Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Physical Measurements
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. X-ray Crystallography
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Thermal Properties
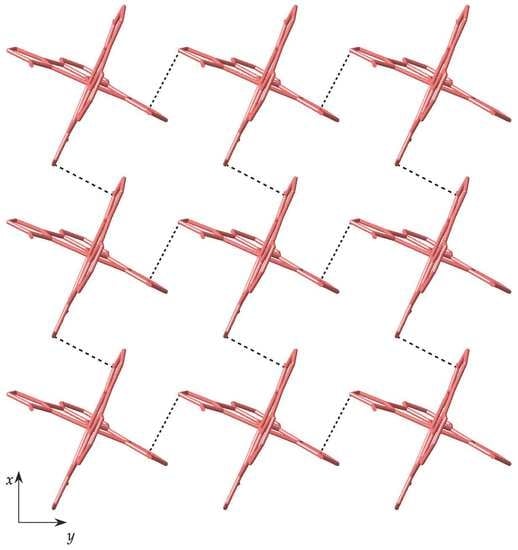
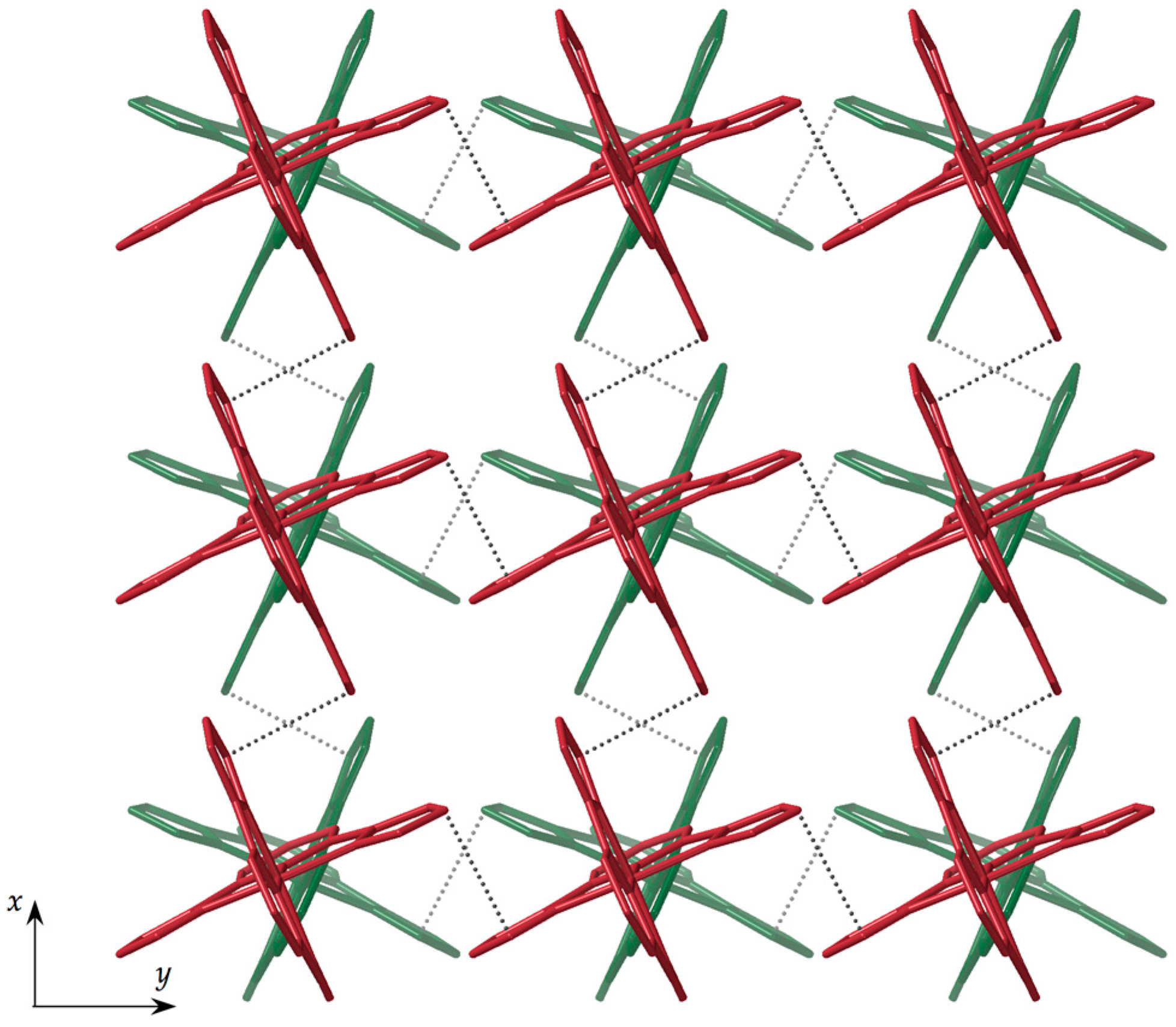
3.2. Structural Description
3.3. Magnetic Properties
3.4. Photomagnetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartual-Murgui, C.; Akou, A.; Thibault, C.; Molnár, G.; Vieu, C.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Spin-crossover metal-organic frameworks: Promising materials for designing gas sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O. Spin-transition polymers: From molecular materials toward memory devices. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, K.; Ruben, M. Emerging trends in spin crossover (SCO) based functional materials and devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 176–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baadji, N.; Sanvito, S. Giant resistance change across the phase transition in spin-crossover molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, O. Spin-crossover molecular materials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1996, 1, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O. Molecular Magnetism; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA; pp. 10010–14906.
