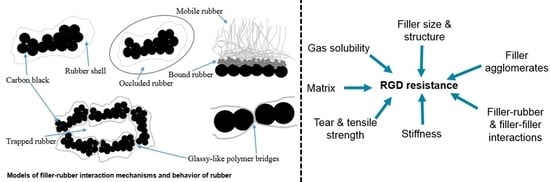
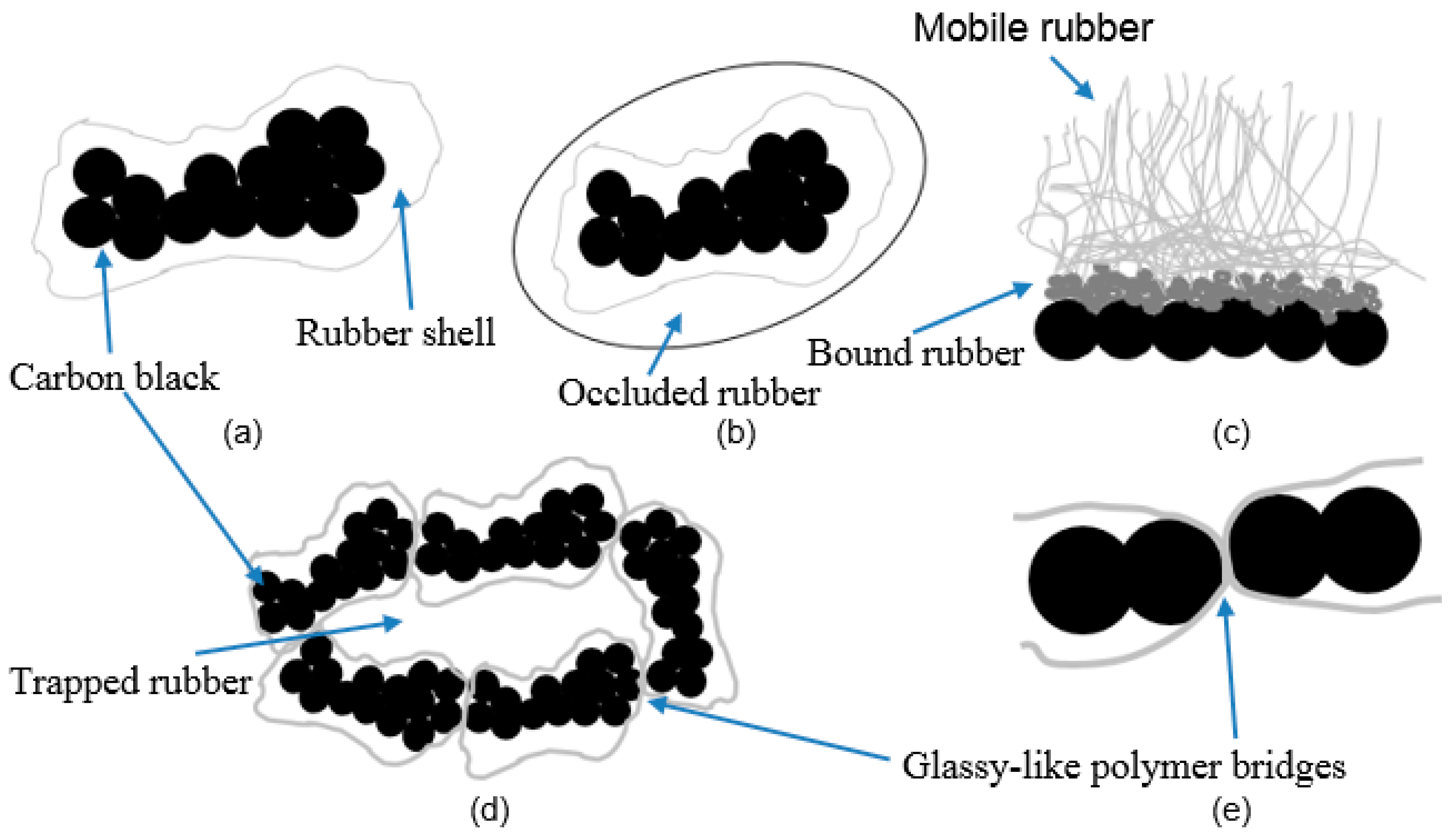
The Effect of the Surface Area of Carbon Black Grades on HNBR in Harsh Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rapid Gas Decompression Test
2.3. Tensile Test
2.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Investigations of CB Filled Samples by TEM
3.2. CB Grade Influence on Dynamic Mechanical Properties
3.3. CB Grade Influence on Tensile Properties
3.4. CB Effect on Rapid Gas Decompression
3.5. SEM Based Fractography
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann, W. Rubber Technology Handbook, 2nd ed.; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany; Vienna, Austria; New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Zakaria, S. Gas-induced damage in elastomeric composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 3017–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, Z.; Lang, R.W. Characterization of the fracture behavior of NBR and FKM grade elastomers for oilfield applications. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2010, 17, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Savvas, T.; Kelly, C.T. “Explosive Decompression Failure” of Rubbers: A Review of the Origins of Pneumatic Stress Induced Rupture in Elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1994, 67, 384–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, E. Elastomeric Seals for Rapid Gas Decompression Applications in High-Pressure Services. In BHR Group Limited Research Report 485 for the Health; BHR Group Limited for the Health and Safety Executive: Sudbury, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Major, Z.; Lederer, K.; Moitzi, M.; Mitterhuber, M.; Schwarz, T.; Lang, R.W. Development of a Test and Failure Analysis Methodology for Elastomeric Seals Exposed to Explosive Decompression. Eng. Struct. Integr. Res. Dev. Appl. 2006, 2, 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Yamabe, J.; Nishimura, S. Influence of carbon black on decompression failure and hydrogen permeation properties of filled ethylene-propylene-diene-methylene rubbers exposed to high-pressure hydrogen gas. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3172–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, J.; Nishimura, S. Influence of fillers on hydrogen penetration properties and blister fracture of rubber composites for O-ring exposed to high-pressure hydrogen gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrittesser, B.; Pinter, G.; Schwarz, T.; Kadar, Z.; Nagy, T. Rapid gas decompression performance of elastomers—A study of influencing testing parameters. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 2, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embury, P. High-pressure gas testing of elastomer seals and a practical approach to designing for explosive decompression service. Seal. Technol. 2004, 2004, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrittesser, B.; Pinter, G.; Schwarz, T.; Nagy, T.; Urbán, M. Fracture and Fatigue Behavior of Elastomers Used in the Oil and Gas Industry. In Proceedings of the High Performance for Oil and Gas, Oil and Gas Polymer Engineering Texas Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 10–12 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mbwadzawo, T.; Hodzic, A. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Elastomeric O-Rings and Spring Seals Fractured during Rapid Gas Decompression. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Composite Materials (ECCM16), Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vorotnikov, D.A. Dissipative solutions for equations of viscoelastic diffusion in polymers. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2008, 339, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comyn, J. Polymer Permeability; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hertz, D.L. Elastomers in CO2. In Proceedings of the High Performance Elastomers & Polymers for Oil & Gas 2012 International Conference, Aberdeen, UK, 20–21 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Daou, F.; de Miranda, C.R.; de Oliveira, J.L.; Engelke, B.; Borman, C.; Le Roy-Delage, S.; Lungwitz, B. Swelling of Elastomers in CO2 Environment: Testing Methodology and Experimental Data. In Proceedings of the SPE International SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Maracaibo, Venezuela, 21 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, G.; Klüppel, M.; Vilgis, T.A. Reinforcement of elastomers. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, J.; Niedermeier, W.; Luginsland, H.-D. The effect of filler–filler and filler–elastomer interaction on rubber reinforcement. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.J. Effects of carbon blacks with various structures on vulcanization and reinforcement of filled ethylene-propylene-diene rubber. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orion Engineered Carbons GmbH. What Is Carbon Black? Luxembourg, Germany, 2015; Available online: https://www.thecarycompany.com/media/pdf/specs/orion-what-is-carbon-black.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2018).
- Carbon Black. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol93/mono93-6.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2018).
