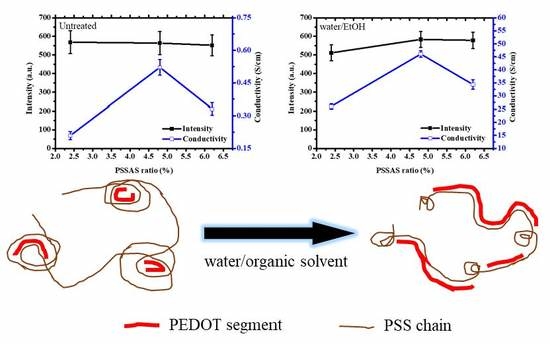
Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities
Abstract
Share and Cite
Rwei, S.-P.; Lee, Y.-H.; Shiu, J.-W.; Sasikumar, R.; Shyr, U.-T. Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers 2019, 11, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
Rwei S-P, Lee Y-H, Shiu J-W, Sasikumar R, Shyr U-T. Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleRwei, Syang-Peng, Yi-Huan Lee, Jia-Wei Shiu, Ragu Sasikumar, and Uin-Ting Shyr. 2019. "Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities" Polymers 11, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134
APA StyleRwei, S.-P., Lee, Y.-H., Shiu, J.-W., Sasikumar, R., & Shyr, U.-T. (2019). Characterization of Solvent-Treated PEDOT:PSS Thin Films with Enhanced Conductivities. Polymers, 11(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010134