Experimental Investigations on the Electrical Conductivity and Complex Dielectric Permittivity of ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 and 0.4) Ferrites in a Low-Frequency Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sample Characterization and Experiments
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4. Magnetic Properties
3.5. Electrical and Dielectric Properties
3.5.1. Complex Impedance
3.5.2. Electrical Conductivity
3.5.3. Complex Dielectric Permittivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.; Mamba, B.B. Ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications in electronic device. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 215, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakaloudi, V.; Zaspalis, V.T. A new Mn–Zn ferrite for high-speed data transmission applications in telecommunication networks. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2540–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Devi, K.S.P.; Dutta, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Pramanik, P.; Dhara, D. Biocompatible mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging applications. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 431, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, H.B.; Hathiya, L.J.; Joshi, H.H.; Tanna, A.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Photocatalytic MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Mat. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmurugan, R.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Sendhilnathan, S.; Jeyadevan, B. Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for ferrofluid preparation: Study on thermal–magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 298, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, E.M.; Khairy, M.; Mousa, M.A. Effect of morphology and particle size on the electrical properties of nano-nickel ferrite. J. Mat. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 7381–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardile, H.; Somvanshi, S.B.; Chavan, A.R.; Pandit, A.; Jadhav, K. Effect of Cd2+ doping on structural, morphological, optical, magnetic and wettability properties of nickel ferrite thin films. Optik 2020, 207, 164462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, M. Comparative studies on impact of synthesis methods on structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 8, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaescu, I.; Lungu, A.; Marin, C.N.; Vlazan, P.; Sfirloaga, P.; Turi, G.M. Experimental investigations of the structural transformations induced by the heat treatment in manganese ferrite synthesized by ultrasonic assisted co-precipitation method. Cer. Int. 2016, 42, 16744–16748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbe, A.V.; Kounsalye, J.S.; Somvanshi, S.B.; Kumar, A.; Jadhav, K. Cation distribution, magnetic and hyperfine interaction studies of Ni–Zn spinel ferrites: Role of Jahn Teller ion (Cu2+) substitution. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, M.; Srinatha, N.; Matteppanavar, S.; Angadi, B.; Sahoo, B.; Rudraswamy, B. Effect of Zn substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline NiFe2O4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4946–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.R.; Lincoln, C.A.; Ravinder, D.; Ahmad, S.I. Structural, morphological, luminescence, magnetic, and electrical transport properties of zinc-doped MnFe2O4 nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, T.; Atif, M.; Rehman, A.U.; Wahab, H.; Khalid, W.; Ali, Z.; Nadeem, M. Colossal permittivity, resistive and magnetic properties of zinc substituted manganese ferrites. