Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
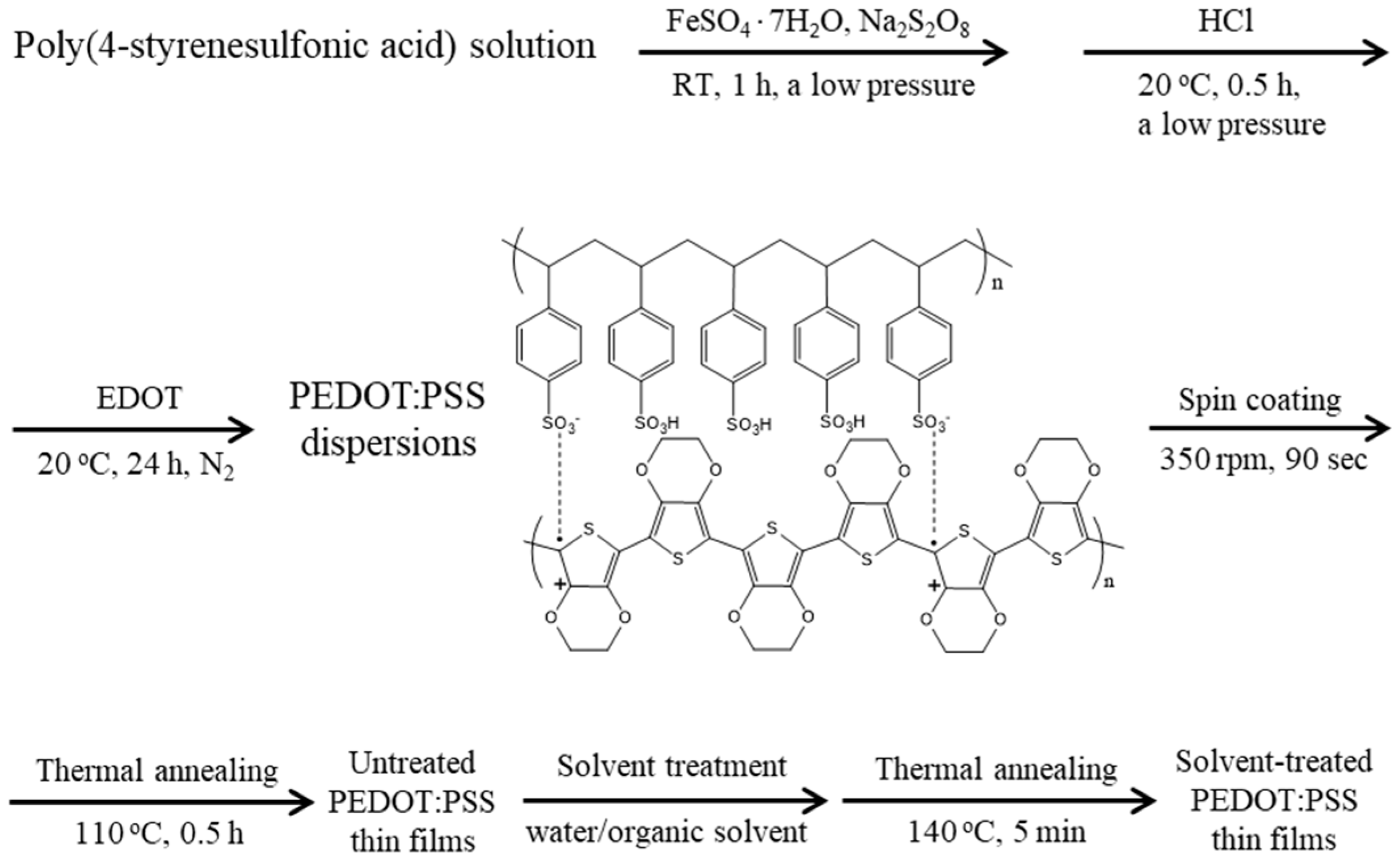
2.2. Fabrication of PEDOT:PSS Dispersions
2.3. Fabrication of Untreated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films
2.4. Fabrication of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films
2.5. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
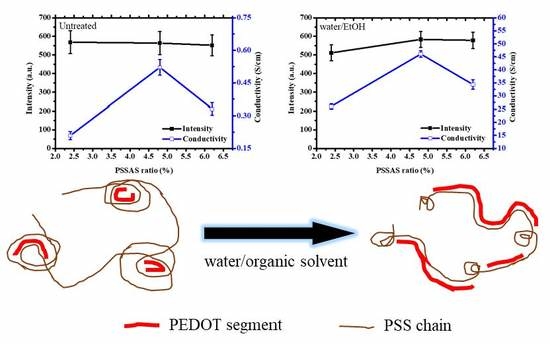
3.1. XRD Measurements of the PEDOT:PSS Thin Films
3.2. Electrical Conductivity of the PEDOT:PSS Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, Y.H.; Nikolov, N.; Pollack, S.K.; Mastrangelo, J.; Martin, B.D.; Shashidhar, R. Towards a transparent, highly conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispin, X.; Jakobsson, F.L.E.; Crispin, A.; Grim, P.C.M.; Andersson, P.; Volodin, A.; Haesendonck, C.V.; Auweraer, M.V.D.; Salaneck, W.R.; Berggren, M. The origin of the high conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT-PSS) plastic electrodes. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Johansson, M.; Andersson, M.R.; Hummelen, J.C.; Inganäs, O. Polymer photovoltaic cells with conducting polymer anodes. Adv. Funct. 2002, 14, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Zuccarello, G.; Ahlskog, M.; Inganäs, O. Electrochromic and highly stable poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) switches between opaque blue-black and transparent sky blue. Polymer 1994, 35, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granström, M.; Berggren, M.; Inganäs, O. Micrometer- and nanometer-sized polymeric light-emitting diodes. Science 1995, 267, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, F.; Morrison, J.T. 3,4-Polyethylenedioxythiophene (PEDT): Conductive coatings technical applications and properties. Synth. Met. 1997, 85, 1397–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, C.; Menon, R.; Heeger, A.J. Polymer light-emitting diodes with polyethylene dioxythiophene-polystyrene sulfonate as the transparent anode. Synth. Met. 1997, 87, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, H.W.; Wehrmann, R.; Kirchmeyer, S. Electrochromic window based on conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonate). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Ha, S.R.; Choi, H.; Uh, K.; Kundapur, U.; Park, S.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.M. Polymerizable supramolecular approach to highly conductive PEDOT:PSS patterns. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19231–19237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Cai, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L. Research progress on conducting polymer based supercapacitor electrode materials. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmeyer, S.; Reuter, K. Scientific importance, properties, and growing applications of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J. “Secondary doping” methods to significantly enhance the conductivity of PEDOT:PSS for its application as transparent electrode of optoelectronic devices. Displays 2013, 34, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.C.; Jiang, Q.L.; Xu, J.K. Effective approaches to improve the electrical conductivity of PEDOT:PSS: A review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.X.; Xu, J.K.; Lu, B.Y.; Xie, Y.; Huang, R.J.; Li, L.F. Thermoelectric performance of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate). Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 2202–2205. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lu, B.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; Yue, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P. Highly conducting freestanding poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrenesulfonate) films with improved thermoelectric performances. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 2481–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. Highly electrical and thermoelectric properties of a PEDOT:PSS thin-film via direct dilution–filtration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60708–60712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, A.M.; Kemerink, M.; Kok, M.M.D.; Vinken, E.; Maturova, K.; Janssen, R.A.J. Conductivity, work function, and environmental stability of PEDOT:PSS thin films treated with sorbitol. Org. Electron. 2008, 9, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. Anion effect on salt-induced conductivity enhancement of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) films. Org. Electron. 2010, 11, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, T.; Hikawa, H.; Katsunuma, M.; Okuzaki, H. Synthesis of highly conductive PEDOT:PSS and correlation with hierarchical structure. Polymer 2018, 140, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. PEDOT:PSS films with significantly enhanced conductivities induced by preferential solvation with cosolvents and their application in polymer photovoltaic cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4927–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasmundtveit, K.E.; Samuelsent, E.J.; Pettersson, L.A.A.; Inganäs, O.; Johansson, T.; Feidenhans, R. Structure of thin films of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Synth. Met. 1999, 101, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Kvarnström, C.; Fröberg, K.; Ivaska, A. Electrochemically controlled surface morphology and crystallinity in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films. Synth. Met. 2001, 122, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.G.; Brédas, J.L. Electronic evolution of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT): From the isolated chain to the pristine and heavily doped crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16880–16889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, D.E.; Joo, J. Enhancement of electrical conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(4-styrenesulfonate) by a change of solvents. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Xu, Q.; Chu, C.W.