The Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Electrochemistry and Discharge Performance of a CeO2/Al6061 Anode for an Al-Air Battery via Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Experiment and Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
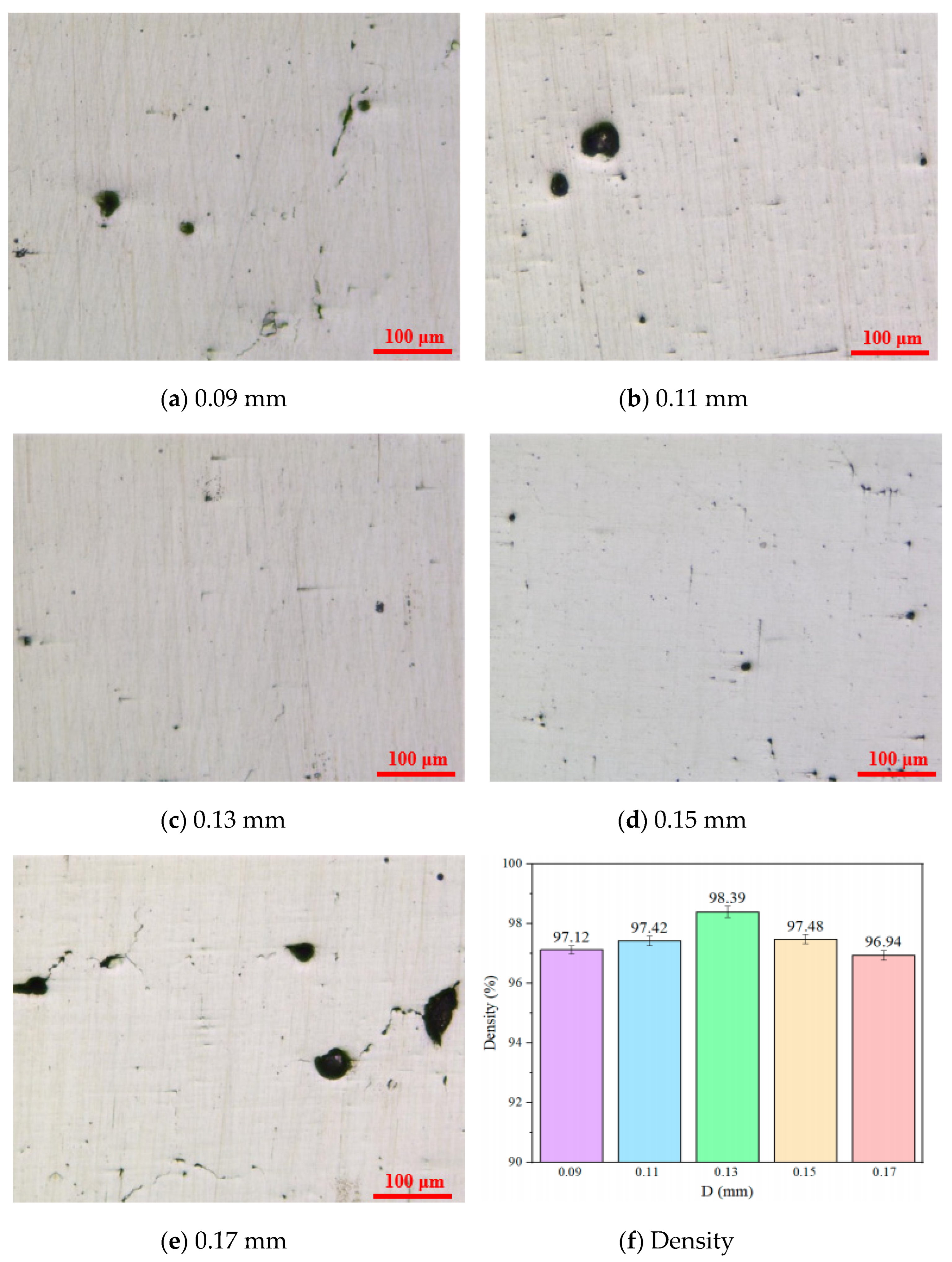
3.1. Surface Morphology and Density
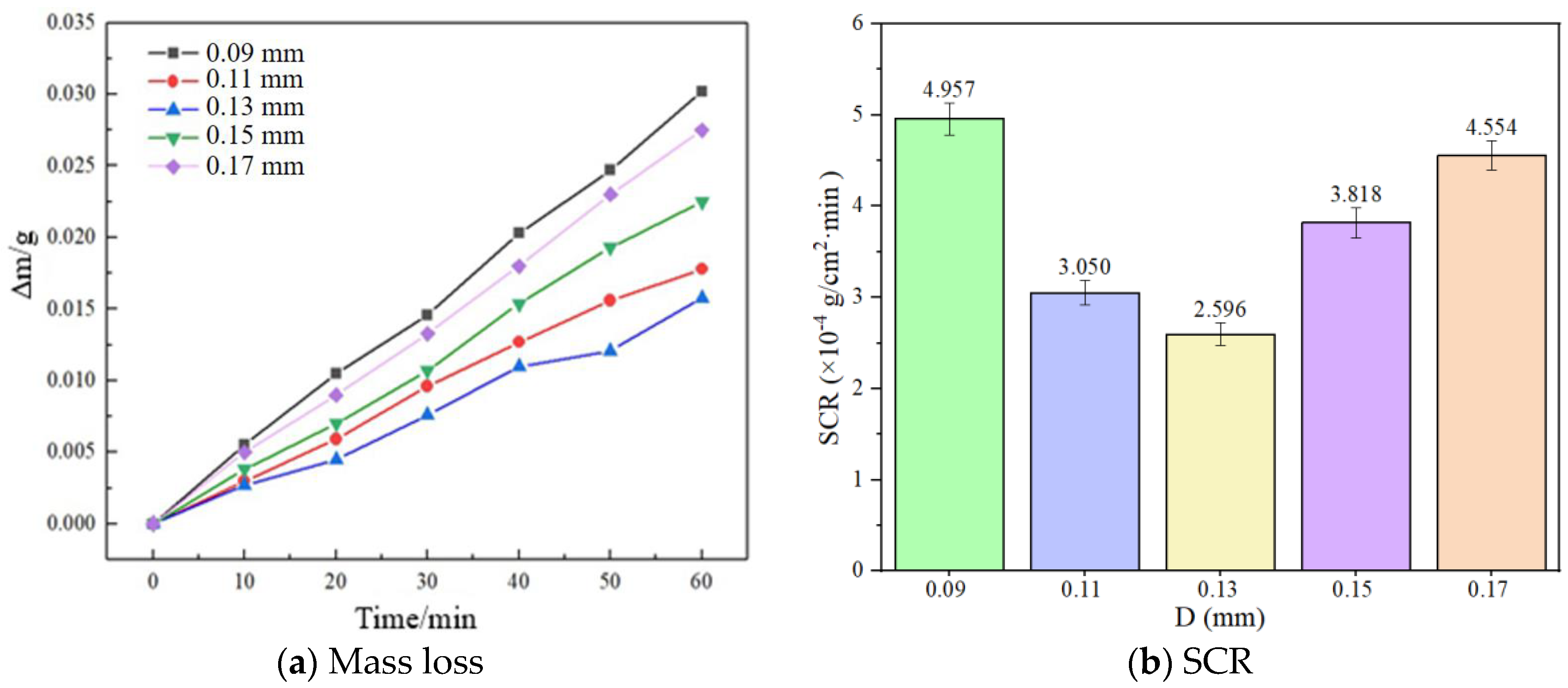
3.2. Self-Corrosion Rate
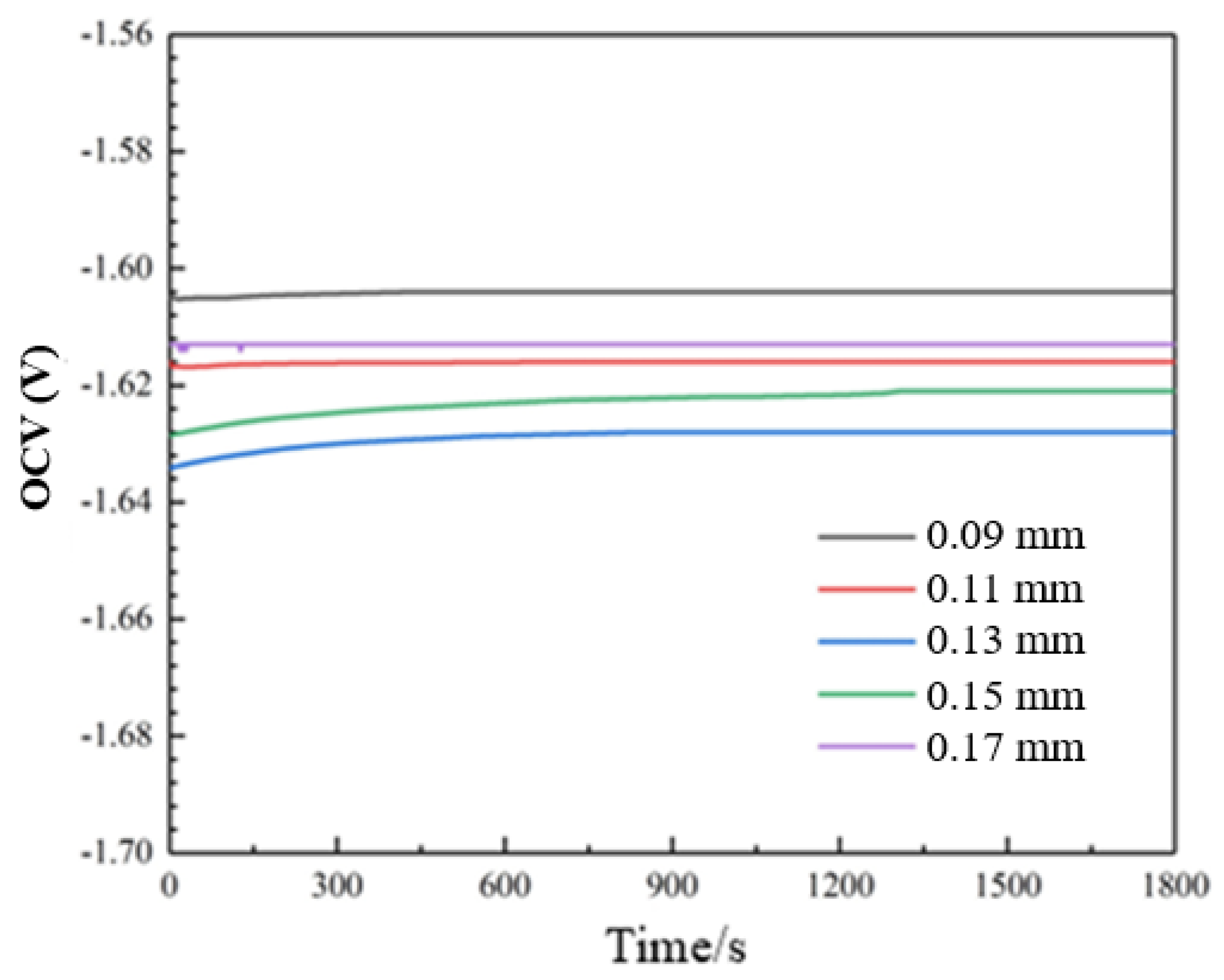
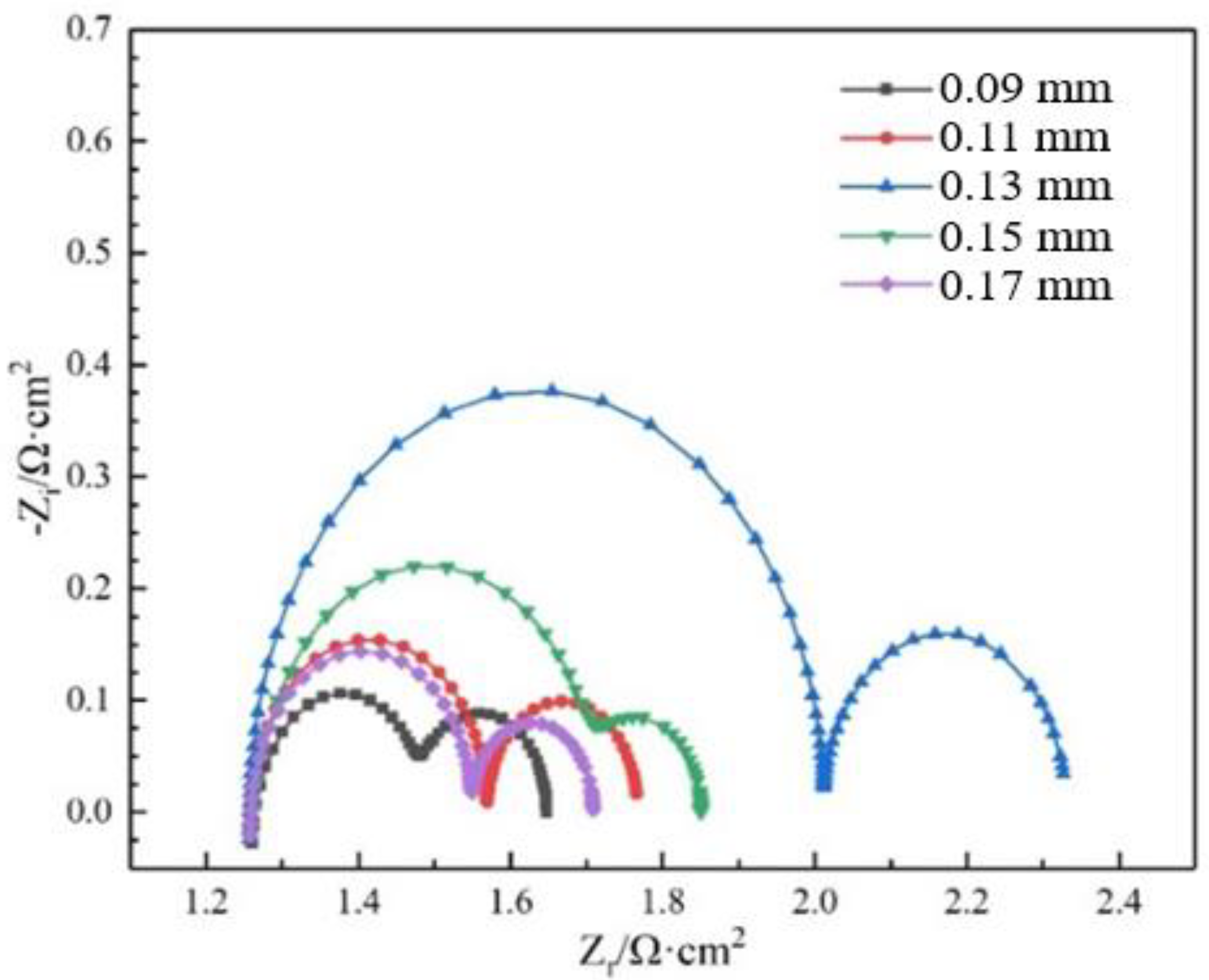
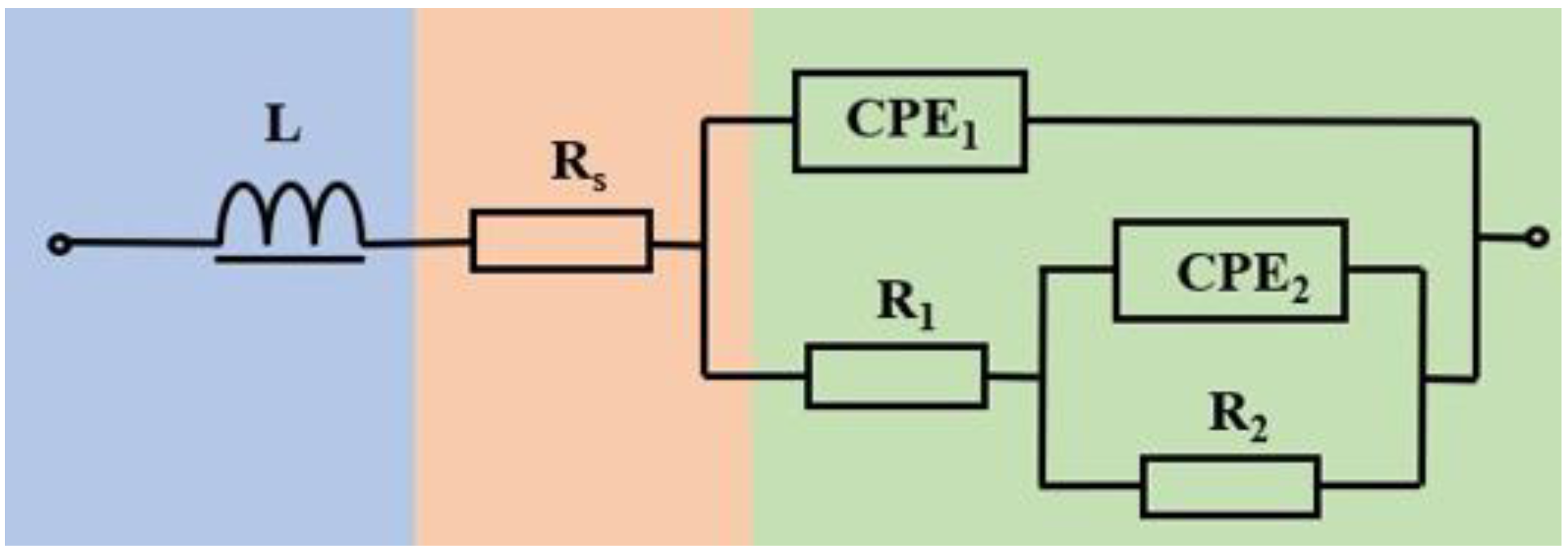
3.3. Electrochemical Behavior
3.4. Discharge Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Lai, G.; Gu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. High specific capacity microfluidic Al-air battery with the double-side reactive anode. J. Power Sources 2024, 611, 234764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Wei, Z.S.; Li, S.Q.; Cui, L.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Zeng, R.C. Corrosion inhibition of polyelectrolytes to the Al anode in Al-air battery: A comparative study of functional group effect. J. Power Sources 2024, 592, 233907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wang, W.; Bu, L.X. Investigations on Mn shielding the negative effect of Fe in the aluminum alloy anodes used for Al-air batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2024, 28, 2547–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, O.; Kaya, M.F.; Erol, H. Investigation of the AlB2 intermetallic phases effect on A-Zn-B alloys’ electrochemical performance in Al-air battery anodes. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wang, K.; Pei, P.; Zhong, L.; Zuttel, A.; Pham, T.H. Zinc carboxylate optimization strategy for extending Al-air battery system’s lifetime. Appl. Energy 2023, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, W.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Corrosion inhibition of L-tryptophan on Al-5052 anode for Al-air battery with alkaline electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2023, 564, 232866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; He, P.; Yu, F.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Hu, W. Performance improvement for aluminum-air battery by using alloying anodes prepared from commercially pure aluminum. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, K.; Fatih, Y.; İlyas, H. Characterization of the structural and tribological properties of medical Ti6Al4V alloy produced in different production parameters using selective laser melting. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 6, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Ren, N.F. Simulation and experimental studies on process parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting of stainless steel 316L. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, K.; Pang, C.Y. Study on the effects of the processing parameters on the single tracks and the block support structures fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2024, 36, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhakumar, R.; Venkatesan, K. A process parameters review on selective laser melting-based additive manufacturing of single and multi-material: Microstructure, physical properties, tribological, and surface roughness. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhan, J.; Lu, Y.; Lin, J. Effect of energy input on the density and shape memory effect of NiTi alloy by selective laser melting in different hatch spacing. Mater. Technol. 2021, 37, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, G.; Erguder, T.O.; Hacisalihoglu, E.Y. Wear and thermal behavior of TiAlN thin films onto Ti6Al4V alloy manufactured by selective laser melting method. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 10, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.L.; Liu, B.Y.; Tran, H.C. Optimized hatch space selection in double-scanning track selective laser melting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 2989–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Takano, N.; Mizutani, M. Material properties of selective laser melting additive-manufactured Ti6Al4V alloys with different porosities. Precis. Eng. 2023, 83, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneti, R.K.; Morgan, R.; Atre, S.V. Effect of process parameters on the selective laser melting (SLM) of tungsten. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 71, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gutzeit, K.; Hotz, H. Selective laser melting (SLM) of AISI 316L-impact of laser power, layer thickness, and hatch spacing on roughness, density, and microhardness at constant input energy density. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, I.; Yiliz, F.; Celik, A. The effects of build orientation and hatch spacing on mechanical properties of medical Ti-6Al-4V alloy manufactured by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 802, 140649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Shen, X.; Zhou, H. Effect of hatch spacing on the quality of Inconel 