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 923, 166454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, R.; Baldissera, M.R.; Da Silva, M.R.A.; Da Silveira, C.A.; Soares, D.A.W.; Perazolli, P.A.; Da Silva, M.R.; Zaghete, M.A. Structural and magnetic characterization of MnxZn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.2, 0.35, 0.65, 0.8, 1.0) ferrites obtained by the citrate precursor method. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, D.; Drofenik, M.; Žnidaršic, A. Sintering of MnZn-ferrite powders prepared by hydrothermal reactions between oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1945–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, E.V.; Al-Omari, I.A.; Malini, K.A.; Joy, P.A.; Kumar, D.S.; Yoshida, Y. Impact of zinc substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of chemically derived nanosized manganese zinc mixed ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Heda, I.; Dhahri, R.; Massoudi, J.; Dhahri, E.; Bahri, F.; Khirouni, K.; Costa, B.F.O. Study of the structural, electrical, dielectric properties and transport mechanisms of Cu0.5Fe2.5O4 ferrite nanoparticles for energy storage, photocatalytic and microelectronic applications. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, S.; Malec, D.; Bley, V.; Mary, D.; Schlegel, B. New Use of Mn-Zn Ferrite Material in Power Electronics Integrated LC Filters. Engineering 2017, 9, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Davis, E.A. Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Elliot, S.R. A.c. conduction in amorphous chalcogenide and pnictide semiconductors. Adv. Phys. 1987, 36, 135–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pathak, S.; Jain, K.; Singh, A.; Basheed, G.A.; Pant, R.P. Low-temperature large-scale hydrothermal synthesis of optically active PEG-200 capped single domain MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 904, 163992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; de Hasseth, J.A. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ercuta, A. Sensitive AC hysteresigraph of extended driving field capability. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, A.; Malaescu, I.; Marin, C.N.; Vlazan, P.; Sfirloaga, P. The electrical properties of manganese ferrite powders prepared by two different methods. Phys. B Cond. Matter. 2015, 462, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D150-98; Standard Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Iyer, R.; Desai, R.; Upadhyay, R.V. Low temperature synthesis of nanosized Mn1−xZnxFe2O4 ferrites and their characterizations. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, T.T.; Srivastava, C.M.; Venkataramani, N.; Patni, M.J. Infrared absorption in spinel ferrites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1984, 6, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, M.K. FT-IR studies of Cu substituted Ni-Zn ferrites for structural and vibrational investigations. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2015, 4, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, E.C.; Soibam, I. Effect of Zn doping on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Indian J. Phys. 2017, 91, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Shao-Yun, F. Synthesis of nanocrystalline Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 via in situ polymerization technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaag, P.J.V.; Noordermeer, A.; Johnson, M.T.; Bongers, P.E. Size-dependent Curie temperature in nanoscale MnFe2O4 particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalan, E.V.; Malini, K.A.; Saravanan, S.; Kumar, D.S.; Yoshida, Y.; Anantharaman, M.R. Evidence for polaron conduction in nanostructured manganese ferrite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 185005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Sorenson, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.G.; Delvin, E.; Kostidas, A. Size-dependent magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 fine particles synthesized by coprecipitation. