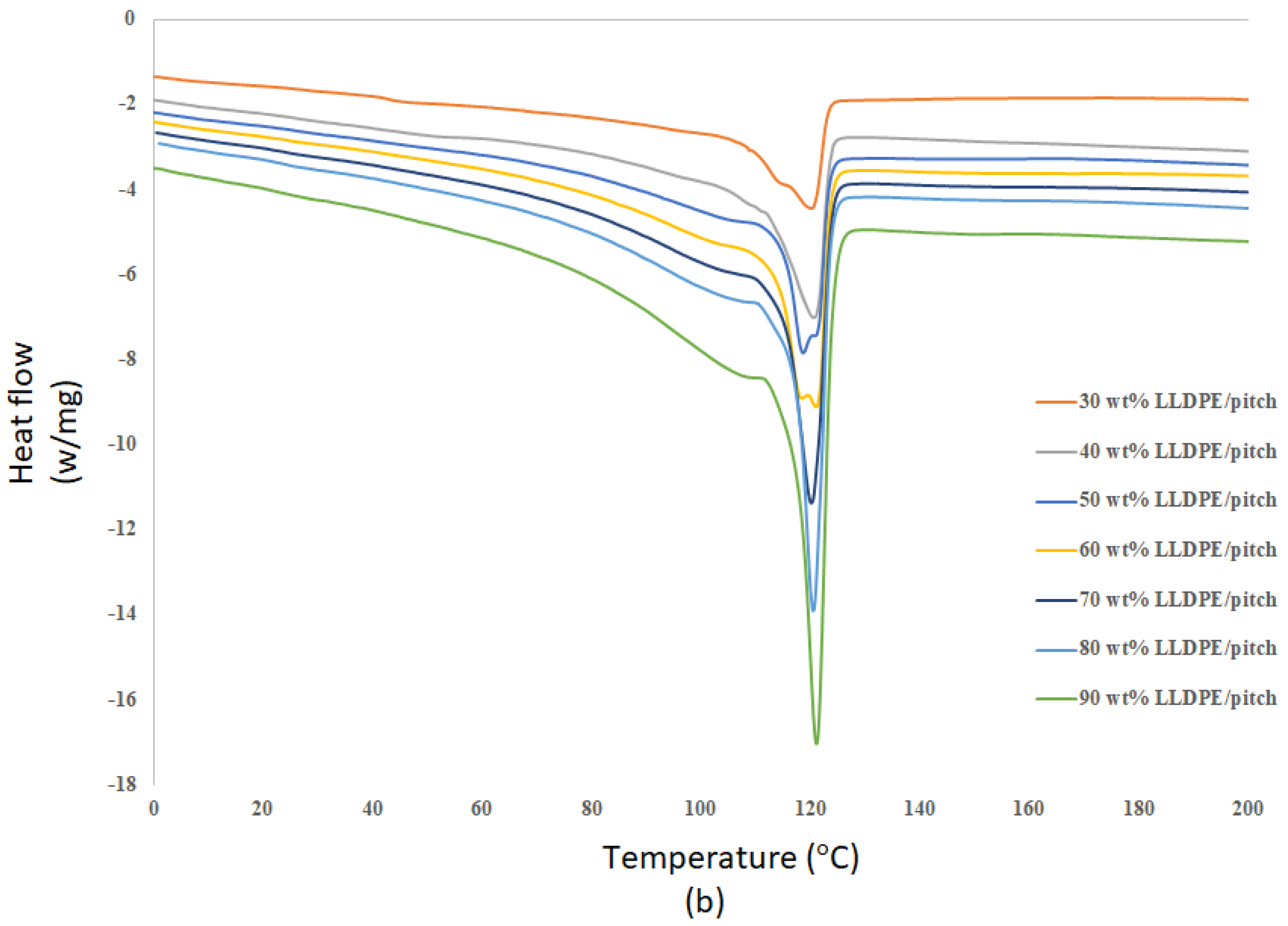
4.4. DSC for LLDPE/Mesophase Pitch Blends
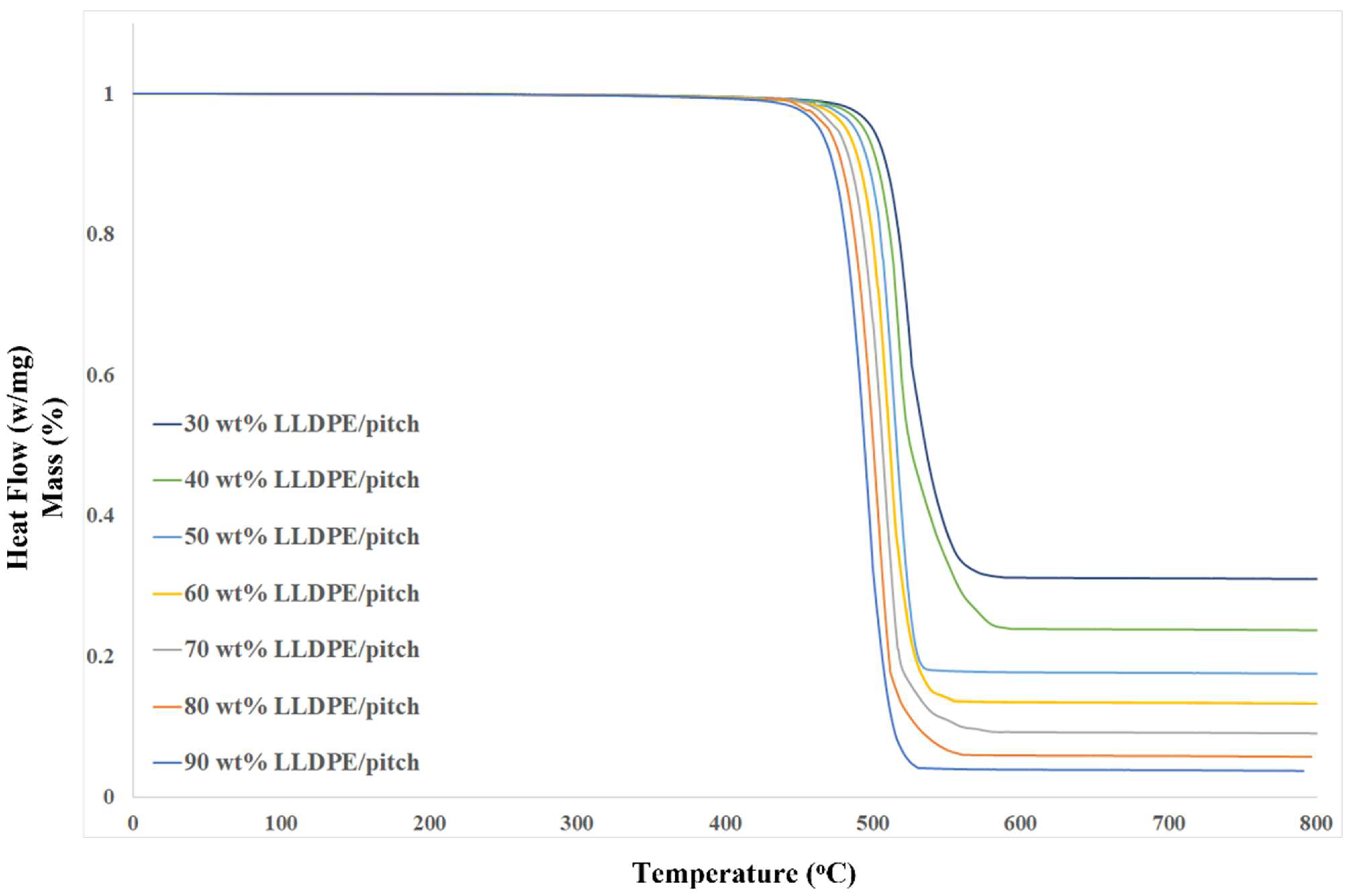
4.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis of LLDPE/MP Blends
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Toh, H.W.; Toong, D.W.Y.; Ng, J.C.K.; Ow, V.; Lu, S.; Tan, L.P.; Wong, P.E.H.; Venkatraman, S.; Huang, Y.; Ang, H.Y. Polymer blends and polymer composites for cardiovascular implants. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utracki, L.A. Economics of polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1982, 22, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macosko, C.W. Morphology Development and Control in Immiscible Polymer Blends. In Macromolecular Symposia; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000; Volume 149, pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Włoch, M.; Datta, J. Rheology of polymer blends. In Rheology of Polymer Blends and Nanocomposites: Theory, Modelling and Applications, 1st ed.; Thomas, S.C.S., Chandran, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A.; Wilkie, C.A. (Eds.) Polymer Blends Handbook, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukov, N.A.; Ligidov, M.K.; Pakhomov, S.I.; Mikitaev, A.K. Polypropylene polymer blends. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzer, E. Carbon Fibres Present State and Future Expectations. In Carbon Fibers Filaments and Composites; Figueired, J.L., Bernardo, C.A., Baker, R.T., Huttinger, K.J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: London, UK, 1990; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S. Recent progress in fabrication, structure, and properties of carbon fibers. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, S.Y. History and Structure of Carbon Fibers. In Carbon Fibers; Springer: Incheon, Korea, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.M.; Khan, M.; Rahatekar, S. Manufacturing carbon fibres from pitch and polyethylene blend precursors: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7786–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, F.; Yoon, S.H.; Korai, Y.; Mochida, I. Structure of round-shaped methylnaphthalene-derived mesophase pitch-based carbon fibres prepared by spinning through a Y-shaped die hole. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 4567–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Long, G. A fractal model for capillary flow through a single tortuous capillary with roughened surfaces in fibrous porous media. Fractals 2021, 28, 2150017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Cui, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and Applications of Carbonaceous Mesophase: A Review. In Nematic Liquid Crystals, 1st ed.; Carlescu, I., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.M.; Maeda, T.; Tokumitsu, K.; Mondori, J.; Mochida, I. Preparation of isotropic pitch precursors for general purpose carbon fibers (GPCF) by air blowing-II. Air blowing of coal tar, hydrogenated coal tar, and petroleum pitches. Carbon 1993, 31, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Rajabpour, S.; Joshi, K.; Kowalik, M.; Croom, B.; Schwab, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bumgardner, C.; Brown, K.R.; et al. Graphene reinforced carbon fibers. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.Q.; Lee, J.K.Y.; Chinnappan, A.; Loc, N.H.; Tran, L.T.; Ji, D.; Jayathilaka, D.; Kumar, V.V.; Ramakrishna, S. High-performance carbon fiber/gold/copper composite wires for lightweight electrical cables. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palmenaer, A.; Wortberg, G.; Drissen, F.; Seide, G. Production of Polyethylene Based Carbon Fibres. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortberg, G.; De Palmenaer, A.; Beckers, M.; Seide, G.; Gries, T. Polyethylene-Based Carbon Fibers by the Use of Sulphonation for Stabilization. Fibers 2015, 3, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-W.; Lee, H.-M.; Kim, B.S.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kwac, L.-K.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Preparation and thermal properties of polyethylene-based carbonized fibers. Carbon Lett. 2015, 16, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.S.; Kim, B.-H.; Yoon, S.-H. Pitch based carbon fibers for automotive body and electrodes. Carbon Lett. 2014, 15, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujadas, P.; Blanco, A.; Cavalaro, S.; de la Fuente, A.; Aguado, A. The need to consider flexural post-cracking creep behavior of macro-synthetic fiber reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Toshima, H.; Korai, Y.; Takashi, H. Oxygen distribution in the mesophase pitch fibre after oxidative stabilization. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Fabrication and properties of carbon fibers Review. Materials 2009, 2, 2369–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bhat, G.S. Carbon Fibers from Polyethylene-Based Precursors. Mater. Manuf. Process. 