Influence of the Soluble–Insoluble Ratios of Cyclodextrins Polymers on the Viscoelastic Properties of Injectable Chitosan–Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
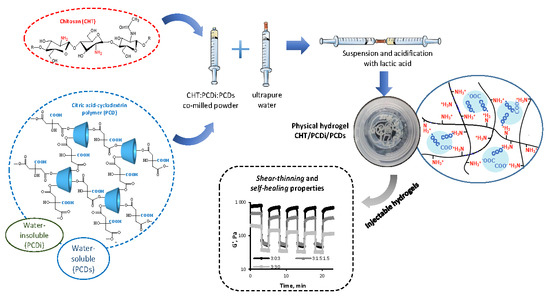
2.2.1. Preparation of CHT/PCD Powders
2.2.2. Preparation of Injectable Hydrogels
2.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.5. The Inverted-Vial Test for Gel Formation
2.2.6. Rheological Analysis
2.2.7. Injectability Test
2.2.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of the Injectable CHT/PCDi/PCDs Hydrogel
3.2. FT–IR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. Inverted-Vial Test for Gel Formation
3.5. Rheological Analysis
3.6. The Injectability Test
3.6.1. Injection Force Profile
3.6.2. In Batch Structural Integrity of Hydrogels
3.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padmanabhan, A.; Nair, L.S. Chitosan Hydrogels for Regenerative Engineering. In Chitin and Chitosan for Regenerative Medicine; Springer Series on Polymer and Composite Materials; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 3–40. ISBN 978-81-322-2510-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sivashanmugam, A.; Arun Kumar, R.; Vishnu Priya, M.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of injectable polymeric hydrogels for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 543–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvendiren, M.; Lu, H.D.; Burdick, J.A. Shear-thinning hydrogels for biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2011, 8, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Vig, K.; Singh, S.R. Advanced Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, D. Preparation and characterization of chitosan based injectable hydrogels enhanced by chitin nano-whiskers. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu Priya, M.; Sivshanmugam, A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Goudouri, O.M.; Sun, W.; Hwang, N.; Deepthi, S.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Injectable osteogenic and angiogenic nanocomposite hydrogels for irregular bone defects. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Y. Rheological, mechanical and degradable properties of injectable chitosan/silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite/glycerophosphate hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 64, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi-Meshkin, H.; Andreas, K.; Matin, M.M.; Sittinger, M.; Bidkhori, H.R.; Ahmadiankia, N.; Bahrami, A.R.; Ringe, J. Chitosan-based injectable hydrogel as a promising in situ forming scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.Y. Injectable hydrogels prepared from partially oxidized hyaluronate and glycol chitosan for chondrocyte encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Moreira Teixeira, L.S.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Karperien, M.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Feijen, J. Injectable chitosan-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2544–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Ahuja, N.; Ma, C.; Liu, X. Injectable scaffolds: Preparation and application in dental and craniofacial regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2017, 111, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agossa, K.; Lizambard, M.; Rongthong, T.; Delcourt-Debruyne, E.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Physical key properties of antibiotic-free, PLGA/HPMC-based in-situ forming implants for local periodontitis treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, J.; Chen, H.; Jiang, G.; Lin, Y.; Ding, F. Preparation and properties of crosslinked chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel for injectable drug delivery systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Faneca, H.; Lima, M.P.; Gil, M.H.; Figueiredo, M.M. In Situ Forming Chitosan Hydrogels Prepared via Ionic/Covalent Co-Cross-Linking. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Atluri, P.; Burdick, J.A. Methods to Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application as Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Leena, R.S.; Selvamurugan, N. Chitosan based biocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellá, M.C.G.; Lima-Tenório, M.K.; Tenório-Neto, E.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Muniz, E.C.; Rubira, A.F. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariatinia, Z.; Jalali, A.M. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Wu, H. Injectable hydrogels embedded with alginate microspheres for controlled delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Koushik, C.; Saravanan, S.; Moorthi, A.; Vairamani, M.; Selvamurugan, N. A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oryan, A.; Sahvieh, S. Effectiveness of chitosan scaffold in skin, bone and cartilage healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levengood, S.L.