Enhanced Proton Conductivity in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Membranes by Incorporating Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate
Abstract
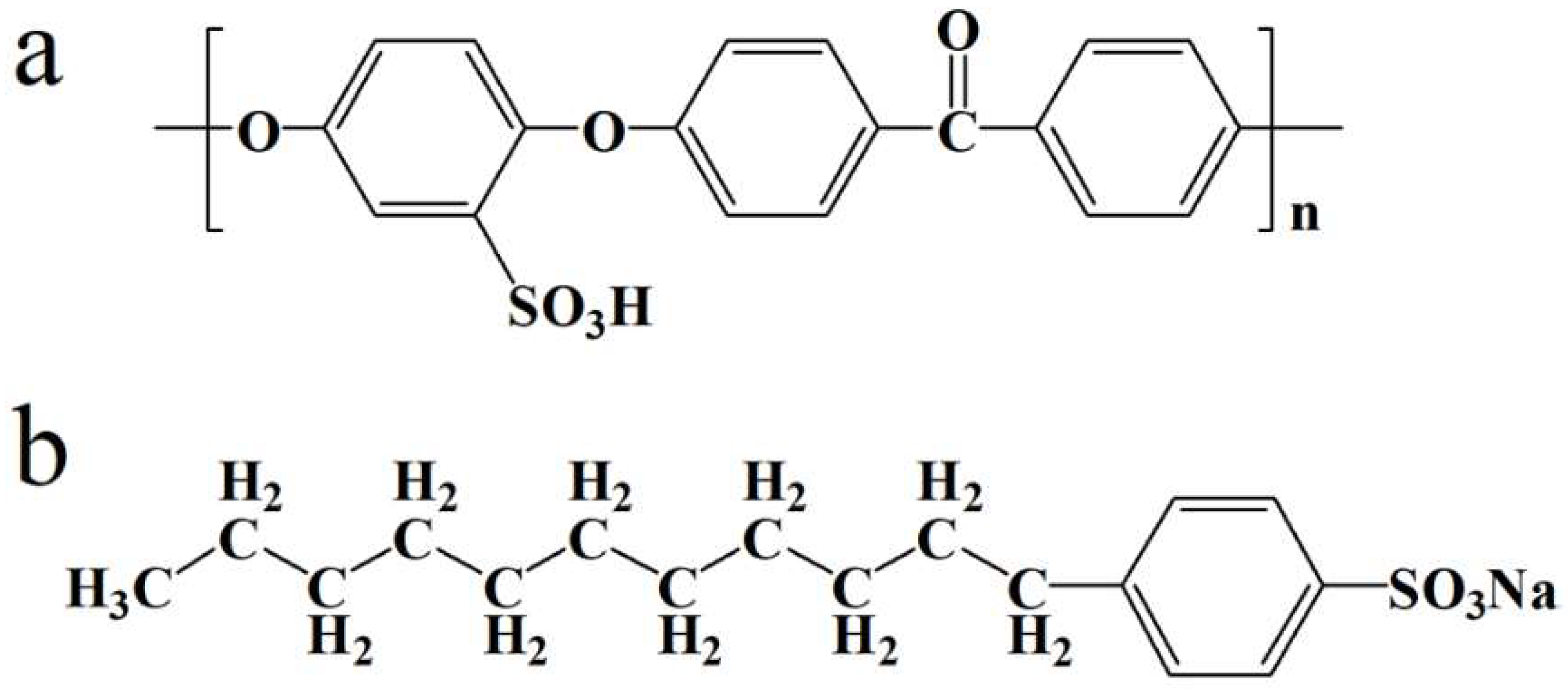
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Observation of SPEEK/SDBS Membranes
3.2. IECs of SPEEK/SDBS Membranes
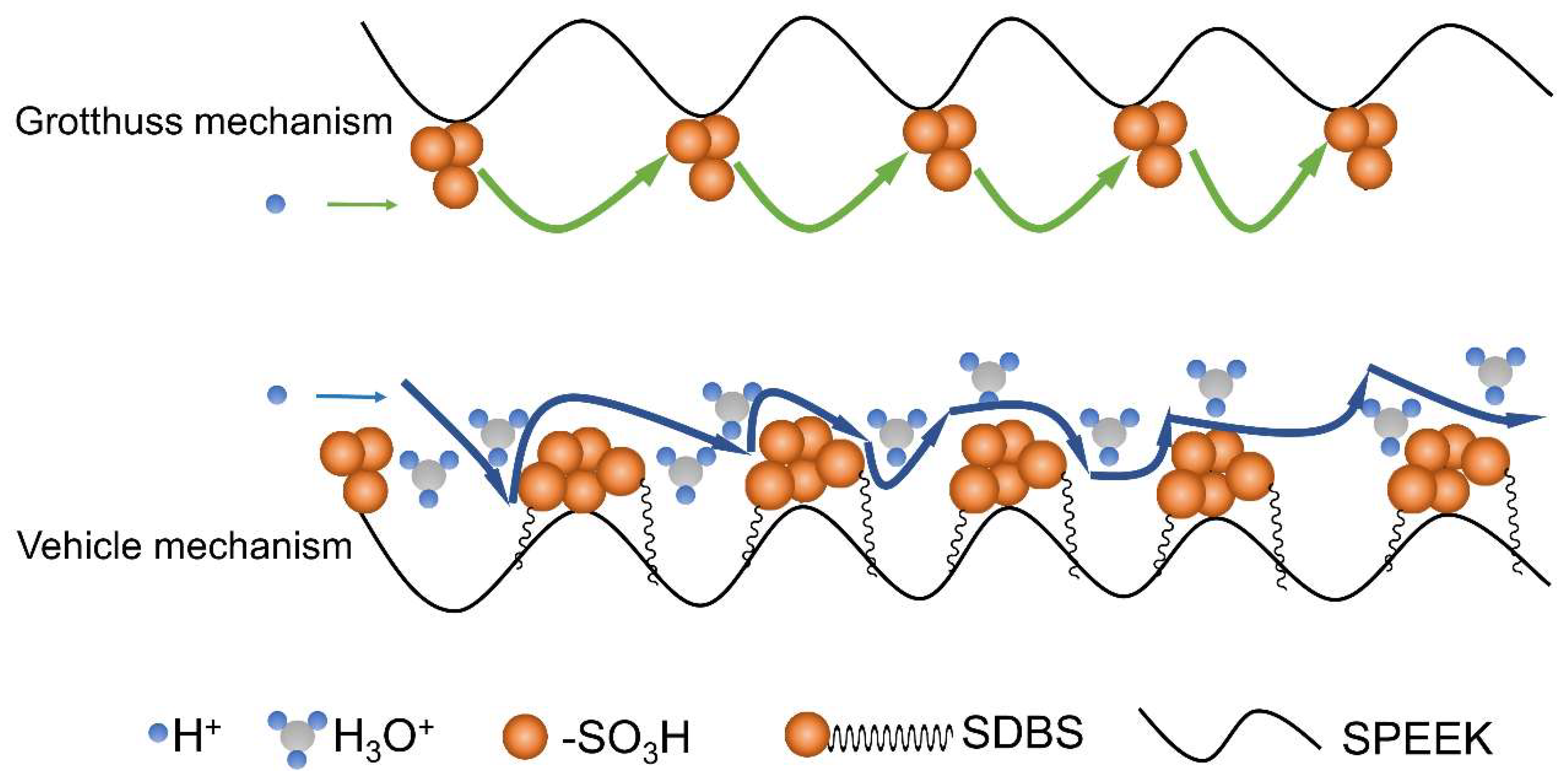
3.3. Proton Conductivity and Water Uptake of SPEEK/SDBS Membranes
3.4. Activation Energy for Proton Conduction in SPEEK/SDBS Membranes
3.5. Stability of SPEEK Nanocomposite Membranes
3.6. Mechanical Properties of SPEEK/SDBS Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.K.; Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Silicate-based polymer-nanocomposite membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 842–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X. Constructing Continuous Proton-Conducting Highways within Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Nitrile) Composite Membrane by Incorporating Amino-Sulfo-Bifunctionalized GO. Polymers 2018, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Nguyen, T.X.H.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.-T.; Lee, J.H. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Recent advances and challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Bhat, S.D.; Pillai, V.K. Simultaneous unzipping and sulfonation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes to sulfonated graphene nanoribbons for nanocomposite membranes in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.J.; Liu, S.X.; Jia, H.N.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J. The roles of solvent type and amount of residual solvent on determining the structure and performance of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Lin, Y.K.; Ma, H.F.; Jia, H.N.; Liu, X.; Lin, J. Preparation of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) membrane using ethanol/water mixed solvent. Mater. Lett. 2016, 169, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Kim, K. Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) and Perfluorosulfonic Acid Composite Membranes Containing Perfluoropolyether Grafted Graphene Oxide for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnian, M.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Gashoul, F. Comprehensive investigation of physicochemical and electrochemical properties of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes with different degrees of sulfonation for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Energy 2017, 125, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Jia, H.N.; Lin, Y.K.; Qian, H.X.; Lin, J. Effect of clay modification on the structure and properties of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK)/clay nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laberty-Robert, C.; Vallé, K.; Pereira, F.; Sanchez, C. Design and properties of functional hybrid organic-inorganic membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 961–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Shahi, V.K. Organic-inorganic nanocomposite polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 945–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.J.; Song, G.; Jia, H.N.; Shi, Z.Z.; Liu, S.X.