Abstract
One of today’s most-used glass products is a composite made of at least two glass panels connected with a soft polymeric interlayer—laminated glass. The mechanical properties of such elements are influenced by interlayer properties and the type of glass used. In this work, experimental and numerical analyses of laminated glass panels exposed to four-point bending are performed to observe and compare the stresses and displacements caused by different parameters, such as temperature, load duration, the thickness and type of the interlayers, as well as the symmetrical and nonsymmetrical disposition of the glass plates’ thickness. The numerical analysis was verified by four-point bending experimental tests. After validation, a parametric study on these influences was performed. To obtain the relationship between the load duration, temperature, and thickness of the interlayer compared to the maximal displacement (as a measure of flexural stiffness) and tension stress in the bottom glass plate, an analytical polynomial of a sixth total order is proposed. Isosurfaces are created, showing the dependence of stresses and displacements on the specified parameters as well as clearly showing differences in the behavior of laminated glass panels for the same conditions but with different interlayers. Based on the findings of the parametric study, conclusions are derived about the flexural stiffness and stress distribution in two-plate laminated glass with PVB and ionoplast interlayers.
1. Introduction
Laminated glass consists of several glass plates connected by polymorphic intermediate layers. Today, facade systems are made of this material, areas above valuable archaeological sites are paved with it, and attractive pedestrian bridges as well as stairs are made with it. Interest in the use of laminated glass in construction has increased due to the fact that laminated glass retains a particularly interesting transparency compared to monolithic glass, and its advantages over monolithic glass include greater impact resistance, improved sound resistance, and better thermal insulation inside a building. The most important advantage of laminated glass over monolithic glass is its improved safety, which is most visible in the case of breakages of the structure, i.e., if the glass surface is broken into fragments, the interlayer will preserve them together and prevent complete disintegration, avoiding destruction or injuries. Despite the growing use of these types of glass structures, the norms for their calculation are not yet fully defined, nor are the national supplements of individual countries. Therefore, it is important to experimentally and numerically test such structures that will contribute to the improvement and completion of engineering calculations. Given the fact that such elements are exposed to different atmospheric and environmental conditions, it is important to examine how they behave under these influences. One of these is the determination of the performance of laminated glass at different temperatures in addition to its response to load over time due to temperature changes. Since we are talking about the composite material of glass and interlayers, it is necessary to include the action and change in the performance of each material separately, but also to consider the behavior of the whole.
Therefore, the most important characteristics of glass as a material and of the interlayers will be shown below, with reference to previous research on both.
1.1. Glass as Material
SiO2-Na2O-CaO (with additional ingredients) is the most commonly used type of glass, called soda–lime glass (referred to in the text as “glass”). Soda-lime glass, produced by the float process, can be used without any additional treatment if there are no additional demands for increased safety, strength, design, etc. In the production process, a molten tin (tin bath) is a base for cooling and transporting a molten glass, consequently producing a flat surface that does not require any postprocessing treatment. After acquiring a solid state in a further part of the production process, the glass ribbon is heated and slowly cooled to release residual stresses (annealing).
The mechanical properties of glass and the characteristic bending strengths according to EN16612 [1] are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. By adding different additional ingredients to the chemical composition, it is possible to impact some glass properties, such as heat resistance, color, etc. Except for changes in ingredients, there are physical treatments that can improve glass mechanical properties. One of the most-used processes is tempering, a process that can be accomplished by a chemical treatment or by heating and quickly cooling glass panels. The final result of both processes is prestressing, which results in an increased tensile strength of the glass panels. Besides higher strength, glass develops the ability of safe breakage. The difference between the fracture pattern of the annealed and tempered glass is presented in Figure 1. Annealed glass produces large and sharp pieces that can cause injuries, while tempered glass develops small, cubical, and harmless pieces. Heat-strengthened glass is tempered glass but with a lower level of prestressing [2]. The glass modulus is not affected by additional processing (tempering, etc.) or atmospheric conditions. Besides the glass type, the loading also has a significant impact on the breakage pattern. For static loading, the cracks are primarily transversal and straight, and the total length of the cracks is smaller than those that are circular-shaped and produced by impact loading [3,4,5,6]. The mechanical characteristics of glass are not affected by changes in the temperature in the interval of the ambient temperatures.

Table 1.
Basic mechanical properties of glass according to EN16612 [1].

Table 2.
Characteristic bending strength of each type of glass according to EN16612 [1].
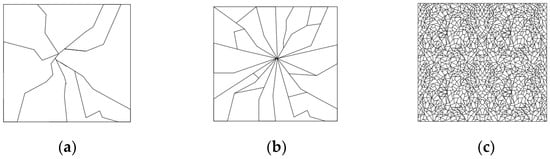
Figure 1.
Breakage pattern for each type of glass: (a) annealed glass/float glass; (b) heat-strengthened glass; (c) thermally toughened glass [2].
1.2. Laminated Glass—Type of Interlayers
Laminated glass can be produced from any type of glass by coupling at least two glass panels with an interlayer, providing a better load capacity and postbreakage safety by ensuring the integrity of glass during a breakage. Interlayers in laminated glass are usually transparent polymer materials with large variations in their mechanical properties depending on temperature, load duration, moisture, etc., and they ensure coupled behavior and a postbreakage capacity [3,4,5,6,7,8]. The mechanical behavior of laminated glass structures could be bounded between two limit states: one in which we neglect the influence of interlayers and observe laminated glass as two separate plates without friction, and a monolithic behavior where we observe a laminated glass panel with full shear transfer through an interlayer [9,10]. The positioning of a structure within the presented limits depends on the type of loading and load duration, the mechanical characteristics of the interlayer, and the type of boundary conditions. For high-velocity loads (impact), the interlayer mostly behaves very stiffly, and it is possible to observe the panel as monolithic, while at static loading we emphasize the influence of the viscoelastic character of the interlayer.
Once a plate is broken, fragments remain adhered to the interlayer. In a tensile zone, that adhesion does not provide any specific benefit. However, in the compression zone, the remaining glass fragments can create additional bearing capacity while making contact with each other, and by doing so, transfer compression stresses.
1.3. Influence of Interlayers’ Behavior on the Capacity of Laminated Glass Plates
The most commonly used interlayers in laminated glass structures are PVB (polyvinyl butyral), EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate), and ionoplast. In a static analysis, the mechanical properties of interlayers are primarily affected by temperature conditions, moisture, and load duration. Therefore, the researchers were engaged in the experimental and computer testing of samples of these materials in addition to defining parameters to describe the behavior of these materials. Studies in the literature [11] have shown that the mechanical properties of polymer interlayers show dependence on multiple external influences, such as current temperature, heat cycles, or exposure to moisture. The influence of temperature as a parameter in the analysis of influences on the relaxation behavior of polymers was analyzed in [12], in which it was found that an increase in the temperature reduces the relaxation time of the polymer. This property was included in the model as a variable of a function of time [13]. Taking all of the above characteristics into consideration, the material parameters of the generalized Maxwell chain model for two types of interlayers, such as PVB-based (TROSIFOL® BG R20 from Kuraray, Tokyo, Japan) and EVA-based EVALAM® 80–120 (from Evalam, Coruna, Spain), were defined, which enables the description of their time- and temperature-dependent behavior [14]. Static shear experimental testing [15] and long-term testing [16] also showed shear modulus degradation for temperature increases and for longer load durations.
For numerical simulations of laminated glass behavior, different models of interlayers are used. The chosen model of interlayer material depends on the type of loading: hyperelastic models [5] and rate-dependent hyperelastic models [7] are often used for the dynamic type of loading, while some authors consider elastoplastic models for high strain rates [17] and nonlinear elastic hardening materials [18] for static loading.
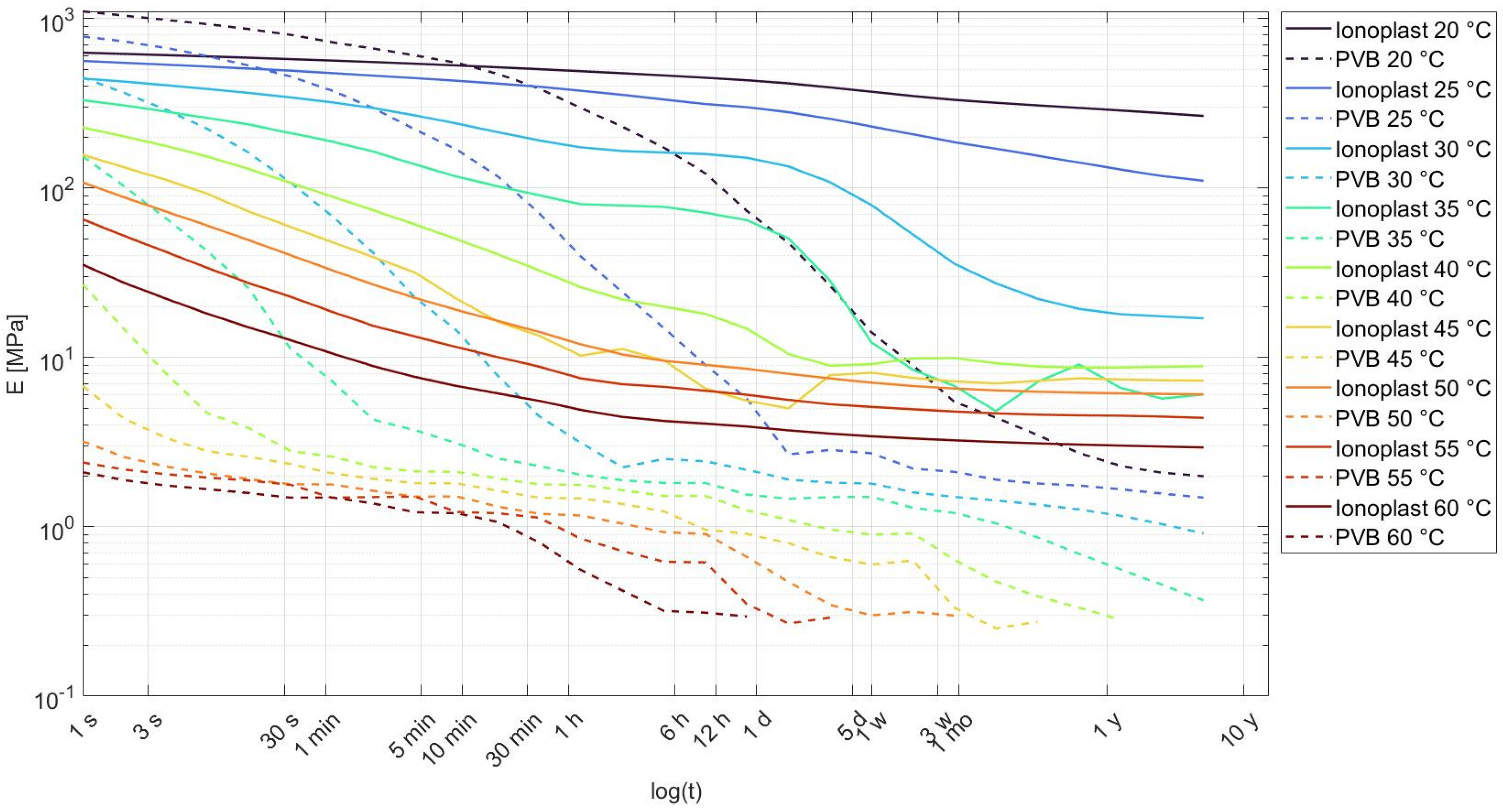
The material specifications of interlayers are summarized in Table 3, and graphs with Young’s moduli are presented in Figure 2. All information regarding ionoplast and PVB interlayers is taken from the available technical documentation [19,20]. The thickness of an interlayer is mainly in the range of 0.36 to 2.28 mm; it differs depending on the type of interlayer and the physical requirements.
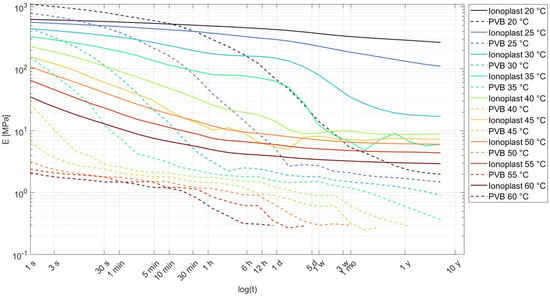
Figure 2.
Comparison of Young’s modulus, E (MPa), degradation for the ionoplast and PVB interlayers in dependence on the load duration log, (t(s)), at different temperatures, T (°C) [19,20].
PVB (polyvinyl butyral) is a synthetic polymer of the polyvinyl acetate family, one of the most-used materials for coupling glass panels. The mechanical properties of this material show a significant dependence on temperature, load duration [17,21,22], and moisture [23]. There are numerous types of PVB interlayers used for different primary purposes (acoustic, structural, and solar). These types of interlayers have different material properties, resulting in different stiffnesses and different glass transition temperatures (Tg) [24]. Here, we will observe the structural behavior of PVB. The mechanical properties (shear modulus) of PVB interlayers show a discrepancy when comparing specimens produced from PVB before the autoclave process and those who are embedded inside laminated glass with the autoclave process [25]. Since heat and pressure from the autoclave process have an influence on this material, it is more preferable to observe PVB characteristics while embedded in laminated glass. PVB interlayers show significant degradation of shear transfer at increased temperatures.
EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) is a copolymer interlayer material, a moisture-resistant interlayer [23] that is often used for specific purposes, such as photovoltaic cells or if a colored design is required. Except for some experiments, which provide specific types of results, there is not much available information about the material characteristics of EVA interlayers. The production of laminated glass with this interlayer is less demanding and does not require an autoclave process [24]. Tests on small-scale samples of laminated glass with PVB and EVA interlayers from the literature (see [14]), in a dynamic single-lap shear test and dynamic torsion tests, show differences between these two interlayers. For samples tested at different frequencies (dynamic tests) and temperatures, PVB showed a generally stiffer response compared to EVA, but that was valid only for temperatures under 40 °C. Additionally, at a significantly lower temperature (around −20 °C), where other interlayers have almost brittle behavior, EVA interlayers show better impact resistance (penetration resistance) due to their low glass-transition temperatures [24]. On the other hand, four-point bending tests at room temperature [26] showed similar behavior of a laminated glass panel with an EVA interlayer and PVB interlayer. EVA interlayers have thermorheologically complex behavior [27]. By testing samples of EVA interlayers, authors [28] describe behavior with two types of constitutive models regarding the type of loading. At a small strain, EVA is described with time-dependent behavior (linear viscoelasticity), and for large deformations, where nonlinear stress–strain behavior occurs, material behavior is described with a hyperelastic model. These models are derived from dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA), uniaxial tests, and biaxial tests, and they can be used for modeling the postbreakage capacity of laminated elements.
In [29], the authors tested samples of different types of PVB and EVA interlayers loaded in static single-lap shear tests, and in [30] PVB samples were tested in double-lap long-term tests. In [29], the temperature and strain rate are varied, and a different humidity and temperature are observed in [30]. Both tests confirmed the significant dependence of interlayer characteristics on temperature, as well as their minor sensitivity to humidity. These shear tests could be characterized as being more appropriate for describing interlayer behavior in laminated glass panels in an unfractured state. In [31], the authors first presented an overview of the generally used methods for determining polymer thermoviscoelastic behavior, and thereafter presented the results of dynamic-torsion cyclic tests on small samples of laminated glass. In these types of tests, laminated glass samples are glued for rheometers, which can affect the final results.
When observing all of the mentioned tests, one can find that some tests for the determination of interlayer mechanical characteristics are performed on samples of interlayer materials only (no glass panels involved), and others are performed on coupled elements with glass parts. Interlayers are not predetermined for usage as stand-only elements, and in laminated glass panels, they are dominantly loaded in shear. Tests on raw materials should always be validated with large-scale tests on laminated glass [32].
