Facile Synthesis of Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores by Microwave Drying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MSQ Aerogel
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Controllable Preparation of MSQ Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores
3.1.1. Effect of Gelation Agent (PO) on Pore Structures of MSQ Aerogels
3.1.2. Effect of Catalyst (HCl) on Pore Structures of MSQ Aerogels
3.1.3. Effect of Solvent on Pore Structures of MSQ Aerogels
3.1.4. Effect of Microwave Power on Pore Structures of MSQ Aerogels
3.2. Thermal Stability of Typical MSQ Aerogel
3.3. Discussion on Microwave Drying Mechanism of MSQ Aerogel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorcheh, A.S.; Abbasi, M.H. Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 199, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsing, N.; Schubert, U. Aerogels-Airy Materials: Chemistry, Structure, and Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 37, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubesh, L.W. Aerogels: The world’s lightest solids. Chem. Ind.-Lond. 1990, 24, 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Aegerter, M.; Leventis, N.; Koebel, M.M. Aerogels Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.M.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.H.; Li, J.Y.; Li, Q.N.; Zhang, L. The extraction of uranium using graphene aerogel loading organic solution. Talanta 2017, 166, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, X.X.; Feng, X.L.; Ye, X.; Fu, J. Small-Sized Mg-Al LDH Nanosheets Supported on Silica Aerogel with Large Pore Channels: Textural Properties and Basic Catalytic Performance after