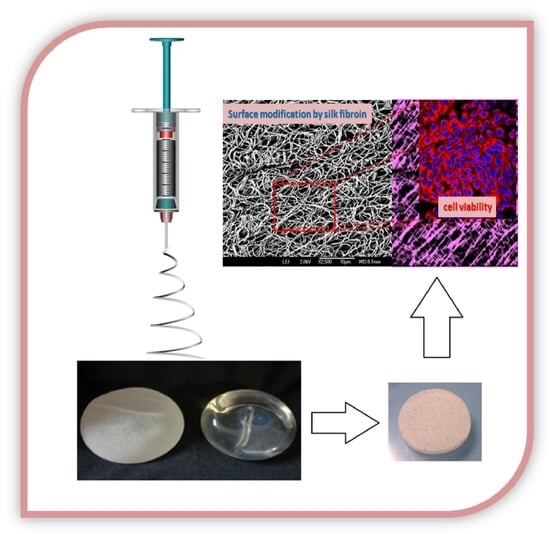
Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fibroin Preparation
2.2. Estimation of Fibroin Concentration
Electrophoresis Assay
2.3. Fibroin/PEO Scaffold Preparation
2.4. Characterization of Fiber Morphology
2.5. Contact Angle Measurement
2.6. Scaffold Properties by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and X-Ray Diffraction
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Cell Viability Assays
2.9. Evaluation of Cell Morphology
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of Fibroin Concentration
3.2. Characterization of Fiber Morphology
3.3. Contact Angle Measurement
3.4. Scaffold Properties by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and X-Ray Diffraction
3.5. Cell Viability
3.6. Evaluation of Cell Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Nanoscale graphene doped with highly dispersed silver nanoparticles: Quick synthesis, facile fabrication of 3D membrane-modified electrode, and super performance for electrochemical sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, M.M.; Jana, R.; Mühlstädt, M.; Maenz, S.; Andrews, J.; Su, Z.; Grasl, C.; Jandt, K.D. In situ formation of nanohybrid shish-kebabs during electrospinning for the creation of hierarchical shish-kebab structures. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Electrospinning design of functional nanostructures for biosensor applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M.; et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.M.; George, J.H. Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science. 2005, 310, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, D.O.; Eschbach, L.; Riehle, M.O.; Curtis, A.S.; Richards, R.G. Microtopography of metal surfaces influence fibroblast growth by modifying cell shape, cytoskeleton, and adhesion. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Jandt, K.D.; Wei, G. Protein-mimetic peptide nanofibers: Motif design, self-assembly synthesis, and sequence-specific biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 80, 94–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Nakabayashi, N. 14-Interaction between biomaterials and cell tissues. In Surfaces and Interfaces for Biomaterials; Vadgama, P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in wound healing: A comprehensive review. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffer, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Kluge, J.; Dorfmann, L.; Kaplan, D.L.; Leisk, G. Silk-based electrospun tubular scaffolds for tissue-engineered vascular grafts. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Román-Doval, R.; Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Cruz-Martínez, H.; Carrasco-Torres, G.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R. Enhancing electrospun scaffolds of PVP with polypyrrole/iodine for tissue engineering of skin regeneration by coating via a plasma process. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.L.; Hubbell, J.A. Polymeric biomaterials with degradation sites for proteases involved in cell migration. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Ghezzo, F.; Roso, M.; Danesin, R.; Palù, G.; Bagno, A.; Modesti, M.; Castagliuolo, I.; Dettin, M. Electrospun scaffolds of self-assembling peptides with poly (ethylene oxide) for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2526–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentivanyi, A.; Assmann, U.; Schuster, R.; Glasmacher, B. Production of biohybrid protein/PEO scaffolds by electrospinning. Eig. Anwend. Tech. Werkst. 2009, 40, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytemiz, D.; Fukuda, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Asano, A.; Nakazawa, T. Ch.; Kameda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Nakazawa, Y. Compatibility evaluation of non-woven sheet composite of silk fibroin and polyurethane in the wet state. Polymer 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inpanya, P.; Faikrua, A.; Ounaroon, A.; Sittichokechaiwut, A.; Viyoch, J. Effects of the blended fibroin/aloe gel film on wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.G.; Scheibel, T.R. Composite materials based on silk proteins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yucel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling silk fibroin particle features for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrasco-Torres, G.; Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R.; Andrade-Jorge, E.; Villa-Treviño, S.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.G.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R. Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest, and mitochondrial apoptosis after combined treatment of hepatocarcinoma cells with maleic anhydride derivatives and quercetin. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: Good solvent, non-specific polymer-polymer interaction limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic parameter study for ultra-fine fiber fabrication via electrospinning process. Polymer. 