Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CB Modification
2.1.1. 4-Aminobenzoyl-Functionalized Carbon Black (ABCB)
2.1.2. Benzoxazine-Functionalized Carbon Black (BZCB)
2.1.3. Ag-Anchored ABCB (Ag-ABCB)
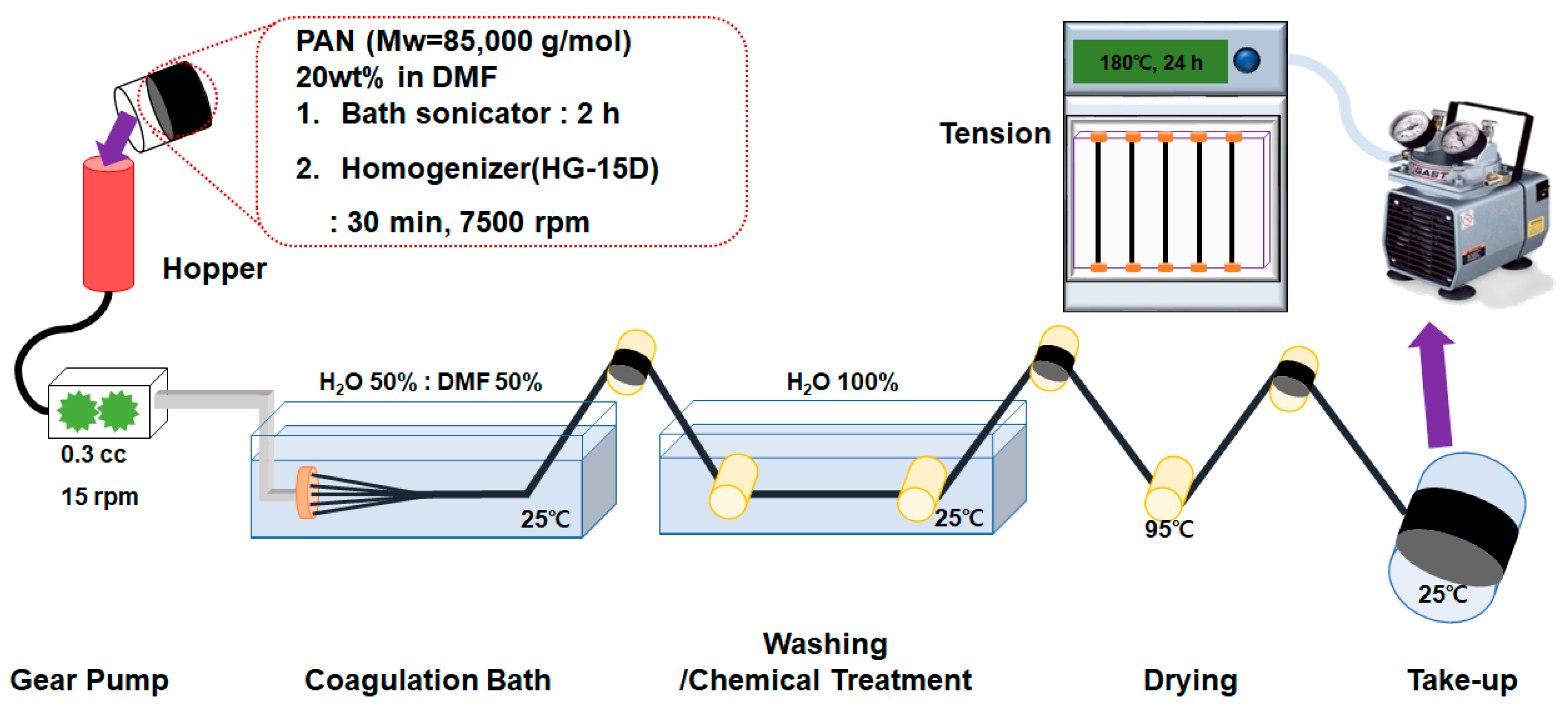
2.2. Preparation of Fibers
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CB Functionalization
3.2. Thermal Properties of Modified CB
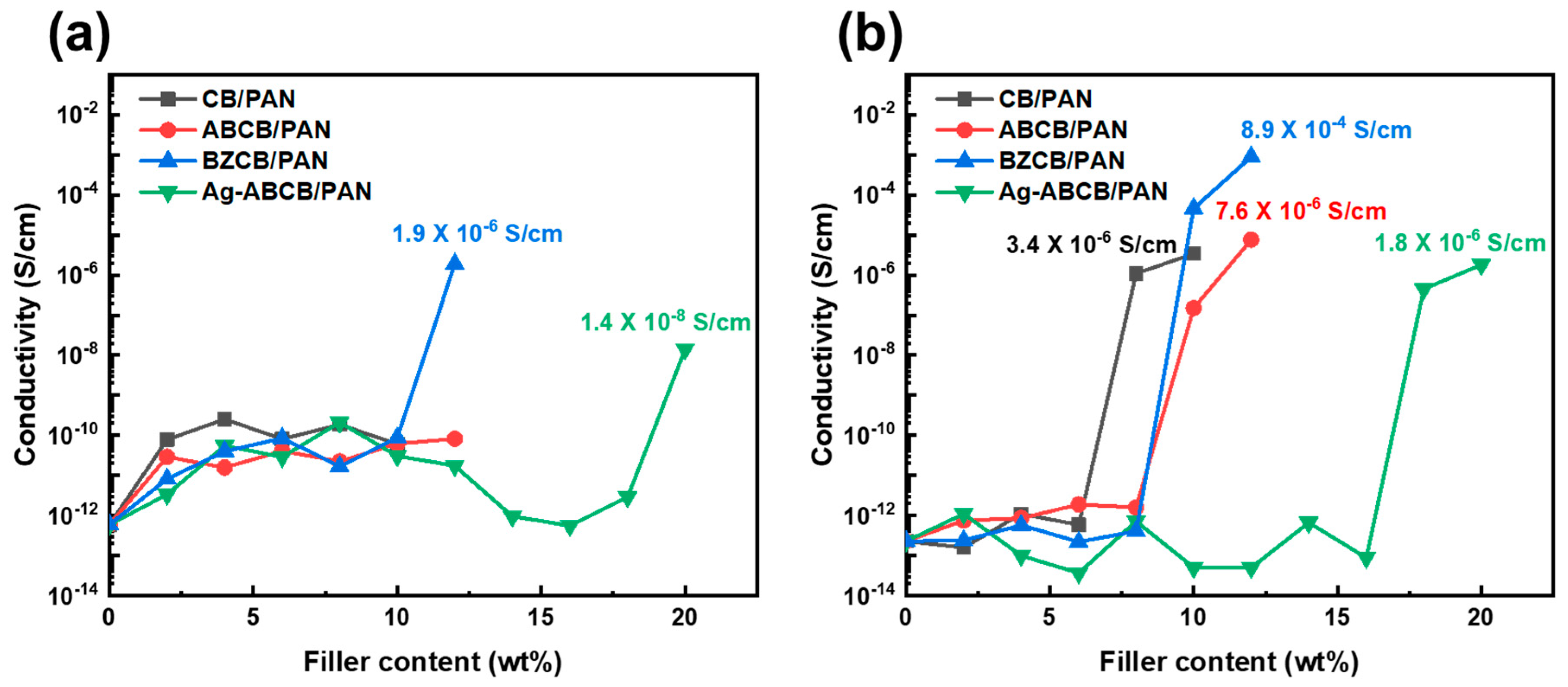
3.3. Electrical Properties of Modified CB/PAN Fibers
3.4. Effect of Annealing on Fiber Diameter
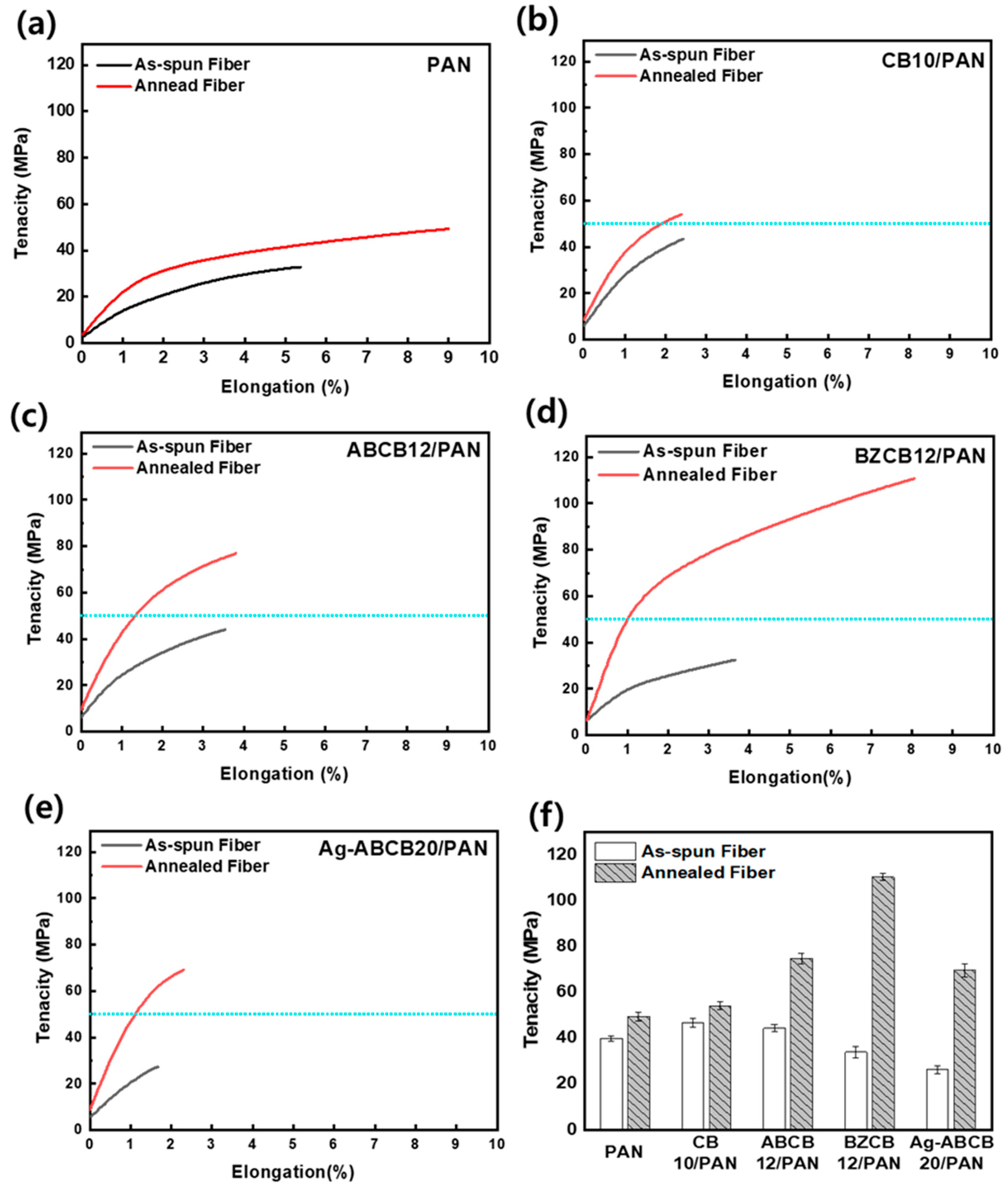
3.5. Mechanical Properties of Modified CB/PAN Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.M. Fiber-Based Wearable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Fabrication, Devices, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancos, L.; Thronickle, W.; Ristol, S. Smart Fabrics White Paper; Atos: Bezons, French, 2017; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.F.; Menezes, F.; Montagna, L.S. Preparation and characterization of antistatic packaging for electronic components based on poly(lactic acid)/carbon black composites. J. Appl. Polym. 2019, 136, 47273–47280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 319–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Polyhedra Nanopapers: An Advanced Binder-Free Electrode for High-Performance Supercapacitors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5240–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T. Electronic Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 1–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yeom, B.; Prima, M.D.; Su, X.; Kim, J.G. A stretchable nanoparticle conductors with self-organized conductive pathways. Nature 2013, 500, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssefi, M.; Fanaei, E.; Shanbeh, M. Strain Sensors Based on Electroless Ni-P Plated Polyester Woven Fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Long, G.; Hu, X.; Wong, K.; Lau, W.; Fan, M. Conductive polymer nanocomposites with hierarchical multi-scale structures via self-assembly of carbon-nanotubes on graphene on polymer-microspheres. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7877–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Ahmad, S.; Chiu, F.