Biphasic WO3 Nanostructures via Controlled Crystallization: Achieving High-Performance Electrochromism Through Amorphous/Crystalline Heterointerface Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Preparation of Phase-Engineered Bilayer WO3 Thin Films
2.2. Structural and Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
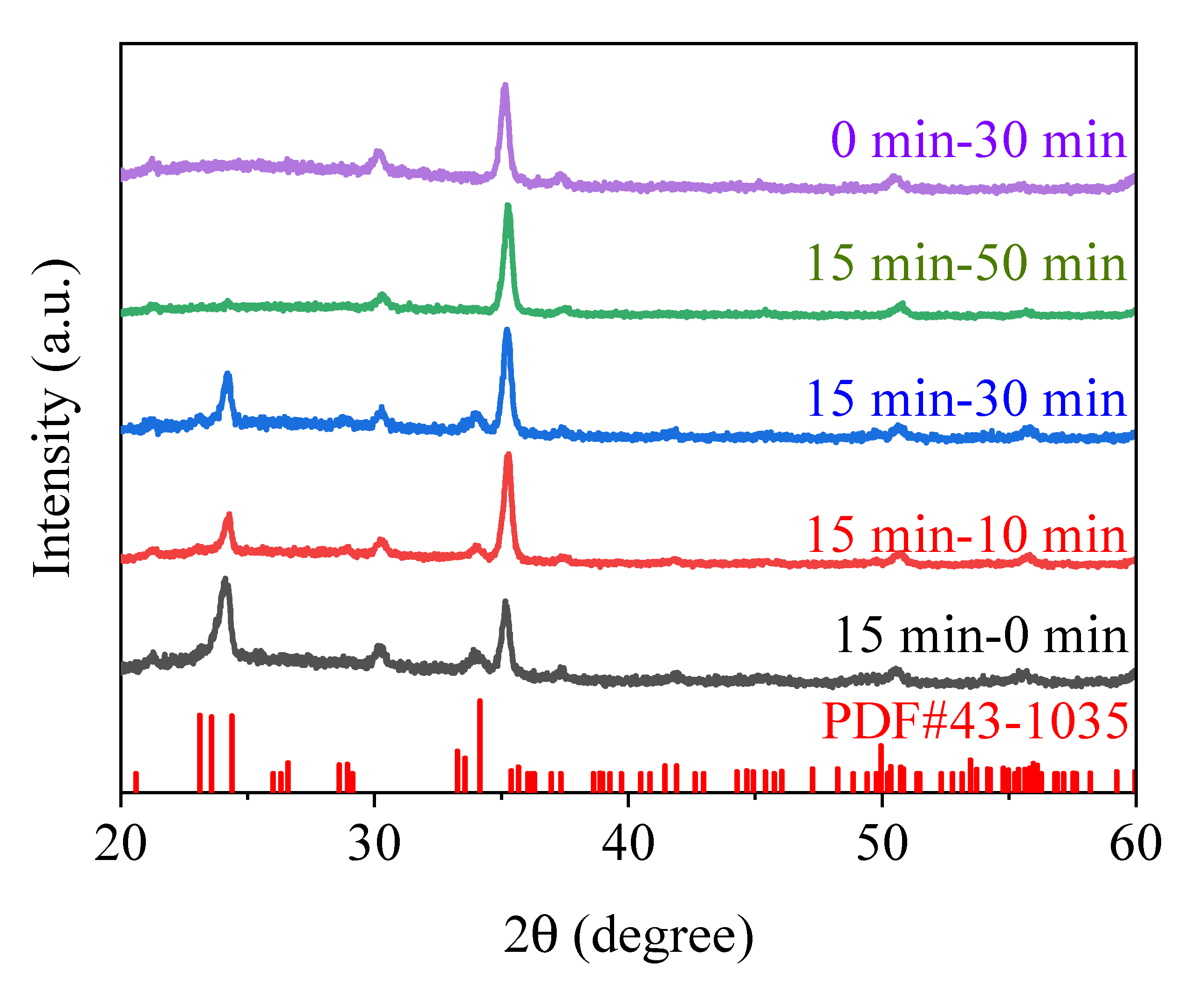
3.1. Structural Characterization of Phase-Engineered Bilayer WO3 Thin Films
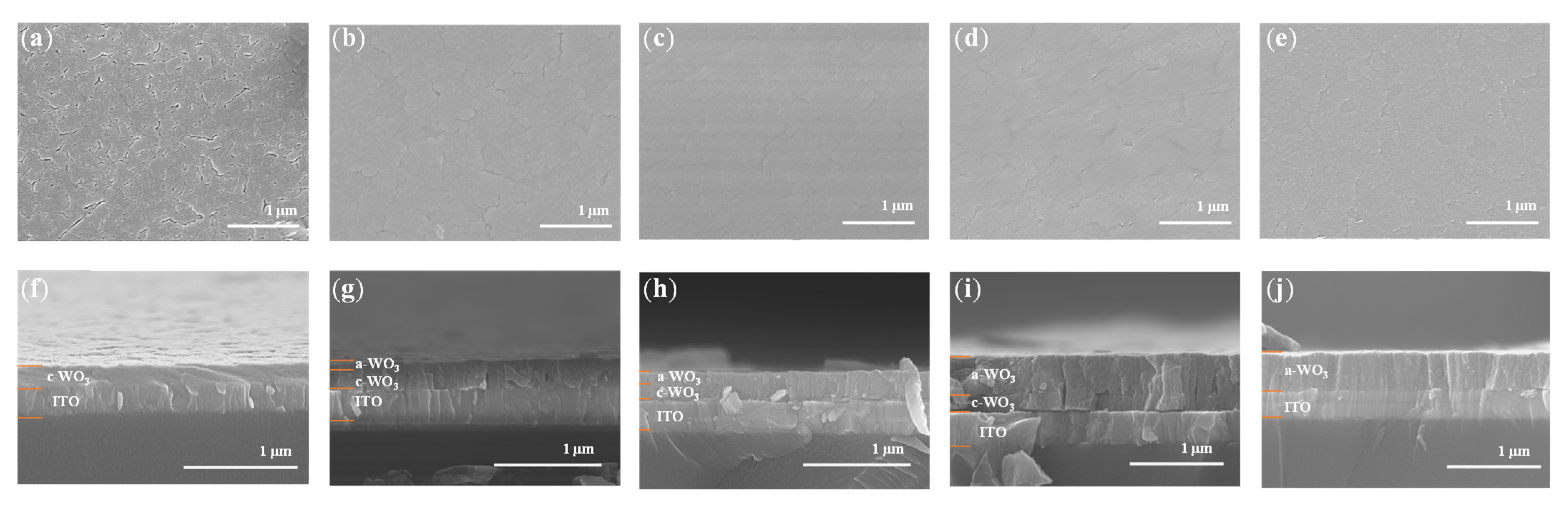
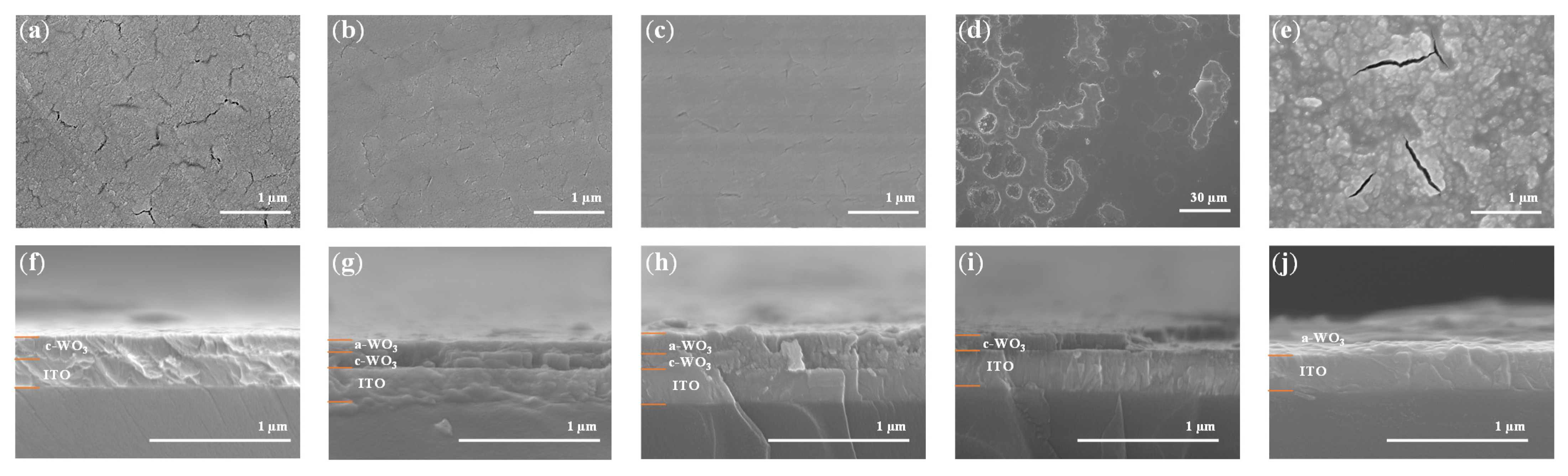
3.2. Morphological and Cross-Sectional Analysis
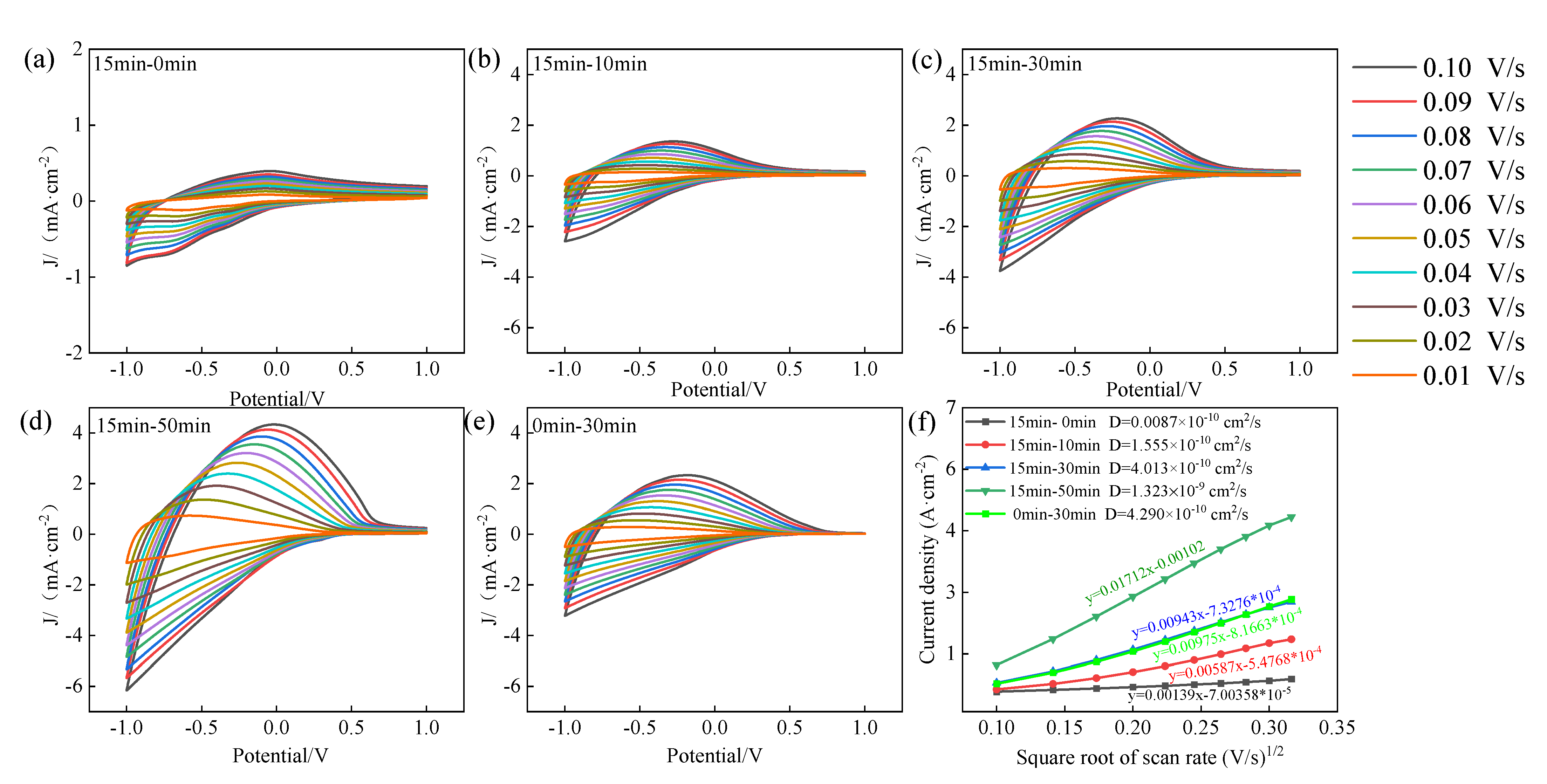
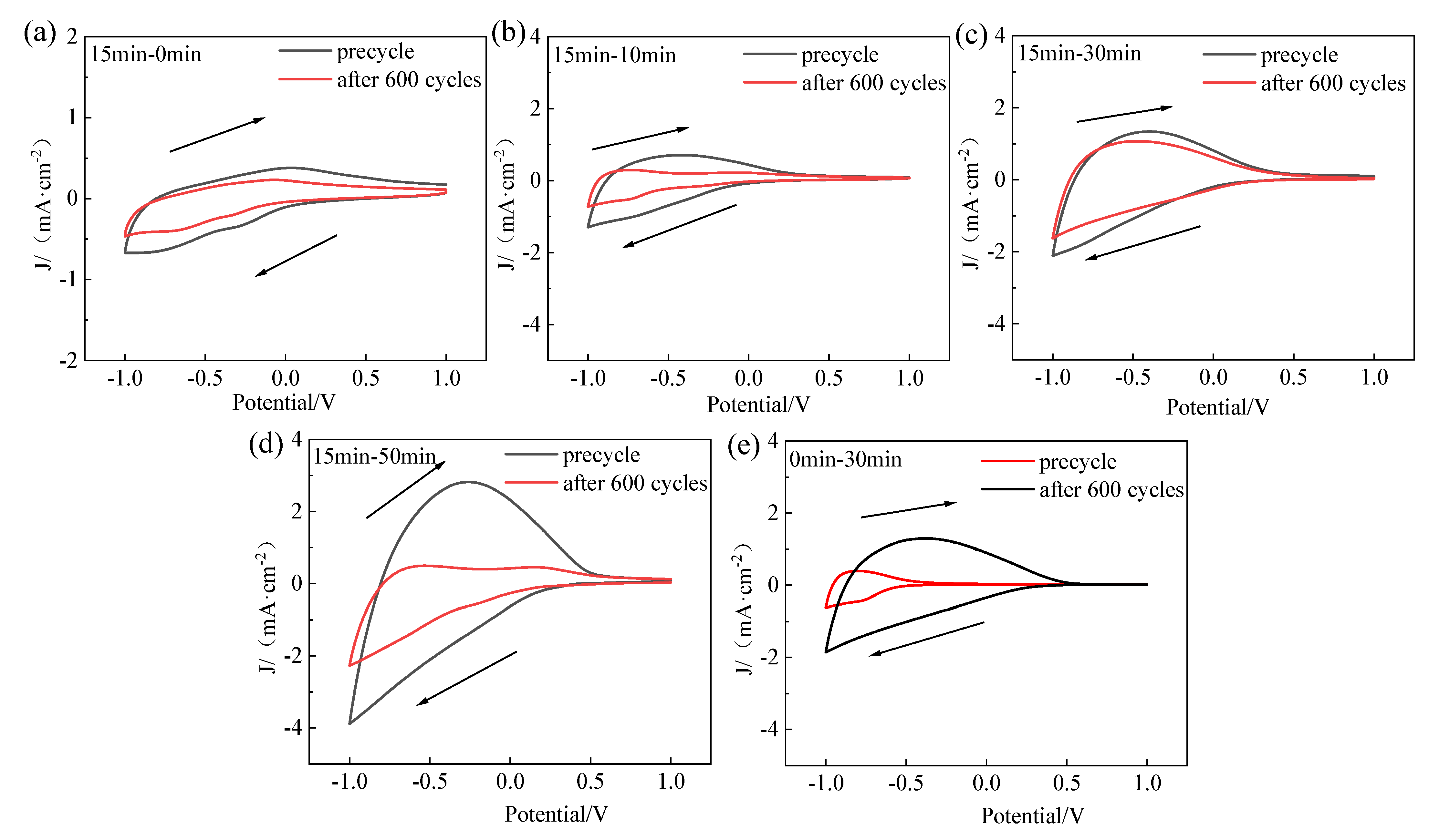
3.3. Electrochromic Performance Evaluation
3.4. Optical Performance Analysis
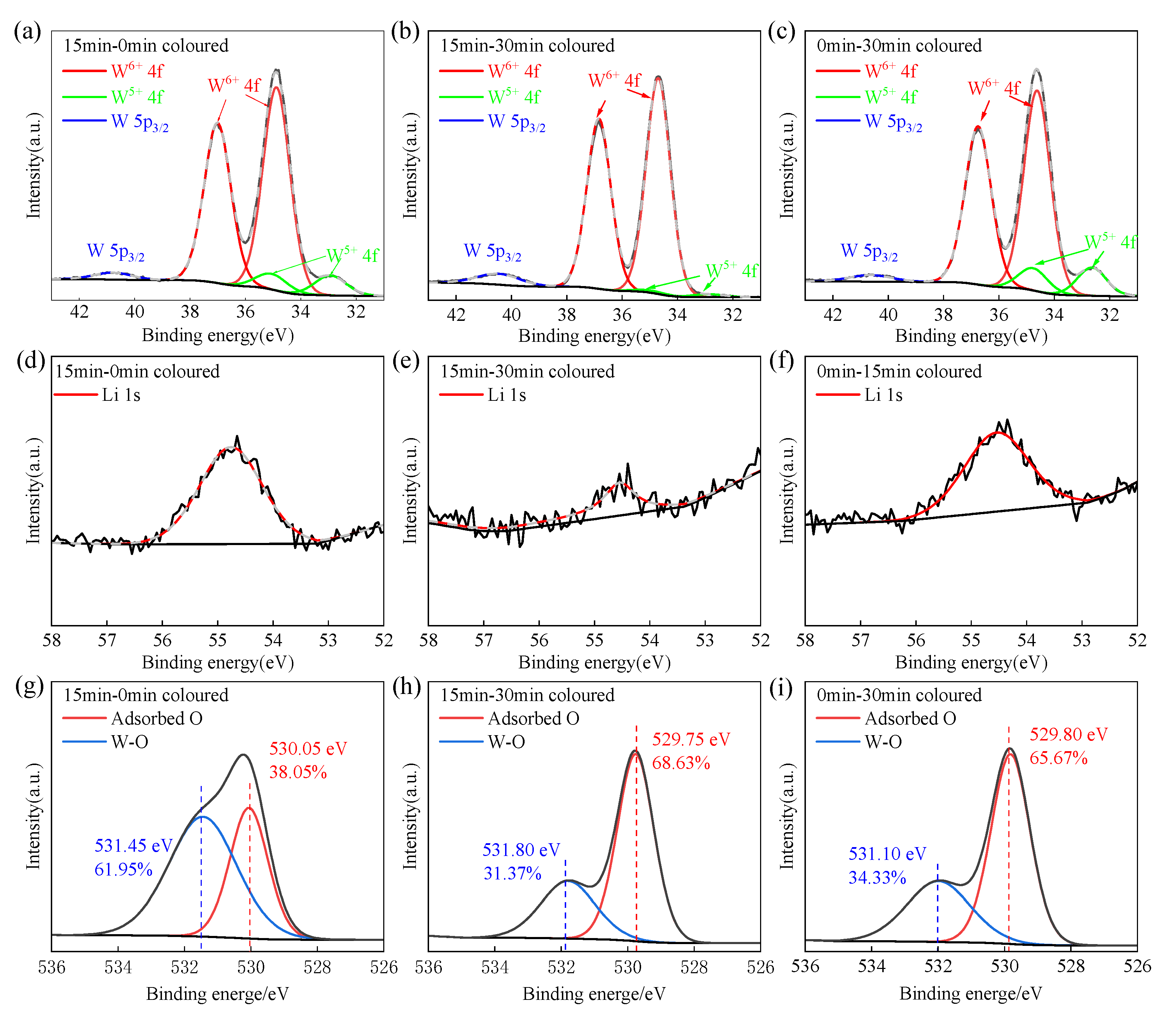
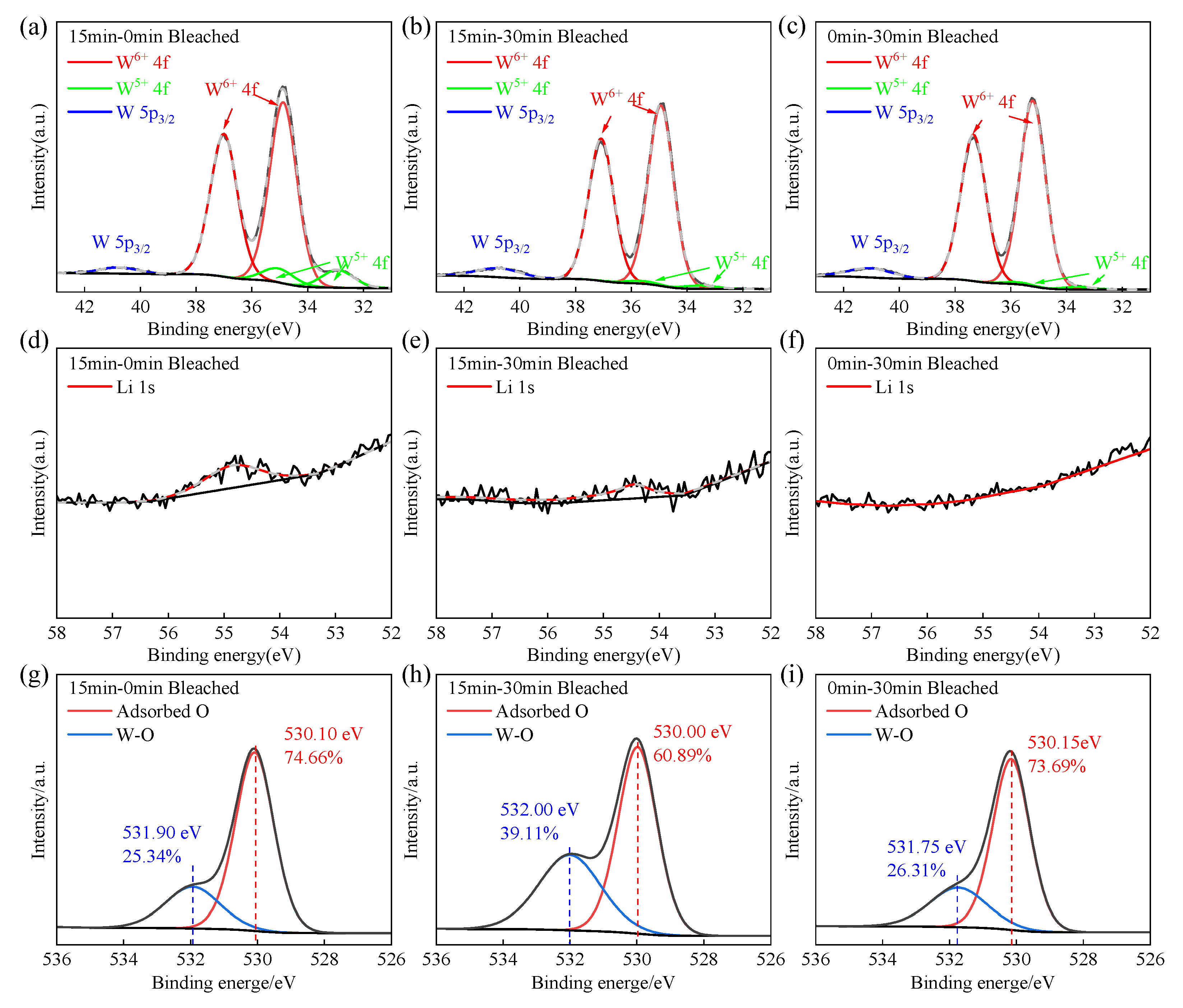
3.5. XPS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khandelwal, H.; Schenning, A.P.H.J.; Debije, M.G. Infrared Regulating Smart Window Based on Organic Materials. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602209–1602227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavale, A.; Ayr, U.; Fiorito, F.; Martellotta, F. Smart Electrochromic Windows to Enhance Building Energy Efficiency and Visual Comfort. Energies 2020, 13, 1449–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cong, S.; Geng, F.; Zhao, Z. Fusing electrochromic technology with other advanced technologies: A new roadmap for future development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020, 140, 100524–100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primiceri, V.; Pugliese, M.; Giannuzzi, R.; Esposito, M.; Gigli, G.; Maiorano, V.; Cossari, P. Enhanced Durability of an All-Solid-State WO3 Based Electrochromic Device on a Single Substrate by Using a Complementary Anodically Coloring Poly(o-ethoxyaniline). ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 5735–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.; Song, G.; Rougier, A.; Lee, C.S. Evaluation of low-voltage-driven multi-colored electrochromic device based on dry-deposited V2O5. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 257, 112341–112368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Yang, D.; Mo, J.; Jin, Z.; Chang, S. Construction of TiO2/WO3/TiO2 double heterojunction films for excellent electrochromic performance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11443–11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Tao, X.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, J.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Xie, A. Electrochromic composites films composed of MoO3 doped by tungsten atoms with remarkable response speed and color rendering efficiency via electrochemical deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Djaoued, H.; Vienneau, G.; Robichaud, J.; Brown, D.; Brüning, R.; Djaoued, Y. Electrochromic and colorimetric properties of anodic NiO thin films: Uncovering electrochromic mechanism of NiO. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 335, 135648–135659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. High-performance electrochromic WO3 film driven by controllable crystalline structure and its all-solid-state device. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 237, 111564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, B.; Zhai, J.; Diao, X. Fast-switching quasi-solid state electrochromic full device based on mesoporous WO3 and NiO thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 200, 110017–110025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mo, H.; Li, R.; Zhou, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Luo, J. The Counterbalancing Role of Oxygen Vacancy between the Electrochromic Properties and the Trapping Effect Passivation for Amorphous Tungsten Oxide Films. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2300219–2300231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Tan, H.H.; Wu, Y. Rational Design of Oxygen Deficiency-Controlled Tungsten Oxide Electrochromic Films with an Exceptional Memory Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32658–32665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, R.-T. Capturing ion trapping and detrapping dynamics in electrochromic thin films. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2294–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Liu, H.; Cai, C. Exploring the electronic structure and lithium diffusion kinetics of amorphous tungsten oxide. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 095117–095122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xie, D.; Shi, F.; Wang, D.; Ge, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Tu, J. Crystalline/amorphous tungsten oxide core/shell hierarchical structures and their synergistic effect for optical modulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 460, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, W.; Miao, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. Bifunctional aligned hexagonal/amorphous tungsten