High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
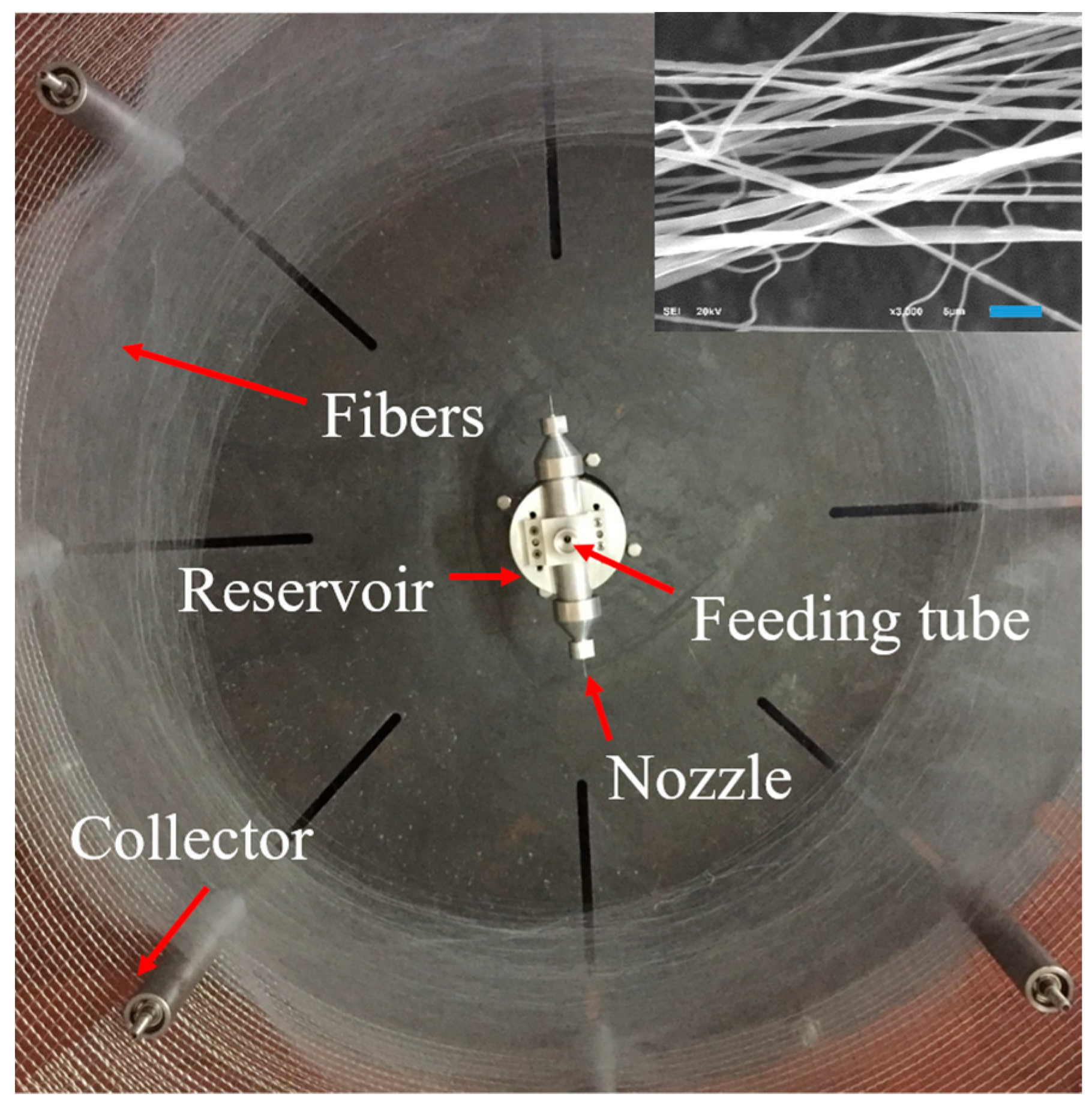
2.2. Fabrication of Pure PEO Nanofibers
2.3. Fabrication of CCS/PEO Nanofibers with High Content of Chitosan
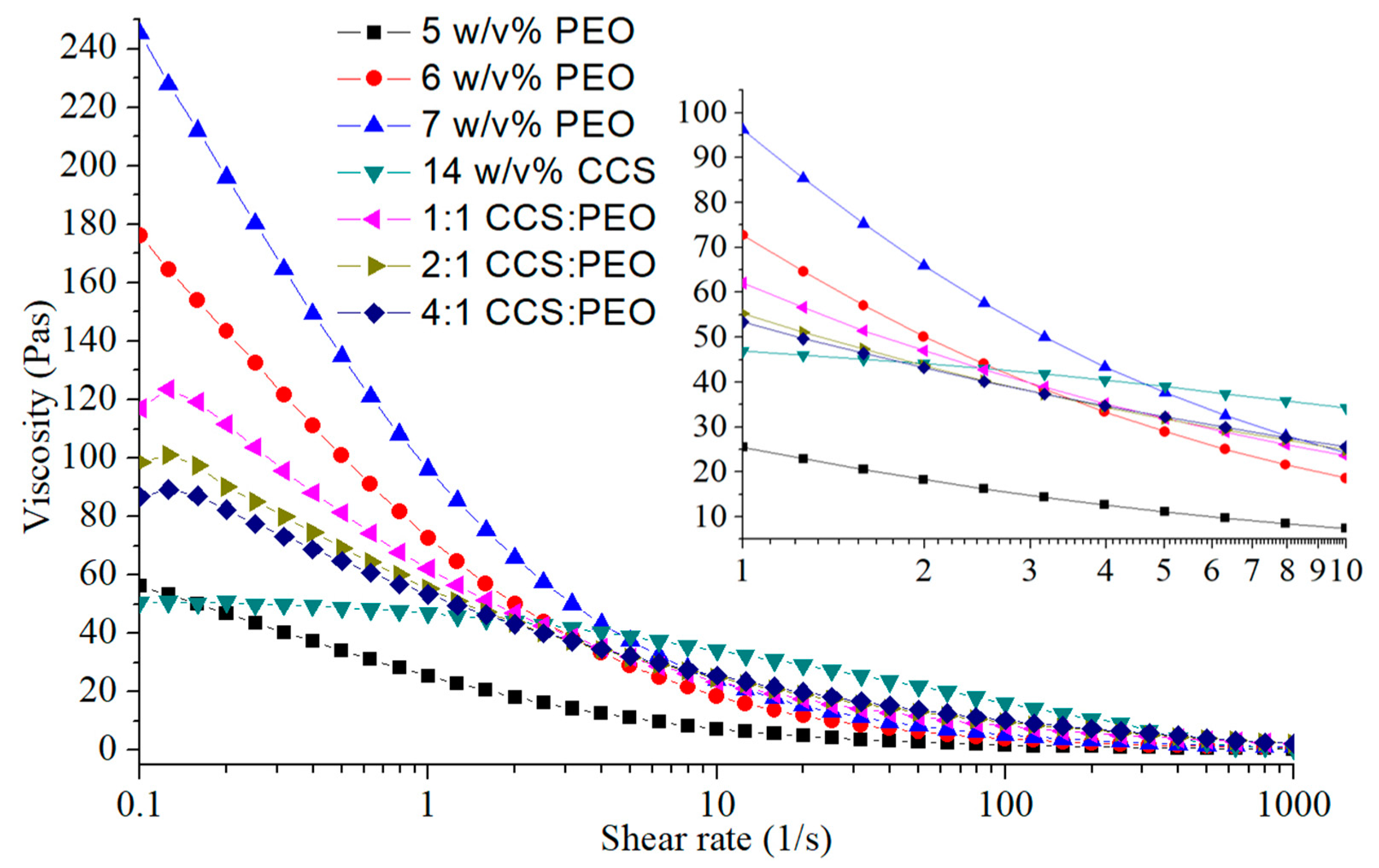
2.4. Viscosity Measurements
2.5. Fiber Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
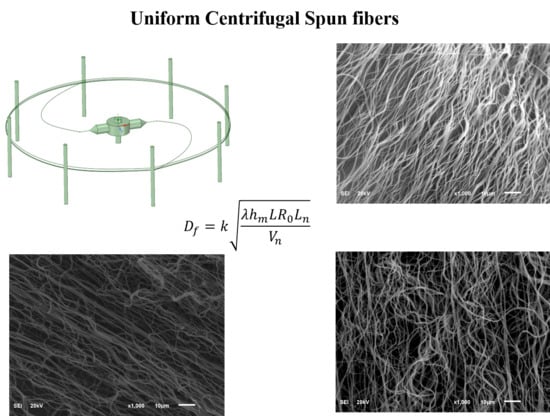
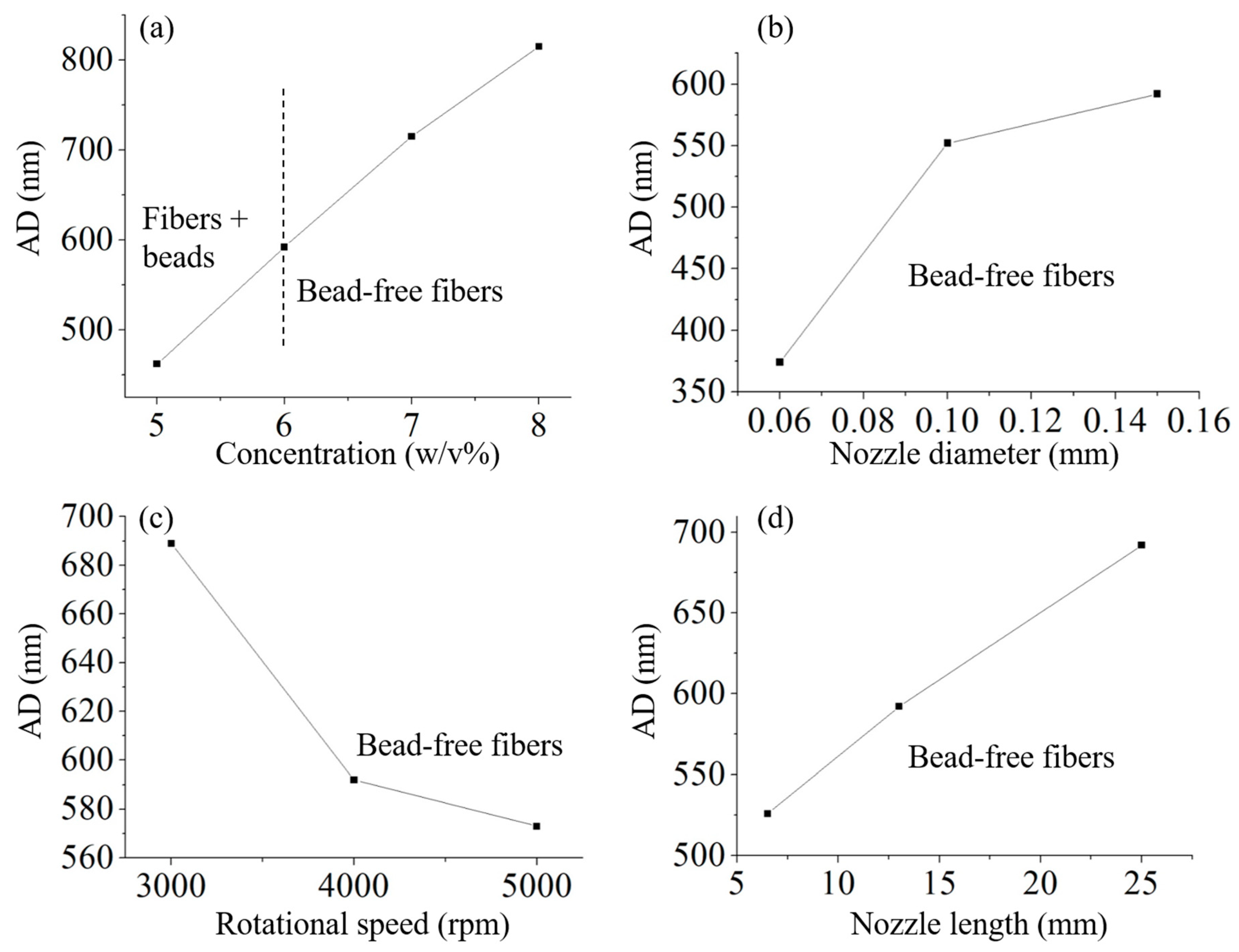
3.1. Building Empirical Model
3.2. Fabrication of CCS/PEO Nanofibers and Validation of Empirical Model
3.3. Characterization of Mechanical Properties
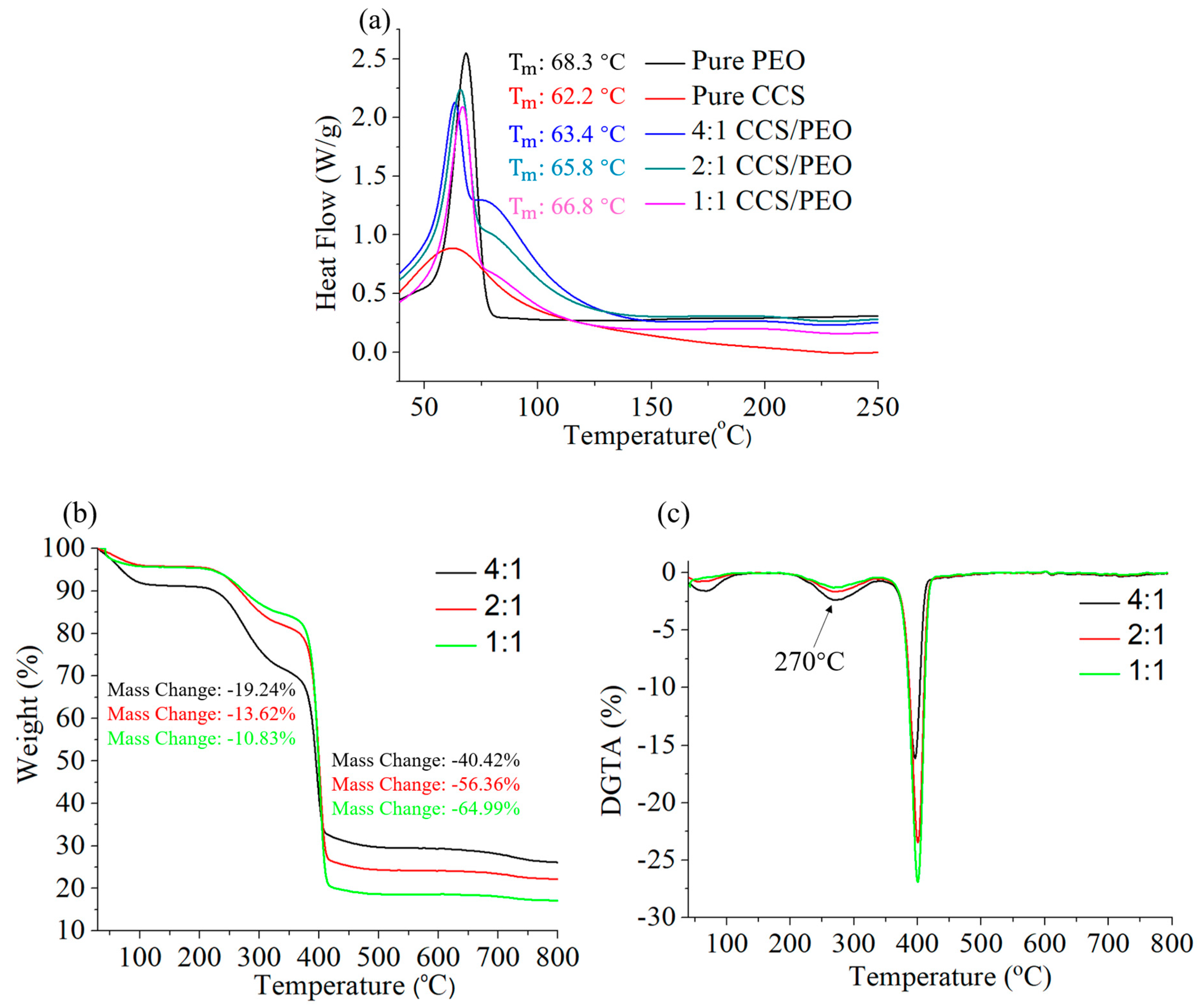
3.4. Thermal Characteristics of CCS/PEO Nanofibers
3.5. Chemical Composition of CCS/PEO Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quinones, J.P.; Peniche, H.; Peniche, C. Chitosan based self-assembled nanoparticles in drug delivery. Polymers 2018, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ways, T.M.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan and its derivatives for application in mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, K.; Afifi, A.M.; Jahangirian, H.; Webster, T.J. Biomedical applications of chitosan electrospun nanofibers as a green polymer—Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.; Ata, S.; Islam, A. Stimuli responsive biopolymer (chitosan) based blend hydrogels for wound healing application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.W.; Paras, C.B.; Weng, H.; Punnakitikashem, P.; Su, L.C.; Vu, K.; Tang, L.P.; Yang, J.; Nguyen, K.T. Dual growth factor releasing multi-functional nanofibers for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9351–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sinha-Ray, S. A review on biopolymer-based fibers via electrospinning and solution blowing and their applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Cheng, F.; Gao, S.Z.; Wu, Z.H.; Dong, L.L.; Lin, S.H.; Luo, Z.; Li, X.Y. Preparation, characterization, antibacterial properties, and hemostatic evaluation of ibuprofen-loaded chitosan/gelatin composite films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y. Rationally designed particle preloading method to improve protein delivery performance of electrospun polyester nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.H.; Lei, H.; Fan, D.D.; Duan, Z.G.