Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Nafion and a Superacidic Inorganic Additive for Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
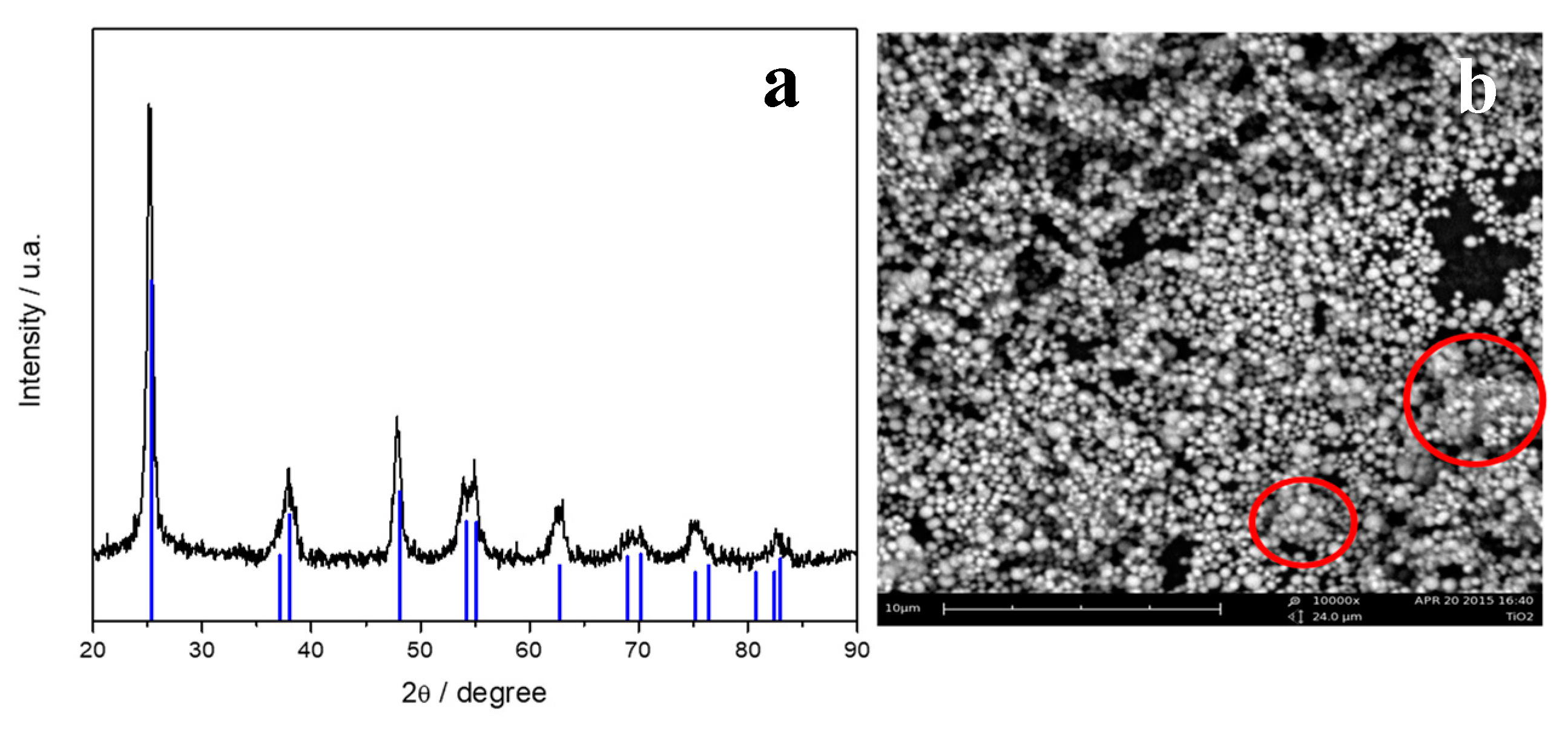
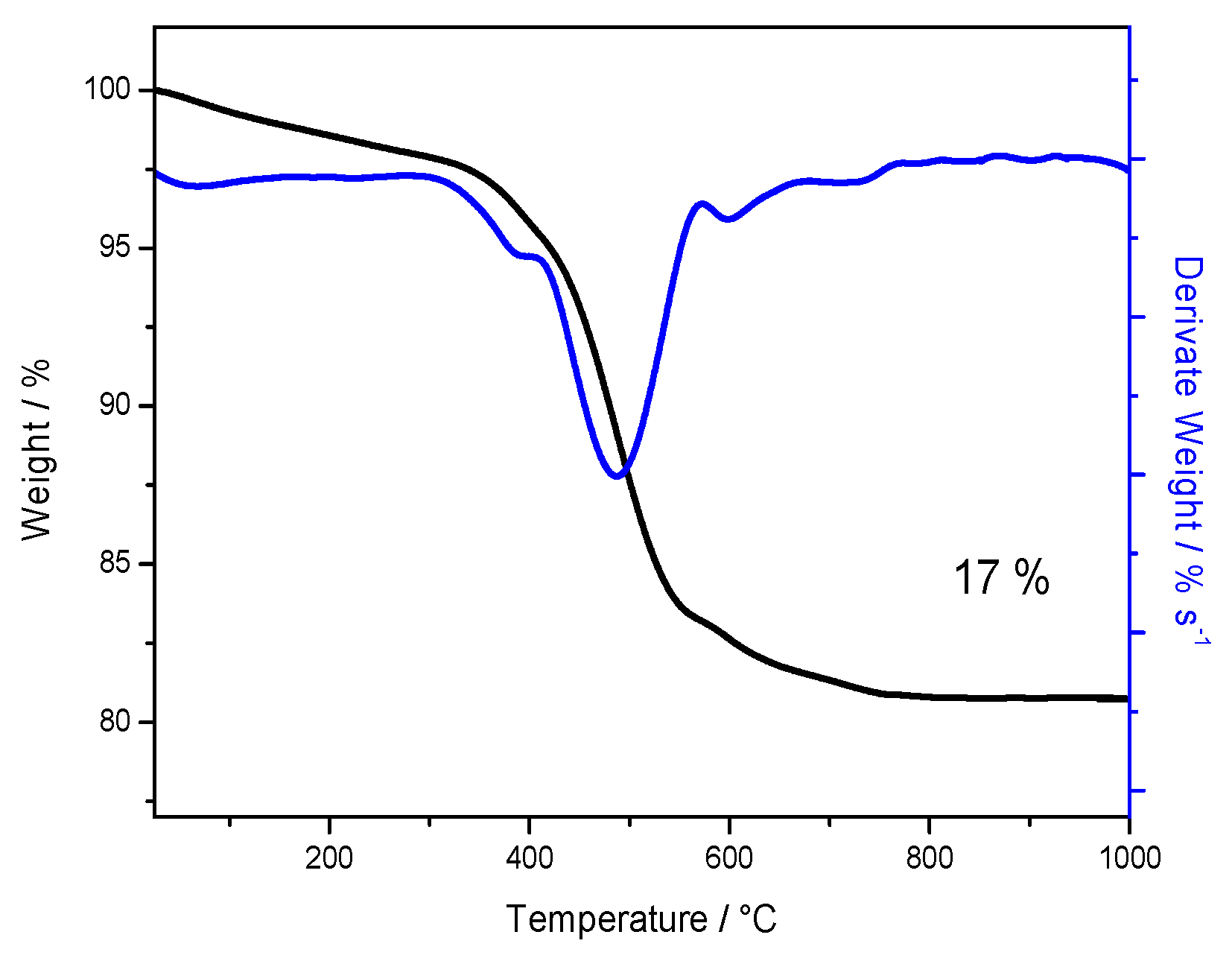
3.1. Characterization of Powder
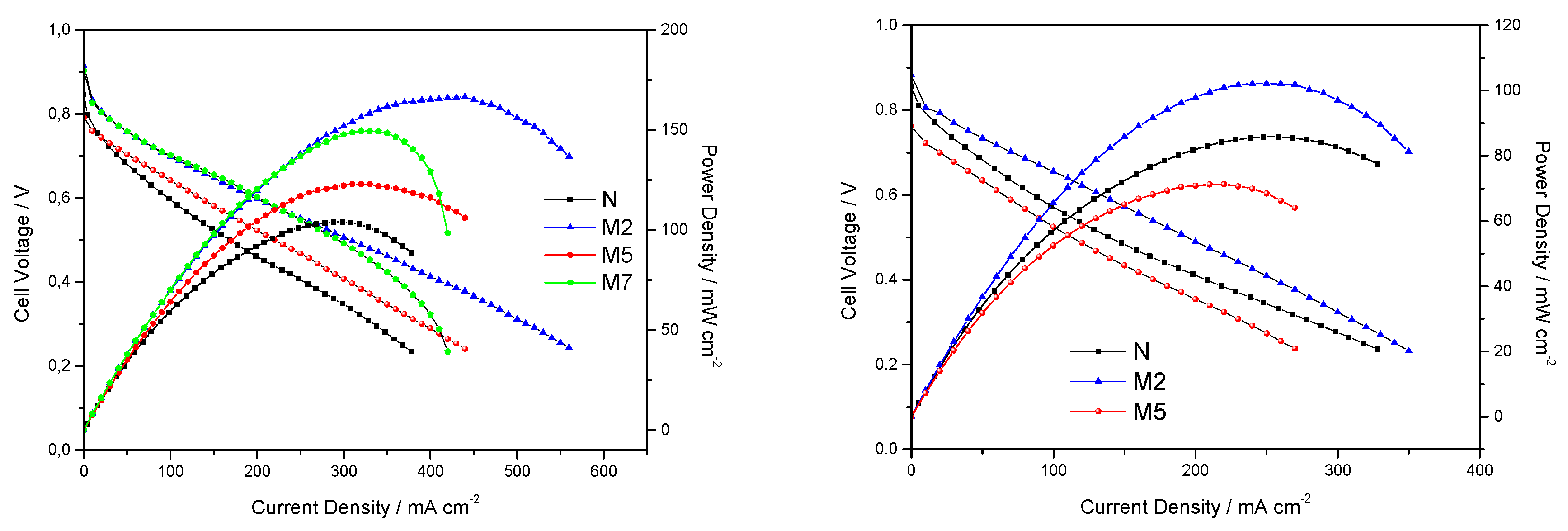
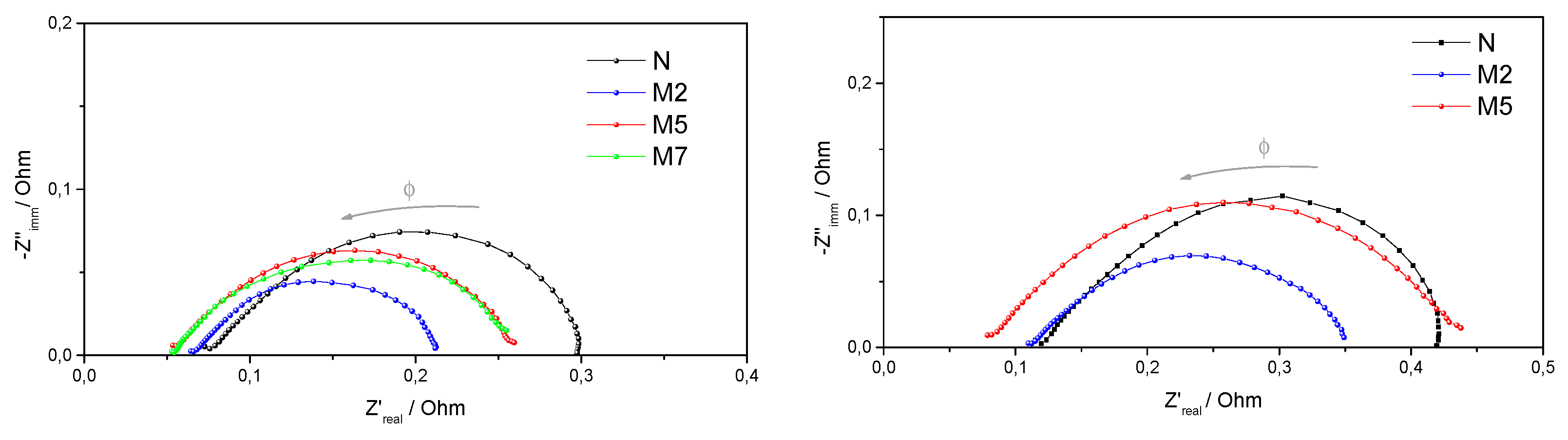
3.2. Characterization of the Composite Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosli, R.E.; Sulong, A.B.; Daud, W.R.W.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M.I.; Majlan, E.H.; Haque, M.A. A review of high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell (HT-PEMFC) system. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 2017, 42, 9293–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Nguyen, T.X.H.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.T.; Lee, J.H. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Recent advances and challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Simon, L.C.; Flowler, M.; Grot, S. Mechanical Properties of NafionTM Electrolyte Membranes under Hydrated Conditions. Polymer 2005, 46, 11707–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Rahman, S.U. Proton conductivity and characterization of novel composite membranes for medium-temperature fuel cells. Desalination 2006, 193, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Amjadi, M. Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 2010, 35, 9349–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciola, M.; Capitani, D.; Donnadio, A.; Frittella, V.; Pica, M.; Sganappa, M. Preparation, Proton Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Nafion 117–Zirconium Phosphate Sulphophenylphosphonate Composite Membranes. Fuel Cells 2009, 4, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.; Moore, R. State of understanding of nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.F.; Pan, C.; Jensen, J.O.; Noye, P.; Bjerrum, N.J. Cross-linked polybenzimidazole membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipioni, R.; Gazzoli, D.; Teocoli, F.; Palumbo, O.; Paolone, A.; Ibris, N.; Brutti, S.; Navarra, M.A. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite polymer membranes containing functionalized SnO2 additives. Membranes 2014, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccà, A.; Carbone, A.; Passalacqua, A.; D’Epifanio, A.; Licoccia, S.; Traversa, E.; Sala, E.; Traini, F.; Ornelas, R. Nafion—TiO2 hybrid membranes for medium temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2005, 152, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjemian, K.T.; Dominey, R.; Krishnan, L.; Ota, H.; Majsztrik, P.; Zhang, T.; Mann, J.; Kirby, B.; Gatto, L.; Velo-Simpson, M.; et al. Function and characterization of metal oxide-Nafion composite membranes for elevated-temperature H2/O2 PEM fuel cells. Chem. Mat. 2006, 18, 2238–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branchi, M.; Sgambetterra, M.; Pettiti, I.; Panero, S.; Navarra, M.A. Functionalized Al2O3 particles as additives in proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 2015, 40, 14757–14767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, F.; Baglio, V.; Di Blasi, O.; Staiti, P.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A.S. Solid polymer electrolyte based on sulfonated polysulfone membranes and acidic silica for direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2012, 216, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Ledesma-Garcia, J.; Arriaga, L.G.; Aricò, A.S. High temperature operation of a composite membrane-based solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyser. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7350–7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikhil, H.J.; Dunn, K.; Datta, R. Synthesis and characterization of Nafion®-MO2 (M = Zr, Si, Ti) nanocomposite membranes for higher temperature PEM fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arico, A.S.; Baglio, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Creti, P.; Antonucci, P.L.; Antonucci, V. Influence of the acid-base characteristics of inorganic fillers on the high temperature performance of composite membranes in direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2003, 152, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, B.; Velmurugan, R.; Swaminathan, M. TiO2–SO42− as a novel solid acid catalyst for highly efficient, solvent free and easy synthesis of chalcones under microwave irradiation. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, M.A.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. New, high temperature superacid zirconia-doped Nafion™ composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3210–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allodi, V.; Brutti, S.; Giarola, M.; Sgambetterra, M.; Navarra, M.A.; Panero, S.; Mariotto, G. Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of A Nanosized Sulfated TiO2 Filler and of Nanocomposite Nafion Membranes. Polymers 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Kosma, V.; Simari, C.; Ranieri, G.A.; Sgambetterra, M.; Panero, S.; Navarra, M.A. An NMR study on the molecular dynamic and exchange effects in composite Nafion/sulfated titania membranes for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 14651–14660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgambetterra, M.; Panero, S.; Hassoun, J.; Navarra, M.A. Hybrid membranes based on sulphated titania nanoparticles as low cost proton conductors. Ionics 2013, 19, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierke, T.D.; Hsu, W.Y. The Cluster-Network Model of Ion Clustering in Perfluorosulfonated Membranes. In Perfluorinated Ionomer Membranes; Eisemberg, A., Yeager, H.L., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; Volume 180, pp. 283–307. ISBN 13: 9780841206984. [Google Scholar]
