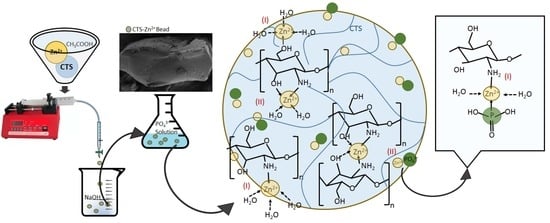
Chitosan–Zinc(II) Complexes as a Bio-Sorbent for the Adsorptive Abatement of Phosphate: Mechanism of Complexation and Assessment of Adsorption Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis Methods and Instruments
2.3. Adsorbent Preparation and Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Zn(II)–CTS Bio-Sorbent
3.1.1. FT-IR Analysis
3.1.2. SEM Analysis
3.1.3. Determination of pHPZC
3.2. Phosphate Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Effect of Bio-Sorbent Dose
3.2.2. Effect of pH
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
3.2.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.2.6. Effect of Coexisting Ions
3.3. Mechanisms of Zn(II)–CTS Complexation and Phosphate Adsorption
3.4. Evaluation of Zn(II)–CTS Bio-Sorbent
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinge, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, G.K.; Brett, S.W.; Guy, J.A.; Lester, J.N. Review: Phosphorus removal and recovery technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 212, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Removal of phosphate anions using the modified chitosan beads: Adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism studies. Powder Technol. 2015, 277, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wu, C.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X. Adsorptive characteristics of phosphate from aqueous solutions by miex resin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowmya, A.; Meenakshi, S. An efficient and regenerable quaternary amine modified chitosan beads for the removal of nitrate and phosphate anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliem, M.K.; Komarneni, S.; Abu Khadra, M.R. Phosphate removal from solution by composite of MCM-41 silica with rice husk: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalley, J.; Han, C.; Li, X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Nadagouda, M.N. Phosphate adsorption using modified iron oxide-based sorbents in lake water: Kinetics, equilibrium, and column tests. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, I.T.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. Phosphorus and bacterial growth in drinking water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3242–3245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Quality Criteria for Water; EPA 440/5-86-001; Office of Water Regulation and Standard: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4222–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awual, M.R.; Jyo, A.; Ihara, T.; Seko, N.; Tamada, M.; Lim, K.T. Enhanced trace phosphate removal from water by zirconium(IV) loaded fibrous adsorbent. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4592–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamani, J.S.; Lounsbury, A.W.; Zimmerman, J.B. Towards a selective adsorbent for arsenate and selenite in the presence of phosphate: Assessment of adsorption efficiency, mechanism, and binary separation factors of the chitosan-copper complex. Water Res. 2016, 88, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madill, E.A.W.; Garcia-Valdez, O.; Champagne, P.; Cunningham, M.F. CO2-responsive graft modified chitosan for heavy metal (nickel) recovery. Polymers 2017, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vahala, R. Synthesis, characterization and exploitation of nano-TiO2/feldspar embedded chitosan beads towards UV-assisted adsorptive abatement of aqueous arsenic (As). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.M.; Meenakshi, S. A dendrimer-like hyper branched chitosan beads toward fluoride adsorption from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, M.; Bahrami, H.; Arami, M. Feldspar/titanium dioxide/chitosan as a biophotocatalyst hybrid for the removal of organic dyes from aquatic phases. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40247–40256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaninia, M.H.; Wilson, L.D. Cross-linked chitosan beads for phosphate removal from aqueous solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Qian, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, M.; Huang, W. Rapid and effective removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution using novel chitosan and laponite-based nanocomposite as adsorbent. Polymers 2017, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan-Zn complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, S.; Fu, T.; Fan, W.; Zheng, H.; Lu, Q.; Bi, X. Study on the thermal degradation kinetics and pyrolysis characteristics of chitosan-Zn complex. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 122, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chesnutt, B.M.; Haggard, W.O.; Bumgardner, J.D. Deacetylation of chitosan: Material characterization and in vitro evaluation via albumin adsorption and pre-osteoblastic cell cultures. Materials 2011, 4, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Shen, D. Effect of reaction temperature and reaction time on the preparation of low-molecular-weight chitosan using phosphoric acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. Calculation of Mark–Houwink–Sakurada (MHS) equation viscometric constants for chitosan in any solvent–temperature system using experimental reported viscometric constants data. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 477–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.N.; Teixeira, V.G.; Delpech, M.C.; Souza, J.V.S.; Costa, M.A.S. Viscometric study of chitosan solutions in acetic acid/sodium acetate and acetic acid/sodium chloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, M.R.; Tuutijärvi, T.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vahala, R. Adsorptive removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous phase by feldspars: Kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhavelu, S.; Thambidurai, S. Preparation of chitosan-zinc oxide complex during chitin deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiselvi, K.; Thambidurai, S. Synthesis of porous chitosan-polyaniline/ZnO hybrid composite and application for removal of reactive orange 16 dye. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Lackner, K.S. Kinetic analysis of an anion exchange absorbent for CO2 capture from ambient air. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Shang, J.K. Synthesis of mesoporous cerium-zirconium binary oxide nanoadsorbents by a solvothermal process and their effective adsorption of phosphate from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 268, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Proc. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Adsorption of fluoride to UiO-66-NH2 in water: Stability, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.H.; Szeto, Y.S.; McKay, G. Intraparticle diffusion processes during acid dye adsorption onto chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2897–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R. Phosphate adsorption from aqueous solutions by zirconium (IV) loaded cross-linked chitosan particles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Processes, and Modeling; Walter de Gruyter: Munchen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A.; Sari, A.; Isildak, O. Adsorption thermodynamics of stearic acid onto bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M. Chemical Engineering Kinetics, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, F.; Pakizeh, M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Hg(II) adsorption onto MCM-41 modified by ZnCl2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Peng, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, X. Facile preparation of EDTA-functionalized chitosan magnetic adsorbent for removal of Pb(II). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Dong, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, L. Removal of arsenic from water: Effects of competing anions on As(III) removal in KMnO4–Fe(II) process. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3891–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhazi, M.; Desbrières, J.; Tolaimate, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Vottero, P.; Alagui, A. Contribution to the study of the complexation of copper by chitosan and oligomers. Polymer 2001, 43, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xiao, H.; Chen, X.; Lackner, K.S. The effect of moisture on the hydrolysis of basic salts. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18326–18330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Xie, Q.; Qi, C.; Zhao, L.; Wu, D. Phosphate removal using zinc ferrite synthesized through a facile solvothermal technique. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, J.-A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for phosphate adsorption to magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sangeetha, D. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of adsorption of phosphate onto ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, M.; Weiss, D.; Bluck, M.; Vilar, R. Adsorption kinetics, capacity and mechanism of arsenate and phosphate on a bifunctional TiO2-Fe2O3 bi-composite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 364, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boujelben, N.; Bouzid, J.; Elouear, Z.; Feki, M.; Jamoussi, F.; Montiel, A. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution using iron coated natural and engineered sorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yan, L.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Qin, L.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Du, B. Efficient removal of phosphate by facile prepared magnetic diatomite and illite clay from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| C0 (mg/L) | qe(exp) | Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | Intra-particle diffusion | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear regression | |||||||||||
| qe(cal) | k1 | R2 | Δq | qe(cal) | k2 | R2 | Δq | kp | C | ||
| 1 | 1.99 | 0.61 | 0.003 | 0.66 | 3.85 | 2.01 | 0.029 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.030 | 0.875 |
| 5 | 6.34 | 1.85 | 0.004 | 0.55 | 3.27 | 5.85 | 1.476 | 0.998 | 1.03 | 0.067 | 3.541 |
| 10 | 10.44 | 4.64 | 0.002 | 0.76 | 3.22 | 10.46 | 0.004 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.150 | 4.312 |
| Nonlinear regression | |||||||||||
| 1 | 1.99 | 1.97 | 0.029 | 0.98 | 0.34 | 2.08 | 0.020 | 0.981 | 0.17 | - | - |
| 5 | 6.34 | 5.87 | 0.067 | 0.99 | 0.06 | 6.16 | 0.016 | 0.992 | 0.15 | - | - |
| 10 | 10.44 | 9.59 | 0.048 | 0.91 | 0.25 | 10.13 | 0.007 | 0.984 | 0.20 | - | - |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax | KL | RL | R2 | Δq | KF | 1/n | R2 | Δq | |
| 293 | 7.37 | 1.32 | 0.05–0.43 | 0.99 | 0.31 | 3.72 | 0.27 | 0.99 | 0.04 |
| 298 | 5.33 | 1.85 | 0.03–0.34 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 3.12 | 0.22 | 0.98 | 0.06 |
| 303 | 5.40 | 1.56 | 0.04–0.38 | 0.99 | 0.18 | 2.92 | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.1 |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | Sips | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax | KL | R2 | Δq | KF | 1/n | R2 | Δq | qs | Ks | nS | R2 | Δq | |
| 293 | 6.75 | 2.11 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 3.77 | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.05 | 17.1 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.03 |
| 298 | 4.98 | 3.19 | 0.93 | 0.16 | 3.17 | 0.20 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 6.94 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.04 |
| 303 | 5.12 | 2.25 | 0.93 | 0.11 | 3.01 | 0.23 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 7.26 | 0.77 | 0.48 | 0.96 | 0.08 |
| T (K) | ∆G (kJ/mol) | ∆H (kJ/mol) | ∆S (J/K∙mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | −5.27 | −37.86 | −111.32 |
| 298 | −4.60 | ||
| 303 | −4.15 |
| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | qmax (mg/g) | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn(II)–CTS | 5 | 7.37 | 4 | Present |
| Zn(II)–CTS | 5 | 6.3 | natural | Present |
| Chitosan | 5 | 1.45 | natural | Present |
| Chitosan | 5 | 4.75 | 4 | Present |
| Naturally iron oxide coated sand | 5–30 | 0.88 | 5 | [50] |
| Synthetic iron oxide coated sand | 5–30 | 1.50 | 5 | [50] |
| Zinc ferrite | 5 | 5.23 | - | [46] |
| Magnetic illite clay | 10–100 | 5.48 | - | [51] |
| ZCB | 5–50 | 60.60 | 4 | [3] |
| Quaternized chitosan beads | 1000 | 59.00 | - | [5] |
| TiO2 | - | 2.63 | 5 | [49] |
| ZnCl2–carbon | 10 | 5.10 | - | [48] |
| Magnetic iron | 2–20 | 5.03 | - | [47] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yazdani, M.R.; Virolainen, E.; Conley, K.; Vahala, R. Chitosan–Zinc(II) Complexes as a Bio-Sorbent for the Adsorptive Abatement of Phosphate: Mechanism of Complexation and Assessment of Adsorption Performance. Polymers 2018, 10, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010025
Yazdani MR, Virolainen E, Conley K, Vahala R. Chitosan–Zinc(II) Complexes as a Bio-Sorbent for the Adsorptive Abatement of Phosphate: Mechanism of Complexation and Assessment of Adsorption Performance. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleYazdani, Maryam Roza, Elina Virolainen, Kevin Conley, and Riku Vahala. 2018. "Chitosan–Zinc(II) Complexes as a Bio-Sorbent for the Adsorptive Abatement of Phosphate: Mechanism of Complexation and Assessment of Adsorption Performance" Polymers 10, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010025
APA StyleYazdani, M. R., Virolainen, E., Conley, K., & Vahala, R. (2018). Chitosan–Zinc(II) Complexes as a Bio-Sorbent for the Adsorptive Abatement of Phosphate: Mechanism of Complexation and Assessment of Adsorption Performance. Polymers, 10(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010025