A Novel Approach to Grain Shape Factor in 3D Hexagonal Cellular Automaton
Abstract
1. Introduction
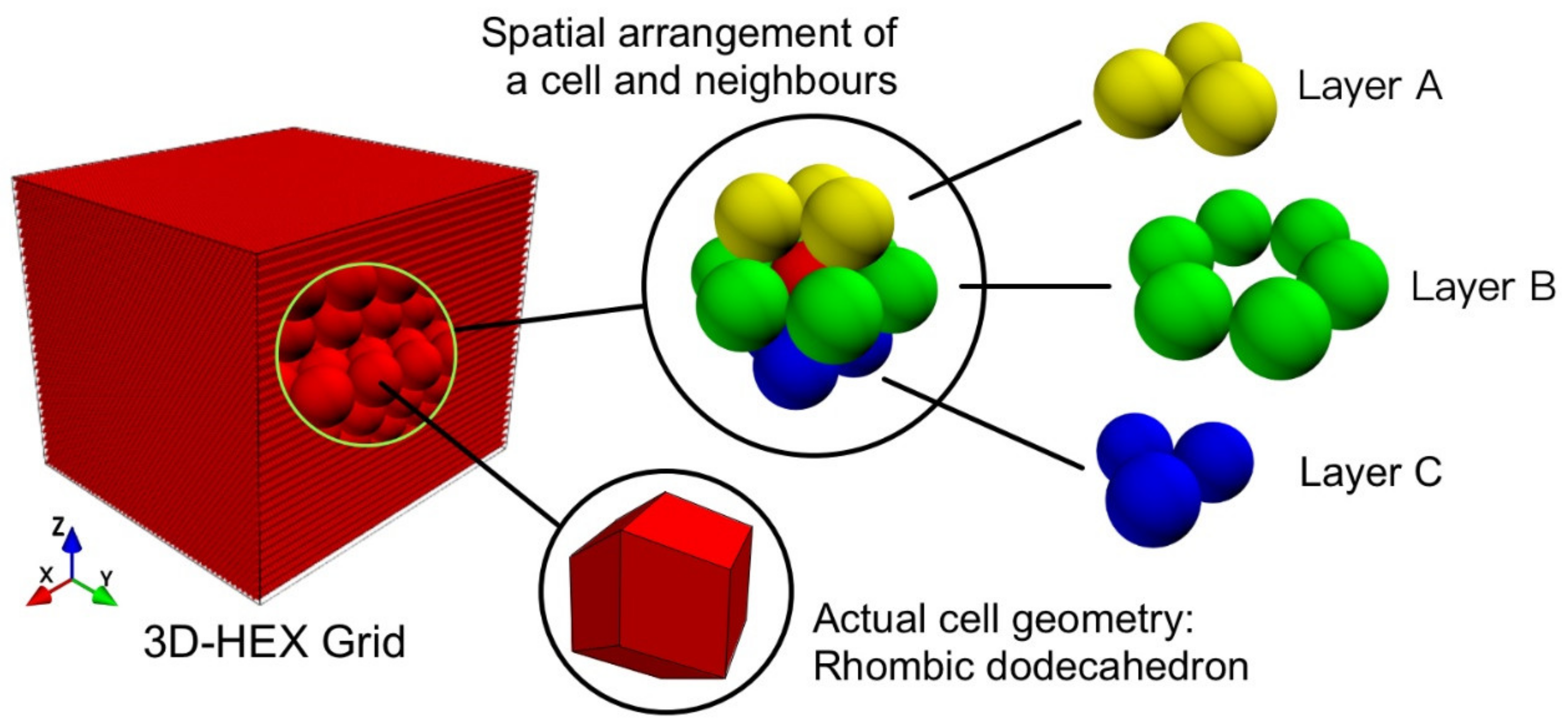
2. Model and Calculation
3. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashemi, S.; Kalidindi, S.R. A Machine Learning Framework for the Temporal Evolution of Microstructure during Static Recrystallization of Polycrystalline Materials Simulated by Cellular Automaton. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 188, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Rout, M.; Min, K.-M.; Chen, S.-F.; Lee, M.-G. A Fully Coupled Crystal Plasticity-Cellular Automata Model for Predicting Thermomechanical Response with Dynamic Recrystallization in AISI 304LN Stainless Steel. Mech. Mater. 2022, 167, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, M.S.; Ploshikhin, V. Implementation of Nucleation in Cellular Automaton Simulation of Microstructural Evolution during Additive Manufacturing of Al Alloys. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, J.; Natsume, Y. Three-Dimensional Large-Scale Grain Growth Simulation Using a Cellular Automaton Model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 199, 110729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Moodispaw, M.P.; Luo, A.A. Cellular Automaton Simulation and Experimental Validation of Eutectic Transformation during Solidification of Al-Si Alloys. Npj Comput. Mater. 2022, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hong, K.; Shin, Y.C. A Novel 3D Cellular Automata-Phase Field Model for Computationally Efficient Dendrite Evolution during Bulk Solidification. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 192, 110405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutaro, J.; Stump, B.; Shukla, P. Discrete Event Cellular Automata: A New Approach to Cellular Automata for Computational Material Science. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 219, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Ridgeway, C.D.; Cinkilic, E.; Lu, Y.; Luo, A.A. Predicting Gas and Shrinkage Porosity in Solidification Microstructure: A Coupled Three-Dimensional Cellular Automaton Model. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 49, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, R.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Tian, G. Cellular Automata Simulation of Grain Growth of Powder Metallurgy Nickel-Based Superalloy. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amri, N.; El Amri, A.; El Bouayadi, R.; El Hassouani, Y.; Bouachrine, M.; Zorkani, I. Modeling Phase Change Materials Using Cellular Automata. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Benyounes, H., Bouchaala, F.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1076, pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tian, X.; Wu, G.; Zhu, H.; Ou, H.; Cui, Z. Coupled Quantitative Modeling of Microstructural Evolution and Plastic Flow during Continuous Dynamic Recrystallization. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 156, 103372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, C. Cellular Automata in Triangular, Pentagonal, and Hexagonal Tessellations. In Cellular Automata: A Volume in the Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science, 2nd ed.; Adamatzky, A., Ed.; Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-1-4939-8700-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fuyong, S.; Wenli, L.; Zhi, W. Three-Dimensional Cellular Automaton Simulation of Austenite Grain Growth of Fe-1C-1.5Cr Alloy Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolchigo, M.; Plotkowski, A.; Belak, J. Sensitivity of Cellular Automata Grain Structure Predictions for High Solidification Rates. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 196, 110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Pu, Z.; Liu, D.-R. Prediction of Grain-Size Transition during Solidification of Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloys by an Improved Three-Dimensional Sharp-Interface Model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 203, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shterenlikht, A.; Margetts, L. Three-Dimensional Cellular Automata Modelling of Cleavage Propagation across Crystal Boundaries in Polycrystalline Microstructures. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Lu, Y.; Ridgeway, C.D.; Cinkilic, E.; Luo, A.A. Three-Dimensional Cellular Automaton Simulation of Coupled Hydrogen Porosity and Microstructure during Solidification of Ternary Aluminum Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, X.; Xue, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Lee, P.D. Predicting Hydrogen Microporosity in Long Solidification Range Ternary Al-Cu-Li Alloys by Coupling CALPHAD and Cellular Automata Model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 222, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, K.; Zhou, G.; Tang, W.; Shen, Y.; Tang, D.; Li, D. Simulation of Strain Induced Abnormal Grain Growth in Aluminum Alloy by Coupling Crystal Plasticity and Phase Field Methods. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 3873–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavizadeh, S.A.; Eshraghi, M.; Felicelli, S.D. Three-Dimensional Phase Field Modeling of Columnar to Equiaxed Transition in Directional Solidification of Inconel 718 Alloy. J. Cryst. Growth 2020, 549, 125879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Ridgeway, C.D.; Moodispaw, M.P.; Luo, A.A. Multi-Component Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study of Dendritic Growth during Solidification Processing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 286, 116829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. A Continuous-Discontinuous Cellular Automaton Method for Cracks Growth and Coalescence in Brittle Material. Acta Mech. Sin. 2014, 30, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, C.; Kim, N. A Fully Coupled Crystal Plasticity-Cellular Automata Model for Dynamic Recrystallization of Metallic Materials. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 149, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Yang, G. Cellular Automata Simulation of Grain Growth of Powder Metallurgy Ni-Based FGH98 Superalloys during Solution Treatment. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Zheng, B.; Du, H. Phase Field Simulation on the Effect of Micropore Morphology on Grain Growth in Porous Ceramics. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 131, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagigas-Muñiz, D.; Diaz-del-Rio, F.; Sevillano-Ramos, J.L.; Guisado-Lizar, J.-L. Efficient Simulation Execution of Cellular Automata on GPU. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 118, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Hilden, M.M.; Yahyaei, M. A 3D Cellular Automata Ore Stockpile Model—Part 1: Simulation of Size Segregation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorato, R.; Arroyo, M.; Andò, E.; Gens, A. Sphericity Measures of Sand Grains. Eng. Geol. 2019, 254, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Matías, I.; Ayala, D.; Hiller, D.; Gutsch, S.; Zacharias, M.; Estradé, S.; Peiró, F. Sphericity and Roundness Computation for Particles Using the Extreme Vertices Model. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 30, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Schon, A.; Apoena Castro, N.; dos Santos Barros, A.; Eduardo Spinelli, J.; Garcia, A.; Cheung, N.; Luiz Silva, B. Multiple Linear Regression Approach to Predict Tensile Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC) Alloys. Mater. Lett. 2021, 304, 130587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linear Regression Using R: An Introduction to Data Modeling. Available online: https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/textbooks/399 (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Crowder, S.; Delker, C.; Forrest, E.; Martin, N. Monte Carlo Methods for the Propagation of Uncertainties. In Introduction to Statistics in Metrology; Crowder, S., Delker, C., Forrest, E., Martin, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 153–180. ISBN 978-3-030-53329-8. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, L.; Shi, J. A Novel Approach to Grain Shape Factor in 3D Hexagonal Cellular Automaton. Crystals 2023, 13, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030544
Bao L, Shi J. A Novel Approach to Grain Shape Factor in 3D Hexagonal Cellular Automaton. Crystals. 2023; 13(3):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030544
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Lei, and Jun Shi. 2023. "A Novel Approach to Grain Shape Factor in 3D Hexagonal Cellular Automaton" Crystals 13, no. 3: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030544
APA StyleBao, L., & Shi, J. (2023). A Novel Approach to Grain Shape Factor in 3D Hexagonal Cellular Automaton. Crystals, 13(3), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030544