An ionoplast interlayer is an ionomer-based material that provides the highest level of structural performance [23], but it is also the most expensive one. It was originally developed for hurricane-resistant glass surfaces on building facades [6]. Since the degree of coupling glass plates in a laminated structure depends upon the shear stiffness of the polymeric interlayer, ionoplast is the best option when there are high demands for strength and resistance [33]. In four-point bending experimental tests [34], laminated glass with an ionoplast interlayer shows a higher initial failure load and ultimate load (providing better postbreakage capacity) than laminated glass with PVB and EVA interlayers.

Table 3.
Basic mechanical properties of the interlayers [19,20,24].
Table 3.
Basic mechanical properties of the interlayers [19,20,24].
| PVB (Structural) | EVA [34] | Ionoplast | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 1070 kg/m3 | 970 kg/m3 | 950 kg/m3 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.476 | 0.32 | 0.458 |
| Glass transition temperature [24] | 12–25 °C | −28 °C | 55 °C |
Regarding everything that has been mentioned, in the numerical model we included the material model of the interlayers, which involves the degradation of Young’s modulus, E, and the shear modulus, G, in dependence on the load duration log, (t(s)), at different temperatures, T (°C). These parameters are dominant in laminated glass structures’ exposed bending.
2. Experimental Tests
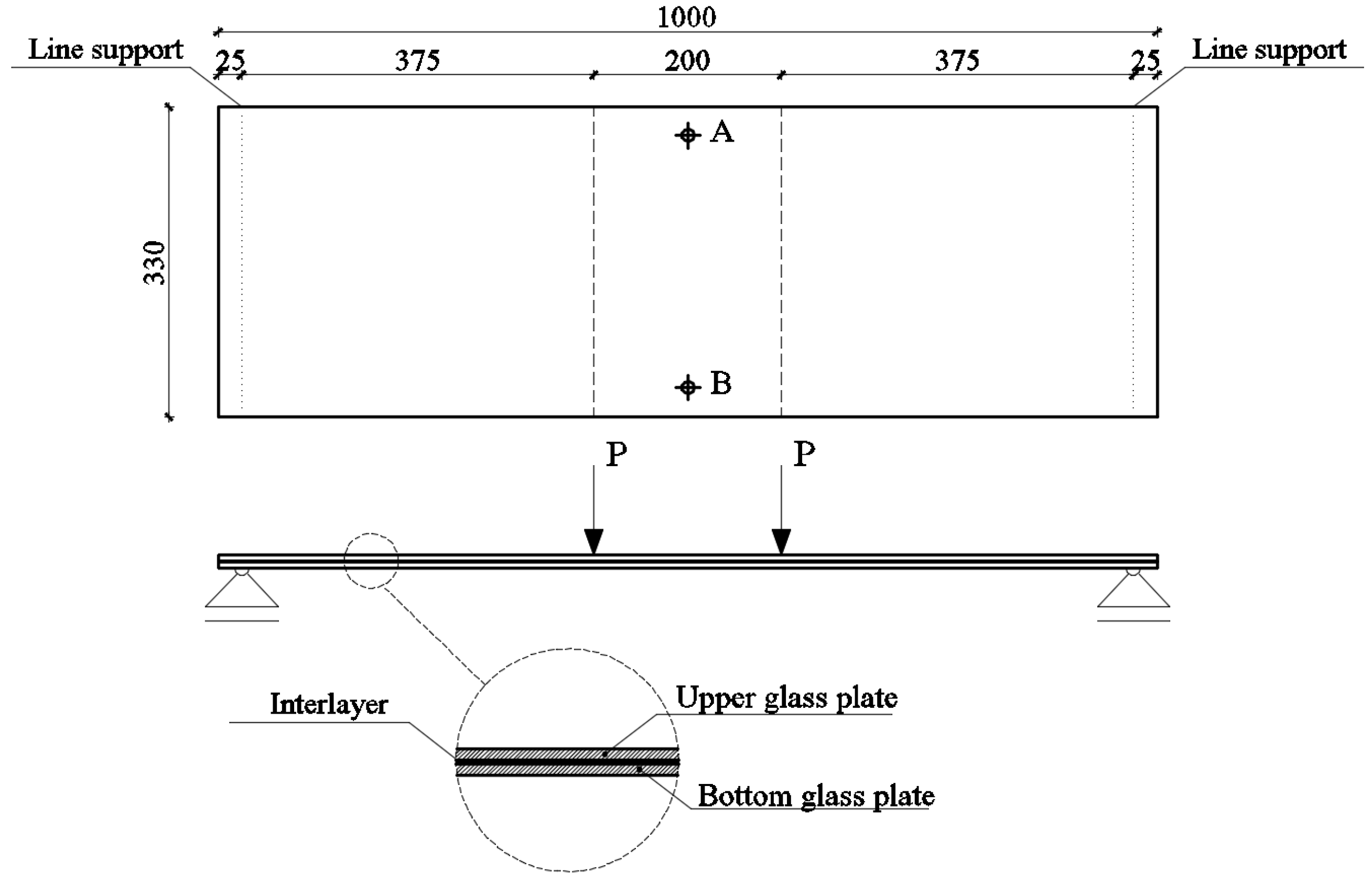
The available data and the mentioned analyses suggest the need for a parametric analysis of the influence of temperature change on the behavior of laminated glass loaded outside the plane. In order to perform this analysis, it is necessary to verify the numerical model with an experimental test. The experimental test on laminated glass specimens was carried out in the Structural Laboratory of the Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture and Geodesy. Laminated glass specimens were exposed to four-point bending. Specimens were made out of two tempered glass panels with a thickness of 6 mm. Glass panels were connected with a 0.76 mm-thick Saflex DG41 PVB (EASTMAN, Kingsport, TN, USA; E1min,25 °C = 387 MPa; G1min, 25 °C = 131 MPa; ν = 0.476) interlayer. The span was 950 mm, while the width and length of the specimen were 330 mm and 1000 mm, respectively. Hard contact of the steel bearing and the glass panel was prevented with 0.1 mm-thick rubber protection. The specimens were bent uniformly, increasing the bending stress at a rate of 2.0 N/mm2.s, until failure occurred, according to EN 1288-3 [35]. Specimens were exposed to the same load at the same temperature (25 °C) and moisture conditions (50%). All of the specimens were produced one year before the test, and they were stored in the same conditions.
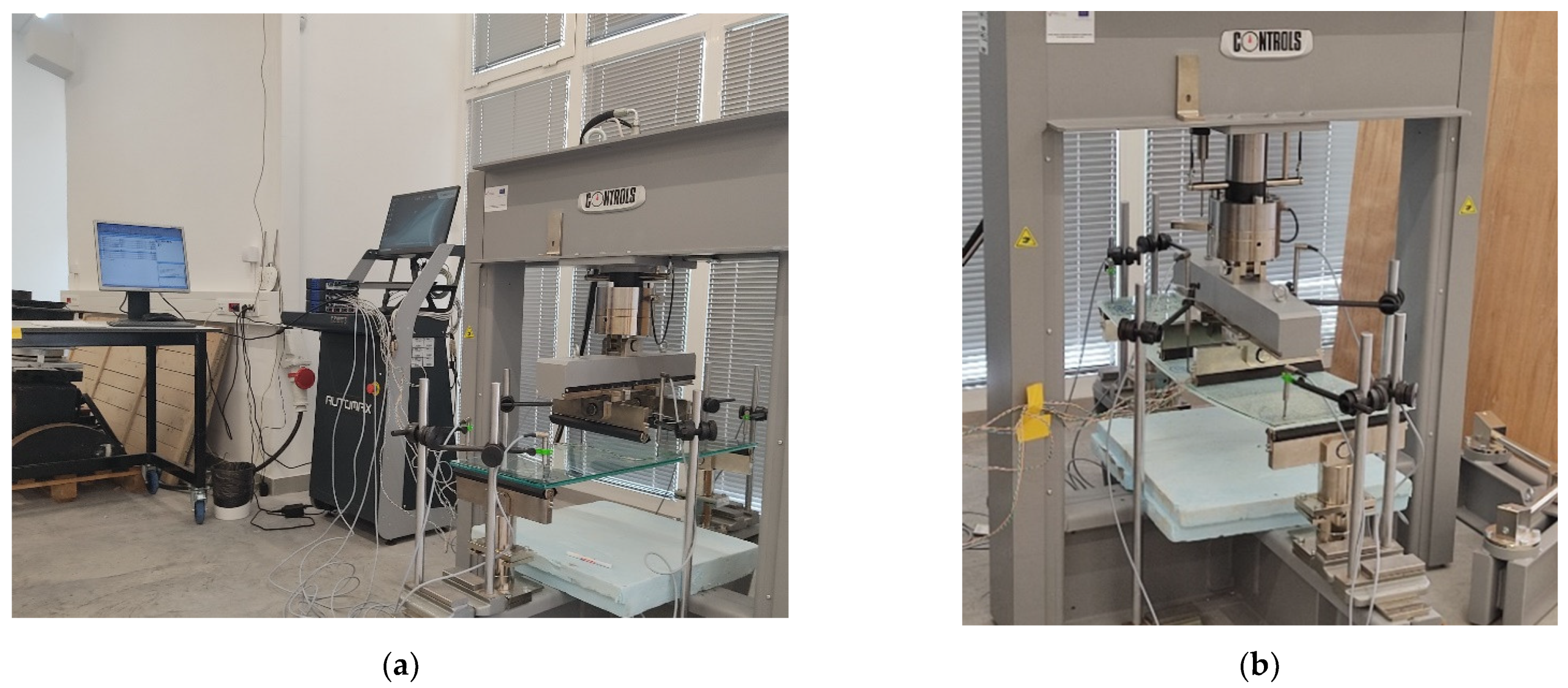
The experiments were performed on a CONTROLS Automax Multitest (CONTROLS, Milan, Italy) loading device. The samples were placed on cylindrical supports and separated with rubber pads. For the data acquisition, a QUANTUM MX840B (HBM, Darmstadt, Germany) was employed, with a sampling frequency of 300 Hz. Force and displacement were measured with CONTROLS implemented acquisition. Additionally, the deflections were measured with six linear variable displacement transducers (LVDTs), which were arranged symmetrically on the specimen: two at the mid-span and four at the bearings. The applied force was controlled by a CONTROLS device at each step.
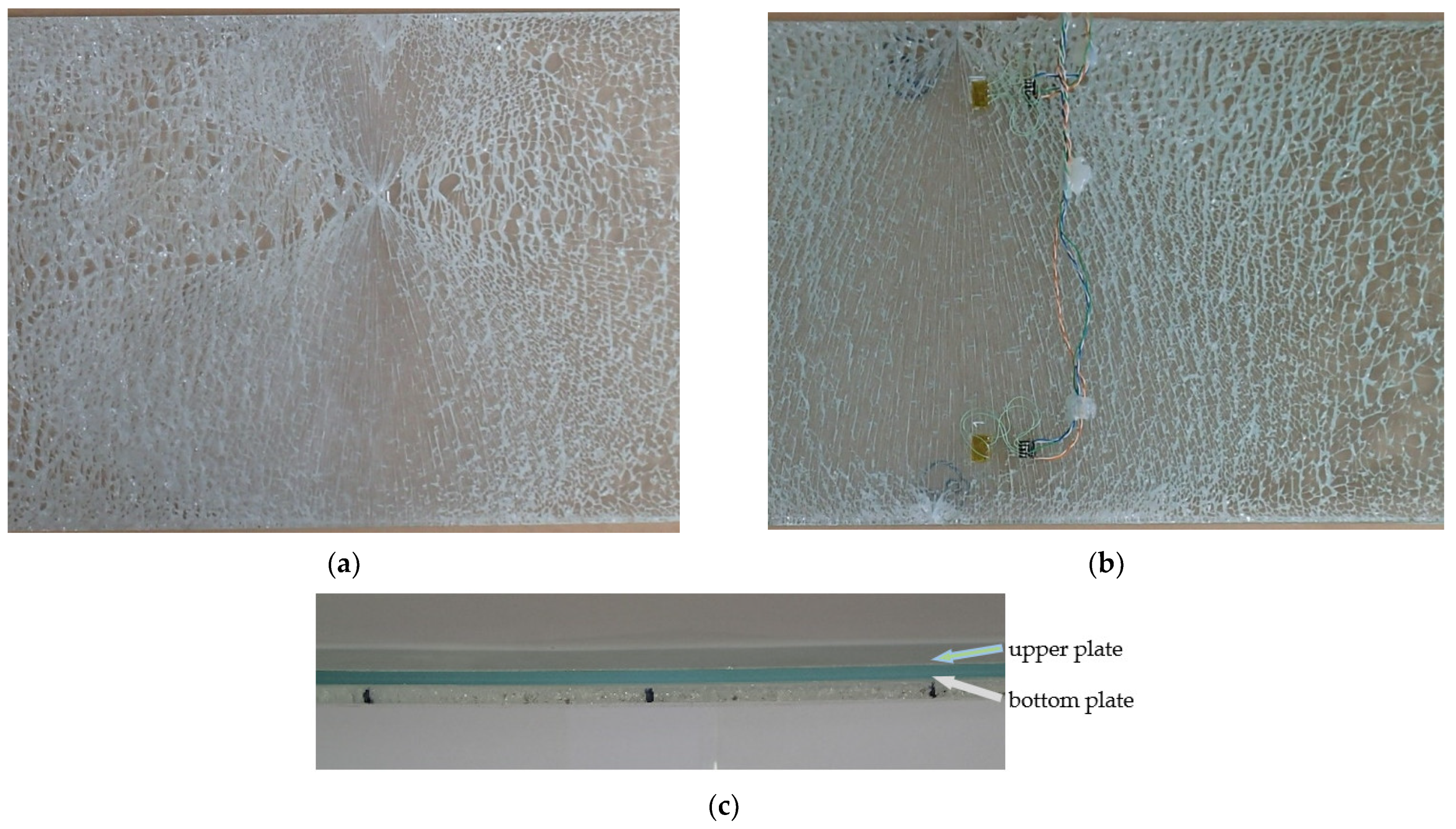
The test setup is presented in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Strains at the upper and bottom glass plates at points A and B (marked on Figure 3) were measured with four strain gauges. In all of the specimens, fractures occurred on the bottom plate, while the upper plate remained undamaged; see Figure 5. After the initial cracking of the bottom plate, the load-bearing capacity is reduced. After complete cracking, the glass can no longer withstand tensile stresses, but glass fragments remain attached to the polymer interlayer. In this phase, the polymer can provide the tensile force together with the lower part of the upper plate to withstand bending moments. At this stage, the load capacity also depends on the size of the fragments, which is directly related to the type of glass. In our experimental tests, fracturing occurs at the bottom plate, and such a cracked panel remains loaded with 1 kN of force without a significant increase in deflection.
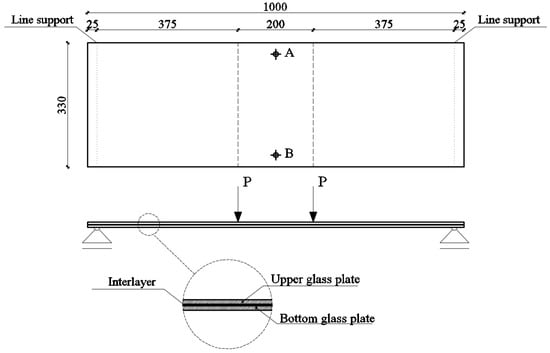
Figure 3.
Test setup for the four-point bending test.

Figure 4.
