Reusable Xerogel Containing Quantum Dots with High Fluorescence Retention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Synthesis of Mono-6-thio-β-cyclodextrin (mSH-CD)
2.4. Preparation of mSH-CD Capped CdTe (βCD-CdTe)
2.5. Preparation of HEMA-Ad@βCD-CdTe Complex
2.6. Preparation of the Xerogel
2.7. Detection of Analytes
2.8. Estimation of the Number of βCD Molecules Bound to One CdTe Particle and Calculating Inclusion Rate of HEMA-Ad@βCD-CdTe
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of the Xerogel
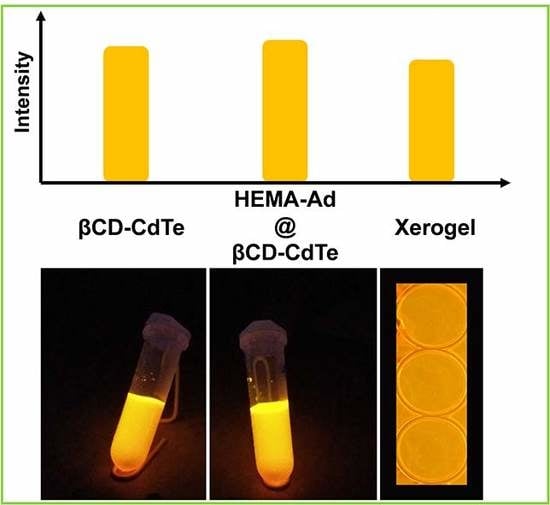
3.2. Fluorescence Property of the Xerogel
3.3. The Detecting Performance and Reusable Ability of the Xerogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, G.H.; Abdelhady, A.L.; Ning, Z.; Thon, S.M.; Bakr, O.M.; Sargent, E.H. Colloidal Quantum Dot Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12732–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvi, S.; Credi, A. Luminescent sensors based on quantum dot-molecule conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4275–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, N.; Spillmann, C.M.; Algar, W.R.; Pons, T.; Stewart, M.H.; Oh, E.; Susumu, K.; Díaz, S.A.; Delehanty, J.B.; Medintz, I.L. Energy Transfer with Semiconductor Quantum Dot Bioconjugates: A Versatile Platform for Biosensing, Energy Harvesting, and Other Developing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 536–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Nie, S. Chemical analysis and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Analyst 2004, 129, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-H.; Wang, H.-Q.; Zhang, H.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Hua, X.-F.; Cao, Y.-C.; Huang, Z.-L.; Zhao, Y.-D. Purification of denatured bovine serum albumin coated CdTe quantum dots for sensitive detection of silver(I) ions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Qian, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ao, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, H. A fluorometric assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on β-cyclodextrin-modified carbon quantum dots through host–guest recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, S.; Cao, S.; Zhu, A.; Shi, G. Functional surface engineering of quantum dot hydrogels for selective fluorescence imaging of extracellular lactate release. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arachchige, I.U.; Brock, S.L. Highly Luminescent Quantum-Dot Monoliths. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1840–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arachchige, I.U.; Brock, S.L. Sol–Gel Methods for the Assembly of Metal Chalcogenide Quantum Dots. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yue, X.; Dai, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, Z. Glucose Biosensor Based on Nanocomposite Films of CdTe Quantum Dots and Glucose Oxidase. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6580–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamedov, A.A.; Belov, A.; Giersig, M.; Mamedova, N.N.; Kotov, N.A. Nanorainbows: Graded Semiconductor Films from Quantum Dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7738–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattás-Asfura, K.M.; Zheng, Y.; Micic, M.; Snedaker, M.J.; Ji, X.; Sui, G.; Orbulescu, J.; Andreopoulos, F.M.; Pham, S.M.; Wang, C.; et al. Immobilization of Quantum Dots in the Photo-Cross-Linked Poly(ethylene glycol)-Based Hydrogel. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 10464–10469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yao, D.; Guo, R.; Deng, L.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Composites of Polymer Hydrogels and Nanoparticulate Systems for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2054–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanan, J.L.; Arachchige, I.U.; Brock, S.L. Porous Semiconductor Chalcogenide Aerogels. Science 2005, 307, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hendel, T.; Lesnyak, V.; Kuehn, L.; Herrmann, A.-K.; Bigall, N.C.; Borchardt, L.; Kaskel, S.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmueller, A. Mixed Aerogels from Au and CdTe Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, L.; Esteves, R.J.A.; Hafiz, S.; Özgür, Ü.; Arachchige, I.U. Metal–Semiconductor Hybrid Aerogels: Evolution of Optoelectronic Properties in a Low-Dimensional CdSe/Ag Nanoparticle Assembly. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9810–9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, D.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. Enzyme-Encapsulating Quantum Dot Hydrogels and Xerogels as Biosensors: Multifunctional Platforms for Both Biocatalysis and Fluorescent Probing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.; Lesnyak, V.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmueller, A. Quantum-Dot-Based (Aero)gels: Control of the Optical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.-H.; You, Y.