Effect of Unbleached Rice Straw Cellulose Nanofibers on the Properties of Polysulfone Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Rice Straw Pulp
2.3. Xylanases Pretreatment of Unbleached Rice Straw Pulps
2.4. Isolation of Cellulose Nanofibers from Xylanase-Treated Unbleached Pulp
2.5. Preparation of PSF/RSNF Membrane
2.6. Characterization of PSF/RSNF Membrane
2.7. Preparation and Characterization of Lime Nanoparticles Suspension
2.8. Evaluation of Membranes Properties
2.8.1. Porosity
2.8.2. Pure Water Flux and Fouling
2.8.3. Removing Lime Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of RSNF on Viscosity of PSF Solution
3.2. Effect of RSNF on Microscopic Structure of PSF Membranes
3.3. Effect of RSNF on Mechanical Properties of PSF Films
3.4. Effect of RSNF on Hydrophilicity and Porosity of PSF Membranes
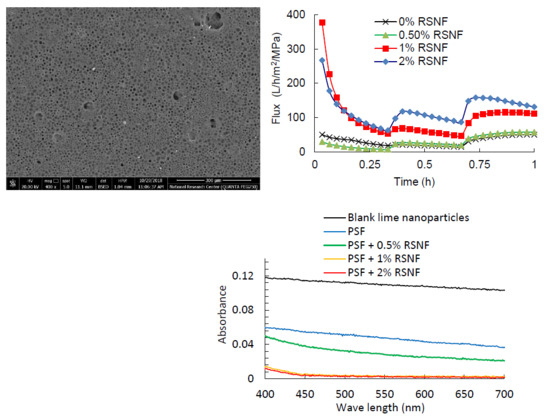
3.5. Effect of RSNF on Water Flux and Fouling of PSF Films
3.6. Rejection of Lime Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mark, H.F. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.K.; Lim, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Yoo, S.J.; Sung, Y.-E.; Park, H.S.; Jang, J.H. A Review on Membranes and Catalysts for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Single Cells. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; De, S. State-of-the-Art Materials and Spinning Technology for Hemodialyzer Membranes. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 216–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Pirouzfar, V.; Abedini, R.; Pedram, M.Z. The influence of nanoparticles on gas transport properties of mixed matrix membranes: An experimental investigation and modeling. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Manna, P.; Bhattacharya, A. Sulfonated polysulfone-preparative routes and applications in membranes used for pressure driven techniques. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2016, 53, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsvik, I.L.; Hagg, M.-B. Pressure Retarded Osmosis and Forward Osmosis Membranes: Materials and Methods. Polymers 2013, 5, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iojoiu, C.; Sanchez, J.-Y. Polysulfone-based Ionomers for Fuel Cell Applications. High Perform. Polym. 2009, 21, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, H. Polymeric membrane materials for artificial organs. J. Artif. Organs 2008, 11, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.D.; Oliveira, T.; Livingston, A.G.; Li, K. Membranes for the dehydration of solvents by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Abed, M.M.; Li, K. Preparation and characterization of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) based ultrafiltration membranes using nano γ-Al2O3. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliwati, E.; Ismail, A. Effect of additives concentration on the surface properties and performance of PVDF ultrafiltration membranes for refinery produced wastewater treatment. Desalination 2011, 273, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.C.; Merkel, T.C.; Freeman, B.D.; Spontak, R.J.; He, Z.; Pinnau, I. Ultrapermeable, Reverse-Selective Nanocomposite Membranes. Science 2002, 296, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, H.; Yu, P.; Luo, Y. Polyamide thin-film composite membrane based on nano-silica modified polysulfone microporous support layer for forward osmosis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 20177–20187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sarif, M.; Ismail, S. Development of an integrally skinned ultrafiltration membrane for wastewater treatment: effect of different formulations of PSf/NMP/PVP on flux and rejection. Desalination 2005, 179, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunos, M.Z.; Harun, Z.; Basri, H.; Ismail, A.F. Studies on fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) on polysulfone membranes: Effect of polyethylene glycol (PEG). Desalination 2014, 333, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Performance Improvement of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membrane Using Well-Dispersed Polyaniline–Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) Nanocomposite as the Additive. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 51, 4661–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorani, S.; Simonsen, J.; Atre, S. Nano-enabled microtechnology: polysulfone nanocomposites incorporating cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2007, 14, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L. Permeability and morphology study of polysulfone composite membrane blended with nanocrystalline cellulose. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2882–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, P.; Ghaemi, N.; Ghari, H.S.; Norouzi, M. Mitigation of fouling of polyethersulfone membranes using an aqueous suspension of cellulose nanocrystals as a nonsolvent. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L. Preparation and characterization of polysulfone membrane incorporating cellulose nanocrystals extracted from corn husks. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Bai, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, H. Papermaking Effluent Treatment: A New Cellulose Nanocrystalline/Polysulfone Composite Membrane. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, L.; Qu, P.; Bai, L. Preparation and characteristics of polysulfone dialysis composite membranes modified with nanocrystalline cellulose. BioResources 2011, 6, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Daria, M.; Fashandi, H.; Zarrebini, M.; Mohamadi, Z. Contribution of polysulfone membrane preparation parameters on performance of cellulose nanomaterials. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 015306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, P.; Ghaemi, N.; Sadeghi Ghari, H. An ultra-antifouling polyethersulfone membrane embedded with cellulose nanocrystals for improved dye and salt removal from water. Cellulose 2017, 24, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ding, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, L. Preparation and Characterization of Polysulfone/Sulfonated Polysulfone/Cellulose Nanofibers Ternary Blend Membranes. BioResources 2015, 10, 2936–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Tang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Wang, S. Polyethersulfone composite membrane blended With cellulose fibrils. BioResources 2010, 5, 2323–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhong, L.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L. Surface modification of cellulose nanofibers and their effects on the morphology and properties of polysulfone membranes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 397, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilakati, G.D.; Hoek, E.M.; Mamba, B.B. Probing the mechanical and thermal properties of polysulfone membranes modified with synthetic and natural polymer additives. Polym. Test. 2014, 34, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Benavente, J.; Garcia-Valls, R. Lignin-based membranes for electrolyte transference. J. Power Sources 2005, 145, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, K. Enhancing the Compatibility, Hydrophilicity and Mechanical Properties of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes with Lignocellulose Nanofibrils. Polymers 2016, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Berglund, L.; Hassan, E.; Abou-Zeid, R.; Oksman, K. Effect of xylanase pretreatment of rice straw unbleached soda and neutral sulfite pulps on isolation of nanofibers and their properties. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2939–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglieri, G.; Mondelli, C.; Daniele, V.; Pusceddu, E.; Trapananti, A. Synthesis and X-Ray Diffraction Analyses of Calcium Hydroxide Nanoparticles in Aqueous Suspension. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2013, 3, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Improving the antifouling property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of dextran grafted halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Berglund, L.; Abou-Zeid, R.; Hassan, E.; Abou-Elseoud, W.; Oksman, K. Nanocomposite Film Based on Cellulose Acetate and Lignin-Rich Rice Straw Nanofibers. Materials 2019, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgranges, L.; Grebille, D.; Calvarin, G.; Chevrier, G.; Floquet, N.; Niepce, J.-C. Hydrogen thermal motion in calcium hydroxide: Ca(OH)2. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 1993, 49, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Tang, H.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, S. Preparation and characterization of composite membranes of polysulfone and microcrystalline cellulose. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 112, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Viscosity (Pa.s) |
|---|---|
| PSF | 434 ± 0.71 |
| PSF + 0.5% RSNF | 533 ± 0.82 |
| PSF + 1.0% RSNF | 634 ± 1.41 |
| PSF + 2.0% RSNF | 988 ± 5.65 |
| Sample | Diameter of Pores at Surface (µm) |
|---|---|
| PSF | 2.9 ± 1.2 |
| PSF + 0.5% RSNF | 5.9 ± 3.4 |
| PSF + 1.0% RSNF | 5.8 ± 0.8 |
| PSF + 2.0% RSNF | 15.3 ± 8.6 |
| Sample | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Strain at Maximum Load (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSF | 3.88 ± 0.40 | 164.8 ± 16.2 | 24.1 ± 2.3 |
| PSF + 0.5% RSNF | 5.00 ± 0.51 | 229.9 ± 27.3 | 20.6 ± 3.9 |
| PSF + 1.0% RSNF | 3.50 ± 0.47 | 186.9 ± 18.9 | 19.1 ± 1.7 |
| PSF + 2.0% RSNF | 3.84 ± 1.16 | 176.5 ± 26.6 | 19.3 ± 2.4 |
| Sample | Contact Angle (°) | Water Absorption (%) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSF | 89.9 ± 0.4 | 84.2 ± 2.7 | 45.5 ± 2.9 |
| PSF + 0.5% RSNF | 80.1 ± 5.2 | 83.6 ± 2.4 | 54.3 ± 4.6 |
| PSF + 1.0 % RSNF | 81.5 ± 4.2 | 125.7 ± 5.9 | 69.8 ± 4.8 |
| PSF + 2.0 % RSNF | 82.7 ± 1.6 | 119.6 ± 6.8 | 66.6 ± 6.1 |
| Samples | Flux rate (L/h/m2/MPa) |
|---|---|
| Polysulfone (PSF) | 1.027 ± 0.12 |
| PSF/0.5 % RSNF | 4.00 ± 0.40 |
| PSF/1 % RSNF | 10.27 ± 1.06 |
| PSF/2 % RSNF | 10.78 ± 1.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, M.; Abou Zeid, R.E.; Abou-Elseoud, W.S.; Hassan, E.; Berglund, L.; Oksman, K. Effect of Unbleached Rice Straw Cellulose Nanofibers on the Properties of Polysulfone Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060938
Hassan M, Abou Zeid RE, Abou-Elseoud WS, Hassan E, Berglund L, Oksman K. Effect of Unbleached Rice Straw Cellulose Nanofibers on the Properties of Polysulfone Membranes. Polymers. 2019; 11(6):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060938
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Mohammad, Ragab E. Abou Zeid, Wafaa S. Abou-Elseoud, Enas Hassan, Linn Berglund, and Kristiina Oksman. 2019. "Effect of Unbleached Rice Straw Cellulose Nanofibers on the Properties of Polysulfone Membranes" Polymers 11, no. 6: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060938
APA StyleHassan, M., Abou Zeid, R. E., Abou-Elseoud, W. S., Hassan, E., Berglund, L., & Oksman, K. (2019). Effect of Unbleached Rice Straw Cellulose Nanofibers on the Properties of Polysulfone Membranes. Polymers, 11(6), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060938