A view of the experiment: (a) test setup before loading; (b) breakage of bottom glass plate during the experiment.
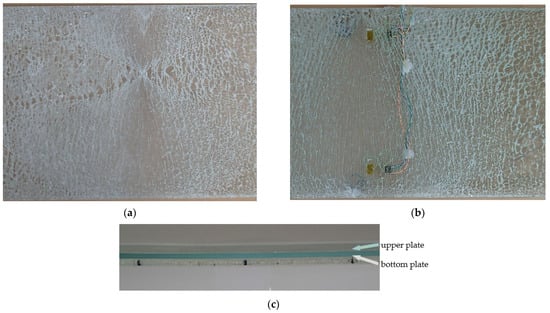
Figure 5.
Photography of fracture pattern on specimens: (a) S1; (b) S3; and (c) side view on center of laminated glass panel.
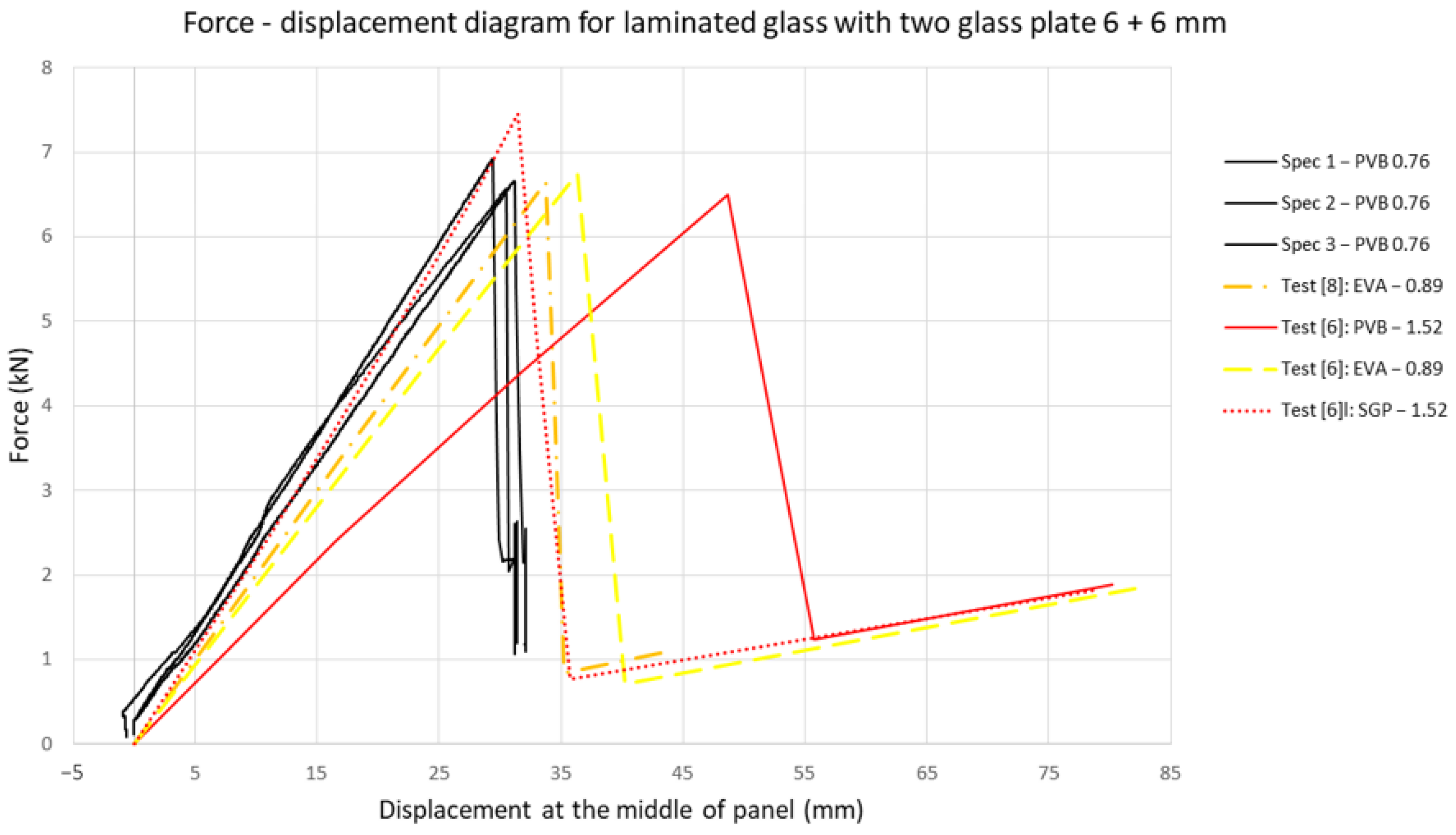
The results for all of the tested specimens are presented in Figure 6 and compared to the four-point bending tests on glass elements of Pankhardt and Balázs [8]. In the graph, only the results of the laminated glass panel tests are presented. It is evident that the results at room temperature do not differ significantly. The contribution of the interlayer to the global behavior of the glass panels at room temperature is minimal. Another comparison curve is from the experimental tests provided by Serafinavicius et al. [6], where the authors tested laminated glass composed of two 6 mm thick panels with PVB (1.52 mm), EVA (0.89 mm), and SGP (1.52 mm) interlayers.
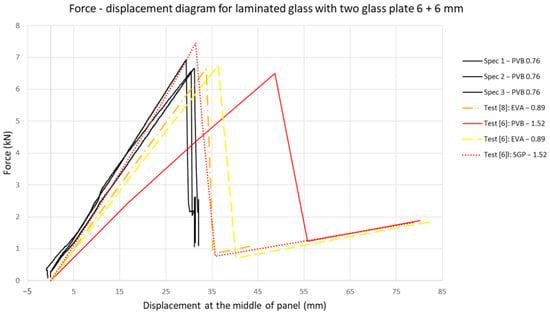
Figure 6.
Results of the four-point bending test: force-displacement diagram compared with experimental results from the literature [6,8].
These results showed a good accordance, regardless of the differences in span and the slightly different thicknesses of the interlayers. It is visible that at room temperature and for similar thicknesses (0.89 mm and 0.76 mm), the EVA [6,8] and PVB interlayers provide approximately the same ultimate loading. As expected, the SentryGlas ionoplast interlayer, at the same thickness (1.52 mm) as PVB [6], shows a much stiffer response, and thus an increase in the ultimate strength. It is important to mention that we defined the term “ultimate strength” as a breakage of the bottom (tensile) glass plate, while the upper glass plate remains undamaged. The performed tests, as well as the results from [6], confirm that after the breakage of the bottom glass plate, the laminated glass panel provides bearing capacity. After breakage, the panels are unloaded, but a permanent deformation of 12 mm remains. The deformed and damaged specimens are removed and placed on a flat surface with the broken glass plate facing upwards (loaded with own weight). The permanent deformation remains even 3 months after the test, regardless of the slight tendency of a weight force to straighten the panel. This permanent deformation is a product of bulk volume increase in the breakage of a tempered glass panel, which as a consequence has a plastic deformation of the interlayer.
Although interlayers and glass panels have significantly different mechanical behavior, it is proven [36] that, with increasing interlayer thickness, the ultimate load of glass panels also increases.
In all of the specimens exposed to four-point bending, fractures occur in the zone of the maximum moment (between the applied forces) on tensile glass plates, which is typical for static loading. It is visible in [37] that dynamic loading fracturing mostly occurs at the contact surface.
3. Numerical Model
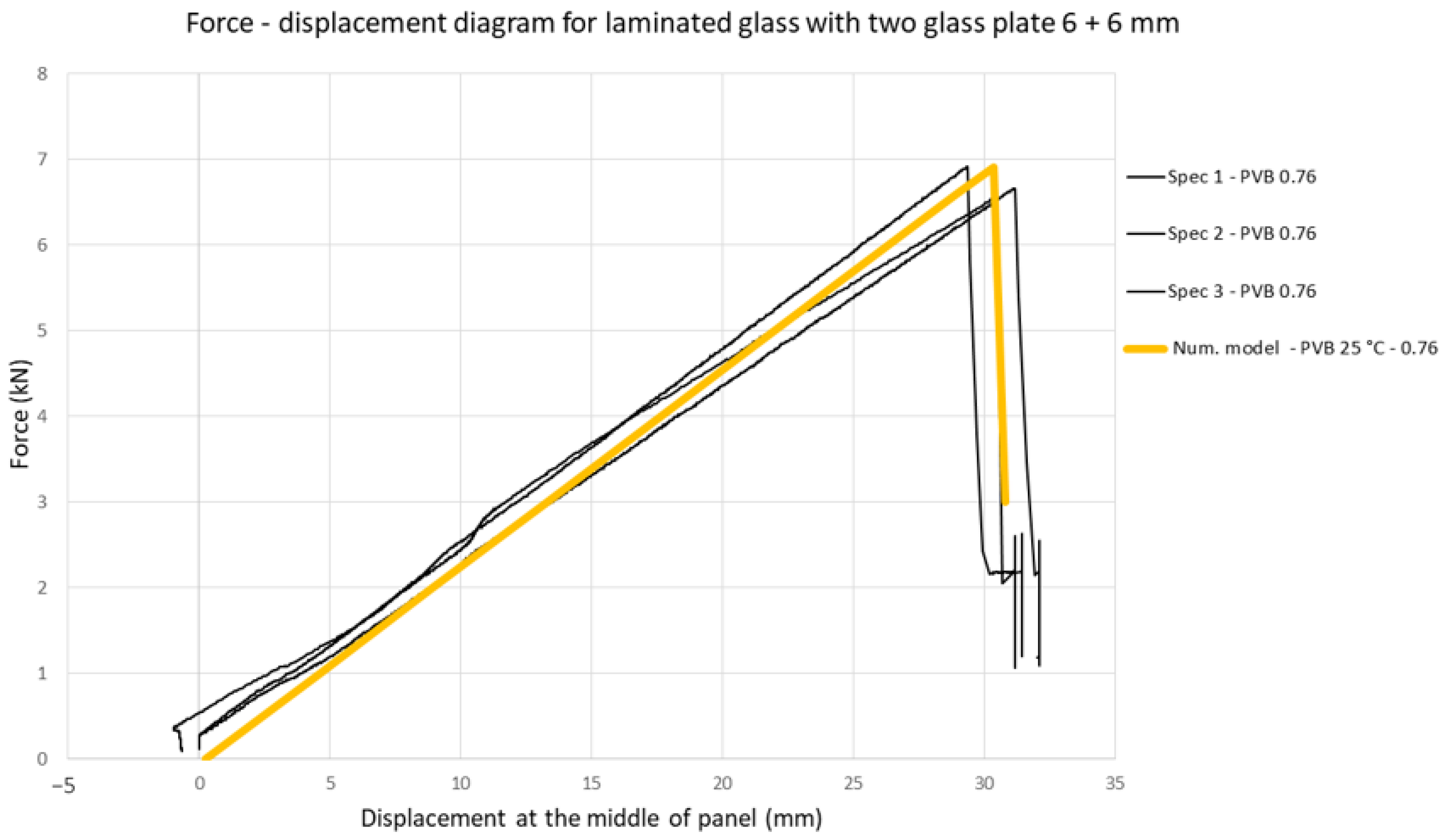
Based on geometry and the loading of the presented experimental tests, the numerical model is developed. The model is developed in ANSYS software, and it consists of two glass plates connected with an interlayer. The model is discretized with 3D solid elements, with minimal two-element through-thickness of the interlayer, and the element-size ratio for the glass panel is not bigger than 1.5 interlayer elements. Contact between the glass and interlayer is defined as an absolute bond, such that only interlayer shear deformation occurs in the middle, without any sliding. The glass panel is supported on two ends with a span of 95 cm. The load is placed at the same positions as in the four-point bending test, with two line loads at equal distances from center of plate, 10 cm on each side from the mid-span. The used material characteristics for the glass are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, and those for PVB in Table 3, as well as Figure 2. Some basic information for the numerical model is presented in Table 4. For the validation of the experimental test, Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio are adopted according to the total test duration and test temperature (E1min,25 °C = 387 MPa; G1min,25 °C = 131 MPa; ν = 0.476). The shear modulus is calculated in dependence to Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio. The numerical model (with PVB) is validated with the presented experimental data for the first loading stage (fracture on the bottom glass plate). In Figure 7, a good coincidence in the numerical compared to the experimental results can be seen. Since the obtained numerical results showed a good accordance with the experimental results, this model was considered to be validated for further analyses. This all served as an introduction and validation for the following parametric analysis.

Table 4.
Basic information about the finite-element model in ANSYS [38].
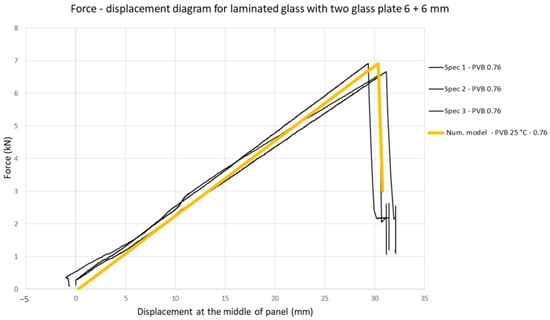
Figure 7.
Force-displacement diagram: results of four-point bending from the numerical and experimental tests.
For the PVB material model in further analyses, different values of Young’s modulus and the shear modulus, G, in dependence to the load duration and temperature are used (Figure 2). This is accepted because in observed bending tests, the panel is loaded until the fracturing of one plate occurs. For this type of loading, the interlayer is exposed to a small strain, lower than the failure strain of the glass that occurs on laminated glass elements [21]. The failure strain of the glass plate is approximately 0.167% for a glass strength of 120 MPa and an elastic modulus of 70 GPa. Since the interlayer is placed in the middle of the laminated glass element with a dominant bending deformation, it is exposed to a very small strain in the unfractured state.
Based on the validated numerical model, other models with different geometries (regarding the possible thickness of the glass and interlayer) and interlayers are developed. These models are used in the parametric study.
4. A Parametric Study of Interlayer Properties on Bearing Capacity of Laminated Glass Panels
For the parametric analysis, twelve different geometries are developed. All of the models have a span of 950 mm and a width of 330 mm. Each panel is loaded with a total force of 1 kN divided into two lines uniformly distributed with 15,151 N/mm′. The description of the geometries and interlayers is presented in Table 5. For the interlayer thicknesses of t = 1.52 mm and t = 2.28 mm, both PVB and ionoplast interlayers are used, while for lower thicknesses PVB is used in the models with t = 0.76 mm and ionoplast for the models with t = 0.89 mm. The main goal is to use the same total thickness of glass panels but nonsymmetrically placed in the tensile and compressive zones (glass thickness of 10 mm + 6 mm and 6 mm + 10 mm). With a fixed force, the temperature and load duration are varied, and the influence of those two parameters on stresses in the bottom glass plate as well as total deflection is analyzed for different geometries.

Table 5.
Basic information about geometries of finite-element models in ANSYS [38].
To obtain the relationship between the load duration, ambient temperature, and thickness of the interlayer compared to the maximum deflection (as a measure of flexural stiffness) and tension stress in the bottom glass plate, an analytical polynomial of three independent variables with unknown coefficients is used. Every functional independence of these three variables (load duration, ambient temperature, and thickness of interlayer) is defined by a second-order polynomial that generated a sixth-total-order polynomial:
where x, y, and z are independent variables assigned to the physical values of the logarithm of load duration in seconds, ambient temperature in °C, and interlayer thickness in mm; the Fs are unknown coefficients.