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Yan, S. A novel silk fibroin scaffolds with oriented multichannels. Mater. Lett. 2013, 105, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, G.C.; Nascimento, F.V.; Hernandez-Montelongo, J.; Machado, D.; Lancellotti, M.; Beppu, M.M. Synthesis and properties of silk fibroin/konjac glucomannan blend beads. Polymers 2018, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.B.; Kushwaha, R.K.; Ratna, D. Novel green method of preparation of a poly (ethylene oxide)/graphene nanocomposite using organic salt assisted dispersion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30555–30563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, A.J.; Kubow, K.E.; Klotzsch, E.; Garcia-Fuentes, M.; Smith, M.L.; Vogel, V.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Optimization strategies for electrospun silk fibroin tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kundu, J.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Martens, P.; Kundu, S.C. Silk fibroin/poly(vinyl alcohol) photocrosslinked hydrogels for delivery of macromolecular drugs. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia–Lazcano, A.A.; Román–Doval, R.; de la Cruz–Burelo, D.; Millán–Casarrubias, E.J.; Rodríguez–Ortega, A. Enhancing surface properties of breast implants by using electrospun silk fibroin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2018, 106, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1392–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Nagapudi, K.; Apkarian, R.P.; Chaikof, E.L. Engineered collagen–PEO nanofibers and fabrics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Baughman, C.B.; Kaplan, D.L. In vitro evaluation of electrospun silk fibroin scaffolds for vascular cell growth. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Vepari, C.; Jin, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Zipursky, S.L.; Matsudaira, P.; Baltimore, D.; Darnell, J. Section 18.1, The actin cytoskeleton. In Molecular Cell Biology, 4th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21493/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Yan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk fibroin/chondroitin sulfate/hyaluronic acid ternary scaffolds for dermal tissue reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6771–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Silk fibroin based biomimetic artificial extracellular matrix for hepatic tissue engineering applications. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Cerón, J.A.; Jiménez-Pérez, V.M.; Molina-Paredes, A.A.; Rasika Dias, H.V.; Chávez-Reyes, A.; Ram Paudel, H.; Ochoa, M.E.; Muñoz-Flores, B.M. Luminescent silk fibroin with organotin compounds from amino acid schiff bases—Microwave-assisted synthesis, chemo-optical characterization, cytotoxicity, and confocal microscopy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Paredes, A.A.; Jiménez-Pérez, V.M.; Lara-Cerón, J.A.; Moggio, I.; Arias, E.; Santillán, R.; Sánchez, M.; Suacedo-Yañez, A.; Muñoz-Flores, B.M. Fluorescent boron Schiff bases dyes for staining silk fibroin: Green synthesis, structural characterization, DFT, and photophysical properties. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| PEO Concentration (wt%) | Silk Fibroin Concentration (wt%) | Average Fiber Diameter (µm) | Average Superficial Pore (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.191 ± 0.0637 | 1.093 ± 0.388 |
| 1 | 0.274 ± 0.0589 | 1.092 ± 0.356 | |
| 1.5 | 0.223 ± 0.0619 | 1.080 ± 0.416 | |
| 2.5 | 0.5 | 0.208 ± 0.0504 | 1.180 ± 0.369 |
| 1 | 0.184 ± 0.0552 | 1.089 ± 0.433 | |
| 1.5 | 0.232 ± 0.0509 | 0.953 ± 0.355 |
| Implant without Scaffold | 2% PEO–0.5% Fibroin | 2% PEO–1% Fibroin | 2% PEO–1.5% Fibroin | 2.5% PEO–0.5% Fibroin | 2.5% PEO–1% Fibroin | 2.5% PEO–1.5% Fibroin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115.6 ± 0.6° | 48.3 ± 2.4° | 44.5 ± 2° | 40 ± 1° | 31.3 ± 2.3° | 27 ± 2.6° | 24.7 ± 2° |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrasco-Torres, G.; Valdés-Madrigal, M.A.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R.; De la Cruz-Burelo, E.; Román-Doval, R.; Valencia-Lazcano, A.A. Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers 2019, 11, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030451
Carrasco-Torres G, Valdés-Madrigal MA, Vásquez-Garzón VR, Baltiérrez-Hoyos R, De la Cruz-Burelo E, Román-Doval R, Valencia-Lazcano AA. Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030451
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrasco-Torres, Gabriela, Manuel A. Valdés-Madrigal, Verónica R. Vásquez-Garzón, Rafael Baltiérrez-Hoyos, Eduard De la Cruz-Burelo, Ramón Román-Doval, and Anaí A. Valencia-Lazcano. 2019. "Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide" Polymers 11, no. 3: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030451
APA StyleCarrasco-Torres, G., Valdés-Madrigal, M. A., Vásquez-Garzón, V. R., Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R., De la Cruz-Burelo, E., Román-Doval, R., & Valencia-Lazcano, A. A. (2019). Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers, 11(3), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030451