The Modulation of Chitosan-DNA Interaction by Concentration and pH in Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.4. Tethering DNA by Magnetic Tweezers
3. Results and Discussions
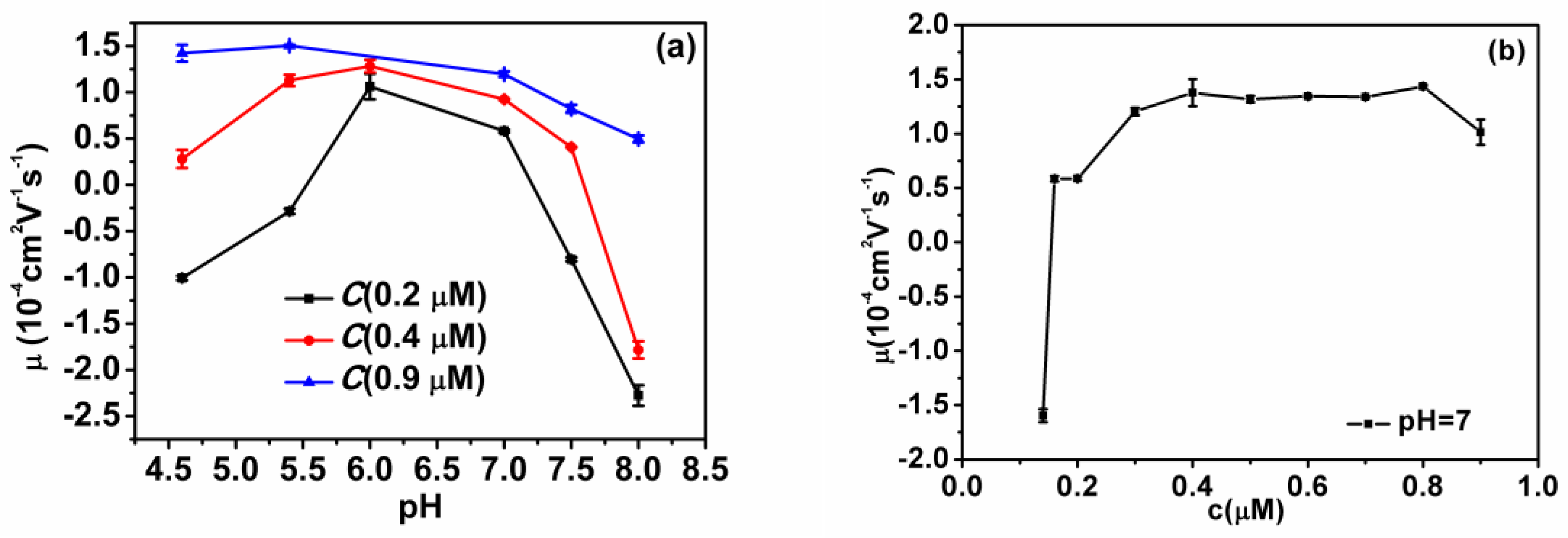
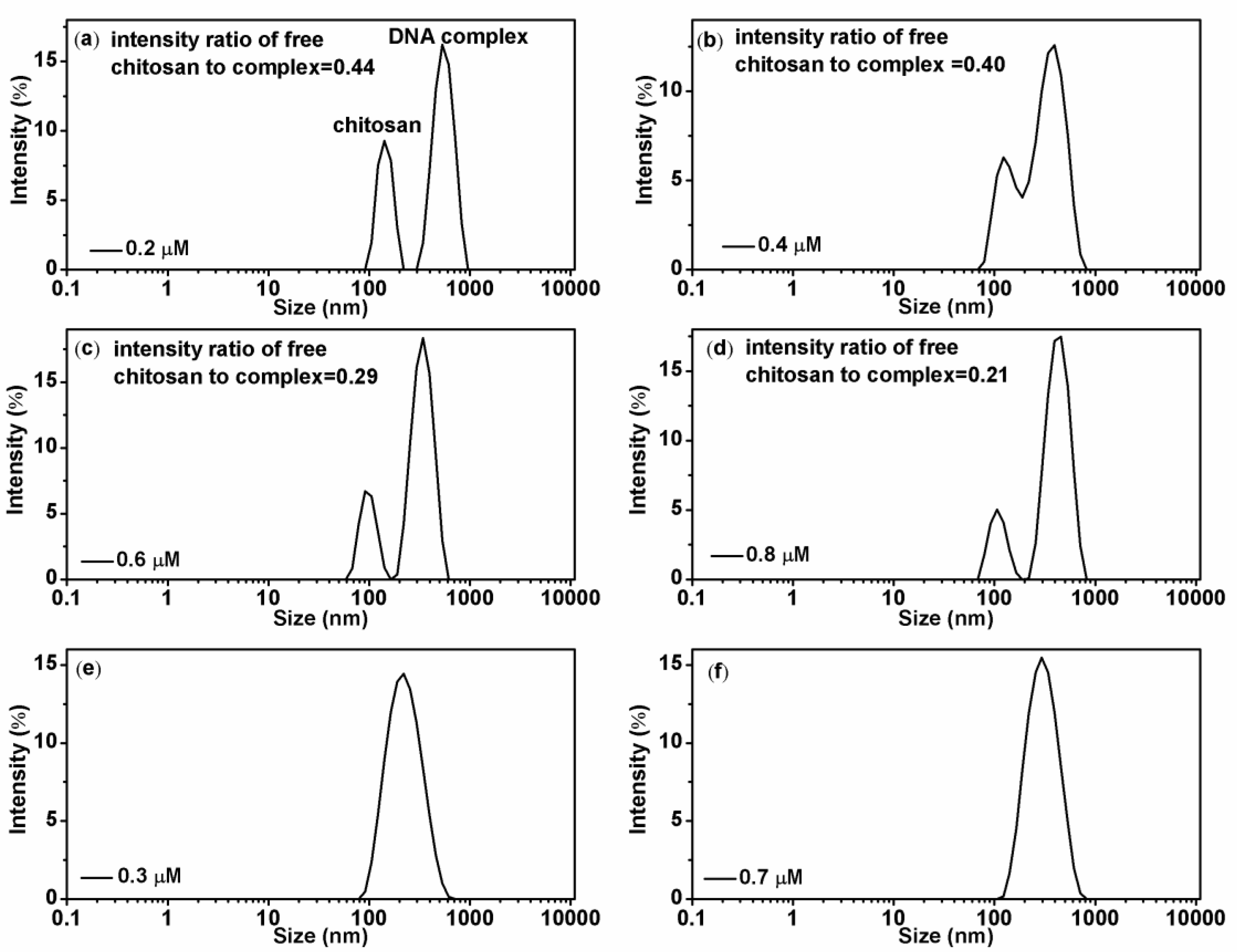
3.1. Electrophoretic Mobility and Particle Size of DNA-Chitosan Complex
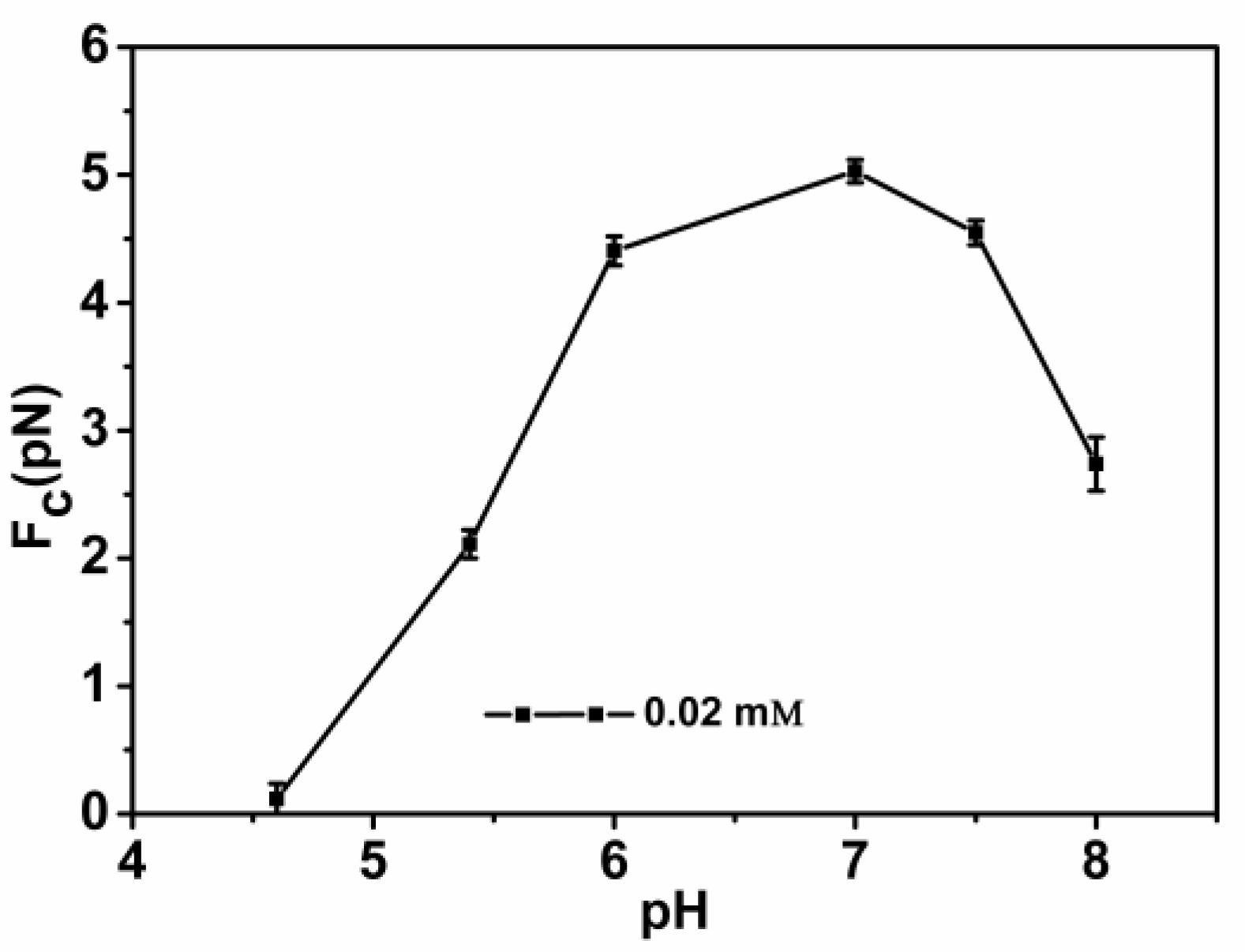
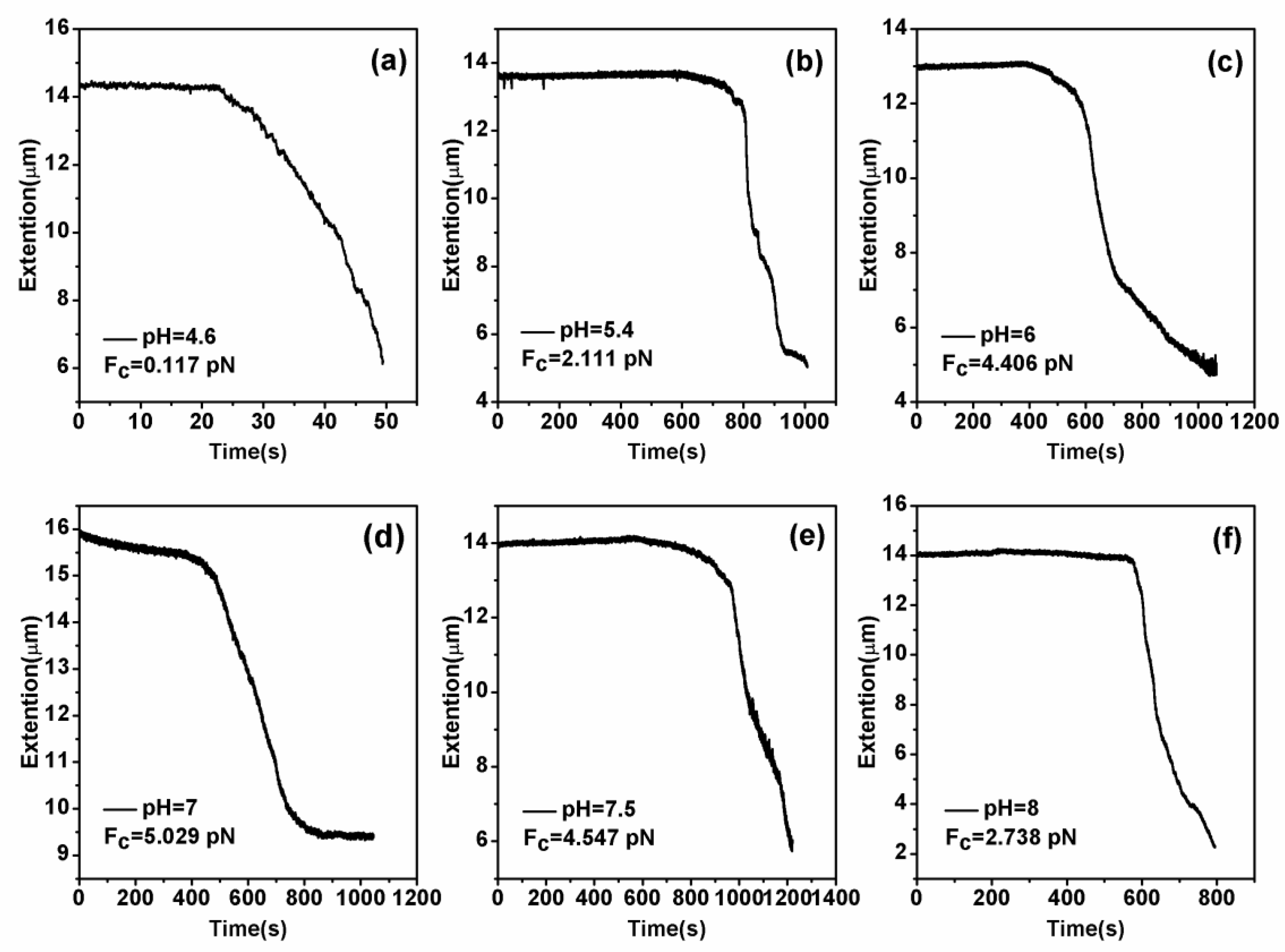
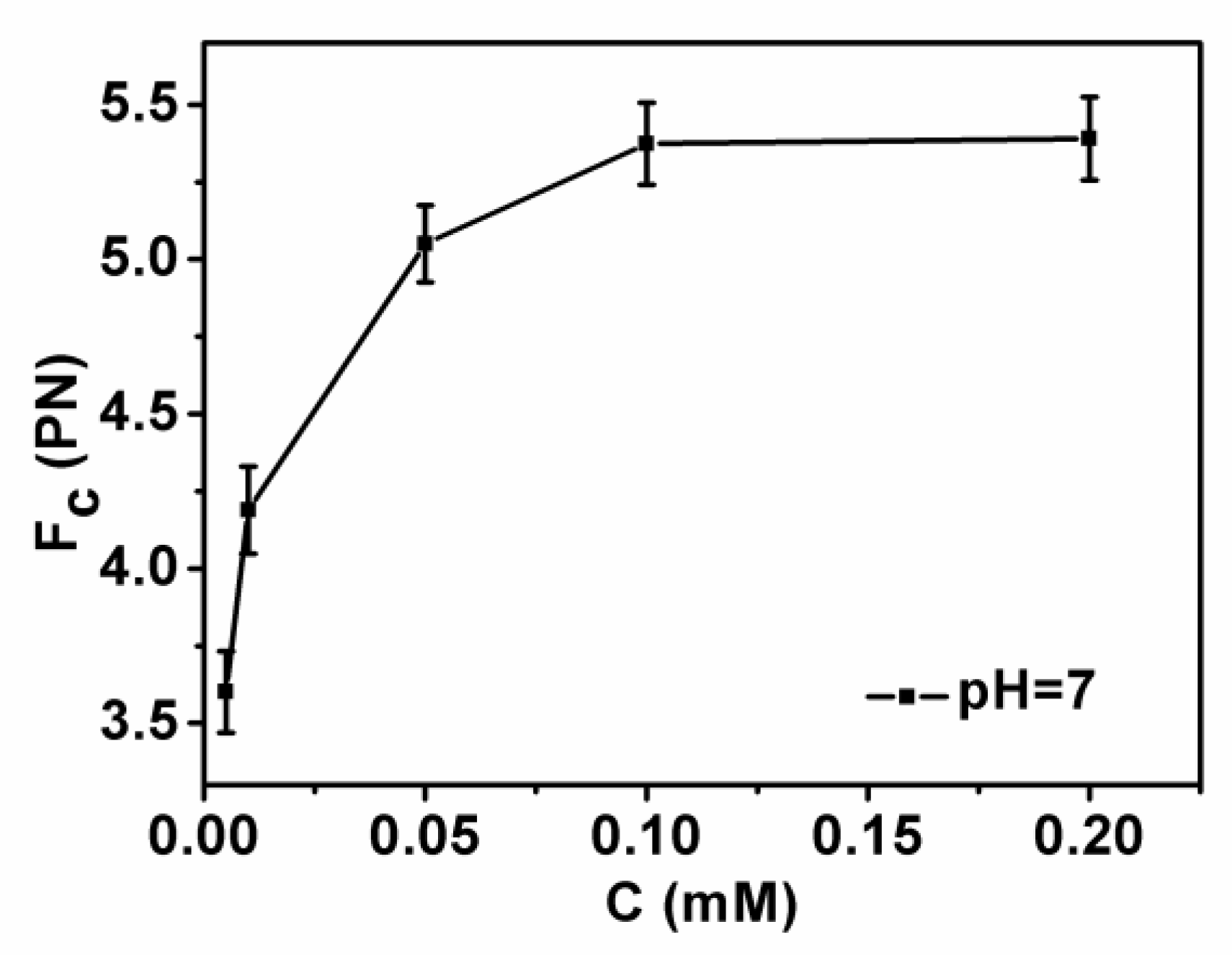
3.2. Condensing Force of Tethered DNA Induced by Chitosan
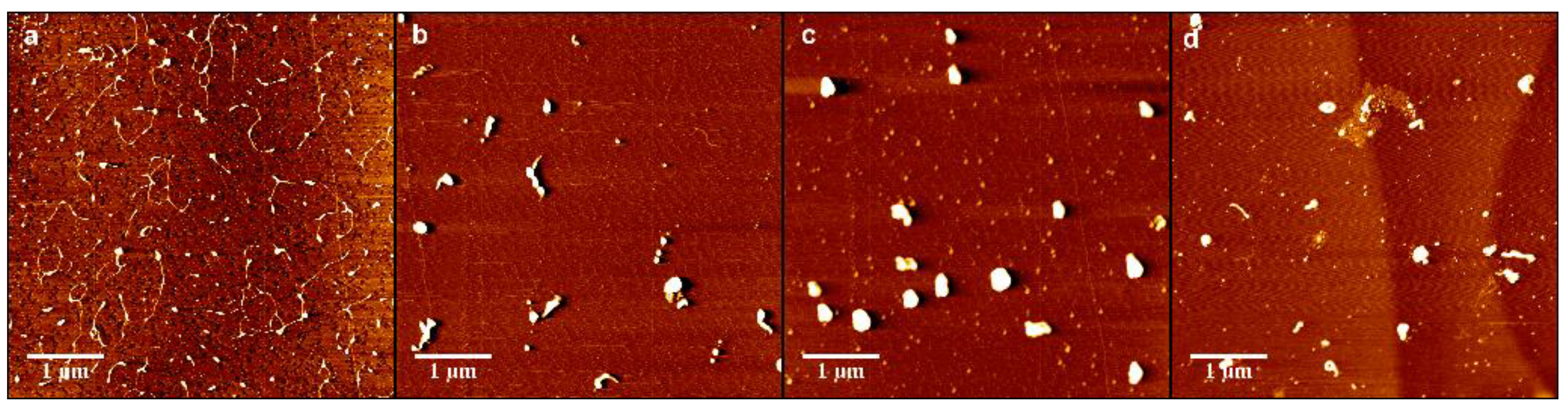
3.3. DNA-Chitosan Morphology by Atomic Force Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livolant, F. Ordered phases of DNA in vivo and in vitro. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1991, 176, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Dias, R.S.; Rosa, M.; Lindman, B. DNA–cationic amphiphile interactions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 228, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.M.; Somia, N. Gene-therapy-promises, problems and prospects. Nature 1997, 389, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.J.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A.; Thomas, T. Polyamine–DNA interactions and development of gene delivery vehicles. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Klibanov, A.M. Non-viral gene therapy: Polycation-mediated DNA delivery. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 62, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Iwaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K. Small anion with higher valency retards the compaction of DNA in the presence of multivalent cation. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Cao, B.; Guo, Z.; Yang, G. Single molecular demonstration of modulating charge inversion of DNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Yang, G. The effect of pH on charge inversion and condensation of DNA. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G. The suppression and promotion of DNA charge inversion by mixing counterions. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, S.; Man, B.; Yang, G. Ethanol induces condensation of single DNA molecules. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4425–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G. Modulation and control of DNA charge inversion. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 128706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, y.; Yang, G. DNA Compaction and Charge Inversion Induced by Organic Monovalent Ions. Polymers 2017, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, S.; Man, B.; Yang, G. DNA condensations on mica surfaces induced collaboratively by alcohol and hexammine cobalt. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengarelli, V.; Auvray, L.; Pastré, D.; Zeghal, M. Charge inversion, condensation and decondensation of DNA and polystyrene sulfonate by polyethylenimine. Eur. Phys. J. E 2011, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Ran, S. Two-stage DNA compaction induced by silver ions suggests a cooperative binding mechanism. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 205102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, y.; Yang, G. DNA Phase Transition in Charge Neutralization and Comformation Induced by Trivalent-Hydrolysed Metal Ions. Polymers 2018, 10, 394. [Google Scholar]
- Maclaughlin, F.C.; Mumper, R.J.; Wang, J.; Tagliaferri, J.M.; Gill, I.; Hinchcliffe, M. Chitosan and depolymerized chitosan oligomers as condensing carriers for in vivo plasmid delivery. J. Control. Release 1998, 56, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illum, L.; Farraj, N.F.; Davis, S.S. Chitosan as a novel nasal delivery system for peptide drugs. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 1186–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appden, T.J.; Adler, J.; Davis, S.S.; Illum, S.L. Chitosan as a nasal delivery system: Evaluation of the effect of chitosan on mucociliary clearance rate in the frog palate model. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 122, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño-Gómez, B.; Duncan, R. Evaluation of the biological properties of soluble chitosan and chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. (Amst.) 1997, 148, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilium, L. Chitosan and its use as a pharmaceutical excipient. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Nah, J.W.; Kwon, Y.; Koh, J.J.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, S.W. Water-soluble and low molecular weight chitosan-based plasmid DNA delivery. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köping-Höggárd, M.; Meí nikova, Y.S.; Várum, K.M.; Lindman, B.; Aryursson, p. Relationship between the physical shape and the efficiency of oligomeric chitosan as a gene delivery system in vitro and in vivo. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, I.; VáAgen, S.R.; Sande, S.A.; Smistad, G.; Karlsen, J. Interactions between liposomes and chitosan ii: Effect of selected parameters on aggregation and leakage. Int. J. Pharm. (Amst.) 1997, 146, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, S.; VáRum, K.M.; Stokke, B.T. Structural analysis of chitosan mediated DNA condensation by AFM: Influence of chitosan molecular parameters. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, A.; Cremer, K.; Kreuter, J. Preparation and characterization of chitosan microspheres as drug carrier for prednisolone sodium phosphate as model for anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Control. Release 1996, 39, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, S.; Imai, T.; Otagiri, M. Controlled release of indomethacin by chitosan-polyelectrolyte complex: Optimization and in vivo/in vitro evaluation. J. Control. Release 1993, 25, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonsen, M.W.; Smidsrod, O. Hydrogen ion titration of chitosans with varying degrees of N -acetylation by monitoring induced 1 H-NMR chemical shifts. Polymers 1995, 26, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.P.; TøMmeraas, K.; VáRum, K.M.; Østgaard, K. Electrophoretic light scattering studies of chitosans with different degrees of N-acetylation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, N.G.M.; Várum, K.M.; Artursson, P. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly absorbable drugs. 1: Influence of molecular weight and degree of acetylation on drug transport across human intestinal epithelial (caco-2) cells. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaduzzi, F.; Bomboi, F.; Bonincontro, A.; Bordi, F.; Casciardi, S.; Chronopoulou, L. Chitosan–DNA complexes: Charge inversion and DNA condensation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatorre-Meda, M.; Taboada, P.; Sabín, J.; Krajewska, B.; Varela, L.M.; Rodríguez, J.R. DNA-chitosan complexation: A dynamic light scattering study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravoanaya, L.M.; Soltero, J.F.; Rinaudo, M. DNA/chitosan electrostatic complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.L.; Lavertu, M.; Winnik, F.M.; Buschmann, M.D. Stability and binding affinity of DNA/chitosan complexes by polyanion competition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosse, C.; Croquette, V. Magnetic tweezers: Micromanipulation and force measurement at the molecular level. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 3314–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G. The Modulation of Chitosan-DNA Interaction by Concentration and pH in Solution. Polymers 2019, 11, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040646
Ma F, Wang Y, Yang G. The Modulation of Chitosan-DNA Interaction by Concentration and pH in Solution. Polymers. 2019; 11(4):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040646
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Fangqin, Yanwei Wang, and Guangcan Yang. 2019. "The Modulation of Chitosan-DNA Interaction by Concentration and pH in Solution" Polymers 11, no. 4: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040646
APA StyleMa, F., Wang, Y., & Yang, G. (2019). The Modulation of Chitosan-DNA Interaction by Concentration and pH in Solution. Polymers, 11(4), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040646



