Biodegradable Polylactide/TiO2 Composite Fiber Scaffolds with Superhydrophobic and Superadhesive Porous Surfaces for Water Immobilization, Antibacterial Performance, and Deodorization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of the ES PLA/TiO2 fiber scaffold
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Antibacterial Activity Measurement
2.5. Deodorization Performance Evaluation
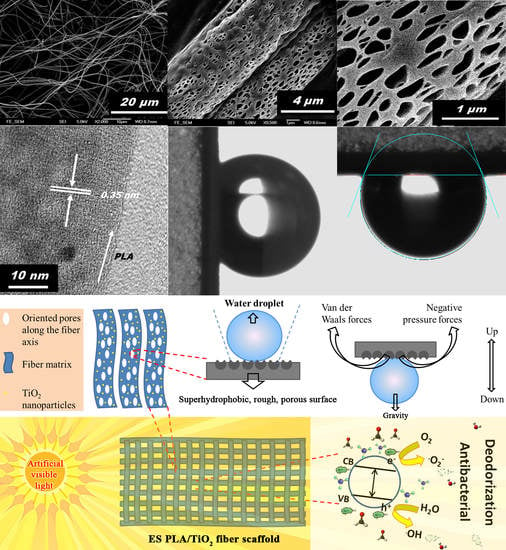
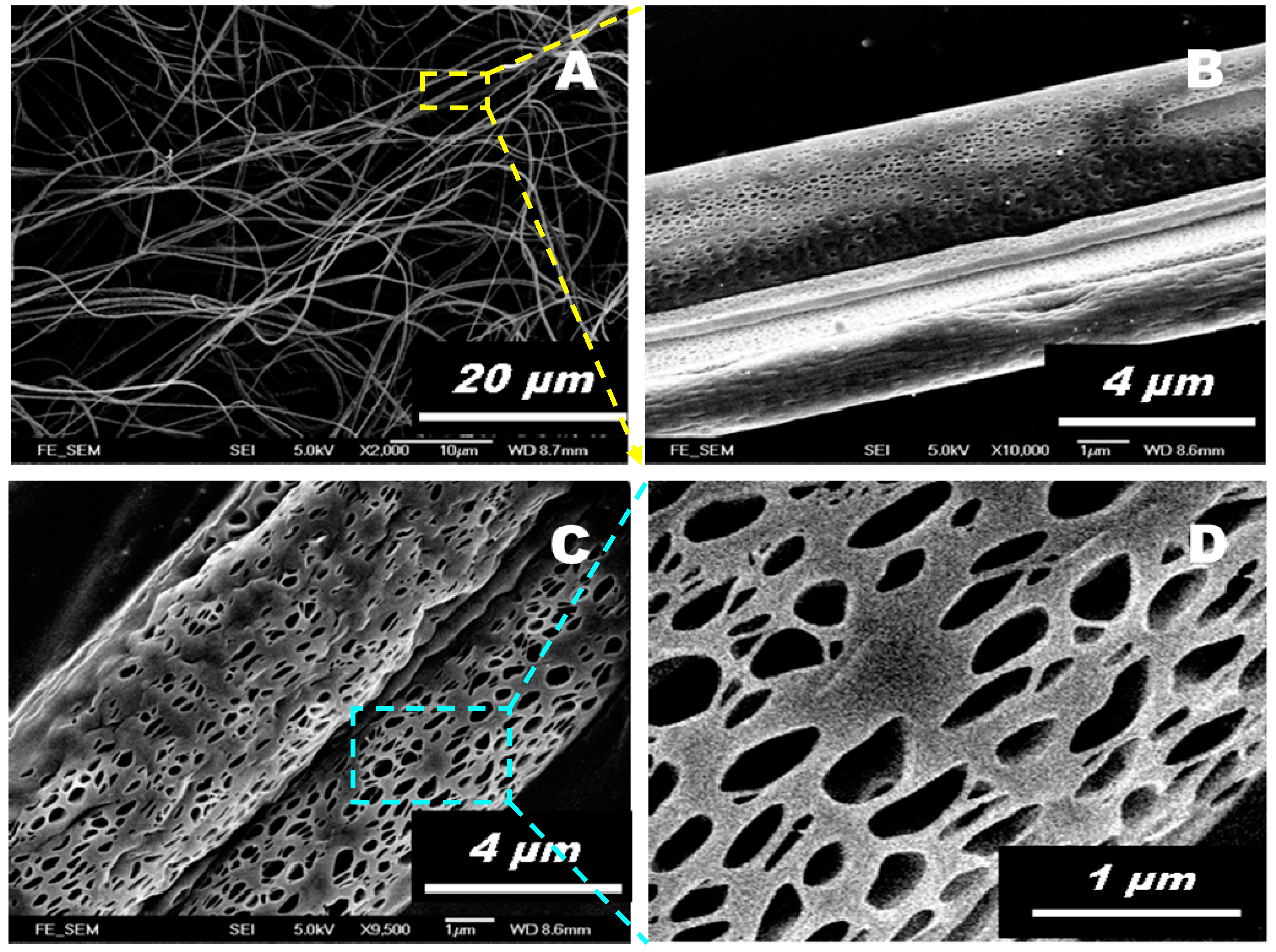
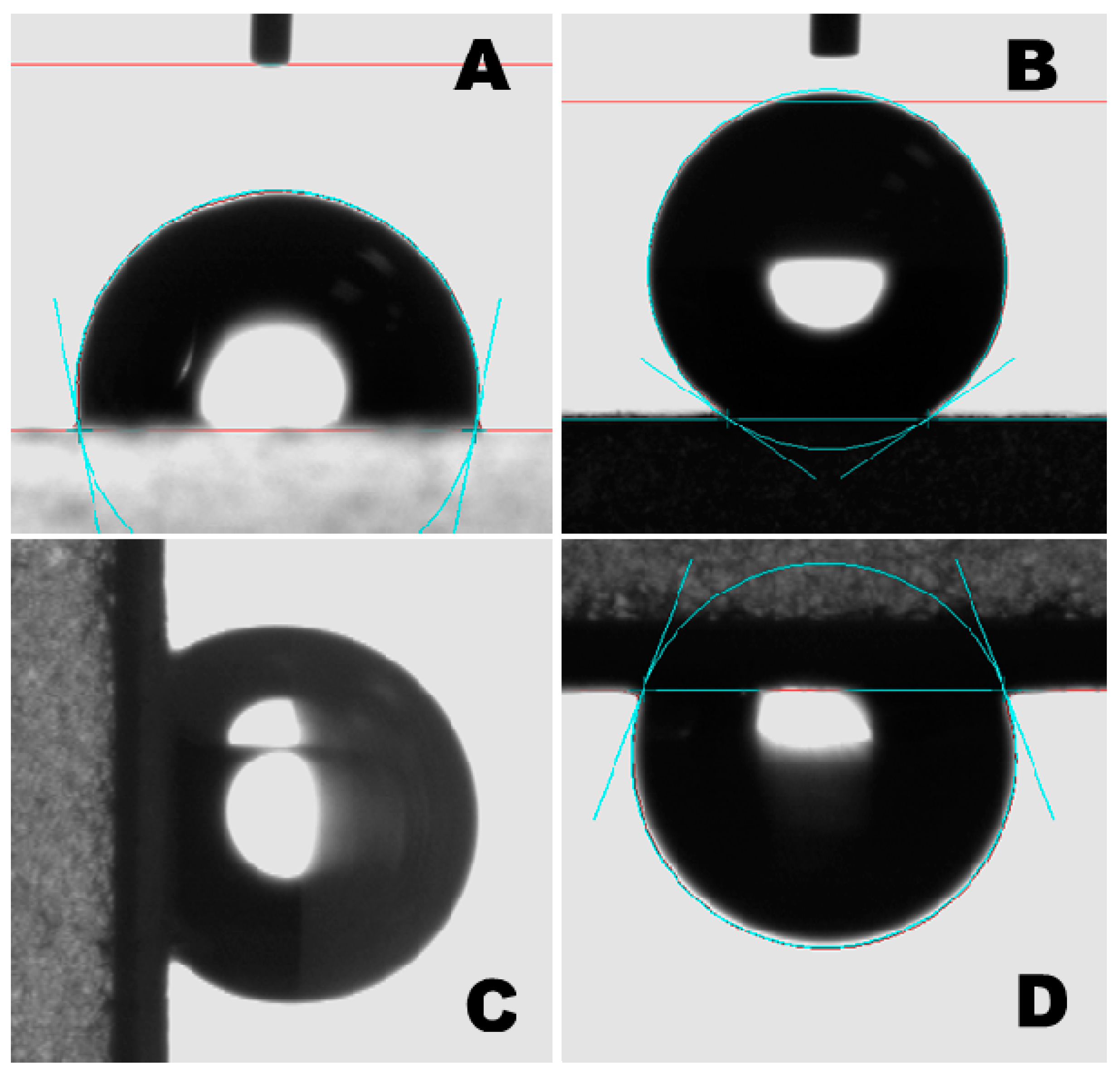
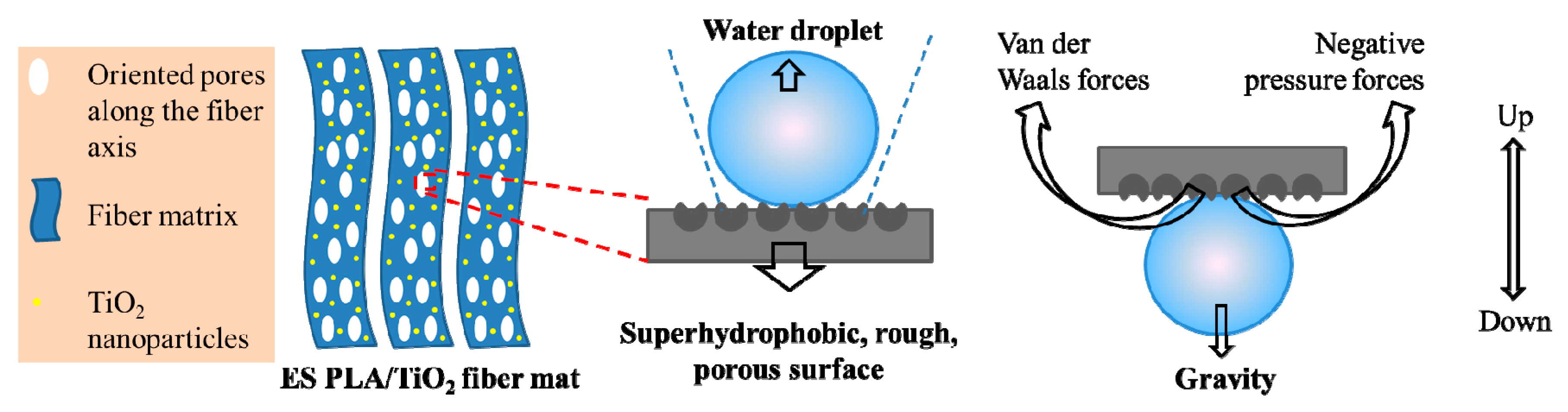
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Coordination-Driven Controlled Assembly of Polyphenol-Metal Green Coating on Wood Micro-Grooved Surfaces: A Novel Approach to Stable Superhydrophobicity. Polymers 2017, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-F.; Wang, W.-N.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Hu, C.-C.; Lai, J.-Y. Facile Fabrication of Durable Superhydrophobic Films from Carbon Nanotube/Main-Chain Type Polybenzoxazine Composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods. Polymers 2017, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad Karim, A.; Rothstein, J.P.; Kavehpour, H.P. Experimental study of dynamic contact angles on rough hydrophobic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Bio-Inspired, Smart, Multiscale Interfacial Materials. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Liang, Y.A.; Hsieh, S.T.; Zesch, W.; Chan, W.P.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Feng, X.; Feng, L.; Sun, T.; Zhai, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic Aligned Polystyrene Nanotube Films with High Adhesive Force. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, C.-Y.; Qu, D.-H.; Long, Y.-T.; Feringa, B.L.; Tian, H. Exploring a naturally tailored small molecule for stretchable, self-healing, and adhesive supramolecular polymers. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Sun, N.; Nielsen, S.O.; Stogin, B.B.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Wong, T.-S. Hydrophilic directional slippery rough surfaces for water harvesting. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq0919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallqvist, V.; Claesson, P.M.; Swerin, A.; Östlund, C.; Schoelkopf, J.; Gane, P.A.C. Influence of Surface Topography on Adhesive and Long-Range Capillary Forces between Hydrophobic Surfaces in Water. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9197–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Petal Effect: A Superhydrophobic State with High Adhesive Force. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-M.; Bai, J.; Shao, D.; Qiu, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.-M.; Chen, L.; et al. Antibacterial and biodegradable tissue nano-adhesives for rapid wound closure. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Xiao, H.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X.; Bu, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, Z.; et al. SiO2 loading into polydopamine-functionalized TiO2 nanotubes for biomedical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 364, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotovvati, B.; Namdari, N.; Dehghanghadikolaei, A. On Coating Techniques for Surface Protection: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska-Krepsztul, J.; Rydzkowski, T.; Borowski, G.; Szczypiński, M.; Klepka, T.; Thakur, V.K. Recent progress in biodegradable polymers and nanocomposite-based packaging materials for sustainable environment. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An Overview of Polylactides as Packaging Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, M.C.; Krieghoff, J.; Mikos, A.G. Synthetic Polymers. In Principles of Regenerative Medicine, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 559–590. [Google Scholar]
- Thauvin, C.; Schwarz, B.; Delie, F.; Allémann, E. Functionalized PLA polymers to control loading and/or release properties of drug-loaded nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassalle, V.; Ferreira, M.L. PLA Nano- and Microparticles for Drug Delivery: An Overview of the Methods of Preparation. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valo, H.; Peltonen, L.; Vehviläinen, S.; Karjalainen, M.; Kostiainen, R.; Laaksonen, T.; Hirvonen, J. Electrospray Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Drugs in Poly(L-lactic acid) Nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Megna, B. Structure-property relationship of PLA-Opuntia Ficus Indica biocomposites. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 167, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lan, X.-R.; Bao, R.-Y.; Lei, Y.; Cao, Z.-Q.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.-B. High-performance porous polylactide stereocomplex crystallite scaffolds prepared by solution blending and salt leaching. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, G.; Dong, Z. Fabrication and Properties of the Electrospun Polylactide/Silk Fibroin-Gelatin Composite Tubular Scaffold. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-Y.; Cui, L.-Y.; Zeng, R.-C.; Li, S.-Q.; Chen, X.-B.; Zheng, Y.; Kannan, M.B. Advances in functionalized polymer coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloys—A review. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Yang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Fei, B.; Xin, J.H. Visible light-active sub-5nm anatase TiO2 for photocatalytic organic pollutant degradation in water and air, and for bacterial disinfection. Catal. Commun. 2015, 72, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omastová, M.; Číková, E.; Mičušík, M. Electrospinning of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Fibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, D. Cotton fabric-based facile solar photocatalytic purification of simulated real dye wastes. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9922–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Rao, A.; Tiwari, A.; Yashwanth, P.; Lal, M.; Dubey, U.; Aich, S.; Roy, B. Study on the effects of Cl and F doping in TiO2 powder synthesized by a sol-gel route for biomedical applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 134, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured Fibers via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xue, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Pan, C. Lattice distortion mechanism study of TiO2 nanoparticles during photocatalysis degradation and reactivation. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 057105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial Activity of Nanosilver Ions and Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xin, J.H.