Preparation of Xylan-g-/P(AA-co-AM)/GO Nanocomposite Hydrogel and its Adsorption for Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of GO
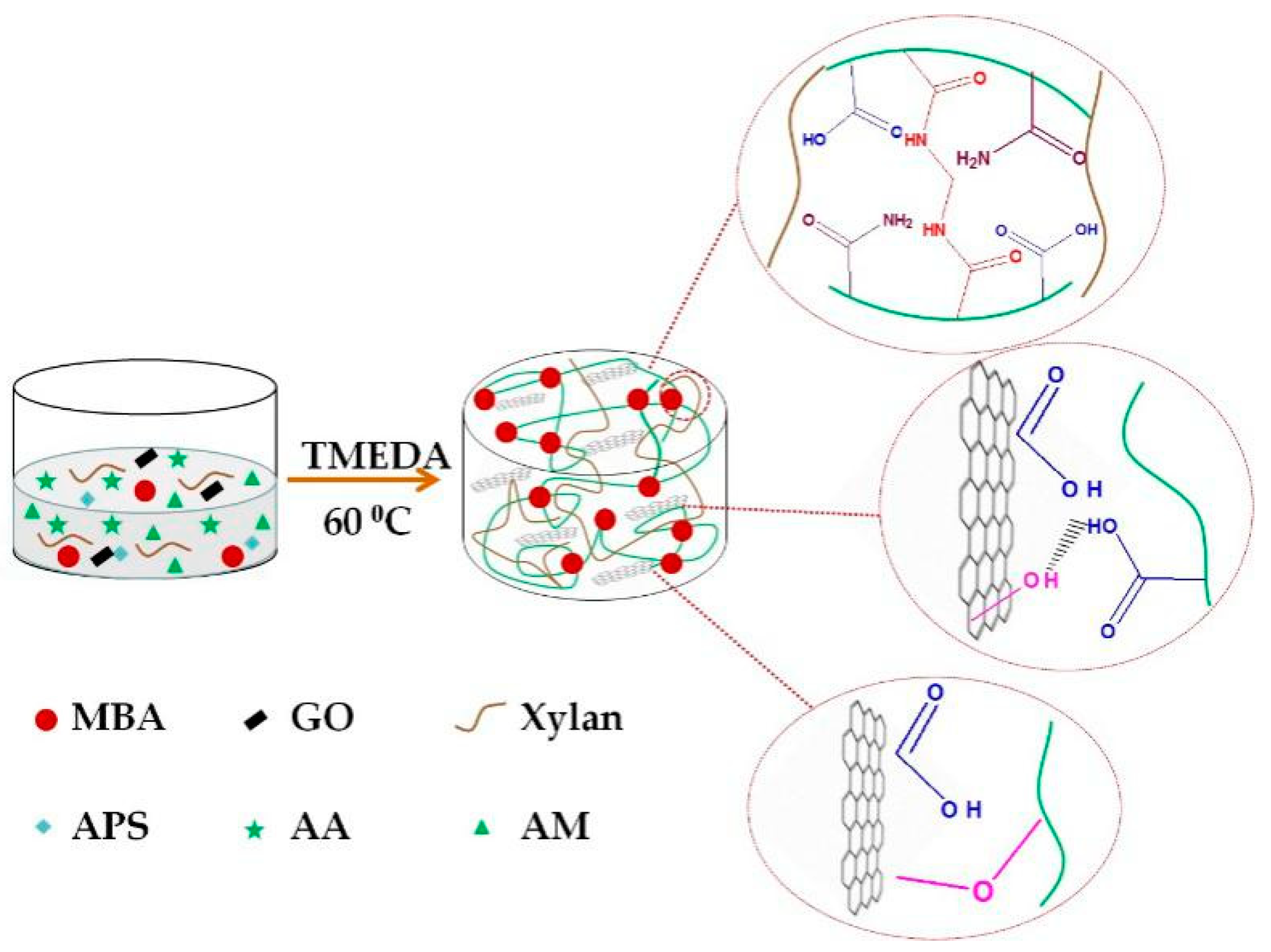
2.3. Preparation of Xylan-g-P(AA-co-AM)/GO Hydrogels
2.4. Characterization of Prepared Hydrogels
2.5. Metal Ion Adsorption and Desorption of Hydrogels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Hydrogels
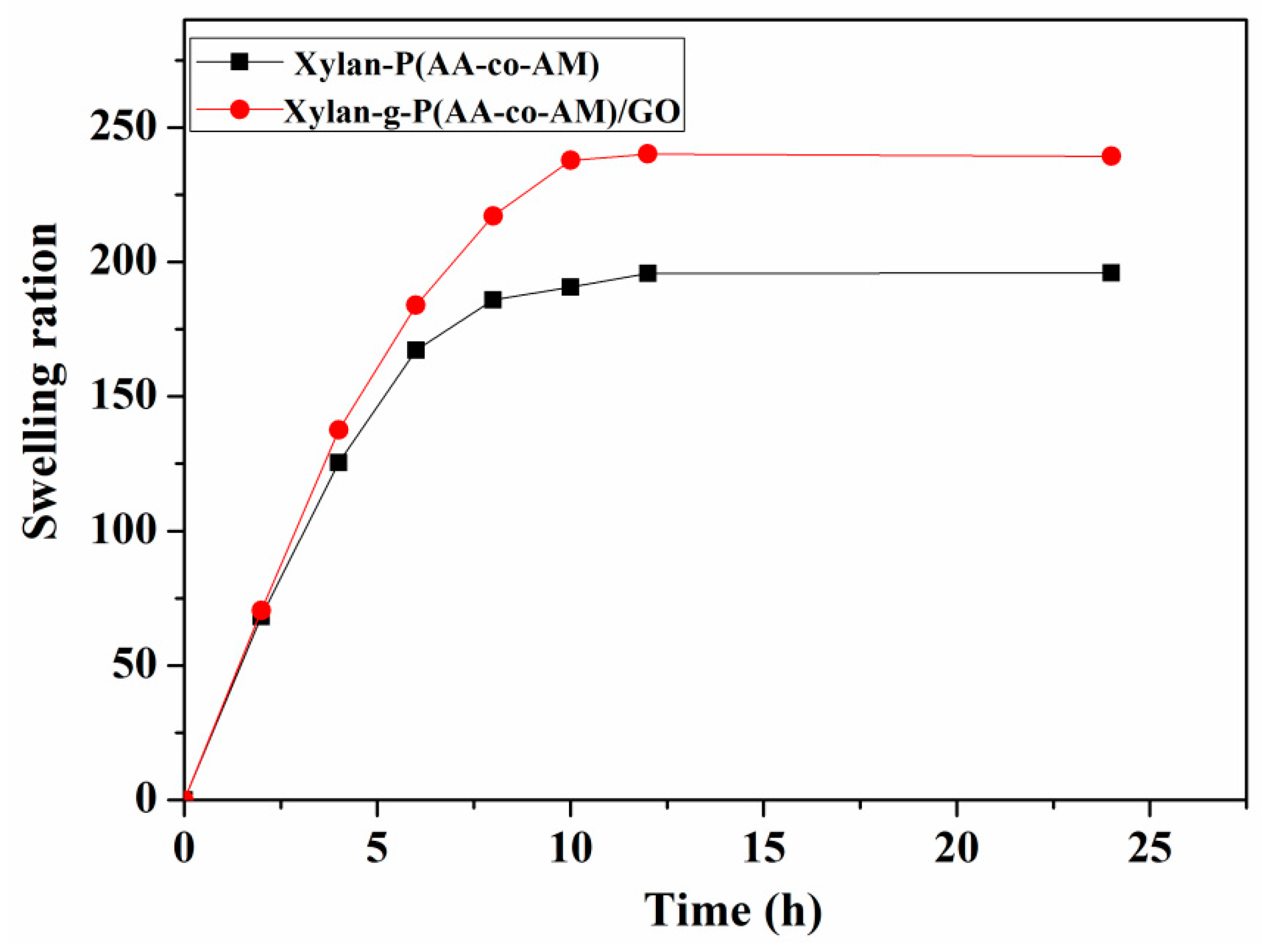
3.2. Swelling Behavior Studies of Hydrogels in Deionized Water
3.3. The Effect of GO on the Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
3.4. Metal Ion Adsorption of Hydrogels
3.4.1. FTIR and EDX of the Hydrogels after Adsorption
3.4.2. The Influence of GO on the Adsorption Properties of Hydrogel
3.4.3. The Influence of pH on the Adsorption Properties of Hydrogel
3.4.4. Adsorption Kinetics of Hydrogels on Metal Ions (Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+)
3.5. The Desorption and Regeneration Properties of Prepared Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, X.W.; Zhong, L.X.; Ren, J.L. Highly Effective adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by macroporous xylan-rich hemicelluloses-based hydrogel. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, S.S.; Goyal, D. Removal of heavy metals from waste tea leaves from aqueous solution. Eng. Life Sci. 2005, 5, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.Q.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.M.; Yu, L.P.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y.P. A novel method for amino starch preparation and its adsorption for Cu(II) and Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Guo, X.Y.; Huang, H.L. Adsorption of chromium(III) on lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7709–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannamba, B.; Reddy, K.L.; AppaRao, B.V. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Kavipriya, M.; Karthika, C.; Radhika, M.; Vennilamani, N.; Pattabhi, S. Utilization of various agricultural wastes for activated carbon preparation and application for the removal of dyes and metal ions from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Venditti, R.A.; Pawlak, J.J.; El-tahlawy, K. Crosslinked hemicellulose citrate-chitosan aerogel foams. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Q. Synthesis and characterization of a novel super-absorbant based on wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Huang, S.; Chen, H. Binding of four heavy metals to hemicelluloses from rice bran. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.G.; Arena, C.P.; Beebe, D.J. Development of macroporous poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel arrays within microfluidic channels. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3316–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblad, M.S.; Ranucci, E.; Albertsson, A.C. Biodegradable polymers from renewable sources. New hemicellulose-based hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2001, 22, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröndahl, M.; Teleman, A.; Gatenholm, P. Effect of acetylation on the material properties of glucuronoxylan from aspen wood. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 52, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Sun, R.C.; Tomkinson, J. Preparation of sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic succinates using NBS as a catalyst. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Liu, C.B.; Tang, Y.H.; Luo, S.L.; Zeng, Z.B.; Liu, Y.T.; Xu, R.; Chu, L. Sponge-like polysiloxane-graphene oxide gel as a highly efficient and renewable adsorbent for lead and cadmium metals removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.H.; Liao, J.; He, B.Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.A.; Huang, X.H.; Zhou, L. One-step fabrication of graphene oxide enhanced magnetic composite gel for highly efficient dye adsorption and catalysis. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Luo, J.M.; Liu, C.B.; Chu, L.; Ma, J.H.; Tang, Y.H.; Zeng, Z.B.; Luo, S.L. A highly efficient polyampholyte hydrogel sorbent based fixed-bed process for heavy metal removal in actual industrial effluent. Water Res. 2016, 89, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, N. Preparation of hemicellulose-based hydrogel and its application as an adsorbent towards heavy metal ions. BioResources 2018, 13, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.; Cote, L.J.; Huang, J. Graphene oxide: Surface activity and two-dimensional assembly. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1954–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Chhowalla, M. Chemically derived graphene oxide: Towards large-area thin-film electronics and optoelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2392–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.M.; Sun, R.C.; Tomkinson, J.; Fowler, P. Acetylation of wheat straw hemicellulose B in a new non-aqueous swelling system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.S.; Wang, X.X.; Yuan, J. Ultrathin graphene: Electrical properties and highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 6589–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Harzandi, A.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Synthesis of a novel polysaccharide-based superadsorbent hydrogel via graft copolymerization of acrylic acid onto κ-carrageenan in air. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mohdy, H.L.A. Water sorption behavior of CMC/PAM hydrogels prepared by γ-irradiation and release of potassium nitrate as agrochemical. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D. Polydopamine-mediated surface-functionalization of graphene oxide for heavy metal ions removal. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 224, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Jalajamony, S.; Sreekumari, S.S. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by amine and carboxylate functionalised bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 65, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, S.; Liu, H. Hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose for removal heavy metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Feng, K.; Tang, B. Surface decoration of amino-functionalized metal-organic framework/graphene oxide composite onto polydopamine-coated membrane substrate for highly efficient heavy metal removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Number | GO (mg) | AA (g) | AM (g) | APS (wt%) | MBA (wt%) | Compressive Strength (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0.72 | 0.5 | 11.5 ± 4.6 |
| 2 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 0.72 | 0.5 | 27.8 ± 5.7 |
| 3 | 20 | 3 | 2 | 0.72 | 0.5 | 95 ± 5.4 |
| 4 | 30 | 3 | 2 | 0.72 | 0.5 | 203 ± 8.3 |
| Metal Ions | Cycle 1 | Cycle 2 | Cycle 3 | Cycle 4 | Cycle 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (mg/g) | R (%) | A (mg/g) | R (%) | A (mg/g) | R (%) | A (mg/g) | R (%) | A (mg/g) | R (%) | |
| Pb2+ | 660 | 99% | 598 | 90% | 596 | 89% | 588 | 88% | 580 | 87% |
| Cd2+ | 264 | 94% | 250 | 89% | 245 | 88% | 233 | 83% | 224 | 80% |
| Zn2+ | 135 | 96% | 132 | 92% | 126 | 88% | 120 | 83% | 115 | 80% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, W.; Chang, M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Ren, J. Preparation of Xylan-g-/P(AA-co-AM)/GO Nanocomposite Hydrogel and its Adsorption for Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers 2019, 11, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040621
Kong W, Chang M, Zhang C, Liu X, He B, Ren J. Preparation of Xylan-g-/P(AA-co-AM)/GO Nanocomposite Hydrogel and its Adsorption for Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers. 2019; 11(4):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040621
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Weiqing, Minmin Chang, Chunhui Zhang, Xinxin Liu, Bei He, and Junli Ren. 2019. "Preparation of Xylan-g-/P(AA-co-AM)/GO Nanocomposite Hydrogel and its Adsorption for Heavy Metal Ions" Polymers 11, no. 4: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040621
APA StyleKong, W., Chang, M., Zhang, C., Liu, X., He, B., & Ren, J. (2019). Preparation of Xylan-g-/P(AA-co-AM)/GO Nanocomposite Hydrogel and its Adsorption for Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers, 11(4), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040621