Activation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaief, M.; Antonyuk, S.; Hentzschel, C.M.; Leopold, C.S.; Heinrich, S.; Smirnova, I. A novel process for coating of silica aerogel microspheres for controlled drug release applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 160, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.F.; Schmid, L.; Burgi, T.; Maciejewski, M.; Baiker, A.; Gunther, D.; Schneider, M. Nondestructive sol-gel immobilization of metal (salen) catalysts in silica aerogels and xerogels. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Jiang, S.C.; Yao, Z.P.; Sheng, S.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhou, B.; Du, A. Research on Heat Transfer Characteristics of Nano-porous Silica Aerogel Material and its Application on Mars surface Mission. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 924, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Xie, T. Advances of thermal conductivity models of nanoscale silica aerogel insulation material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 81, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Yao, J.X.; Mao, D.; Xing, C.J.; Lai, X.Y. Preparation of SiO2 Aerogels Heat Insulation Composites Reinforced by Aramid Fiber. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2009, 38, 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, G.G.; Yilmaz, E.; Deveci, H. Sustainable nanocomposites of epoxy and silica xerogel synthesized from corn stalk ash: Enhanced thermal and acoustic insulation performance. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 150, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotana, F.; Pisello, A.L.; Moretti, E.; Buratti, C. Multipurpose characterization of glazing systems with silica aerogel: In-field experimental analysis of thermal-energy, lighting and acoustic performance. Build. Environ. 