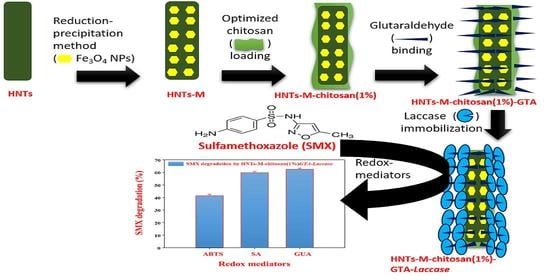
Chitosan-Grafted Halloysite Nanotubes-Fe3O4 Composite for Laccase-Immobilization and Sulfamethoxazole-Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
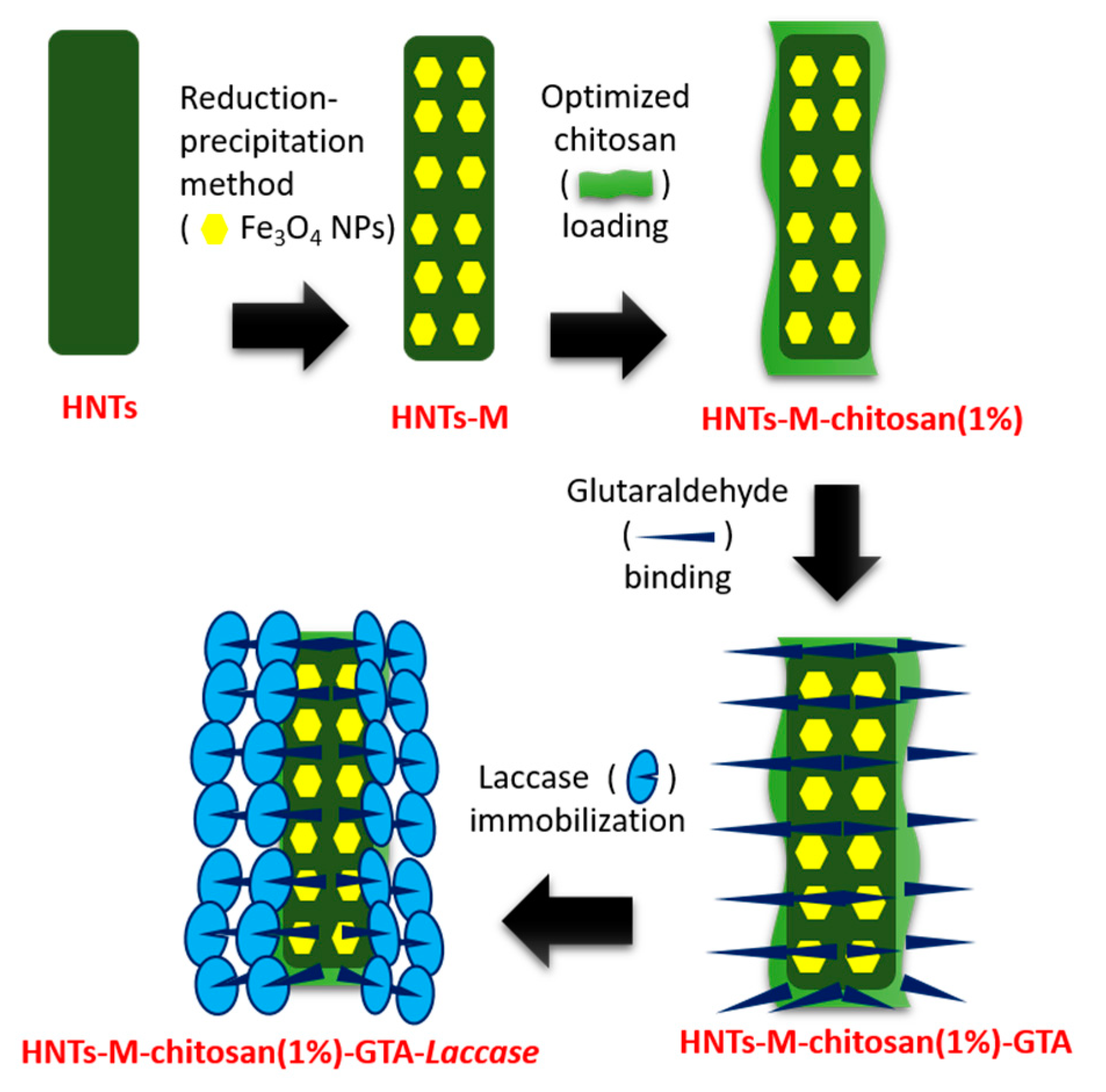
2.2. Synthesis of HNTs-M-Chitosan
2.3. Laccase Immobilization on Synthesized Materials
2.4. Characterizations of Nano-Supports
2.5. Immobilized Laccase Biocatalysis
2.6. SMX Degradation by HNTs-M-Chitosan (1%)-GTA-Laccase
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
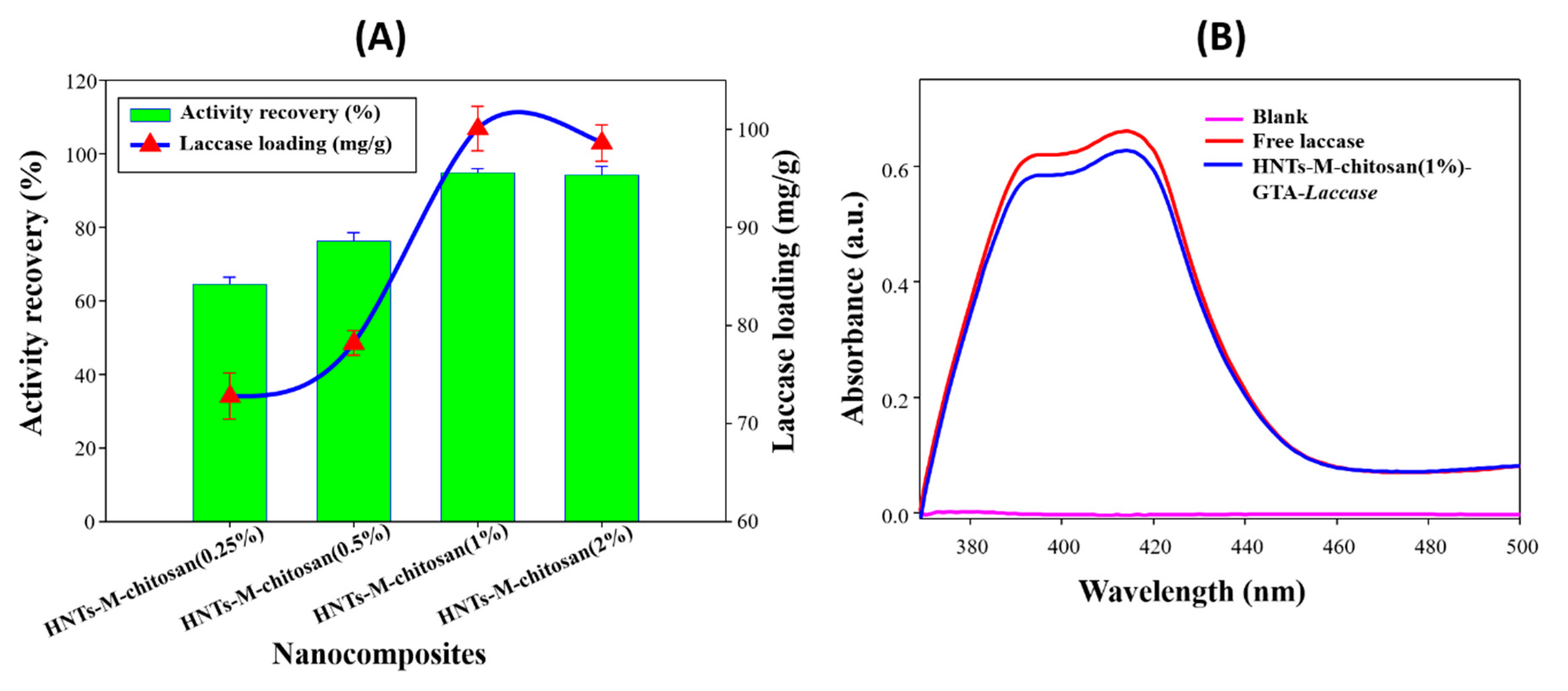
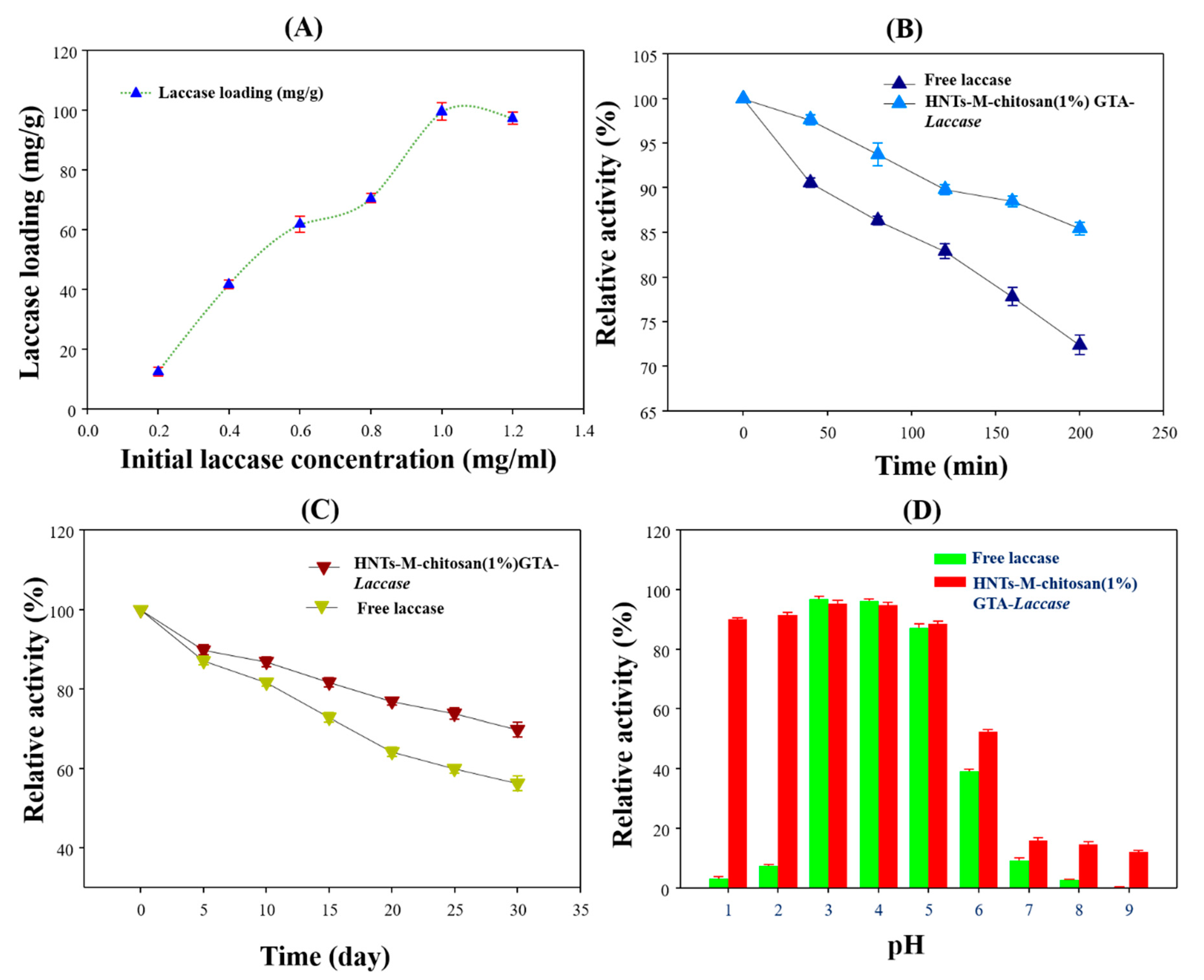
3.2. Laccase Immobilization on Developed Nano-Supports
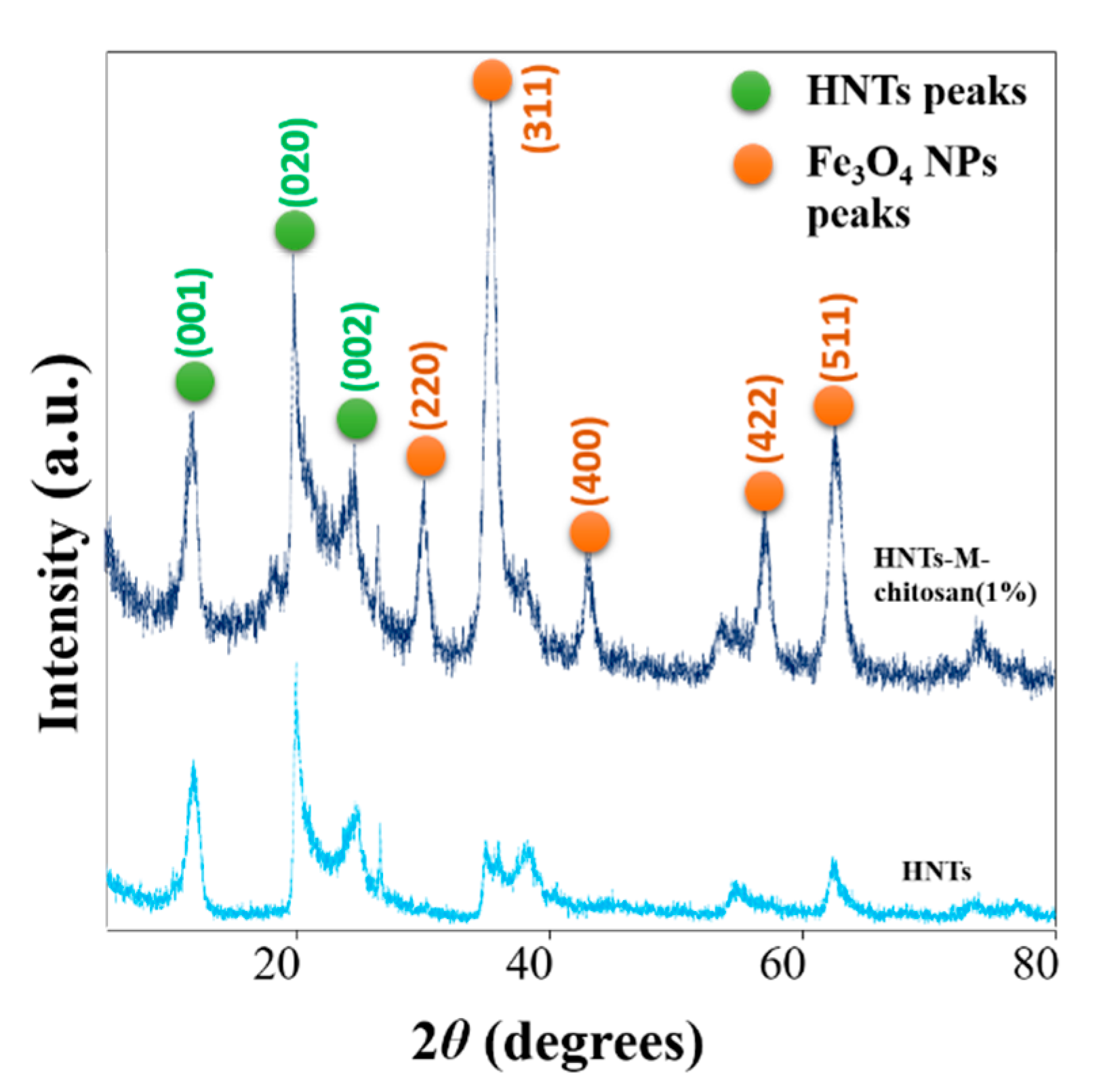
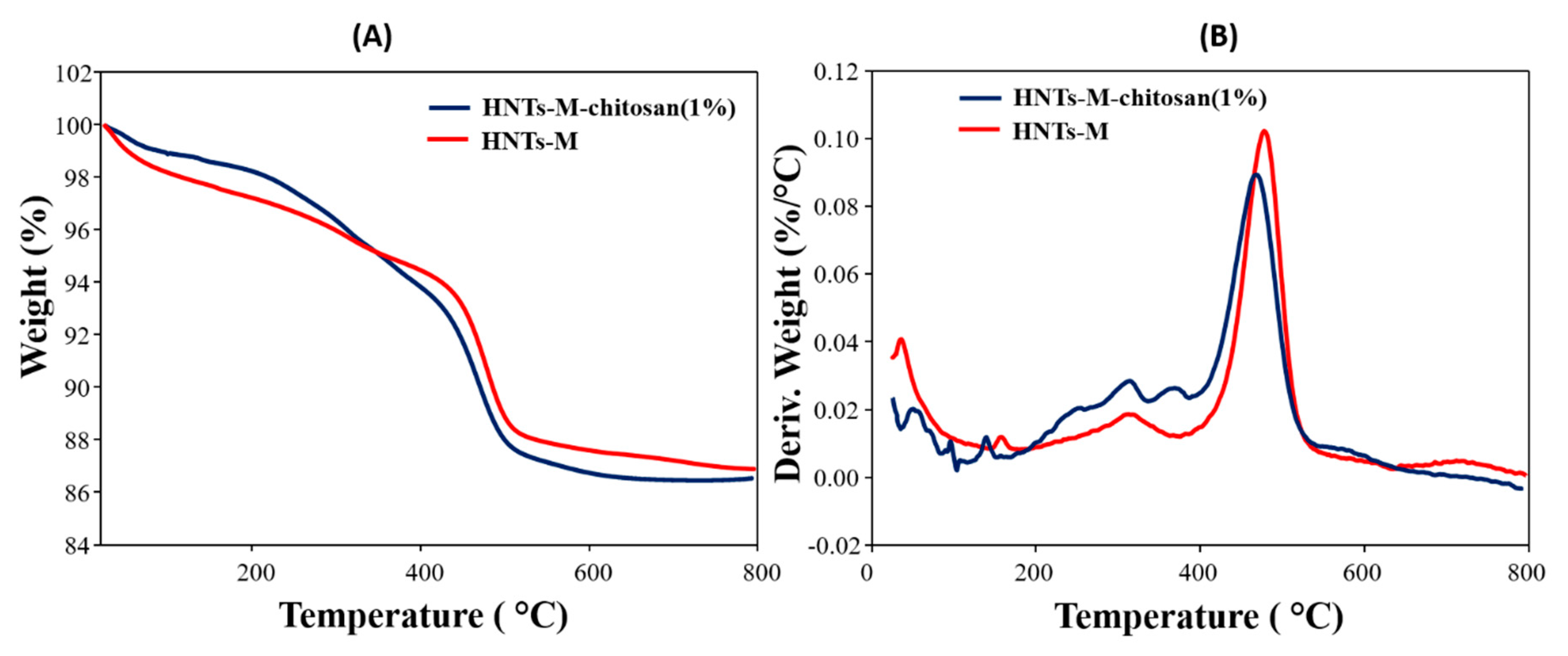
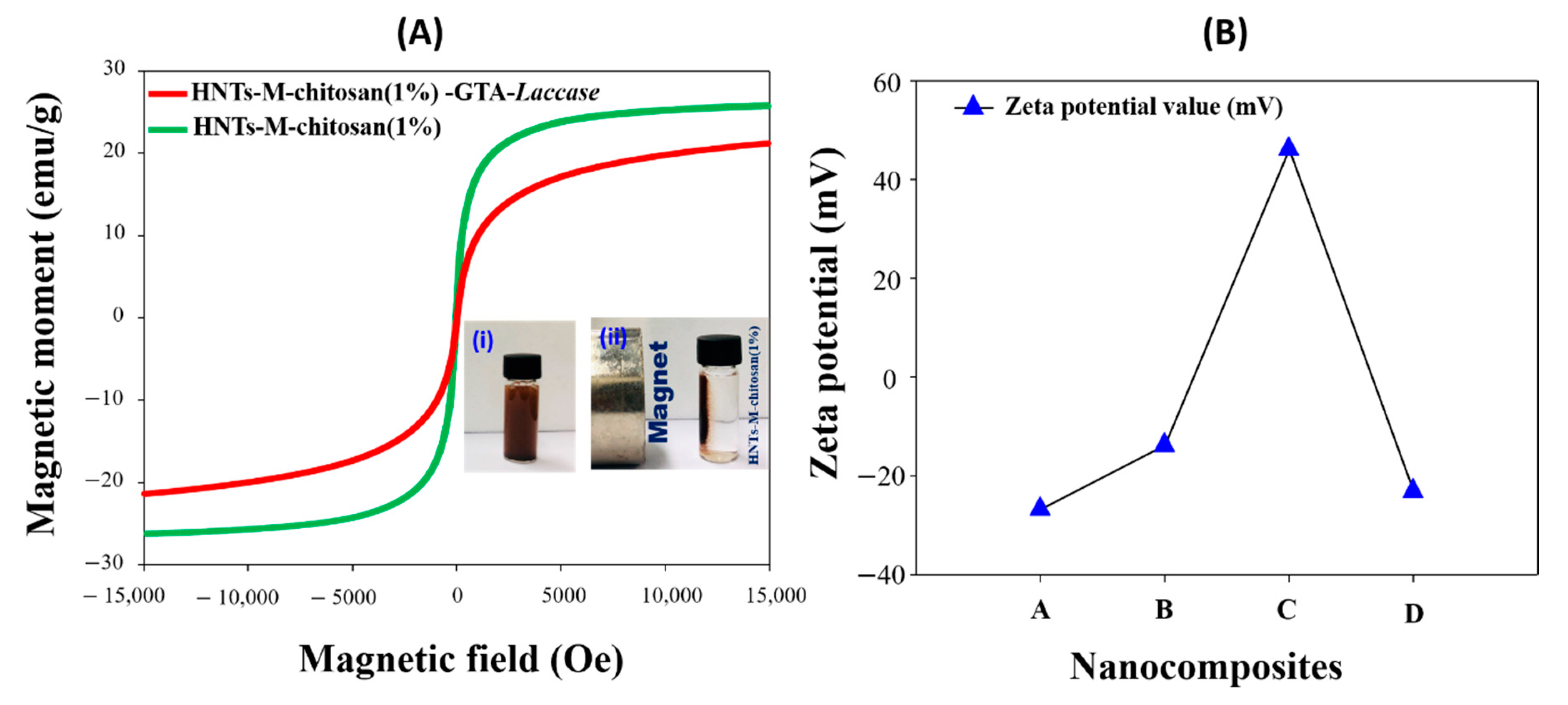
3.3. Characterizations
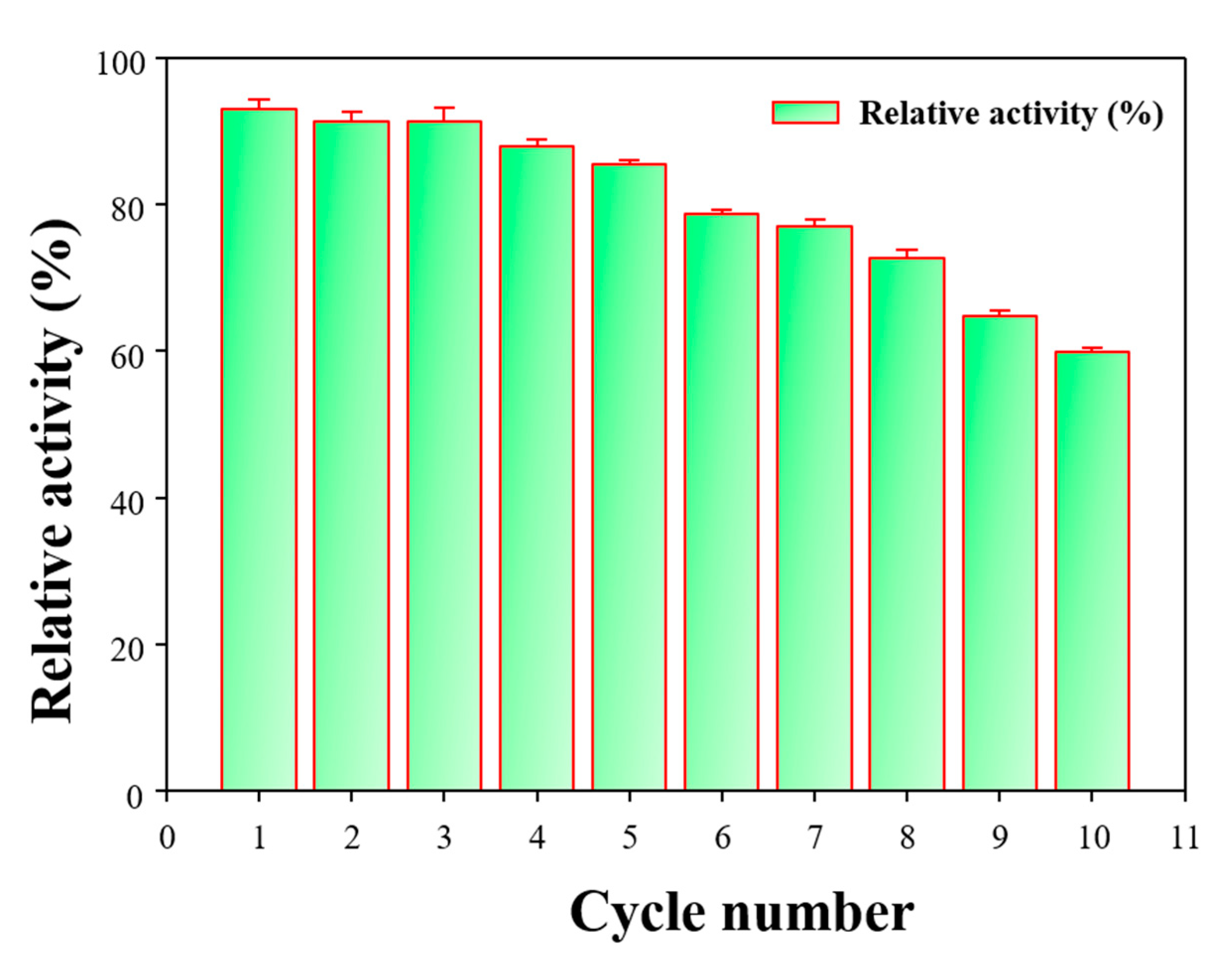
3.4. Bio-Catalytic Properties of HNTs-M-Chitosan (1%)-GTA-Laccase
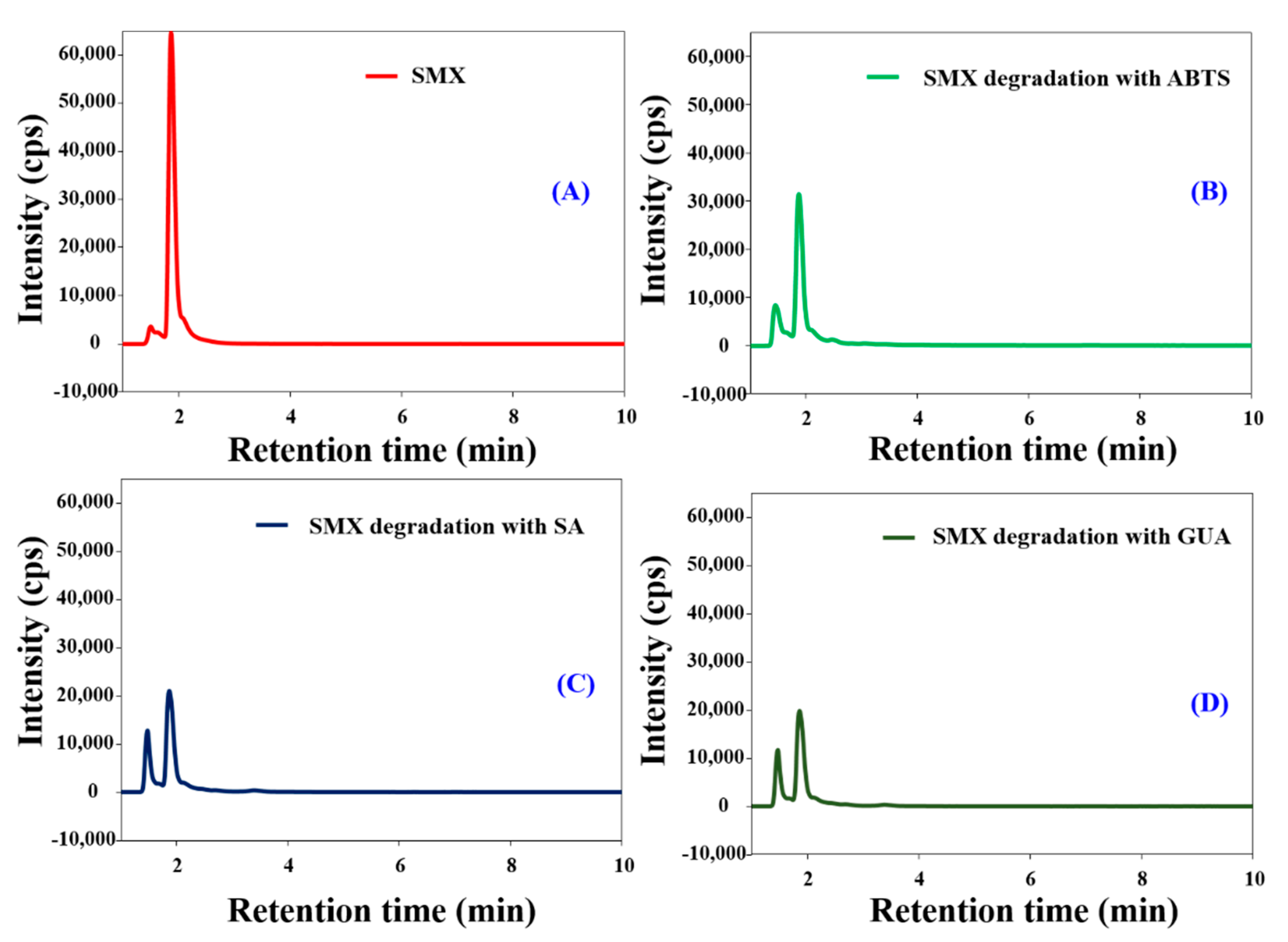
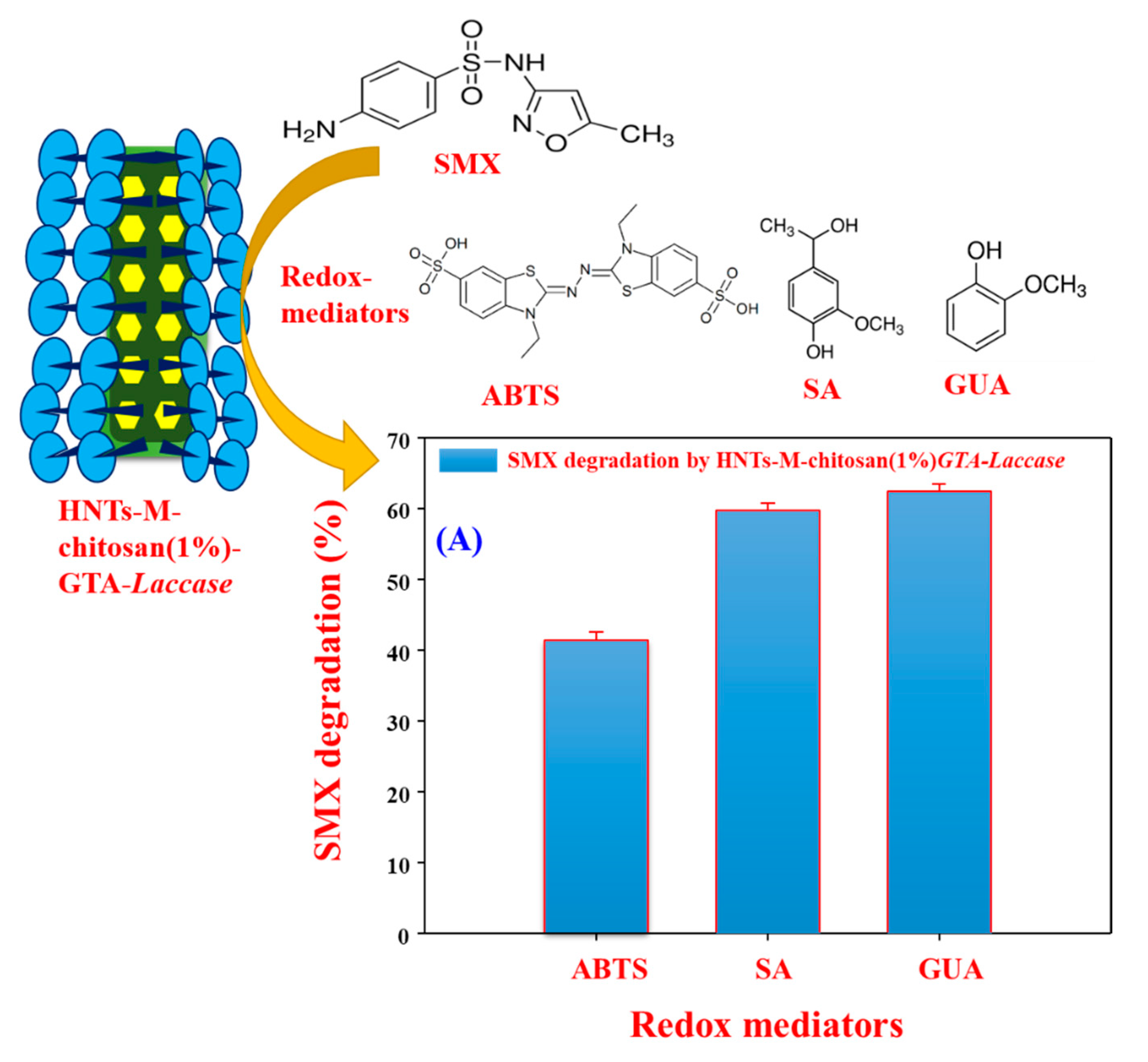
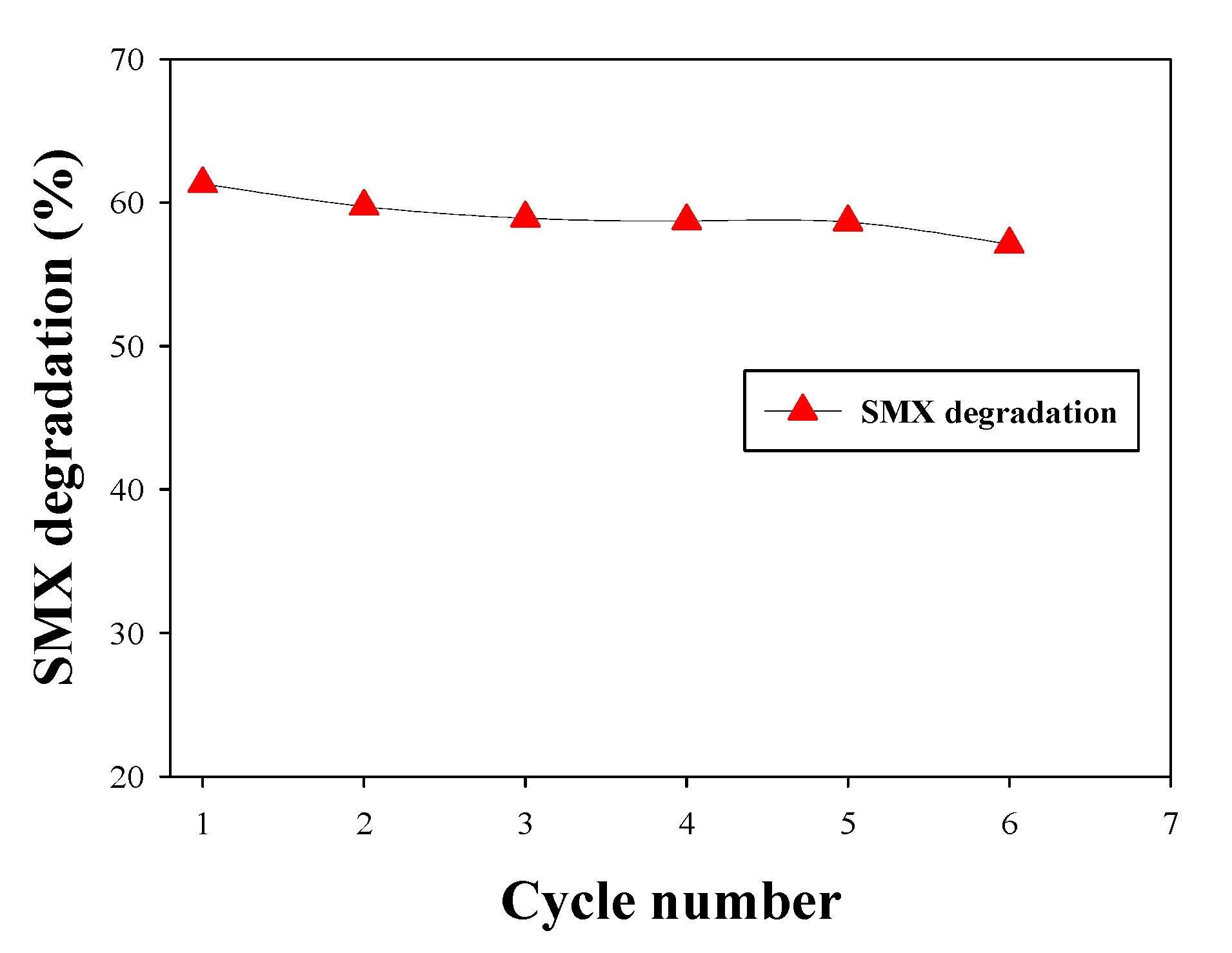
3.5. Biocatalytic Degradation of SMX
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, J.; Fu, J.J.; Wang, Q.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Laccase: A green catalyst for the biosynthesis of poly-phenols. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Zhao, Y.; Noreen, S.; Shah, S.Z.H.; Bharagava, R.N.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Modifying bio-catalytic properties of enzymes for efficient biocatalysis: A review from immobilization strategies viewpoint. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2019, 37, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Editorial for special issue: Enzyme immobilization and its applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Puna, J.; Gomes, J. A review on bio-based catalysts (immobilized enzymes) used for biodiesel production. Energies 2020, 13, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y. Laccase Immobilization for Water Purification: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 403, 126272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Tran, V.H.; Merenda, A.; Johir 1, M.A.H.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H. Removal of organic micro-pollutants by conventional membrane bioreactors and high-retention membrane bioreactors. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhu, M. Visible-light-assisted peroxymonosulfate activation over Fe(II)/V(IV) self-doped FeVO4 nanobelts with enhanced sulfamethoxazole degradation: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Munguambe, D.M.; Tharmavaram, M.; Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Manuscript title: Halloysite nanotubes-An efficient ‘nano-support’ for the immobilization of α-amylase. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 136, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danyliuk, N.; Tomaszewska, J.; Tatarchuk, T. Halloysite nanotubes and halloysite-based composites for environmental and biomedical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.A.; Jang, J.; Lee, D.S. Supermagnetically Tuned Halloysite Nanotubes Functionalized with Aminosilane for Covalent Laccase Immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15492–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin. Polymers 2020, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Huang, Z.; Jin, L.; Ba, X.; Li, Y.; You, L.; et al. Etching of halloysite nanotubes hollow imprinted materials as adsorbent for extracting of Zearalenone from grain samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, L.; Hueso, J.L.; Ortega-Liébana, M.C.; Santamaría, J.; Cronin, S.B. Evaluation of gold-decorated halloysite nanotubes as plasmonic photocatalysts. Catal. Commun. 