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Shinar, J. On the mechanism of conductivity enhancement in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) film through solvent treatment. Polymer 2004, 45, 8443–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Conductivity enhancement of PEDOT:PSS films through the surface treatment with organic solvent. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 2880–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.S.; Whang, W.T.; Chen, C.P.; Chen, Y.-C. High-conductivity poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) film for use in ITO-free polymer solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5948–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasud, M. Dissociation constants of some carboxylic acids in mixed aqueous solvents. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1959, 32, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrón, D.; Butí, S.; Ruiz, M.; Barbosa, J. Evaluation of acidity constants and preferential solvation in tetrahydrofuran–water mixtures. Polyhedron 1999, 18, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Masunaga, H.; Fujiwara, A.; Okuzaki, H.; Sasaki, T. PEDOT nanocrystal in highly conductive PEDOT:PSS polymer films. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3859–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Solvent Treatment | Films | Fitted 2θ (Degree) | Fitted Intensity (Arbitrary Unit, a.u.) | Conductivity (S/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Film A | 18.51 | 527.42 | 0.21 |
| 24.40 | 568.51 | |||
| Film B | 18.55 | 539.14 | 0.52 | |
| 24.52 | 563.85 | |||
| Film C | 18.46 | 544.76 | 0.33 | |
| 24.40 | 551.90 | |||
| Water/acetone | Film A | 18.73 | 458.37 | 19.89 |
| 24.25 | 503.96 | |||
| Film B | 18.99 | 543.25 | 35.33 | |
| 24.56 | 570.61 | |||
| Film C | 18.22 | 554.81 | 30.43 | |
| 24.60 | 546.81 | |||
| Water/MeOH | Film A | 18.52 | 428.14 | 14.99 |
| 24.28 | 467.49 | |||
| Film B | 18.08 | 504.42 | 40.51 | |
| 24.65 | 577.62 | |||
| Film C | 18.21 | 546.55 | 32.37 | |
| 24.82 | 566.53 | |||
| Water/EtOH | Film A | 17.70 | 422.28 | 25.99 |
| 24.80 | 511.06 | |||
| Film B | 17.89 | 533.55 | 46.07 | |
| 24.51 | 583.45 | |||
| Film C | 18.09 | 569.63 | 34.35 | |
| 24.82 | 578.58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rwei, S.-P.; Lee, Y.-H.; Shiu, J.-W.; Sasikumar, R.; Shyr, U.-T. Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers 2019, 11, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
Rwei S-P, Lee Y-H, Shiu J-W, Sasikumar R, Shyr U-T. Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleRwei, Syang-Peng, Yi-Huan Lee, Jia-Wei Shiu, Ragu Sasikumar, and Uin-Ting Shyr. 2019. "Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities" Polymers 11, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
APA StyleRwei, S.-P., Lee, Y.-H., Shiu, J.-W., Sasikumar, R., & Shyr, U.-T. (2019). Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers, 11(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134