Switchable Wettability of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA) Coated PET Fabric for Moisture Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
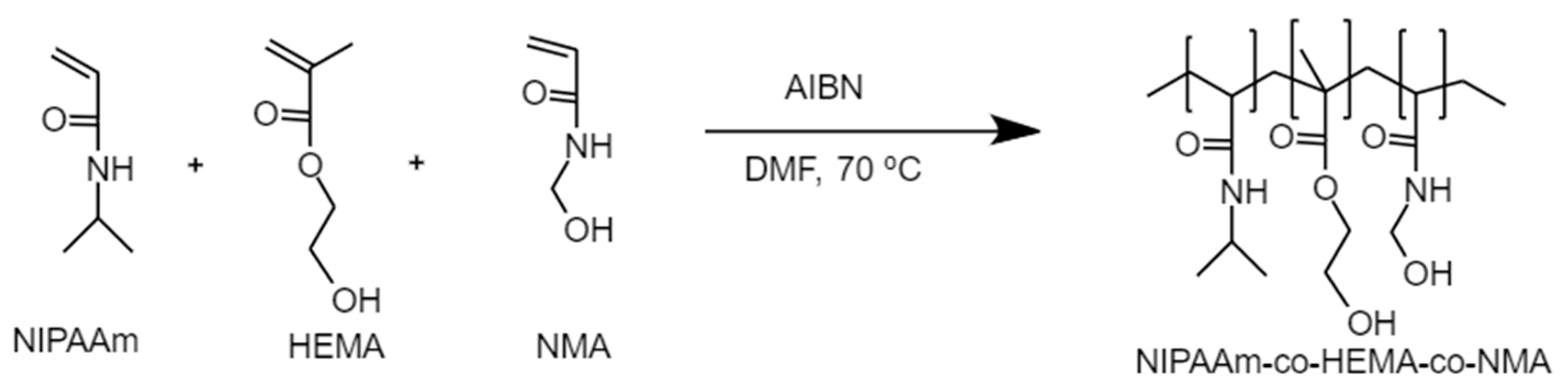
2.2. Synthesis of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA)
2.2.1. Synthesis of P1
2.2.2. Synthesis of P2
2.2.3. Synthesis of P3
2.3. Fabrication of Copolymer Coated PET Fabrics
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
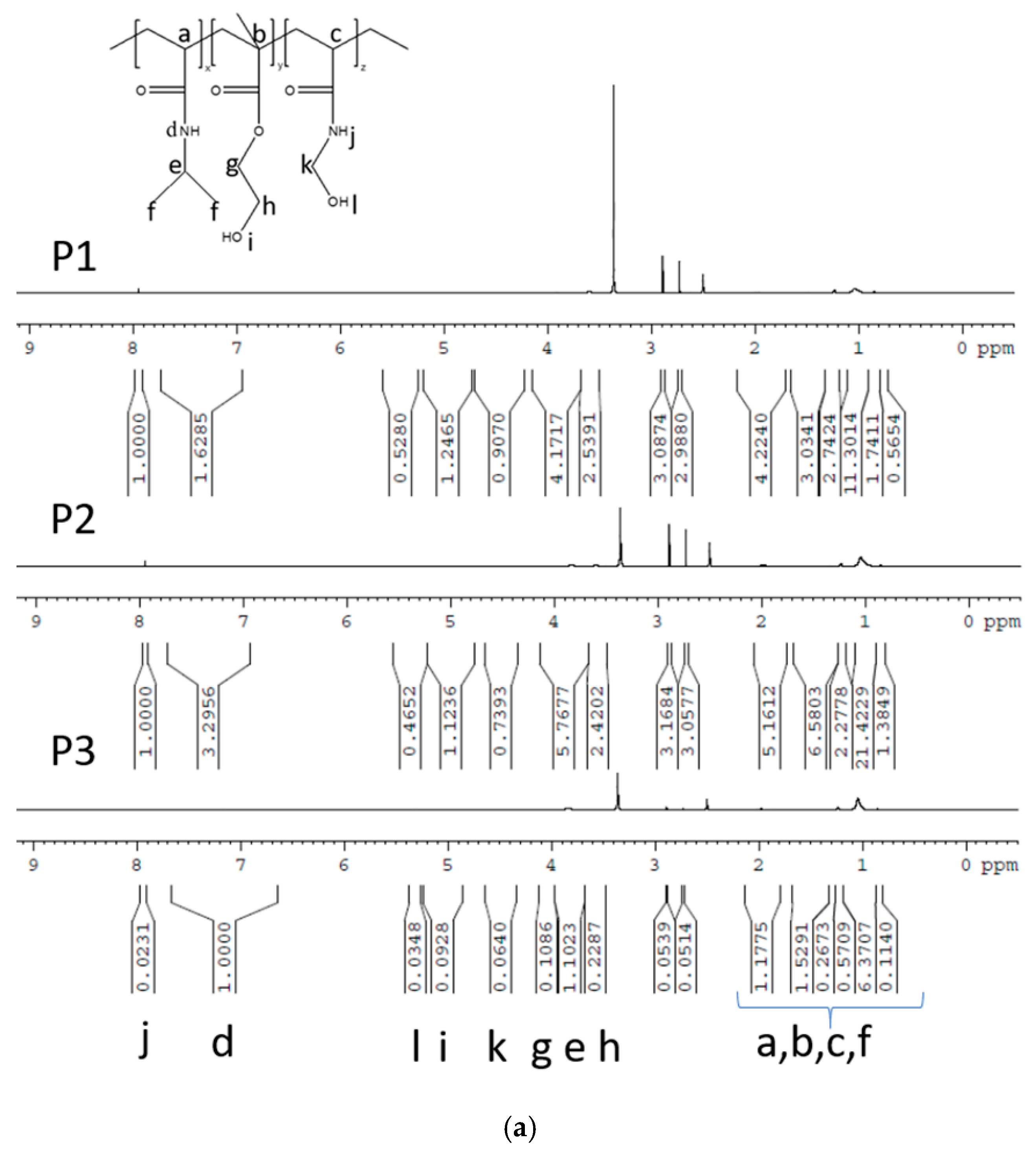
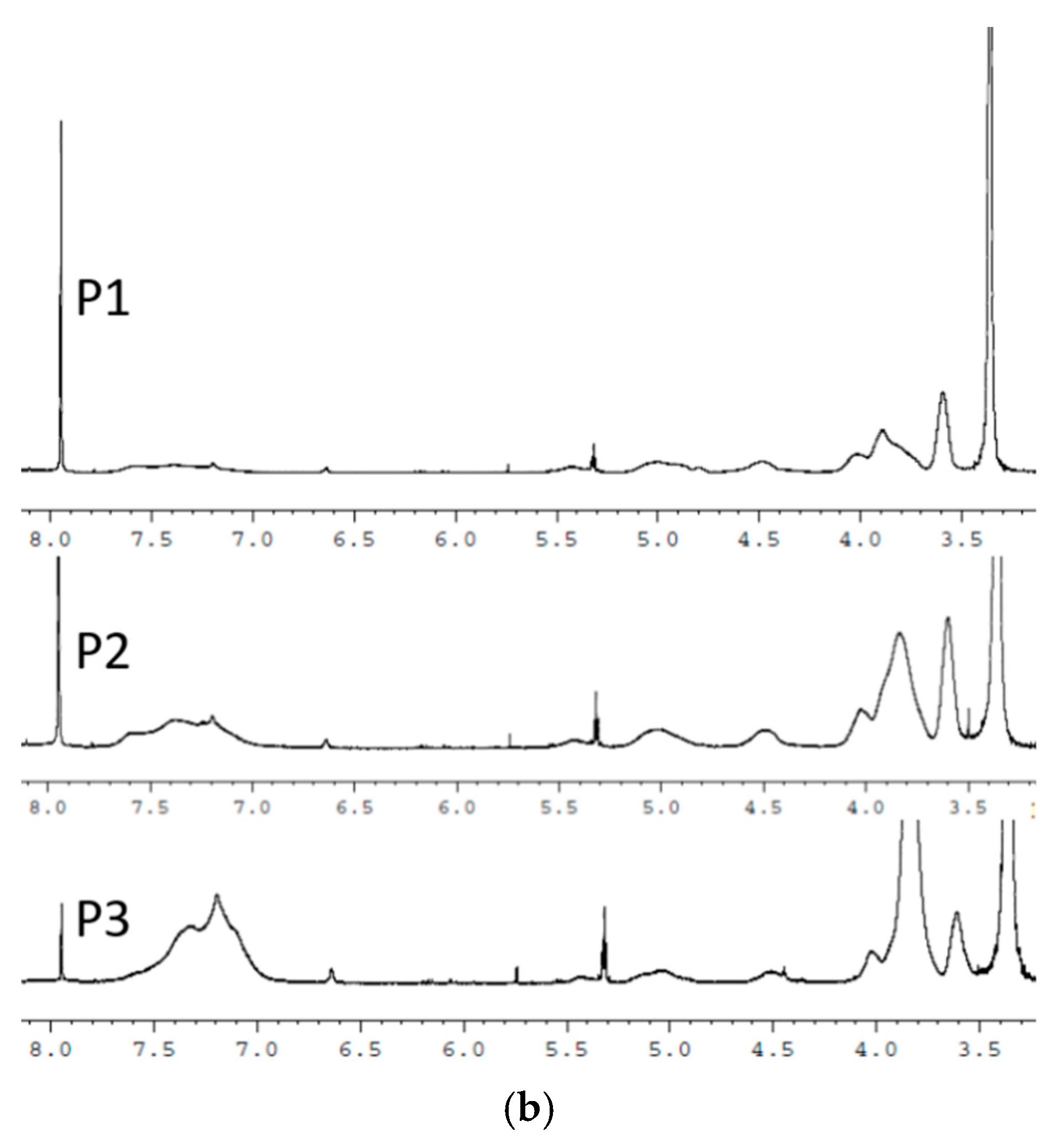
3.1. NMR Spectroscopy
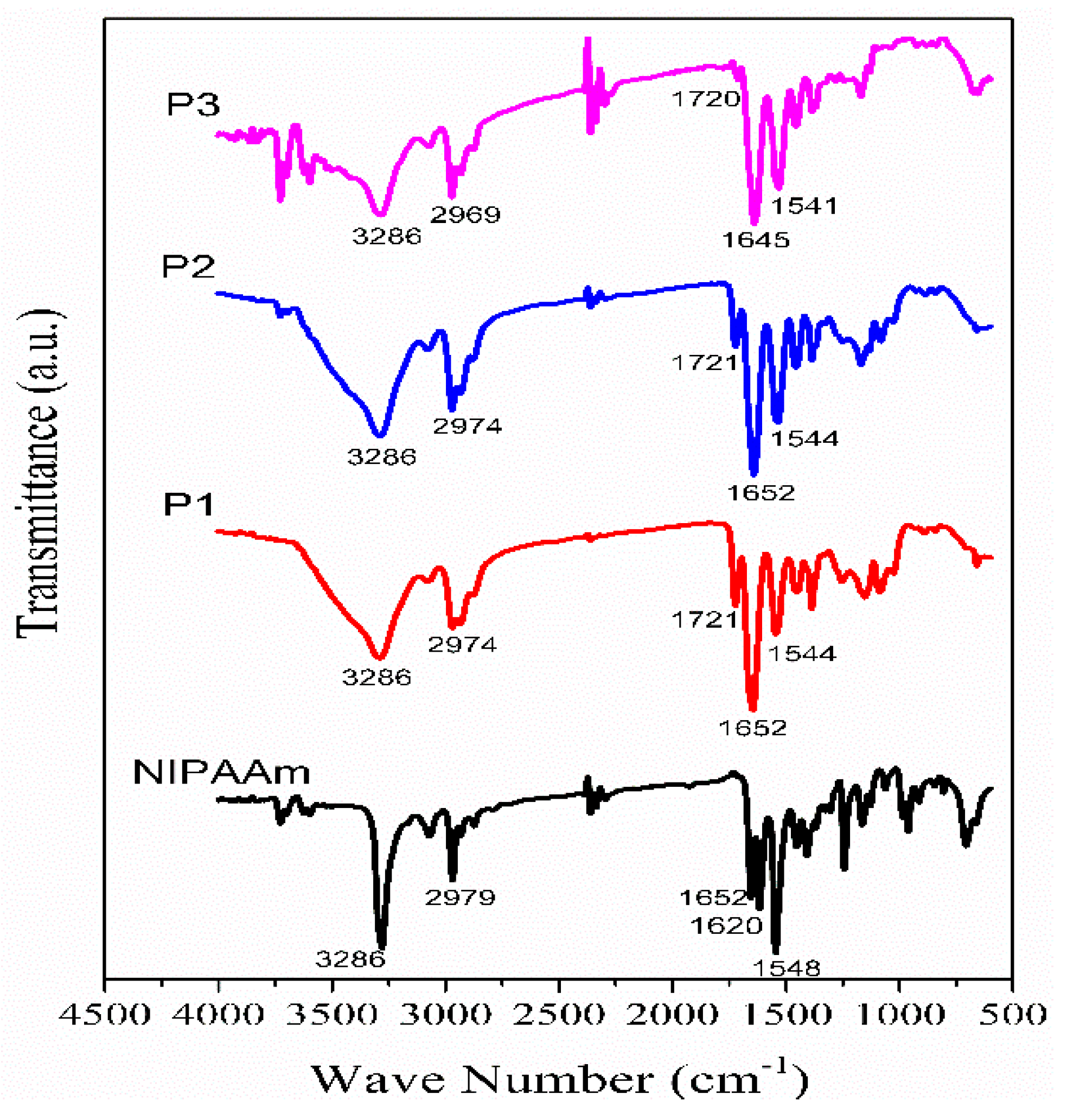
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
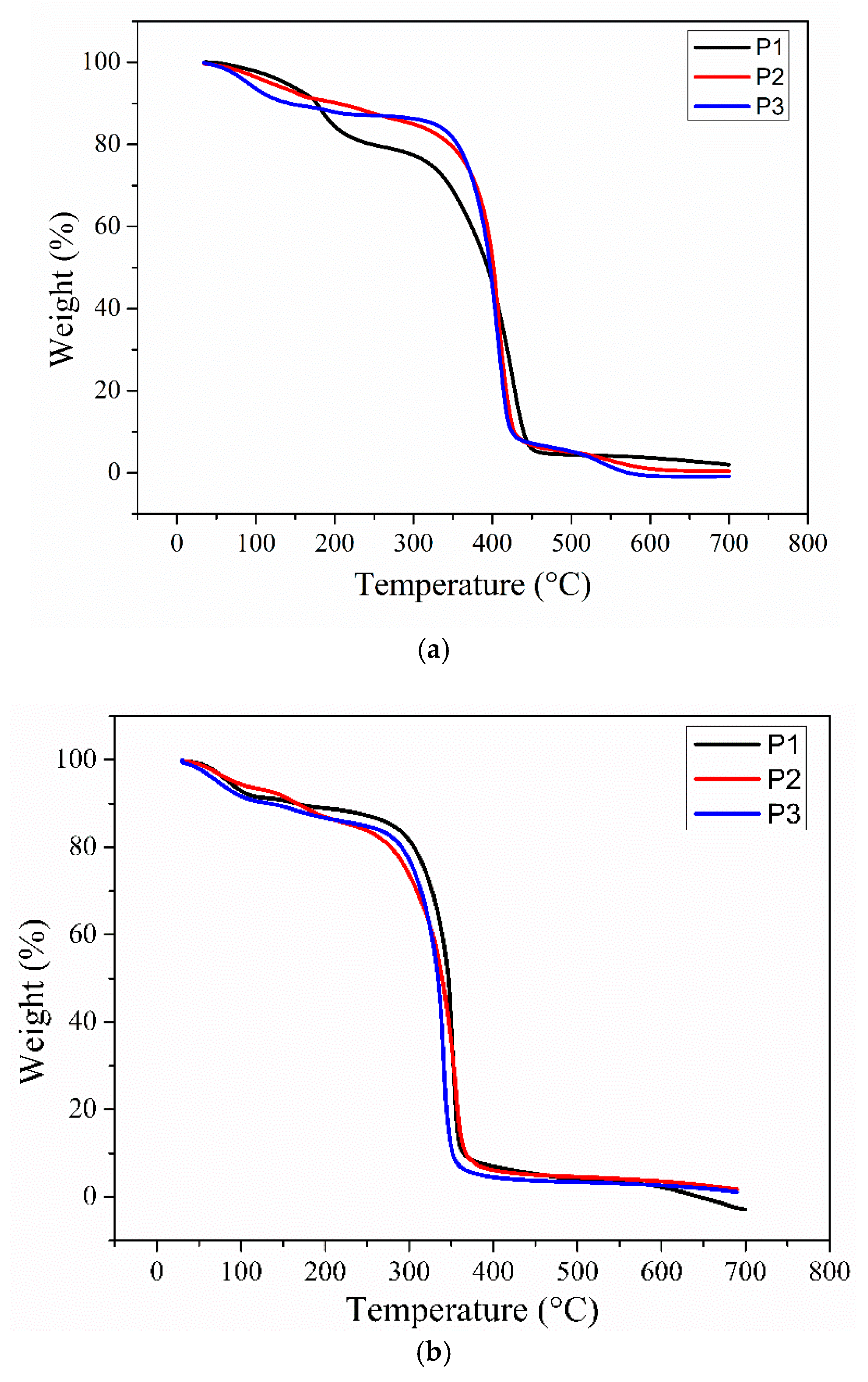
3.3. Thermal Behavior
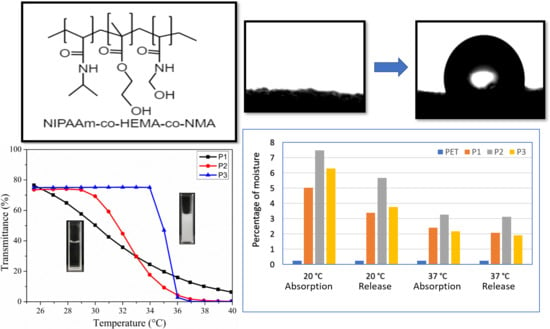
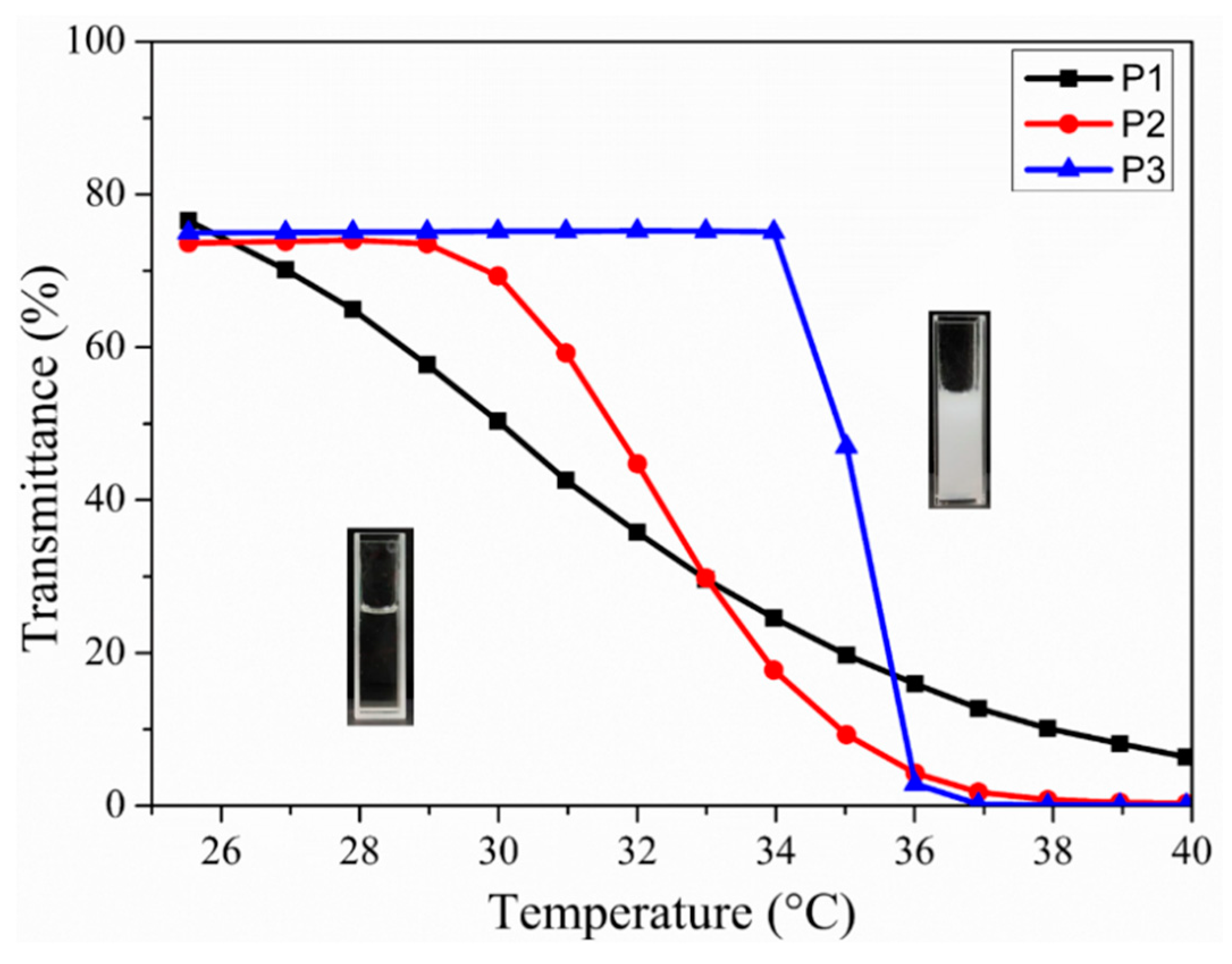
3.4. LCST
3.5. Swelling Test
3.6. Surface Wettability
3.7. Moisture Management
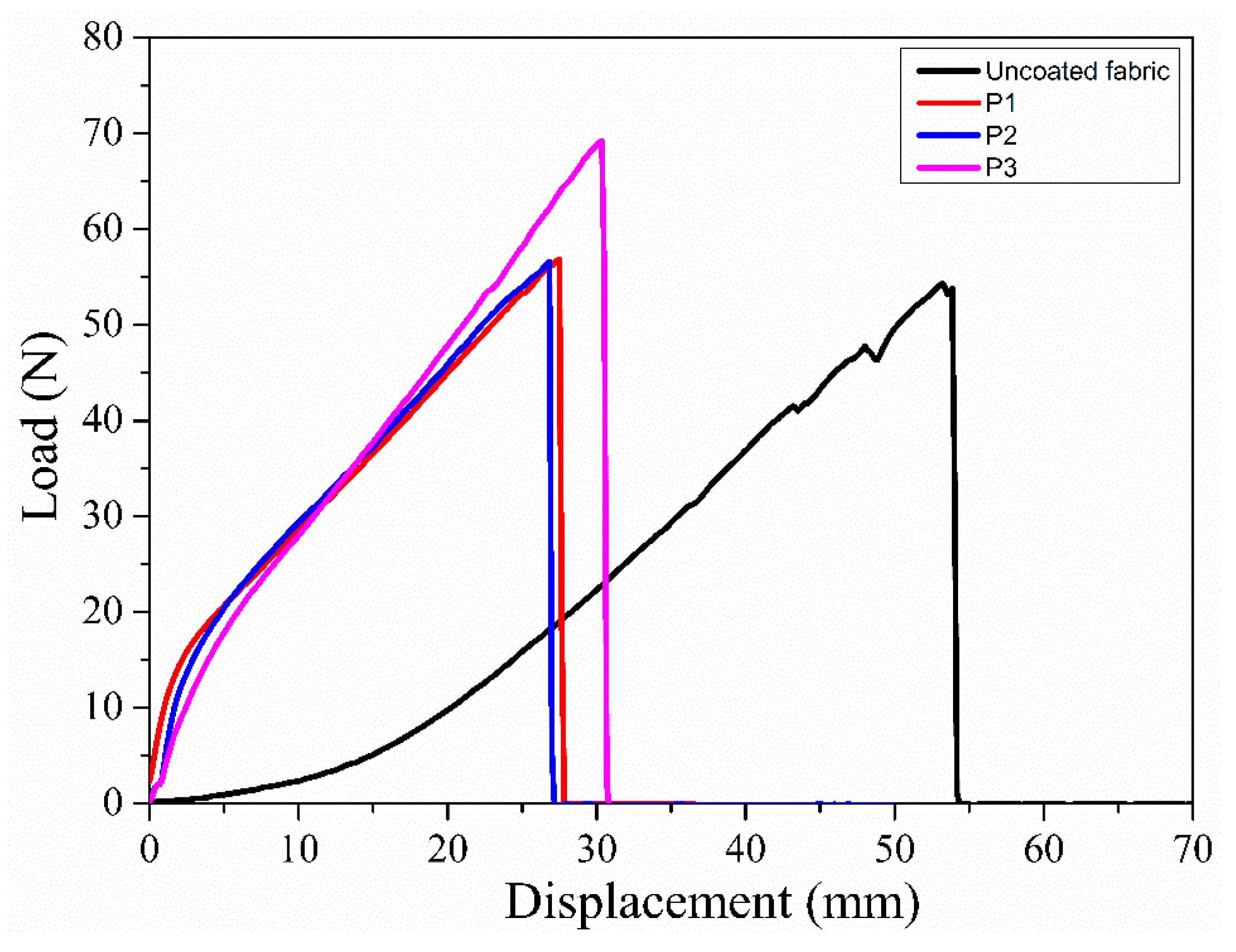
3.8. Mechanical Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.-J.; Matsunaga, Y.T. Thermo-responsive polymers and their application as smart biomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4307–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Meng, H.; Li, G.; Ibekwe, S.I. A review of stimuli-responsive polymers for smart textile applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, F.D.; Theato, P. Temperature-and