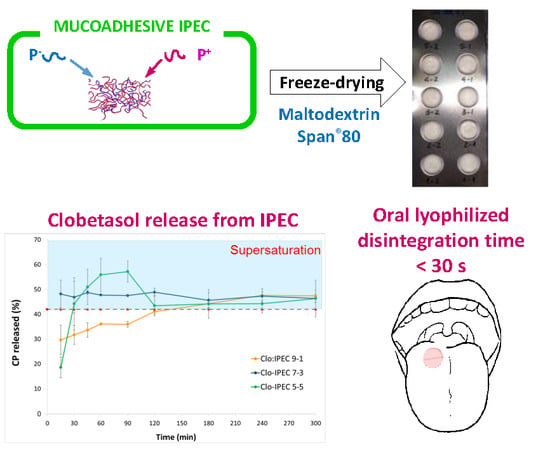
Mucoadhesive Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes for the Buccal Delivery of Clobetasol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Placebo and CP Loaded IPECs
2.3. IPEC Characterization
2.3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.3.2. Zeta-Potential Measurements
2.3.3. Modulated DSC Analysis
2.3.4. FTIR-Spectroscopy
2.4. In Vitro Mucoadhesive Properties of Placebo IPECs
2.5. Preparation of Oral Lyophilisates
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release Test
2.7. HPLC Method
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Placebo IPECs
3.2. Oral Lyophilisates Containing Placebo IPEC
3.3. CP Loaded IPECs
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourganis, V.; Karamanidou, T.; Kammona, O.; Kiparissides, C. Polyelectrolyte complexes as prospective carriers for the oral delivery of protein therapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 111, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfurhood, J.A.; Sun, H.; Kabb, C.P.; Tucker, B.S.; Matthews, J.H.; Luesch, H.; Sumerlin, B.S. Poly(N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide)–valproic acid conjugates as block copolymer nanocarriers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4983–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillen, K.; Vandervoort, J.; Van den Mooter, G.; Ludwig, A. Evaluation of ciprofloxacin-loaded Eudragit® RS100 or RL100/PLGA nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, B.; Bigucci, F.; Mercolini, L.; Musenga, A.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Zecchi, V. Novel mucoadhesive nasal inserts based on chitosan/hyaluronate polyelectrolyte complexes for peptide and protein delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafin, R.I. Interpolymer combinations of chemically complementary grades of Eudragit copolymers: A new direction in the design of peroral solid dosage forms of drug delivery systems with controlled release. Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Reineker, P. Stoichiometric polyelectrolyte complexes of ionic block copolymers and oppositely charged polyions. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartig, M.S.; Greene, R.R.; Dikov, M.M.; Prokop, A.; Davidson, J.M. Multifunctional nanoparticulate polyelectrolyte complexes. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2353–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafin (Moustafine), R.I.; Semina, I.I.; Garipova, V.A.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Sitenkov, Y.A.; Salakhova, A.R.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Cilurzo, F. Comparative study of polycomplexes based on Carbopol® and oppositely charged polyelectrolytes as a new oral drug delivery system. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilurzo, F.; Musazzi, U.M.; Franzè, S.; Selmin, F.; Minghetti, P. Orodispersible dosage forms: Biopharmaceutical improvements and regulatory requirements. Drug Discov. Today 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilurzo, F.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Selmin, F.; Epstein, J.B.; Gaeta, G.M.; Colella, G.; Minghetti, P. A new mucoadhesive dosage form for the management of oral lichen planus: Formulation and clinical study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidelines for the Management of Oral Lichen Planus in Secondary Care—October 2010. Available online: www.bsom.org.uk/LP_guidelines_-_BSOM.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2018).