P(x,y,z) = F1 + F2 ∙ x + F3 ∙ y + F4 ∙ x2 +F5 ∙ Fx ∙ y + F6 ∙ y2 + F7 ∙ x2 ∙ y + F8 ∙ x ∙ y2 + F9 ∙ x2 ∙ y2
+ F10 ∙0z + F11 ∙1x ∙ z + F12 ∙ y ∙ z + F13 ∙ x2 ∙xz + F14 ∙ x ∙xy ∙ z + F15 ∙ y2 ∙yz + F16 ∙6x2
∙6y ∙ z + F17 ∙7x ∙ y2 ∙ z+ F18 ∙8x2 ∙8y2 ∙8z + F19 ∙z2 + F20 ∙0x ∙ z2 + F21 ∙1y ∙ z2 + F22
∙2x2 ∙2z2 + F23 ∙3x ∙ y ∙ z2 + F24 ∙4F2 ∙4F2 +F25 ∙ x2 ∙ y ∙ z2 + F26 ∙ x ∙ y2 ∙ z2 + F27 ∙7 2 ∙
y2 ∙ z2
+ F10 ∙0z + F11 ∙1x ∙ z + F12 ∙ y ∙ z + F13 ∙ x2 ∙xz + F14 ∙ x ∙xy ∙ z + F15 ∙ y2 ∙yz + F16 ∙6x2
∙6y ∙ z + F17 ∙7x ∙ y2 ∙ z+ F18 ∙8x2 ∙8y2 ∙8z + F19 ∙z2 + F20 ∙0x ∙ z2 + F21 ∙1y ∙ z2 + F22
∙2x2 ∙2z2 + F23 ∙3x ∙ y ∙ z2 + F24 ∙4F2 ∙4F2 +F25 ∙ x2 ∙ y ∙ z2 + F26 ∙ x ∙ y2 ∙ z2 + F27 ∙7 2 ∙
y2 ∙ z2
The unknown coefficients are solved iteratively by MATLAB [39], and the nlinfit function is used. The coefficients are calculated using a nonlinear least-squares estimation [40]. The solution has converged successfully for all of the datasets.
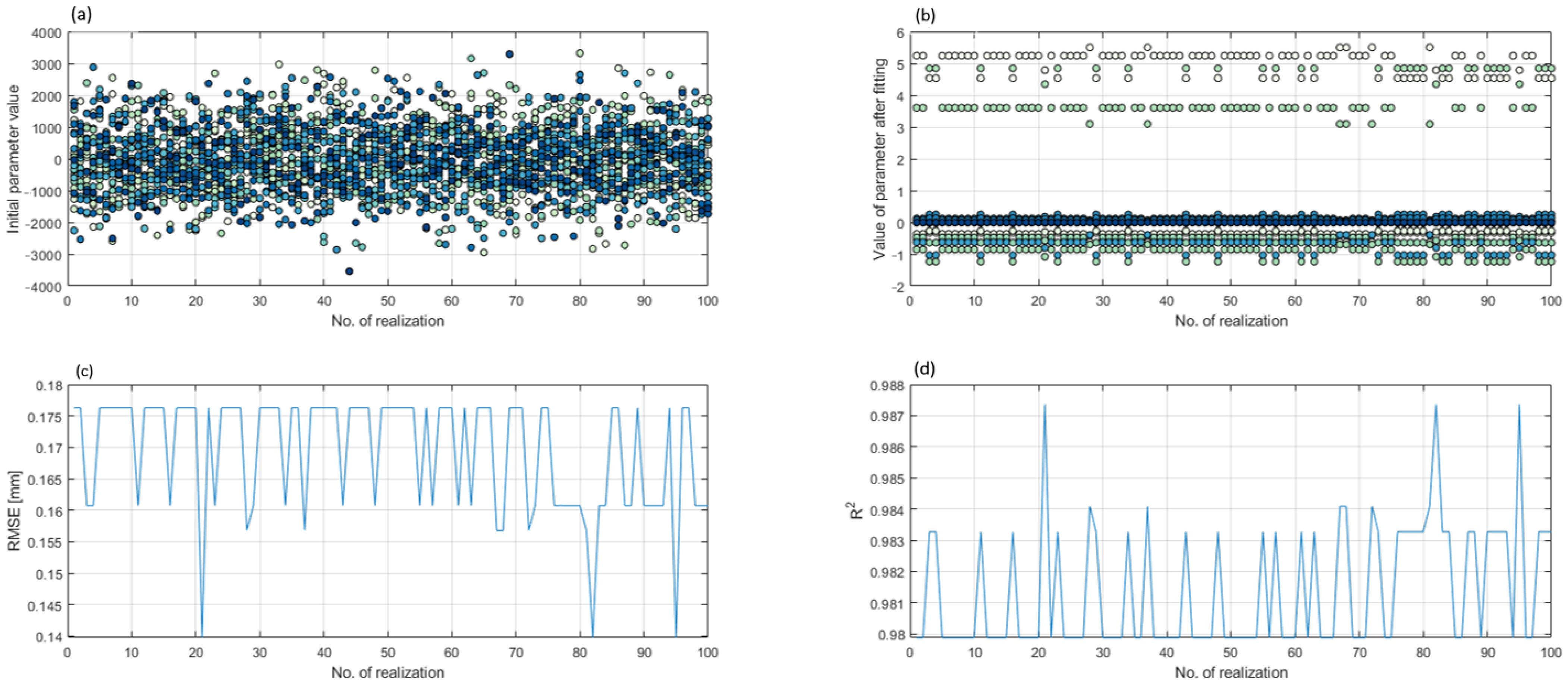
For every fit, multiple fitting realizations were performed to avoid locking to the nearest target-function minimum instead of the global optimal point. The initial values of the coefficients were randomly chosen using a normal distribution, with the mean at 0 and a standard deviation of 1000. For every dataset, 100 realizations were performed. Every calculation converged up to four potential solutions. In the case of a single solution, it was chosen as the optimal one; in the case of multiple potential solutions, the optimal solution was chosen by the criterion of the lowest RMSE.
An example of the calculation is shown in Figure 8. In the top-left panel, a set of initial values are displayed, and in the top-right panel calculated values are displayed. The color of a point indicates a specific coefficient. All of the calculated solutions can be sorted into three unique solutions. The metrics displayed in the bottom panels are used as the criteria for the most successful fit. The solution with an RMSE of 0.1397 is chosen as the optimal one, as is displayed in the bottom-left panel. The R2 metric in the bottom-right panel is in agreement with this choice, as the highest R2 is with this solution.
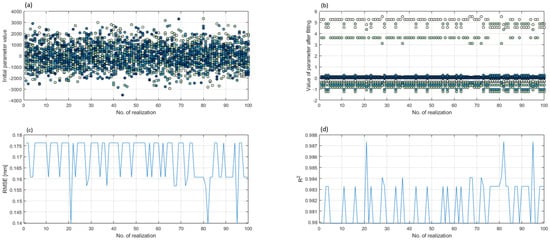
Figure 8.
Panels representing an example of calculation: (a) initial parameter values; (b) calculated parameter values: (c) root-mean-square error (RMSE); and (d) determination coefficient.
The datasets used to obtain functions are divided into two classes of materials (PVB and ionoplast) and three classes of glass plate-thickness combinations. Every dataset consists of 48 gridded entries, four sets along the duration dimension, four along the temperature dimension, and three along the interlayer thickness dimension. The datasets are listed in Appendix A. The calculated coefficients for the displacement functions for the three glass plate-thickness combinations are listed in Appendix B.
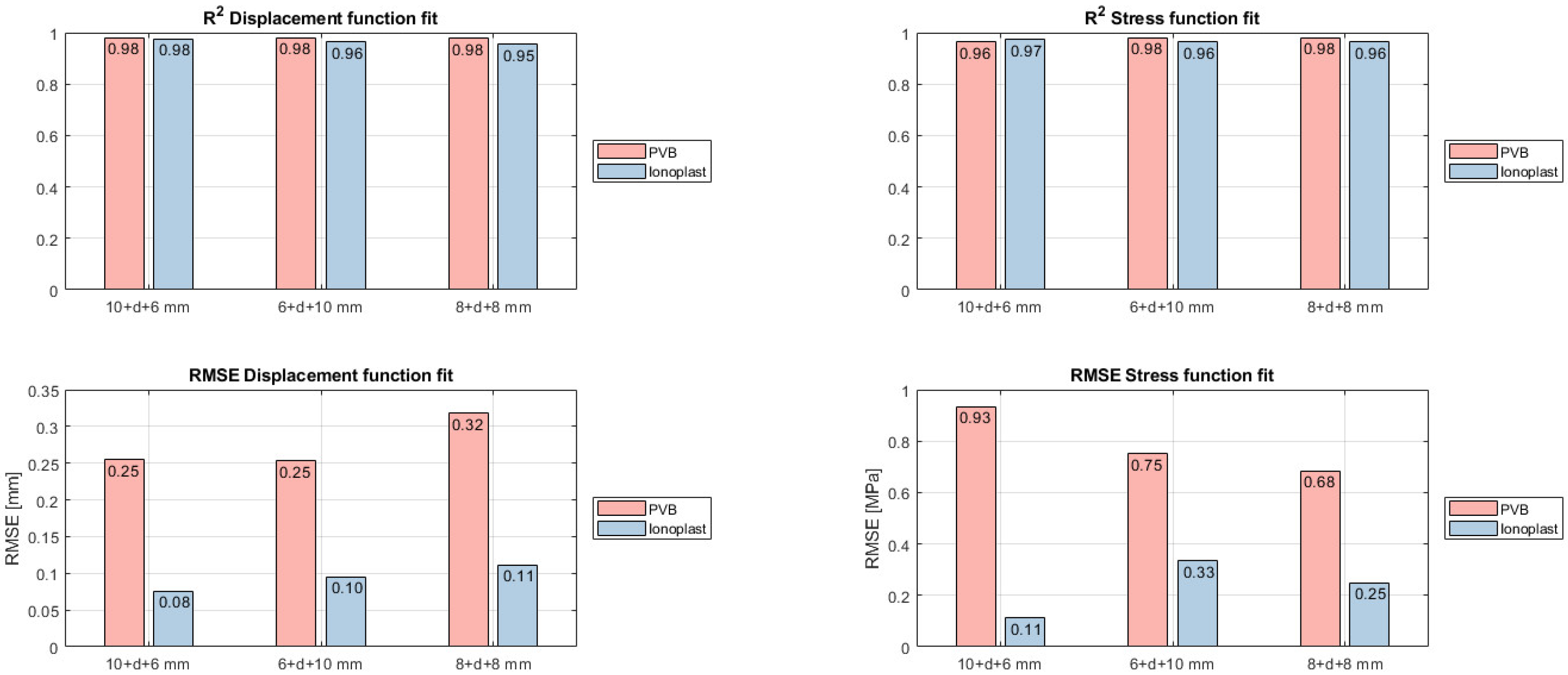
The results presented in Figure 9 display a good fit between the provided data and the analytical model. The average error (RMSE) for the displacement function is less than 0.32 mm for PVB interlayers and 0.11 mm for ionoplast interlayers, and the RMSE for the stress function is under 0.93 MPa for PVB interlayers and less than 0.33 MPa for ionoplast interlayers. The coefficient of determination, R2, is above 0.95 for both interlayers, which suggests a strong relationship between the data and the model. The almost-identical R2 and the larger RMSE for PVB interlayers are due to the wider spread of results in PVB interlayers. The explanation for the discrepancies is numerical data errors in both numerical modeling and function fitting and a dismissed higher-order polynomial that were not taken into account due to the data dissipation.
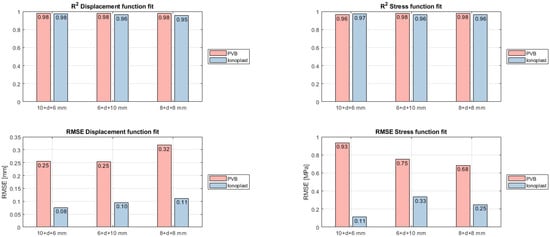
Figure 9.
Fitting results of displacement (left panel) and stress function (right panel).
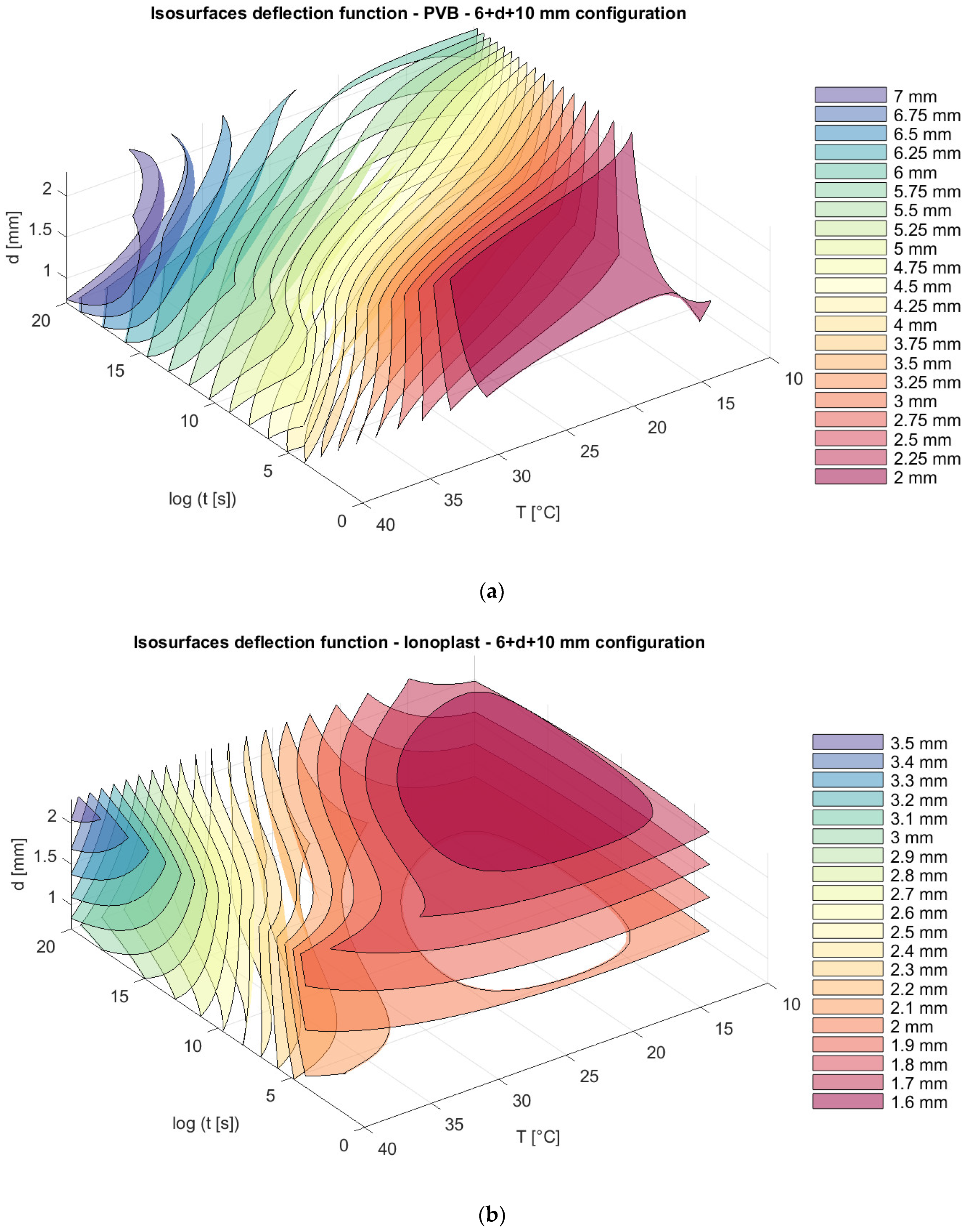
Finally, for all of the information, isosurfaces were created, showing the dependence of the deflection and stress on the specified parameters. The isosurfaces clearly show differences in the behavior of laminated glass panels along described independent variables at different plate-thickness dispositions and for different interlayers. Generally, ionoplast interlayers show higher flexural rigidity and better behavior when higher temperatures and load durations are involved. On the other hand, PVB interlayers have a lower capacity for these types of static loads. As we can see in Figure 10, glass panels with PVB interlayers show larger deflection (for long time loading and an increasing temperature this deflection is double) in comparison with ionoplast interlayers for the presented combinations (thickness of the glass panel, load duration, and temperature).
