Chitosan Based Self-Assembled Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polyelectrolyte Complexes
2.1. Chitosan Based PEC Nanoparticles and Their Application in Drug Delivery
2.1.1. Chitosan-Alginate PEC Nanoparticles
Plain Complex Coacervation by Mixing Dilute Solutions of CS and ALG
Ionotropic Pregelation of Alginate Followed by Complexation with Chitosan
Oil-in-Water (O/W) Microemulsion of Alginate Followed by Ionotropic Gelation and Further Complexation with Chitosan
2.1.2. Chitosan-Pectin PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.3. Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.4. Chitosan-Carboxymethyl Chitosan PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.5. Chitosan-Chondroitin Sulfate PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.6. Chitosan-Heparin and Chitosan-Hyaluronan PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.7. Chitosan and Poly(γ-Glutamic Acid) PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.8. Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) PEC Nanoparticles
2.1.9. Chitosan PEC Nanoparticles with Other Polyanions
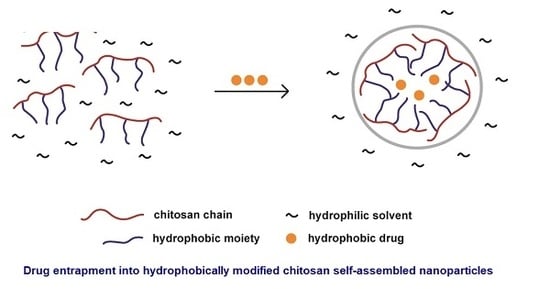
3. Hydrophobic Modification of Chitosan and Derivatives for Self-Assembly
3.1. Hydrophobically Modified Chitosan and Chitosan Oligosaccharides
3.2. Hydrophobically Modified Glycol Chitosan
3.3. Hydrophobically Modified Carboxymethyl Chitosan
3.4. Hydrophobically Modified Succinyl Chitosan
3.5. Hydrophobically Modified Trimethyl Chitosan
3.6. Other Hydrophobically Modified Chitosan Derivatives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, G.A.F. (Ed.) Structure of Chitin and Chitosan. In Chitin Chemistry; Macmillan: Houndmills, UK, 1992; pp. 1–53. ISBN 978-1-349-11547-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dasha, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A Versatile Semi-Synthetic Polymer in Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengíbar, M.; Harris, R.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Calderón, L.; Sánchez, A.; Heras, A. Role of Physicochemical Properties of Chitin and Chitosan on Their Functionality. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2014, 8, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Izumi, R.; Osaki, T.; Ifuku, S.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H.; Minami, S.; Okamoto, Y. Chitin, Chitosan, and Its Derivatives for Wound Healing: Old and New Materials. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 104–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illum, L.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Fisher, A.N.; Davis, S.S. Chitosan as a Novel Nasal Delivery System for Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 51, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chan, J.W.; Moretti, A.; Uhrich, K.E. Designing polymers with sugar-based for bioactive delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, C.; Gogoi, P.; Maji, T.K. Chitosan: A Promising Biopolymer in Drug Delivery Applications. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.; Muzzarelli, R.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Vimal, A.; Kumar, A. Why Chitosan? From Properties to Perspective of Mucosal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Anaya, L.M.; Soltero, J.F.A.; Rinaudo, M. DNA/Chitosan Electrostatic Complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jata, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Novel Hydrophilic Chitosan-Polyethylene Oxide Nanoparticles as Protein Carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Laouini, A.; Fessi, H.; Charcosset, C. Preparation of Chitosan–Tpp Nanoparticles Using Microengineered Membranes—Effect of Parameters and Encapsulation of Tacrine. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 482, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, L.T.K.; Wang, S.-L.; Hiep, Ð.M.; Luong, P.M.; Vui, N.T.; Ðinh, T.M.; Dzung, N.A. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles by Spray Drying, and Their Antibacterial Activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegger, B.R.; Bäurer, B.; Mirzayeva, A.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Bach, M. Systematic Approach for Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles via Emulsion Crosslinking as Potential Adsorbent in Wastewater Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.G.; Lee, C.M.; Park, H.J. O/W Emulsification for the Self-Aggregation and Nanoparticle Formation of Linoleic Acids Modified Chitosan in the Aqueous System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3135–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafshgari, M.H.; Khorram, M.; Mansouri, M.; Samimi, A.; Osfouri, S. Preparation of Alginate and Chitosan Nanoparticles Using a New Reverse Micellar System. Iran. Polym. J. 2012, 21, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumitsu, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Fukumori, Y. Chitosan Gadopentetic Acid Complex for Gadolinium Neutron-Capture Therapy of Cancer Nanoparticles: Preparation by Novel Emulsion-Droplet Coalescent Technique and Characterization. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shering, M.A.; Kannan, C.; Kumar, K.S.; Kumar, V.S.; Suganeshwari, M. Formulation of 5-Fluorouracil Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles by Emulsion Droplet Coalescence Method for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 2011, 2, 926–931. [Google Scholar]
- Luque-Alcaraz, A.G.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Arguelles-Monal, W. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation and Their Ability as a Drug Nanocarrier. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59250–59256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y. Self-Assembled Lecithin/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery: Preparation and Functional Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, V.B.V.; Yoshida, C.M.P.; Pereira, S.M.S.S.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Franco, T.T. Electrostatic Self-Assembled Chitosan-Pectin Nano- and Microparticles for Insulin Delivery. Molecules 2017, 22, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehn, J.-M. Perspectives in Supramolecular Chemistry—From Molecular Recognition towards Molecular Information Processing and Self-Organization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1990, 29, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateescu, M.A.; Ispas-Szabo, P.; Assaad, E. The Concept of Self-Assembling and the Interactions Involved. In Controlled Drug Delivery. The Role of Self-Assembling Multi-Task Excipients, 1st ed.; Mateescu, M.A., Ispas-Szabo, P., Assaad, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-1-907568-45-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M. Advances in Self-Assembled Chitosan Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.