- Selmin, F.; Franceschini, I.; Cupone, I.E.; Minghetti, P.; Cilurzo, F. Aminoacids as non-traditional plasticizers of maltodextrins fast-dissolving films. Carbohyd. Pol. 2015, 115, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbig, M.E.; Evers, D.H. Correlation of hydrotropic solubilization by urea with log D of drug molecules and utilization of this effect for topical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilurzo, F.; Minghetti, P.; Selmin, F.; Casiraghi, A.; Montanari, L. Polymethacrylate salts as new low-swellable mucoadhesive materials. J. Control. Release 2003, 88, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, E.; Wisniewski, N.; Peppas, N.A. Evidence of mucoadhesion by chain interpenetration at a poly(acrylic acid)/mucin interface using ATR–FTIR spectroscopy. J. Control. Release 1993, 26, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, R.I.; Kabanova, T.V.; Zhdanova, E.R.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Garipova, V.A.; Nasibullin, S.F.; Kemenova, V.A. Synthesis and physicochemical evaluation of new carrier based on interpolyelecrtolyte complex formed by Eudragit® EPO and Carbomer 940. Pharm. Chem. J. 2010, 44, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, R.I.; Kabanova, T.V.; Semina, I.I.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Garipova, V.A.; Shilovskaya, E.V.; Nasibullin, S.F.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Kazakova, R.R.; Kemenova, V.A. Biopharmaceutical assessment of a polycomplex matrix system based on Carbomer 940 and Eudragit® EPO for colon-specific drug delivery. Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, R.I.; Kabanova, T.V.; Zhdanova, E.R.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Garipova, V.A.; Nasibullin, S.F.; Kemenova, V.A. Diffusion-transport properties of a polycomplex matrix system based on Eudragit® EPO and Carbomer 940. Pharm. Chem. J. 2010, 44, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Kabanova, T.V.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Characteristics of interpolyelectrolyte complexes of Eudragit E 100 with Eudragit L 100. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.; Selmin, F.; Baldassari, S.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Caviglioli, G.; Cilurzo, F.; Minghetti, P.; Parodi, B. A focus on mucoadhesive polymers and their application in buccal dosage forms. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarkah, Y.; Green, R.J.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Probing the mucoadhesive interactions between porcine gastric mucin and some water-soluble polymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, H.; Slade, L. Another view of trehalose for drying and stabilizing biological materials. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1992, 5, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, J.H.; Crowe, L.M.; Carpenter, J.F. Preserving dry biomaterials: The water replacement hypothesis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1993, 6, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Pikal, M. Design of freeze-drying processes for pharmaceuticals: Practical advice. Pharm Res. 2004, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikal, M.J.; Shah, S.; Roy, M.L.; Putman, R. The secondary drying stage of freeze drying: Drying kinetics as a function of temperature and chamber pressure. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 60, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaeghere, F.; Allémann, E.; Feijen, J.; Kissel, T.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Freeze-drying and lyopreservation of diblock and triblock poly (lactic acid)-poly (ethylene oxide)(PLA-PEO) copolymer nanoparticles. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, A.E.; Illum, L.; Davis, S.S. Preparation of biodegradable, surface engineered PLGA nanospheres with enhanced lymphatic drainage and lymph node uptake. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobio, M.; Gref, R.; Sanchez, A.; Langer, R.; Alonso, M.J. Stealth PLA–PEG nanoparticles as protein carriers for nasal administration. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redhead, H.M.; Davis, S.S.; Illum, L. Drug delivery in poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles surface modified with poloxamer 407 and poloxamine 908: In Vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Grade (Code) | Type of Polymer | Viscosity (0.5%, pH 7.5), cP | MW (kDa) | Mesh Size—Distance between Crosslinks (kDa) | ζ (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2020 | Carbomer interpolymer. Type B (copolymer of AA and EG crosslinked with AEPE) | 47,000–77,000 | 4500 | 11.4 | −36.2 ± 2.7 |
| C71G | Carbomer homopolymer. Type A (PAA, crosslinked with AEPE) | 4000–11,000 | 3000 | 237.6 | −51.0 ± 2.0 |
| C10 * | Carbomer interpolymer. Type A (block copolymer of EG and a long chain alkyl acid ester) | 45,000–65,000 | 3000 | - * | −33.3 ± 2.1 |
| NAA-1 * | Polycarbophil (PAA, crosslinked with DVG) | 2000–12,000 | 3000 | - * | −40.1 ± 2.1 |
| EPO | Butylated methacrylate copolymer | - | 150 | - | 45.7 ± 2.1 |
| Tablet Code | Tablet Composition (%, w/w) | Disintegration Time (s) | Dh (nm) | ζ (mV) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPEC 1 | IPEC 8 | DS | S80 | T80 | ||||
| 1 | 10% | - | 40.9 | - | - | 6 | 149 ± 42 (54.9%) | n.d. |
| 2 | 10% | - | 81.8 | - | - | n.d. * | - | - |
| 3 | - | 10% | 40.9 | - | - | 11 | 136 ± 16 (95.6%) | −26.6 ± 0.7 |
| 4 | - | 10% | 81.8 | - | - | n.d. * | - | - |
| 5 | 10% | - | 40.9 | 0.01 | - | 20 | 141 ± 0 (97.8%) | −26.6 ± 0.6 |
| 6 | 10% | - | 40.9 | 0.1 | - | 6 | 132 ± 8 (90.0%) | −25.8 ± 0.1 |
| 7 | 10% | - | 40.9 | 0.5 | - | 26 | 145 ± 8 (98.4%) | −26.0 ± 1.3 |
| 8 | 10% | - | 40.9 | - | 0.01 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 9 | 10% | - | 40.9 | - | 0.1 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 10 | 10% | - | 40.9 | - | 0.5 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 11 | - | 10% | 40.9 | 0.01 | - | 33 | 125 ± 10 (100%) | −26.3 ± 1.9 |
| 12 | - | 10% | 40.9 | 0.1 | - | 12 | 111 ± 9 (100%) | −25.1 ± 3.0 |
| 13 | - | 10% | 40.9 | 0.5 | - | 15 | 114 ± 12 (98.2%) | −19.0 ± 2.1 |
| 14 | - | 10% | 40.9 | - | 0.01 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 15 | - | 10% | 40.9 | - | 0.1 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 16 | - | 10% | 40.9 | - | 0.5 | n.d. ** | - | - |
| 17 | 20% | - | 40.9 | 0.5 | - | 26 | 165 ± 1 (100%) | −46.9 ± 1.2 |
| Samples Name | Tg (°C) | Composition (mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| EPO | 52.1 ± 1.2 | - |
| C71G | 129.5 ± 1.2 | - |
| C2020 | 125.2 ± 1.2 | - |
| C10 | 126.5 ± 1.2 | - |
| NAA-1 | 131.3 ± 1.5 | - |
| C71G/EPO | 132.8 ± 1.2 | 2.12:1 * |
| C2020/EPO | 133.5 ± 1.2 | 1.73:1 * |
| C10/EPO | 134.8 ± 1.1 | 2.11:1 * |
| NAA-1/EPO | 138.5 ± 1.3 | 1.66:1 * |
