Lithographically Ordered FePt L10 Dots with High Coercivity for Logic-Conditioned Magnetic Nanostructures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method of Pre-Patterning and Magnetic Elements Nanofabrication
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results
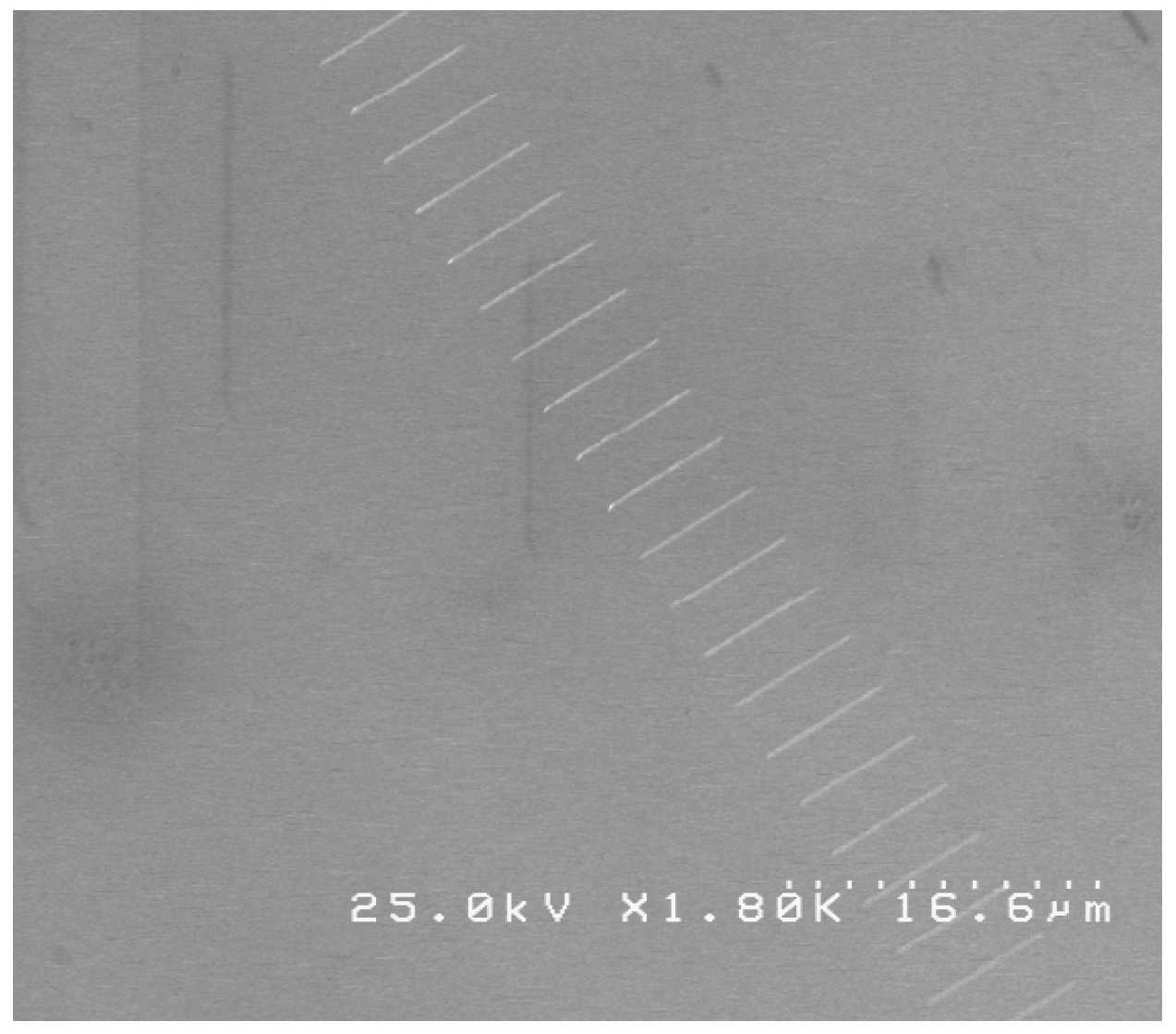
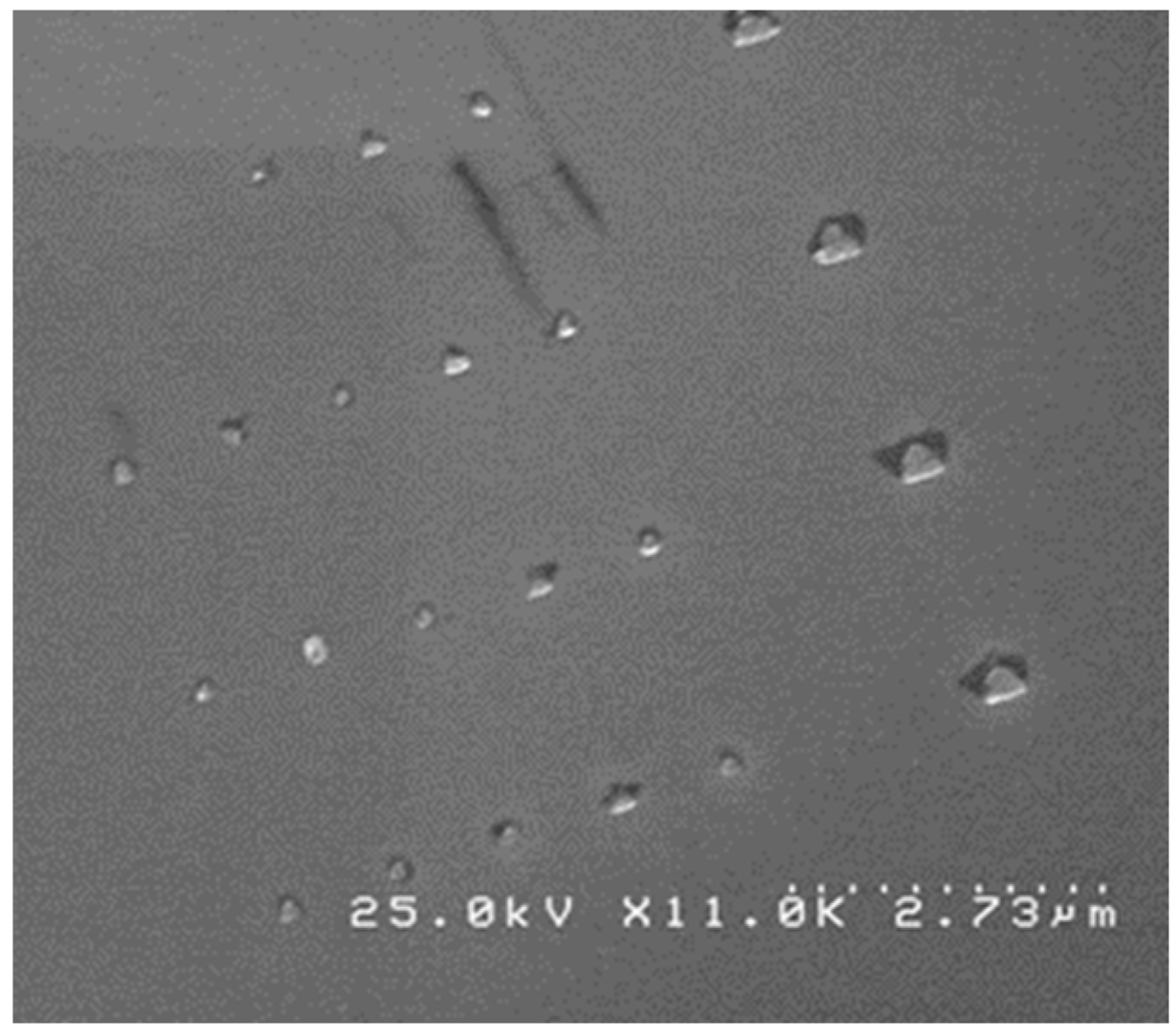
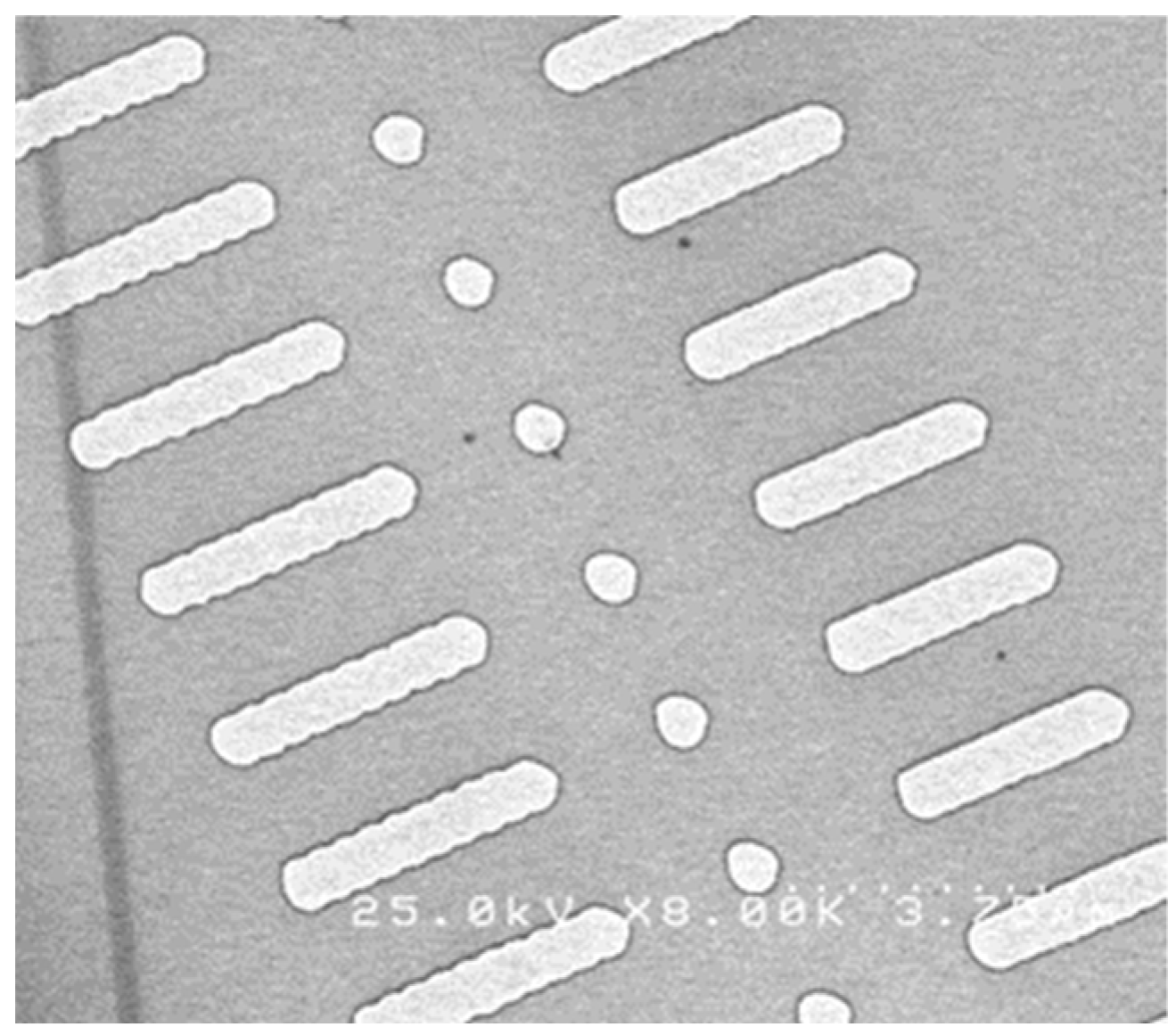
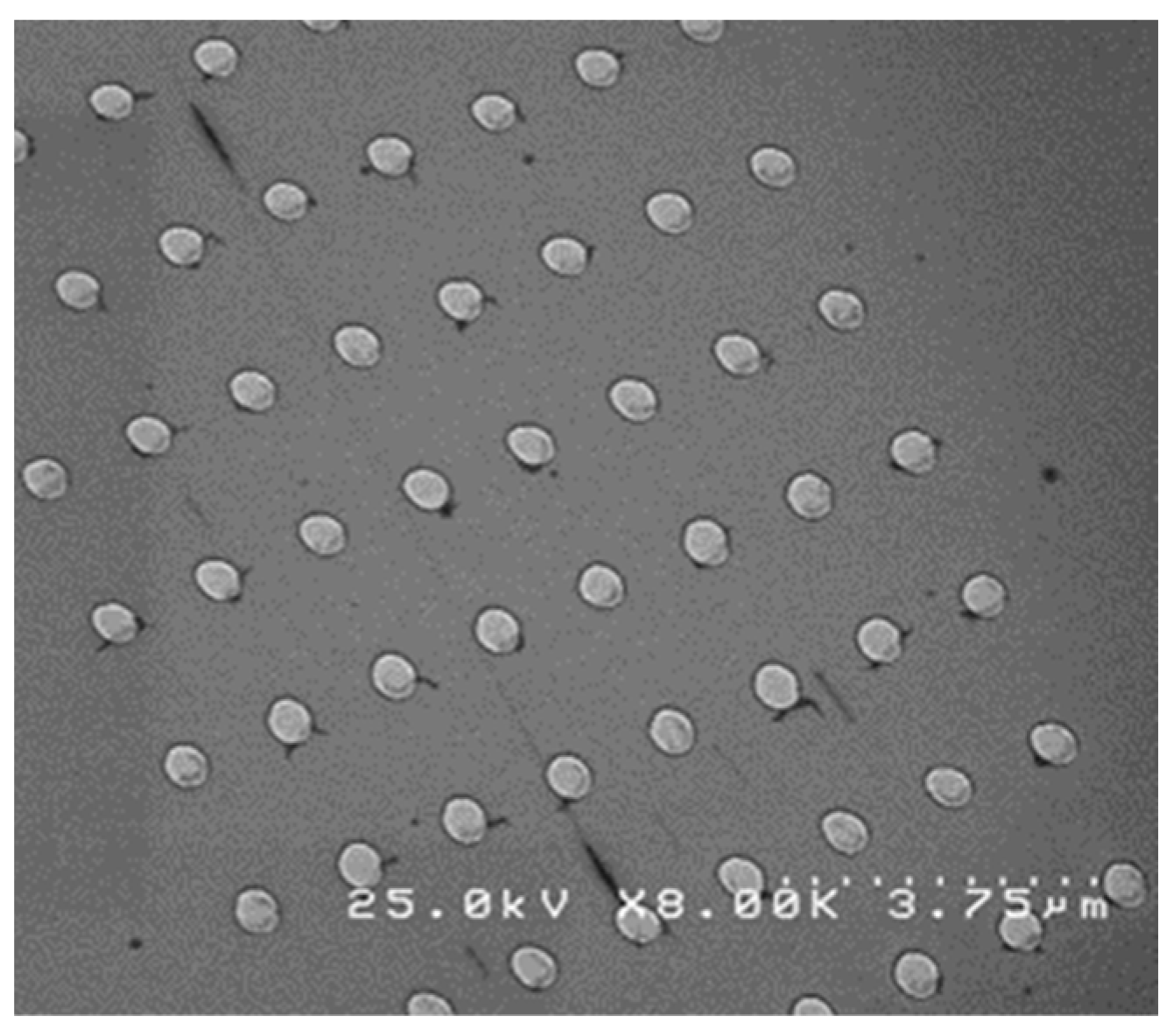
3.1. Complex Morphology Analysis
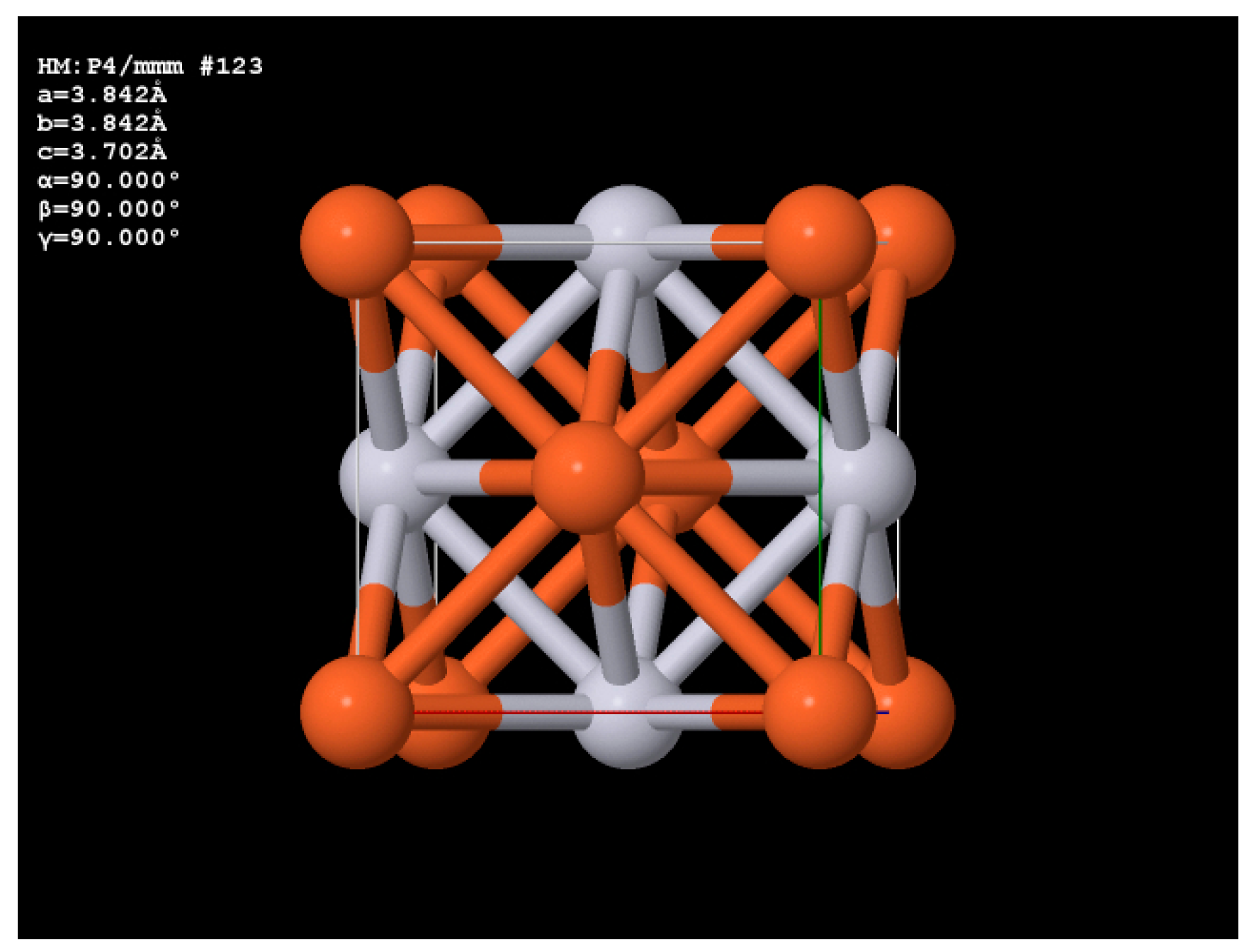
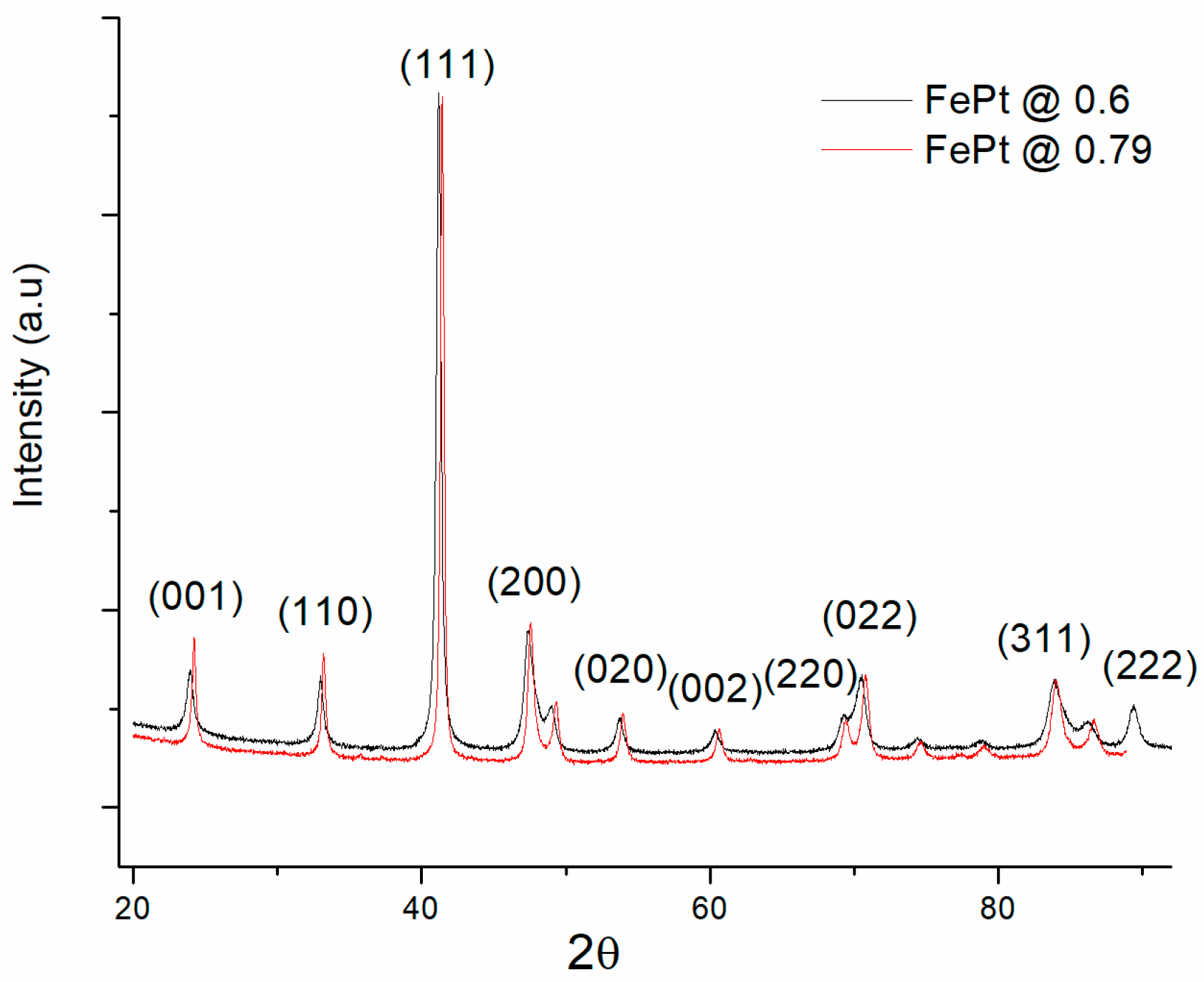
3.2. Structural Analysis of the Regular Arrays of Magnetic Structures
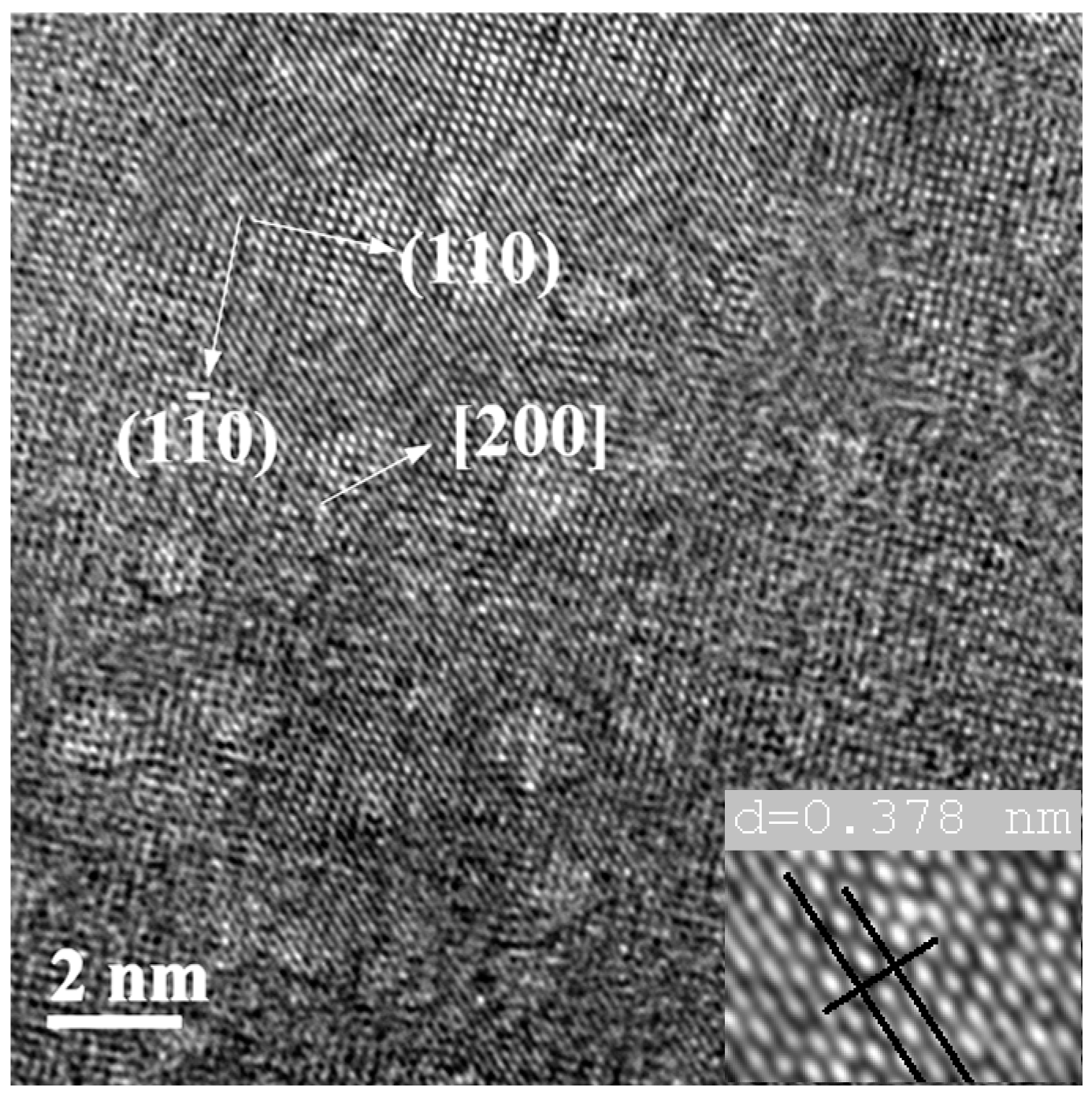
3.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy and Electron Diffraction Results
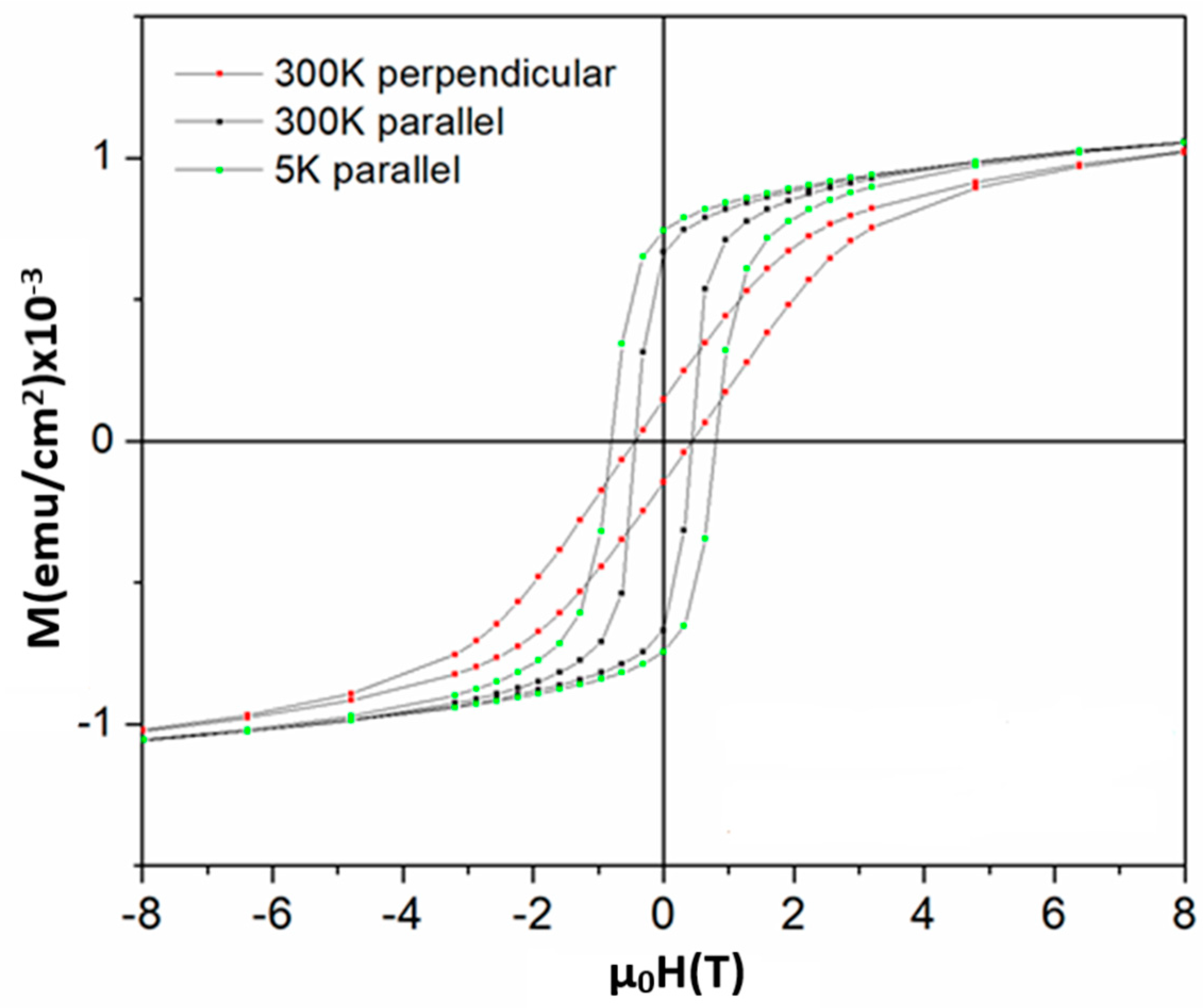
3.4. Magnetic Investigations of the Regular Arrays of Magnetic Nanostructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.B.; Norris, D.J.; Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Wong, P.K.L.; Xu, Y.B. Hybrid