-C. Graphene oxide dispersed polyvinyl chloride/alkyd green nanocomposite film: Processing and physico-mechanical properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 68, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide/carboxymethylcellulose/alginate composite blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.B.; Bansal, R.C.; Wang, M.J. Carbon Black: Science and Technology; Marcel Decker: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 1–461. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, I.J.; Peeten, T.L. Carbon Black: Production, Properties, and Uses; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–293. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C. Carbon black filled conducting polymers and polymer blends. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2002, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Ahn, D.; Lee, S.; Yeo, S.Y. Electrical properties of silver-attached amine functionalized carbon black/polyethylene terephthalate fibers prepared by melt-spinning. Polymers 2019, 11, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Chang, S.S.; Lian, N.Y. Preparation and characterization of carbon black/polybutylene terephthalate/polyethylene terephthalate antistatic fiber with sheath–core structure. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Saito, K.; Sawa, G.; Kitagawa, K. Percolation threshold of carbon black-polyethylene composites. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 36, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Xiao, D.; Erogbogbo, F.; Keles, O. A hierarchical approach for creating electrically conductive network structure in polyurethane nanocomposites using a hybrid of graphene nanoplatelets, carbon black and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 161, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.S.; Huang, W.M.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.J.; Du, S.Y. Significantly reducing electrical resistivity by forming conductive Ni chains in a polyurethane shape-memory polymer/carbon-black composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 204101–204103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.T.; Sabo, A.; Pica, A.P. Electrical permittivity and conductivity of carbon black-polyvinyl chloride composites. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 6867–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, C.P.; Gerspacher, M.; Nikiel, L. Carbon black dispersion by electrical measurements. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2000, 53, 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, D.; Yeo, S.Y.; Lee, S. Electrical percolation threshold of carbon black in a polymer matrix and its application to antistatic fiber. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6338–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Han, S.W.; Kwon, Y.D.; Tan, L.S.; Baek, J.B. Functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with various 4-substituted benzoic acids in mild polyphosphoric acid/phosphorous pentoxide. Carbon 2008, 46, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, R.; Espinosa, M.A.; Galia, M.; Diz, V.C.; Ronda, J.C.; Reina, J.A. Synthesis of Novel Benzoxazines Containing Glycidyl Groups: A Study of the Crosslinking Behavior. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2006, 44, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yeo, S.Y. Highly conductive polymer/metal/carbon nanotube composite fibre prepared by the melt-spinning process. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazinani, S.; Ajji, A.; Dubois, C. Structure and properties of melt-spun PET/MWCNT nanocomposite fibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.M.; Tan, L.S.; Baek, J.B. Defect/Edge-selective functionalization of carbon materials by direct friedel–crafts acylation reaction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606317–1606325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.H.; Chen, J.K.; Cheng, C.C.; Su, C.I.; Chang, F.C. Low-surface-free-energy polybenzoxazine/polyacrylonitrile fibers for biononfouling membrane. Polymer 2013, 54, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Agag, T. Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–712. [Google Scholar]
- Chook, S.W.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Ayob, M.K.; Chee, K.L.; Huang, N.M.; Neoh, H.M.; Lim, H.N.; Jamal, R.; Rahman, R.M.F.R.A. Antibacterial performance of Ag nanoparticles and AgGO nanocomposites prepared via rapid microwave-assisted synthesis method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadik-Khanolkar, S.; Donthula, S.; Sotiriou-Leventis, C.; Leventis, N. Polybenzoxazine aerogels. 1.high-yield room-temperature acid catalyzed synthesis of robust monoliths, oxidative aromatization, and conversion to microporous carbons. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.G.; Liao, C.S. Benzoxazine as a reactive noncovalent dispersant for carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36012–36016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xing, D.; Xie, Y.; Teh, K.S.; Zhang, B.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y. Electrical conductivity investigation of a nonwoven fabric composed of carbonfibers and polypropylene/polyethylene core/sheath bicomponentfibers. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.R.; Gong, T.; Pu, J.H.; Bao, R.-Y.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, M.B.; Yang, W. Effect of phase coarsening under melt annealing on the electrical performance of polymer composites with a double percolation structure. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Minus, M.L.; Chae, H.G.; Kumar, S. Processing, Structure, and Properties of PAN/MWNT Composite Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Cayla, A.; Odent, S.; Lutz, V.; Devaux, E.; Campagne, C. Processing and characterization of polyethersulfone wet-spun nanocomposite fibres containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Synth. Met. 2016, 217, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Diameter (µm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN | CB10/PAN | ABCB12/PAN | BZCB12/PAN | Ag-ABCB20/PAN | |
| As-spun Fiber | 53.9 ± 1.3 | 48.5 ± 1.3 | 43.6 ± 1.0 | 39.9 ± 0.5 | 43.6 ± 0.9 |
| Annealed Fiber | 41.4 ± 2.3 | 41.9 ± 0.4 | 36.7 ± 1.5 | 36.2 ± 0.6 | 34.1 ± 0.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, D.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, H.-d.; Yeo, S.Y. Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black. Polymers 2020, 12, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010179
Ahn D, Choi H-J, Kim H-d, Yeo SY. Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Damiro, Hyun-Jung Choi, Ho-dong Kim, and Sang Young Yeo. 2020. "Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black" Polymers 12, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010179
APA StyleAhn, D., Choi, H.-J., Kim, H.-d., & Yeo, S. Y. (2020). Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black. Polymers, 12(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010179




