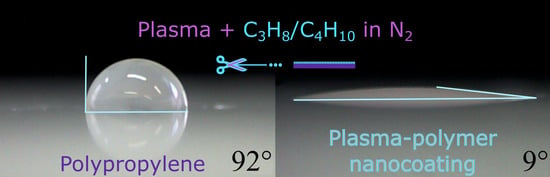
Fast Surface Hydrophilization via Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Biological and Technical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
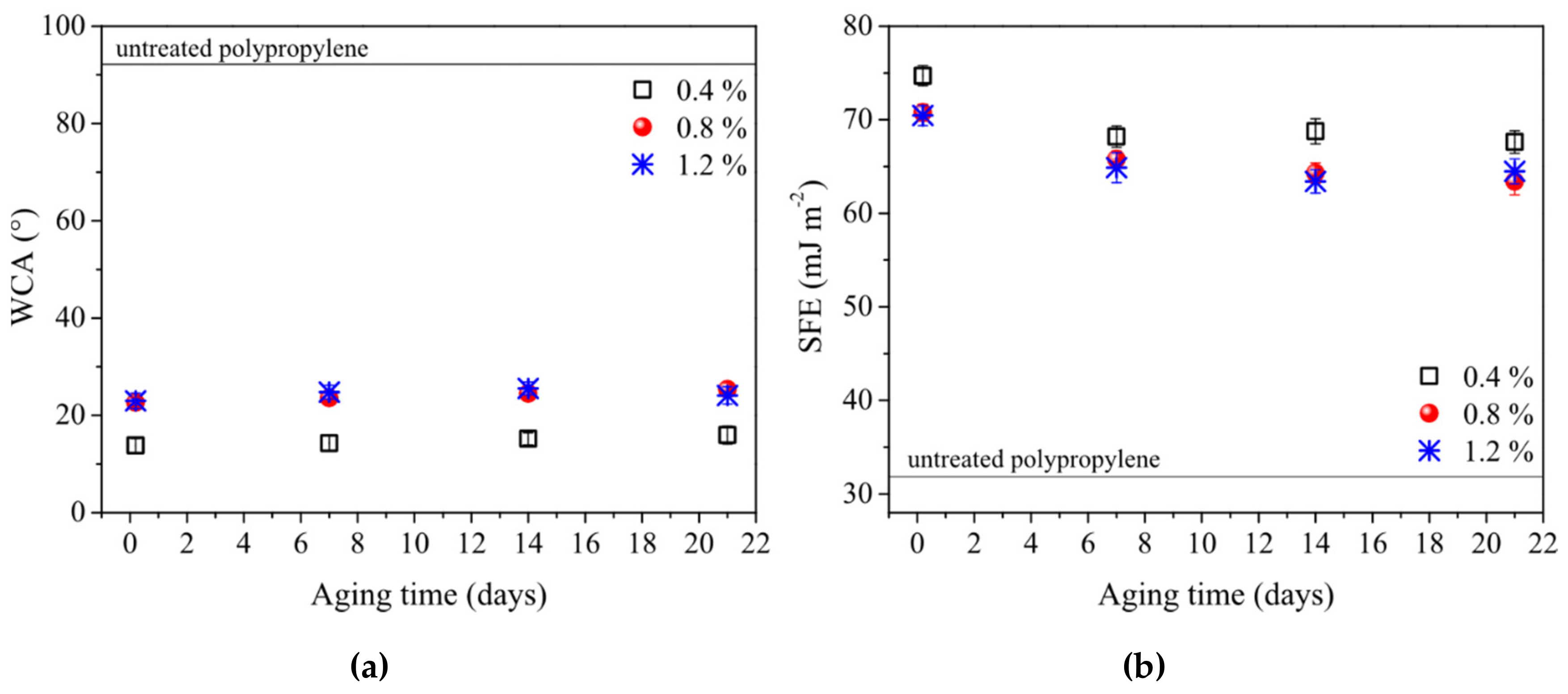
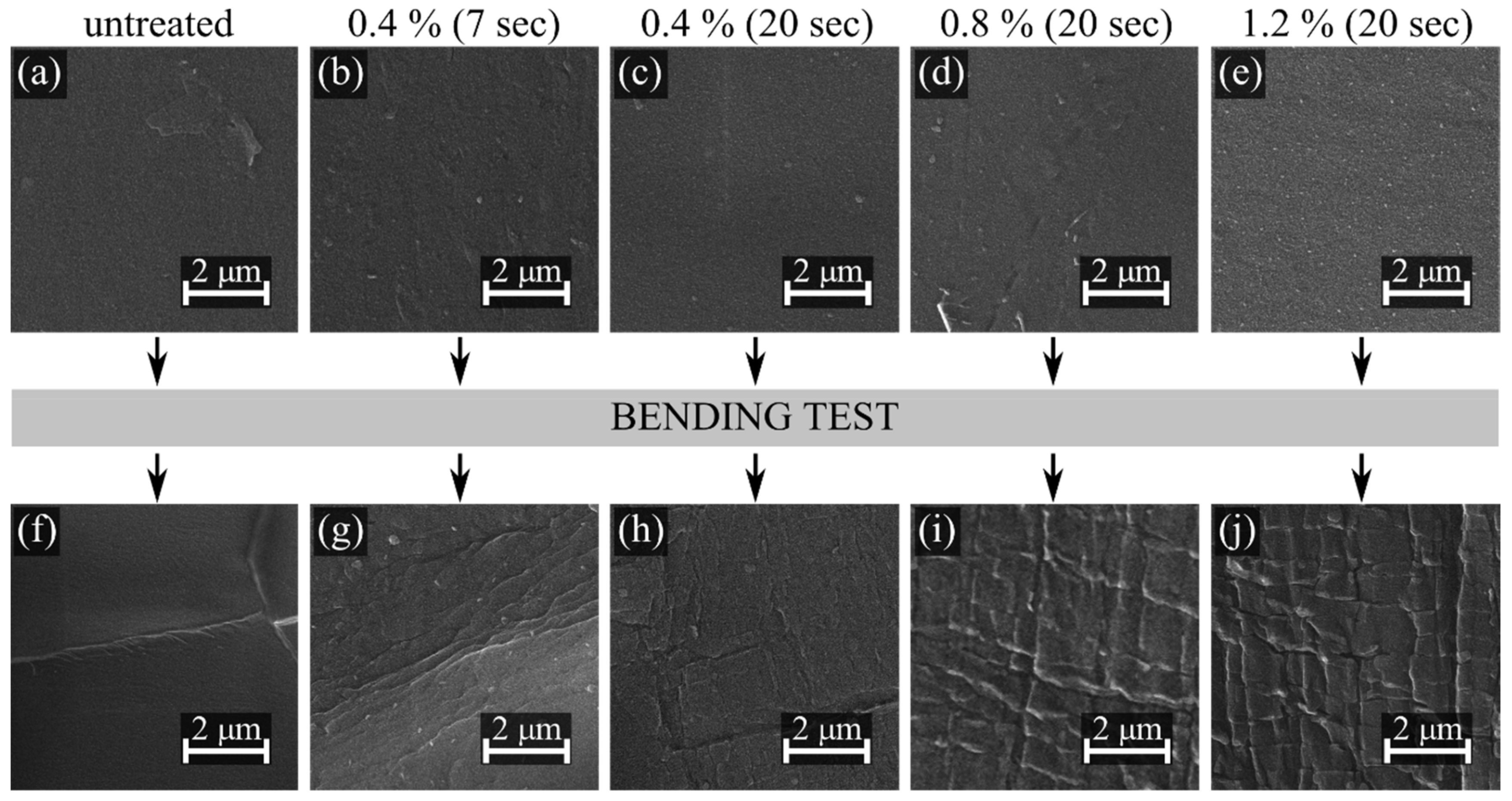
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, R.J.; Lovell, P.A. Introduction to Polymers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781439894156. [Google Scholar]
- Olatujni, O. Natural Polymers; Olatunji, O., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-26412-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mascia, L. Polymers in Industry from A to Z: A Concise Encyclopedia; WILEY-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9783527644049. [Google Scholar]
- Nemani, S.K.; Annavarapu, R.K.; Mohammadian, B.; Raiyan, A.; Heil, J.; Haque, M.A.; Abdelaal, A.; Sojoudi, H. Surface Modification of Polymers: Methods and Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1801247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, P.; Messori, M. Surface Modification of Polymers. In Modification of Polymer Properties; Jasso-Gastinel, C.F., Kenny, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 109–130. ISBN 978-0-323-44353-1. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Dinh, D.K.; Abbas, Q.; Imran, M.; Sattar, H.; Ul Ahmad, A. Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification. Surfaces 2019, 2, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotoh, K.; Yasukawa, A.; Kobayashi, Y. Wettability characteristics of poly(ethylene terephthalate) films treated by atmospheric pressure plasma and ultraviolet excimer light. Polym. J. 2011, 43, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimor, M.; Ráhel’, J.; Černák, M.; Imahori, Y.; Štefečka, M.; Kando, M. Atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment of polyester nonwoven fabrics for electroless plating. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2003, 172, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, M.; Toselli, M.; Pilati, F.; Fabbri, E.; Fabbri, P.; Pasquali, L.; Nannarone, S. Prevention of plasticizer leaching from PVC medical devices by using organic–inorganic hybrid coatings. Polymer (Guildf) 2004, 45, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehr, C. Plasma surface modification of polymers for biomedical use. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2003, 208, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, D.; Höcker, H. Polymers for Biomedical Applications: Improvement of the Interface Compatibility. In Biomedical Applications Polymer Blends. Advances in Polymer Science; Eastmond, G.C., Höcker, H., Klee, D., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1999; Volume 149, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, S.; Hagiwara, K.; Hasebe, T.; Hotta, A. Surface modification of polymers by plasma treatments for the enhancement of biocompatibility and controlled drug release. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2013, 233, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, A.S.; Mahapatro, A. Polymers for Biomedical Applications; American Chemical Society.: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Lin, C.-W.; Mansour, R.; Gu, F. Improving biocompatibility by surface modification techniques on implantable bioelectronics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Idris, A. Overview of PES biocompatible/hemodialysis membranes: PES–blood interactions and modification techniques. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 574–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macgregor, M.; Vasilev, K. Perspective on Plasma Polymers for Applied Biomaterials Nanoengineering and the Recent Rise of Oxazolines. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihan, T.G.; Ionita, M.D.; Popescu, R.G.; Iordachescu, D. Effect of hydrophilic–hydrophobic balance on biocompatibility of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)–hydroxyapatite (HA) composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 118, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, C.P.; McDonnell, K.A.; Onayemi, O.D.; O’Gara, J.P.; Dowling, D.P. Evaluation of Protein Adsorption on Atmospheric Plasma Deposited Coatings Exhibiting Superhydrophilic to Superhydrophobic Properties. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mredha, M.T.I.; Pathak, S.K.; Tran, V.T.; Cui, J.; Jeon, I. Hydrogels with superior mechanical properties from the synergistic effect in hydrophobic–hydrophilic copolymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocijan, A.; Conradi, M.; Hočevar, M. The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, G.; Galler, K.M. Biocompatibility of biomaterials—Lessons learned and considerations for the design of novel materials. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Qu, X.; Lu, J.; Zhu, C.; Wan, L.; Yang, J.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. Characterization of surface property of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) after oxygen plasma treatment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4777–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francolini, I.; Vuotto, C.; Piozzi, A.; Donelli, G. Antifouling and antimicrobial biomaterials: An overview. APMIS 2017, 125, 392–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrata-Wesolek, A. Antifouling surfaces in medical application. Polimery 2013, 58, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pardo, I.; van der Ven, L.; van Benthem, R.; de With, G.; Esteves, A. Hydrophilic Self-Replenishing Coatings with Long-Term Water Stability for Anti-Fouling Applications. Coatings 2018, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskens, P.; Wouters, M.; Rentrop, C.; Vroon, Z. A brief review of environmentally benign antifouling and foul-release coatings for marine applications. J. Coatings Technol. Res. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, B.; Bedwell, I.; Dimas, J.; Scardino, A.; Tang, Y.; Sammut, K. Effects of Various Antifouling Coatings and Fouling on Marine Sonar Performance. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Černák, M.; Kováčik, D.; Ráhel’, J.; St’ahel, P.; Zahoranová, A.; Kubincová, J.; Tóth, A.; Černáková, L. Generation of a high-density highly non-equilibrium air plasma for high-speed large-area flat surface processing. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2011, 53, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, F.; Di Mundo, R.; Cappelluti, D.; D’Agostino, R. SuperHydrophobic and SuperHydrophilic Polycarbonate by Tailoring Chemistry and Nano-texture with Plasma Processing. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D. Status and potential of atmospheric plasma processing of materials. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film 2011, 29, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noeske, M.; Degenhardt, J.; Strudthoff, S.; Lommatzsch, U. Plasma jet treatment of five polymers at atmospheric pressure: Surface modifications and the relevance for adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2004, 24, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehocký, M.; Drnovská, H.; Lapčíková, B.; Barros-Timmons, A.M.; Trindade, T.; Zembala, M.; Lapčík, L. Plasma surface modification of polyethylene. Colloid. Surf. A 2003, 222, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorai, R.; Kushner, M.J. A model for plasma modification of polypropylene using atmospheric pressure discharge. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, K.; Steffen, H.; von Woedtke, T.; Schröder, K.; Weltmann, K.-D. High Rate Etching of Polymers by Means of an Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egitto, F.D. Plasma etching and modification of organic polymers. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Han, S.; Beag, Y.W.; Koh, S.K. Hydrophilic surface formation on polymers by ion-assisted reaction. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 48, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerenser, L.J. XPS studies of in situ plasma-modified polymer surfaces. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1993, 7, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsougeni, K.; Petrou, P.S.; Tserepi, A.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Gogolides, E. Nano-texturing of poly (methyl methacrylate) polymer using plasma processes and applications in wetting control and protein adsorption. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarmoutsou, A.; Charitidis, C.A.; Gnanappa, A.K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. Nanomechanical and nanotribological properties of plasma nanotextured superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic polymeric surfaces. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 505711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.; Plummer, C.; Bisson, I.; Frey, P.; Hilborn, J. Plasma-induced graft polymerization of acrylic acid onto poly (ethylene terephthalate) films: Characterization and human smooth muscle cell growth on grafted films. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.X.; Klee, D.; Plüster, W.; Severich, B.; Höcker, H. Surface modification of polyurethane by plasma-induced graft polymerization of poly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wavhal, D.S.; Fisher, E.R. Hydrophilic modification of polyethersulfone membranes by low temperature plasma-induced graft polymerization. J. Membrane Sci. 2002, 209, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M.; Belfort, G. Surface modification of ultrafiltration membranes by low temperature plasma II. Graft polymerization onto polyacrylonitrile and polysulfone. J. Membrane Sci. 1996, 111, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yao, L.; Sun, S.; Gao, Z.Q.; Qiu, Y.P. Effect of storage condition and aging on acrylic acid inverse emulsion surface-grafting polymerization of PET films initiated by atmospheric pressure plasmas. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.; Kirkhorn, S.; Olafsen, K.; Redford, K.; Stori, A. Modification of polyolefin surfaces by plasma-induced grafting. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahners, T.; Prager, L.; Pender, A.; Gutmann, J.S. Super-wetting surfaces by plasma- and UV-based grafting of micro-rough acrylate coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarratta, V.; Vohrer, U.; Hegemann, D.; Müller, M.; Oehr, C. Plasma functionalization of polypropylene with acrylic acid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, H. Plasma Polymer Films; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 1–86094–467–1. [Google Scholar]
- Foest, R.; Kindel, E.; Ohl, A.; Stieber, M.; Weltmann, K.D. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure discharges for surface modification. Plasma Phys. Contr. F. 2005, 47, B525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M.; Johansson, J.-Å.; Burns, N.L.; Yasuda, H.K. Protein adsorption at n-butane plasma polymer surfaces. Colloid. Surface. B 1996, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merche, D.; Vandencasteele, N.; Reniers, F. Atmospheric plasmas for thin film deposition: A critical review. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 4219–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Trentesaux, M.; Gengembre, L.