Advances of Yb:CALGO Laser Crystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Properties
2.1. Crystal Preparation and Structure
2.2. Spectroscopic Properties
2.3. Thermal Characteristics

3. Advanced Progress
3.1. Yb:CALGO in CW Lasers
3.1.1. High Power and High Efficiency Yb:CALGO Lasers
3.1.2. Broad Wavelength and Dual-Wavelength Tunable Yb:CALGO Laser
3.1.3. Mode-Tunable Structured Light Lasers with Yb:CALGO
3.2. Yb:CALGO in Ultrashort Pulse Lasers
3.2.1. Ultrashort Pulses with SESAM Mode Locking in Yb:CALGO Lasers
3.2.2. Ultrashort Pulses with Kerr-Lens Mode-Locking in Yb:CALGO Lasers
3.2.3. Ultrashort Pulses from SESAM and Kerr-Lens Mode-Locked Yb:CALGO Lasers
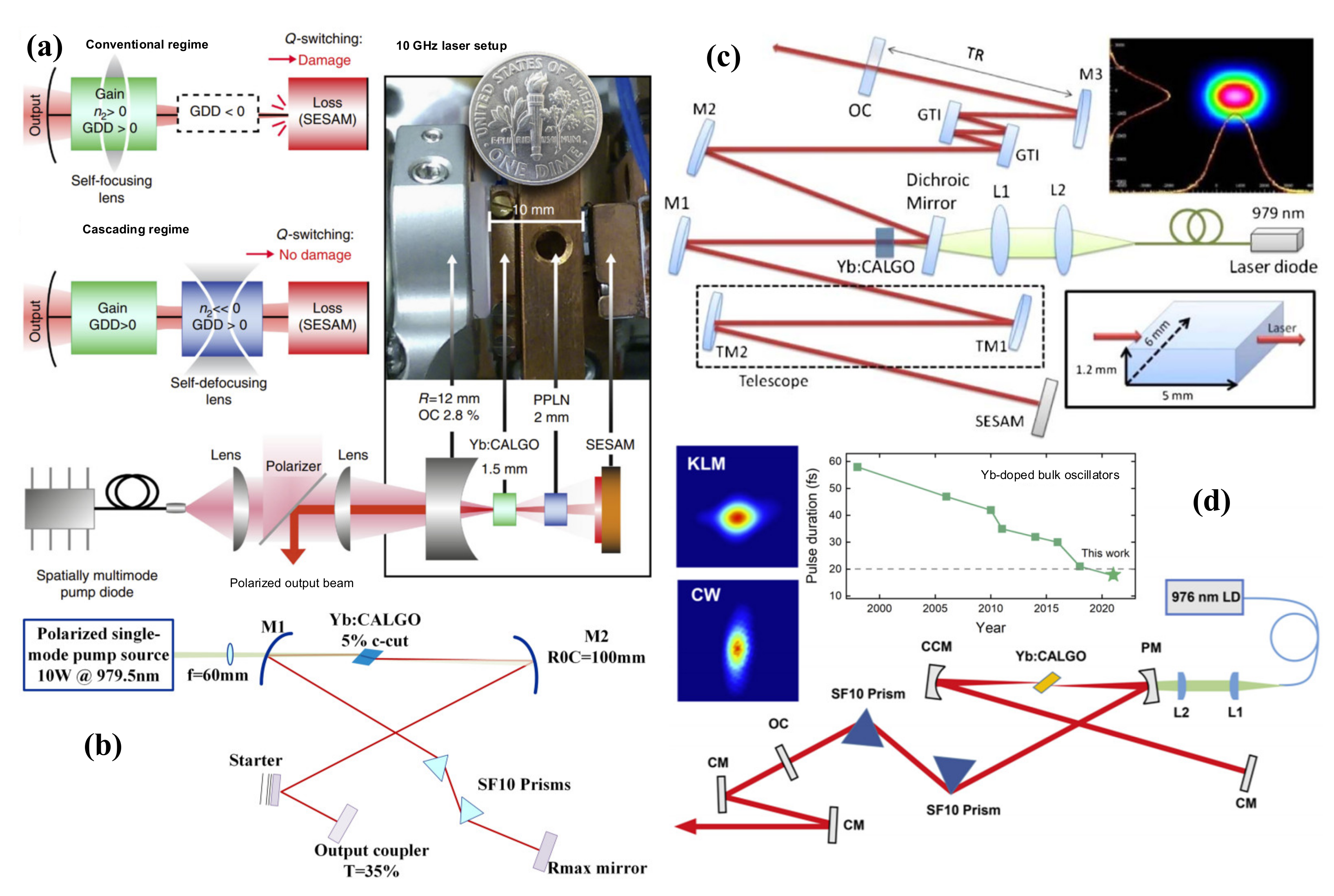
3.2.4. Ultrashort Pulses with Other Methods in Yb:CALGO Lasers

3.2.5. Ultrashort Pulses in Thin-Disk Yb:CALGO Lasers
4. Conclusive Remarks
- (1)
- Yb:CALGO produced the ultrafast lasers with highest intracavity peak power of 44 MW [121].