718 alloy part. Materials 2024, 17, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W.; Ge, J.; Liang, J. Effect of hatch spacing on melt pool and as-built quality during selective laser melting of stainless Steel: Modeling and experimental approaches. Materials 2019, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ren, Y.; Cui, L.S.; Yang, Q.; Hao, S.J. Effect of laser hatch spacing on the pore defects, phase transformation and properties of selective. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 840, 142965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Nie, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H. Cracking criterion for high strength Al-Cu alloys fabricated by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, B.; Zhai, Z. Research on microstructure and properties of AlSi10Mg fabricated by selective laser melting. Materials 2022, 15, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekok, M.A.; Setchi, R.; Ryan, M.; Han, Q.Q.; Gu, D.D. Effect of process parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AA2024 fabricated using selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 112, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Nagarajan, B.; Nie, X.; Zeng, X. Top surface roughness evolution during selective laser melting of AlCu5MnCdVA aluminum alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Chen, Y.B.; Chen, X.; Starostenkov, M.D.; Dong, G.J. Densification, microstructural features and tensile properties of selective laser melted AlMgSiScZr alloy from single track to block specimen. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufis, P.; Mylona, V.; Politis, C.; Avgouropoulos, G.; Lianos, P. Study of some basic operation conditions of an Al-air battery using technical grade commercial aluminum. J. Power Sources 2020, 450, 227624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, K.; Lu, W.Y.; Peng, K.; Tian, Z.L. Investigation of commercial aluminum alloys as anode materials for alkaline aluminum-air batteries. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2022, 7, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancrecious, J.K.; Deepa, J.P.; Jayan, V. Nanoceria induced grain refinement in electroless Ni-B-CeO2 composite coating for enhanced wear and corrosion resistance of Aluminium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 356, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Yao, J.; Song, H. An environmental friendly self-healing coating with Silane/Ce-ZSM-5 zeolite structure for corrosion protection of aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 436, 128290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Laser Power | Scanning Speed | Hatch Spacing | Layer Thickness | Scanning Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 300 W | 1000 mm/s | 0.09, 0.11, 0.13, 0.15, 0.17 mm | 30 μm | Island |
| Hatch Spacing | Electrochemical Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| E (v) | Icorr (A/cm2) | Rp (Ω∙cm2) | |
| 0.09 mm | −1.613 | 2.422 × 10−2 | 1.8 |
| 0.11 mm | −1.624 | 2.199 × 10−2 | 2.0 |
| 0.13 mm | −1.634 | 2.012 × 10−2 | 2.2 |
| 0.15 mm | −1.628 | 2.245 × 10−2 | 2.0 |
| 0.17 mm | −1.620 | 2.326 × 10−2 | 1.9 |
| Hatch Spacing | 0.09 mm | 0.11 mm | 0.13 mm | 0.15 mm | 0.17 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/Ω·cm2 | 1.012 × 10−6 | 9.472 × 10−7 | 4.721 × 10−7 | 9.525 × 10−7 | 9.550 × 10−7 |