- Matsumoto, T.; Newton, G.N.; Shiga, T.; Hayami, S.; Matsui, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Kumai, R.; Murakami, Y.; Oshio, H. Programmable spin-state switching in a mixed-valence spin-crossover iron grid. Nature Comm. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Kojima, T.; Dai, J.W.; Yoshida, T.; Breedlove, B.K.; Zhang, W.X.; Iguchi, H.; Sato, O.; Kawano, M.; Yamashita, M. Direct observation of ordered high-spin-low-spin intermediate states of an iron(III) three-step spin-srossover somplex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5184–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, E.A.; Moth-Poulsen, K.; Van Der Zant, H.S.J.; Paaske, J.; Hedegård, P.; Flensberg, K.; Bendix, J.; Bjørnholm, T. Electrical manipulation of spin states in a single electrostatically gated transition-metal complex. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baadji, N.; Piacenza, M.; Tugsuz, T.; Della Sala, F.; Maruccio, G.; Sanvito, S. Electrostatic spin crossover effect in polar magnetic molecules. Nature Mater. 2009, 8, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkowicz, D.; Rams, M.; Misek, M.; Kamenev, K.V.; Tomkowiak, H.; Katrusiak, A.; Sieklucka, B. Enforcing multifunctionality: A pressure-induced spin-crossover photomagnet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8795–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallois, B.; Real, J.A.; Hauw, C.; Zarembowitch, J. Structural changes associated with the spin transition in bis(isothiocyanato)bis(1,10-phenanthroline)iron: A single-crystal x-ray investigation. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamachi, T.; Gruber, M.; Davesne, V.; Bowen, M.; Boukari, S.; Joly, L.; Scheurer, F.; Rogez, G.; Yamada, T.K.; Ohresser, P.; et al. Robust spin crossover and memristance across a single molecule. Nature Commun. 2012, 3, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnár, G.; Demont, P.; Menegotto, J. Observation of a thermal hysteresis loop in the dielectric constant of spin crossover complexes: Towards molecular memory devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2069–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromí, G.; Aguilà, D.; Gamez, P.; Luis, F.; Roubeau, O. Design of magnetic coordination complexes for quantum computing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusniyarov, M.M. How to switch spin-crossover metal complexes at constant room temperature. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 15178–15191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Garcia, Y. Spin state switching in iron coordination compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 342–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niel, V.; Thompson, A.L.; Muñoz, M.C.; Galet, A.; Goeta, A.E.; Real, J.A. Crystalline-state reaction with allosteric effect in spin-crossover, interpenetrated networks with magnetic and optical bistability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3760–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niel, V.; Thompson, A.L.; Goeta, A.E.; Enachescu, C.; Hauser, A.; Galet, A.; Muñoz, M.C.; Real, J.A. Thermal- and photoinduced spin-state switching in an unprecedented three-dimensional bimetallic coordination polymer. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro-López, L.; Valverde-Muñoz, F.J.; Seredyuk, M.; Muñoz, M.C.; Haukka, M.; Real, J.A. Guest induced strong cooperative one- and two-step spin transitions in highly porous iron(ii) hofmann-type metal-organic frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 7038–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.J.; Zenere, K.A.; Ragon, F.; Southon, P.D.; Kepert, C.J.; Neville, S.M. Guest programmable multlstep spin crossover in a porous 2-D Hofmann-type material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudder, M.L.; Craig, D.C.; Goodwin, H.A. Hydrogen bonding influences on the properties of heavily hydrated chloride salts of iron(II) and ruthenium(II) complexes of 2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine, 2,6-bis(1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine and 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2005, 7, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyarto, K.H.; Scudder, M.L.; Craig, D.C.; Goodwin, H.A. Electronic and structural properties of the spin crossover systems bis(2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine)iron(II)thiocyanate and selenocyanate. Aust. J. Chem. 2000, 53, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochenie, C.; Bauer, W.; Railliet, A.P.; Schlamp, S.; Garcia, Y.; Weber, B. Large thermal hysteresis for iron(II) spin crossover complexes with N-(Pyrid-4-yl)isonicotinamide. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 11563–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Bauer, W.; Obel, J. An iron(II) spin-crossover complex with a 70 K wide thermal hysteresis loop. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10098–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, G.A.; Roubeau, O.; Aromí, G. Spin state switching in 2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine (3-bpp) based Fe(II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 269, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.F.; Guionneau, P.; Nguyen, O.; Costa, J.S.; Marcén, S.; Chastanet, G.; Marchivie, M.; Goux-Capes, L. A guideline to the design of molecular-based materials with long-lived photomagnetic lifetimes. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 4582–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcén, S.; Lecren, L.; Capes, L.; Goodwin, H.A.; Létard, J.F. Critical temperature of the LIESST effect in a series of hydrated and anhydrous complex salts [Fe(bpp)2]X2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 358, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchen, T.; Gütlich, P.; Sugiyarto, K.H.; Goodwin, H.A. High-spin → low-spin relaxation in [Fe(bpp)2](CF3SO3)2·H2O after LIESST and thermal spin-state trapping - Dynamics of spin transition versus dynamics of phase transition. Chem. Eur. J. 1996, 2, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; Giménez-López, M.C.; Romero, F.M.; Asthana, S.; Desplanches, C.; Létard, J.-F. Structural, thermal and photomagnetic properties of spin crossover [Fe(bpp)2]2+ salts bearing [Cr(L)(ox)2]− anions. Dalton Trans. 2009, 38, 8087–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornet-Mollá, V.; Duan, Y.; Giménez-Saiz, C.; Tang, Y.Y.; Li, P.F.; Romero, F.M.; Xiong, R.G. A ferroelectric iron(ii) spin crossover material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14052–14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lang, S.A. Novel two step synthesis of pyrazoles and isoxazoles from aryl methyl ketones. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1977, 14, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELX Version 2014/7. Available online: http://shelx.uni-ac.gwdg.de/SHELX/index.php (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; Giménez-López, M.C.; Romero, F.M. Structural, thermal, and magnetic study of solvation processes in spin-crossover [Fe(bpp)2][Cr(L)(Ox)2]2 nH2O complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 11266–11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, E.; Giménez-López, M.C.; Giménez-Saiz, C.; Romero, F.M. Spin crossover complexes as building units of hydrogen-bonded nanoporous structures. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2009, 11, 2198–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornet-Mollá, V.; Duan, Y.; Giménez-Saiz, C.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Romero, F.M. Hydrogen-bonded networks of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ spin crossover complexes and dicarboxylate anions: Structural and photomagnetic properties. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 17918–17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyarto, K.H.; McHale, W.A.; Craig, D.C.; Rae, A.D.; Scudder, M.L.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin transition centres linked by the nitroprusside ion. the cooperative transition in bis(2,6-bis(pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine)iron(II) nitroprusside. Dalton Trans. 2003, 12, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyarto, K.H.; Goodwin, H.A. Coordination of Pyridine-Substituted Pyrazoles and Their Influence on the Spin State of Iron(II). Aust. J. Chem. 1988, 41, 1645–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.F. Photomagnetism of iron(ii) spin crossover complexes—The T(LIESST) approach. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, H.H.; Doak, G.O. The basicities of substituted pyridines and their 1-oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 4441–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compound | 1·4H2O |
|---|---|
| Formula | C34H34FeN12O8 |
| Formula weight | 794.58 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | Pc |
| a/Å | 8.17633(10) |
| b/Å | 8.15854(9) |
| c/Å | 26.9671(3) |
| α/° | - |
| β/° | 92.0138(10) |
| γ/° | - |
| V/Å3 | 1797.78(4) |
| Z | 2 |
| T/K | 120(2) |
| ρcalcd/g·cm−3 | 1.468 |
| λ/Å | 0.71073 |
| θ-range/° | 2.870–29.963 |
| No. of rflns. collected | 84313 |
| No. of indep. rflns./Rint | 9867/0.0635 |
| Restraints/parameters | 18/532 |
| R1/wR2 (I > 2σ(I)) 1 | 0.0324/0.0664 |
| R1/wR2 (all data) 1 | 0.0398/0.0711 |
| Δρmax and Δρmin /e·Å−3 | 0.265/−0.395 |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.016(5) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jornet-Mollá, V.; Giménez-Saiz, C.; Romero, F.M. Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions. Crystals 2018, 8, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110439
Jornet-Mollá V, Giménez-Saiz C, Romero FM. Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions. Crystals. 2018; 8(11):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110439
Chicago/Turabian StyleJornet-Mollá, Verónica, Carlos Giménez-Saiz, and Francisco M. Romero. 2018. "Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions" Crystals 8, no. 11: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110439
APA StyleJornet-Mollá, V., Giménez-Saiz, C., & Romero, F. M. (2018). Synthesis, Structure, and Photomagnetic Properties of a Hydrogen-Bonded Lattice of [Fe(bpp)2]2+ Spin-Crossover Complexes and Nicotinate Anions. Crystals, 8(11), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110439