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, S.S.; Yu, Y.Y. Novel enzymatic crosslinked hydrogels that mimic extracellular matrix for skin wound healing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 5909–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.B.; Krolicka, M.; van den Broek, L.A.M.; Frissen, A.E.; Boeriu, C.G. Water-soluble chitosan derivatives and ph-responsive hydrogels by selective c-6 oxidation mediated by tempo-laccase redox system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.A.; Dominguez-Robles, J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larraneta, E. Implantable polymeric drug delivery devices: Classification, manufacture, materials, and clinical applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Piri, H.; Parnian, M.J. Electrospun nanofiber membrane of peo/chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.L.; Xie, S.; Sung, X.X.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, Z.Y. Optimization of airflow field via solution blowing for chitosan/peo nanofiber formation. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wyman, I.W. Supramolecular nanostructures based on cyclodextrin and poly(ethylene oxide): Syntheses, structural characterizations and applications for drug delivery. Polymers 2016, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis-Tanguay, L.; Camire, A.; Renaud, M.; Chabot, B.; Lajeunesse, A. Sorption capacities of chitosan/polyethylene oxide (peo) electrospun nanofibers used to remove ibuprofen in water. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhiranon, S.; DeFine, L.A.; Alexander, T.S.; Kyu, T. Genistein-modified poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(d,l-lactic acid) electrospun mats with improved antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, F.; Nie, J. Electrospun water-soluble carboxyethyl chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membrane as potential wound dressing for skin regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.P.; Sell, S.A.; Boland, E.