oxide core/shell nanorod arrays with enhanced electrochromic and pseudocapacitive performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16867–16875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poongodi, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ponpandian, N.; Meena, P.; Masuda, Y.; Lee, C. Electrodeposition of WO3 nanostructured thin films for electrochromic and H2S gas sensor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.N.; Sattar, S.A.; Shaik, H.; Reddy, G.V.A.; Jafri, R.I.; Merum, D.; Pawar, A.S.; Nunna, G.P.; Premkumar, R.; Ansar, S.; et al. Effect of partial pressure of oxygen, target current, and annealing on DC sputtered tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films for electrochromic applications. Solid State Ion. 2023, 399, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yamazaki, T.; Shen, Y.; Kikuta, T.; Nakatani, N. Influence of annealing on microstructure and NO2-sensing properties of sputtered WO3 thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 128, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efkere, H.İ.; Gümrükçü, A.E.; Özen, Y.; Kınacı, B.; Aydın, S.Ş.; Ates, H.; Özçelik, S. Investigation of the effect of annealing on the structural, morphological and optical properties of RF sputtered WO3 nanostructure. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2021, 622, 413350–413358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Annealing effect on the electrochromic properties of amorphous WO3 films in Mg2+ based electrolytes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 270, 124745–124752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y. Effect of In