| IPEC Code | Composition (%, w/w) | ζ (mV) | Dh (nm) | MDF (kPa) | WA (mJ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | NAA1 | C10 | C71G | C2020 | |||||
| 1 | 67 | 33 | - | - | - | 14.7 ± 0.5 | 154 ± 9 (98.0%) | 111 ± 10 | 2611 ± 413 |
| 2 | 50 | 50 | - | - | - | −5.5 ± 2.5 | 154 ± 0 (97.6%) | 100 ± 13 | 1848 ± 335 |
| 3 | 33 | 67 | - | - | - | −16.0 ± 0.4 | 168 ± 4 (96.1%) | 49 ± 6 | 741 ± 33 |
| 4 | 67 | - | 33 | - | - | 7.7 ± 1.0 | 222 ± 9 (94.1%) | 85 ± 20 | 1462 ± 210 |
| 5 | 50 | - | 50 | - | - | −5.1 ± 0.9 | 158 ± 4 (96.2%) | 103 ± 1 | 2154 ± 66 |
| 6 | 33 | - | 67 | - | - | −13.7 ± 0.5 | 149 ± 13 (52.7%) | 45 ± 6 | 643 ± 57 |
| 7 | 67 | - | - | 33 | - | 4.3 ± 1.6 | 195 ± 12 (63.7%) | 94 ± 17 | 1902 ± 322 |
| 8 | 50 | - | - | 50 | - | −47.8 ± 2.7 | 175 ± 17 (97.2%) | 67 ± 31 | 1272 ± 448 |
| 9 | 33 | - | - | 67 | - | −28.8 ± 1.7 | 188 ± 9 (96.4%) | 55 ± 9 | 1010 ± 95 |
| 10 | 67 | - | - | - | 33 | −28.2 ± 4.0 | 166 ± 9 (90.0%) | 89 ± 25 | 656 ± 51 |
| 11 | 50 | - | - | - | 50 | −28.2 ± 3.5 | 192 ± 11 (83.3%) | 43 ± 2 | 678 ± 25 |
| 12 | 33 | - | - | - | 67 | −20.6 ± 1.8 | 225 ± 9 (71.9%) | 57 ± 5 | 802 ± 109 |
| Composition | CP Content (%) | Dh (nm) | ζ (mV) | MDF (kPa) | WA (mJ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretic | Actual | |||||
| CP-IPEC 50:50 | 50 | 53.2 ± 0.3 | 401 ± 295 | −11.3 ± 2.1 | 30 ± 6 | 2530 ± 58 |
| CP-IPEC 60:40 | 60 | 56.1 ± 1.4 | 435 ± 197 | −9.0 ± 1.2 | 22 ± 5 | 2988 ± 110 |
| CP-IPEC 70:30 | 70 | 62.1 ± 5.3 | 431 ± 119 | −10.8 ± 1.2 | 18 ± 2 | 2550 ± 27 |
| CP-IPEC 80:20 | 80 | 79.4 ± 0.2 | 560 ± 116 | 6.8 ± 2.8 | 16 ± 2 | 1400 ± 26 |
| CP-IPEC 90:10 | 90 | 88.5 ± 12.6 | 416 ± 6 | 3.8 ± 2.2 | 15 ± 1 | 820 ± 19 |
| Formulation | Tablet Composition (%w/w) | Dh | Disintegration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | IPEC | Span®80 | DS | Time (s) | Dh (nm) | ζ (mV) | ||
| 1 | CP-IPEC 50:50 | 0.29 | 1.20 | 98.50 | 299 ± 122 (95.6%) | <30 | 323 ± 69 | 1.08 ± 0.16 |
| 2 | CP-IPEC 60:40 | 0.24 | 1.21 | 98.55 | 419 ± 81 | <30 | 363 ± 122 | −0.99 ± 1.25 |
| 3 | CP-IPEC 70:30 | 0.21 | 1.21 | 98.59 | 306 ± 198 | <30 | 350 ± 87 | −4.42 ± 0.46 |
| 4 | CP-IPEC 80:20 | 0.18 | 1.21 | 98.61 | 369 ± 178 | <30 | 448 ± 122 | −2.90 ± 1.64 |
| 5 | CP-IPEC 90:10 | 0.16 | 1.21 | 98.63 | 518 ± 88 | <30 | 356 ± 70 | 3.27 ± 0.60 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garipova, V.R.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Selmin, F.; Cilurzo, F.; Moustafine, R.I. Mucoadhesive Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes for the Buccal Delivery of Clobetasol. Polymers 2018, 10, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010085
Garipova VR, Gennari CGM, Selmin F, Cilurzo F, Moustafine RI. Mucoadhesive Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes for the Buccal Delivery of Clobetasol. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaripova, Venera R., Chiara G. M. Gennari, Francesca Selmin, Francesco Cilurzo, and Rouslan I. Moustafine. 2018. "Mucoadhesive Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes for the Buccal Delivery of Clobetasol" Polymers 10, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010085
APA StyleGaripova, V. R., Gennari, C. G. M., Selmin, F., Cilurzo, F., & Moustafine, R. I. (2018). Mucoadhesive Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes for the Buccal Delivery of Clobetasol. Polymers, 10(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010085