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 9288–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmurugan, R.; Jeyadevan, B.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Sendhilnathan, S. Effect of zinc substitution on Co-Zn and Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 288, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsa, F.; Torgeson, D.R.; Martin, S.W.; Patel, H.K. Relaxation and fluctuations in glassy-fast-ion conductors Wide-frequency-range NMR and conductivity measurements. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajlaoui, M.E.; Dhahri, R.; Hnainia, N.; Benchaabane, A.; Dhahri, E.; Khirouni, K. Dielectric spectroscopy study of the Ni0.2Zn0.8Fe2O4 spinel ferrite as a function of frequency and temperature. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 262, 114683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Nadeem, M.; Hassan, M.M. Investigation of conduction and relaxation phenomena in LaFe0.9Ni0.1O3 by impedance spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 155401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debye, P. Polar Molecules; Chemical Catalog Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Malaescu, I.; Lungu, A.; Marin, C.N.; Sfirloaga, P.; Vlazan, P.; Brindusoiu, S.; Poienar, M. Temperature dependence of the dynamic electrical properties of Cu1+xMn1−xO2 (x = 0 and 0.06) crednerite materials. Cer. Intern. 2018, 44, 11610–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajlaoui, M.E.; Gharbi, S.; Dhahri, E.; Khirouni, K. Impedance spectroscopy and giant permittivity study of spinel ZnFe2O4 ferrite as a function of frequency and temperature. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 906, 164361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Universal Relaxation Law, 1st ed.; Chelsea Dielectrics Press: London, UK, 1996; pp. 198–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ponpandian, N.; Balaya, P.; Narayanasamy, A. Electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of nanocrystalline NiFe2O4 spinel. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, 3221–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.R. A theory of a.c. conduction in chalcogenide glasses. Philos. Mag. B 1977, 36, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya, J.; Sekaran, G.; Bououdina, M. Effect of Cu2+ doping on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 particles/sheets/flakes-like nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustundağ, M.; Aslan, M. Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Ca-Doped Mn-Ferrite. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 130, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wang, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Fan, R. Doped ceramics of indium oxides for negative permittivity materials in MHz-kHz frequency regions. J. Mat. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, R. Dielectric dispersion of copper/rutile cermet: Dielectric resonance, relaxation, and plasma oscillation. Scripta Mater. 2021, 190, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Qian, L.; Dang, F.; Liu, Y.; Fan, R.; Wang, X.; Dou, S. C/SiO2 meta-composite: Overcoming the λ/a relationship limitation in metamaterials. Carbon 2017, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhanov, A.V.; Algarou, N.A.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Baykal, A.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Vinnik, D.A.; Vakhitov, M.G.; Klygach, D.S.; Silibin, M.V.; et al. Peculiarities of the microwave properties of hard–soft functional composites SrTb0.01Tm0.01Fe11.98O19–AFe2O4 (A = Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, or Mn). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32638–32651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, K.R.; Kumar, K.V.; Ravinder, D. Structural and Electrical Conductivity Studies in Nickel-Zinc Ferrite. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2012, 02, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.S.; Song, W.L.; Hou, Z.L.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 2010, 48, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaife, B.K. Principles of Dielectrics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Batoo, K.M. Study of dielectric and impedance properties of Mn ferrites. Phys. B Cond. Matter. 2011, 406, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
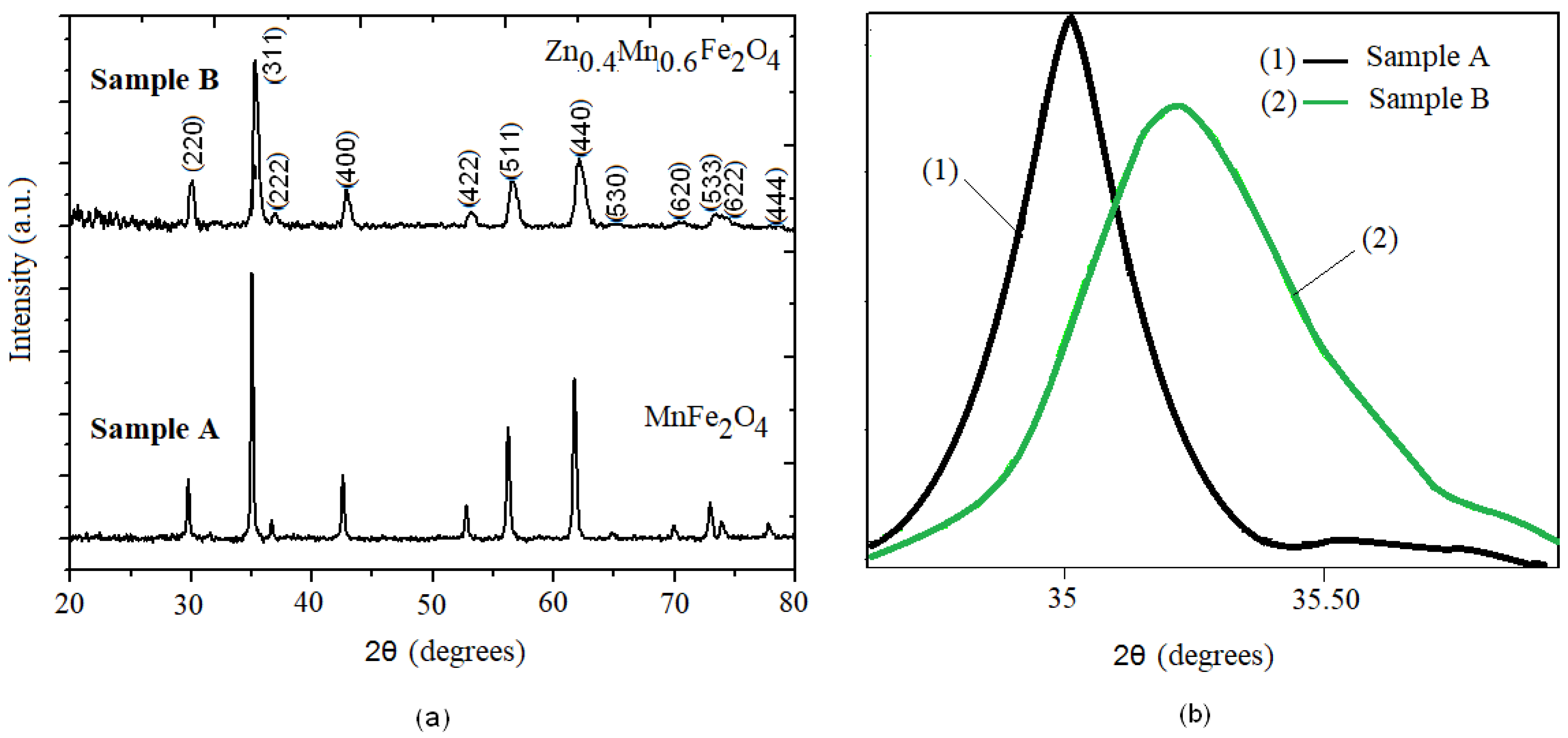
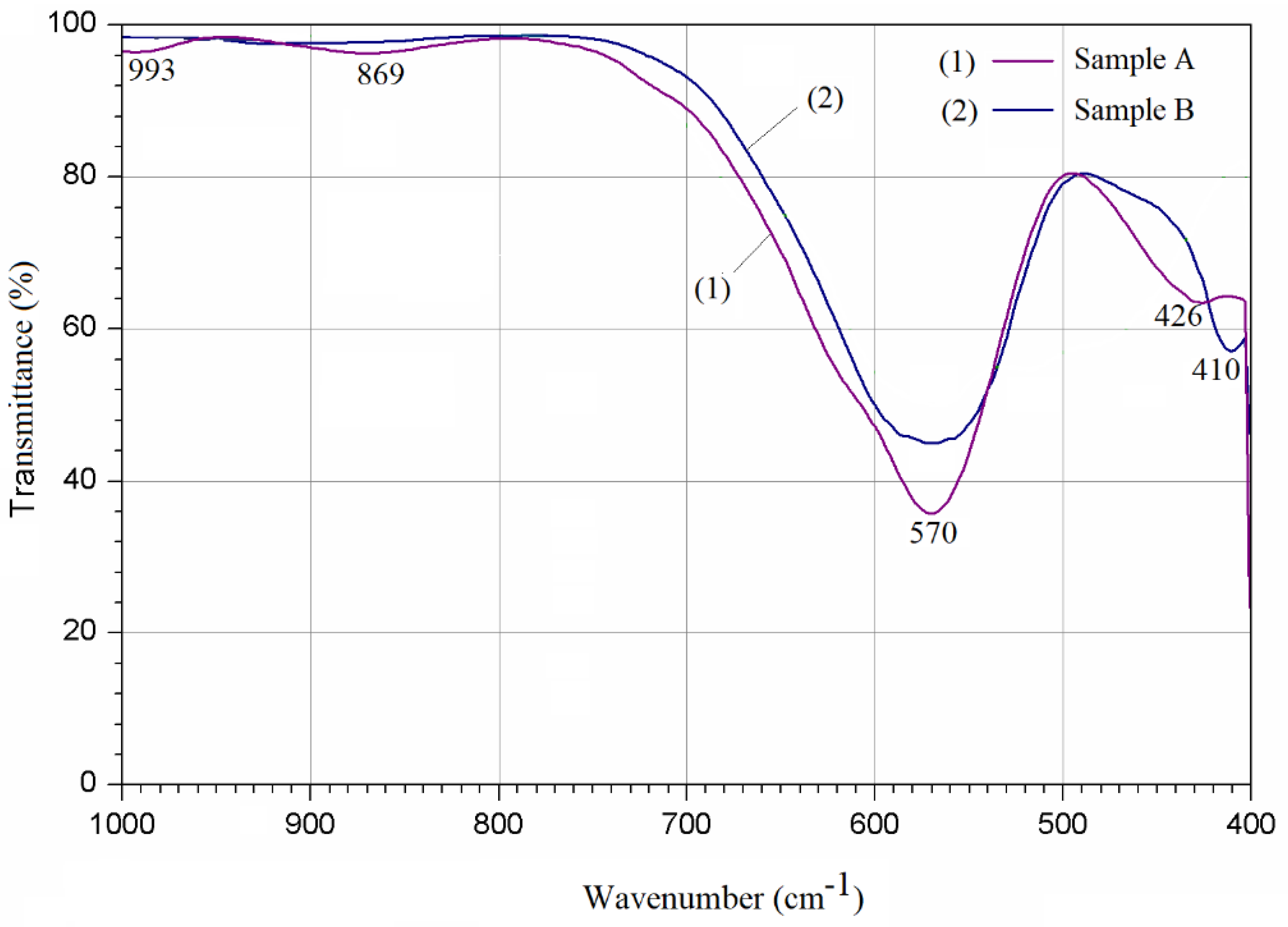
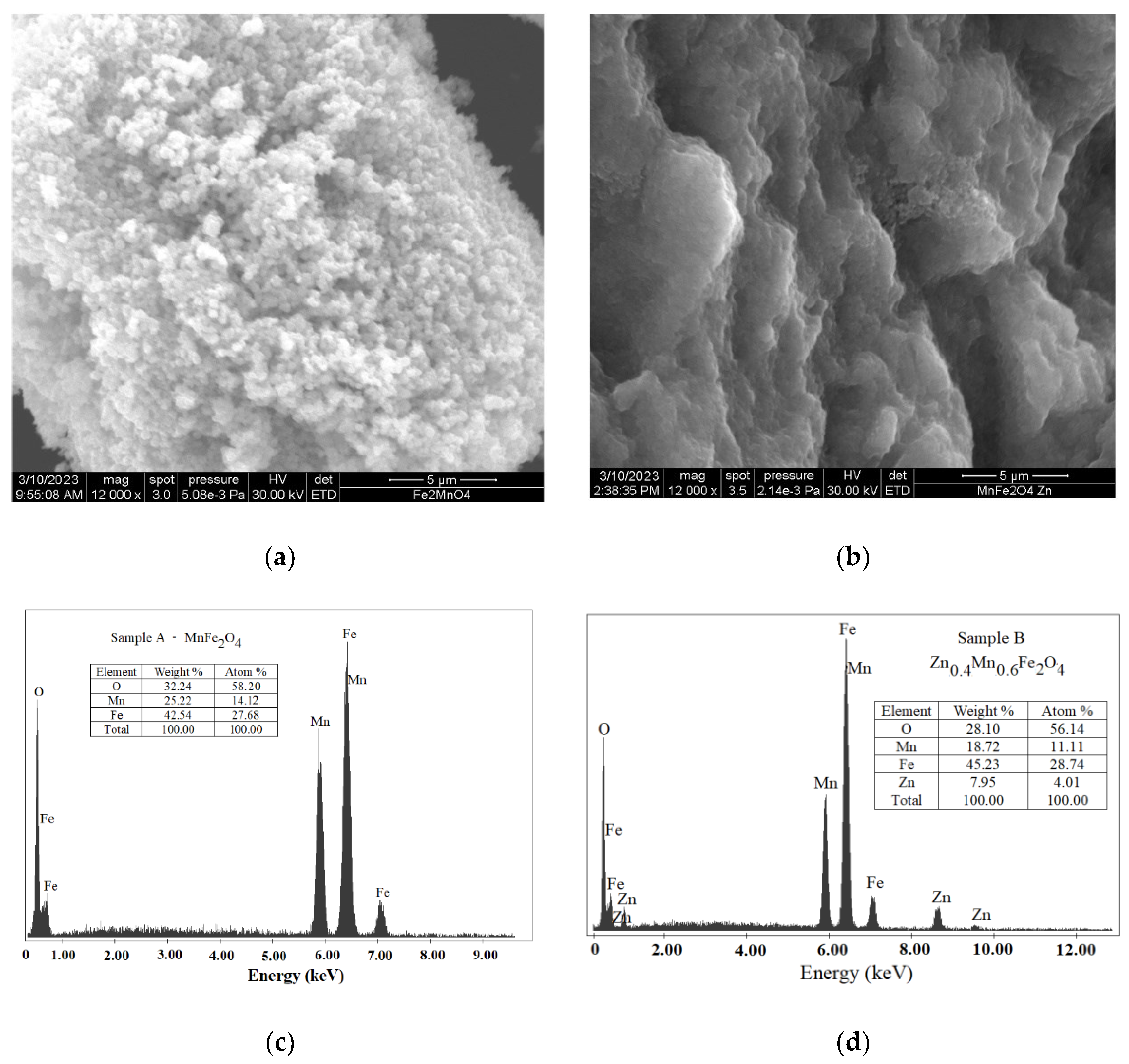
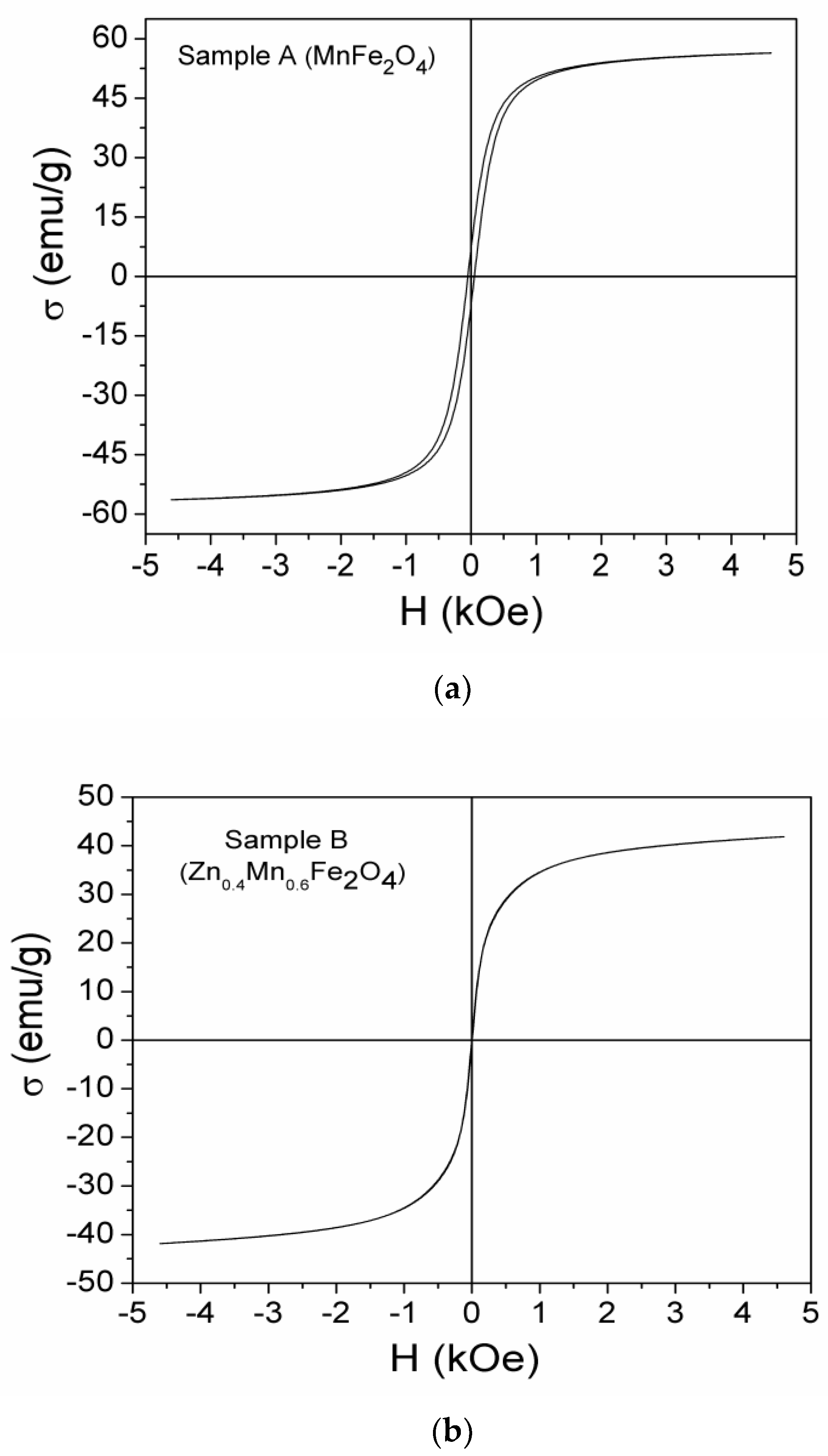
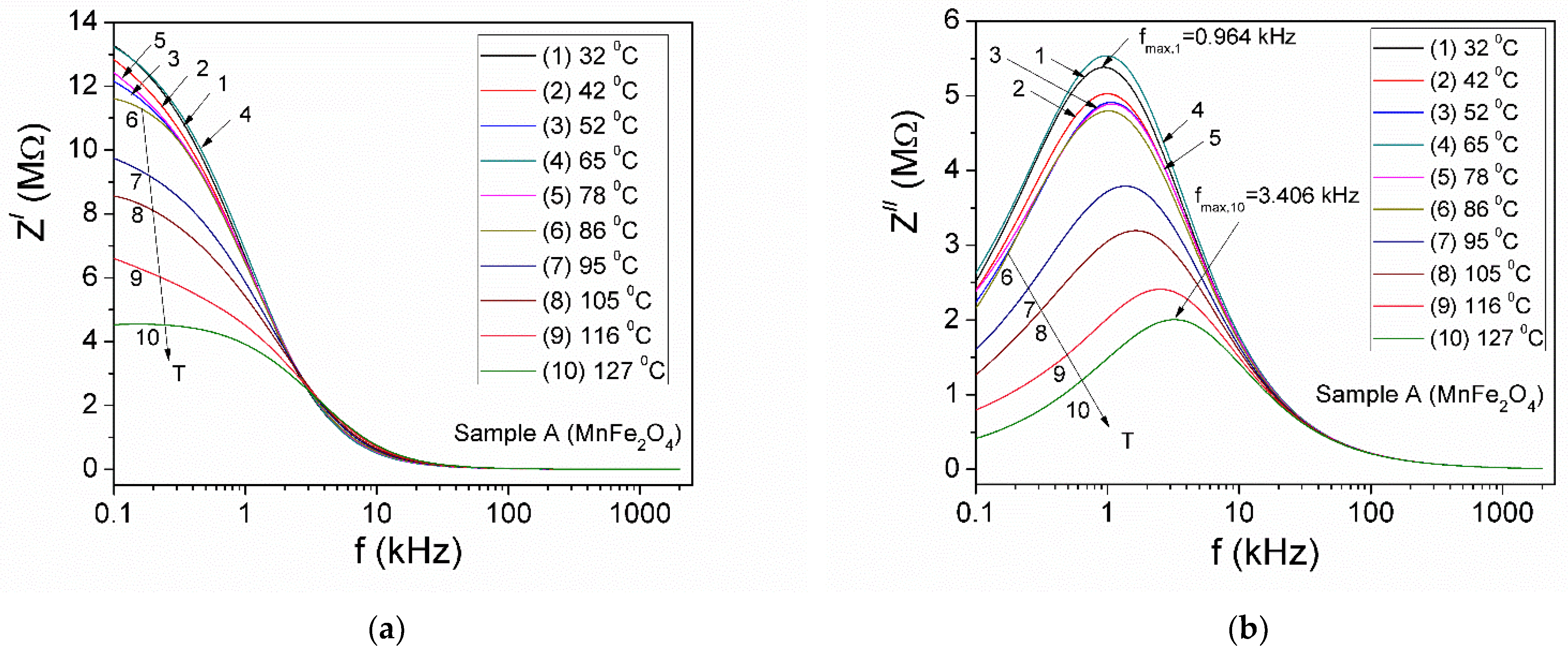

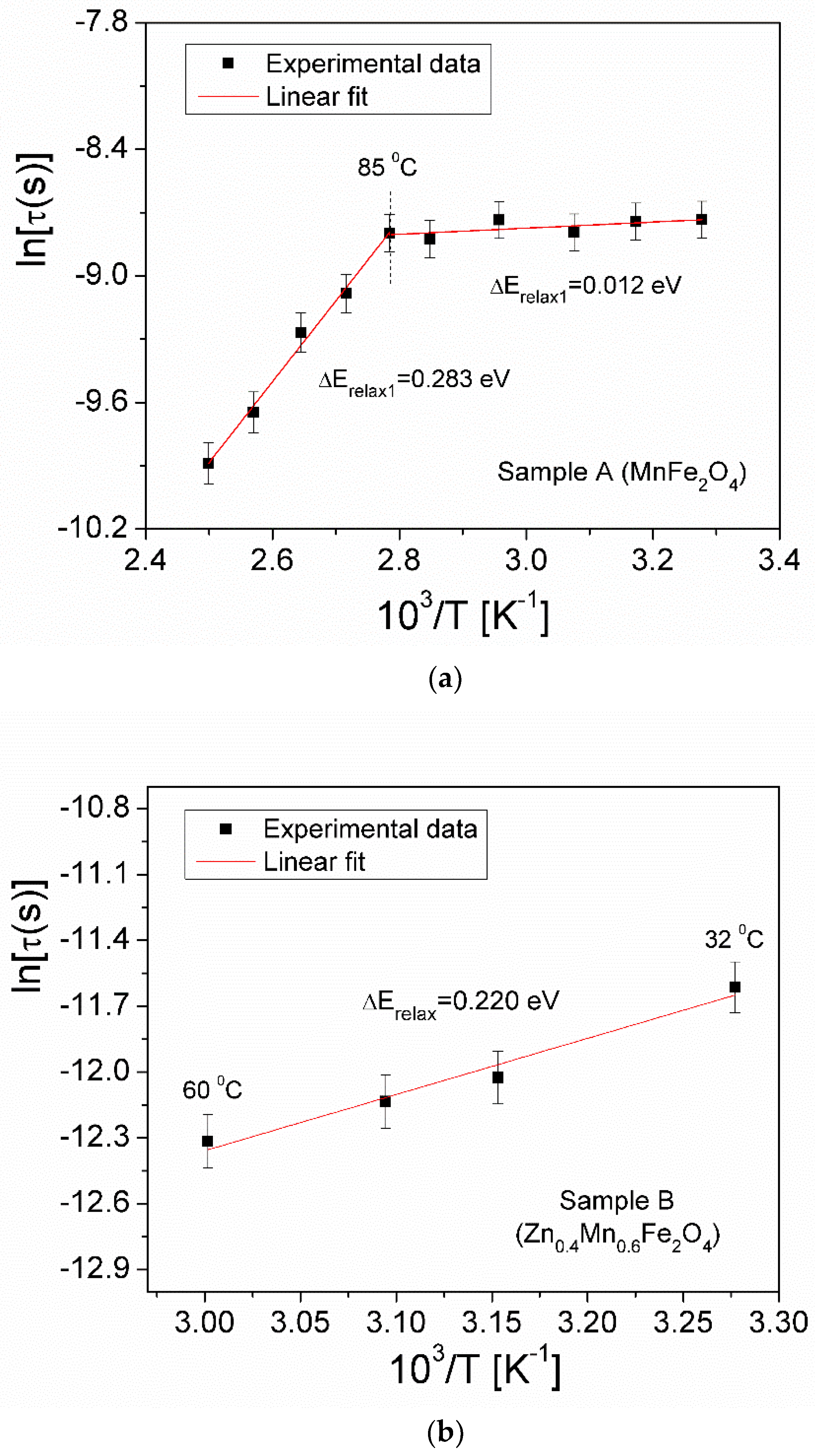
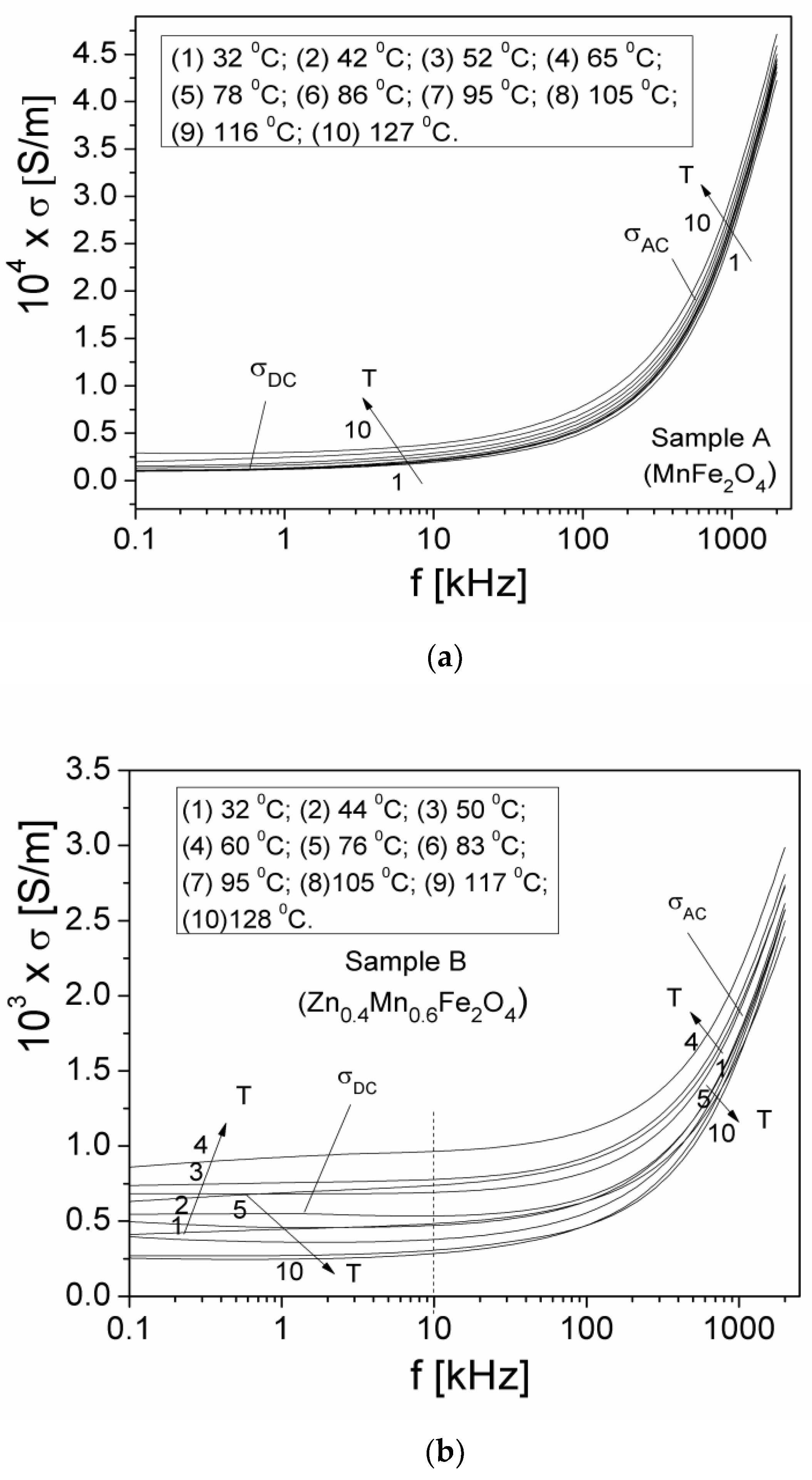
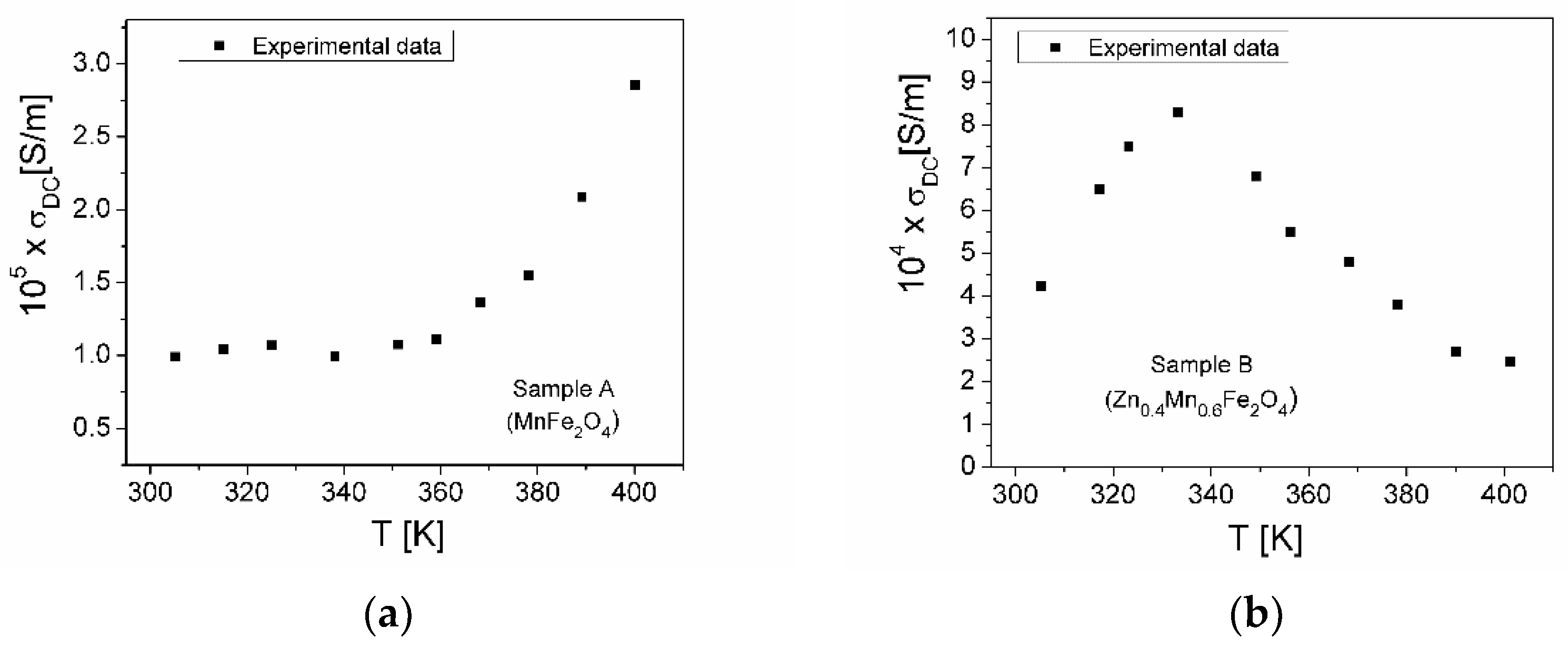
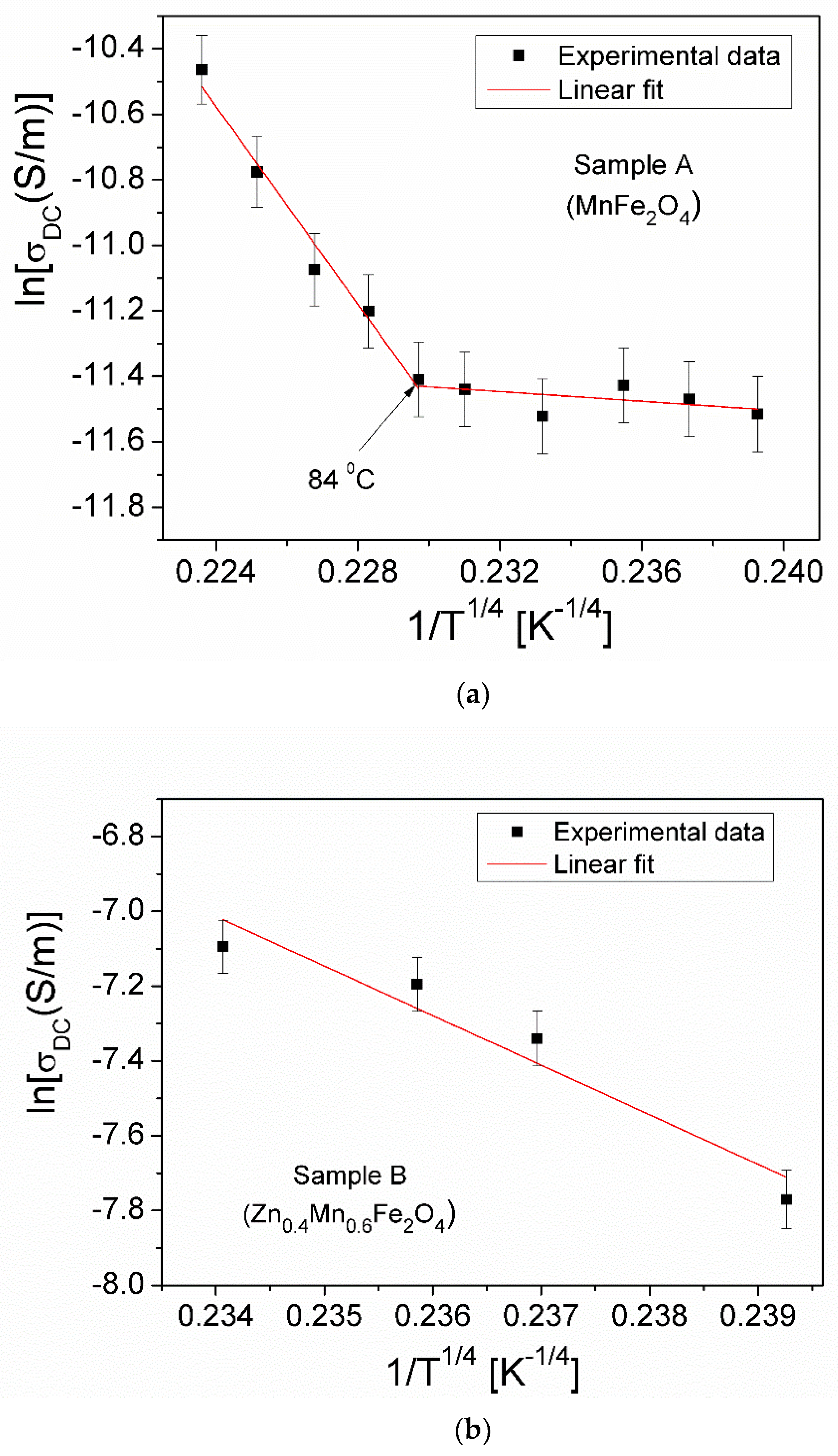
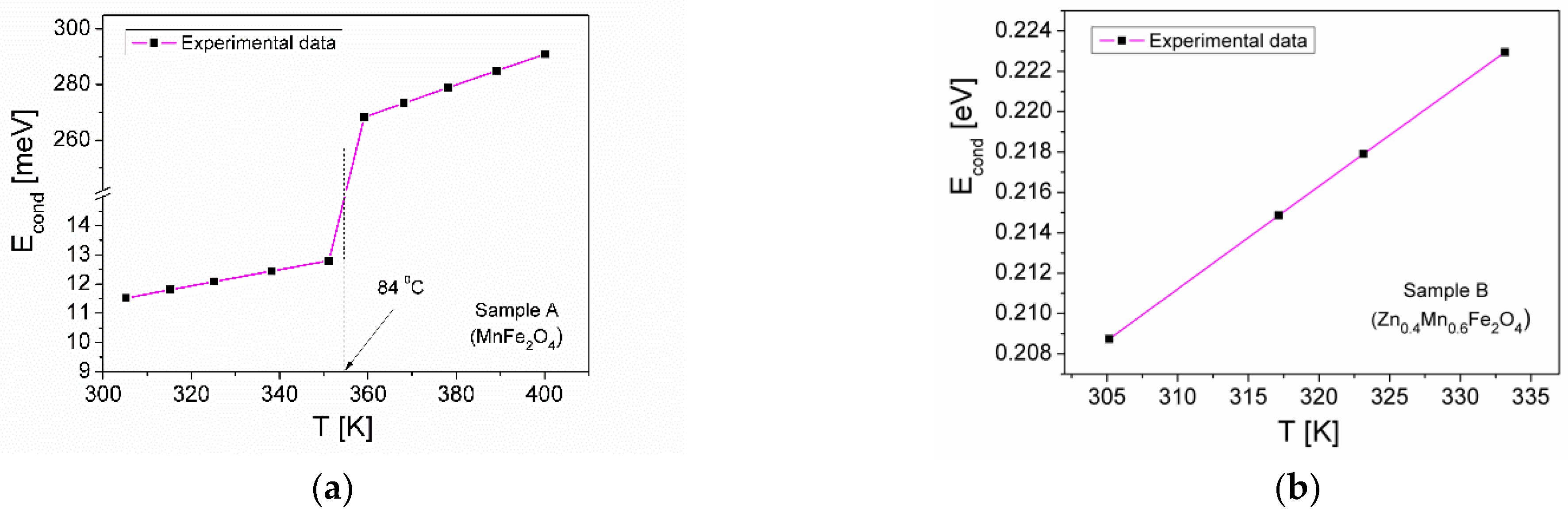
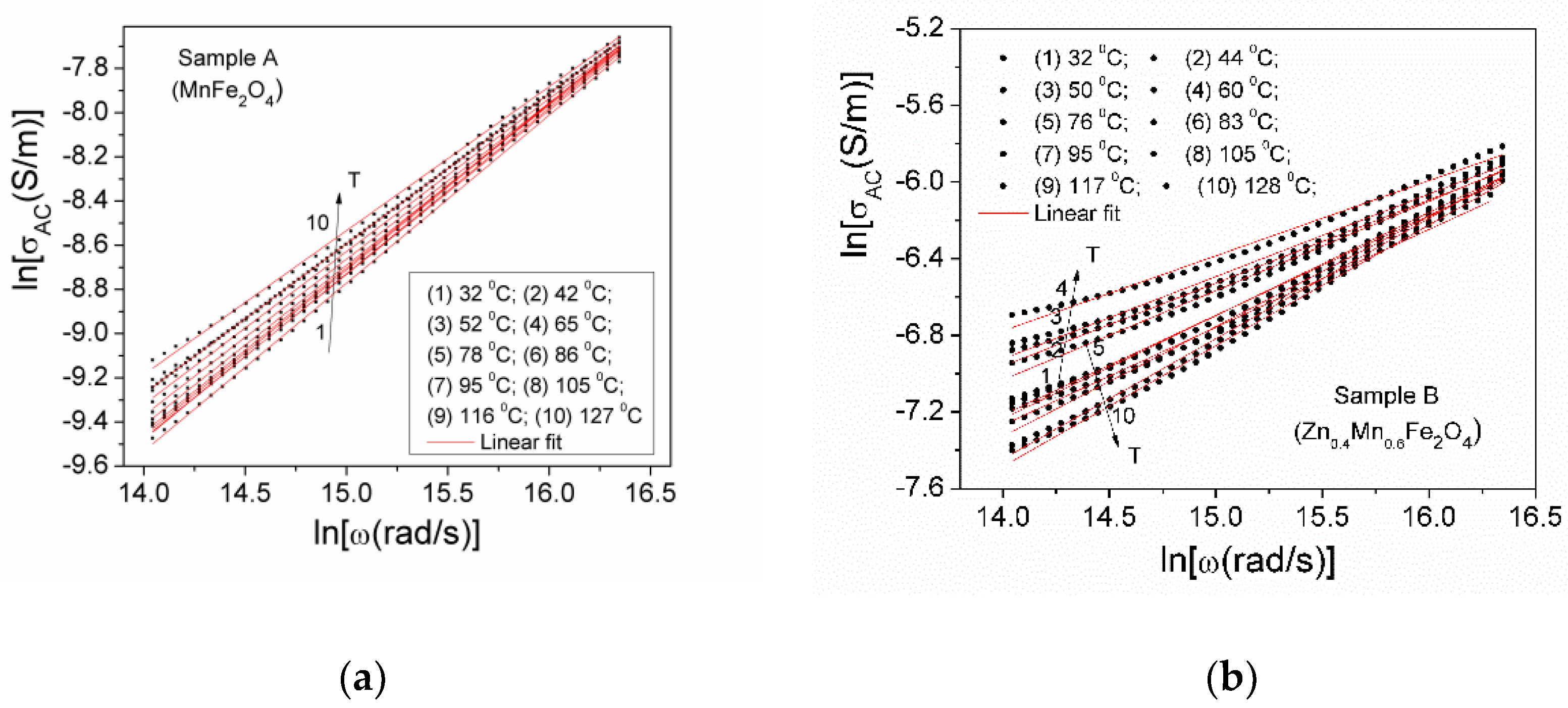
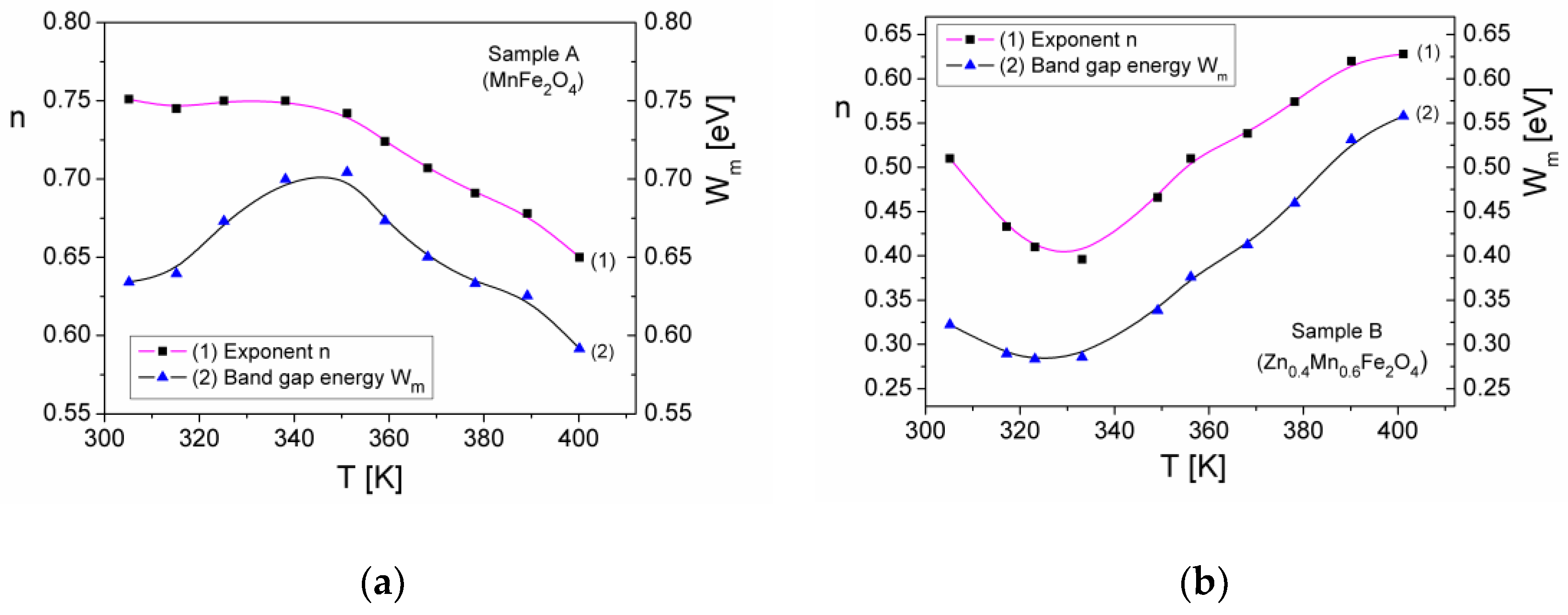
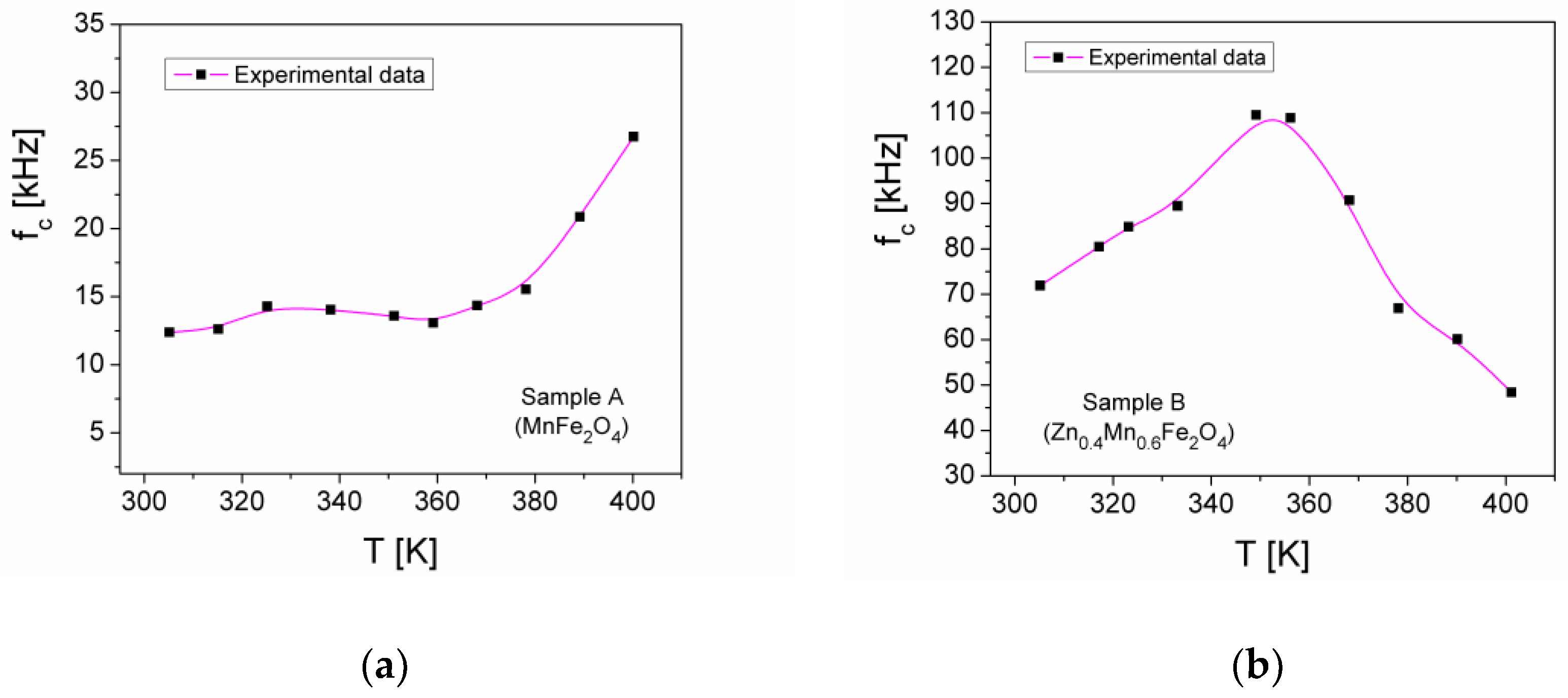

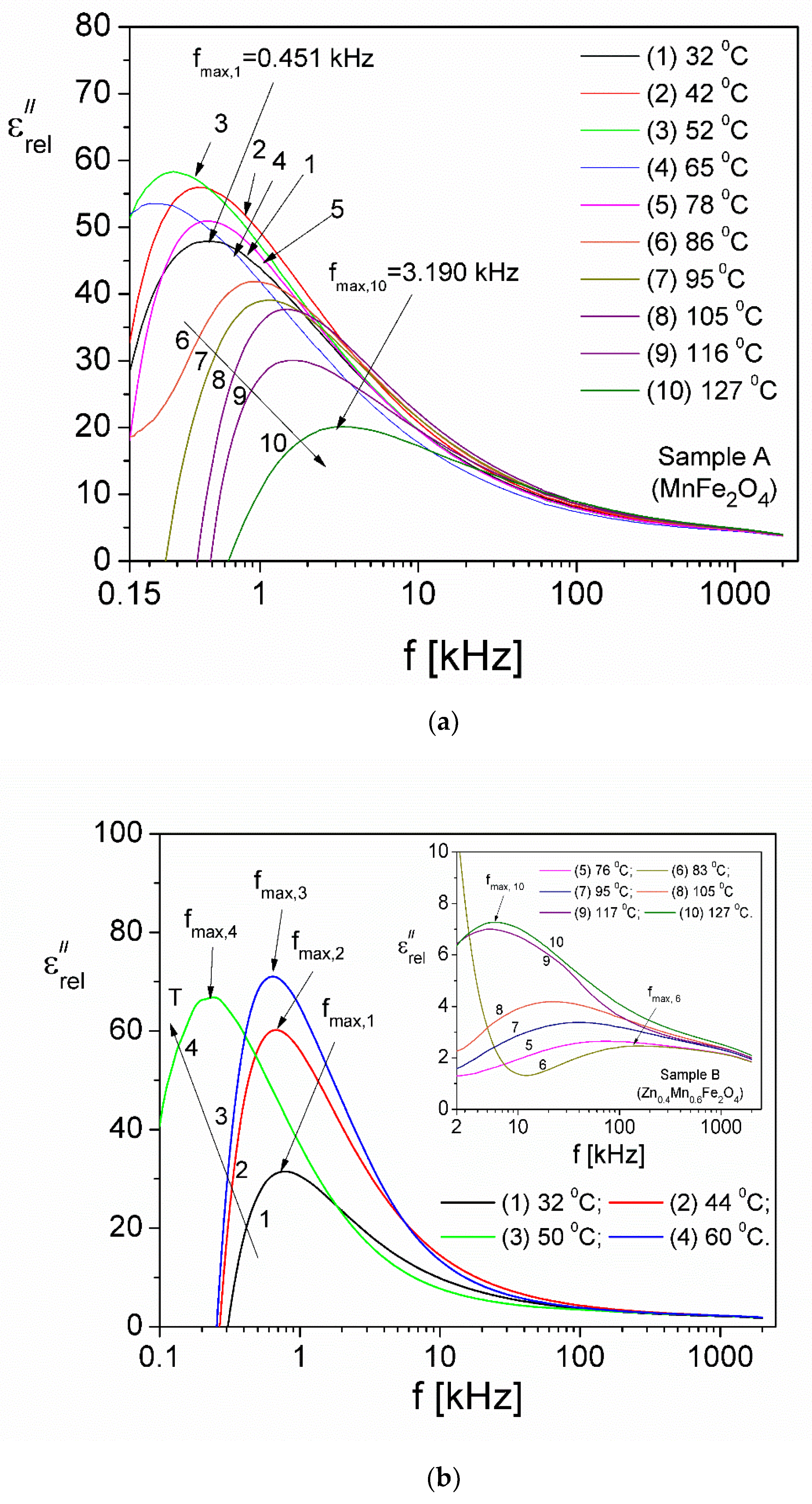
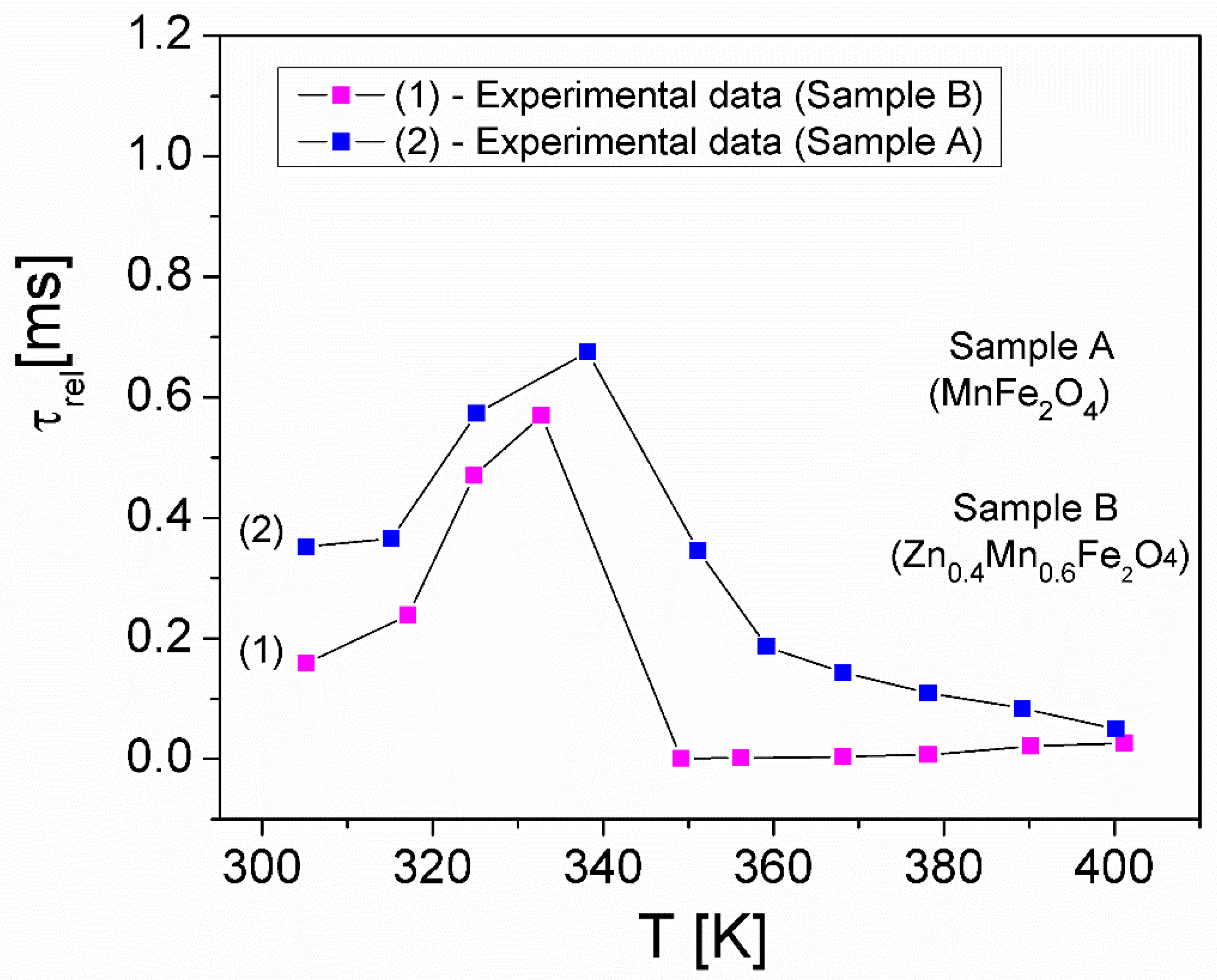
| Samples | Zn Concentration (x) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Lattice Constant (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A (MnFe2O4) | 0 | 45 | 8.498(1) |
| B (Zn0.4Mn0.6Fe2O4) | 0.4 | 23.9 | 8.48(1) |
| Sample | σs [emu/g] | Hc [kOe] | σr [emu/g] | σr/σs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (MnFe2O4) | 58.76 | 0.049 | 7.13 | 0.121 |
| B (Zn0.4Mn0.6Fe2O4) | 44.21 | - | - | - |
| Sample A | Sample B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°C) | ln[A0 (S/msn)] | n | R2 | TB (°C) | ln[A0 (S/msn)] | n | R2 |
| 32 | −19.97196 | 0.75 | 0.9995 | 32 | −14.41251 | 0.510 | 0.9934 |
| 42 | −19.87659 | 0.745 | 0.9994 | 44 | −13.02810 | 0.433 | 0.9910 |
| 52 | −19.97192 | 0.749 | 0.9995 | 50 | −12.94721 | 0.430 | 0.9909 |