| Rs/Ω·cm2 | 1.225 | 1.357 | 1.508 | 1.254 | 1.349 |
| CPE1/F·cm−2 | 4.394 × 10−3 | 1.445 × 10−3 | 1.134 × 10−3 | 2.453 × 10−4 | 1.169 × 10−3 |
| R1/Ω·cm2 | 2.309 × 10−1 | 3.132 × 10−1 | 7.555 × 10−1 | 4.581 × 10−1 | 2.935 × 10−1 |
| CPE2/F·cm−2 | 3.271 × 10−2 | 6.703 | 5.417 | 3.140 × 10−2 | 1.262 |
| R2/Ω·cm2 | 1.140 × 10−1 | 1.980 × 10−1 | 3.182 × 10−1 | 1.377 × 10−1 | 1.586 × 10−1 |
| ꭓ2 | 2.742 × 10−4 | 9.622 × 10−4 | 4.863 × 10−4 | 4.872 × 10−4 | 6.972 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Duan, W. The Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Electrochemistry and Discharge Performance of a CeO2/Al6061 Anode for an Al-Air Battery via Selective Laser Melting. Crystals 2024, 14, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090797
Li Y, Duan W. The Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Electrochemistry and Discharge Performance of a CeO2/Al6061 Anode for an Al-Air Battery via Selective Laser Melting. Crystals. 2024; 14(9):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090797
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yinbiao, and Weipeng Duan. 2024. "The Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Electrochemistry and Discharge Performance of a CeO2/Al6061 Anode for an Al-Air Battery via Selective Laser Melting" Crystals 14, no. 9: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090797
APA StyleLi, Y., & Duan, W. (2024). The Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Electrochemistry and Discharge Performance of a CeO2/Al6061 Anode for an Al-Air Battery via Selective Laser Melting. Crystals, 14(9), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090797