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B Mater. Biol. Med. 2014, 2, 3161–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buriuli, M.; Verma, D. Polyelectrolyte Complexes (PECs) for Biomedical Applications. In Advances in Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications; Advanced Structured Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 45–93. ISBN 978-981-10-3327-8. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Recent development of chitosan-based polyelectrolyte complexes with natural polysaccharides for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltrowski, M.; Morcellet, M.; Martel, B. Cyclodextrin Polymers and/or Cyclodextrin Derivatives with Complexing Properties and Ion-Exchange Properties and Method for the Production Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 6,660,804, 9 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, B.; Ruffin, D.; Weltrowski, M.; Lekchiri, Y.; Morcellet, M. Water-soluble polymers and gels from the polycondensation between cyclodextrins and poly(carboxylic acid)s: A study of the preparation parameters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fernandez, M.J.; Tabary, N.; Chai, F.; Cazaux, F.; Blanchemain, N.; Flament, M.-P.; Martel, B. New multifunctional pharmaceutical excipient in tablet formulation based on citric acid-cyclodextrin polymer. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; Tabary, N.; Leclercq, L.; Junthip, J.; Degoutin, S.; Aubert-Viard, F.; Cazaux, F.; Lyskawa, J.; Janus, L.; Bria, M.; et al. Multilayered textile coating based on a β-cyclodextrin polyelectrolyte for the controlled release of drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogrovejo-Valdivia, A.; Rahmouni, O.; Tabary, N.; Maton, M.; Neut, C.; Martel, B.; Blanchemain, N. In vitro evaluation of drug release and antibacterial activity of a silver-loaded wound dressing coated with a multilayer system. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Anes, A.; Gargouri, M.; Laure, W.; Van Den Berghe, H.; Courcot, E.; Sobocinski, J.; Tabary, N.; Chai, F.; Blach, J.-F.; Addad, A.; et al. Bioinspired Titanium Drug Eluting Platforms Based on a Poly-β-cyclodextrin–Chitosan Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly Targeting Infections. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12882–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerghemmi, S.; Degoutin, S.; Tabary, N.; Cazaux, F.; Maton, M.; Gaucher, V.; Janus, L.; Neut, C.; Chai, F.; Blanchemain, N.; et al. Triclosan loaded electrospun nanofibers based on a cyclodextrin polymer and chitosan polyelectrolyte complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchemain, N.; Martel, B.; FLORES, C.; CAZAUX, F.; CHAI, F.; TABARY, N.; HEREDIA, M.L. Method for the Production of Hydrogel Comprising Chitosan and Negatively Charged Polyelectrolytes, and Cellular, Porous Material Resulting from Said Hydrogel. U.S. Patent Application 15/740,414, 5 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, C.; Lopez, M.; Tabary, N.; Neut, C.; Chai, F.; Betbeder, D.; Herkt, C.; Cazaux, F.; Gaucher, V.; Martel, B.; et al. Preparation and characterization of novel chitosan and β-cyclodextrin polymer sponges for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.R.; Cipriano, B.H. Gel Formation: Phase Diagrams Using Tabletop Rheology and Calorimetry. In Molecular Gels; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 241–252. ISBN 978-1-4020-3352-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Hansen, M.B.; Löwik, D.W.P.M.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Li, Y.; Jansen, J.A.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G. Oppositely Charged Gelatin Nanospheres as Building Blocks for Injectable and Biodegradable Gels. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H119–H124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhou, Y.-N.; Wang, H.-S.; Wan, T.; Zhong, C.; Chu, L.-Q. Injectable self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan-zinc supramolecular hydrogels and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, J.; Ran, L.; Yu, K.; Lu, B.; Lan, G.; Dai, F.; Lu, F. An injectable self-healing hydrogel with adhesive and antibacterial properties effectively promotes wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejardi, A.; Hernández, R.; Criado, M.; Santos, J.I.; Etxeberria, A.; Sarasua, J.R.; Mijangos, C. Novel hydrogels of chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-glycolic acid copolymer with enhanced rheological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimzon, I.K.D.; Knepper, T.P. Degree of deacetylation of chitosan by infrared spectroscopy and partial least squares. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Montelongo, J.; Naveas, N.; Degoutin, S.; Tabary, N.; Chai, F.; Spampinato, V.; Ceccone, G.; Rossi, F.; Torres-Costa, V.; Manso-Silvan, M.; et al. Porous silicon-cyclodextrin based polymer composites for drug delivery applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, D. Synthesis and characterization of a chitosan based nanocomposite injectable hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anraku, M.; Iohara, D.; Hiraga, A.; Uekama, K.; Ifuku, S.; Pipkin, J.D.; Hirayama, F. Formation of Elastic Gels from Deacetylated Chitin Nanofibers Reinforced with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzacchiello, A.; Ambrosio, L. Structure-Property Relationships in Hydrogels. In Hydrogels; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2009; pp. 9–20. ISBN 978-88-470-1103-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rogina, A.; Ressler, A.; Matić, I.; Gallego Ferrer, G.; Marijanović, I.; Ivanković, M.; Ivanković, H. Cellular hydrogels based on pH-responsive chitosan-hydroxyapatite system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbois, R.; Noël, S.; Léger, B.; Tilloy, S.; Menuel, S.; Addad, A.; Martel, B.; Ponchel, A.; Monflier, E. Ruthenium-containing β-cyclodextrin polymer globules for the catalytic hydrogenation of biomass-derived furanic compounds. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyondi, D.; Webster, T.J.; Banerjee, R. A nanoparticulate injectable hydrogel as a tissue engineering scaffold for multiple growth factor delivery for bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.; Doumit, M.; Rockwell, G. The Biomechanics and Optimization of the Needle-Syringe System for Injecting Triamcinolone Acetonide into Keloids. J. Med. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5162394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.B.; Almeida, R.D.; Pasquali, M.; Borges, S.P.; Fook, M.L.; Lisboa, H.M. Physical characterization and modeling of chitosan/peg blends for injectable scaffolds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilurzo, F.; Selmin, F.; Minghetti, P.; Adami, M.; Bertoni, E.; Lauria, S.; Montanari, L. Injectability Evaluation: An Open Issue. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.-Y.; Kuo, T.-F.; Wu, H.-D.; Yang, J.-C.; Lee, S.-Y. A novel injectable chitosan/polyglutamate polyelectrolyte complex hydrogel with hydroxyapatite for soft-tissue augmentation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarçin, E.; Lee, T.Y.; Karuthedom, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Brennan, M.A.; Lee, D.H.; Marrella, A.; Zhang, J.; Syla, D.; Zhang, Y.S.; et al. Injectable shear-thinning hydrogels for delivering osteogenic and angiogenic cells and growth factors. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivashanmugam, A.; Charoenlarp, P.; Deepthi, S.; Rajendran, A.; Nair, S.V.; Iseki, S.; Jayakumar, R. Injectable Shear-Thinning CaSO4/FGF-18-Incorporated Chitin–PLGA Hydrogel Enhances Bone Regeneration in Mice Cranial Bone Defect Model. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42639–42652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Group | CHT, % w/v | PCDi, % w/v | PCDs, % w/v | UPW, % v/v | LA, % v/v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3:0:3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 93 | 1 |
| 3:1.5:1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 93 | 1 |
| 3:3:0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 93 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palomino-Durand, C.; Lopez, M.; Cazaux, F.; Martel, B.; Blanchemain, N.; Chai, F. Influence of the Soluble–Insoluble Ratios of Cyclodextrins Polymers on the Viscoelastic Properties of Injectable Chitosan–Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Application. Polymers 2019, 11, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020214
Palomino-Durand C, Lopez M, Cazaux F, Martel B, Blanchemain N, Chai F. Influence of the Soluble–Insoluble Ratios of Cyclodextrins Polymers on the Viscoelastic Properties of Injectable Chitosan–Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Application. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020214
Chicago/Turabian StylePalomino-Durand, Carla, Marco Lopez, Frédéric Cazaux, Bernard Martel, Nicolas Blanchemain, and Feng Chai. 2019. "Influence of the Soluble–Insoluble Ratios of Cyclodextrins Polymers on the Viscoelastic Properties of Injectable Chitosan–Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Application" Polymers 11, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020214
APA StylePalomino-Durand, C., Lopez, M., Cazaux, F., Martel, B., Blanchemain, N., & Chai, F. (2019). Influence of the Soluble–Insoluble Ratios of Cyclodextrins Polymers on the Viscoelastic Properties of Injectable Chitosan–Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Application. Polymers, 11(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020214