- (2)
- Yb:CALGO laser reached the highest slop efficiency as 84% (near the quantum-defect-limited slope efficiency) in a microchip laser scheme [41].
- (3)
- Yb:CALGO empowered a wavelength-tunable laser with a tuning range as broad as 90 nm [43].
- (4)
- Yb:CALGO permitted the highest peak power of 1.7 MW in a sub-50 fs diode-pumped laser oscillator [45].
- (5)
- Yb:CALGO could operate in a microchip laser with length of 3.4 mm and produced multi-watt emission [41].
- (6)
- Yb:CALGO allowed a new mode-locking regime producing 100 fs pulses at 540 MHz repetition rate with 760 mW of average output power [98].
- (7)
- Yb:CALGO enabled direct emission of watt-level 10-gigahertz pulses from a simple and small straight laser cavity [99].
- (8)
- Yb:CALGO created the shortest pulses with time duration of 17.8 fs in a Kerr-lens mode-locked architecture [110].
- (9)
- Yb:CALGO optical frequency comb created the narrowest free-running CEO linewidth as 1.6 kHz and a comb optical linewidth narrower than 28 kHz in 1 ms observation time at 1064 nm [118].
- (10)
- Yb:CALGO-based regenerative amplifier demonstrated the first sub-100 fs pulses with 11 W average power, 3.7 GW peak power and 43 kHz repetition rate without resorting to nonlinear spectral broadening [119].
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargrove, L.E.; Fork, R.L.; Pollack, M.A. Locking of He–Ne Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity Modulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1964, 5, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, F.J.; Hellwarth, R.W. Giant Optical Pulsations from Ruby. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, D.; Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 1985, 56, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N. Nonlinear Optics; World Scientific: Singapore, 1996; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Kawata, S.; Sun, H.-B.; Tanaka, T.; Takada, K. Finer features for functional microdevices. Nature 2001, 412, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Han, B.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, C.H.; Chen, Q.D.; Sun, H.B. Femtosecond laser programmed artificial musculoskeletal systems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. Ultrafast lasers—Reliable tools for advanced materials processing. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.C.; Gandhi, H.H.; Mazur, E.; Sundaram, S.K. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: A review. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2015, 7, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Kwok, S.J.J. Light in diagnosis, therapy and surgery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H.; He, H. Molecular Response of Skin to Micromachining by Femtosecond Laser. Front. Phys. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, F.; Byer, R. Modeling and CW operation of a quasi-three-level 946 nm Nd: YAG laser. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1987, 23, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cante, S.; Valle, S.; Yoon, S.J.; Mackenzie, J.I. 60-W 946-nm cryogenically-cooled Nd:YAG laser. Appl. Phys. B 2019, 125, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Li, X.; Mei, F.; Chen, D.; Yan, R. 30 mJ, 1 kHz sub-nanosecond burst-mode Nd:YAG laser MOPA system. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 36129–36136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davide Di Dio Cafiso, S.; Ugolotti, E.; Schmidt, A.; Petrov, V.; Griebner, U.; Agnesi, A.; Cho, W.B.; Jung, B.H.; Rotermund, F.; Bae, S.; et al. Sub-100-fs Cr:YAG laser mode-locked by monolayer graphene saturable absorber. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1745–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae Cho, W.; Schmidt, A.; Young Choi, S.; Petrov, V.; Griebner, U.; Steinmeyer, G.; Lee, S.; Yeom, D.-I.; Rotermund, F. Mode locking of a Cr:YAG laser with carbon nanotubes. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2669–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Dai, S.; Yin, H.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z. Passively Q-switched yellow laser at 589 nm by intracavity frequency-doubled c-cut composite Nd:YVO4 self-Raman laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 133, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, R.; Wang, X.; Teng, H.; Zhu, J.; Wei, Z. Generation of 172 fs pulse from a Nd: YVO4 picosecond laser by using multi-pass-cell technique. Appl. Phys. B 2021, 127, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. Laser emission with low quantum defect in Yb:CaGdAlO4. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.D.; Tang, D.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Li, D.Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.W.; Cong, Z.H.; Xu, J. Room temperature diode-pumped Yb:CaYAlO4 laser with near quantum limit slope efficiency. Laser Phys. Lett. 2011, 8, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, D.; Wu, F.; Xia, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Crystal growth and spectroscopic properties of Yb:CaYAlO4 single crystal. J. Cryst. Growth 2010, 312, 2117–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.M.; Druon, F.; Stoian, R.; Boudeile, J.; Zaouter, Y.; Hanna, M.; Balembois, F.; Georges, P.; Petit, J.; Golner, P.; et al. New Yb-doped crystals for high-power and ultrashort lasers. In Proceedings of the Femtosecond Phenomena and Nonlinear Optics III Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 29 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Descamps, D.; Guichard, F.; Petit, S.; Beauvarlet, S.; Comby, A.; Lavenu, L.; Zaouter, Y. High-power sub-15 fs nonlinear pulse compression at 515 nm of an ultrafast Yb-doped fiber amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1804–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.P.; Banerjee, S.; Mason, P.; Smith, J.; Spear, J.; De Vido, M.; Ertel, K.; Butcher, T.; Quinn, G.; Clarke, D.; et al. Second and third harmonic conversion of a kilowatt average power, 100-J-level diode pumped Yb:YAG laser in large aperture LBO. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1808–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Zhang, H.; Zu, J.; Chen, J. Buildup dynamics of a pulsating dissipative soliton in an all-normal-dispersion PM Yb-doped fiber laser with a NALM. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosello-Mecho, X.; Delgado-Pinar, M.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; Kir’yanov, A.V.; Andres, M.V. Application of WGM Resonances to the Measurement of the Temperature Increment of Ho and Ho-Yb Doped Optical Fibers Pumped at 1125 and 975 nm. Sensors 2021, 21, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Viana, B.; Goldner, P. High thermal conductivity and low quantum defect in Yb:CaGdAlO4, a new infrared laser material for high power applications. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Photonics (TOPS), Vienna, Austria, 6–9 February 2005; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Loiko, P.; Becker, P.; Bohaty, L.; Liebald, C.; Peltz, M.; Vernay, S.; Rytz, D.; Serres, J.M.; Mateos, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Sellmeier equations, group velocity dispersion, and thermo-optic dispersion formulas for CaLnAlO4 (Ln = Y, Gd) laser host crystals. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.Q.; Xu, X.D.; Xia, C.T.; Zheng, L.H.; Aka, G.; Yu, H.H.; Sai, Q.L.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Crystal growth, polarized spectra, and laser performance of Yb:CaGdAlO4crystal. Laser Phys. 2016, 26, 045803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digonnet, M.J.F.; Jaffrès, A.; Ricaud, S.; Suganuma, A.; Viana, B.; Loiseau, P.; Georges, P.; Druon, F.; Jiang, S.; Dries, J.C. Yb: CALGO as material for high power ultrafast laser and focus on thermal conductivity variation. In Proceedings of the Optical Components and Materials X, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Verdùn, H.R.; Thomas, L.M. Growth, Optical Properties, and Stimulated Emission of Nd-Doped Aluminates with the K2NiF4 Structure. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid State Lasers, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 5–7 March 1990; p. MT4. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, P.O.; Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. Inhomogeneous broadening of optical transitions in Yb:CaYAlO4. Opt. Mater. 2008, 30, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagatskii, A.A.; Kuleshov, N.V.; Shcherbitskii, V.G.; Kleptsyn, V.F.; Mikhailov, V.P.; Ostroumov, V.G.; Huber, G. Lasing characteristics of a diode-pumped Nd3+: CaGdAlO4crystal. Quantum Electron. 1997, 27, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentsch, K.S.; Weichelt, B.; Günster, S.; Druon, F.; Georges, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Graf, T. Yb:CaF2 thin-disk laser. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, V.; Camy, P.; Doualan, J.L.; Portier, X.; Moncorgé, R. Spectroscopy ofYb3+:CaF2: From isolated centers to clusters. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 085131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druon, F.; Ricaud, S.; Papadopoulos, D.N.; Pellegrina, A.; Camy, P.; Doualan, J.L.; Moncorgé, R.; Courjaud, A.; Mottay, E.; Georges, P. On Yb:CaF2 and Yb:SrF2: Review of spectroscopic and thermal properties and their impact on femtosecond and high power laser performance [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Su, L.; Xu, J. Generation of 33 fs pulses directly from a Kerr-lens mode-locked Yb:CaYAlO_4 laser. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiko, P.; Druon, F.; Georges, P.; Viana, B.; Yumashev, K. Thermo-optic characterization of Yb:CaGdAlO_4 laser crystal. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talik, E.; Kisielewski, J.; Zajdel, P.; Guzik, A.; Wierzbicka, E.; Kania, A.; Kusz, J.; Miga, S.; Szubka, M. XPS spectroscopy, structural, magnetic and dielectric investigations of CaGdAlO4 and Yb:CaGdAlO4 single crystals. Opt. Mater. 2019, 91, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druon, F.; Balembois, F.; Georges, P. New laser crystals for the generation of ultrashort pulses. C. R. Phys. 2007, 8, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzio, F.; Kemnitzer, M.; Guandalini, A.; Kienle, F.; Veronesi, S.; Tonelli, M.; Aus der Au, J.; Agnesi, A. Ultrafast, solid-state oscillators based on broadband, multisite Yb-doped crystals. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 11782–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiko, P.; Serres, J.M.; Mateos, X.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.; Jambunathan, V.; Navratil, P.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Microchip Yb:CaLnAlO4 lasers with up to 91% slope efficiency. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2431–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasselet, E.; Malinauskas, M.; Zukauskas, A.; Juodkazis, S. Photopolymerized microscopic vortex beam generators: Precise delivery of optical orbital angular momentum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 211108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beil, K.; Deppe, B.; Krankel, C. Yb:CaGdAlO4 thin-disk laser with 70% slope efficiency and 90 nm wavelength tuning range. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano, P.; Georges, P.; Druon, F.; Descamps, D.; Cormier, E. 32-fs Kerr-lens mode-locked Yb:CaGdAlO4 oscillator optically pumped by a bright fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6001–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manjooran, S.; Major, A. Diode-pumped 45 fs Yb:CALGO laser oscillator with 1.7 MW of peak power. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2324–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sroor, H.; Huang, Y.-W.; Sephton, B.; Naidoo, D.; Vallés, A.; Ginis, V.; Qiu, C.-W.; Ambrosio, A.; Capasso, F.; Forbes, A. High-purity orbital angular momentum states from a visible metasurface laser. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B.; Didierjean, J.; Balembois, F.; Druon, F.; Georges, P. Quest of athermal solid state laser: Case of Yb:CaGdAlO4. In Proceedings of the Photonics Europe, Strasbourg, France, 3–7 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Z.; Xu, X.D.; Cheng, S.S.; Zhou, D.H.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Z.W.; Xia, C.T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.M.; et al. Polarized spectral properties of Nd3+ ions in CaYAlO4 crystal. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 101, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, J.; Kaluza, M.C.; Kloepfel, D.; Vorholt, C.; Kahle, M.; Liebetrau, H.; Seifert, R.; Hein, J. Measurement of temperature-dependent absorption and emission spectra of Yb:YAG, Yb:LuAG, and Yb:CaF2 between 20 °C and 200 °C and predictions on their influence on laser performance. JOSA B 2012, 29, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouter, Y.; Didierjean, J.; Balembois, F.; Leclin, G.L.; Druon, F.; Georges, P.; Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. 47-fs diode-pumped Yb3+:CaGdAlO4 laser. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caracciolo, E.; Kemnitzer, M.; Guandalini, A.; Pirzio, F.; Agnesi, A.; Aus der Au, J. High pulse energy multiwatt Yb:CaAlGdO4 and Yb:CaF2 regenerative amplifiers. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 19912–19918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudeile, J.; Druon, F.; Hanna, M.; Georges, P.; Zaouter, Y.; Cormier, E.; Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. Continuous-wave and femtosecond laser operation of Yb:CaGdAlO4 under high-power diode pumping. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1962–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Y.; Lan, Y.; Ma, X. Thermal management of graphene-induced high-power semiconductor laser package with bidirectional conduction structure. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Viana, B.; Goldner, P.; Roger, J.-P.; Fournier, D. Thermomechanical properties of Yb3+ doped laser crystals: Experiments and modeling. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 123108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Digonnet, M.J.F.; Jaffres, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Loiseau, P.; Viana, B.; Doualan, J.L.; Moncorgé, R. UV-visible luminescence properties of the broad-band Yb:CALGO laser crystal. In Proceedings of the Optical Components and Materials XII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–12 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, R.; Loiko, P.; Major, A.; Clarkson, W.A.; Shori, R.K. Thermal lensing in diode-pumped Yb:CALGO and Yb:KGW lasers. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXIX: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–6 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Calendron, A.L. Dual-crystal Yb:CALGO high power laser and regenerative amplifier. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 26174–26181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Druon, F.; Olivier, M.; Jaffres, A.; Loiseau, P.; Aubry, N.; DidierJean, J.; Balembois, F.; Viana, B.; Georges, P. Magic mode switching in Yb:CaGdAlO4 laser under high pump power. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 4138–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasse, K.; Calmano, T.; Deppe, B.; Liebald, C.; Krankel, C. Efficient Yb3+:CaGdAlO4 bulk and femtosecond-laser-written waveguide lasers. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3552–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, K.; Kränkel, C. Yb:CALGO waveguide laser written with 1 MHz-repetition rate fs-laser. In Proceedings of the Laser Congress 2019 (ASSL, LAC, LS&C), Vienna, Austria, 29 September–3 October 2019; p. ATu1A.7. [Google Scholar]
- Manjooran, S.; Major, A.; Clarkson, W.A.; Shori, R.K. Comparative studies of high power diode-pumped Yb:CALGO and Yb:KYW lasers. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXVIII: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, M.A.R.; Loiko, P.; Major, A.; Clarkson, W.A.; Shori, R.K. Intracavity loss measurement in a diode-pumped Yb:CALGO laser. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXVIII: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, W.A.; Ricaud, S.; Jaffres, A.; Loiseau, P.; Viana, B.; Weichelt, B.; Abdou-Ahmed, M.; Voss, A.; Graf, T.; Rytz, D.; et al. Yb:CaGdAlO4 thin-disk. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXI: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, A.R.; Akbari, R.; Major, A.; Clarkson, W.A.; Shori, R.K. Dual-wavelength Yb:CALGO laser with wavelength spacing tunability. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXIX: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–6 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ricaud, S.; Jaffres, A.; Loiseau, P.; Viana, B.; Weichelt, B.; Abdou-Ahmed, M.; Voss, A.; Graf, T.; Rytz, D.; Delaigue, M.; et al. Yb:CaGdAlO4 thin-disk laser. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4134–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudeile, J.; Didierjean, J.; Balembois, F.; Druon, F.; Georges, P.; Petit, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. High power diode pumped Yb3+:CaGdAlO4 laser. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Photonics, Nara, Japan, 27–30 January 2008; p. WE28. [Google Scholar]