-Z. Reversible and Multisensitive Quantum Dot Gels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4306–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Kennedy, S.R.; Soriano, M.L.; Jones, C.D.; Valcarcel, M.; Steed, J.W. Fluorescent carbon dot-molecular salt hydrogels. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6139–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Ma, D.; Zhang, L.-M. Fabrication and properties of a supramolecular hybrid hydrogel doped with CdTe quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58746–58754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Kennedy, S.R.; Steed, J.W.; Valcárcel, M. Fluorescent carbon quantum dot hydrogels for direct determination of silver ions. Talanta 2016, 151, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Maitra, U. A novel strategy towards designing a CdSe quantum dot-metallohydrogel composite material. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14979–14985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Liang, R.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Carbon Dots-Based Ultrathin Films with Enhanced Quantum Yield and Temperature Sensing Performance. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 5426–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.; Oh, J.H.; Hong, S.P.; Do, Y.R.; Jang, S.-Y. Optical Properties Enhancement of Electrosprayed Quantum Dot/Polymer Nanohybrid Films by a Solvent Vapor Treatment. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.N.; Luong, A.J.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Ritchie, R.O.; Alivisatos, A.P. Cavitation-Induced Stiffness Reductions in Quantum Dot–Polymer Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Son, K.J.; Kim, B.; Koh, W.-G. Phenol biosensor based on hydrogel microarrays entrapping tyrosinase and quantum dots. Analyst 2010, 135, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-H.; Bang, J.-H.; Hong, K.B.; Park, M.-H. Fabrication of highly photoluminescent quantum dot-polymer composite micropatterned surface using thiol-ene chemistry. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 96700–96705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnee, V.P.; Bright, C.J.; Nallon, E.C.; Polcha, M.P. Contact printing of a quantum dot and polymer cross-reactive array sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 236, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczewski, D.; Tomczak, N.; Han, M.-Y.; Vancso, G.J. Introduction of Quantum Dots into PNIPAM microspheres by precipitation polymerization above LCST. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczewski, D.; Tomczak, N.; Han, M.-Y.; Vancso, G.J. Stimulus Responsive PNIPAM/QD Hybrid Microspheres by Copolymerization with Surface Engineered QDs. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Jiang, M. Supramolecular Hydrogels with CdS Quantum Dots Incorporated by Host–Guest Interactions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 1736–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Chen, G.; Jiang, M. Electrochemically sensitive supra-crosslink and its corresponding hydrogel. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Guo, M.; Jiang, M. Dual Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogel Based on Hybrid Inclusion Complex (HIC). Macromolecules 2010, 43, 8086–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Rechberger, F.; Niederberger, M. Three-Dimensional Assembly of Yttrium Oxide Nanosheets into Luminescent Aerogel Monoliths with Outstanding Adsorption Properties. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derfus, A.M.; Chan, W.C.W.; Bhatia, S.N. Probing the Cytotoxicity of Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, R. A Toxicologic Review of Quantum Dots: Toxicity Depends on Physicochemical and Environmental Factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; He, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, B.; Sexton, D.W.; Wileman, T.; Roberts, A.A.; Hamilton, C.J.; Liu, R.; Chao, Y.; et al. Sulforaphane Protects the Liver against CdSe Quantum Dot-Induced Cytotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Li, H. Chiral recognition of amino acids based on cyclodextrin-capped quantum dots. Small 2008, 4, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Han, C. Sonochemical Synthesis of Cyclodextrin-Coated Quantum Dots for Optical Detection of Pollutant Phenols in Water. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6053–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, S.; Liang, Y.; Yu, Y. The molecular recognition of beta-cyclodextrin modified CdSe quantum dots with tyrosine enantiomers: Theoretical calculation and experimental study. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1031, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X.; Dong, C. Sensitive and selective detection of l-tryptophan using Mn-ZnS QDs as the ratiometric emission probe. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3227–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, W. Cyclodextrin-clicked silica/CdTe fluorescent nanoparticles for enantioselective recognition of amino acids. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5621–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, D.