-C.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, L.-L.; Yang, Q.; Lu, H.-Y. Novel Amphiphilic Folic Acid-Cholesterol-Chitosan Micelles for Paclitaxel Delivery. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Li, W.; Yu, C.; Zhao, C.; Jin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Dong, S.; Lu, X. Amphiphilically Modified Chitosan Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanphan, W.; Choofong, S.; Rimdusit, P. Deoxycholate-Chitosan Nanospheres Fabricated by γ-Irradiation and Chemical Modification: Nanoscale Synthesis and Controlled Studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 123, 3309–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Longobardi, L.; Granero-Molto, F.; Myers, T.J.; Yan, Y.; Spagnoli, A. Use of Glycol Chitosan Modified by 5β-Cholanic Acid Nanoparticles for the Sustained Release of Proteins During Murine Embryonic Limb Skeletogenesis. J. Control. Release 2010, 144, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yhee, J.Y.; Son, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C. Self-Assembled Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles for Disease-Specific Theranostics. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalve, Y.; Sierra, L.; López, B.L. Preparation and Characterization of Succinyl-Chitosan Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Macromol. Symp. 2015, 354, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.H. Chitosan Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes as Potential Carrier Materials in Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanov, V. Fundamentals of Polyelectrolyte Complexes in Solution and the Bulk. In Multilayer Thin Films: Sequential Assembly of Nanocomposite Materials; Decher, G., Schlenoff, J.B., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 47–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida, E.; Osada, Y.; Ohno, H. Formation of Interpolymer Complexes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1980, 17, 683–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Recent Development of Chitosan-Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes with Natural Polysaccharides for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, N.; Shimoda, K. Macromolecule Complexes of Chitosan. In Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility, 2nd ed.; Dumitriu, S., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 679–706. [Google Scholar]
- Peniche, C.; Argüelles-Monal, W. Chitosan Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 168, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, M. Chitosan/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Polyelectrolyte Complex Scaffolds for Pulp Cells Regeneration. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2007, 22, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, H.; Kikuchi, Y. Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose with Chitosan. Makromol. Chem. 1979, 180, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharabasy, A.M.; Moghannem, S.A.; El-Mazny, W.N. Physical Preparation of Alginate/Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complexes for Biomedical Applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, G.F.; Frade, M.A.C.; Andrade, T.A.M.; Leite, M.N.; Bueno, C.Z.; Moraes, A.M.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. Chitosan-Alginate Membranes Accelerate Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, A.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Peniche, C. Diffusion through Membranes of the Polyelectrolyte Complex of Chitosan and Alginate. Macromol. Biosci. 2003, 3, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, W.H.; Ha, W.S. Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Sodium Alginate with Chitosan or Its Derivatives for Microcapsules. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæther, H.V.; Holme, H.K.; Maurstad, G.; Smidsrød, O.; Stokke, B.T. Polyelectrolyte Complex Formation Using Alginate and Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavasit, V.; Kienzle-Sterzer, C.; Torres, J.A. Formation and Characterization of an Insoluble Polyelectrolyte Complex Chitosan-Polyacrylic Acid. Polym. Bull. 1988, 19, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, H.C.; Fonseca, J.L.; Pereira, M.R. Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes: Preparation, Characterization and Permeability Studies. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arguelles-Monal, W.; Cabrera, G.; Peniche, C.; Rinaudo, M. Conductometric Study of the Inter-Polyelectrolyte Reaction between Chitosan and Poly(Galacturonic Acid). Polymer 1999, 41, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabe, P.; Peniche, C.; Argüelles-Monal, W. Swelling Behavior of Chitosan/Pectin Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes. Effect of Thermal Cross-Linking. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, B.; Bigucci, F.; Abruzzo, A.; Corace, G.; Cerchiara, T.; Zecchi, V. Freeze-Dried Chitosan/Pectin Nasal Inserts for Antipsychotic Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.D.; Tu, H.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, J.W.; Liu, J. pH-Sensitivity of the Swelling of a Chitosan-Pectin Polyelectrolyte Complex. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1997, 245, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguelles-Monal, W.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Lizardi, J.; Peniche, C.; Higuera-Ciapara, I. Chitin and Chitosan in Gel Network Systems. In Acs Symposium Series; Bohidar, H., Dubin, P., Osada, Y., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 102–121, ISBN13 9780841237612; eISBN 9780841219342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.N.; Novaes, D.S.; Rabelo, R.B.; Celebi, P.; Chevallier, D.; Mantovani, M.; Beppu, R.S.; Vieira, R.S. Bsa and Fibrinogen Adsorption on Chitosan/κ-Carrageenan Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.F.; Piai, J.F.; Schuquel, I.T.A.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Chitosan/Heparin and N,N,N-Trimethyl Chitosan/Heparin Obtained at Different pH: I. Preparation, Characterization, and Controlled Release of Heparin. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpa, S.; Srinivasan, R. Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Glycol Chitosan with Some Mucopolysaccharides: Dielectric Properties and Electric Conductivity. Biopolymers 1984, 23, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, O.; Koseva, N.; Manolov, N.; Rashkov, I. Polyelectrolyte Complex between Chitosan and Poly(2-Acryloylamido-2-Methylpropanesulfonic Acid). Polym. Bull. 1999, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berth, G.; Voig, A.; Dautzenberg, H.; Donath, E.; Moehwald, H. Polyelectrolyte Complexes and Layer-by-Layer Capsules from Chitosan/Chitosan Sulfate. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamzazade, A.I.; Nasibov, S.M. Formation and Properties of Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Chitosan Hydrochloride and Sodium Dextran sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 50, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Radzi, R.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Minami, S. Characterization of Chitosan-Carboxymethyl Dextran Nanoparticles as a Drug Carrier and as a Stimulator of Mouse Splenocytes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 1401–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Delair, T. Stabilization of Chitosan/Hyaluronan Colloidal Polyelectrolyte Complexes in Physiological Conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 119, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalevée, G.; Sudre, G.; Montembault, A.; Meadows, J.; Malaise, S.; Crépet, A.; David, L.; Delair, T. Polyelectrolyte Complexes Via Desalting Mixtures of Hyaluronic Acid and Chitosan. Physicochemical Study and Structural Analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateescu, M.A.; Ispas-Szabo, P.; Assaad, E. Chitosan-Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes as Pharmaceutical Excipients. In Controlled Drug Delivery. The Role of Self-Assembling Multi-Task Excipients, 1st ed.; Mateescu, M.A., Ispas-Szabo, P., Assaad, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 127–161. ISBN 978-1-907568-45-9. [Google Scholar]
- Peniche, H.; Peniche, C. Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Contribution to Nanomedicine. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zen, Z.W.; Xiao, R.Z.; Xie, T.; Zhou, G.L.; Zhan, X.R.; Wang, S.L. Recent Advances of Chitosan Nanoparticles as Drug Carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, B.; Bruheim, O.; Espevik, T.; Smidsrød, O.; Soon-Shiong, P.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Alginate Polycation Microcapsules I. Interaction between Alginate and Polycation. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, J.P.; van der Linden, E.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Sagis, L.M.C. Preparation Methods of Alginate Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, X. Facile Preparation of Well-Defined near-Monodisperse Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles (Cs/Sal Nps) Via Ionotropic Gelification: A Suitable Technique for Drug Delivery Systems. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuwavila, N.P.; Perera, A.D.L.C.; Samarakoon, S.R.; Soysa, P.; Karunaratne, V.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Karunaratne, D.N. Chitosan-Alginate Nanoparticle System Efficiently Delivers Doxorubicin to Mcf-7 Cells. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Gupta, S.; Narang, R.K.; Budhiraja, R.D. Amoxicillin Loaded Chitosan-Alginate Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles as Mucopenetrating Delivery System for H. Pylori. Sci. Pharm. 2011, 79, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goycoolea, F.M.; Lollo, G.; Remuñán-López, C.; Quaglia, F.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan-Alginate Blended Nanoparticles as Carriers for the Transmucosal Delivery of Macromolecules. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.A.; Bourbon, A.I.; Vicente, A.A.; Cerqueira, M.A. Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Vitamin B2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunchu, S.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Rojsitthisak, P. Effects of Preparation Parameters on the Characteristics of Chitosanealginate Nanoparticles Containing Curcumin Diethyl Disuccinate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 28, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motwani, S.K.; Chopra, S.; Talegaonkar, S.; Kohli, K.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K. Chitosan-Sodium Alginate Nanoparticles as Submicroscopic Reservoirs for Ocular Delivery: Formulation, Optimisation and in Vitro Characterisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Su, M.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Meng, F.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Z. Synthesis of Thiolated Chitosan and Preparation Nanoparticles with Sodium Alginate for Ocular Drug Delivery. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Sampaio, P.; Neufeld, R.; Ferreira, D. Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles Are Effective for Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Chauhan, N.; Gopal, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N. Development and Evaluation of Alginate-Chitosan Nanocapsules for Controlled Release of Acetamiprid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazori, T.; Khoshayan, M.R.; Azizi, E.; Yazdizade, P.; Nomani, A.; Haririan, I. Evaluation of Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles as Antisense Delivery Vector: Formulation, Optimization and in Vitro Characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, A.; Alimohammadian, M.H.; Gazori, T.; Riazi-rad, F.; Fatemi, S.M.R.; Parizadeh, A.; Haririan, I.; Havaskary, M. Comparison of Chitosan, Alginate and Chitosan/Alginate Nanoparticles with Respect to Their Size, Stability, Toxicity and Transfection. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsutthiwong, P.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Nimmannit, U. Preparation of Turmeric Oil-Loaded Chitosan-Alginate Biopolymeric Nanocapsules. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 29, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebinişan, D.; Holban, M.; Şunel, V.; Popa, M.; Desbrieres, J.; Lionte, C. Novel Acyl Derivatives of N-(P-Aminobenzoyl)-l-Glutamine Encapsulated in Polymeric Nanocapsules with Potential Antitumoral Activity. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 571–577. Available online: http://www.cellulosechemtechnol.ro/pdf/CCT45,9-10%282011%29/p.571-577.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Wang, T.; He, N. Preparation, Characterization and Applications of Low-Molecular-Weight Alginate-Oligochitosan Nanocapsules. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marudova, M.; MacDougall, A.J.; Ring, S.G. Pectin-Chitosan Interactions and Gel Formation. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.A.; Kök, S.M.; Harding, S.E.; Adams, G. Polysaccharide Drug Delivery Systems Based on Pectin and Chitosan. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2010, 27, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, N.P.; Schiffman, J.D. Characterization of Self-Assembled Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles Formed from Chitosan and Pectin. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3441–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Bellich, B.; Blasi, P.; Virgilio, F.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan-Pectin Hybrid Nanoparticles Prepared by Coating and Blending Techniques. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 84, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Azi, O.S.M.; Tan, Y.T.F.; Wong, T.W. Transforming Large Molecular Weight Pectin and Chitosan into Oral Protein Drug Nanoparticulate Carrier. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 84, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriani, Y.; Grasianto; Siswanta; Mudasir. Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Chitosan-Pectin Nanoparticles as a Potential Carrier for Curcumin Delivery and Its In Vitro Release Study. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2015, 7, 167–173. Available online: http://www.arjournals.org/index.php/ijdd/article/view/1775/pdf (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Wan, H.; Yang, B.; Sun, H. Pectin-Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles for Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Nisin. Am. J. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A.; Fresneau, M.P.; Marazuela, A.; Fabra, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, C.; Lucas, J.M.; Viton, C.; Domard, A.; Pichot, C.; Delair, T. Formation and Properties of Positively Charged Colloids Based on Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Biopolymers. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7766–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delair, T. Colloidal Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Chitosan and Dextran Sulfate Towards Versatile Nanocarriers of Bioactive Molecules. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, M.; Vitharana, S.N.; Peek, L.J.; Coop, T.; Berkland, C. Polyelectrolyte Complexes Stabilize and Controllably Release Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiyaboonchai, W.; Limpeanchob, N. Formulation and Characterization of Amphotericin B-Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Berkland, C. Controlled Release of Repifermin® from Polyelectrolyte Complexes Stimulates Endothelial Cell Proliferation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Benson, H.A.E.; Mukkur, T.K.S.; Rigby, P.; Chen, Y. Preliminary Studies on the Development of Iga-Loaded Chitosan-Dextran Sulphate Nanoparticles as a Potential Nasal Delivery System for Protein Antigens. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Drogoz, A.; David, L.; Domard, A.; Charles, M.-H.; Verrier, B.; Delair, T. Polysaccharide-Based Vaccine Delivery Systems: Macromolecular Assembly, Interactions with Antigen Presenting Cells, and in Vivo Immunomonitoring. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogoz, A.; Munier, S.; Verrier, B.; David, L.; Domard, A.; Delair, T. Towards Biocompatible Vaccine Delivery Systems: Interactions of Colloidal Pecs Based on Polysaccharides with Hiv-1 P24 Antigen. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyasan, W.; Praputbut, S.; Kompella, U.B.; Srinivas, S.P.; Tiyaboonchaia, W. Penetration of Mucoadhesive Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles into the Porcine Cornea. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 149, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mohanraj, V.J.; Wang, F.; Benson, H.A.E. Designing Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles Using Charge Ratios. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Ferreira, D. Development and Characterization of New Insulin Containing Polysaccharide Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2006, 53, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Ferreira, D.; Neufeld, R. Oral Bioavailability of Insulin Contained in Polysaccharide Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3054–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Shi, R.; Ben Borgens, R. Chitosan Nanoparticle-Based Neuronal Membrane Sealing and Neuroprotection Following Acrolein Induced Cell Injury. J. Biol. Eng. 2010, 4, 2. Available online: http://www.jbioleng.org/content/4/1/2 (accessed on 25 January 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboktakin, M.R.; Tabatabaie, R.M.; Maharramovb, A.; Ramazanov, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of pH-Dependent Glycol Chitosan and Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles for Effective Brain Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.D.; Vanjari, Y.H.; Sancheti, K.H.; Patel, H.M.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Surana, S.J.; Pardeshi, C.V. New Nasal Nanocomplex Self-Assembled from Charged Biomacromolecules: N,N,N-Trimethyl Chitosan and Dextran Sulphate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, A.; Rani, V.V.D.; Krishna, R.; Sreeja, V.; Selvamurugan, N.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Studies of Chitosan, O-Carboxymethyl and N,O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snima, K.S.; Jayakumar, R.; Unnikrishnan, A.G.; Nair, S.V.; Lakshmanan, V.-K. O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles for Metformin Delivery to Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, A.; Maya, S.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Tamurab, H.; Jayakumar, R. Efficient Water Soluble O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanocarrier for the Delivery of Curcumin to Cancer Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Xia, G.; Bao, Z.; Feng, C.; Cheng, X.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Chitosan Based Nanoparticles as Protein Carriers for Efficient Oral Antigen Delivery I. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourya, V.K.; Inamdar, N.N.; Tiwari, A. Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Its Applications. Adv. Mat. Lett. 2010, 1, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Cheng, X.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Chen, X. Positive/Negative Surface Charge of Chitosan Based Nanogels and Its Potential Influence on Oral Insulin Delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, D.