- Leblanc, J. Rubber–filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 627–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savetlana, S.; Zulhendri; Sukmana, I.; Saputra, F.A. The effect of carbon black loading and structure on tensile property of natural rubber composite. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 223, 12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohls, D.J.; Beaucage, G. Rational design of reinforced rubber. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübler, N.; Fritzsche, J.; Klüppel, M. Mechanical and electrical analysis of carbon black networking in elastomers under strain. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V. Carbon Black Filler Reinforcement of Elastomers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, Queen Mary, UK, October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gent, A.N.; Lindley, P.B. Internal Rupture of Bonded Rubber Cylinders in Tension. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1959, 249, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.A.C.; Mullins, L.; Payne, A.R. Stress Softening in Natural Rubber Vulcanizates. Part II. Stress Softening Effects in Pure Gum and Filler Loaded Rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1966, 39, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Mi, X. Carbon black filled powdered natural rubber: Preparation, particle size distribution, mechanical properties, and structures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORSOK. Qualification of Non-Metallic Sealing Materials and Manufacturers, 1st ed.; (NORSOK M-710); Norwegian Technology Center: Trondheim, Norway, 1994; Available online: http://www.standard.no/pagefiles/1152/m-cr-710r1.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2018).
- Balasooriya, W.; Schrittesser, B.; Pinter, G.; Schwarz, T. Induced material degradation of elastomers in harsh environments. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, W.; Schrittesser, B.; Karunakaran, S.; Schlögl, S.; Pinter, G.; Schwarz, T.; Kadar, Z. Influence of Thermo-Oxidative Ageing of HNBR in Oil Field Applications. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 373, 1600093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L. Multiwall carbon nanotube elastomeric composites: A review. Polymer 2007, 48, 4907–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monaghan, K.J.; Newlands, C.; Ho, E. Specification of Elastomeric Materials for Rapid Gas Decompression Applications. In Proceedings of the Oilfield Engineering with Polymers Conference: 5th International MERL Conference, London, UK, 29–30 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, D. Next Generation HNBR Grades—New Materials for Oilfield Application. In Proceedings of the Oilfield Engineering with Polymers Conference: 5th International MERL Conference, London, UK, 29–30 March 2006. [Google Scholar]










| Grade | Content 1 | Content 2 |
|---|---|---|
| HNBR1 | large size (10 phr) | middle size (75 phr) |
| HNBR2 | large size (75 phr) | middle size (10 phr) |
| HNBR3 | large size (40 phr) | middle size (45 phr) |
| HNBR4 | large size (10 phr) | small size (75 phr) |
| Description | Rating |
|---|---|
| No internal cracks, holes, or blisters of any size. | 0 |
| Less than 4 internal cracks, each shorter than 50% of the cross-section, with a total crack length less than the cross-section | 1 |
| Less than 6 internal cracks, each shorter than 50% of the cross-section, with a total crack length of fewer than 2.5 times the cross-section. | 2 |
| Less than 9 internal cracks of which max. 2 cracks can have a length between 50% and 80% of the cross-section. | 3 |
| More than 8 internal cracks, or one or more cracks longer than 80% of the cross-section. | 4 |
| Crack(s) going through the entire cross-section or complete separation of the seal into fragments. | 5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balasooriya, W.; Schrittesser, B.; Pinter, G.; Schwarz, T.; Conzatti, L. The Effect of the Surface Area of Carbon Black Grades on HNBR in Harsh Environments. Polymers 2019, 11, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010061
Balasooriya W, Schrittesser B, Pinter G, Schwarz T, Conzatti L. The Effect of the Surface Area of Carbon Black Grades on HNBR in Harsh Environments. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalasooriya, Winoj, Bernd Schrittesser, Gerald Pinter, Thomas Schwarz, and Lucia Conzatti. 2019. "The Effect of the Surface Area of Carbon Black Grades on HNBR in Harsh Environments" Polymers 11, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010061
APA StyleBalasooriya, W., Schrittesser, B., Pinter, G., Schwarz, T., & Conzatti, L. (2019). The Effect of the Surface Area of Carbon Black Grades on HNBR in Harsh Environments. Polymers, 11(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010061