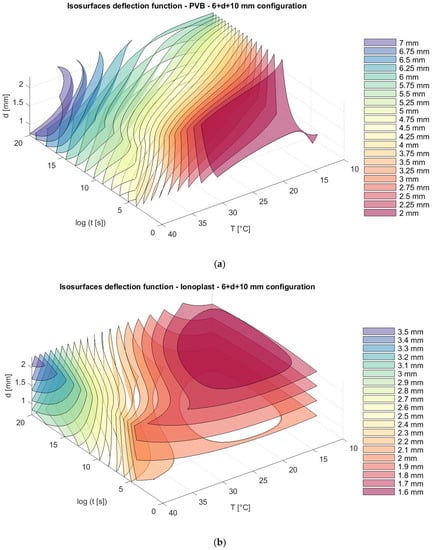
Figure 10.
Isosurfaces for deflection in a model with an upper glass plate of 6 mm + a bottom glass plate of 10 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
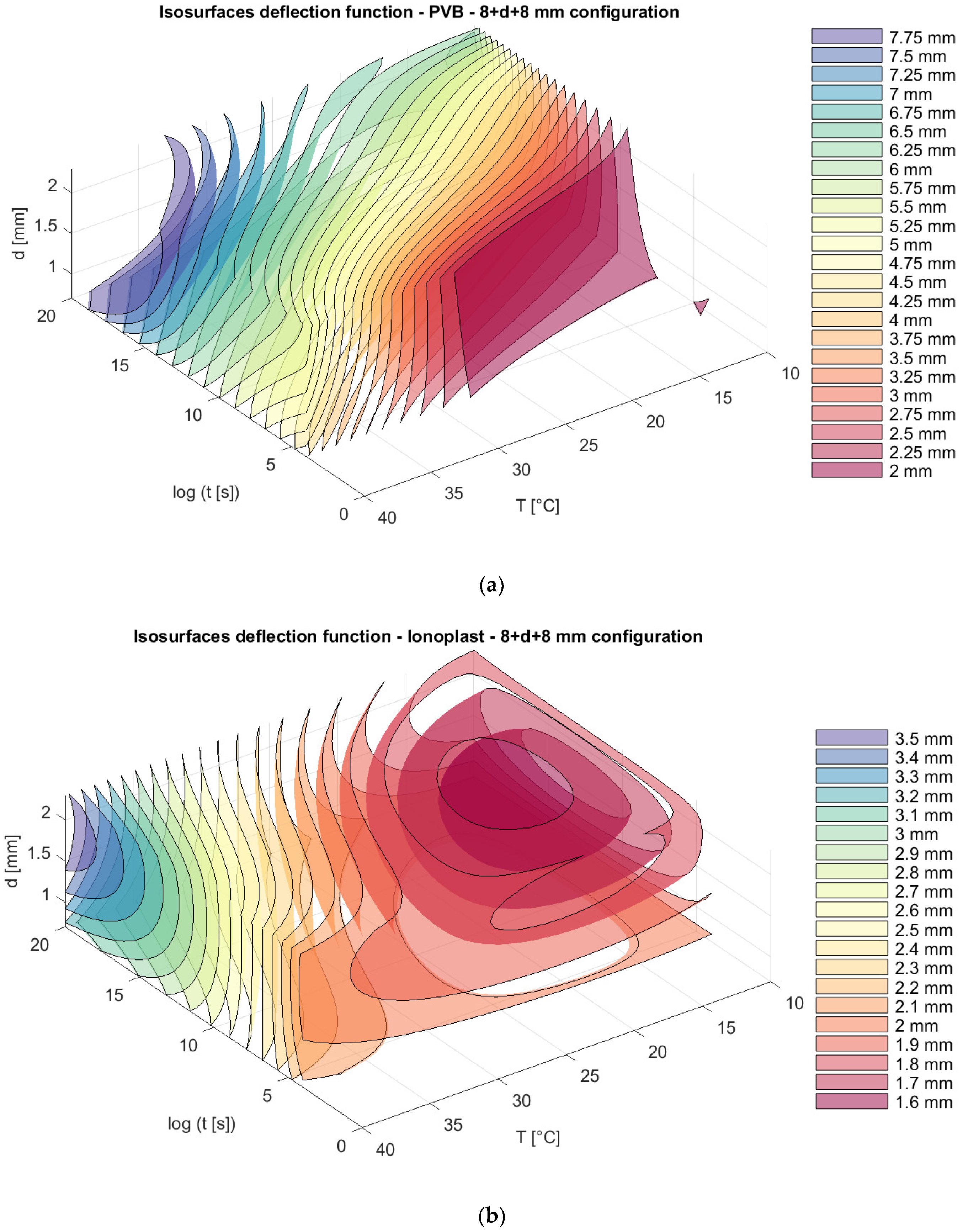
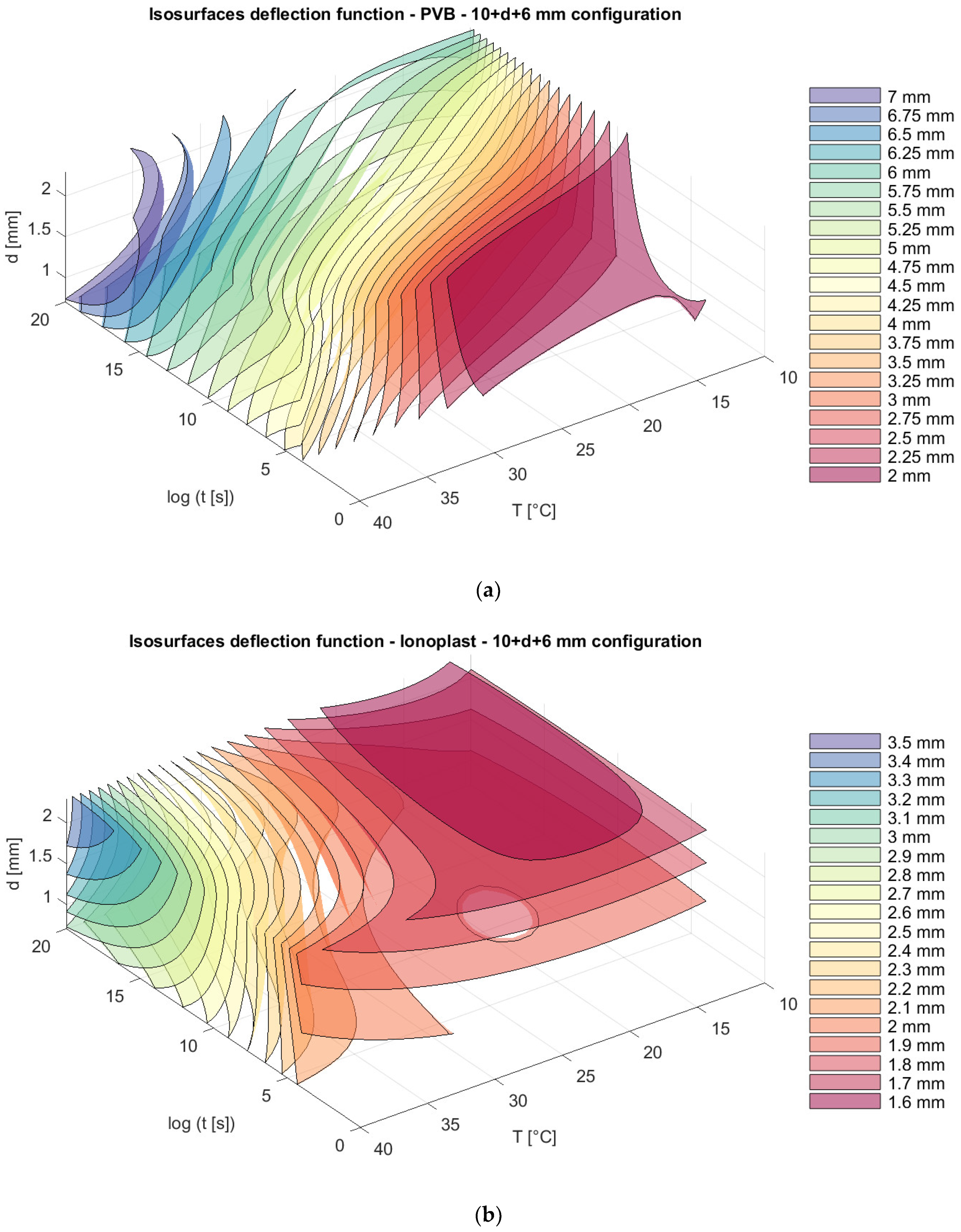
The total thickness of the glass in all of the presented models is 16 mm, but with different distributions of thickness in the glass panels: 6 mm + 10 mm; 8 mm + 8 mm; and 10 mm + 6 mm. We can notice that, for nonsymmetrical panels, the position of thinner and thicker glass plates (6 mm + 10 mm and 10 mm + 6 mm) does not provide the difference in the total deflection of the panels, and those values are slightly lower than the deflection from a symmetrical distribution of plates (8 mm + 8 mm) (Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12).
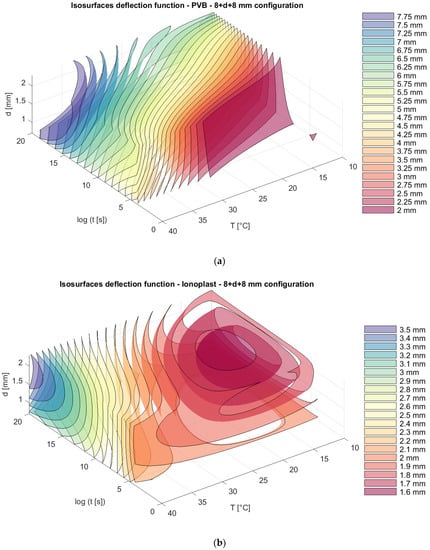
Figure 11.
Isosurfaces for deflection in a model with an upper glass plate of 8 mm + a bottom glass plate of 8 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
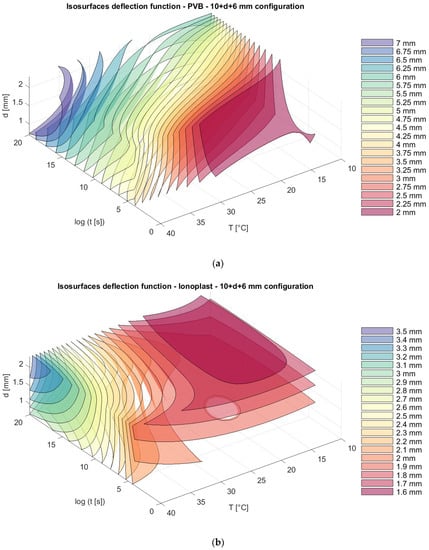
Figure 12.
