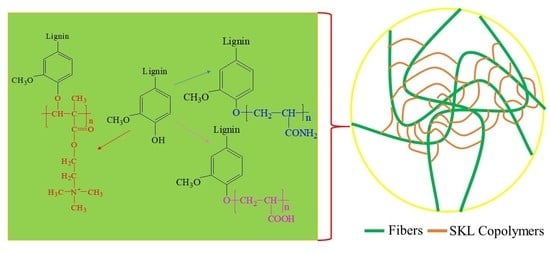
Preparation and Characterization of Softwood Kraft Lignin Copolymers as a Paper Strength Additive
Abstract
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Xu, D.; Xu, L.; Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, G. Preparation and Characterization of Softwood Kraft Lignin Copolymers as a Paper Strength Additive. Polymers 2018, 10, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070743
Liu Z, Xu D, Xu L, Kong F, Wang S, Yang G. Preparation and Characterization of Softwood Kraft Lignin Copolymers as a Paper Strength Additive. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070743
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhongming, Dingding Xu, Lei Xu, Fangong Kong, Shoujuan Wang, and Guihua Yang. 2018. "Preparation and Characterization of Softwood Kraft Lignin Copolymers as a Paper Strength Additive" Polymers 10, no. 7: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070743
APA StyleLiu, Z., Xu, D., Xu, L., Kong, F., Wang, S., & Yang, G. (2018). Preparation and Characterization of Softwood Kraft Lignin Copolymers as a Paper Strength Additive. Polymers, 10(7), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070743