Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Hemocompatibility of the Composites Based on Biodegradable Poly(Ether-Ester-Urethane) and Phosphorylcholine-Containing Copolymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PEEU
2.3. Preparation of Poly(MPC-co-EHMA) (PMEH)
2.4. Preparation of PEEU/PMEH Composite Films
2.5. Characterization and Instruments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Stability
3.2. Tensile Properties
3.3. Surface and Bulk Hydrophilicity
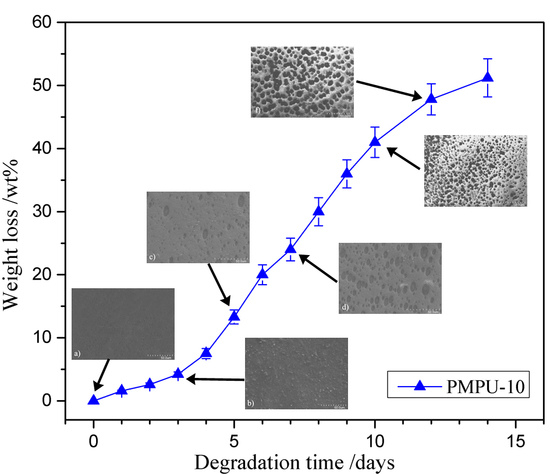
3.4. In Vitro Degradation
3.5. Protein Adsorption
3.6. Platelet Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heath, D.E.; Cooper, S.L. Polyurethanes; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Chen, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyurethane based on poly(ε-caprolactone) and L-lysine ethyl ester diisocyanate. Front. Mater. Sci. 2009, 3, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xiao, M.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Z. Preparation, physicochemical properties and hemo-compatibility of biodegradable chitooligosaccharide-based polyurethane. Polymers 2018, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Hu, Z.; Xu, A.; Liu, R.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. The preparation and performance of a new polyurethane vascular prosthesis. Cell. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 66, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Kang, C.; Chen, J.; Ye, D.; Qiu, S.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Y. Surface modification of polyurethane towards promoting the ex vivo cytocompatibility and in vivo biocompatibility for hypopharyngeal tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2012, 28, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Kumari, T.V.; Jayabalan, M. In vitro studies on the effect of physical cross-linking on the biological performance of aliphatic poly(urethane urea) for blood contact applications. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Sartori, S.; Boffito, M.; Mattu, C.; Rienzo, A.M.D.; Boccafoschi, F.; Ciardelli, G. Biomimetic myocardial patches fabricated with poly(ɛ-caprolactone) and polyethylene glycol-based polyurethanes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2014, 102, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelcher, S.A. Biodegradable polyurethanes: Synthesis and applications in regenerative medicine. Tissue Eng. B 2008, 14, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Hyon, S.; Ikada, Y. Water-curable and biodegradable prepolymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Sacks, M.S.; Beckman, E.J.; Wagner, W.R. Biodegradable poly(ether ester urethane) urea elastomers based on poly(ether ester) triblock copolymers and putrescine: synthesis, characterization and cytocompatibility. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, J.H.D.; Spaans, C.J.; Dekens, F.G.; Pennings, A.J. On the role of aminolysis and transesterification in the synthesis of ɛ-caprolactone and L-lactide based polyurethanes. Polym. Bull. 1998, 41, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaans, C.J.; Groot, J.H.D.; Dekens, F.G.; Pennings, A.J. High molecular weight polyurethanes and a polyurethane urea based on 1,4-butanediisocyanate. Polym. Bull. 1998, 41, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Z. Synthesis and characterization of a new biodegradable polyurethanes with good mechanical properties. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Xia, Y.; Yin, S.; Hou, Z.; Wu, R. Influence of well-defined hard segment length on the properties of medical segmented polyesterurethanes based on poly(ε-caprolactone-co-L-lactide) and aliphatic urethane diisocyanates. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Po. 2017, 66, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, B.; Eyster, T.W.; Ma, P.X. Super stretchable electroactive elastomer formation driven by aniline trimer self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5668–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Liang, Y.; Ma, P.X. Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, B.; Yin, Z.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Adhesive hemostatic conducting injectable composite hydrogels with sustained drug release and photothermal antibacterial activity to promote full-thickness skin regeneration during wound healing. Small 2019, 15, 1900046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; McClung, W.G.; Brash, J.L. Lysine-PEG-modified polyurethane as a fibrinolytic surface: Effect of PEG chain length on protein interactions, platelet interactions and clot lysis. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochynska, A.I.; Hannink, G.; Grijpma, D.W.; Buma, P. Tissue adhesives for meniscus tear repair: An overview of current advances and prospects for future clinical solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. M. 2016, 27, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Hou, Z. Synthesis of a novel biomedical poly(ester urethane) based on aliphatic uniform-size diisocyanate and the blood compatibility of PEG-grafted surfaces. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 32, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Z. A mild method for surface-grafting PEG onto segmented poly(ester-urethane) film with high grafting density for biomedical purpose. Polymers 2018, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Feng, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Shi, C.; Khan, M.; Guo, J. Grafting of phosphorylcholine functional groups on polycarbonate urethane surface for resisting platelet adhesion. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Effects of solid substrate on structure and properties of casting waterborne polyurethane/carboxymethylchitin films. Polymer 2004, 45, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Salama, H.; Sabaa, M.; Saad, G. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable copoly(ether-ester-urethane)s and their chitin whisker nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yin, S.; Hou, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q. Preparation, physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of biodegradable poly(ether-ester-urethane) and chitosan oligosaccharide composites. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Gong, Y. Improved biocompatibility of phosphorylcholine end-capped poly(butylene succinate). Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, S.; Nakashima, K.; Gong, Y. Surface reconstruction and hemo-compatibility improvement of a phosphorylcholine end-capped poly(butylene succinate) coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 2972–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Ueda, T.; Nakabayashi, N. Preparation of phospholipid polylners and their properties as polymer hydrogel membranes. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, J.A.; Chapman, D. Biomembrane surfaces as models for polymer design: The potential for haemocompatibility. Biomaterials 1984, 5, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korematsu, A.; Takemoto, Y.; Nakaya, T.; Inoue, H. Synthesis, characterization and platelet adhesion of segmented polyurethanes grafted phospholipid analogous vinyl monomer on surface. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Mahara, A.; Kakinoki, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishihara, K. Durable modification of segmented polyurethane for elastic blood-contacting devices by graft-type 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine copolymer. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. E 2014, 25, 1514–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Biocompatible elastomers composed of segmented polyurethane and 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2000, 11, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Ye, S.H.; Nieponice, A.; Soletti, L.; Wagner, W.R. A small diameter, fibrous vascular conduit generated from a poly (ester urethane) urea and phospholipid polymer blend. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.P.; Nakabayashi, N.; Iwasaki, Y.; Boland, T.; Laberge, M. Frictional properties of poly(MPC-co-BMA) phospholipid polymer for catheter applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Tanaka, S.; Furukawa, N.; Kurita, K.; Nakabayashi, N. Improved blood compatibility of segmented polyurethanes by polymeric additives having phospholipid polar groups. I. Molecular design of polymeric additives and their functions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Hanyuda, H.; Nakabayashi, N. Synthesis of phospholipid polymers having a urethane bond in the side chain as coating material on segmented polyurethane and their platelet adhesion-resistant properties. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Khan, A.; Roohpour, N.; Glogauer, M.; Rehman, I. Protein adsorption capability on polyurethane and modified-polyurethane membrane for periodontal guided tissue regeneration applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohpour, N.; Wasikiewicz, J.M.; Moshaverinia, A.; Paul, D.; Grahn, M.F.; Rehman, I.U.; Vadgama, P. Polyurethane membranes modified with isopropyl myristate as a potential candidate for encapsulating electronic implants: A study of biocompatibility and water permeability. Polymers 2010, 2, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, F.C.; Yang, M.C. Effect of conjugated linoleic acid immobilization on the hemocompatibility of cellulose acetate membrane. Colloid. Surface. B 2006, 47, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Yang, M.C. Swelling and biocompatibility of sodium alginate/poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, P.; Queiroz, A.; Higa, O.; Buffa, F.; Abraham, G. Segmented poly(esterurethane urea)s from novel urea-diol chain extenders: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro biological properties. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Xia, Y.; Jia, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, N. Preparation and properties of biomedical segmented polyurethanes based on poly(ether ester) and uniform-size diurethane diisocyanates. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. E 2007, 28, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, H. Effects of polyvinylpyrrolidone on structure and performance of composite scaffold of chitosan superfine powder and polyurethane. Adv. Polym. Tech. 2012, 31, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Sun, B.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, M.; Chu, X.; Yuan, P.; Shen, J. Anticoagulant polyurethane substrates modified with poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) via SI-RATRP. Colloid. Surface. B 2018, 163, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Bae, J.; Kim, J.; Na, K.; Lee, E. Long acting porous microparticle for pulmonary protein delivery. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2007, 333, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Sakata, S.; Kakinoki, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishihara, K. Effects of molecular architecture of phospholipid polymers on surface modification of segmented polyurethanes. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. E 2014, 25, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyomoto, M.; Ishihara, K. Self-initiated surface graft polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyrthyl phosphorylcholine on poly(ether ether ketone) by photoirradiation. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2009, 1, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockman, K.; Kizhakkedathu, J.; Santerre, J. Hemocompatibility studies on a degradable polar hydrophobic ionic polyurethane (D-PHI). Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Winnik, F. Group reorientation and migration of amphiphilic polymer bearing phosphorylcholine functionalities on surface of cellular membrane mimicking coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederberg, F.; Bowden, T.; Nilsson, B.; Hong, J.; Hilborn, J. Phosphoryl choline introduces dual activity in biomimetic ionomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15350–15351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Films | PMPU-0 | PMPU-5 | PMPU-10 | PMPU-20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | |||||
| PEEU/g | 4.0 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.2 | |
| PMEH/g | 0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | |
| PMEH content/wt% | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| Films | Strain at Break (%) | Ultimate Stress (MPa) | Yield Stress (MPa) | Yield strain (%) | Initial Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMPU-0 | 932 ± 41 | 20.8 ± 2.4 | 9.97 ± 1.2 | 51.1 ± 4.2 | 19.5 |
| PMPU-5 | 925 ± 38 | 22.9 ± 2.3 | 8.15 ± 1.05 | 43.3 ± 3.3 | 18.8 |
| PMPU-10 | 825 ± 32 | 18.2 ± 1.9 | 7.26 ± 0.92 | 41.3 ± 3.4 | 17.5 |
| PMPU-20 | 820 ± 34 | 15.8 ± 1.4 | 6.20 ± 0.76 | 39.8 ± 3.0 | 15.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Jia, Q.; Xiao, M.; Hou, Z. Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Hemocompatibility of the Composites Based on Biodegradable Poly(Ether-Ester-Urethane) and Phosphorylcholine-Containing Copolymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050860
Zhang J, Yang B, Jia Q, Xiao M, Hou Z. Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Hemocompatibility of the Composites Based on Biodegradable Poly(Ether-Ester-Urethane) and Phosphorylcholine-Containing Copolymer. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050860
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jun, Bing Yang, Qi Jia, Minghui Xiao, and Zhaosheng Hou. 2019. "Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Hemocompatibility of the Composites Based on Biodegradable Poly(Ether-Ester-Urethane) and Phosphorylcholine-Containing Copolymer" Polymers 11, no. 5: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050860
APA StyleZhang, J., Yang, B., Jia, Q., Xiao, M., & Hou, Z. (2019). Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Hemocompatibility of the Composites Based on Biodegradable Poly(Ether-Ester-Urethane) and Phosphorylcholine-Containing Copolymer. Polymers, 11(5), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050860