Characterization and Optimization of PLA Stereocomplexed Hydrogels for Local Gene Delivery Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Synthesis of Triblock Copolymers
2.4. DNA Loaded 3LM Micelle Preparation
2.5. Stereocomplexed Hydrogel Preparation
2.6. Hydrogel Degradation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Block Copolymers
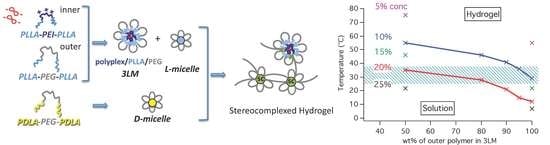
3.2. 3LM and Hydrogel Formation
3.3. Effect of Formulation on Micelle Size and Composition
3.4. Gelation Mechanism and Sol-to-gel Phase Transition
3.5. Mechanical Strength
3.6. Effect of PEG Block Length on the Hydrogels
3.7. Hydrogel Degradation Study
3.8. Hydrogel Analysis by Solid-State NMR
3.9. Gene Delivery Prospectives of 3LM-hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krebs, M.D.; Jeon, O.; Alsberg, E. Localized and Sustained Delivery of Silencing RNA from Macroscopic Biopolymer Hydrogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9204–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Khanh, N.; Alsberg, E. Bioactive factor delivery strategies from engineered polymer hydrogels for therapeutic medicine. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1235–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.D.; Mora, E.M.; Roh, J.W.; Nishimura, M.; Lee, S.J.; Stone, R.L.; Bar-Eli, M.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. Chitosan hydrogel for localized gene silencing. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, H.S. DNA nanogels composed of chitosan and Pluronic with thermo-sensitive and photo-crosslinking properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 373, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giano, M.C.; Ibrahim, Z.; Medina, S.H.; Sarhane, K.A.; Christensen, J.M.; Yamada, Y.; Brandacher, G.; Schneider, J.P. Injectable bioadhesive hydrogels with innate antibacterial properties. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.M.; Zhao, Y.M.; Sun, H.H.; Jin, T.; Wang, Q.T.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Z.F.; Jin, Y. Novel glycidyl methacrylated dextran (Dex-GMA)/gelatin hydrogel scaffolds containing microspheres loaded with bone morphogenetic proteins: Formulation and characteristics. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Padmashali, R.M.; Andreadis, S.T. Cell-controlled and spatially arrayed gene delivery from fibrin hydrogels. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.D.; Salter, E.; Chen, E.; Sutter, K.A.; Alsberg, E. Calcium alginate phosphate-DNA nanoparticle gene delivery from hydrogels induces in vivo osteogenesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Shibata, T.; Shimada, A.; Ideno, H.; Nakashima, K.; Tabata, Y.; Nifuji, A. Cationized gelatin hydrogels mixed with plasmid DNA induce stronger and more sustained gene expression than atelocollagen at calvarial bone defects in vivo. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, F.Q.; Shah, Z.; Cheng, X.J.; Kong, M.; Feng, C.; Chen, X.G. Nano-polyplex based on oleoyl-carboxymethy-chitosan (OCMCS) and hyaluronic acid for oral gene vaccine delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinle, H.; Ionescu, T.M.; Schenk, S.; Golombek, S.; Kunnakattu, S.J.; Ozbek, M.T.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.P.; Avci-Adali, M. Incorporation of Synthetic mRNA in Injectable Chitosan-Alginate Hybrid Hydrogels for Local and Sustained Expression of Exogenous Proteins in Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilhano, R.S.; Madrigal, J.L.; Wong, K.; Williams, P.A.; Martin, P.K.M.; Yamaguchi, F.S.M.; Samoto, V.Y.; Han, S.W.; Silva, E.A. Injectable alginate hydrogel for enhanced spatiotemporal control of lentivector delivery in murine skeletal muscle. J. Control. Release 2016, 237, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, S.; Borzacchiello, A.; Netti, P.A. Perspectives on: PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers and their biomedical applications. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2006, 21, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Ning, W.; Wang, J.M.; Choi, A.; Lee, P.Y.; Tyagi, P.; Huang, L. Controlled gene delivery system based on thermosensitive biodegradable hydrogel. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.C.; He, C.L.; Cheng, Y.L.; Li, D.S.; Gong, Y.B.; Liu, J.G.; Tian, H.Y.; Chen, X.S. PLK1shRNA and doxorubicin co-loaded thermosensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogels for osteosarcoma treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8723–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, F.K.; Seidlits, S.K.; Tang, A.; Crowther, R.S.; Carney, D.H.; Barry, M.A.; Mikos, A.G. In vitro release of plasmid DNA from oligo (poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Wang, D.Q.; Hedley, M.L.; Barman, S.P. Gene delivery with in-situ crosslinking polymer networks generates long-term systemic protein expression. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Jeon, O.; Krebs, M.D.; Schapira, D.; Alsberg, E. Sustained localized presentation of RNA interfering molecules from in situ forming hydrogels to guide stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6278–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Tae, G. Formulation and in vitro characterization of an in situ gelable, photo-polymerizable Pluronic hydrogel suitable for injection. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Jeon, O.; Dang, P.N.; Huynh, C.T.; Varghai, D.; Riazi, H.; McMillan, A.; Herberg, S.; Alsberg, E. RNA interfering molecule delivery from in situ forming biodegradable hydrogels for enhancement of bone formation in rat calvarial bone defects. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ganesh, S.; Amiji, M. Non-condensing polymeric nanoparticles for targeted gene and siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomas, H. Injectable and biodegradable hydrogels: Gelation, biodegradation and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2193–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, Y.H. Thermosensitive sol-gel reversible hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Unfer, R.C.; Mallapragada, S.K. Dual-role self-assembling nanoplexes for efficient gene transfection and sustained gene delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, K.L.; Li, J. Supramolecular Anchoring of DNA Polyplexes in Cyclodextrin-Based Polypseudorotaxane Hydrogels for Sustained Gene Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3162–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; van Ee, R.J.; Timmer, K.; Craenmehr, E.G.M.; Huang, J.H.; Oner, F.C.; Dhert, W.J.A.; Kragten, A.H.M.; Willems, N.; Grinwis, G.C.M.; et al. A novel injectable thermoresponsive and cytocompatible gel of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) with layered double hydroxides facilitates siRNA delivery into chondrocytes in 3D culture. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Mukose, T.; Yamaoka, T.; Yamane, H.; Sakurai, S.; Kimura, Y. Novel thermo-responsive formation of a hydrogel by stereo-complexation between PLLA-PEG-PLLA and PDLA-PEG-PDLA block copolymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2001, 1, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.G.; Fujiwara, T. Controlled Thermoresponsive Hydrogels by Stereocomplexed PLA-PEG-PLA Prepared via Hybrid Micelles of Pre-Mixed Copolymers with Different PEG Lengths. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. Poly (lactide) stereocomplexes: Formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.G.; Kandil, R.; Kraus, T.; Elsayed, M.; Merkel, O.M.; Fujiwara, T. Three-Layered Biodegradable Micelles Prepared by Two-Step Self-Assembly of PLA-PEI-PLA and PLA-PEG-PLA Triblock Copolymers as Efficient Gene Delivery System. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Li, Y.; Abebe, D.G.; Xie, Y.R.; Kandil, R.; Kraus, T.; Gomez-Lopez, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Merkel, O.M. Folate receptor targeted three-layered micelles and hydrogels for gene delivery to activated macrophages. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.G.; Kandil, R.; Kraus, T.; Elsayed, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Merkel, O.M. Biodegradable Three-Layered Micelles and Injectable Hydrogels. In Non-Viral Gene Delivery Vectors: Methods and Protocols; Candiani, G., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1445, pp. 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.M.; Simmons, K.L.; Gutowska, A.; Jeong, B. Sol-gel transition temperature of PLGA-g-PEG aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.G.; Liu, K.Y.; Mishra, S.R.; Wu, A.H.F.; Lamb, R.N.; Fujiwara, T. Time-resolved SANS analysis of micelle chain exchange behavior: Thermal crosslink driven by stereocomplexation of PLA-PEG-PLA micelles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96019–96027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Micelle ID | 3LM Composition I/O Polymer Weight Ratio (%) a | D-Micelle Polymer Weight Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Polymer | Outer Polymer | short-PEG | long-PEG | ||
| PLLA-PEI-PLLA (1700-2000-1700) | PLLA-PEG-PLLA (800-2000-800) | PLLA-PEG-PLLA (1200-2000-1200) | PDLA-PEG-PDLA (800-2000-800) | PDLA-PEG-PDLA (800-3350-800) | |
| 3LM-1/1 | 50 | 50 | |||
| 3LM-1/5 | 17 | 83 | |||
| 3LM-1/10 b | 9 | 91 | |||
| 3LM-1/20 | 5 | 95 | |||
| 3LM-1/1-1200 | 50 | 50 | |||
| D-micelle–S c | 100 | 0 | |||
| D-micelle–70S | 70 | 30 | |||
| D-micelle–50S | 50 | 50 | |||
| D-micelle–30S | 30 | 70 | |||
| D-micelle–0S | 0 | 100 | |||
| 3LM (inner/outer) PLLA-PEI-PLLA a/PLLA-PEG-PLLA b | D-micelle PDLA-PEG-PDLA (800-2000-800)/(800-3350-800) | Sol-to-Gel Transition Temperature (°C) | Time before Starting to Flow c (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3LM-1/5 | D-micelle | 45 | 1 |
| D-micelle–70S d | 50 | 10 | |
| D-micelle–50S | 60 | >60 | |
| D-micelle–30S | 70 | >60 | |
| D-micelle–100S | 65 | 3 |
| Sample | Evaluation | Method | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3LM | Loading efficiency [31] | Heparin extraction | >50% |
| Micelle stability [31] | SYBR Gold Assay | No DNA exclusion | |
| DNA release [31] | Dextran Sulfate competition assay | No release at pH 7.4 Rapid release at pH 4.5 | |
| Cell toxicity [31] | MTT Assay | Higher IC50 than PEI-polyplex | |
| RAW 264.7 Uptake [32] | FA-modified 3LM with YOYO-1 labeled DNA | Highly specific uptake in activated macrophages | |
| GFP expression in RAW 264.7 [32] | Flow cytometry | High uptake in activated cells | |
| GFP expression in primary spleen macrophages [32] | Flow cytometry | Significantly higher expression in activated cells | |
| 3LM- hydrogel | DNA release [32] | SYBR Gold Assay | No release at pH 7.4 Slow release at pH 4.5 |
| Macrophage uptake [32] | Flow cytometry | High uptake from pH 4.5 supernatant |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.-Y.; Abebe, D.G.; Wiley, E.R.; Fujiwara, T. Characterization and Optimization of PLA Stereocomplexed Hydrogels for Local Gene Delivery Systems. Polymers 2019, 11, 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050796
Liu K-Y, Abebe DG, Wiley ER, Fujiwara T. Characterization and Optimization of PLA Stereocomplexed Hydrogels for Local Gene Delivery Systems. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kwei-Yu, Daniel G. Abebe, Elizabeth Rachel Wiley, and Tomoko Fujiwara. 2019. "Characterization and Optimization of PLA Stereocomplexed Hydrogels for Local Gene Delivery Systems" Polymers 11, no. 5: 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050796
APA StyleLiu, K.-Y., Abebe, D. G., Wiley, E. R., & Fujiwara, T. (2019). Characterization and Optimization of PLA Stereocomplexed Hydrogels for Local Gene Delivery Systems. Polymers, 11(5), 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050796