Isosurfaces for deflection in a model with an upper glass plate of 10 mm + a bottom glass plate of 6 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
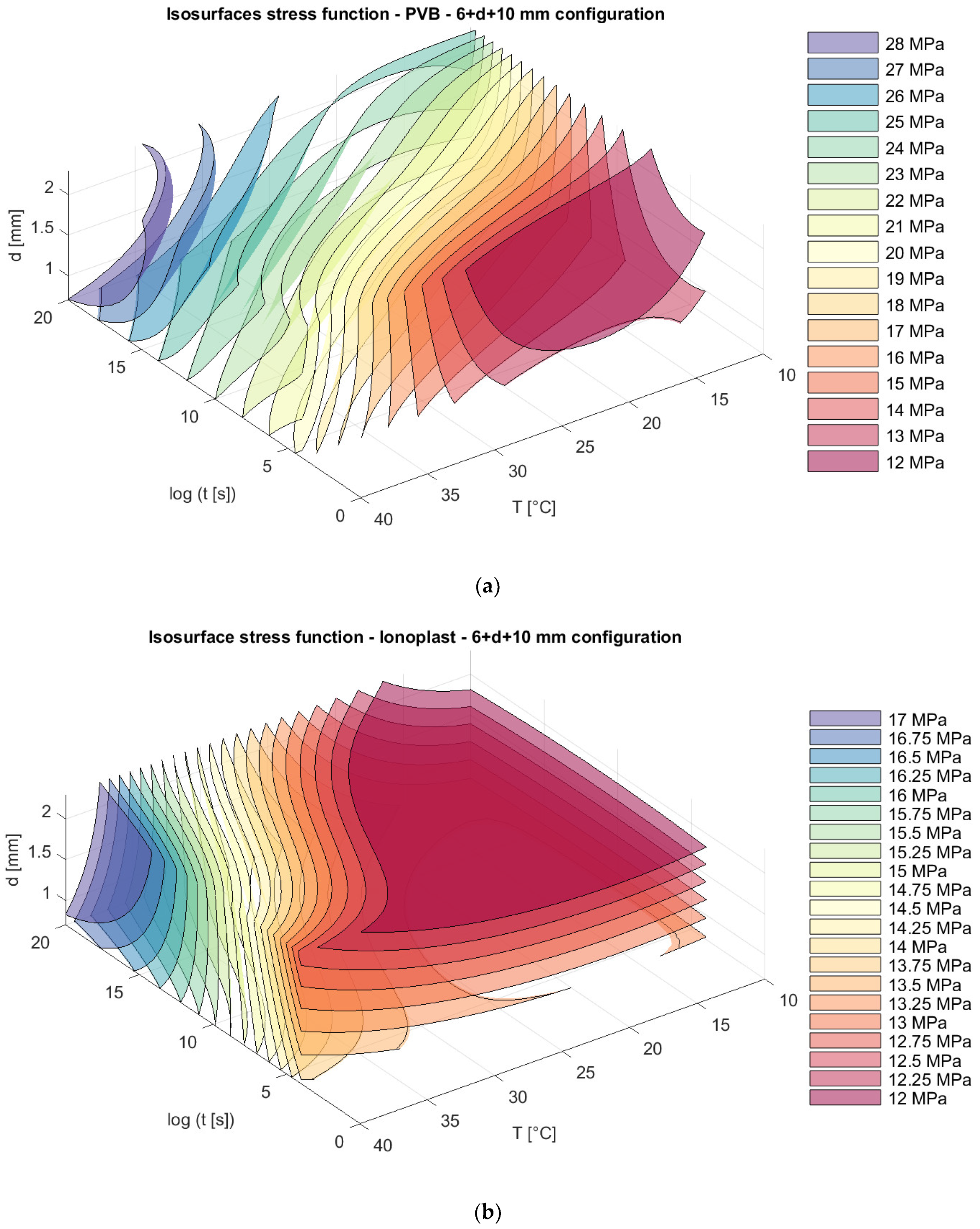
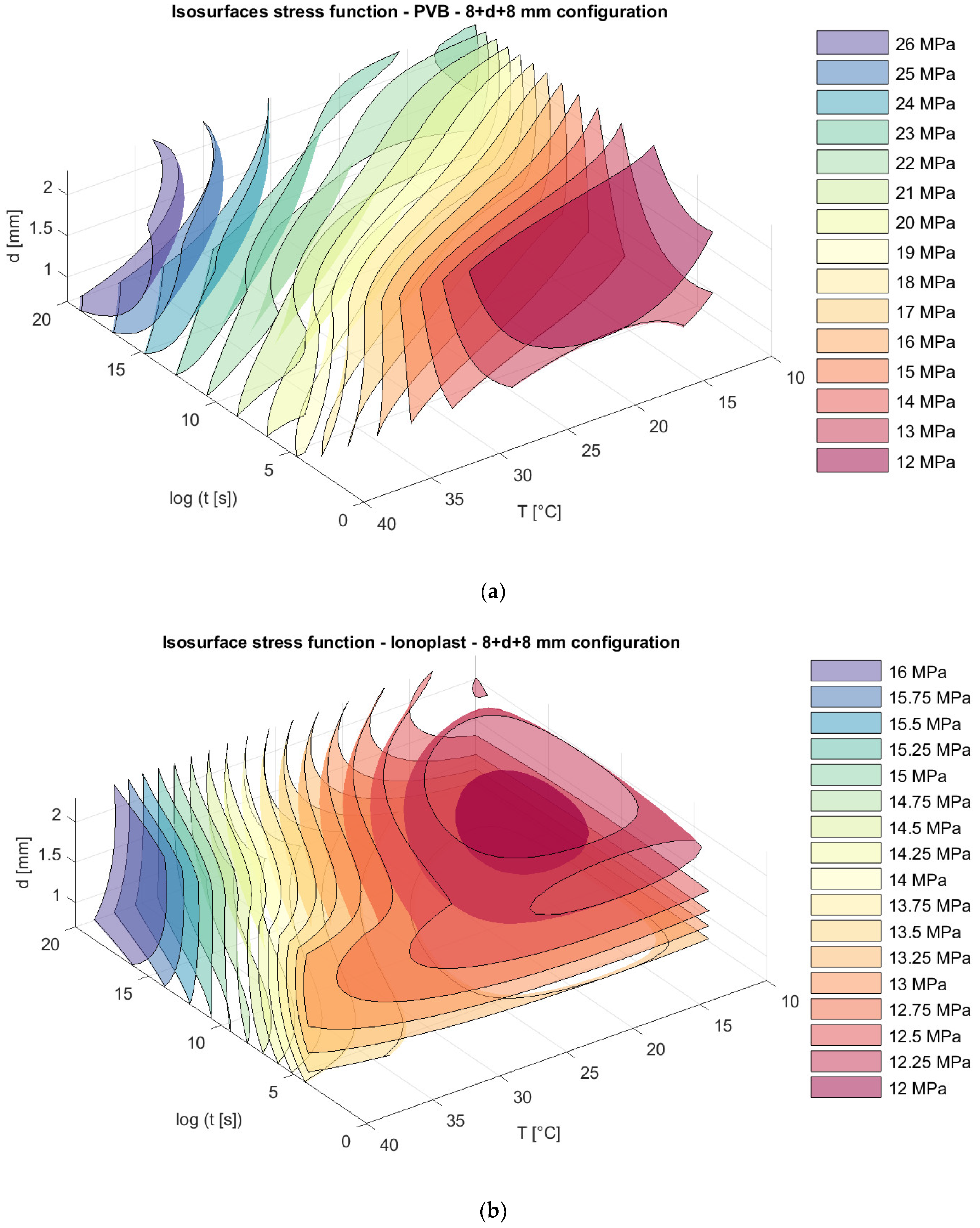
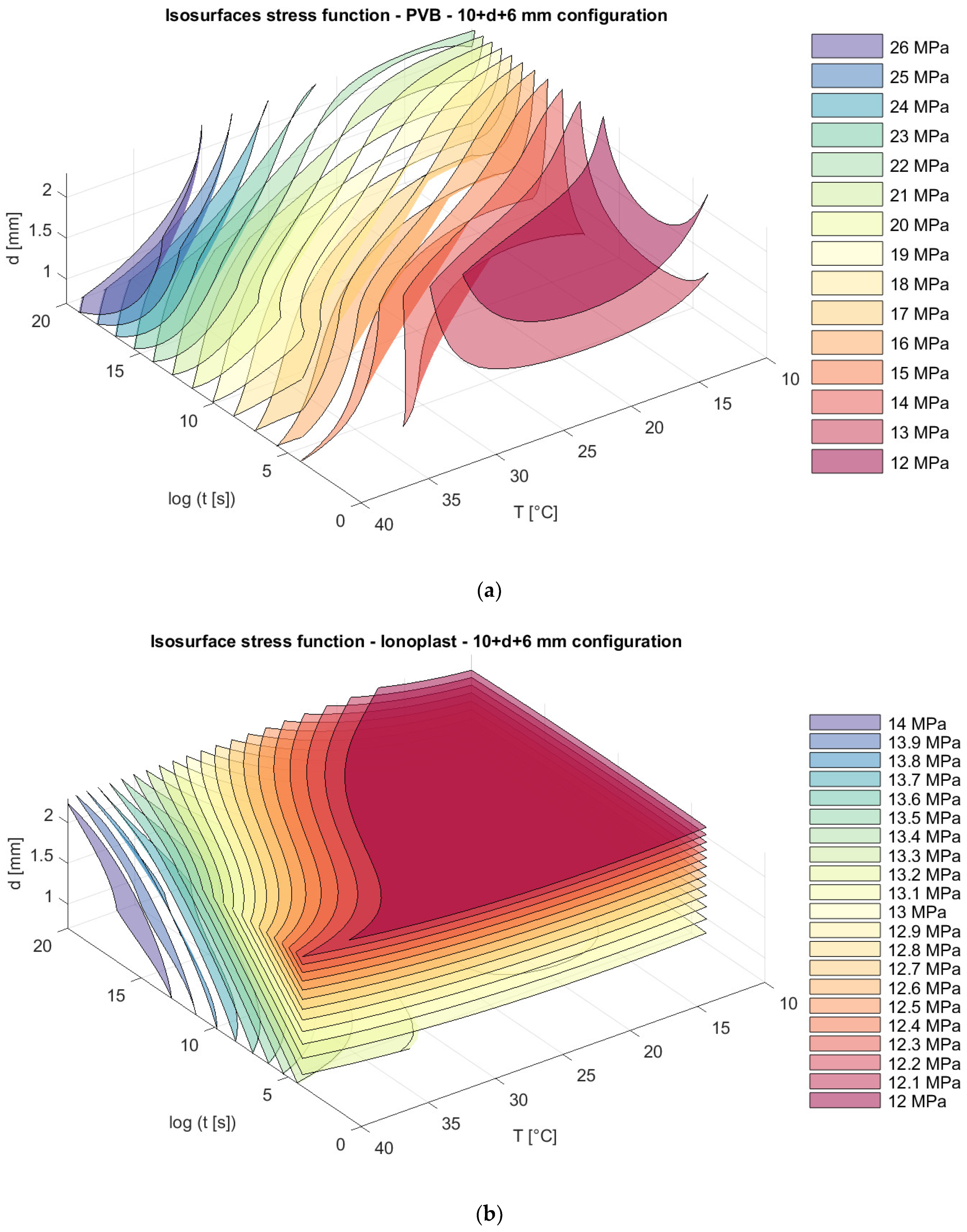
For the same laminated glass panels, appropriate isosurfaces for stresses are presented in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15.
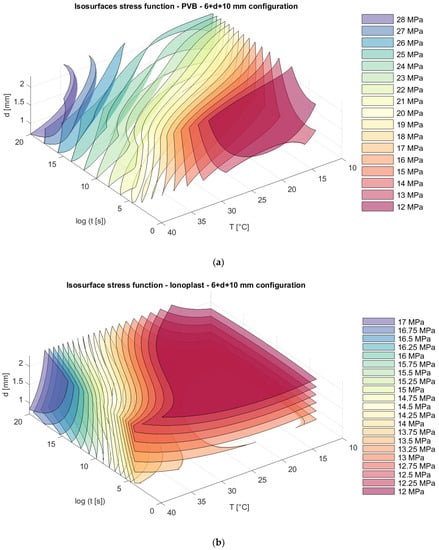
Figure 13.
Isosurfaces for stress in a model with an upper glass plate of 6 mm + a bottom glass plate of 10 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
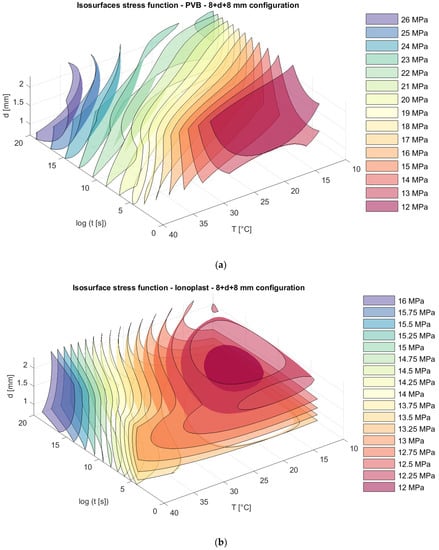
Figure 14.
Isosurfaces for stress in a model with an upper glass plate of 8 mm + a bottom glass plate of 8 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
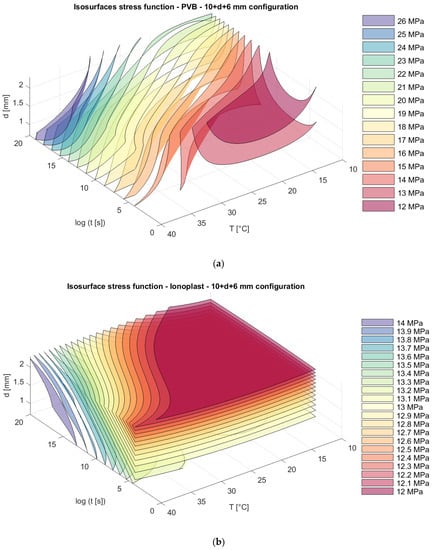
Figure 15.
Isosurfaces for stress in a model with an upper glass plate of 10 mm + a bottom glass plate of 6 mm with (a) PVB interlayers; (b) ionoplast interlayers.
Analyzing stress in regard to thickness dispositions, we can notice that for nonsymmetrical glass plate dispositions, greater stress appears in cases where the thicker glass plate is at the bottom (6 mm + 10 mm) for both types of interlayers. The greatest difference is visible sfor a loading of one month at 30 °C. For example, in this case, the stresses in laminated glass with a disposition of 6 mm + 10 mm with PVB interlayers are 19.23% greater (Figure 13a and Figure 15a) than those of laminated glass with a disposition of 10 mm + 6 mm. Additionally, for laminated glass panels with ionoplast interlayers, stresses are 7.05% greater than those for laminated glass with a disposition of 10 mm + 6 mm (Figure 13b and Figure 15b). The symmetrical disposition (8 mm + 8 mm) shows values of stress between two presented limits (6 mm + 10 mm and 10 mm + 6 mm) (Figure 14).
For temperatures up to 25 °C, an increase in interlayer thickness, for the ionoplast model, shows the positive effect of increasing the panel stiffness, resulting in lower deflection. For example, a glass panel with a disposition of 6 mm + 10 mm with an ionoplast interlayer thickness of 0.89 mm has 15.91% larger deflection compared to the same disposition glass panel with an ionoplast interlayer thickness of 2.28 mm. However, for temperatures above 35 °C, this effect is different, and for a long-term load the increase in interlayer thickness brings an 11.94% larger deflection of the panel when comparing an ionoplast interlayer thickness of 0.89 mm with one of 2.28 mm.
A different trend is observed in the model with PVB interlayers where it can be seen that, at lower temperatures (up to 25 °C) and shorter loadings, an increase in interlayer thickness does not provide any influence on the deflection. For longer loadings, an increase in the thickness of PVB interlayers shows an unfavorable effect, where deflection is approximately 13.62% higher when increasing the interlayer thickness from 0.76 mm to 2.28 mm when exposed to temperatures up to 25 °C. This difference between deflections decreases during higher temperatures (40 °C).
For long-term loading and increased temperatures, PVB interlayers show unfavorable effects regarding bearing capacity in comparison with stiffer interlayers, such as ionomers. These observations also match those of other experimental tests in the literature; see [41]. In graphs from Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15, we can see the benefits of ionoplast interlayers, but taking into consideration all other aspects, such as cost and availability, gives PVB interlayers the advantage, regardless of their slightly lower bearing capacity.
5. Conclusions
In this work, experimental and numerical analyses of laminated glass panels exposed to four-point bending (EN 1288-3:2000 [35]) are presented. First, the validation of the numerical model is performed, and then a model with different geometries is developed. Models composed of two glass plates with different thicknesses coupled with two types of interlayers are tested. The parametric study performed presents the influence of the temperature, load duration, type, and thickness of the interlayers, and the symmetric as well as nonsymmetric dispositions of the thicknesses of glass plates on the stresses and deflections of the laminated glass panels. To obtain the relationship between the load duration, temperature, and thickness of the interlayers compared to the maximum deflection (as a measure of flexural stiffness) and tension stress in the bottom glass plate, an analytical polynomial of three independent variables with unknown coefficients is defined. Every functional independence of these three variables (load duration, ambient temperature, and thickness of the interlayers) is defined by a second-order polynomial that generated a sixth-total-order polynomial. Isosurfaces are created, showing the dependence of the deflection and stress on the specified parameters, and clearly showing differences in the behavior of laminated glass panels for the same conditions with different interlayers.
The observed parameters have a significant influence on the bearing capacity of laminated glass panels, and they are of great importance in the design of glass structures. From the parametric study we can conclude that:
- Comparing deflections, laminated glass panels with ionoplast interlayers provide generally higher stiffness than the same model with PVB (Saflex DG41) interlayers does. This behavior is expected, because an ionoplast interlayer is an ionomer-based material that provides the highest level of structural performance [23], which contributes to increasing the stiffness of laminated glass and thus causes less deflection.
- Taking into account that the total thickness of glass in all of the models is 16 mm, we can see that, for nonsymmetrical panels, the position of thinner and thicker plates (6 mm + 10 mm and 10 mm + 6 mm) does not provide a difference in the total deflection of the panels, and these values are slightly lower than those from symmetrical dispositions of plates (8 mm + 8 mm). The dominant influence on the size of the deflection is the total thickness of the panels, which justifies the different approaches of calculating the effective thickness of the panels.
- When comparing the stresses on the bottom plate, we can see that due to the asymmetric dispositions of the plate, higher stresses occur in cases where the plate is thicker at the bottom. This behavior is expected, because that part of the panel has a higher bending stiffness, withstanding higher load levels, resulting in higher stresses in that part. In the case of symmetrical dispositions (8 mm + 8 mm) of the panel, the expected stress values are between the previously mentioned two load limits for laminated glass with a panel disposition of 6 mm + 10 mm and 10 mm + 6 mm.
- For lower temperatures (up to 20 °C), an increase in the interlayer thickness, for the ionoplast model, shows the positive effect of increasing the panel stiffness, resulting in lower deflection. However, for temperatures above 35 °C, that effect disappears, and for long-term loading, the increase in the interlayer thickness brings a slightly higher deflection of the panel. A different trend is observed in the model with PVB (Saflex DG41, EASTMAN, Kingsport, TN, USA) interlayers, where it can be seen that at lower temperatures and shorter loadings, the increased thickness of the interlayers does not provide any influence on the deflection. The PVB (Saflex DG41) will be able to transfer a significant amount of shear force between the glass plates, and in this case the laminated panel has a bending stiffness of a similar magnitude to an equivalent monolithic panel of the same overall thickness.