Situ Heating on the Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Tungsten Trioxide Thin Films. Materials 2024, 17, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, E.T.; Hassan, A.I.; Mohamed, F.A.; Wahid, M.H.A.; Fakhri, M.A. A sight of view on electrical impacts, structural properties and surface roughness of tungsten trioxide thin film: Effect of substrate temperatures in WO3/Si device fabrication. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 035508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Cao, W.; Wang, N.; Xia, Y.; Feng, Q.; Qiao, S. All-Covalent Organic Framework Nanofilms Assembled Lithium-Ion Capacitor to Solve the Imbalanced Charge Storage Kinetics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fan, Z.; Ding, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xuan, Y. Amorphous and Porous Tungsten Oxide Films for Fast-Switching Dual-Band Electrochromic Smart Windows. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 11, 2202115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Hu, P.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L. Amorphous materials emerging as prospective electrodes for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Chem 2023, 9, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atak, G.; Pehlivan, I.B.; Montero, J.; Granqvist, C.G.; Niklasson, G.A. Electrochromic tungsten oxide films prepared by sputtering: Optimizing cycling durability by judicious choice of deposition parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 367, 137233–137267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sychov, M.; Eruzin, A.; Semenova, A.; Katashev, P.; Mjakin, S.; Zhukov, M.V.; Aglikov, A.; Nosonovsky, M.; Skorb, E.V. Deposition