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Mechanism of Surface Charge Triggered Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Opening Upon Chitosan Nanoparticles for Insulin Oral Delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Kong, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Chitosan/O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles for Efficient and Safe Oral Anticancer Drug Delivery: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Park, H.; Cha, D.; Kong, M.; Chen, X. Transport Mechanism of Doxorubicin Loaded Chitosan Based Nanogels across Intestinal Epithelium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Lopes, L.C.; Valente, A.J.M.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Effect of Stoichiometry and pH on the Structure and Properties of Chitosan/Chondroitin Sulfate Complexes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umerska, A.; Corrigan, O.I.; Tajber, L. Design of Chondroitin Sulfate-Based Polyelectrolyte Nanoplexes: Formation of Nanocarriers with Chitosan and a Case Study of Salmon Calcitonin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, J.P.; Cousse, H.; Neuzil, E. Biochemical Basis of the Pharmacologic Action of Chondroitin Sulfates on the Osteoarticular. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 31, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.-Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Li, P.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Huang, S.-J.; Wang, L.-F. Antitumor Efficacy of Doxorubicin Released from Crosslinked Nanoparticulate Chondroitin Sulfate/Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhai, G. Chondroitin Sulfate-Based Nanocarriers for Drug/Gene Delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, V.E.; Gomes, M.E.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Chitosan-Chondroitin Sulfate Nanoparticles for Controlled Delivery of Platelet Lysates in Bone Regenerative Medicine. J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 2012, 6, s47–s59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.-S.; Chiang, C.-H.; Hong, P.-D.; Yeh, M.-K. Influence of Charge on Fitc-Bsa-Loaded Chondroitin Sulfate-Chitosan Nanoparticles upon Cell Uptake in Human Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4861–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, Z.; Capila, I.; Venkataraman, G.; Sasisekharan, R. Heparin and Heparan Sulfate: Analyzing Structure and Microheterogeneity. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 207, pp. 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, K.-H.; Park, S.R.; Min, B.-H. Chitosan/Heparin Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles (100~200 nm) Covalently Bonded with Pei for Enhancement of Chondrogenic Phenotype. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 342, pp. 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalat, M.; Alcouffe, P.; David, L.; Delair, T. Controlling the Complexation of Polysaccharides into Multi-Functional Colloidal Assemblies for Nanomedicine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peniche, H.; Reyes, F.; Aguilar, M.R.; Rodríguez, G.; Abradelo, C.; García, L.; Peniche, C.; Román, J.S. Thermosensitive Macroporous Cryogels Functionalized With Bioactive Chitosan/Bemiparin Nanoparticles. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.T.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wu, M.F.; Wang, J.L.; Young, T.H.; Han, J.L.; Hsieh, K.H. Evaluation of Chitosan/γ-Poly(Glutamic Acid) Polyelectrolyte Complex for Wound Dressing Materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-T.; Liang, H.-F.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Lee, P.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Sung, H.-W. Novel Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery via the Paracellular Pathway. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, I.; Bodnár, M.; Filipcsei, G.; Hartmann, J.F.; Daróczi, L.; Zrínyi, M.; Borbély, J. Nanoparticles Prepared by Self-Assembly of Chitosan and Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008, 295, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-N.; Wey, S.-P.; Juan, J.-H.; Sonaje, K.; Ho, Y.-C.; Chuang, E.-Y.; Hsu, C.-W.; Yen, T.-C.; Lin, K.-J.; Sung, H.-W. The Glucose-Lowering Potential of Exendin-4 Orally Delivered via a pH-Sensitive Nanoparticle Vehicle and Effects on Subsequent Insulin Secretion in Vivo. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sonaje, K.; Li, K.M.; Juang, J.-H.; Mi, F.-L.; Yang, H.-W.; Sung, H.-W. Multi-Ion-Crosslinked Nanoparticles with pH-Responsive Characteristics for Oral Delivery of Protein Drugs. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Lin, Y.-H.; Juang, J.-H.; Wey, S.-P.; Chen, C.-T.; Sung, H.-W. In Vivo Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2329–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.E.S.; Sandoval-Herrera, I.E.; Zavala-Betancourt, S.A.; Oliveira, H.C.; Ledezma-Pérez, A.S.; Romero, J.; Fraceto, L.F. γ-Polyglutamic Acid/Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Plant Growth Regulator Gibberellic Acid: Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, Y.; Ge, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Che, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Y. Microstructure Formation and Property of Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanoparticles Prepared by Macromolecular Complex. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidenko, N.; Blanco, M.D.; Peniche, C.; Becherán, L.; Guerrero, S.; Teijón, J.M. Effects of Different Parameters on the Characteristics of Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanoparticles Obtained by the Method of Coacervation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherán, L.; Bocourt, M.; Pérez, J.; Peniche, C. Chitosan in Biomedicine. From Gels to Nanoparticles. In Advances in Chitin Science, Proceeding of the 6th Iberoamerican Chitin Symposium and 12th International Conference on Chitin and Chitosan, VI SIAQ/XII ICCC, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2–5 September 2012; Campana, S.P., Masumi, M.M., Flamingo, A., Eds.; São Carlos-IQSC: São Carlos, Brasil, 2014; pp. 217–224. ISBN 078-85-63191-03-8 (v1.4). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-W.; Hon, M.-H. Polyion Complex Nanofibrous Structure Formed by Self-Assembly of Chitosan and (Acrylic Acid). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-M. Effect of Experimental Parameters on the Formation of Chitosan-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanofibrous Scaffolds and Evaluation of Their Potential Application as DNA Carrier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, H.-C.; Misran, M. Preparation and Characterization of pH Dependent Κ-Carrageenan-Chitosan Nanoparticle as Potential Slow Release Delivery Carrier. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Grenha, A. Chitosan/Carrageenan Nanoparticles: Effect of Cross-Linking with Tripolyphosphate and Charge Ratios. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ahuja, M. Carboxymethyl Gum Kondagogu-Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles: Preparation and Characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, M.; Xue, J.; Luo, Y. Formation of Redispersible Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles from Gallic Acid-Chitosan Conjugate and Gum Arabic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Raja, M.A.; Zeenat, S.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation and Characterization of Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles Based on Poly (Malic Acid), Chitosan. A pH-Dependent Delivery System. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Ni, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, G. Preparation of Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles of Chitosan and Poly(2-Acry1amido-2-Methylpropanesulfonic Acid) for Doxorubicin Release. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 58, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, J.; Guillet, P.; Schumers, J.-M.; Duhem, N.; Prèat, V.; Gohy, J.-F. Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles from Chitosan and Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Polystyrene-Block-Poly(Acrylic Acid). J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4484–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jo, W.H.; Jeong, S.Y. Preparation of chitosan self-aggregates as a gene delivery system. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Gihm, S.H.; Park, C.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Kwon, I.C.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S.Y. Structural Characteristics of Size-Controlled Self-Aggregates of Deoxycholic Acid-Modified Chitosan and Their Application as a DNA Delivery Carrier. Bioconjugate Chem. 2001, 12, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Liu, L.-R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Self-aggregated nanoparticles of cholesterol-modified chitosan conjugate as a novel carrier of epirubicin. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled nanoparticles of 6-O-cholesterol-modified chitosan for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Ren, G.F.; Yuan, H.; Du, Y.Z.; Zeng, S. Shell cross-linked stearic acid grafted chitosan oligosaccharide self-aggregated micelles for controlled release of paclitaxel. Colloids Surf. B 2006, 50, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.-Q.; Wu, X.-L.; Du, Y.-Z.; You, J.; Yuan, H. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of shell crosslinked stearic acid-grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles encapsulating doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.Q.; Yang, F.L.; Hu, F.Q.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H.; Yu, H.Y. Core-modified chitosan-based polymeric micelles for controlled release of doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.-Q.; Liu, L.-N.; Du, Y.-Z.; Yuan, H. Synthesis and antitumor activity of doxorubicin conjugated stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide polymeric micelles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6955–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, H. Polymeric micelle composed of PLA and chitosan as a drug carrier. J. Polym. Res. 2009, 16, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, J.T.; Park, H.J. Size-controlled self-aggregated N-acyl chitosan nanoparticles as a vitamin C carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, J.P.; Gothelf, K.V.; Kjems, J.; Caballero, A.M.H.; Schmidt, C.; Covas, C.P. N,O6-partially acetylated chitosan nanoparticles hydrophobically-modified for controlled release of steroids and vitamin E. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Chaidedgumjorn, A.; Rojanarata, T.; Apirakaramwong, A.; Phongying, S.; Choochottiros, C.; Chirachanchai, S. Incorporation of camptothecin into N-phthaloyl chitosan-g-mPEG self-assembly micellar system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Choochottiros, C.; Chirachanchai, S. Camptothecin-incorporating N-phthaloylchitosan-g-mPEG self-assembly micellar system: Effect of degree of deacetylation. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 60, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Choochottiros, C.; Chirachanchai, S. N-Phthaloylchitosan-g-mPEG design for all-trans retinoic acid-loaded polymeric micelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, F.; Jia, L.; Yu, W.; Liu, M. Self-assembled micelles of N-phthaloychitosan-g-polyvinylpyrrolidone for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Yaping, L.; Huang, J. Fabrication of cationic nanomicelle from chitosan-graft-polycaprolactone as the carrier of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 76, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Xiang, L.; Chen, Y. Preparation of self-assembled nanoparticles of chitosan oligosaccharide-graft-polycaprolactone as a carrier of bovine serum albumin drug. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Silva, D.; Goncalves, V.; Sarmento, B. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-grafted-polycaprolactone micelles for modulate intestinal paclitaxel delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Le, V.; Lang, M.; Liu, J. Preparation of polysaccharide derivates chitosan-graft-poly(varepsilon-caprolactone) amphiphilic copolymer micelles for 5-fluorouracil drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 116, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, M.A.; Arif, M.; Feng, C.; Zeenat, S.; Liu, C.G. Synthesis and evaluation of pH-sensitive, self-assembled chitosan-based nanoparticles as efficient doxorubicin carriers. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 31, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, Y.-H. Tumor targetability and antitumor effect of docetaxel-loaded hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.H.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, S.M.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.G.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K.; et al. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles-encapsulated camptothecin enhance the drug stability and tumor targeting in cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Oh, Y.-K.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. Tumor-homing glycol chitosan/polyethylenimine nanoparticles for the systemic delivery of siRNA in tumor-bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2010, 144, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Nam, J.