spintronic materials: Growth, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 99, 27–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedmedenko, E.Y.; Kawakami, R.K.; Sheka, D.D.; Gambardella, P.; Kirilyuk, A.; Hirohata, A.; Binek, C.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Sanvito, S.; Kirby, B.J.; et al. The 2020 magnetism roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 453001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, J.R.; Medwal, R.; Gupta, S.; Gogia, K.; Vas, J.V.; Gupta, R.; Deka, A.; Rawat, R.S.; Subramanian, A.; Fukuma, Y. Nonstoichiometric FePt Nanoclusters for Heated Dot Magnetic Recording Media. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 7079–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medwal, R.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, S.; Chae, K.H.; Asokan, K.; Deen, G.R.; Rawat, R.S.; Katiyar, R.S.; Annapoorni, S. Self-Stabilized Carbon-L10 FePt Nanoparticles for Heated Dot Recording Media. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2018, 9, 5504105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Xiao, S.G.; Hsu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Feldbaum, M.; Klemmer, T.; Kubota, Y.; Thiele, J.-U.; et al. Heated Dot Magnetic Recording Media—Path to 10 TDOTS/in2. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference of Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (ICAUMS), Tainan, Taiwan, 1–5 August 2016; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, L. Storage Physics and Noise Mechanism in Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.J.; Takahashi, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Ishio, S.; Kondo, Y.; Ariake, J. Towards an understanding of microstructure of patterned FePt dots by magnetometry using pulse fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 349, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.J.; Takahashi, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Ishio, S.; Kondo, Y.; Ariake, J.; Xue, D.S. Understanding magnetic properties of arrays of small FePt dots with perpendicular anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3737–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Sun, S.H.; Wilson, R.J.; White, R.L.; Pourmand, N.; Wang, S.X. Spin valve sensors for ultrasensitive detection of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biological applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 126, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, C.D.; Hansteen, F.; Kimel, A.V.; Kirilyuk, A.; Tsukamoto, A.; Itoh, A.; Rasing, T. All-Optical Magnetic Recording with Circularly Polarized Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 047601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, I.; Vahaplar, K.; Stamm, C.; Kachel, T.; Pontius, N.; Dürr, H.A.; Ostler, T.A.; Barker, J.; Evans, R.F.L.; Chantrell, R.W.; et al. Transient ferromagnetic-like state mediating ultrafast reversal of antiferromagnetically coupled spins. Nature 2011, 472, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, S.; Gottwald, M.; Lambert, C.H.; Steil, D.; Uhlíř, V.; Pang, L.; Hehn, M.; Alebrand, S.; Cinchetti, M.; Malinowski, G.; et al. Engineered materials for all-optical helicity-dependent magnetic switching. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Patz, A.; Mouchliadis, L.; Yan, J.Q.; Lograsso, T.A.; Perakis, I.E.; Wang, J.G. Femtosecond switching of magnetism via strongly correlated spin–charge quantum excitations. Nature 2013, 496, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, H. The application of spintronic devices in magnetic bio-sensing. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asia Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ASQED), Penang, Malaysia, 3–4 August 2010; pp. 