2014, 81, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, N.; Motahari, S.; Atoufi, Z.; Motlagh, G.H.; Najafi, M. Thermal, mechanical, and acoustic properties of silica-aerogel/UPVC composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Adachi, I.; Kawai, H.; Kubo, M.; Sato, T. Recent progress in silica aerogel Cherenkov radiator. Phys. Procedia 2012, 37, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.D.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Y.M. Facile co-precursor sol-gel synthesis of a novel amine-modified silica aerogel for high efficiency carbon dioxide capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firoozmandan, M.; Moghaddas, J.; Yasrebi, N. Performance of water glass-based silica aerogel for adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 79, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Nourmoradi, H.; Shokouhi, M. Removal of copper (II) and nickel (II) from aqueous media using silica aerogel modified with amino propyl triethoxysilane as an adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetic, and isotherms study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Dai, C.; Zhang, H.Q.; Peng, S.T.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.D. Regeneration of mesoporous silica aerogel for hydrocarbon adsorption and recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Xia, W.; Zou, R.Q.; Han, R.P. Alkylated phase change composites for thermal energy storage based on surface-modified silica aerogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, S.S. Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 1931, 127, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, K.; Aizawa, M.; Nakanishi, K.; Handa, T. Elastic organic–inorganic hybrid aerogels and xerogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 48, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. Facile synthesis of marshmallow-like macroporous gels usable under harsh conditions for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.V.; Kulkami, M.M.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Seth, T. Superhydrophobic silica aerogels based on methyltrimethoxysilane precursor. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 330, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Z.; Li, W.Y.; Yang, H.; Kanamori, K.; Zhu, Y.; Nakanishi, K. Pore structure control of macroporous methylsilsesquioxane monoliths prepared by in situ two-step processing. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Z.; Li, W.Y.; Yang, H.; Kanamori, K.; Zhu, Y.; Nakanishi, K. Gelation behavior and phase separation of macroporous methylsilsesquioxane monoliths prepared by in situ two-step processing. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.J.; Yang, H.; Gong, L.L.; Cheng, X.D. Rapid synthesis of sodium silicate based hydrophobic silica aerogel granules with large surface area. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Maeno, A.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. Dynamic spring-back behavior in evaporative drying of polymethylsilsesquioxane monolithic gels for low-density transparent thermal superinsulators. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 434, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duraes, L.; Matias, T.; Patricio, R.; Portugal, A. Silica based aerogel-like materials obtained by quick microwave drying. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 2013, 44, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, K.; Achard, P.; Biwole, P.; Stipetic, M. Hygro-thermal properties of silica aerogel blankets dried using microwave heating for building thermal insulation Kevin insulation. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Z.; Li, W.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Kanamori, K. Macroporous SiO2 monoliths prepared via sol-gel process accompanied by phase separation. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2013, 29, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ding, Z.S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Xu, X.P. Sol-gel process kinetics for Si(OEt)4. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1989, 112, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.Y.; Benziger, J.B. Structural Evolution of Alkoxide Silica Gels to Glass: Effect of Catalyst pH. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, J.; Jaroniec, M. 2D-NLDFT adsorption models for porous oxides with corrugated cylindrical pores. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiki, I.; Ota, M.; Sato, Y.; Inomata, H. VOCs (acetone, toluene, and n-hexane) adsorption equilibria on mesoporous silica (MCM-41) over a wide range of supercritical carbon dioxide conditions: Experimental and theoretical approach by the Dubinin–Astakhov equation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2015, 403, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K. Sol-gel process of oxides accompanied by phase separation. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 79, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K. Pore Structure Control of Silica Gels Based on Phase Separation. J. Porous Mater. 1997, 4, 67–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the MSQ aerogels are available from the authors. |

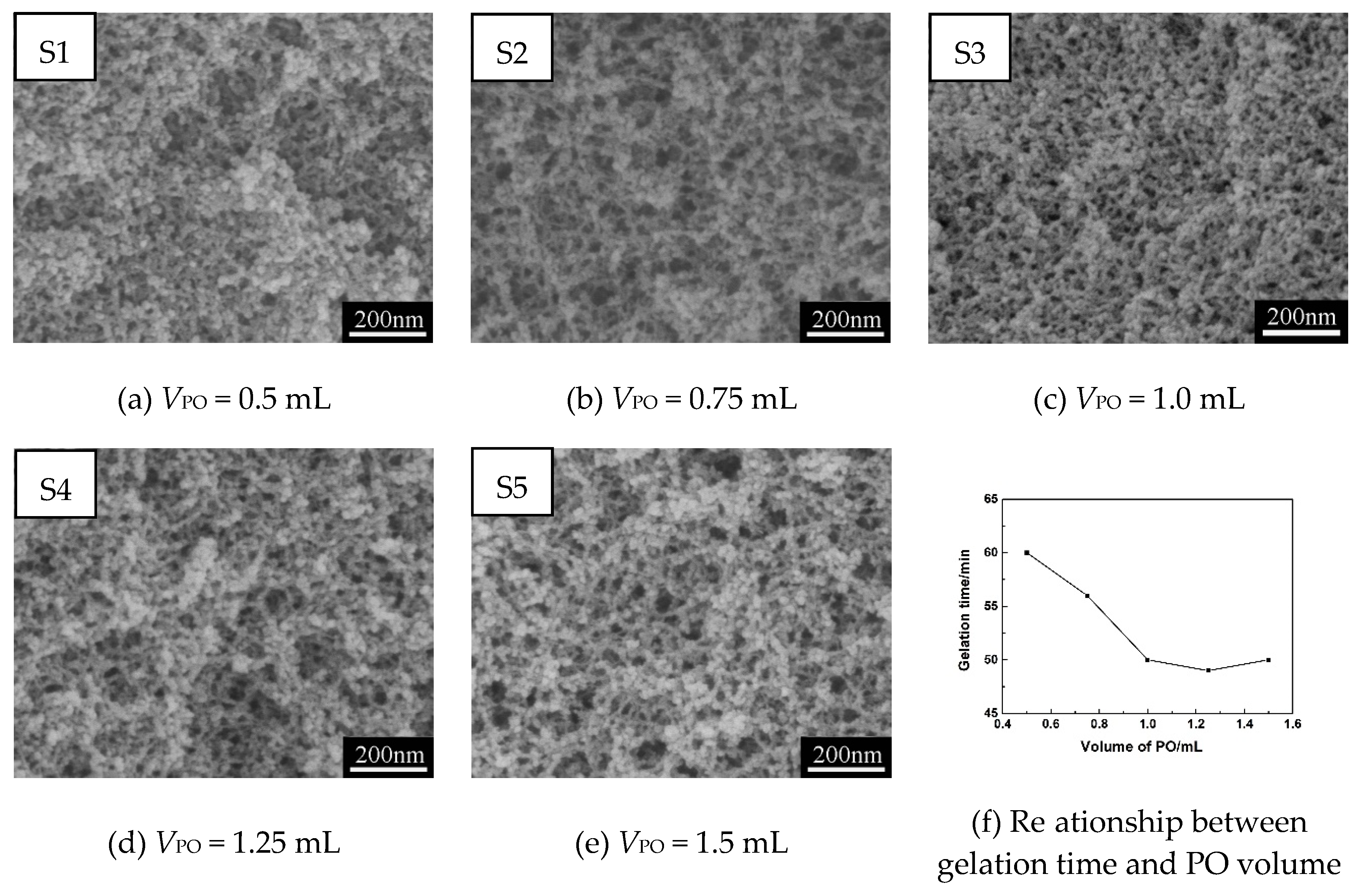

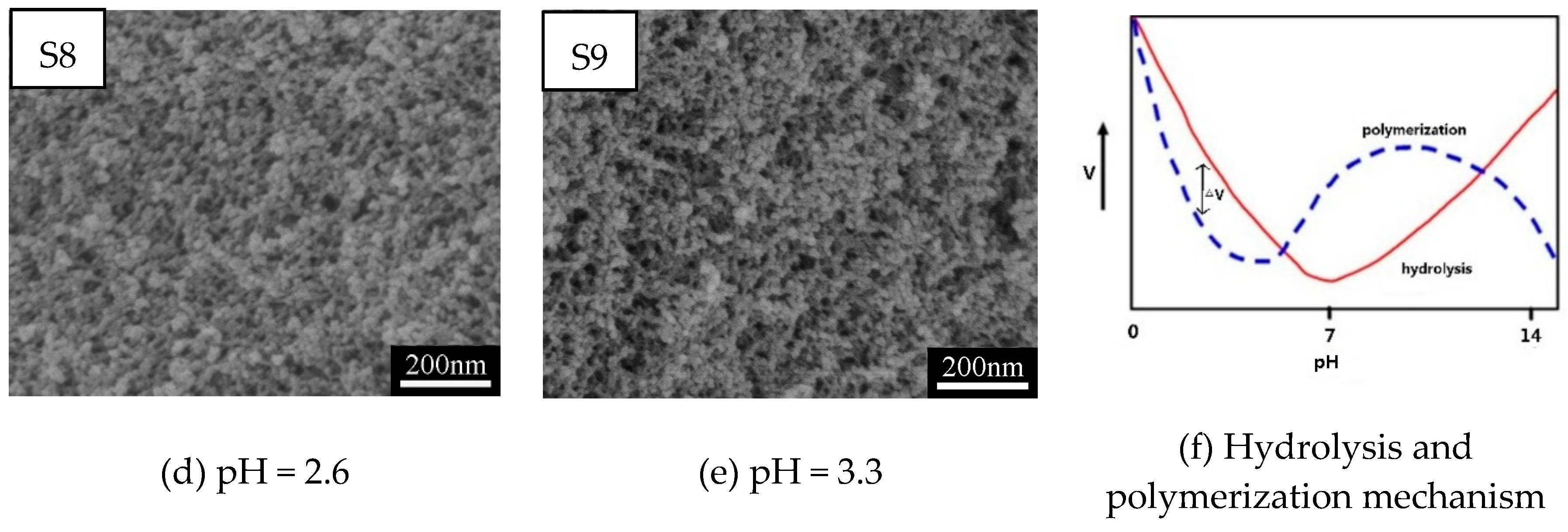
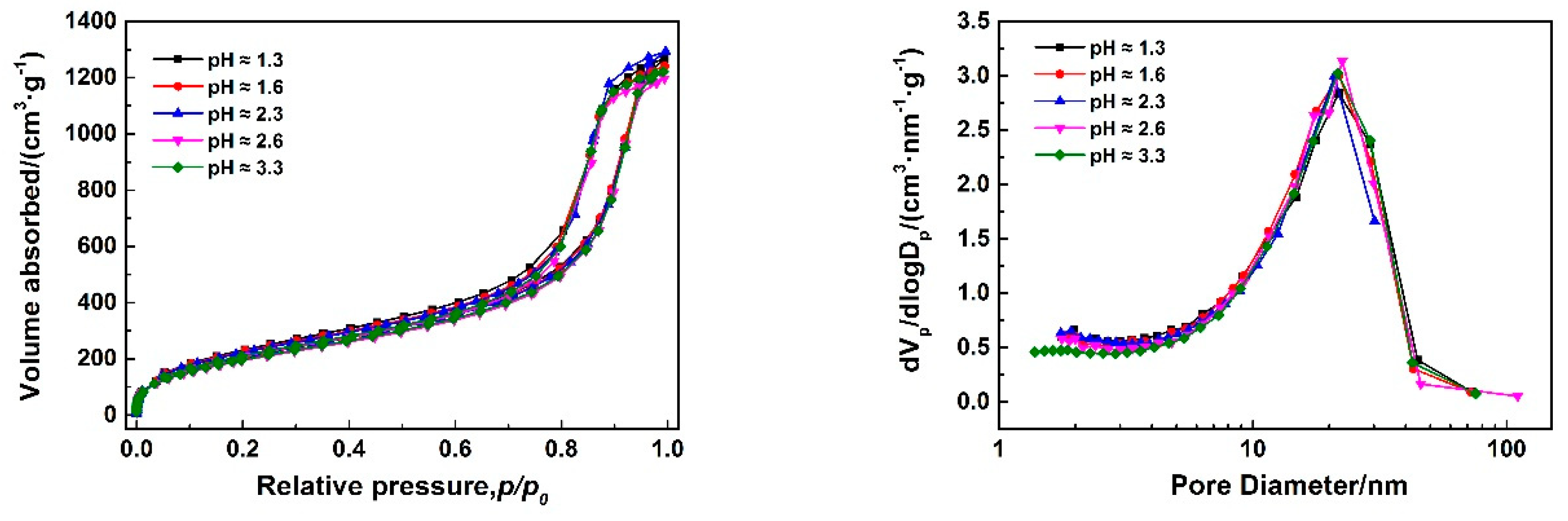




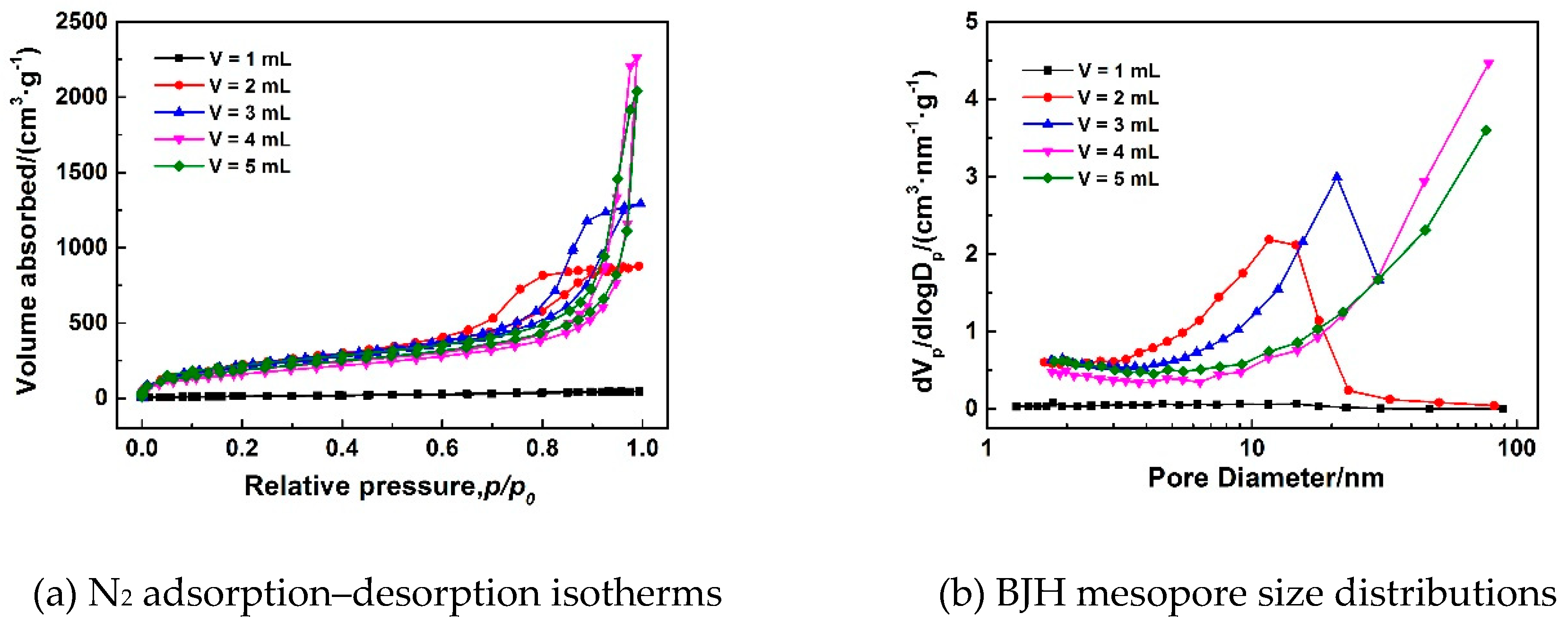
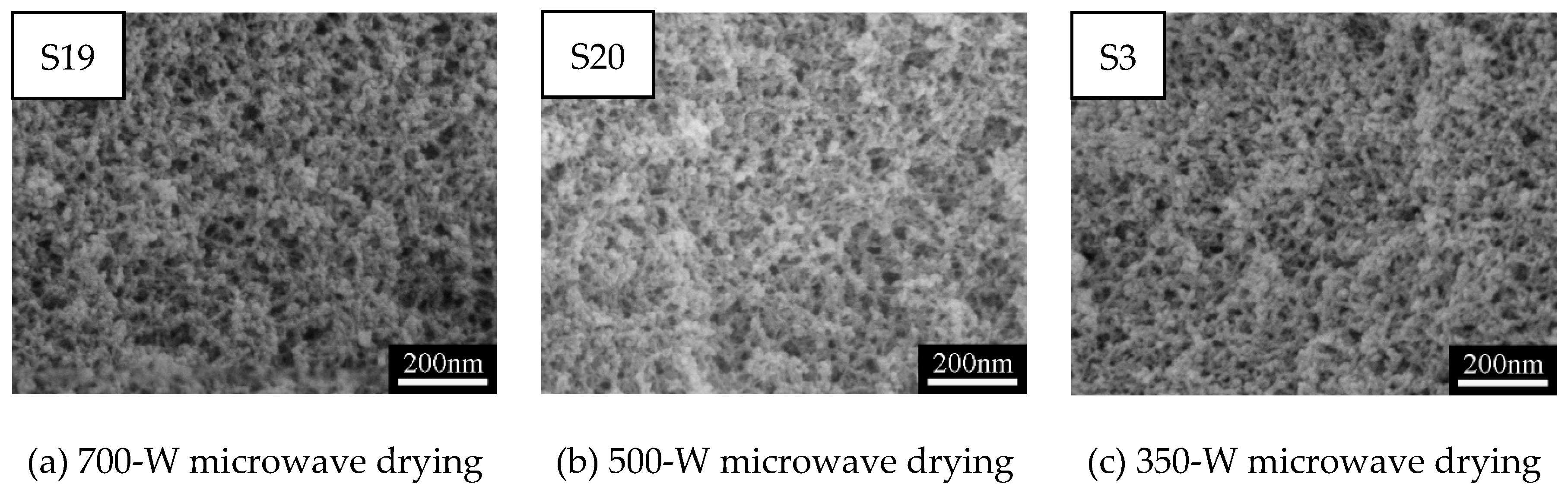

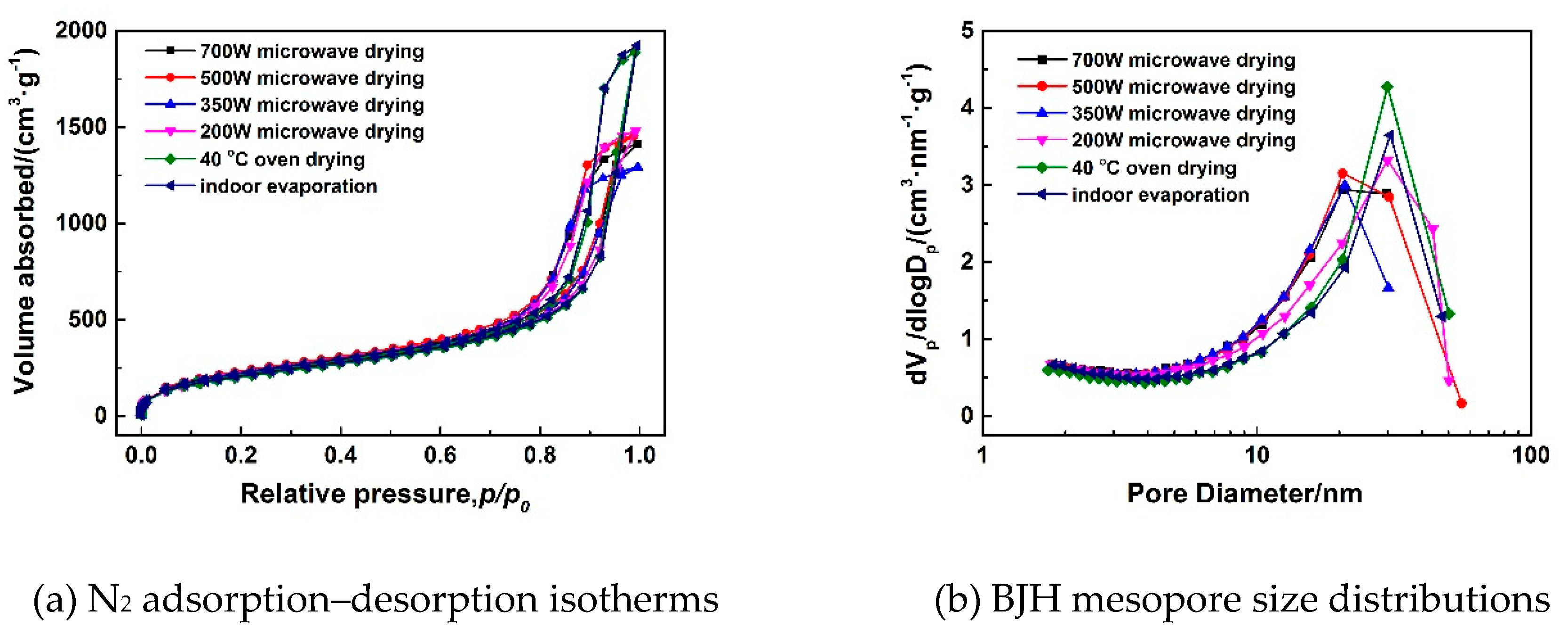

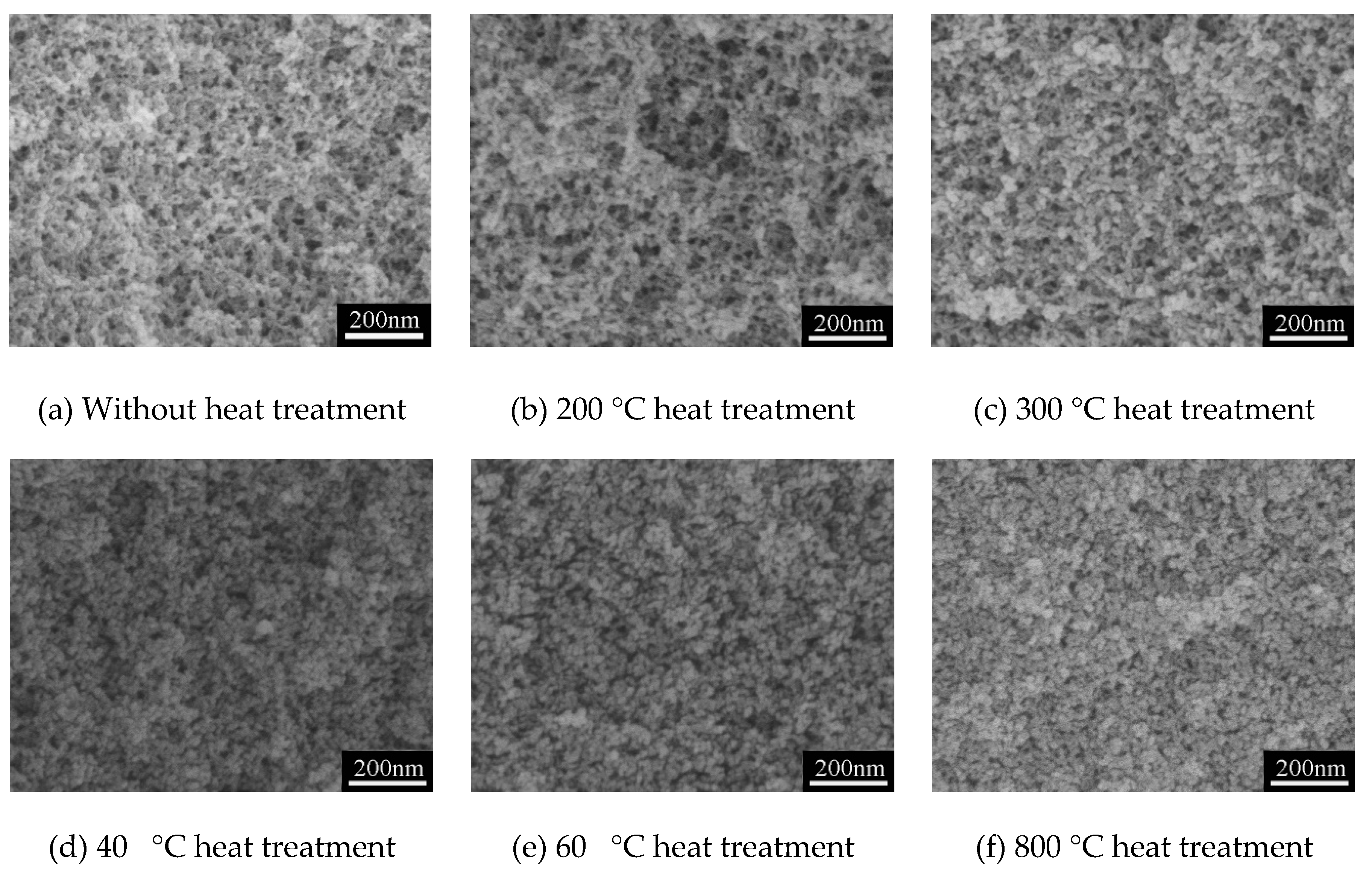


| Sample | VMTMS (mL) | VHCl (mL) | CHCl (mol/L) | VMeOH (mL) | MCTAC (g) | VPO (mL) | Drying Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 0.5 | 350 W microwave |
| 2 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 350 W microwave |
| 3 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 4 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.25 | 350 W microwave |
| 5 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.5 | 350 W microwave |
| 6 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 7 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.05 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 8 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.005 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 9 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.001 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 10 | 3 | 2.25 | 0.00667 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 11 | 3 | 2.0 | 0.0075 | 1.0 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 12 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.015 | 2.0 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 13 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 2.25 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 14 | 3 | 3 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 15 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 16 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.01 | 1.0 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 17 | 3 | 2.0 | 0.01 | 2.0 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 18 | 3 | 2.5 | 0.01 | 2.