1994, 9, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.E.; Behr, M.J.; Patton, J.T.; Hukkanen, E.J.; Landes, B.G.; Wang, W.; Horstman, N.; Rix, J.E.; Keane, D.; Weigand, S.; et al. High-Modulus Low-Cost Carbon Fibers from Polyethylene Enabled by Boron Catalyzed Graphitization. Small 2017, 13, 1701926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, M.J.; Landes, B.G.; Barton, B.E.; Bernius, M.T.; Billovits, G.F.; Hukkanen, E.J.; Patton, J.T.; Wang, W.; Wood, C.; Keane, D.T.; et al. Structure-property model for polyethylene-derived carbon fiber. Carbon 2016, 107, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D. Carbon Fibers from Oriented Polyethylene Precursors. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 1993, 6, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postema, A.R.; De Groot, H.; Pennings, A.J. Amorphous carbon fibres from linear low density polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 4216–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Preparation of carbon fibers from linear low density polyethylene. Carbon 2015, 94, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-W.; Lee, H.-M.; An, J.-H.; Kim, B.-S.; Min, B.-G.; Kang, S.-J.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Effects of cross-linking methods for polyethylene-based carbon fibers: Review. Carbon Lett. 2015, 16, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penning, J.P.; Lagcher, R.; Pennings, A.J. The effect of diameter on the mechanical properties of amorphous carbon fibres from linear low density polyethylene. Polym. Bull. 1991, 25, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, A.; Pujadas, P.; López-Carreño, R.D.; Meza, L.M.; Pardo-Bosch, F. Mechanical Optimization of Concrete with Recycled PET Fibres Based on a Statistical-Experimental Study. Materials 2021, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustead, I. Eco-Profiles of the European Plastics Industry Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE); PlasticsEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, R.C.; Donnet, J.B. Pyrolytic Formation of High-performance Carbon Fibres. In Comprehensive Polymer Science and Supplements; Bevington, G.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, J.R.; Black, K.J.T. Structural Characterization of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches. Energy Fuels 1993, 7, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujadas, P.; Blanco, A.; Cavalaro, S.; Aguado, A. Plastic fibres as the only reinforcement for flat suspended slabs: Experimental investigation and numerical simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 57, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.P.; Wadgaonkar, K.; Mehta, L.; Jagtap, R. Enhancement of mechanical and barrier properties of LLDPE composite film via PET fiber incorporation for agricultural application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.; Khan, M.; Rahatekar, S. Manufacturing Pitch and Polyethylene Blends-Based Fibres as Potential Carbon Fibre Precursors. Polymer 2021, 13, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standards. BS ISO 11566: Carbon Fibre-Determination of the Tensile Properties of the Tensile-Filament Specimens; British Standards Institute: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fakirov, S.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Lin, R.J.T.; Fuchs, C.; Friedrich, K. Contribution of Coalescence to Microfibril Formation in Polymer Blends during Cold Drawing. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2007, 46, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Blanco, C.; Rand, B. Large diameter carbon fibres from mesophase pitch. Carbon 2002, 40, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasser, W.; Schmidt, H.W.; Giesa, R. Fibers spun from poly(ethylene terephthalate) blended with a thermotropic liquid crystalline copolyester with non-coplanar biphenylene units. Polymer 2001, 42, 8517–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pan, D.; He, H. Morphology Development of Polymer Blend Fibers along Spinning Line. Fibers 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Nunez, R.; Favis, B.D.; Carreau, P.J.; Lavallée, C. Factors influencing the formation of elongated morphologies in immiscible polymer blends during melt processing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sundararaj, U. Morphology development of polymer blends in extruder: The effects of compatibilization and rotation rate. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iii, C.L.T.; Moldenaers, P. Microstructural Evolution in Polymer Blends. Annu. Rev. Fluild Mech. 2002, 34, 177–210. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. The Formation of Emulsions in Definable Fields of Flow. R. Soc. 1934, 146, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.; Grace, H.P. Dispersion Phenomena in High Viscosity Immiscible Fluid Systems and Application of Static Mixers As Dispersion Dispersion Phenomena in High Viscosity Immiscible Fluid Systems and Application O F Static Mixers as Dispersion Devices in Such Systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1982, 14, 225–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, W. Performance of Straw/Linear Low Density Polyethylene Composite Prepared with Film-Roll Hot Pressing. Polymers 2020, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durmus, A.; Kaşgöz, A.; Macosko, C.W. Mechanical properties of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE)/clay nanocomposites: Estimation of aspect ratio and interfacial strength by composite models. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2008, 47, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.H.; Liu, G.Q.; Caiyi, H.; Shangguan, L.J. Mechanical properties and thermal behaviour of LLDPE/MWNTs nanocomposites. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evstatiev, M.; Fakirov, S.; Bechtold, G.; Friedrich, K. Structure-Property Relationships of Injection- and Compression-Molded Microfibrillar-Reinforced PET/PA-6 Composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2000, 19, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Montiel, A.; Keskkula, H.; Paul, D.R. Impact-modified nylon 6/polypropylene blends: 1. Morphology-property relationships. Polymer 1995, 36, 4587–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, I.S.; Kumar, V.; Palanivelu, K. Thermal characterisation of LDPE and LLDPE blends. Thermochim. Acta 1988, 131, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Cao, D.; Chen, S.; Xie, Q.; Lou, W.; Wu, H. Dielectric properties and thermal conductivity of epoxy composites using core/shell structured Si/SiO2/Polydopamine. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 140, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xu, D.; Dong, Z.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Banks, S.W. Processing Thermogravimetric Analysis Data for Isoconversional Kinetic Analysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass Pyrolysis: Case Study of Corn Stalk. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottom, R. Thermogravimetric Analysis. In Principles and Applications of Thermal Analysis, 1st ed.; Gabbott, P., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddawi, A.; Jones, J.M.; Williams, A.; Wójtowicz, M.A. Kinetics of the Thermal Decomposition of Biomass. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

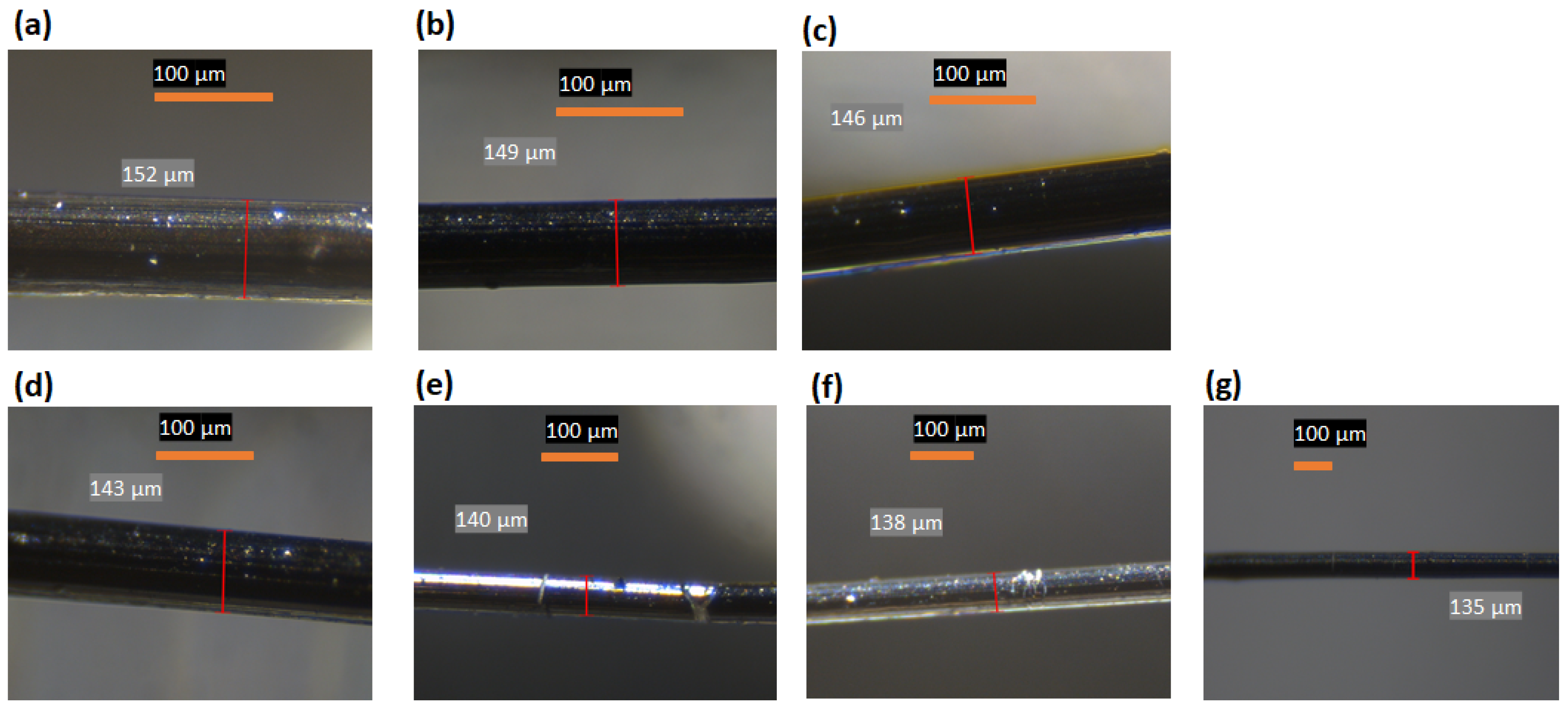
| Blend Designation | Fibre Diameter, µm |
|---|---|
| LLDPE (30 wt%)/MP | 152 (±0.54) |
| LLDPE (40 wt%)/MP | 149 (±0.30) |
| LLDPE (50 wt%)/MP | 146 (±0.36) |
| LLDPE (60 wt%)/MP | 143 (±0.38) |
| LLDPE (70 wt%)/MP | 140 (±0.51) |
| LLDPE (80 wt%)/MP | 138 (±0.53) |