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J. Proton conductivity improvement of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) nanocomposite membranes with sulfonated halloysite nanotubes prepared via dopamine-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A. Composite membranes based on sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) and SDBS-adsorbed graphene oxide for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24862–24869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Park, J.O.; Pak, C.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.C.; Chang, H. Design and Synthesis of Cross-Linked Copolymer Membranes Based on Poly(benzoxazine) and Polybenzimidazole and Their Application to an Electrolyte Membrane for a High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cell. Polymers 2013, 5, 77–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Guiver, M.D.; Lee, Y.M. Sulfonated hydrocarbon membranes for medium-temperature and low-humidity proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1443–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.J.; Liu, S.X.; Dai, W.X.; Zhai, S.X.; Lin, J. Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Incorporating Phosphotungstic Acid Anchored on Imidazole-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F951–F958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Dai, W.X.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.X.; Bian, X.M.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J. Nanocomposite proton exchange membranes based on phosphotungstic acid immobilized by polydopamine-coated halloysite nanotubes. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wang, Q.; Cong, C.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Influence of alkaline 2D carbon nitride nanosheets as fillers for anchoring HPW and improving conductivity of SPEEK nanocomposite membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 10317–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; He, X.; Jiang, Z. Proton exchange nanohybrid membranes with high phosphotungstic acid loading within metal-organic frameworks for PEMFC applications. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 240, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, A.B.; Gopu, S.; Li, W. Enhancement of proton exchange membrane fuel cells performance at elevated temperatures and lower humidities by incorporating immobilized phosphotungstic acid in electrodes. J. Power Sources 2014, 263, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Lin, Y.K.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J.; Nazarenko, S. Solvent-free Fabrication of Proton Conducting Membranes Based on Commercial Elastomers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 26, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.J.; Shi, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J. Effect of residual casting solvent content on the structure and properties of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, T.Y.; Dogan, H.; Unveren, E.E.; Eker, E. Sulfonated PEEK and fluorinated polymer based blends for fuel cell applications: Investigation of the effect of type and molecular weight of the fluorinated polymers on the membrane’s properties. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12038–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Yan, X.; He, G.; Wu, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. SPEEK proton exchange membranes modified with silica sulfuric acid nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11853–11861. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.C.; Cheng, H.P.; Kuo, J.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y. Blended Nafion®/SPEEK direct methanol fuel cell membranes for reduced methanol permeability. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, A.M.; Biasizzo, M.; Trotta, F.; del Río, C.; Várez, A.; Levenfeld, B. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated PEEK-WC-PES copolymers for fuel cell proton exchange membrane application. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 93, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. Proton conductivity: Materials and applications. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 610–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudgar, A.; Narasimachary, S.P.; Eikerling, M. Hydrated Arrays of Acidic Surface Groups as Model Systems for Interfacial Structure and Mechanisms in PEMs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20469–20477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. On the development of proton conducting polymer membranes for hydrogen and methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. On the development of proton conducting materials for technological applications. Solid State Ion. 1997, 97, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Novak, A. Proton conductors: Classification and conductivity. In Proton Conductors: Solids, Membranes and Gels-Materials and Devices; Colomban, P., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 38–60. [Google Scholar]






| Performance | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK | 1.72 | 63.7 | 63.0 | 110 |
| SPEEK/SDBS-2 | 1.70 | 56.6 | 52.8 | 85 |
| SPEEK/SDBS-4 | 1.42 | 45.4 | 44.9 | 58 |
| SPEEK/SDBS-10 | 0.92 | - | 37.9 | 29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, S.; Dai, W.; Lin, J.; He, S.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L. Enhanced Proton Conductivity in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Membranes by Incorporating Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate. Polymers 2019, 11, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020203
Zhai S, Dai W, Lin J, He S, Zhang B, Chen L. Enhanced Proton Conductivity in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Membranes by Incorporating Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Shaoxiong, Wenxu Dai, Jun Lin, Shaojian He, Bing Zhang, and Lin Chen. 2019. "Enhanced Proton Conductivity in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Membranes by Incorporating Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate" Polymers 11, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020203
APA StyleZhai, S., Dai, W., Lin, J., He, S., Zhang, B., & Chen, L. (2019). Enhanced Proton Conductivity in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Membranes by Incorporating Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate. Polymers, 11(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020203