-O.; Park, R.-W.; Chung, H.; Seo, S.B.; Kim, I.-S.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on glycol chitosan bearing 5β-cholanic acid for RGD peptide delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-M.; Li, Y.-J.; Qiu, L.-Y.; Jin, Y. Self-aggregated nanoparticles of cholesterol-modified glycol chitosan conjugate: Preparation, characterization, and preliminary assessment as a new drug delivery carrier. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, B.S.; Chi, S.C.; Park, E.S.; Lee, K.C.; Youn, Y.S. Self-assembled glycol chitosan nanogels containing palmityl-acylated exendin-4 peptide as a long-acting anti-diabetic inhalation system. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiñones, J.P.; Gothelf, K.V.; Kjems, J.; Caballero, A.M.H.; Schmidt, C.; Covas, C.P. Self-assembled nanoparticles of glycol chitosan—Ergocalciferol succinate conjugate, for controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, J.P.; Gothelf, K.V.; Kjems, J.; Yang, C.; Caballero, A.M.H.; Schmidt, C.; Covas, C.P. Self-assembled nanoparticles of modified-chitosan conjugates for the sustained release of dl-α-tocopherol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiñones, J.P.; Gothelf, K.V.; Kjems, J.; Heras, A.; Schmidt, C.; Peniche, C. Novel Self-assembled Nanoparticles of Testosterone-Modified Glycol Chitosan and Fructose Chitosan for Controlled Release. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2013, 3, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Min, K.H.; Min, D.S.; Kim, A.Y.; Lee, C.-M.; Cho, Y.W. Hydrotropic oligomer-conjugated glycol chitosan as a carrier of paclitaxel: Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo biodistribution. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.M.; Oh, K.T.; Baik, H.J.; Lee, B.R.; Lee, A.H.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. A self-organized 3-diethylaminopropyl-bearing glycol chitosan nanogel for tumor acidic pH targeting: In vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 78, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.J.; Jang, J.-S.; Cho, Y.W.; Chung, H.; Park, R.-W.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, J.Y.; Seo, S.B.; Park, C.R.; Jeong, S.Y. Biodistribution and anti-tumor efficacy of doxorubicin loaded glycol-chitosan nanoaggregates by EPR effect. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Chen, X.; Ren, G. The preparation and characterization of a novel amphiphilic oleoyl-carboxymethyl chitosan self-assembled nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.J.; Dang, Q.F.; Ma, F.K.; Chen, X.G.; Park, H.J.; Kim, B.K. Preparation and evaluation of oleoyl-carboxymethy-chitosan(OCMCS) nanoparticles as oral protein carriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Meng, X.; Park, H.J. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on linoleic-acid modified carboxymethyl-chitosan as carrier of adriamycin (ADR). Curr. Appl. Phys. 2007, 7, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangyang, X.; Ling, L.; Jianping, Z.; Shiyue, L.; Jir, Y.; Xiaojin, Y.; Jinsheng, R. Preparation and characterization of N-succinyl-N′-octyl chitosan micelles as doxorubicin carriers for effective anti-tumor activity. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 55, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.P.; Yuan, L.H.; Chen, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, F. Interactions between N-succinyl-chitosan and bovine serum albumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ding, Y.; Yu, L.L.; Ping, Q. Polymeric micelle systems of hydroxycamptothecin based on amphiphilic N-alkyl-N-trimethyl chitosan derivatives. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 55, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bei, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.F.; You, B.G.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Chen, W.L.; Xia, P.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X.J.; Zhu, Q.L.; et al. Application of the central composite design to optimize the preparation of novel micelles of harmine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.F.; You, B.G.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Chen, W.L.; Xia, P.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X.J.; Zhu, Q.L.; et al. Novel self-assembled micelles based on palmitoyl-trimethyl-chitosan for efficient delivery of harmine to liver cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Sonaje, K.; Ho, Y.C.; Chen, C.T.; Juang, J.H.; Sung, H.W. Oral delivery of peptide drugs using nanoparticles self-assembled by poly(gamma-glutamic acid) and a chitosan derivative functionalized by trimethylation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Jin, X.; Li, N.; Ju, C.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.; Ping, Q. The mechanism of enhancement on oral absorption of paclitaxel by N-octyl-O-sulfate chitosan micelles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4609–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qu, G.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X.; Yao, Z.; Guo, Q.; Ding, Q.; Yuan, S.; Shen, Z.; Ping, Q.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, efficacy and safety of N-octyl-O-sulfate chitosan micelles loaded with paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, G.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Ping, Q. PEG conjugated N-octyl-O-sulfate chitosan micelles for delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 37, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, R.D.O.; Pereira, S.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Schmitt, C.C.; Neumann, M.G. Self-aggregated nanoparticles of N-dodecyl,N′-glycidyl(chitosan) as pH-responsive drug delivery systems for quercetin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Procedure | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex coacervation | ||||
| CS added into ALG CS into ALG-DOX | Ibuprofen Dipyridamole | 320 to 700 b | +6.34 b to –44.5 b,* | [67] |
| Gatifloxacin a | 347 c | +38.6 c | [73] | |
| Doxorubicin | 100 ± 28 b | +36 ± 3 b | [68] | |
| 100 ± 35 c | +35 ± 4 c | |||
| ALG added into CS ALG into Thiolated CS | Amoxicillin a | 264 to >601 | + 35 to + 61.9 | [69] |
| Fluorescein | 338 ± 16 b | +34 ± 8 b | [74] | |
| isothiocyanate | 266 ± 7 c | +30 ± 4 c | ||
| Fluorescein | 338 ± 16 b | +34 ± 8 b | ||
| isothiocyanate | 266 ± 7 c | +30 ± 4 c | ||
| ALG + TPP added into CS | Insulin | 260–525 | +41 to +50 | [70] |
| Ionotropic pregelation of alginate plus PEC coating with CS | ||||