- Slade, S.M.; Ralph, T.R.; de Ponce León, C.; Campbell, S.A.; Walsh, F.C. The Ionic Conductivity of a Nafion® 1100 Series of Proton-exchange Membranes Re-cast from Butan-1-ol and Propan-2-ol. Fuel Cells 2010, 10, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakandan, S.; Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Muthumeenal, A. Enhancing proton conduction of sulfonated poly (phenylene ether ether sulfone) membrane by charged surface modifying macromolecules for H2/O2 fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2015, 78, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano, K.; Hirasawa, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Yano, S. Order-disorder transition of ionic clusters in ionomers. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Epifanio, A.; Navarra, M.A.; Weise, C.; Mecheri, B.; Farrington, J.; Licoccia, S.; Greenbaum, S. Composite Nafion/Sulfated Zirconia Membranes: Effect of the Filler Surface Properties on Proton Transport Characteristics. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, L.G.; Delgado, P.G.; Kawano, Y. Thermal stability and decomposition of Nafion® membranes with different cations. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 75, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.H.; Kawano, Y. Thermal behavior of Nafion membranes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1999, 58, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgambetterra, M.; Brutti, S.; Allodi, V.; Mariotto, G.; Panero, S.; Navarra, M.A. Critical Filler Concentration in Sulfated Titania-Added Nafion™ Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Energies 