- For higher temperatures and longer loadings, the increase in the interlayer thickness shows an unfavorable effect, where deflection is increased with an increased interlayer thickness. The same effect is visible for the load duration, where we observe greater deflections for longer load durations in both models, but this trend is more pronounced in models with PVB (Saflex DG41) interlayers. When this type of PVB is exposed to higher temperatures, its stiffness decreases, which is clearly manifested by the fall of Young’s modulus, and it begins to behave in a similar manner to rubber, which results in an increased deflection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G. and P.M.; methodology, M.G., G.G., V.D. and P.M.; software, V.D.; validation, M.G., G.G. and V.D.; investigation, M.G., G.G., V.D. and P.M.; resources, M.G., G.G., V.D. and P.M.; data curation, G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G., G.G., V.D. and P.M.; writing—review and editing, M.G. and P.M.; visualization, G.G. and V.D.; supervision, M.G. and P.M.; project administration, M.G.; funding acquisition, M.G. and V.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported through project KK.01.1.1.02.0027, a project cofinanced by the Croatian Government and the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund, the Competitiveness and Cohesion Operational Programme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the company DIALUX d.o.o. and Ivan Kuran from Split, Croatia for providing laminated glass samples for use in the experimental program and for giving technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
The dataset with 48 gridded entries, consisting of four sets of load duration, four sets of temperature, and three sets of interlayer thickness, is presented in Table A1, Table A2 and Table A3. The datasets are used to obtain functions, and they are divided into two classes of materials (PVB and ionoplast) and three classes of glass plate-thickness dispositions.

Table A1.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 10 + d + 6 (mm).
Table A1.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 10 + d + 6 (mm).
| Deflection 10 + 2.28 + 6 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.642 | 1.960 | 4.185 | 5.737 | 1.645 | 1.652 | 1.657 | 1.660 |
| 25 | 1.673 | 4.255 | 5.586 | 6.141 | 1.660 | 1.690 | 1.739 | 1.820 |
| 30 | 1.920 | 5.580 | 6.048 | 6.753 | 1.684 | 1.770 | 2.232 | 2.081 |
| 40 | 5.200 | 6.320 | 6.996 | 7.421 | 1.865 | 2.964 | 3.329 | 3.467 |
| Bottom panel stress 10 + 2.28 + 6 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 11.820 | 12.273 | 14.893 | 21.577 | 11.809 | 11.821 | 11.834 | 11.840 |
| 25 | 11.865 | 15.169 | 20.949 | 23.349 | 11.834 | 11.885 | 11.963 | 12.090 |
| 30 | 12.218 | 20.897 | 22.930 | 25.903 | 11.874 | 12.012 | 12.605 | 13.226 |
| 40 | 19.276 | 24.102 | 26.977 | 28.790 | 12.150 | 13.382 | 13.739 | 13.882 |
| Deflection 10 + 1.52 + 6 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.835 | 2.077 | 3.909 | 5.403 | 1.837 | 1.843 | 1.847 | 1.852 |
| 25 | 1.858 | 3.963 | 5.245 | 5.827 | 1.848 | 1.872 | 1.907 | 1.971 |
| 30 | 2.040 | 5.234 | 5.724 | 6.500 | 1.866 | 1.931 | 2.279 | 2.732 |
| 40 | 4.860 | 6.015 | 6.778 | 7.279 | 2.000 | 2.858 | 3.158 | 3.274 |
| Bottom panel stress 10 + 1.52 + 6 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 12.614 | 12.910 | 14.676 | 19.998 | 12.605 | 12.612 | 12.621 | 12.624 |
| 25 | 12.641 | 14.731 | 19.339 | 21.891 | 12.620 | 12.652 | 12.703 | 12.783 |
| 30 | 12.886 | 19.266 | 21.429 | 24.810 | 12.646 | 12.732 | 13.159 | 13.615 |
| 40 | 17.619 | 22.710 | 26.000 | 28.180 | 12.822 | 13.733 | 14.000 | 14.113 |
| Deflection 10 + 0.76 + 6 (mm) | Deflection 10 + 0.89 + 6 (mm) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 2.064 | 2.210 | 3.457 | 4.736 | 1.978 | 1.981 | 1.984 | 1.988 |
| 25 | 2.077 | 3.447 | 4.561 | 5.157 | 1.984 | 2.000 | 2.023 | 2.065 |
| 30 | 2.181 | 4.525 | 5.031 | 5.907 | 1.996 | 2.038 | 2.266 | 2.576 |
| 40 | 4.177 | 5.323 | 6.241 | 6.922 | 2.083 | 2.664 | 2.881 | 2.967 |
| Bottom panel stress 10 + 0.76 + 6 (MPa) | Bottom panel stress 10 + 0.89 + 6 (MPa) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 13.508 | 13.630 | 14.740 | 16.885 | 13.133 | 13.138 | 13.140 | 13.145 |
| 25 | 13.516 | 14.725 | 16.105 | 18.756 | 13.142 | 13.161 | 13.185 | 13.232 |
| 30 | 13.605 | 15.964 | 18.195 | 22.075 | 13.157 | 13.203 | 13.481 | 13.813 |
| 40 | 15.320 | 19.515 | 23.544 | 26.557 | 13.256 | 13.898 | 14.103 | 14.182 |

Table A2.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 6 + d + 10 (mm).
Table A2.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 6 + d + 10 (mm).
| Deflection 6 + 2.28 + 10 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.640 | 1.960 | 4.183 | 5.733 | 1.645 | 1.652 | 1.657 | 1.660 |
| 25 | 1.670 | 4.253 | 5.582 | 6.135 | 1.660 | 1.690 | 1.739 | 1.825 |
| 30 | 1.919 | 5.575 | 6.042 | 6.742 | 1.680 | 1.770 | 2.232 | 2.810 |
| 40 | 5.201 | 6.312 | 6.982 | 7.395 | 1.865 | 2.964 | 3.329 | 3.467 |
| Bottom panel stress 6 + 2.28 + 10 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 11.440 | 12.784 | 19.698 | 24.349 | 11.444 | 11.490 | 11.522 | 11.559 |
| 25 | 11.619 | 19.910 | 23.896 | 25.557 | 11.536 | 11.710 | 11.940 | 12.301 |
| 30 | 12.631 | 23.876 | 25.274 | 27.401 | 11.674 | 12.083 | 13.761 | 15.617 |
| 40 | 22.746 | 26.094 | 28.146 | 29.511 | 12.461 | 16.096 | 17.201 | 17.612 |
| Deflection 6 + 1.52 + 10 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.835 | 2.077 | 3.907 | 5.402 | 1.837 | 1.843 | 1.847 | 1.852 |
| 25 | 1.858 | 3.962 | 5.242 | 5.824 | 1.848 | 1.872 | 1.907 | 1.971 |
| 30 | 2.042 | 5.231 | 5.720 | 6.493 | 1.866 | 1.931 | 2.279 | 2.732 |
| 40 | 4.855 | 6.010 | 6.768 | 7.260 | 2.001 | 2.857 | 3.158 | 3.274 |
| Bottom panel stress 6 + 1.52 + 10 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 12.362 | 13.416 | 19.086 | 23.483 | 12.365 | 12.403 | 12.429 | 12.459 |
| 25 | 12.506 | 19.249 | 23.014 | 24.730 | 12.439 | 12.579 | 12.761 | 13.044 |
| 30 | 13.292 | 22.984 | 24.426 | 26.707 | 12.549 | 12.873 | 14.176 | 15.649 |
| 40 | 21.833 | 25.279 | 27.528 | 29.051 | 13.166 | 16.037 | 16.947 | 17.291 |
| Deflection 6 + 0.76 + 10 (mm) | Deflection 6 + 0.89 + 10 (mm) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 2.063 | 2.203 | 3.421 | 4.707 | 2.022 | 2.026 | 2.029 | 2.032 |
| 25 | 2.076 | 3.440 | 4.540 | 5.133 | 2.029 | 2.045 | 2.068 | 2.110 |
| 30 | 2.180 | 4.520 | 5.013 | 5.888 | 2.041 | 2.083 | 2.312 | 2.624 |
| 40 | 4.174 | 5.317 | 6.230 | 6.907 | 2.129 | 2.713 | 2.931 | 3.018 |
| Bottom panel stress 6 + 0.76 + 10 (MPa) | Bottom panel stress 6 + 0.89 + 10 (MPa) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 13.400 | 14.093 | 17.921 | 21.643 | 13.218 | 13.247 | 13.267 | 13.290 |
| 25 | 13.498 | 17.992 | 21.160 | 22.867 | 13.273 | 13.376 | 13.509 | 13.712 |
| 30 | 14.006 | 21.102 | 22.528 | 25.042 | 13.354 | 13.589 | 14.504 | 15.552 |
| 40 | 20.108 | 23.399 | 26.025 | 27.994 | 13.797 | 15.833 | 16.507 | 16.767 |

Table A3.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 8 + d + 8 (mm).
Table A3.
Dataset for plate-thickness disposition 8 + d + 8 (mm).
| Deflection 8 + 2.28 + 8 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.614 | 1.971 | 4.223 | 6.060 | 1.815 | 1.821 | 1.825 | 1.831 |
| 25 | 1.647 | 4.621 | 5.851 | 6.597 | 1.827 | 1.852 | 1.892 | 1.963 |
| 30 | 1.918 | 6.266 | 6.460 | 7.800 | 1.846 | 1.918 | 2.308 | 2.823 |
| 40 | 5.790 | 7.224 | 7.834 | 8.691 | 1.996 | 2.966 | 3.314 | 3.450 |
| Bottom panel stress 8 + 2.28 + 8 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 11.458 | 12.591 | 18.121 | 22.108 | 12.360 | 12.388 | 12.409 | 12.434 |
| 25 | 11.600 | 18.718 | 21.654 | 23.277 | 12.417 | 12.527 | 12.675 | 12.907 |
| 30 | 12.449 | 22.383 | 22.975 | 25.827 | 12.504 | 12.767 | 13.872 | 15.103 |
| 40 | 21.317 | 24.517 | 25.973 | 27.980 | 13.010 | 15.424 | 16.212 | 16.514 |
| Deflection 8 + 1.52 + 8 (mm) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 1.812 | 2.084 | 4.223 | 6.061 | 1.815 | 1.821 | 1.258 | 1.831 |
| 25 | 1.837 | 4.265 | 5.851 | 6.597 | 1.827 | 1.852 | 1.892 | 1.963 |
| 30 | 2.040 | 5.827 | 6.458 | 7.470 | 1.846 | 1.918 | 2.308 | 2.822 |
| 40 | 5.356 | 6.826 | 7.834 | 8.501 | 1.996 | 2.966 | 3.314 | 3.449 |
| Bottom panel stress 8 + 1.52 + 8 (MPa) | ||||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 12.361 | 13.225 | 18.121 | 22.108 | 12.360 | 12.390 | 12.409 | 12.435 |
| 25 | 12.471 | 18.217 | 21.654 | 23.227 | 12.417 | 12.528 | 12.675 | 12.907 |
| 30 | 13.111 | 21.603 | 22.975 | 25.171 | 12.504 | 12.767 | 13.872 | 15.103 |
| 40 | 20.580 | 23.776 | 25.973 | 27.534 | 13.010 | 15.424 | 16.212 | 16.514 |
| Deflection 8 + 0.76 + 8 (mm) | Deflection 8 + 0.89 + 8 (mm) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 2.049 | 2.211 | 3.644 | 5.197 | 2.007 | 2.011 | 2.014 | 2.019 |
| 25 | 2.063 | 3.460 | 4.979 | 5.721 | 2.015 | 2.032 | 2.058 | 2.105 |
| 30 | 2.018 | 4.939 | 5.564 | 6.681 | 2.028 | 2.075 | 2.333 | 2.688 |
| 40 | 4.514 | 5.937 | 7.119 | 8.027 | 2.125 | 2.789 | 3.042 | 3.142 |
| ottom panel stress 8 + 0.76 + 8 (MPa) | Bottom panel stress 8 + 0.89 + 8 (MPa) | |||||||
| Temp (°C) | PVB | IONOPLAST | ||||||
| 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | 1 min | 24 h | 1 month | 10 years | |
| 10 | 13.385 | 13.931 | 17.225 | 20.514 | 13.200 | 13.222 | 13.236 | 13.258 |
| 25 | 13.456 | 17.224 | 20.060 | 21.615 | 13.241 | 13.321 | 13.425 | 13.590 |
| 30 | 13.850 | 19.971 | 21.285 | 23.633 | 13.303 | 13.490 | 14.244 | 15.131 |
| 40 | 19.071 | 22.057 | 24.554 | 26.474 | 13.659 | 15.365 | 15.926 | 16.147 |
Appendix B
The calculated coefficients for displacement and stress functions for three glass plate-thickness dispositions are presented in Table A4 and Table A5.

Table A4.
Calculated coefficients for displacement functions (1) for three plate-thickness dispositions.
Table A4.
Calculated coefficients for displacement functions (1) for three plate-thickness dispositions.
| Coefficients for Displacement Function | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | 10 + d + 6 mm PVB | 6 + d + 10 mm PVB | 8 + d + 8 mm PVB | 10 + d + 6 mm Ionoplast | 6 + d + 10 mm Ionoplast | 8 + d + 8 mm Ionoplast |
| F1 | 2.791 × 100 | 2.871 × 100 | 2.910 × 100 | 2.263 × 100 | 1.992 × 100 | −2.809 × 10−1 |
| F2 | 3.290 × 10−2 | 1.531 × 10−2 | 1.750 × 10−1 | −5.358 × 10−2 | 6.979 × 10−2 | 6.894 × 10−1 |
| F3 | 8.810 × 10−3 | 2.529 × 10−3 | 1.416 × 10−2 | −1.987 × 10−2 | 2.648 × 10−2 | 1.708 × 10−1 |
| F4 | −2.880 × 10−3 | −2.442 × 10−3 | −1.257 × 10−2 | 4.104 × 10−3 | −2.826 × 10−3 | −2.654 × 10−2 |
| F5 | −2.783 × 10−2 | −2.660 × 10−2 | −4.955 × 10−2 | 5.285 × 10−3 | −8.877 × 10−3 | −4.392 × 10−2 |
| F6 | −1.292 × 10−3 | −1.168 × 10−3 | −1.699 × 10−3 | 2.399 × 10−4 | −6.416 × 10−4 | −2.636 × 10−3 |
| F7 | 1.836 × 10−3 | 1.787 × 10−3 | 3.079 × 10−3 | −4.501 × 10−4 | 3.457 × 10−4 | 1.675 × 10−3 |
| F8 | 1.030 × 10−3 | 1.007 × 10−3 | 1.553 × 10−3 | −5.441 × 10−5 | 2.151 × 10−4 | 6.741 × 10−4 |
| F9 | −5.742 × 10−5 | −5.634 × 10−5 | −8.522 × 10−5 | 7.458 × 10−6 | −7.622 × 10−6 | −2.530 × 10−5 |
| F10 | 5.708 × 100 | 5.599 × 100 | 7.015 × 100 | −1.170 × 100 | −5.342 × 10−1 | 3.249 × 100 |
| F11 | −1.458 × 100 | −1.436 × 100 | −1.959 × 100 | 3.391 × 10−1 | 9.983 × 10−2 | −9.423 × 10−1 |
| F12 | −7.799 × 10−1 | −7.695 × 10−1 | −9.473 × 10−1 | 1.290 × 10−1 | 3.911 × 10−2 | −1.964 × 10−1 |
| F13 | 7.167 × 10−2 | 7.108 × 10−2 | 1.003 × 10−1 | −1.755 × 10−2 | −4.043 × 10−3 | 3.575 × 10−2 |
| F14 | 1.785 × 10−1 | 1.767 × 10−1 | 2.359 × 10−1 | −4.042 × 10−2 | −1.288 × 10−2 | 4.278 × 10−2 |
| F15 | 1.828 × 10−2 | 1.805 × 10−2 | 2.206 × 10−2 | −2.657 × 10−3 | −9.483 × 10−4 | 2.119 × 10−3 |
| F16 | −3.968 × 10−3 | −3.928 × 10−3 | −5.153 × 10−3 | 8.385 × 10−4 | 3.154 × 10−4 | −3.478 × 10−4 |
| F17 | −8.110 × 10−3 | −8.036 × 10−3 | −1.095 × 10−2 | 2.063 × 10−3 | 5.083 × 10−4 | −1.595 × 10−3 |
| F18 | 1.814 × 10−4 | 1.796 × 10−4 | 2.395 × 10−4 | −4.088 × 10−5 | −1.143 × 10−5 | 1.449 × 10−5 |
| F19 | −1.353 × 100 | −1.321 × 100 | −1.760 × 100 | 3.169 × 10−1 | 1.684 × 10−2 | −1.157 × 100 |
| F20 | 3.504 × 10−1 | 3.443 × 10−1 | 5.087 × 10−1 | −1.093 × 10−1 | −5.482 × 10−3 | 3.262 × 10−1 |
| F21 | 1.748 × 10−1 | 1.714 × 10−1 | 2.248 × 10−1 | −4.197 × 10−2 | −2.992 × 10−3 | 7.059 × 10−2 |
| F22 | −1.779 × 10−2 | −1.763 × 10−2 | −2.709 × 10−2 | 6.027 × 10−3 | 1.461 × 10−4 | −1.245 × 10−2 |
| F23 | −4.278 × 10−2 | −4.220 × 10−2 | −6.037 × 10−2 | 1.270 × 10−2 | 7.323 × 10−4 | −1.615 × 10−2 |
| F24 | −4.177 × 10−3 | −4.100 × 10−3 | −5.248 × 10−3 | 8.110 × 10−4 | 7.145 × 10−5 | −8.424 × 10−4 |
| F25 | 9.932 × 10−4 | 9.803 × 10−4 | 1.350 × 10−3 | −2.447 × 10−4 | −1.785 × 10−5 | 1.653 × 10−4 |
| F26 | 2.078 × 10−3 | 2.055 × 10−3 | 2.963 × 10−3 | −6.981 × 10−4 | −2.049 × 10−5 | 6.098 × 10−4 |
| F27 | −4.897 × 10−5 | −4.843 × 10−5 | −6.678 × 10−5 | 1.328 × 10−5 | 4.615 × 10−7 | −6.677 × 10−6 |

Table A5.