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; Payen, E. Stability study of polyacrylic acid films plasma-polymerized on polypropylene substrates at medium pressure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.J.; Schofield, W.C.E.; Badyal, J.P.S.; Goodwin, A.J.; Merlin, P.J. Atmospheric pressure plasma deposition of structurally well-defined polyacrylic acid films. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Short, R.D.; Matthews, A. Deposition of functional coatings from acrylic acid and octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane onto steel using an atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 203, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topala, I.; Dumitrascu, N.; Popa, G. Properties of the acrylic acid polymers obtained by atmospheric pressure plasma polymerization. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2009, 267, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; Gengembre, L.; Schacht, E.; Payen, E. Deposition of HMDSO-based coatings on PET substrates using an atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Bumgarner, M.O.; Marsh, H.C.; Morosoff, N. Plasma polymerization of some organic compounds and properties of the polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. Edition 1976, 14, 195–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyse, P.; Dams, R.; Paulussen, S.; Houthoofd, K.; Janssen, K.; Jacobs, P.A.; Sels, B.F. Dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure as a tool to deposit versatile organic coatings at moderate power input. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Hegemann, D.; Fortunato, G.; Herrmann, A.S.; Heuberger, M. Plasma Deposition of Permanent Superhydrophilic a-C: H: N Films on Textiles. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Bell, A.T. A Review of Recent Advances in Plasma Polymerization. ACS Sym. Ser. 1979, 108, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, J. Mechanisms of plasma polymerization-reviewed from a chemical point of view. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, H. Polymer films prepared by plasma polymerization and their potential application. Vacuum 1987, 37, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Influence of the RF plasma polymerization process on the barrier properties of coil-coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 53, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.H. Anti-reflective coating for the deep coloring of PET fabrics using an atmospheric pressure plasma technique. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2001, 142, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Múgica-Vidal, R.; Alba-Elías, F.; Sainz-García, E.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Atmospheric plasma-polymerization of hydrophobic and wear-resistant coatings on glass substrates. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 259, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautrin-Ul, C.; Boisse-Laporte, C.; Benissad, N.; Chausse, A.; Leprince, P.; Messina, R. Plasma-polymerized coatings using HMDSO precursor for iron protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2000, 38, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.M.; Choe, H.C.; Jung, S.C.; Kim, B.H. Plasma deposition of a silicone-like layer for the corrosion protection of magnesium. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massines, F.; Sarra-Bournet, C.; Fanelli, F.; Naudé, N.; Gherardi, N. Atmospheric pressure low temperature direct plasma technology: Status and challenges for thin film deposition. Plasma Process. Polym. 2012, 9, 1041–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, I.; Hudec, I.; Volovič, M. Surface modification of textile reinforming material by plasma treatment and plasma polymerization. Chem. Listy 2009, 103, s100–s101. [Google Scholar]