of Nanostructured Tungsten Oxide Layers by a New Method: Periodic Modulation of the Deposition Angle. Langmuir 2023, 39, 12336–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, J. Photocatalytic methane activation by dual reaction sites co-modified WO3. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 46, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Qin, Z.; Xie, C.; Zeng, D. Active edge effect of pothole-rich WO3 nanosheets for enhancing dimethyl trisulfide gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131103–131112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; An, B.; Li, J.; Xie, E. Au-decorated WO3-based sensor for chemiresistive detection of NO2 at 80 °C. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 133985–133998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Dahlman, C.J.; Staller, C.M.; Jiang, T.; Dolocan, A.; Korgel, B.A.; Milliron, D.J. Enhanced Coloration Efficiency of Electrochromic Tungsten Oxide Nanorods by Site Selective Occupation of Sodium Ions. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.-T.; Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G. Sustainable Rejuvenation of Electrochromic WO3 Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28100–28104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Thimmarayan, G.; Balraj, B.; Chandrasekar, N.; Palanisamy, M.; Nagarajan, S.K.; Amirtharajan, S.; Kumar, M.; Sivakumar, C. Surfactants assisted synthesis of WO3 nanoparticles with improved photocatalytic and antibacterial activity: A strong impact of morphology. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 142, 109709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, K.; Ma, T.; Zhang, S.; Dai, W.; Luo, S. Implanted-Electron-hydrogen boosted breaking of W–O bonds to generate crater/oxygen vacancy filled WO3 nanoflakes for efficient oxidation of emerging pollutant. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 890, 161831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Qi, H.; He, Z.; Tang, B. Optimization of Optical Modulation in Amorphous WO3 Thin Films. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2024, 20, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Shu, X.; Qin, Y.; Tan, H.H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y. Structure modulated amorphous/crystalline WO3 nanoporous arrays with superior electrochromic energy storage performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 212, 110579–110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, C.; Herrero, J. Amorphous WO3-thin films with color characteristics tuned by the oxygen vacancies created during reactive DC sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 78, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, W.; Hui, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K. Tungsten oxide polymorphs and their multifunctional applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Geng, Z. Amorphous/crystalline WO3 dual phase laminated films: Fabrication, characterization and evaluation of their electrochromic performance for smart window applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 244, 111820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.; Gao, J.; Cao, H. In situ TEM investigation of hexagonal WO3 irreversible transformation to Li2WO4. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114090–114095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Jia, A.-B.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, S.X.-A. Emerging Electrochromic Materials and Devices for Future Displays. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 14679–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, X.; Lin, K.; Zhao, H.; Yao, Z.; Chi, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, X. Biphasic WO3 Nanostructures via Controlled Crystallization: Achieving High-Performance Electrochromism Through Amorphous/Crystalline Heterointerface Design. Crystals 2025, 15, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040324
Chu X, Lin K, Zhao H, Yao Z, Chi Y, Wang C, Yang X. Biphasic WO3 Nanostructures via Controlled Crystallization: Achieving High-Performance Electrochromism Through Amorphous/Crystalline Heterointerface Design. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040324
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Xuefeng, Kunjie Lin, Haiyang Zhao, Zonghui Yao, Yaodan Chi, Chao Wang, and Xiaotian Yang. 2025. "Biphasic WO3 Nanostructures via Controlled Crystallization: Achieving High-Performance Electrochromism Through Amorphous/Crystalline Heterointerface Design" Crystals 15, no. 4: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040324
APA StyleChu, X., Lin, K., Zhao, H., Yao, Z., Chi, Y., Wang, C., & Yang, X. (2025). Biphasic WO3 Nanostructures via Controlled Crystallization: Achieving High-Performance Electrochromism Through Amorphous/Crystalline Heterointerface Design. Crystals, 15(4), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040324