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Nanofiber technology: Designing the next generation of tissue engineering scaffolds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, J.L.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X. Creating biomimetic anisotropic architectures with co-aligned nanofibers and macrochannels by manipulating ice crystallization. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5780–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.E.; Ko, Y.-G.; Kim, W.I.; Kwon, O.K.; Kwon, O.H. Nanofiber mats composed of a chitosan-poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene oxide) blend as a postoperative anti-adhesion agent. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2017, 105, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienek, D.R.; Hoffman, K.M.; Tutak, W. Blow-spun chitosan/peg/plga nanofibers as a novel tissue engineering scaffold with antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Mi, S.L. Electrospun scaffolds for corneal tissue engineering: A review. Materials 2016, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirtic, J.; Balazic, H.; Zupancic, S.; Kristl, J. Effect of solution composition variables on electrospun alginate nanofibers: Response surface analysis. Polymers 2019, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Jun, Y.; Qin, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, C.; Venkatesh, M.; Barathi, V.A.; Harini, S.; Bairagi, S.; Leng, E.G.T.; Muruganandham, N.; Low, K.Z.W.; Fazil, M.; Loh, X.J.; et al. Bio-inspired crosslinking and matrix-drug interactions for advanced wound dressings with long-term antimicrobial activity. Biomaterials 2017, 138, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal spinning: An alternative approach to fabricate nanofibers at high speed and low cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boda, S.K.; Chen, S.X.; Chu, K.; Kim, H.J.; Xie, J.W. Electrospraying electrospun nanofiber segments into injectable microspheres for potential cell delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25069–25079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Use of airflow to improve the nanofibrous structure and quality of nanofibers from needleless electrospinning. J. Ind. Text. 2014, 45, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; Balachandran, K.; Capulli, A.K.; Golecki, H.M.; Agarwal, A.; Goss, J.A.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Parker, K.K. Engineering hybrid polymer-protein super-aligned nanofibers via rotary jet spinning. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Dulaney, A.R.; Gadley, J.; Maia, J.; Ellison, C.J. A comparative parameter study: Controlling fiber diameter and diameter distribution in centrifugal spinning of photocurable monomers. Polymer 2016, 88, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Xia, L.; Ju, J.G.; Xi, P.; Cheng, B.W.; Liang, Y.X. Preparation and low-temperature gas-sensing properties of sno2 ultra-fine fibers fabricated by a centrifugal spinning process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Ju, J.G.; Xu, W.; Ding, C.K.; Cheng, B.W. Preparation and characterization of hollow fe2o3 ultra-fine fibers by centrifugal spinning. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.C.; Xu, F.H.; Salinas, A.; Lozano, K. Mass production of carbon nanotube reinforced poly(methyl methacrylate) nonwoven nanofiber mats. Carbon 2014, 75, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mei, S.; Kong, L. Study on fabrication technology of nanofibers through centrifugal rotor. Adv. Text. Technol. 2017, 25, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Golecki, H.M.; Yuan, H.; Glavin, C.; Potter, B.; Badrossamay, M.R.; Goss, J.A.; Phillips, M.D.; Parker, K.K. Effect of solvent evaporation on fiber morphology in rotary jet spinning. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13369–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; McIlwee, H.A.; Goss, J.A.; Parker, K.K. Nanofiber assembly by rotary jet-spinning. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, G.; Fu, K.; Lee, H.; Zhang, X. Parameter study and characterization for polyacrylonitrile nanofibers fabricated via centrifugal spinning process. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.Y.; Ozisik, R.; Kotha, S.P.; Underhill, P.T. Highly efficient fabrication of polymer nanofiber assembly by centrifugal jet spinning: Process and characterization. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinian, H.; Valipouri, A.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Alirezazadeh, A. Determining the effect of centrifugal and electrical forces on the jet behaviors, the nanofiber structure, and morphology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.S.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, B.B.; Chen, B.Y.; Lai, Z.L. The movement and forces of spinning solution in the nozzle during high-speed centrifugal spinning. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padron, S.; Fuentes, A.; Caruntu, D.; Lozano, K. Experimental study of nanofiber production through forcespinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 024318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, M.S.N.; Yeh, R.; McKinley, G.H. Iterated stretching, extensional rheology and formation of beads-on-a-string structures in polymer solutions. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2006, 137, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravishankar, P.; Khang, A.; Laredo, M.; Balachandran, K. Using dimensionless numbers to predict centrifugal jet-spun nanofiber morphology. J. Nanomater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, V.M.E.A.L. The dynamics of thin liquid jets in air. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 140, 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mellado, P.; McIlwee, H.A.; Badrossamay, M.R.; Goss, J.A.; Mahadevan, L.; Kit Parker, K. A simple model for nanofiber formation by rotary jet-spinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 203107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. A fundamental study of chitosan/peo electrospinning. Polymer 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Pandit, V.; Elkin, J.; Denman, T.; Cooper, J.A.; Kotha, S.P. Large-scale and highly efficient synthesis of micro- and nano-fibers with controlled fiber morphology by centrifugal jet spinning for tissue regeneration. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Stretching-induced crystallinity and orientation of polylactic acid nanofibers with improved mechanical properties using an electrically charged rotating viscoelastic jet. Polymer 2011, 52, 4303–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-M.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. The combination of electrospinning and forcespinning: Effects on a viscoelastic jet and a single nanofiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Whittingstall, P.; McKinley, G.H. Using filament stretching rheometry to predict strand formation and “processability’’ in adhesives and other non-newtonian fluids. Rheol. Acta 2000, 39, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, R.T.; Harnau, L.; Rauschenbach, S.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K. Polymer nanofibers via nozzle-free centrifugal spinning. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Ahmed, F.; Polley, P.; Giri, J. Fabrication and characterization of core-shell nanofibers using a next-generation airbrush for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41924–41934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.F.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.L.; Pu, H.T. Nanolayer coextrusion: An efficient and environmentally friendly micro/nanofiber fabrication technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 95, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Cui, W.; Li, X.; Jin, Y. Electrospun fibrous mats with high porosity as potential scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.C.; Atkin, N.; Gunning, P.A.; Granville, N.; Wilson, K.; Wilson, D.; Southgate, J. Characterisation of electrospun polystyrene scaffolds for three-dimensional in vitro biological studies. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3136–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kattan, A.; Nirwan, V.P.; Munnier, E.; Chourpa, I.; Fahmi, A.; Kabashin, A.V. Toward multifunctional hybrid platforms for tissue engineering based on chitosan(peo) nanofibers functionalized by bare laser-synthesized au and si nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31759–31766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Mo, X.M.; He, C.L.; Wang, H.S. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen-chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, D.M.; Lemes, A.P.; de Oliveira, S.; Justo, G.Z.; Palladino, M.V.; Duran, N. Electrospun poly(ethylene oxide)/chitosan nanofibers with cellulose nanocrystals as support for cell culture of 3t3 fibroblasts. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3353–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariful, M.I.; Bin Sharif, S.; Lee, J.J.L.; Habiba, U.; Ang, B.C.; Amalina, M.A. Adsorption of divalent heavy metal ion by mesoporous-high surface area chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibrous membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A.E.; Edmondson, D.; Chang, F.C.; Wood, D.; Gong, A.; Levengood, S.L.; Zhang, M.Q. High-throughput and high-yield fabrication of uniaxially-aligned chitosan-based nanofibers by centrifugal electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| CCS:PEO | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Nozzle Diameter (mm) | Nozzle Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4:1 | 4500 | 0.1 | 6.5 |
| 2:1 | 4500 | 0.1 | 13 |
| 1:1 | 5000 | 0.1 | 13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Mei, S.; Dong, Y.; She, F.; Kong, L. High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning. Polymers 2019, 11, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101550
Li Z, Mei S, Dong Y, She F, Kong L. High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhen, Shunqi Mei, Yajie Dong, Fenghua She, and Lingxue Kong. 2019. "High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101550
APA StyleLi, Z., Mei, S., Dong, Y., She, F., & Kong, L. (2019). High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning. Polymers, 11(10), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101550