-L.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.-S.; Li, B.-J.; Zhang, S. Conductive Elastomers with Autonomic Self-Healing Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12127–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Ding, L.-S.; Li, B.-J.; Zhang, S. UV-Blocking Coating with Self-Healing Capacity. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Tang, W. Cyclodextrin capped CdTe quantum dots as versatile fluorescence sensors for nitrophenol isomers. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19540–19546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Nichols, W.T. Cyclodextrin directed self-assembly of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, S.; Ren, J.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Cyclodextrin Functionalized Graphene Nanosheets with High Supramolecular Recognition Capability: Synthesis and Host–Guest Inclusion for Enhanced Electrochemical Performance. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. beta-cyclodextrin functionalized CdTe quantum dots for electrochemiluminescent detection of benzo[a]pyrene. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, J.; Lavelle, N.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X. Size-Dependent Dissociation pH of Thiolate Ligands from Cadmium Chalcogenide Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mi, L.; Wang, P.-N.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.-Y. pH-dependent aggregation and photoluminescence behavior of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots in aqueous solutions. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1948–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Q.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, Q.-J.; Wang, Y.-F.; Li, J.-H.; Li, B.-J.; Zhang, S. Redox- and Glucose-Induced Shape-Memory Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, C.R.; Murray, C.B.; Bawendi, M.G. Long-range resonance transfer of electronic excitations in close-packed CdSe quantum-dot solids. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 8633–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemyev, M.V.; Bibik, A.I.; Gurinovich, L.I.; Gaponenko, S.V.; Woggon, U. Evolution from individual to collective electron states in a dense quantum dot ensemble. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.; Kim, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.-K.; Joo, S.-W.; Lee, K. Fluorescence quenching caused by aggregation of water-soluble CdSe quantum dots. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 359, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanos, V.T.; Mourtzinos, I.; Yannakopoulou, K.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Study of the solubility, antioxidant activity and structure of inclusion complex of vanillin with β-cyclodextrin. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of vanillin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex in electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanowebs: Prolonged shelf-life and high temperature stability of vanillin. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duran, G.M.; Contento, A.M.; Rios, A. beta-Cyclodextrin coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for vanillin sensoring in food samples. Talanta 2015, 131, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Xu, J.-P.; Li, D.; Pang, S.-P.; Fang, Y.; Song, Z.-G.; Ji, J. Fluorescence detection of alkaline phosphatase activity with β-cyclodextrin-modified quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7166–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Herrmann, A.-K.; Haubold, D.; Holzschuh, M.; Simon, F.; Eychmüller, A. Simple and Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Dopamine Based on Assembly of Cyclodextrin-Modified Au Nanoparticles. Small 2016, 12, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Song, D. Dopamine-modified Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots fluorescence probe for the sensitive detection of tyrosinase in serum samples and living cells imaging. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 256, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, Z.-Y.; Ding, L.-S.; Li, B.-J.; Zhang, S. Reusable Xerogel Containing Quantum Dots with High Fluorescence Retention. Polymers 2018, 10, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030310
Liang X-Y, Wang L, Chang Z-Y, Ding L-S, Li B-J, Zhang S. Reusable Xerogel Containing Quantum Dots with High Fluorescence Retention. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030310
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Xiang-Yong, Lu Wang, Zhi-Yi Chang, Li-Sheng Ding, Bang-Jing Li, and Sheng Zhang. 2018. "Reusable Xerogel Containing Quantum Dots with High Fluorescence Retention" Polymers 10, no. 3: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030310
APA StyleLiang, X.-Y., Wang, L., Chang, Z.-Y., Ding, L.-S., Li, B.-J., & Zhang, S. (2018). Reusable Xerogel Containing Quantum Dots with High Fluorescence Retention. Polymers, 10(3), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030310