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 350 W microwave |
| 19 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 700 W microwave |
| 20 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 500 W microwave |
| 21 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 250 W microwave |
| 22 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | 40 °C oven |
| 23 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.24 | 1.0 | evaporation |
| pH | Sp a (m2/g) | Vpore b (cc/g) | Smicro c (m2/g) | Vmicro c (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3 | 786 | 1.9 | 588 | 0.3 |
| 1.6 | 789 | 1.9 | 580 | 0.3 |
| 2.3 | 784 | 1.9 | 596 | 0.3 |
| 2.6 | 731 | 1.8 | 547 | 0.3 |
| 3.3 | 759 | 1.8 | 552 | 0.3 |
| M/W | Sp a (m2/g) | Vpore b (cc/g) | Smicro c (m2/g) | Vmicro c (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.33 | 702 | 2.4 | 494 | 0.2 |
| 0.5 | 741 | 2.6 | 538 | 0.2 |
| 1.0 | 783 | 1.9 | 596 | 0.3 |
| 2.0 | 782 | 1.2 | 575 | 0.3 |
| 3.0 | 772 | 1.0 | 567 | 0.3 |
| 0 | 472 | 1.9 | 52 | 0.04 |
| V/mL | Spa (m2/g) | Vporeb (cc/g) | Smicroc (m2/g) | Vmicroc (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52 | 0.06 | 28 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 784 | 1.3 | 584 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 784 | 1.9 | 596 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 611 | 3.3 | 455 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 714 | 3.0 | 515 | 0.3 |