- Šimor, M.; Ráheľ, J.; Vojtek, P.; Černák, M.; Brablec, A. Atmospheric-pressure diffuse coplanar surface discharge for surface treatments. Appl.Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2716–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelble, D.H. Dispersion-Polar Surface Tension Properties of Organic Solids. J. Adhesion 1970, 2, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E. Superhydrophilic and superwetting surfaces: Definition and mechanisms of control. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18621–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaleh, B.; Parvin, P.; Wanichapichart, P.; Saffar, A.P.; Reyhani, A. Induced super hydrophilicity due to surface modification of polypropylene membrane treated by O2 plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, Y.; Kurihara, S.; Yajima, T.; Seki, Y.; Nakamura, I.; Takano, I. Formation of super-hydrophilic surface of hydroxyapatite by ion implantation and plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 196, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrino, L.; Moroni, G.; Polini, W. Cold plasma treatment of polypropylene surface: A study on wettability and adhesion. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2002, 121, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpilowski, K.; Rymuszka, D.; Holysz, L.; Chibowski, E. Changes in wettability of polycarbonate and polypropylene pretreated with oxygen and argon plasma. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Material Technologies and Modeling MMT-2014, Ariel, Izrael, 28 July 2014; Zinigrad, M., Ed.; 2014; pp. 155–165, ISBN 978-965-91944-2-1. [Google Scholar]
- Slepička, P.; Vasina, A.; Kolská, Z.; Luxbacher, T.; Malinský, P.; Macková, A.; Švorčík, V. Argon plasma irradiation of polypropylene. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2010, 268, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyaraj, K.N.; Selvarajan, V.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Gao, C. Modification of surface properties of polypropylene (PP) film using DC glow discharge air plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3965–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.J.; Myung, S.W.; Lee, C.S.; Choi, H.S. Comparison of the surface characteristics of polypropylene films treated by Ar and mixed gas (Ar/O2) atmospheric pressure plasma. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 295, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harth, K.; Hibst, H. Surface modification of polypropylene in oxygen and nitrogen plasmas. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1993, 59, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.J.; Tang, S.; Myung, S.W.; Lu, N.; Choi, H.S. Surface characteristics of polypropylene film treated by an atmospheric pressure plasma. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massines, F.; Gouda, G.; Gherardi, N.; Duran, M.; Croquesel, E. The role of dielectric barrier discharge atmosphere and physics on polypropylene surface treatment. Plasmas Polym. 2001, 6, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrino, L.; Polini, W.; Sorrentino, L. Ageing time of wettability on polypropylene surfaces processed by cold plasma. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2004, 153, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massines, F.; Gouda, G. A comparison of polypropylene-surface treatment by filamentary, homogeneous and glow discharges in helium at atmospheric pressure. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Leys, C.; Gengembre, L.; Payen, E. Study of the ageing behaviour of polymer films treated with a dielectric barrier discharge in air, helium and argon at medium pressure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7847–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, K.S. Surface Modification of Plastics. In Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook; Kutz, M., Ed.; Plastics Design Library; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 443–487. ISBN 978-0-323-39040-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, T.; Zhang, C.; Long, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, P.; Zhou, Y. Surface modification of polyimide films using unipolar nanosecond-pulse DBD in atmospheric air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3888–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, T.; Xie, Q.; Xu, J.; Yang, W. Hydrophobic treatment on polymethylmethacrylate surface by nanosecond-pulse DBDs in CF4 at atmospheric pressure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablokov, M.; Gilman, A.; Kuznetsov, A. MODIFICATION OF WETTABILITY OF POLYMER SURFACES BY PLASMA. In Proceedings of the 21st Symposium on Application of Plasma Processes Book of Contributed Papers; Medvecká, V., Országh, J., Papp, P., Matějčík, Š., Eds.; Department of Experimental Physics, Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University in Bratislava; Society for Plasma Research and Applications in cooperation with Library and Publishing Centre CU: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2017; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Chang, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ren, C.; Shao, T. Surface modifications of polystyrene and their stability: A comparison of DBD plasma deposition and direct fluorination. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Xie, Q.; Ren, C.; Shao, T. Plasma surface treatment to improve surface charge accumulation and dissipation of epoxy resin exposed to DC and nanosecond-pulse voltages. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 405203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Kong, F.; Yan, P.; Chang, C.; Shao, T. Atmospheric pressure plasmas and direct fluorination treatment of Al2O3-filled epoxy resin: A comparison of surface charge dissipation. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2019, 362, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, J.P. Infrared study of polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1960, 3, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak-Domagala, W. The use of the spectrometric technique FTIR-ATR to examine the polymers surface. In Advanced Aspects of Spectroscopy; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wexler, A.S. Integrated Intensities of Absorption Bands in Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 1967, 1, 29–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klages, C.P.; Hinze, A.; Khosravi, Z. Nitrogen Plasma Modification and Chemical Derivatization of Polyethylene Surfaces—An In Situ Study Using FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy. Plasma Process. Polym. 2013, 10, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellin, N.; de, C.; Campos, J.S. Surface composition analysis of PP films treated by corona discharge. Mater. Res. 2003, 6, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Leys, C.; Gengembre, L.; Payen, E. Comparison between XPS- and FTIR-analysis of plasma-treated polypropylene film surfaces. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak-Domagała, W.; Wrzosek, H.; Szymanowski, H.; Majchrzycka, K.; Brochocka, A. Plasma Modification of Filter Nonwovens Used for the Protection of Respiratory Tracts. Fibres Tex. East. Eur. 2010, 18, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.Y.; Juang, R.S.; Huang, C. Surface Modification of Polypropylene Membrane by RF Methane/Oxygen Mixture Plasma Treatment. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 08KA02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvenket, S.; Rao, G.M.; Komath, M.; Raichur, A.M. Plasma surface modification of polystyrene and polyethylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 236, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutel, B.; Grimblot, J.; Dessaux, O.; Goudmand, P. XPS investigations of nitrogen-plasma-treated polypropylene in a reactor coupled to the spectrometer. Surf. Interface Anal. 2000, 30, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E.; Küttel, O.M.; Martinu, L.; Wertheimer, M.R. Dual-frequency N2 and NH3 plasma modification of polyethylene and polyimide. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1991, 9, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Propane-Butane Concentration (%) | Aging Time (Days) | Atomic Composition (at %) | Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | O/C | N/C | (O+N)/C | ||
| untreated PP | - | 93 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 0 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.08 |
| 0.4 | - | 68 ± 2 | 12 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.47 |
| 0.8 | - | 68 ± 1 | 9 ± 2 | 23 ± 2 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.47 |
| 1.8 | - | 75 ± 1 | 8 ± 1 | 17 ± 2 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.33 |
| 0.4 | 14 | 68 ± 1 | 13 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.46 |
| 0.8 | 14 | 69 ± 1 | 11 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 0.45 |
| 1.2 | 14 | 76 ± 1 | 10 ± 2 | 14 ± 1 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.32 |
| Propane-Butane Concentration (%) | Aging Time (Days) | Functional Groups (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C−C/C−H | C−O | C=O | COO/C−CO−N | C−N | C=N | ||
| untreated PP | - | 87 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.4 | - | 45 | 9 | 10 | 3 | 21 | 12 |
| 0.8 | - | 36 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 29 | 14 |
| 1.2 | - | 35 | 12 | 5 | 2 | 36 | 10 |
| 0.4 | 14 | 48 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 17 | 12 |
| 0.8 | 14 | 36 | 12 | 9 | 2 | 28 | 13 |
| 1.2 | 14 | 36 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 32 | 10 |
| Propane-Butane Concentration (%) | Thickness (nm) | Deposition Rate (nm.s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 23 ± 4 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| 0.8 | 44 ± 2 | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| 1.2 | 94 ± 7 | 4.7 ± 0.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dvořáková, H.; Čech, J.; Stupavská, M.; Prokeš, L.; Jurmanová, J.; Buršíková, V.; Ráheľ, J.; Sťahel, P. Fast Surface Hydrophilization via Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Biological and Technical Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101613
Dvořáková H, Čech J, Stupavská M, Prokeš L, Jurmanová J, Buršíková V, Ráheľ J, Sťahel P. Fast Surface Hydrophilization via Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Biological and Technical Applications. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101613
Chicago/Turabian StyleDvořáková, Hana, Jan Čech, Monika Stupavská, Lubomír Prokeš, Jana Jurmanová, Vilma Buršíková, Jozef Ráheľ, and Pavel Sťahel. 2019. "Fast Surface Hydrophilization via Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Biological and Technical Applications" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101613
APA StyleDvořáková, H., Čech, J., Stupavská, M., Prokeš, L., Jurmanová, J., Buršíková, V., Ráheľ, J., & Sťahel, P. (2019). Fast Surface Hydrophilization via Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Biological and Technical Applications. Polymers, 11(10), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101613