| 65 | −20.17897 | 0.760 | 0.9995 | 60 | −12.26714 | 0.392 | 0.9878 |
| 78 | −19.86704 | 0.742 | 0.9995 | 76 | −13.55826 | 0.466 | 0.9918 |
| 86 | −19.55269 | 0.724 | 0.9995 | 83 | −14.5103 | 0.521 | 0.9947 |
| 95 | −19.27013 | 0.707 | 0.9994 | 95 | −14.7734 | 0.538 | 0.9957 |
| 105 | −19.00402 | 0.691 | 0.9993 | 105 | −15.37215 | 0.574 | 0.9971 |
| 116 | −18.77898 | 0.679 | 0.9992 | 117 | −16.30916 | 0.630 | 0.99738 |
| 127 | −18.29831 | 0.651 | 0.9989 | 128 | −16.23992 | 0.628 | 0.9984 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malaescu, I.; Sfirloaga, P.; Marin, C.N.; Bunoiu, M.O.; Vlazan, P. Experimental Investigations on the Electrical Conductivity and Complex Dielectric Permittivity of ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 and 0.4) Ferrites in a Low-Frequency Field. Crystals 2024, 14, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050437
Malaescu I, Sfirloaga P, Marin CN, Bunoiu MO, Vlazan P. Experimental Investigations on the Electrical Conductivity and Complex Dielectric Permittivity of ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 and 0.4) Ferrites in a Low-Frequency Field. Crystals. 2024; 14(5):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalaescu, Iosif, Paula Sfirloaga, Catalin N. Marin, Madalin O. Bunoiu, and Paulina Vlazan. 2024. "Experimental Investigations on the Electrical Conductivity and Complex Dielectric Permittivity of ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 and 0.4) Ferrites in a Low-Frequency Field" Crystals 14, no. 5: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050437
APA StyleMalaescu, I., Sfirloaga, P., Marin, C. N., Bunoiu, M. O., & Vlazan, P. (2024). Experimental Investigations on the Electrical Conductivity and Complex Dielectric Permittivity of ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 and 0.4) Ferrites in a Low-Frequency Field. Crystals, 14(5), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050437








