Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine Polymorphism Characterized by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.2.1. General
- determination of the peak transition frequencies and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the peaks for transition 7/2→5/2 of the Bi nucleus in all samples after reaching their final state
- observation of the evolution of the NQR spectrum during a certain time after shock freezing the melt of RM-SFLN
- the determination of the peak transition frequencies during a temperature sweep from 153 K to 325 K for the detection of potential phase transitions
- the determination of T2 relaxation times of CS and RM-SFW, partially at different temperatures
2.2.2. Experiment 1
2.2.3. Experiment 2
2.2.4. Experiment 3
2.2.5. Experiment 4
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1
3.2. Experiment 2
3.3. Experiment 3
3.4. Experiment 4
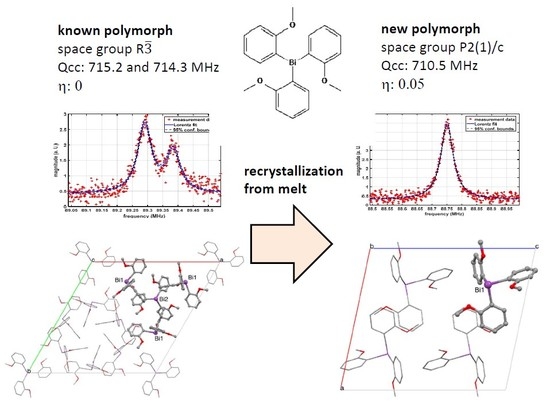
3.5. X-ray Crystallography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Crystallization in the monoclinic space group P2(1)/c with only one molecule Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine in the asymmetric unit
- Consequently, only a single 5/2-7/2 transition is observed at 88.75 MHz @310 K in contrast to the two transitions at 89.38 and 89.29 MHz for the trigonal polymorph which contains two crystallographically distinct molecules of Tris(2-methoxy-Phenyl)Bismuthine in the asymmetric unit.
- The NQR parameters Qcc and η of the new polymorph are 710.5 MHz and 0.05, respectively.
- Relaxometric data for the T2 time constant show a negative temperature coefficient for the new polymorph in contrast to a positive temperature coefficient (not very typical for the so far investigated Bi-Aryl-compounds [23]) of the reference polymorph in CS. This observation suggests clear differences in molecular dynamics.
- The NQR data of the new phase does not depend noticeably on the dynamics of freezing. The end products also show essentially the same FWHM at the same temperature, except for extremely fast freezing, which yields extremely broad (FWHM 1.8 MHz) peaks immediately after solidification. In the further time course, the peaks narrow considerably, even during storage at 77 K.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Empirical formula | C21 H21 Bi O3 | |
| CCDC | 1941426 | |
| Formula weight | 530.36 | |
| Temperature | 100(2) K | |
| Wavelength | 0.71073 Å | |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | |
| Space group | P2(1)/c | |
| Unit cell dimensions | a = 14.7365(5) Å | a = 90°. |
| b = 7.9764(3) Å | b = 101.918(2)°. | |
| c = 16.8250(6) Å | g = 90°. | |
| Volume | 1935.05(12) Å3 | |
| Z | 4 | |
| Density (calculated) | 1.820 Mg/m3 | |
| Absorption coefficient | 9.127 mm−1 | |
| F(000) | 1016 | |
| Crystal size | 0.250 × 0.170 × 0.130 mm3 | |
| Theta range for data collection | 1.412 to 30.000°. | |
| Index ranges | −20 ≤ h ≤ 20, −11 ≤ k ≤ 11, −23 ≤ l ≤ 23 | |
| Absorption Correction | multi-scan/ SADABS | |
| Reflections collected | 57633 | |
| Independent reflections | 5575 [R(int) = 0.0693] | |
| Completeness to theta = 30.000° | 98.8 % | |
| Refinement method | Full-matrix least-squares on F2 | |
| Data / restraints / parameters | 5575 / 0 / 229 | |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.072 | |
| Final R indices [I > 2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0300, wR2 = 0.0848 | |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0343, wR2 = 0.0912 | |
| Extinction coefficient | n/a | |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 1.989 and -3.389 e.Å−3 |
References
- Suits, B.H. Nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy. In Handbook of Applied Solid State Spectroscopy; Vij, D.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.P.; Hahn, E.L. Solid state physics. Supplement 1, nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy. In Solid State Physics, 1st ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1958; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Pen’kov, I.N.; Sofin, I.A. Application of nuclear quadrupole resonance in study of minerals. Int. Geol. Rev. 1967, 9, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, G.M. Second order nuclear quadrupole effects in single crystals: part I. theoretical. Can. J. Phys. 1953, 31, 820–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, J.; Žagar, V.; Asaji, T. NQR investigation and characterization of cocrystals and crystal polymorphs. Hyperfine Interact. 2013, 222, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balchin, E.; Malcolme-Lawes, D.J.; Poplett, I.J.F.; Rowe, M.D.; Smith, J.A.S.; Pearce, G.E.S.; Wren, S.A.C. Potential of nuclear quadrupole resonance in pharmaceutical analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 77, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar]