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Miao, D.; Liu, Y. Synthesis and stabilization of metal nanocatalysts for reduction reactions—A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11157–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Chen, D.; Deng, P.; Liang, J. Fabrication of Amine-Modified Magnetite-Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Sensitive Dopamine Determination. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Chang, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, D. A new insight into PAM/graphene-based adsorption of water-soluble aromatic pollutants. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8650–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Hu, H.; Quan, H.; Wei, H.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, J.; Luo, P.; Liang, Y.; Ou, J.; Chen, D. An iridescent film of porous anodic aluminum oxide with alternatingly electrodeposited Cu and SiO2 nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zavabeti, A.; Quan, H.; Zhu, W.; Wei, H.; Chen, D.; Ou, J.Z. Recent advances in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides for biological sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Mai, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. Selective Enrichment of Clenbuterol onto Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres with Tailor-made Structure and Oxygen Functionalities. Polymers 2019, 11, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xin, J.H.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Kong, Y. Metal-free graphene-based catalyst—Insight into the catalytic activity: A short review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 492, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Hu, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Guo, P.; Xin, M.; Yu, M.; Lin, H. Functionalization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres for the Highly Selective Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions and the Analysis of Food-Grade Fish Samples. Polymers 2018, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Hu, H.; Guo, P.; Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, M. Combining Pickering Emulsion Polymerization with Molecular Imprinting to Prepare Polymer Microspheres for Selective Solid-Phase Extraction of Malachite Green. Polymers 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Quan, H.; Zhong, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D. A