A Light-Mixing Liquid Crystal Lens-Like Cell to Decrease Color Shift and Tune Brightness for Displays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
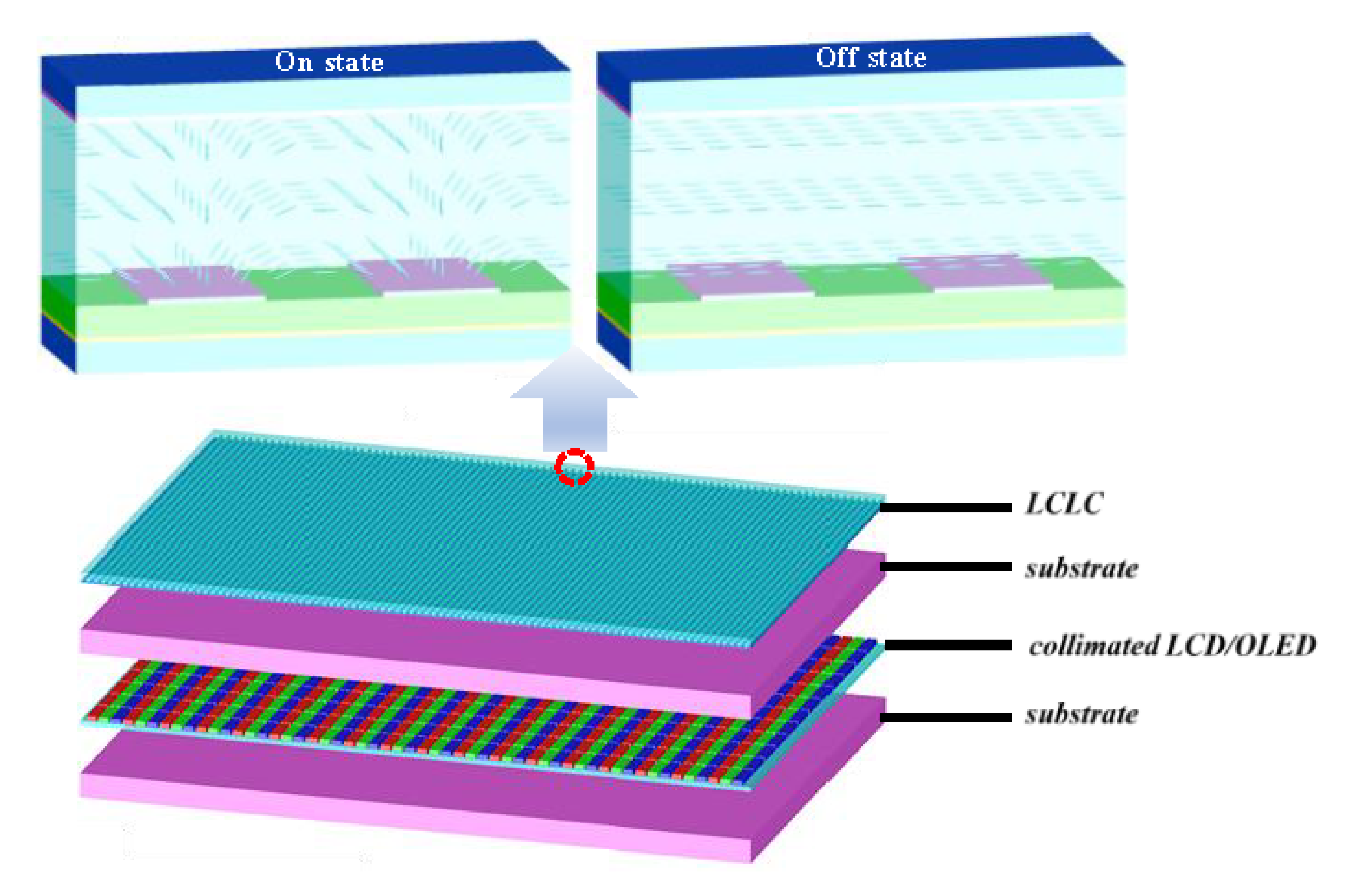
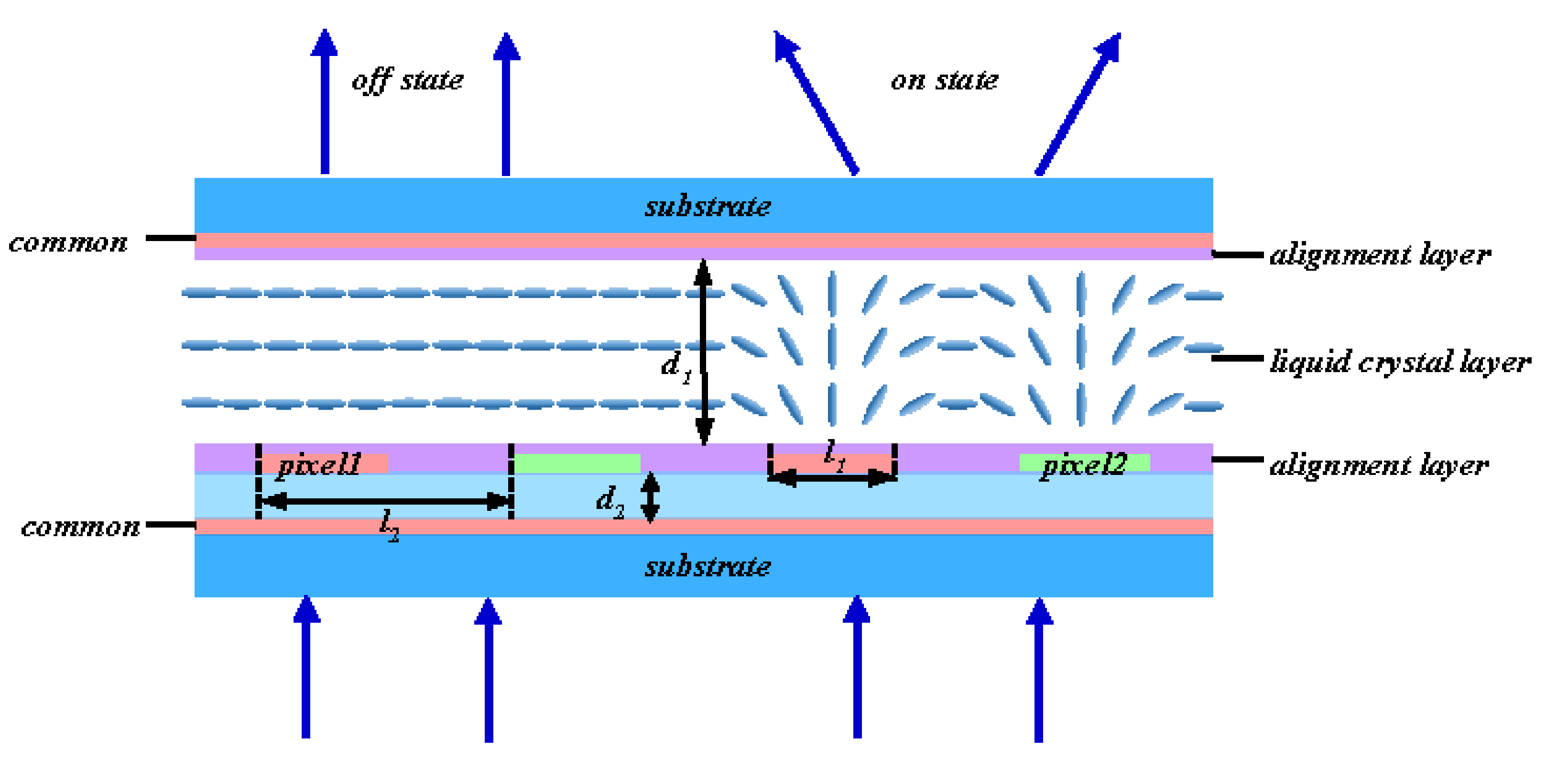
2. Device Structure and Principle
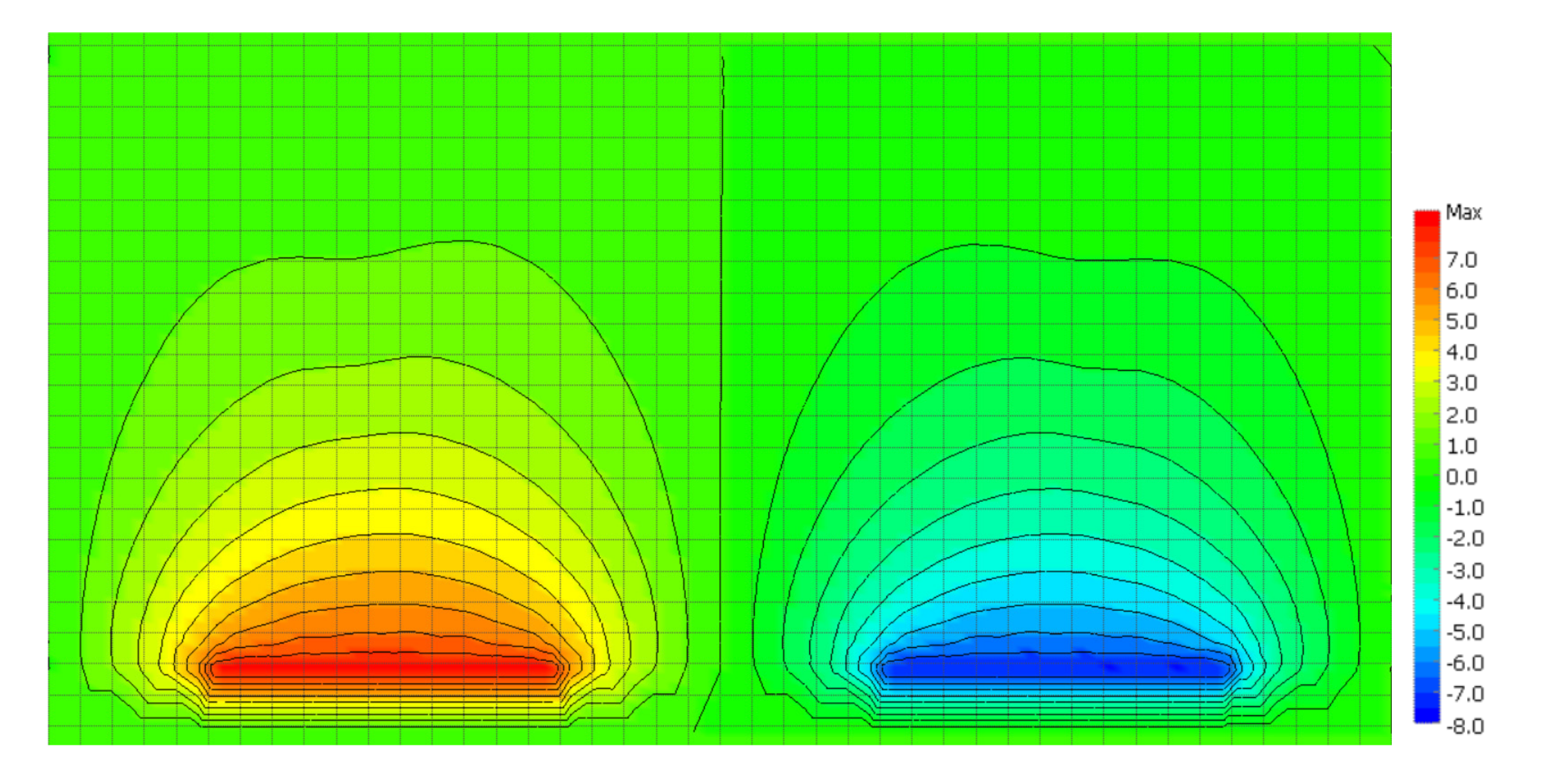
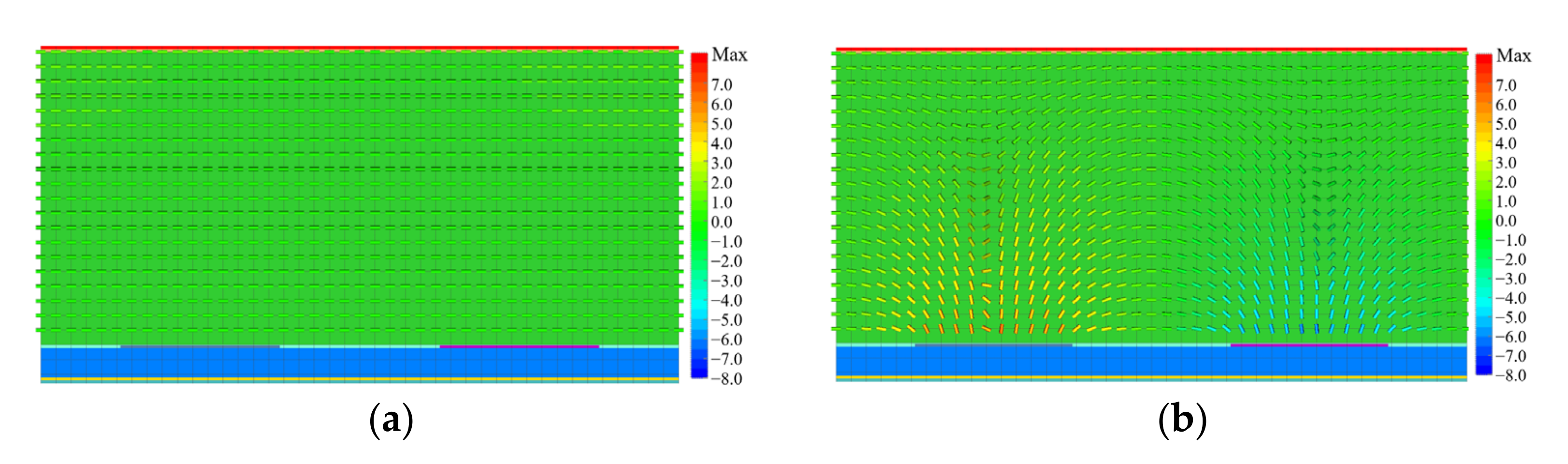
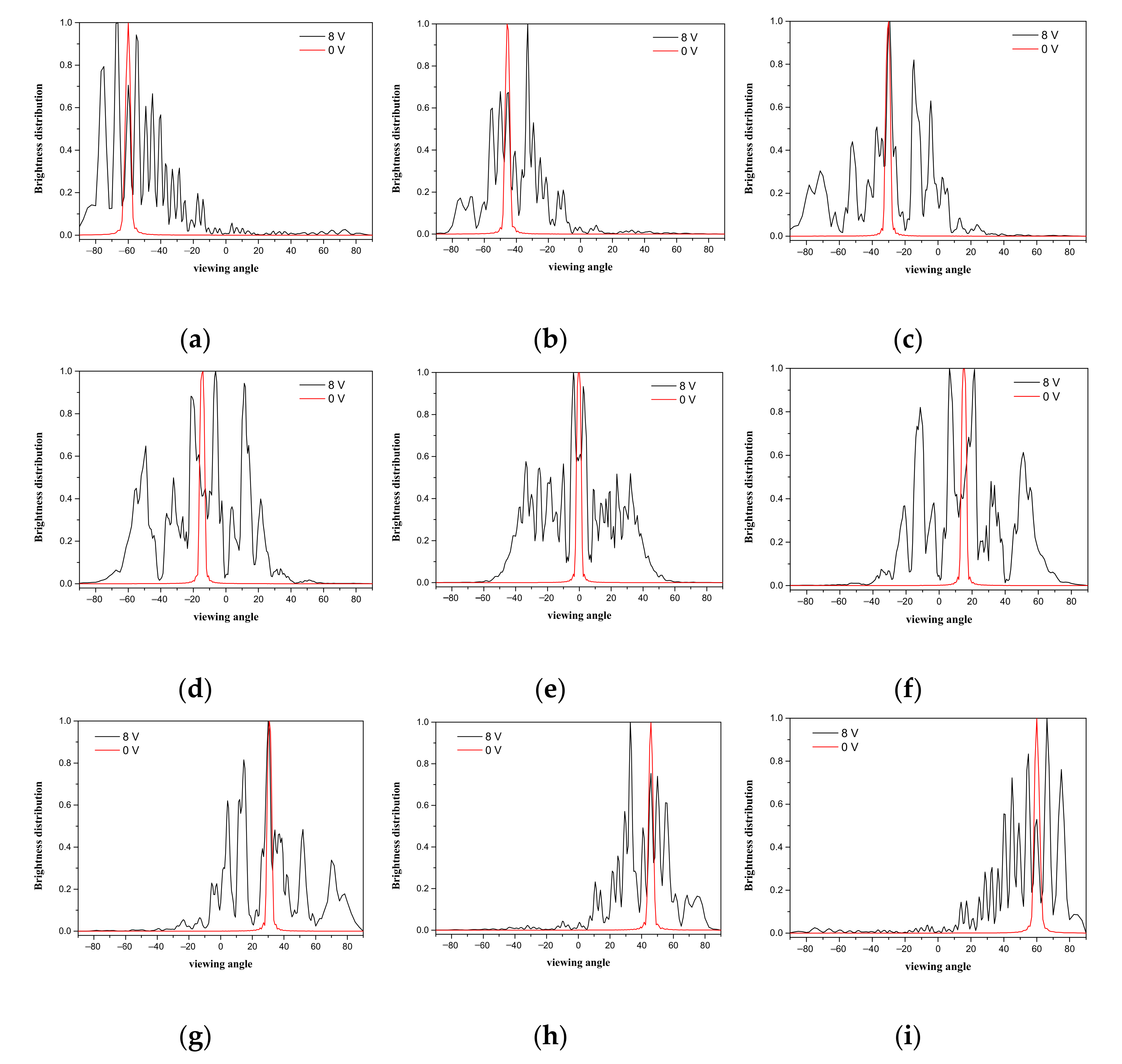
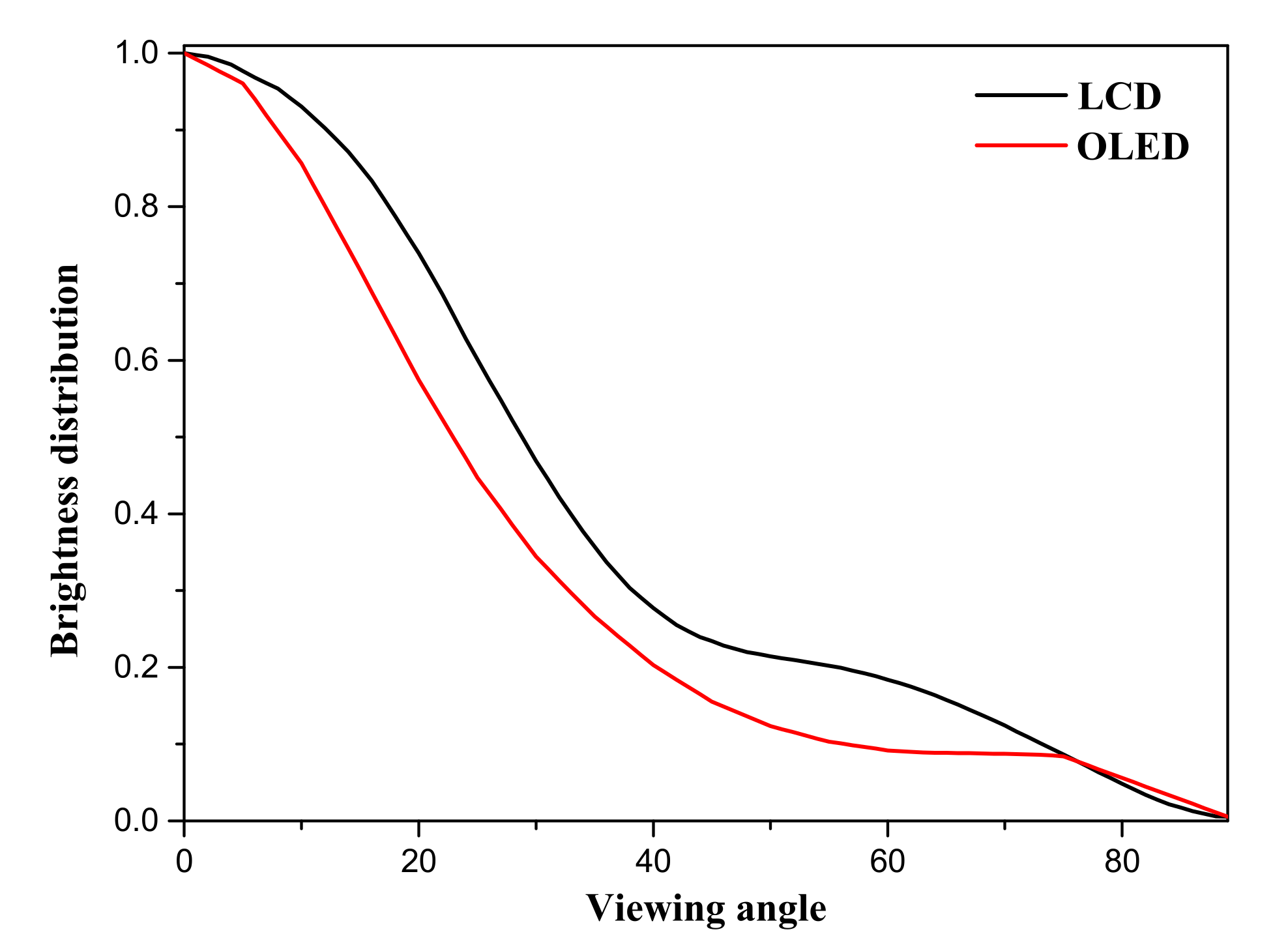
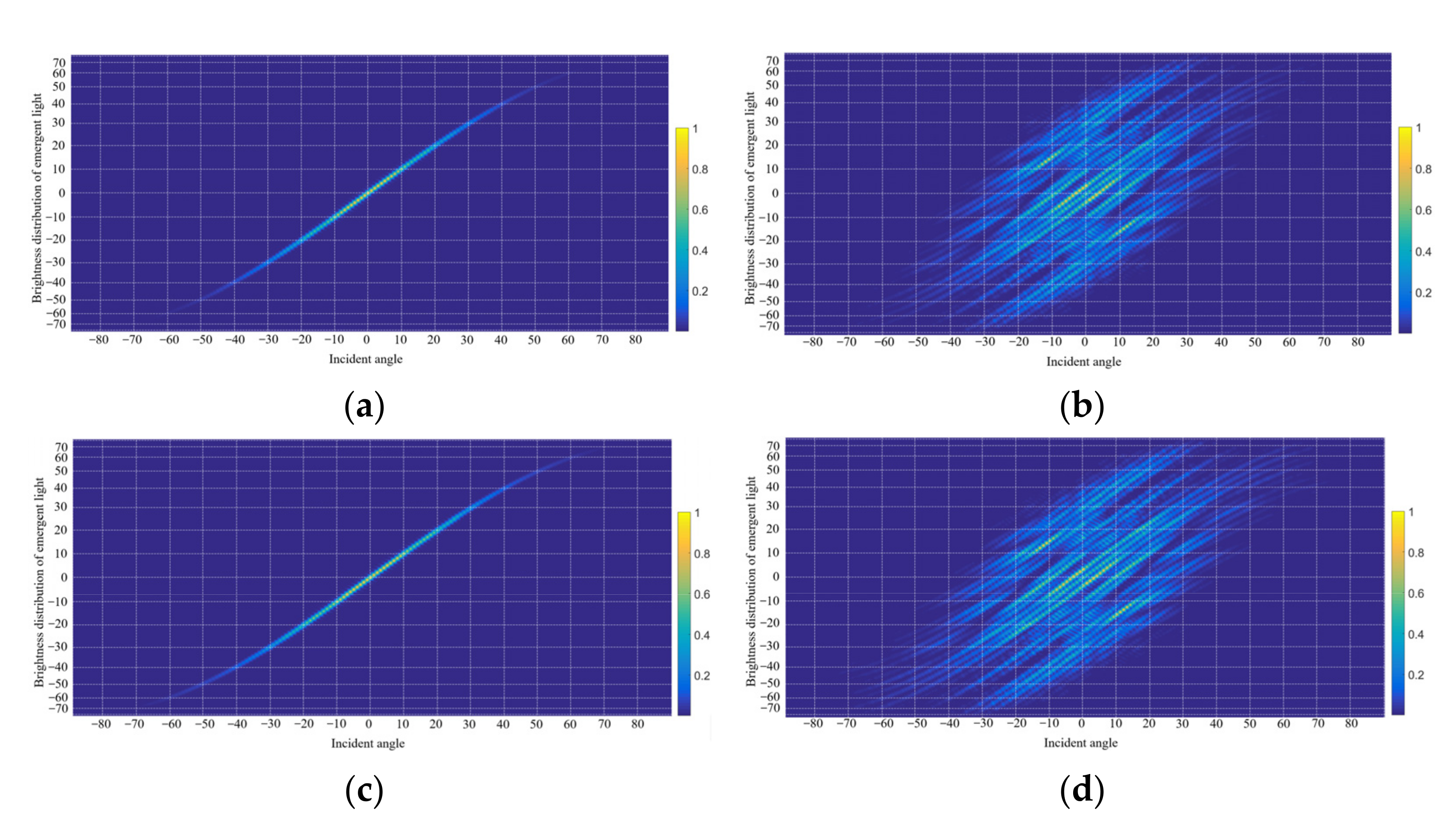
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Hsiang, E.L.; Deng, M.Y.; Wu, S.T. Mini-LED, Micro-LED and OLED displays: Present status and future perspectives. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, B.Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.T. Liquid crystal display and organic light-emitting diode display: Present status and future perspectives. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.S.; Oh, M.; Park, B.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, D. 51-1 Novel Pixel Structure for 8K QUHD LCD Panel with the Enhanced Optical Performances. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2019, 50, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, R.; Maruyama, J.; Murakoso, T.; Ishii, M.; Hiyama, I.; Kato, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Tanioka, K.; Chiba, T. 55-in. 8K4K IPS-LCDs with wide viewing angle, high frame frequency, wide color gamut, and stereoscopic. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 075102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Kurosaki, D.; Nakazawa, Y.; Okazak, I.K.; Oezuka, J. 42-2: Low Power Consumption 8K Liquid Crystal Display with Oxide Semiconductor/Oxide Conductor Pixel (Transparent Pixel). SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2017, 48, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashita, S.; Watanabe, K.; Shimoshikiryoh, F. 6-2: Novel Liquid Crystal Display Mode “UV2A II” with Photo Alignment Technology for a Large-Screen 8K Display. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2019, 50, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Chen, M.; Li, D.; Yu, G.; Sun, Y.B. A controllable viewing angle optical film using micro prisms filled with liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 48, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, S.T.; Lee, S.H. Reducing the color shift of a multidomain vertical alignment liquid crystal display using dual threshold voltages. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 051114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Qi, H.; Ge, Z.; Wu, S.T. Color shift reduction of a multi-domain IPS-LCD using RGB-LED backlight. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 6243–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadt, M.; Seiberle, H.; Schuster, A. Optical patterning of multi-domain liquid-crystal displays with wide viewing angles. Nature 1996, 381, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Oh, S.W.; Huh, J.W.; Yoon, T.H. Four-domain electrode structure for wide viewing angle in a fringe-field-switching liquid crystal display. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Li, X.S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.M.; Sun, Y.B. Low gamma shift blue-phase liquid crystal display with electric filed induced multi-domain electrode structure. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Yoon, T.H. Achromatic wide-view circular polarizers for a high-transmittance vertically-aligned liquid crystal cell. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4683–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H. The Wide View (WV) Film for Enhancing the Field of View of LCDs. J. Disp. Technol. 2005, 1, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Itoh, Y.; Nishiura, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Shinagawa, Y. Performance of a Novel Optical Compensation Film Based on Negative Birefringence of Discotic Compound for Wide-Viewing-Angle Twisted-Nematic Liquid-Crystal Displays. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 36, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kusafuka, K.; Shimizu, H. Optimum Film Compensation of Viewing Angle of Contrast in In-Plane-Switching-Mode Liquid Crystal Display. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, 4822–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Yoon, T.H. Elimination of light leakage over the entire viewing cone in a homogeneously-aligned liquid crystal cell. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5808–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, T.; Yasuda, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Sakai, E.; Mori, H. Novel WV film for wide-viewing-angle TN-mode LCDs. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2012, 15, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y. Low-gamma shift asymmetrical double-side blue-phase liquid crystal display. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, Y.F.; Hong, Q.; Wu, S.T. Compensation Film Designs for High Contrast Wide-View Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 10, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Sohn, I.; Cho, E.; Park, S.; Kim, E. Color Shift Reduction of Liquid Crystal Displays by Controlling Light Distribution Using a Micro-Lens Array Film. J. Disp. Technol. 2012, 8, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Park, H.; Joo, K.I.; Jeong, H.D.; Kim, H.R. Continuous Viewing Angle Distribution Control of Liquid Crystal Displays Using Polarization-Dependent Prism Array Film Stacked on Directional Backlight Unit. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2016, 20, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.W.; Zhu, R.D.; He, J.; Duan, W.; Hu, W.; Lu, Y.Q.; Li, M.C.; Lee, S.L.; Dong, Y.J.; Wu, S.T. Going beyond the limit of an LCD’s color gamut. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, G.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, S.C.; Zhu, R.; Wu, S.T. Analysis and optimization on the angular color shift of RGB OLED displays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 33629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, C.; Whang, K.W. Light outcoupling enhancement from top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes made on a nano-sized stochastic texture surface. Opt. Express 2014, 22, A1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Cheong, H.W.; Lee, C.; Whang, K.W. Increased light extraction efficiency from top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes employing a mask-free plasma-etched stochastic polymer surface. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 095502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, W.; Chu, P.K. Light-emitting diodes enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Yoon, D.M.; Kim, M.; Kim, C.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.H.; Woo, D. Enhancement of hole injection and electroluminescence by ordered Ag nanodot array on indium tin oxide anode in organic light emitting diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 013306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Han, J.; Lee, G.; Sohn, J.; Kwon, Y.; Choi, M.; Lee, C. Enhanced light out-coupling in OLED employing thermal-assisted, self-aggregated silver nano particles. Org. Electron. 2018, 52, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.P.; Choi, B. Enhanced Light Extraction from Bottom Emission OLEDs by High Refractive Index Nanoparticle Scattering Layer. Nanomater. Basel 2019, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, H.; Chu, F.; Guo, Y.Q.; Tian, L.L.; Wang, Q.H.; Sun, Y.B. Large aperture liquid crystal lens array using a composited alignment layer. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 9254–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriezis, E.E.; Elston, S.J. Finite-difference time domain method for light wave propagation within liquid crystal devices. Opt. Commun. 1999, 165, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriezis, E.E.; Elston, S.J. Light wave propagation in liquid crystal displays by the 2-D finite-difference time-domain method. Opt. Commun. 2000, 177, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.K.; Rey, A.D. Computational modeling of the propagation of light through liquid crystals containing twist disclinations based on the finite-difference time-domain method. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopidis, K.P.; Zografopoulos, D.C.; Kriezis, E.E. Rigorous broadband investigation of liquid-crystal plasmonic structures using finite-difference time-domain dispersive-anisotropic models. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2013, 30, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Fukuda, J.I.; Yoshida, H.; Ozaki, M. Finite-difference time-domain analysis of cholesteric blue phase II using the Landau–de Gennes tensor order parameter model. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3380–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Ma, H.M.; Sun, Y.B. Optical simulation of in-plane-switching blue phase liquid crystal display using the finite-difference time-domain method. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, H.; Wang, L.; Ren, G.; Dan, Y.-Q.; Zhong, X.-T.; Ou, J.-Y.; Yuan, J.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-T. A Light-Mixing Liquid Crystal Lens-Like Cell to Decrease Color Shift and Tune Brightness for Displays. Crystals 2022, 12, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12020213
Dou H, Wang L, Ren G, Dan Y-Q, Zhong X-T, Ou J-Y, Yuan J-Y, Zhong Y-T. A Light-Mixing Liquid Crystal Lens-Like Cell to Decrease Color Shift and Tune Brightness for Displays. Crystals. 2022; 12(2):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Hu, Lu Wang, Gan Ren, You-Quan Dan, Xin-Tong Zhong, Jia-Yi Ou, Jia-Yi Yuan, and Yu-Tian Zhong. 2022. "A Light-Mixing Liquid Crystal Lens-Like Cell to Decrease Color Shift and Tune Brightness for Displays" Crystals 12, no. 2: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12020213
APA StyleDou, H., Wang, L., Ren, G., Dan, Y.-Q., Zhong, X.-T., Ou, J.-Y., Yuan, J.-Y., & Zhong, Y.-T. (2022). A Light-Mixing Liquid Crystal Lens-Like Cell to Decrease Color Shift and Tune Brightness for Displays. Crystals, 12(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12020213