| Drying Method | Drying Time | Spa (m2/g) | Vporeb (cc/g) | Smicroc (m2/g) | Vmicroc (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700-W microwave drying | 32 min | 796 | 2.1 | 598 | 0.3 |
| 500-W microwave drying | 33 min | 821 | 2.2 | 617 | 0.3 |
| 350-W microwave drying | 36 min | 784 | 1.9 | 596 | 0.3 |
| 200-W microwave drying | 55 min | 783 | 2.1 | 599 | 0.2 |
| 40 °C oven drying | 24 h | 714 | 2.8 | 491 | 0.3 |
| indoor evaporation | ≥48h | 795 | 2.4 | 610 | 0.3 |
| Temperature (°C) | Spa (m2/g) | Vporeb (cc/g) | Smicroc (m2/g) | Vmicroc (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without heat treatment | 821 | 2.2 | 617 | 0.3 |
| 200 | 788 | 2.1 | 599 | 0.3 |
| 300 | 738 | 2.1 | 545 | 0.3 |
| 400 | 580 | 1.5 | 432 | 0.2 |
| 600 | 471 | 1.1 | 291 | 0.2 |
| 800 | 322 | 0.9 | 210 | 0.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Shan, J.; Lei, W.; Ding, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Facile Synthesis of Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores by Microwave Drying. Polymers 2019, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020375
Guo X, Shan J, Lei W, Ding R, Zhang Y, Yang H. Facile Synthesis of Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores by Microwave Drying. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xingzhong, Jiaqi Shan, Wei Lei, Ronghua Ding, Yun Zhang, and Hui Yang. 2019. "Facile Synthesis of Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores by Microwave Drying" Polymers 11, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020375
APA StyleGuo, X., Shan, J., Lei, W., Ding, R., Zhang, Y., & Yang, H. (2019). Facile Synthesis of Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Uniform Mesopores by Microwave Drying. Polymers, 11(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020375