- Latosinńska, J.N. Applications of nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy in drug development. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, J.; Althoefer, K.; Rowe, M.D.; Poplett, I.J.; Smith, J.A.S. The Emerging Field of Medicines Authentication by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2012, 43, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.D.; Jakobsson, A.; Rowe, M.D.; Smith, J.A.S.; Butt, N.R.; Althoefer, K. Robust detection of stochastic nuclear quadrupole resonance signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 4221–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.C.; Cerioni, L.; Wolfenson, A.E.; Faudone, S.; Cuffini, L.S. Utilization of pure nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy for the study of pharmaceutical crystal forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, E.; Althoefer, K.; Barras, J.; Rowe, M.D.; Smith, J.A.; Pearce, G.E.; Wren, S.A. Quantitative 35Cl nuclear quadrupole resonance in tablets of the antidiabetic medicine diabinese. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5574–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limandri, S.; Visñovezky, C.; Pérez, S.C.; Schurrer, C.A.; Wolfenson, A.E.; Ferro, M.; Cuffini, S.L.; de Souza, J.G.; Aguiar, F.A.; de Gaitani, C.M. Nuclear quadrupole resonance: A technique to control hydration processes in the pharmaceutical industry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, M.; Privalov, A.; Altmann, J.; Anferov, V.; Fujara, F. 1H-14N cross-relaxation in trinitrotoluene-a step toward improved landmine detection. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2002, 35, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudakov, T.N.; Mikhaltsevich, V.T.; Selchikhin, O.P. The use of multi-pulse nuclear quadrupole resonance techniques for the detection of explosives containing RDX. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1997, 30, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinc, R.; Apih, T.; Seliger, J. Nuclear quadrupole double resonance techniques for the detection of explosives and drugs. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2004, 25, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastow, T.J.; Lehmann-Horn, J.A.; Miljak, D.G. 121,123Sb and 75As {NMR} and {NQR} investigation of the tetrahedrite ({Cu}12Sb4S13)–{Tennantite} ({Cu}12As4S13) system and other metal arsenides. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2015, 71, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastow, T.J.; Whitfield, H.J. Crystal data and nuclear quadrupole resonance spectra of tetra-arsenic triselenide. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1977, 10, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann-Horn, J.A.; Miljak, D.G.; O’Dell, L.A.; Yong, R.; Bastow, T.J. Rapid detection of arsenic minerals using portable broadband NQR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6765–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, H.J. Polymorphism in skinnerite, Cu3SbS3. Solid State Commun. 1980, 33, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastow, T.J.; Smith, M.E. 91 Zr NMR characterisation of phases in transformation toughened zirconia. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 1992, 1, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.L. Pure nuclear quadrupole resonance studies of structural phase transitions. J. Magn. Reson. 1975, 20, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Zemnukhova, L.A.; Davidovich, R.L. Nuclear quadrupole resonance study of phase transitions and incommensurability in K2SbF5. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2001, 13, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gösweiner, C.; Lantto, P.; Fischer, R.; Sampl, C.; Umut, E.; Westlund, P.; Kruk, D.; Bödenler, M.; Spirk, S.; Petrovič, A.; et al. Tuning Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance: A Novel Approach for the Design of Frequency-Selective MRI Contrast Agents. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 021076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Umut, E.; Masiewicz, E.; Sampl, C.; Fischer, R.; Spirk, S.; Goesweinerc, C.; Scharfetterc, H. 209 Bi quadrupole relaxation enhancement in solids as a step towards new contrast mechanisms in magnetic resonance imaging. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 12710–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, D.; Masiewicz, E.; Umut, E.; Petrovic, A.; Kargl, R.; Scharfetter, H. Estimation of the magnitude of quadrupole relaxation enhancement in the context of magnetic resonance imaging contrast. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 184306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfetter, H.; Gösweiner, C.; Krassnig, P.J.; Sampl, C.; Thonhofer, M.; Fischer, R.; Spirk, S.; Kargl, R.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Umut, E.; et al. Aspects of structural order in 209 Bi-containing particles for potential MRI contrast agents based on quadrupole enhanced relaxation. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, D.E.; Gutowsky, H.S. Nuclear pure quadrupole relaxation and its temperature dependence in solids. J. Chem. Phys. 1963, 39, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfetter, H.; Bödenler, M.; Narnhofer, D. A cryostatic, fast scanning, wideband {NQR} spectrometer for the {VHF} range. J. Magn. Reson. 2018, 286, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, R.H. An empirical correction for absorption anisotropy. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1995, A51, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keng, T.C.; Lo, K.M.; Ng, S.W. SADABS. University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, H. Zur Theorie der Spin-Gitterrelaxation in Molekülkristallen. Z. Physik. 1951, 130, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.C. Temperature dependence of quadrupole resonance frequencies under constant pressure. J. Chem. Phys. 1960, 32, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, O.; Schier, A.; Schmidbaur, H. The quest for complexes with a coordinative gold-bismuth bond. Organometallics 2003, 22, 4079–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kranendonk, J. Trolanheory of quadrupolar nuclear spin-lattice relaxation. Physica 1954, 20, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kranendonk, J.; Walker, M. Theory of quadrupolar nuclear spin-lattice relaxation due to anharmonic Raman phonon processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 18, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Goesweiner, C.; Masiewicz, E.; Umut, E.; Sampl, C.; Scharfetter, H. Model-free approach to quadrupole spin relaxation in solid 209Bi-aryl compounds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 23414–23423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirnat, J.; Lužnik, J.; Jazbinšek, V.; Žagar, V.; Seliger, J.; Klapötke, T.M.; Trontelj, Z. 14N NQR in the tetrazole family. Chem. Phys. 2009, 364, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, J. D 15. Kristallstrukturuntersuchungen an den Triphenylen des Wismuts, Arsens und Antimons. Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 1942, 104, 305–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, D.M.; Ferguson, G. The stereochemistry of some organic derivatives of Group VB elements. The crystal and molecular structure of triphenylbismuth.The crystal and molecular structure of triphenylbismuth. J. Chem. Soc. A Inorganic Phys. Theor. 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.G.; Blaschette, A.; Henschel, D.; Weitze, A. Redetermination of the crystal structure of triphenylbismuth, (C6H5)3Bi. Z. Krist. New Cryst. Struct. 1995, 210, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bučinský, L.; Jayatilaka, D.; Grabowsky, S. Importance of relativistic effects and electron correlation in structure factors and electron density of diphenyl mercury and triphenyl bismuth. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 6650–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Temperature (K) | CS | RM-SFLN | RM-SFW | RM-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 310 | Site A: 89.384 Site B: 89.290 | 88.754 | 88.751 | 88.759 |
| 77 | not measurable | 90.713 | 90.710 | 90.704 |
| Temperature (K) | CS | RM-SFLN | RM-SFW | RM-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 310 | Site A: 55.3 Site B: 55.6 | not measurable (poor SNR) | 50.1 | 51.2 |
| 77 | not measurable | 264 | 107.1 | 104.2 |
| Time (min) | 26 | 46 | 89 | 1098 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (kHz) | 1844 | 808 | 375 | 264 |
| 95% conf. bounds | (826, 2863) | (189, 1427) | (219, 530) | (195, 333) |
| Parameter | A | fT,0 | vQ3 | g@T0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−48 kg m2 | THz | MHz | 1/K | |
| 42.406 | 15.842 | 91.440 | 18.12 × 10−4 |
| Title | CS Site A | CS Site B | RM-SFW |
|---|---|---|---|
| T2 @Transition 7/2 → 5/2 (μs) | 315 | 67 | 197 |
| Space Group | P2(1)/c This work | Reference Site A [35] | Reference Site B [35] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distances [Å] | Bi1-C1 | 2.247(3) | Bi1-C1 | 2.250(7) | Bi2-C22 | 2.248(7) |
| Bi1-C8 | 2.250(2) | Bi1-C8 | 2.268(8) | |||
| Bi1-C15 | 2.251(4) | Bi1-C15 | 2.260(10) | |||
| Bi1-O1 | 3.106(5) | Bi1-O1 | 3.079(9) | Bi2-O4 | 3.097(9) | |
| Bi1-O2 | 3.059(5) | Bi1-O2 | 3.117(9) | |||
| Bi1-O3 | 3.140(5) | Bi1-O3 | 3.103(8) | |||
| Angles [°] | C1-Bi1-C8 | 95.8(1) | C1-Bi1-C8 | 94.7(3) | C22-Bi-C22A | 93.5(4) |
| C8-Bi1-C15 | 93.4(1) | C8-Bi1-C15 | 95.3(3) | |||
| C1-Bi1-C15 | 93.1(1) | C1-Bi1-C15 | 92.6(3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scharfetter, H.; Fischer, R.; Krassnig, P.; Thonhofer, M.; Theyer, F.; Gösweiner, C. Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine Polymorphism Characterized by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy. Crystals 2019, 9, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090446
Scharfetter H, Fischer R, Krassnig P, Thonhofer M, Theyer F, Gösweiner C. Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine Polymorphism Characterized by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy. Crystals. 2019; 9(9):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090446
Chicago/Turabian StyleScharfetter, Hermann, Roland Fischer, Paul Krassnig, Martin Thonhofer, Felix Theyer, and Christian Gösweiner. 2019. "Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine Polymorphism Characterized by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy" Crystals 9, no. 9: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090446
APA StyleScharfetter, H., Fischer, R., Krassnig, P., Thonhofer, M., Theyer, F., & Gösweiner, C. (2019). Tris(2-Methoxyphenyl)Bismuthine Polymorphism Characterized by Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Spectroscopy. Crystals, 9(9), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090446