| CS into Ca/(ALG + drug) | Insulin | 781 ± 61 b | −15 ± 2 b | [75] |
| 748 ± 217 | −6 ± 2 c | |||
| Vitamin-B2 | 120 ± 50 b | −30.9 ± 0.5 b | [71] | |
| 104 ± 67 c | −29.6 ± 0.1 c | |||
| Acetamiprid | 201.5 | −32.1 | [76] | |
| CS + EGF into Ca/ALG | EGF-antisense a | 194–1435 | ~+30 | [77] |
| CS + plasmid into Ca/ALG | pEGFP plasmid | 161 | +29.3 | [78] |
| o/w ALG microemulsion followed by ionotropic gelation and further complexation with CS | ||||
| Turmeric oil | 522–667 | −21.8 to −22.2 | [79] | |
| A.A. | 400 | [80] | ||
| CDD | 410 ± 20 | 22 ± 1 | [72] | |
| LMWAlg + OligoCS | BSA | 134–229 | [81] | |
| Procedure | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex coacervation | ||||
| Pectin added into CS | Insulin | 441 ± 32 a | [86] | |
| 580–896 b | +62 ± 3 b | |||
| * 650 ± 86 b | +33 ± 4 b | |||
| Curcumin | 10–59 (dry NPs) | [87] | ||
| Insulin | 1175–2618 a | −22.5 to +35.0 a | [23] | |
| 964–2510 b | −22.4 to +33.2 b | |||
| Nisin | 301–712 b | [88] | ||
| None | 560–1000 | +20 to +26 | [84] | |
| CS added into Pectin | None | 460–1110 | +19 to +28 | [84] |
| Combined ionotropic gelation and complex coacervation | ||||
| Pectin + TPP added into CS | Insulin | 375–7239 | +10.6 to +32.7 | [86] |
| CS added into Pectin + TPP | OVA | 250–750 a | −20 to −29 a | [85] |
| CS + TPP added into Pectin | BSA | 200–400 a | −15 to −45 a | [85] |
| 700–1250 b | −38 b | |||
| Ionotropic pregelation of pectin plus PEC coating with CS | ||||
| CS added into Pectin + CaCl2 | OVA | 419 a | −30.4 a | [84] |
| 302–409 b | −21.9 to −26.0 b | |||
| Procedure | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex coacervation | ||||
| DS added into CS | >244 a | −47.1 to −60 a | [99] | |
| BSA | 478–1138 b | −28.0 to +56.4 b | ||
| Rhodamine 6G | 245–3521 b | −31.0 to +34.0 b | ||
| CS added into DS | Insulin | 489–665 b | −0.4 to −21.5 b | [100] |
| 527–1577 b | −20.6 to +11.5 b | [101] | ||
| Amphotericin B | 616–891 a | [93] | ||
| 644–1040 b | −27 to −37 | |||
| REPIFERMIN® | 239 | −18.4 | [94] | |
| 306 | −15.5 | |||
| Mixing with agitation | Hydralazine | 290 ± 60 a | −7 ± 4 a | [102] |
| 340 ± 50 b | −5 ± 1 b | |||
| Hydrophobic moiety | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| deoxycholic acid | DNA | 162 ± 18 a | [145] | |
| ~300 b | ||||
| 130–300 a | [146] | |||
| cholesterol | Epirubicin | 417 ± 18 a | [147] | |
| 338–473 b | ||||
| 6-O-cholesterol | All-trans retinoic acid | 100–240 a | +24.5 to +25.9 a | [148] |
| 192–222 b | ||||
| stearyl | Paclitaxel | 28.1–74.6 a | +39.0 to +53.2 a | [149] |
| 35.8–175.1 b | +44.0 to +58.7 b | |||
| Doxorubicin | 272–322 a | +34.2 to +57.1 a | [150] | |
| 305–355 b | +51.8 to +69.1 b | |||
| 27.4 ± 2.4 a | +52 ± 3 a | [151] | ||
| 20.4 ± 1.1 b | +53.1 ± 14.4 b | |||
| stearyl + doxorubicin | Doxorubicin | 40.1–105.8 b | +32.0 to +43.7 b | [152] |
| Acyl | Rifampin | 154–181 a | [153] | |
| 163–210 b | ||||
| Vitamin C | 444–487 a | +10.2 to +28.9 a | [154] | |
| 216–288 b | +5.9 to +18.4 b | |||
| N,O6-acetyl + steroid | Steroids | 197–358 b | +7 to +22.7 b | [155] |
| N,O6-acetyl + tocopherol | Vitamin E | 275 ± 5 b | +14.9 ± 0.7 b | |
| phthaloyl | Camptothecin | ~170 a | [156] | |
| ~200–267 b | ||||
| ~50–100 a | ||||
| ~100–250 b | [157] | |||
| All-trans retinoic acidPrednisone acetate | ~50–100 a | [158,159] | ||
| ~80–160 b | ||||
| 89.8 a | ||||
| 143.3 b | ||||
| polycaprolactone, (Chitosan-grafted) | 7-Ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin | 47–113 a | +26.7 to +50.8 a | [160] |
| 63–152 b | +25.6 to +48.8 b | |||
| BSA | 168.44 b | [161] | ||
| 200.7 b | ||||
| 435 ± 25 a | ||||
| Paclitaxel | 408–529 b | +27.5 ± 1.1 a | [162] | |
| 61.4–108.6 a | +30.9 to +33.3 b | |||
| 5-Fluorouracil | 67.9–96.7 b | +18.9 to +43.1 b | [163] | |
| N-acetyl histidine | Doxorubicin | 218 a | +40.1 ± 2.8 a | [164] |
| 185.3–218.3 b | +36.3 to +40.1 b |
| Hydrophobic moiety | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholanic acid | Docetaxel | 350 b | +23.8 ± 0.9 a +10.0 ± 0.8 b | [165] |
| Camptothecin | 254 a | [166] | ||
| 279–328 b | ||||
| siRNA | 350 a | [167] | ||
| 250 b | ||||
| RGD peptide | 224 a | [168] | ||
| 189–265 b | ||||
| Cholesterol | Indomethacin | 228 a | [169] | |
| 275–384 b | ||||
| Deoxycholic acid | Palmityl-acylated exendin-4 | ~52–250 a | [170] | |
| Ergocalciferol | Vitamin D2 | 279 ± 7 (PBS) | +7.7 ± 0.1 | [171] |
| dl-α-tocopherol | Vitamin E | 284–496 (PBS) | +11.7 to +36.5 | [172] |
| Testosterone | Testosterone | 332 ± 4 (PBS) | +9.7 ± 0.6 | [173] |
| N,N-diethylnicotinamide-based oligomer | Paclitaxel | 313 ± 20 a | [174] | |
| 331–363 b | ||||
| 3-Diethylaminopropyl | Doxorubicin | 102 a | −0.9 a | [175] |
| Doxorubicin | Doxorubicin | 238 a 342 b | [176] |
| Hydrophobic moiety | Active agent | Particle size (nm) | Zeta-potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oleoyl | Rifampicin | 161.8 a | [177] | |
| Microbial | 157.4–396.7 a | +15.6 to +19.6 a | [178] | |
| antigen | 237.6–482.3 b | +14.2 to +17.1 b | ||
| 331.6–573.9 b | +12.8 to +16.3 b | |||
| Acyl | Adriamycin | 418 ± 18 a | [179] |
| Hydrophobic Moiety | Active Agent | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta-Potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Octyl | Doxorubicin | 130.4–150.1 a | [180] | |
| 155.4–170.1 b | ||||
| Acyl | BSA | ~50–100 a | [181] | |
| ~100–200 b | ||||
| dl-α-tocopherol | Vitamin E | 254 ± 4 | +36.3 ± 0.9 | [172] |
| Hydrophobic Moiety | Active Agent | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta-Potential (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkyl | Hydroxy-camptothecin | 20.8–277.2 a | [182] | |
| 26.0–273.1 b | ||||
| Palmitoyl | Harmine | 193.4 ± 3.1 b | +26.67 b | [183,184] |
| Acyl | Peptide drugs | 101.3–106.3 a | +30.6 to +36.2 a | [185] |
| 522 ± 6 b,* | +14.2 ± 0.6 b,* |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quiñones, J.P.; Peniche, H.; Peniche, C. Chitosan Based Self-Assembled Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Polymers 2018, 10, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030235
Quiñones JP, Peniche H, Peniche C. Chitosan Based Self-Assembled Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030235
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuiñones, Javier Pérez, Hazel Peniche, and Carlos Peniche. 2018. "Chitosan Based Self-Assembled Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery" Polymers 10, no. 3: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030235
APA StyleQuiñones, J. P., Peniche, H., & Peniche, C. (2018). Chitosan Based Self-Assembled Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Polymers, 10(3), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030235