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.Q.; Wu, K.; Saha, R.; Peng, C.Y.; Wang, J.P. Advances in Magnetoresistive Biosensors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, C.; Yari, P.; Wu, K. Recent advances in magnetoresistance biosensors: A short review. Nano Futures 2023, 7, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, A.D.; Vasiliu, F.; Nicula, R.; Bartha, C.; Mercioniu, I.; Crisan, O. Thermodynamic, structural and magnetic studies of phase transformations in MnAl nanocomposite alloys. Mater. Charact. 2018, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, A.D.; Crisan, O.; Randrianantoandro, N.; Valeanu, M.; Morariu, M.; Burkel, E. Crystallization processes in Fe-Pt-Nb-B melt spun ribbons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Biomim. Supramolec. Syst. 2007, 27, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; de Moraes, I.; Eslava, G.G.; Grenier, S.; Bellet-Amalric, E.; Dias, A.; Bonfim, M.; Ranno, L.; Devillers, T.; Dempsey, N.M. A high throughput study of both compositionally graded and homogeneous Fe-Pt thin films. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, H.; et al. A Controllability Investigation of Magnetic Properties for FePt Alloy Nanocomposite Thin Films. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Cai, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, J.; Jiang, T.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Z. Fluence and Temperature Dependences of Laser-Induced Ultrafast Demagnetization and Recovery Dynamics in L10-FePt Thin Film. Materials 2023, 16, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, N.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O. The critical size between single domain and multidomain in L10-FePt. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07D511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Recent Advances in Chemical Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Applications of FePt Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crisan, O.; Crisan, A.D. Lithographically Ordered FePt L10 Dots with High Coercivity for Logic-Conditioned Magnetic Nanostructures. Crystals 2024, 14, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010058
Crisan O, Crisan AD. Lithographically Ordered FePt L10 Dots with High Coercivity for Logic-Conditioned Magnetic Nanostructures. Crystals. 2024; 14(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrisan, Ovidiu, and Alina Daniela Crisan. 2024. "Lithographically Ordered FePt L10 Dots with High Coercivity for Logic-Conditioned Magnetic Nanostructures" Crystals 14, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010058
APA StyleCrisan, O., & Crisan, A. D. (2024). Lithographically Ordered FePt L10 Dots with High Coercivity for Logic-Conditioned Magnetic Nanostructures. Crystals, 14(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010058