light-responsive smart polymer materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7468–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo-and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Liu, H. Multi-responsive hydrogels with UCST-and LCST-induced shrinking and controlled release behaviors of rhodamine B. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2018, 82, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, P. A multifunctional skin-like sensor based on a 3D printed thermo-responsive hydrogel. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S. Phase change materials for smart textiles—An overview. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2008, 28, 1536–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Sultana, M.; Alam, M.; Rahman, M.; Tauer, K.; Gafur, M.; Sharafat, M. Evaluating a simple blending approach to prepare magnetic and stimuli-responsive composite hydrogel particles for application in biomedical field. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.S.; Hudson, S.M. Stimuli-reponsive polymers and their bioconjugates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1173–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, H.G. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocić, D. Polymer-Based Smart Coatings for Comfort in Clothing. Tekstilec 2016, 59, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.; Cristea, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Fundueanu, G. Lower critical solution temperature versus volume phase transition temperature in thermoresponsive drug delivery systems. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Liu, B.H.; Liu, W.G. Temperature/pH dual sensitive N-isopropylacrylamide/ polyurethane copolymer hydrogel-grafted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2006, 76, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashari, A.; Hemmatinejad, N.; Pourjavadi, A. Surface modification of cotton fabric with dual-responsive PNIPAAm/chitosan nano hydrogel. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Synthesis and thermosensitive behavior of polyacrylamide copolymers and their applications in smart textiles. Polymers 2015, 7, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D.; Xin, J.H. In-situ study of the structure and dynamics of thermo-responsive PNIPAAm grafted on a cotton fabric. Polymers 2012, 53, 3577–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkova, I.; Vilumsone, A. Microclimate of Smart Garment. Mater. Sci. 2011, 6, 1691–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, M.; Gardner, C.J.; Kim, G.