| LLDPE (90 wt%)/MP | 135 (±0.24) |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Strain at Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE (30 wt%)/MP | 13.84 (±0.33) | 798 (±4.3) | 0.30 (±0.031) |
| LLDPE (40 wt%)/MP | 17.53 (±0.44) | 817 (±4.5) | 0.36 (±0.038) |
| LLDPE (50 wt%)/MP | 21.47 (±0.34) | 838 (±3.8) | 0.43 (±0.041) |
| LLDPE (60 wt%)/MP | 25.06 (±0.85) | 852 (±5.6) | 0.48 (±0.028) |
| LLDPE (70 wt%)/MP | 28.91 (±0.52) | 873 (±6.9) | 0.56 (±0.021) |
| LLDPE (80 wt%)/MP | 33.06 (±0.48) | 944 (±6.1) | 0.62 (±0.029) |
| LLDPE (90 wt%)/MP | 36.97 (±0.43) | 989 (±3.4) | 0.68 (±0.035) |
| Samples | Melting Temperature (°C) | Crystallization Temperature (°C) | Enthalpy of Fusion (J/g) Sample | Enthalpy of Fusion (J/g) LLDPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE (30 wt%)/MP | 123.1 | 102.1 | 52 | 173 |
| LLDPE (40 wt%)/MP | 123.3 | 102.2 | 74 | 185 |
| LLDPE (50 wt%)/MP | 123.4 | 102.3 | 106 | 212 |
| LLDPE (60 wt%)/MP | 123.5 | 102.4 | 153 | 255 |
| LLDPE (70 wt%)/MP | 123.6 | 102.5 | 181 | 258 |
| LLDPE (80 wt%)/MP | 123.8 | 102.7 | 198 | 247 |
| LLDPE (90 wt%)/MP | 123.9 | 102.9 | 217 | 241 |
| Samples | Onset Degradation Temperature * (°C) | Final Degradation Temperature (°C) | Final Residue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE (30 wt%)/MP | 490.5 | 571.7 | 30 |
| LLDPE (40 wt%)/MP | 481.6 | 539.4 | 27 |
| LLDPE (50 wt%)/MP | 475.2 | 536.3 | 22 |
| LLDPE (60 wt%)/MP | 472.2 | 532.1 | 19 |
| LLDPE (70 wt%)/MP | 462.9 | 528.3 | 15 |
| LLDPE (80 wt%)/MP | 453.4 | 527.1 | 12 |
| LLDPE (90 wt%)/MP | 446.2 | 525.4 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldosari, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Rahatekar, S. Influence of High-Concentration LLDPE on the Manufacturing Process and Morphology of Pitch/LLDPE Fibres. Crystals 2021, 11, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091099
Aldosari SM, Khan MA, Rahatekar S. Influence of High-Concentration LLDPE on the Manufacturing Process and Morphology of Pitch/LLDPE Fibres. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091099
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldosari, Salem Mohammed, Muhammad A. Khan, and Sameer Rahatekar. 2021. "Influence of High-Concentration LLDPE on the Manufacturing Process and Morphology of Pitch/LLDPE Fibres" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091099
APA StyleAldosari, S. M., Khan, M. A., & Rahatekar, S. (2021). Influence of High-Concentration LLDPE on the Manufacturing Process and Morphology of Pitch/LLDPE Fibres. Crystals, 11(9), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091099