2016, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Fedkiw, P.S. Analysis of EIS Technique and Nafion 117 Conductivity as a Function of Temperature and Relative Humidity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, G.A.; Piga, M.; Lavina, S.; Navarra, M.A.; D’Epifanio, A.; Scrosati, B.; Di Noto, V. Characterization of sulfated-zirconia/Nafion® composite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 198, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Membrane | Nafion (wt.%) | TiO2-SO4 (wt.%) | Thickness (µm) | Picture of a typical composite membrane |
| N | 100 | 103 ± 5 | ||
| M2 | 98 | 2 | 107 ± 5 |  |
| M5 | 95 | 5 | 98 ± 5 | |
| M7 | 93 | 7 | 101 ± 5 |
| Membrane | ΔH [J g−1polymer] | Tonset [°C] |
|---|---|---|
| N | 179.29 | 140 |
| M2 | 223.74 | 118 |
| M5 | 339.09 | 142 |
| M7 | 111.18 | 164 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzapioda, L.; Panero, S.; Navarra, M.A. Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Nafion and a Superacidic Inorganic Additive for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050914
Mazzapioda L, Panero S, Navarra MA. Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Nafion and a Superacidic Inorganic Additive for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050914
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzapioda, Lucia, Stefania Panero, and Maria Assunta Navarra. 2019. "Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Nafion and a Superacidic Inorganic Additive for Fuel Cell Applications" Polymers 11, no. 5: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050914
APA StyleMazzapioda, L., Panero, S., & Navarra, M. A. (2019). Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Nafion and a Superacidic Inorganic Additive for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers, 11(5), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050914