The calculated coefficients for stress function (1) for three plate-thickness dispositions.
Table A5.
The calculated coefficients for stress function (1) for three plate-thickness dispositions.
| Coefficients for Stress Function | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | 10 + d + 6 mm PVB | 6 + d + 10 mm PVB | 8 + d + 8 mm PVB | 10 + d + 6 mm Ionoplast | 6 + d + 10 mm Ionoplast | 8 + d + 8 mm Ionoplast |
| F1 | 2.791 × 100 | 2.871 × 100 | 2.910 × 100 | 2.263 × 100 | 1.992 × 100 | −2.809 × 10−1 |
| F2 | 3.290 × 10−2 | 1.531 × 10−2 | 1.750 × 10−1 | −5.358 × 10−2 | 6.979 × 10−2 | 6.894 × 10−1 |
| F3 | 8.810 × 10−3 | 2.529 × 10−3 | 1.416 × 10−2 | −1.987 × 10−2 | 2.648 × 10−2 | 1.708 × 10−1 |
| F4 | −2.880 × 10−3 | −2.442 × 10−3 | −1.257 × 10−2 | 4.104 × 10−3 | −2.826 × 10−3 | −2.654 × 10−2 |
| F5 | −2.783 × 10−2 | −2.660 × 10−2 | −4.955 × 10−2 | 5.285 × 10−3 | −8.877 × 10−3 | −4.392 × 10−2 |
| F6 | −1.292 × 10−3 | −1.168 × 10−3 | −1.699 × 10−3 | 2.399 × 10−4 | −6.416 × 10−4 | −2.636 × 10−3 |
| F7 | 1.836 × 10−3 | 1.787 × 10−3 | 3.079 × 10−3 | −4.501 × 10−4 | 3.457 × 10−4 | 1.675 × 10−3 |
| F8 | 1.030 × 10−3 | 1.007 × 10−3 | 1.553 × 10−3 | −5.441 × 10−5 | 2.151 × 10−4 | 6.741 × 10−4 |
| F9 | −5.742 × 10−5 | −5.634 × 10−5 | −8.522 × 10−5 | 7.458 × 10−6 | −7.622 × 10−6 | −2.530 × 10−5 |
| F10 | 5.708 × 100 | 5.599 × 100 | 7.015 × 100 | −1.170 × 100 | −5.342 × 10−1 | 3.249 × 100 |
| F11 | −1.458 × 100 | −1.436 × 100 | −1.959 × 100 | 3.391 × 10−1 | 9.983 × 10−2 | −9.423 × 10−1 |
| F12 | −7.799 × 10−1 | −7.695 × 10−1 | −9.473 × 10−1 | 1.290 × 10−1 | 3.911 × 10−2 | −1.964 × 10−1 |
| F13 | 7.167 × 10−2 | 7.108 × 10−2 | 1.003 × 10−1 | −1.755 × 10−2 | −4.043 × 10−3 | 3.575 × 10−2 |
| F14 | 1.785 × 10−1 | 1.767 × 10−1 | 2.359 × 10−1 | −4.042 × 10−2 | −1.288 × 10−2 | 4.278 × 10−2 |
| F15 | 1.828 × 10−2 | 1.805 × 10−2 | 2.206 × 10−2 | −2.657 × 10−3 | −9.483 × 10−4 | 2.119 × 10−3 |
| F16 | −3.968 × 10−3 | −3.928 × 10−3 | −5.153 × 10−3 | 8.385 × 10−4 | 3.154 × 10−4 | −3.478 × 10−4 |
| F17 | −8.110 × 10−3 | −8.036 × 10−3 | −1.095 × 10−2 | 2.063 × 10−3 | 5.083 × 10−4 | −1.595 × 10−3 |
| F18 | 1.814 × 10−4 | 1.796 × 10−4 | 2.395 × 10−4 | −4.088 × 10−5 | −1.143 × 10−5 | 1.449 × 10−5 |
| F19 | −1.353 × 100 | −1.321 × 100 | −1.760 × 100 | 3.169 × 10−1 | 1.684 × 10−2 | −1.157 × 100 |
| F20 | 3.504 × 10−1 | 3.443 × 10−1 | 5.087 × 10−1 | −1.093 × 10−1 | −5.482 × 10−3 | 3.262 × 10−1 |
| F21 | 1.748 × 10−1 | 1.714 × 10−1 | 2.248 × 10−1 | −4.197 × 10−2 | −2.992 × 10−3 | 7.059 × 10−2 |
| F22 | −1.779 × 10−2 | −1.763 × 10−2 | −2.709 × 10−2 | 6.027 × 10−3 | 1.461 × 10−4 | −1.245 × 10−2 |
| F23 | −4.278 × 10−2 | −4.220 × 10−2 | −6.037 × 10−2 | 1.270 × 10−2 | 7.323 × 10−4 | −1.615 × 10−2 |
| F24 | −4.177 × 10−3 | −4.100 × 10−3 | −5.248 × 10−3 | 8.110 × 10−4 | 7.145 × 10−4 | −8.424 × 10−4 |
| F25 | 9.932 × 10−4 | 9.803 × 10−4 | 1.350 × 10−3 | −2.447 × 10−4 | −1.785 × 10−5 | 1.653 × 10−4 |
| F26 | 2.078 × 10−3 | 2.055 × 10−3 | 2.963 × 10−3 | −6.981 × 10−4 | −2.049 × 10−5 | 6.098 × 10−4 |
| F27 | −4.897 × 10−5 | −4.843 × 10−5 | −6.678 × 10−5 | 1.328 × 10−5 | 4.615 × 10−7 | −6.677 × 10−6 |
References
- FprEN 16612; Glass in Building—Determination of the Lateral Load Resistance of Glass Panes by Calculation. EUROPEAN STANDARDS s.r.o.: Pilsen, Czech Republic, 2019.
- Grozdanić, G.; Galić, M.; Marović, P. Some Aspects of the Analyses of Glass Structures Exposed to Impact Load. Couple. Syst. Mech. 2021, 10, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Zemanová, A.; Zeman, J.; Šejnoha, M. Phase-Field Fracture Modelling of Thin Monolithic and Laminated Glass Plates under Quasi-Static Bending. Materials 2020, 13, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Maharaj, C.; Zheng, M.; Mohagheghian, I.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y.; Dear, J.P. Impact Response of Laminated Glass with Varying Interlayer Materials. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 139, 103505:1–103505:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmel, M.; Kolling, S.; Osterrieder, P.; Du Bois, P.A. A Finite Element Model for Impact Simulation with Laminated Glass. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2007, 34, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafinavicius, T.; Kvedaras, A.K.; Sauciuvenas, G. Bending Behavior of Structural Glass Laminated with Different Interlayers. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2013, 49, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelfrene, J.; Kuntsche, J.; Van Dam, S.; Van Paepegem, W.; Schneider, J. Critical Assessment of the Post-breakage Performance of Blast Loaded Laminated Glazing: Experiments and Simulations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 88, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhardt, K.; Balázs, G.L. Temperature Dependent Load Bearing Capacity of Laminated Glass Panes. Period. Polytech. Civil Engng. 2010, 54, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Galuppi, L.; Royer-Carfagni, G.F. Effective Thickness of Laminated Glass Beams: New Expression via a Variational Approach. Eng. Struct. 2012, 38, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duser, A.; Jagota, A.; Bennison, S.J. Analysis of Glass/Polyvinyl Butyral Laminates Subjected to Uniform Pressure. ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 1999, 125, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louter, C.; Belis, J.; Veer, F.; Lebet, J.-P. Durability of SG-Laminated Reinforced Glass Beams: Effects of Temperature, Thermal Cycling, Humidity and Load-duration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzl, F.R. Polymer-Mechanik: Struktur und Mechanisches Verhalten von Polymeren; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; ISBN 978-3-642-64858-8. [Google Scholar]
- Brinson, H.F.; Brinson, L.C. Polymer Engineering Science and Viscoelasticity: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4899-7484-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hána, T.; Janda, T.; Schmidt, J.; Zemanova, A.; Šejnoha, M.; Eliášová, M.; Vokáč, M. Experimental and Numerical Study of Viscoelastic Properties of Polymeric Interlayers Used for Laminated Glass: Determination of Material Parameters. Materials 2019, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hána, T.; Eliášová, M.; Machalická, K.; Vokáč, M. Determination of PVB Interlayer’s Shear Modulus and its Effect on Normal Stress Distribution in Laminated Glass Panels. Mater. Sci. Engng. 2017, 251, 012076:1–012076:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolzi, L.; Cattaneo, S.; Orlando, M.; Piscitelli, L.R.; Spinelli, P. Constitutive Relationships of Different Interlayer Materials for Laminated Glass. Compos. Struct. 2020, 244, 112221:1–112221:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, R.; Sato, C.; Lataillade, J.L.; Viot, P. Experimental Study on the Interface Fracture Toughness of PVB (Polyvinyl Butyral)/Glass at High Strain Rates. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2007, 12, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.; Vigh, L.G.; Stocker, G.; Dunai, L. Finite Element Analysis of Laminated Structural Glass Plates with Polyvinyl Butyral ( PVB ) Interlayer. Period. Polytech. Civil Engng. 2012, 56, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASTMAN-Material Properties of PVB Interlayers Used in Saflex DG41, Product Sheets; Saflex DG: Springfield, MA, USA, 2015.
- SentryGlas® Ionoplast Interlayer-Elastic Properties (SG5000). Available online: https://www.trosifol.com/fileadmin/user_upload/technical_information/downloads/sentryglas/150129_Kuraray_TM_Datenblatt_SG.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Hooper, P.A.; Blackman, B.R.K.; Dear, J.P. The Mechanical Behaviour of Poly (Vinyl Bbutyral ) at Different Strain Magnitudes and Strain Rates. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3564–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hao, H.; Shi, Y.; Cui, J. The Mechanical Properties of Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB ) at High Strain Rates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centelles, X.; Martin, M.; Solé, A.; Castro, J.R.; Cabeza, L.F. Tensile Test on Interlayer Materials for Laminated Glass under Diverse Ageing Conditions and Strain Rates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, M.; Poot, B. Influence of temperature on laminated glass performances assembled with various interlayers. In Proceedings of the Conference on Architectural and Structural Applications of Glass (Challeging Glass 5), Ghent, Belgium, 16–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aenlle-Lopez, M.; Noriega, A.; Pelayo, F. Mechanical Characterization of Polyvinil Butyral from Static and Modal Tests on Laminated Glass Beams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 169, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liene, S.; Kinsella, D.; Kozłowski, M. Influence of EVA, PVB and Ionoplast Interlayers on the Structural Behaviour and Fracture Pattern of Laminated Glass. Int. J. Struct. Glas. Adv. Mater. Res. 2019, 3, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Kraus, M.; Schneider, J.; Siebert, G. Investigations on the Thermorheologically Complex Material Behaviour of the laminated Safety Glass Interlayer Ethylene-Vinyl-Acetate. Glass Struct. Eng. 2018, 3, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, M.A.; Schuster, M.; Kuntsche, J.; Siebert, G.; Schneider, J. Parameter Identification Methods for Visco- and Hyperelastic Material Models. Glass Struct. Eng. 2017, 2, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hána, T.; Vokáč, M.; Eliášová, M.; Machalická, K.V. Experimental Investigation of Temperature and Loading Rate Effects on the Initial Shear Stiffness of Polymeric Interlayers. Eng. Struct. 2020, 223, 110728:1–110728:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolzi, L.; Cagnacci, E.; Orlando, M.; Piscitelli, L.; Rosati, G. Long Term Response of Glass-PVB double-lap joints. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, L.; Briccoli Bati, S.; Fagone, M.; Ranocchiai, G.; Zulli, F. Dynamic Torsion Tests to Characterize the Termo-viscoelastic Properties of Polymeric Interlayers for Laminated Glass. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botz, M.; Kraus, M.; Siebert, G. Experimental determination of the shear modulus of polymeric interlayers used in laminated glass. In Proceedings of the Glass Con. Global, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, X. Experimental and Analytical Study on Uniaxial Tensile Property of Ionomer Interlayer at Different Temperatures and Strain Rates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120058:1–120058:18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castori, G.; Speranzini, E. Structural Analysis of Failure Behavior of Laminated Glass. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 125, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1288-3:2002; Glass in Building-Determination of the Bending Strength of Glass-Part 3: Test with Specimen Supported at Two Points (Four-Point Bending). European Committee for Standardization, CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- Asik, M.Z. Laminated Glass Plates: Revealing of Nonlinear Behavior. Comput. Struct. 2003, 81, 2659–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zang, M. The Simulation of Laminated Glass Beam Impact Problem by Developing Fracture Model of Spherical DEM. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2014, 42, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engineering Simulation Software ANSYS, Release 16.2; Ansys Inc.: Canonsburg, DC, USA, 2015.
- Mathematical Computing Software MATLAB, version 2021a; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2021.
- Seber, G.A.F.; Wild, C.J. Nonlinear Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-471-47135-6. [Google Scholar]
- Serafinavičius, T.; Lebet, J.-P.; Louter, C.; Lenkimas, T.; Kuranovas, A. Long-term Laminated Glass Four Point Bending Test with PVB, EVA and SG Interlayers at Different Temperatures. Procedia Eng. 2013, 57, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).