- Scheller, M.; Yarborough, J.M.; Moloney, J.V.; Fallahi, M.; Koch, M.; Koch, S.W. Room temperature continuous wave milliwatt terahertz source. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 27112–27117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Mao, Y.; Flueraru, C. Dual-Source Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Reconstructed on Integrated Spectrum. Int. J. Opt. 2012, 2012, 565823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjooran, S.; Loiko, P.; Major, A. A discretely tunable dual-wavelength multi-watt Yb:CALGO laser. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 124, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, D.; Gao, Y.; Liang, X. Wavelength shift with a diode-pumped continuous-wave Yb:CALGO laser. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, A.; de Oliveira, M.; Dennis, M.R. Structured light. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, A. Structured Light from Lasers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2019, 13, 1900140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Min, C.; Fu, X.; Liu, Q.; Gong, M.; Yuan, X. Optical vortices 30 years on: OAM manipulation from topological charge to multiple singularities. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Céspedes Vicente, O.; Caloz, C. Bessel beams: A unified and extended perspective. Optica 2021, 8, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremidis, N.K.; Chen, Z.; Segev, M.; Christodoulides, D.N. Airy beams and accelerating waves: An overview of recent advances. Optica 2019, 6, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Xie, J.; Jiang, S.; Feng, G.; Zhou, S. Direct emission of chirality controllable femtosecond LG01 vortex beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 201110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Meng, Y.; Fu, X.; Gong, M. Wavelength-tunable Hermite-Gaussian modes and an orbital-angular-momentum-tunable vortex beam in a dual-off-axis pumped Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Meng, Y.; Fu, X.; Gong, M. Dual-wavelength vortex beam with high stability in a diode-pumped Yb:CaGdAlO4laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 055803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bužek, V.; Quang, T. Generalized coherent state for bosonic realization of SU(2)Lie algebra. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1989, 6, 2447–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Fu, X.; Liu, Q.; Gong, M. Vortex lattices with transverse-mode-locking states switching in a large-aperture off-axis-pumped solid-state laser. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2018, 35, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, X.; Gong, M. Periodic-trajectory-controlled, coherent-state-phase-switched, and wavelength-tunable SU(2) geometric modes in a frequency-degenerate resonator. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9543–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Meng, Y.; Fu, X.; Gong, M. Polygonal Vortex Beams. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Shen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Index-Tunable Structured-Light Beams from a Laser with an Intracavity Astigmatic Mode Converter. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 14, 044048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, L.; Cai, F.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y. Broadly tunable optical vortex beam in a diode-pumped Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lei, M.; Lin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Kang, S.; Huang, L. Generation of a mode-tunable optical vortex based on a mirror curvature dynamically controlled Z-shaped resonant cavity. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3079–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tong, L.; Cai, F.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, L. Direct generation of optical vortex arrays by rotating in an all-solid-state Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, A.; Loiko, Y.V.; Kalkandjiev, T.K.; Mompart, J. Conical refraction: Fundamentals and applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2016, 10, 750–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reza, A.R.; Akbari, R.; Fedorova, K.; Sokolovskii, G.; Rafailov, E.; Major, A.; Clarkson, W.A.; Shori, R.K. Diode-pumped Yb:CALGO laser with conical refraction output. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXIX: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–6 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, P.; Si, H.; Fu, X.; Liu, Q. High energy LiDAR source for long distance, high resolution range imaging. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 3655–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.J.; Patel, P.K.; Lindl, J.D.; Atherton, L.J.; Glenzer, S.H.; Haan, S.W.; Kilkenny, J.D.; Landen, O.L.; Moses, E.I.; Nikroo, A.; et al. Progress towards ignition on the National Ignition Facility. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, G.P.A.; Ferguson, A.I. Mode-locking of diode laser-pumped solid-state lasers. Opt. Quantum Electron. 1992, 24, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnesi, A.; Greborio, A.; Pirzio, F.; Reali, G.; Aus der Au, J.; Guandalini, A. 40-fs Yb3+:CaGdAlO4 laser pumped by a single-mode 350-mW laser diode. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 10077–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessandro, G.; Annalisa, G.; Juerg Aus der, A. Sub-100 fs pulses with 12.5-W from Yb:CALGO based oscillators. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Agnesi, A.; Greborio, A.; Pirzio, F.; Ugolotti, E.; Reali, G.; Guandalini, A.; Aus der Au, J. Diode-pumped passively mode-locked tunable Yb:CALGO solid-state laser. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2013, 30, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzio, F.; Cafiso, S.D.; Kemnitzer, M.; Guandalini, A.; Kienle, F.; Veronesi, S.; Tonelli, M.; Aus der Au, J.; Agnesi, A. Sub-50-fs widely tunable Yb:CaYAlO(4) laser pumped by 400-mW single-mode fiber-coupled laser diode. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 9790–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenauer, L.F.; Stolen, R.H. The soliton laser. Opt. Lett. 1984, 9, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.R.; Mayer, A.S.; Klenner, A.; Keller, U. SESAM modelocked Yb:CaGdAlO4 laser in the soliton modelocking regime with positive intracavity dispersion. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6060–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.R.; Mayer, A.S.; Klenner, A.; Keller, U. Femtosecond mode locking based on adiabatic excitation of quadratic solitons. Optica 2015, 2, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.S.; Phillips, C.R.; Keller, U. Watt-level 10-gigahertz solid-state laser enabled by self-defocusing nonlinearities in an aperiodically poled crystal. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenner, A.; Golling, M.; Keller, U. High peak power gigahertz Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 11884–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruger, L.M.; Mayer, A.S.; Okawachi, Y.; Ji, X.; Klenner, A.; Johnson, A.R.; Langrock, C.; Fejer, M.M.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L.; et al. Performance scaling of a 10-GHz solid-state laser enabling self-referenced CEO frequency detection without amplification. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 12755–12770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Pang, M. Revealing the Buildup Dynamics of Harmonic Mode-Locking States in Ultrafast Lasers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2019, 13, 1800333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, H.M.; Herink, G.; Kurtz, F.; Morgner, U. Harmonically mode-locked Yb:CALGO laser oscillator. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 14164–14172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.B.; Feng, G.Y.; Zhou, S.H. Harmonically mode-locked Yb:CALGO laser pumped by a single-mode 1.2 W laser diode. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Su, L.; Xu, J. Diode-pumped Kerr-lens mode-locked Yb:CaGdAlO4laser with tunable wavelength. Laser Phys. Lett. 2016, 13, 015302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, D.N.; Druon, F.; Boudeile, J.; Martial, I.; Hanna, M.; Georges, P.; Petit, P.O.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. Low-repetition-rate femtosecond operation in extended-cavity mode-locked Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shori, R.K.; Clarkson, W.A.; Major, A.; Manjooran, S. Low repetition rate operation of a femtosecond Yb:CALGO laser. In Proceedings of the Solid State Lasers XXVII: Technology and Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 January–1 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Tani, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Raman-assisted broadband mode-locked laser. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaye, F.; Wittwer, V.J.; Modsching, N.; Razskazovskaya, O.; Cormier, E.; Südmeyer, T. Yb.CALGO Oscillator Generates 31-fs Pulses with 389 mW at 29% Efficiency by Cross-Polarized Optical Pumping. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Washington, DC, USA, 10–15 May 2020; p. SF2H.2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Xie, Y.; Gao, F.; Kumar, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; He, J. 17.8 fs broadband Kerr-lens mode-locked Yb:CALGO oscillator. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenner, A.; Keller, U. All-optical Q-switching limiter for high-power gigahertz modelocked diode-pumped solid-state lasers. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 8532–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, G.; Zhou, S. SESAM combined Kerr lens mode locked Yb:CALGO laser pumped by a 1.2 W single mode fiber coupled laser diode. Laser Phys. Lett. 2017, 14, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Zhao, H.; Fedorova, K.A.; Rafailov, E.U.; Major, A. Quantum-dot saturable absorber and Kerr-lens mode-locked Yb:KGW laser with >450 kW of peak power. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Cai, F.; Xu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, L. Nonlinear-mirror mode-locked 1052 nm Yb:CALGO laser. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, E.; Kemnitzer, M.; Guandalini, A.; Pirzio, F.; Aus der Au, J.; Agnesi, A. 28-W, 217 fs solid-state Yb:CAlGdO4 regenerative amplifiers. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 4131–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouysegur, J.; Delaigue, M.; Zaouter, Y.; Honninger, C.; Mottay, E.; Jaffres, A.; Loiseau, P.; Viana, B.; Georges, P.; Druon, F. Sub-100-fs Yb:CALGO nonlinear regenerative amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 5180–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, E.; Kemnitzer, M.; Rumpel, M.; Guandalini, A.; Pirzio, F.; Kienle, F.; Graf, T.; Abdou Ahmed, M.; Aus der Au, J.; Agnesi, A. Single-grating-mirror intracavity stretcher design for chirped pulse regenerative amplification. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, L.M.; Canella, F.; Pirzio, F.; Betz, M.; Vicentini, E.; Coluccelli, N.; Piccinno, G.; Agnesi, A.; Laporta, P.; Galzerano, G. Low-noise Yb:CALGO optical frequency comb. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 19495–19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Liang, H. Multigigawatt 50fs Yb:CALGO regenerative amplifier system with 11W average power and mid-infrared generation. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaud, S.; Jaffres, A.; Wentsch, K.; Suganuma, A.; Viana, B.; Loiseau, P.; Weichelt, B.; Abdou-Ahmed, M.; Voss, A.; Graf, T.; et al. Femtosecond Yb:CaGdAlO4 thin-disk oscillator. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3984–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diebold, A.; Emaury, F.; Schriber, C.; Golling, M.; Saraceno, C.J.; Sudmeyer, T.; Keller, U. SESAM mode-locked Yb:CaGdAlO4 thin disk laser with 62 fs pulse generation. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3842–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Modsching, N.; Paradis, C.; Labaye, F.; Gaponenko, M.; Graumann, I.J.; Diebold, A.; Emaury, F.; Wittwer, V.J.; Sudmeyer, T. Kerr lens mode-locked Yb:CALGO thin-disk laser. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Chemical Properties | Values | Physical Properties | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Space group | I4/mmm () | Density | 5.97 g/cm3 |
| symmetry | C4v | Melting point | 1840 ℃ |
| Lattice dimensions | a = 3.66 Å c = 12.01 Å | Refractive index | no = 1.9331 ne = 1.9564 |
| Lattice volume | 161.15 Å3 | Group velocity dispersion | ∼95 fs2/mm |
| Molecular weight | 288.31 g/mol | Thermo-optic coefficients | dno/dT = –7.6 × 10−6 K−1 dne/dT = –8.6 × 10−6 K−1 |
| Occupation site | Gd3+/Ca2+ | Gain bandwidth | ~90 nm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shen, Y. Advances of Yb:CALGO Laser Crystals. Crystals 2021, 11, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091131
Wang H, Pan J, Meng Y, Liu Q, Shen Y. Advances of Yb:CALGO Laser Crystals. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091131
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Jing Pan, Yuan Meng, Qiang Liu, and Yijie Shen. 2021. "Advances of Yb:CALGO Laser Crystals" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091131
APA StyleWang, H., Pan, J., Meng, Y., Liu, Q., & Shen, Y. (2021). Advances of Yb:CALGO Laser Crystals. Crystals, 11(9), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091131