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.; Jin, S.; Chen, R. Reversible humidity sensitive clothing for personal thermoregulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, G.; Dąbrowska, A. Assessment of the thermoregulation properties of textiles with fibres containing phase change materials on the basis of laboratory experiments. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Son, K. Development of thermoregulating textile materials with microencapsulated phase change materials (PCM). II. Preparation and application of PCM microcapsules. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-T.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Sun, H.-S.; Yoshida, K.; Chen, Y.; Satoh, T.; Kakuchi, T.; Chen, W.-C. Synthesis of multifunctional poly (1-pyrenemethylmethacrylate)-b-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly (N-methylolacrylamide)s and their electrospun nanofibers for metal ion sensory applications. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Tung, S.-H.; Kakuchi, T. Synthesis, morphology and sensory applications of multifunctional rod-coil-coil triblock copolymers and their electrospun nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Weng, N.-K.; Wu, W.-C.; Chen, B.-Y.; Cho, C.-J.; Hsu, I.-J.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-C. Novel highly sensitive and reversible electrospun nanofibrous chemosensor-filters composed of poly (HEMA-co-MNA) and bpy-F-bpy with metal-ion-modulated multicolor fluorescence emission. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Hsu, J.-C.; Chen, W.-C. Thermoresponsive luminescent electrospun fibers prepared from poly (DMAEMA-co-SA-co-StFl) multifunctional random copolymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Cho, C.-J.; Liang, F.-C.; Jeng, R.-J. Novel fluorescent chemosensory filter membranes composed of electrospun nanofibers with ultra-selective and reversible pH and Hg2+ sensing characteristics. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 143, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.R.; Frazier, C.E. Cross-linking poly [(vinyl acetate)-co-N-methylolacrylamide] latex adhesive performance part I: N-methylolacrylamide (NMA) distribution. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2007, 27, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganci, E.; Gorur, M. Synthesis, characterization and chemosensing application of poly (methyl methacrylate-co-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) with densyl side group. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. 2016, 3, 565–582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. Synthesis and unusual volume phase transition behavior of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)–poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) interpenetrating polymer network microgel. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H. Synthesis and solution properties of temperature-sensitive copolymers based on NIPAM. J.Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y. In situ gelation of P (NIPAM-HEMA) microgel dispersion and its applications as injecTable 3D cell scaffold. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.N.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hung, J.J.; Kuo, C.C.; Chen, W.C. Multifunctional Electrospun Nanofibers Prepared from Poly ((N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-(N-hydroxymethylacrylamide)) and Their Blends with 1, 2-Diaminoanthraquinone for NO Gas Detection. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2014, 215, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S.; Florea, L.; Fraser, K.; Diamond, D. Swelling and shrinking properties of thermo-responsive polymeric ionic liquid hydrogels with embedded linear pNIPAAM. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5337–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lai, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Fei, B.; Xin, J.H. Temperature-responsive nanofibers for controllable oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51078–51085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, A.S.; Baji, A. Electrospun Janus Membrane for Efficient and Switchable Oil–Water Separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic properties in nature. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordon, P.; David, H. Coupled diffusion of moisture and heat in hygroscopic textile materials. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1967, 10, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, A.S.; Ganesh, V.A.; Sopiha, K.; Sahay, R.; Baji, A. Investigation of wettability and moisture sorption property of electrospun poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nanofibers. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Feed Molar Ratio (%) NIPAAm:HEMA:NMA | Experimental Molar Ratio (%) NIPAAm:HEMA:NMA | Td (°C) | LCST (°C) | Degree of Swelling (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 50:37.5:12.5 | 48.9:37.5:13.6 | 321 | 31.0 | 1153 |
| P2 | 70:22.5:7.5 | 68.8:23.5:7.7 | 329 | 32.5 | 2200 |
| P3 | 90:7.5:2.5 | 88.9:8.3:2.8 | 341 | 35.5 | 687 |
| Sample | WCA in Air | OCA in Air | ||
| Below LCST | Above LCST | Below LCST | Above LCST | |
| P1 | 0° | 76° | 0° | 0° |
| P2 | 0° | 78° | 0° | 0° |
| P3 | 0° | 102° | 0° | 0° |
| Sample | WCA under oil | OCA under water | ||
| Below LCST | Above LCST | Below LCST | Above LCST | |
| P1 | 81° | 89° | 92° | 105° |
| P2 | 91° | 106° | 119° | 100° |
| P3 | 116° | 115° | 134° | 114° |
| Sample | 20 °C | 37 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption (%) | Release (%) | Absorption (%) | Release (%) | |
| P1 | 5.04 | 3.40 | 2.41 | 2.09 |
| P2 | 7.48 | 5.68 | 3.27 | 3.14 |
| P3 | 6.30 | 3.78 | 2.17 | 1.91 |
| PET | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.26 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhuri, S.; Wu, C.-M. Switchable Wettability of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA) Coated PET Fabric for Moisture Management. Polymers 2020, 12, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010100
Chaudhuri S, Wu C-M. Switchable Wettability of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA) Coated PET Fabric for Moisture Management. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhuri, Shamik, and Chang-Mou Wu. 2020. "Switchable Wettability of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA) Coated PET Fabric for Moisture Management" Polymers 12, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010100
APA StyleChaudhuri, S., & Wu, C.-M. (2020). Switchable Wettability of Poly(NIPAAm-co-HEMA-co-NMA) Coated PET Fabric for Moisture Management. Polymers, 12(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010100