Reduced Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Based Adsorbent for Efficiently Binding with Organic Pollutants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6502–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Lee, K.I.; Ma, K.; Hu, H.; Xin, J.H. Graphene oxide-enhanced sol-gel transition sensitivity and drug release performance of an amphiphilic copolymer-based nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test Microorganism | N0a (CFU/piece) | N24hb for the Control Specimen (CFU/piece) | N24hc for the ES PLA/TiO2 Specimen (CFU/piece) | R1d (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 2.4 × 105 | 1.6 × 106 | < 20 | > 99 |
| Escherichia coli | 2.1 × 105 | 2.5 × 105 | < 20 | > 99 |
| Candida albicans | 2.7 × 105 | 3.9 × 105 | 1.8 × 104 | 93.3 |
| Test Pollutants | Concentration of Pollutants (mg/m3) | R2c (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0a | C2hb | ||
| Ammonia | 1.01 | 0.24 | 76.2 |
| Formaldehyde | 1.07 | 0.39 | 63.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. Biodegradable Polylactide/TiO2 Composite Fiber Scaffolds with Superhydrophobic and Superadhesive Porous Surfaces for Water Immobilization, Antibacterial Performance, and Deodorization. Polymers 2019, 11, 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111860
Wang X, Chen D, Zhang M, Hu H. Biodegradable Polylactide/TiO2 Composite Fiber Scaffolds with Superhydrophobic and Superadhesive Porous Surfaces for Water Immobilization, Antibacterial Performance, and Deodorization. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111860
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaowen, Dongchu Chen, Min Zhang, and Huawen Hu. 2019. "Biodegradable Polylactide/TiO2 Composite Fiber Scaffolds with Superhydrophobic and Superadhesive Porous Surfaces for Water Immobilization, Antibacterial Performance, and Deodorization" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111860
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, D., Zhang, M., & Hu, H. (2019). Biodegradable Polylactide/TiO2 Composite Fiber Scaffolds with Superhydrophobic and Superadhesive Porous Surfaces for Water Immobilization, Antibacterial Performance, and Deodorization. Polymers, 11(11), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111860