2014, 56, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, J.; Yan, H.; Huang, X.; Tan, Y. Advances in Halloysite nanotubes-polysaccharide nanocomposite preparation and applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Wei, R.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y. Chemosphere Fabrication, application, optimization and working mechanism of Fe2O3 and its composites for contaminants elimination from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.; Jee, S.C.; Sung, J.S.; Kadam, A.A. Anti-proliferative applications of laccase immobilized on super-magnetic chitosan-functionalized halloysite nanotubes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Lema, S.; Terol, J.; Fages, E.; Balart, R.; Quiles-Carrillo, L.; Prieto, C.; Torres-Giner, S. Microencapsulation of Copper(II) Sulfate in Ionically Cross-Linked Chitosan by Spray Drying for the Development of Irreversible Moisture Indicators in Paper Packaging. Polymers 2020, 12, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Layered composite based on halloysite and natural polymers: A carrier for the pH controlled release of drugs. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10887–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Core/Shell Gel Beads with Embedded Halloysite Nanotubes for Controlled Drug Release. Coatings 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolinoa, V.; Cavallaroa, G.; Miliotoa, S.; Lazzaraa, G. Polysaccharides/Halloysite nanotubes for smart bionanocomposite materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabermawi, N.M.; Arif, M.; Elsaber, G.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-hakim, Y.M.A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2726–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, A.A.; Jang, J.; Jee, S.C.; Sung, J.S.; Lee, D.S. Chitosan-functionalized supermagnetic halloysite nanotubes for covalent laccase immobilization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, K.; Antorini, M.; Choinowski, T. Crystal structure of a laccase from the fungus Trametes versicolor at 1.90-A resolution containing a full complement of coppers. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37663–37669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodake, G.S.; Yang, J.; Shinde, S.S.; Mistry, B.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Sung, J.S.; Kadam, A.A. Paper waste extracted α-cellulose fibers super-magnetized and chitosan-functionalized for covalent laccase immobilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18687–18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H.; Chang, S. Chitosan modified halloysite nanotubes as emerging porous microspheres for drug carrier. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Miao, S.; Suo, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y. Co-immobilization of laccase and ABTS onto amino-functionalized ionic liquid-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for pollutants removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Liu, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, X. Immobilization of laccase on phase-change microcapsules as self- thermoregulatory enzyme carrier for biocatalytic enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 405, 126695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X. Laccase immobilized on chitosan-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as reusable biocatalyst for degradation of chlorophenol. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1220, 128769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zofair, S.F.F.; Arsalan, A.; Khan, M.A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Younus, H. Immobilization of laccase on Sepharose-linked antibody support for decolourization of phenol red. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricov, L.; Leonties, A.R.; Gîfu, I.C.; Preda, D.; Raducan, A.; Anghel, D.F. Enhancement of laccase immobilization onto wet chitosan microspheres using an iterative protocol and its potential to remove micropollutants. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Li, R. Laccase-mediator system assembling co-immobilized onto functionalized calcium alginate beads and its high-efficiency catalytic degradation for acridine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, Y. Laccase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles modified by amino-functionalized ionic liquid via dialdehyde starch for phenolic compounds biodegradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katana, B.; Rouster, P.; Varga, G.; Muráth, S.; Glinel, K.; Jonas, A.M.; Szilagyi, I. Self-Assembly of Protamine Biomacromolecule on Halloysite Nanotubes for Immobilization of Superoxide Dismutase Enzyme. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouster, P.; Dondelinger, M.; Galleni, M.; Nysten, B.; Jonas, A.M.; Glinel, K. Layer-by-layer assembly of enzyme-loaded halloysite nanotubes for the fabrication of highly active coatings. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Panchal, A.; Fakhrullin, R.; Stavitskaya, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y. An assembly of organic-inorganic composites using halloysite clay nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huang, G.W.; Shen, X.J.; Xiao, H.M.; Fu, S.Y. Controllable fabrication and magnetic-field assisted alignment of Fe3O4-coated Ag nanowires via a facile co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4879–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Deng, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhong, S. PEGylated thermo-sensitive bionic magnetic core-shell structure molecularly imprinted polymers based on halloysite nanotubes for specific adsorption and separation of bovine serum albumin. Polymers 2020, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Jia, Z.; Hu, D.; Luo, Y.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Surface modification of halloysite nanotubes by vulcanization accelerator and properties of styrene-butadiene rubber nanocomposites with modified halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Immobilization of naringinase from penicillium decumbens on chitosan microspheres for debittering grapefruit juice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masjoudi, M.; Golgoli, M.; Nejad, Z.G.; Sadeghzadeh, S.; Borghei, S.M. Pharmaceuticals Removal by Immobilized Laccase on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanocomposite with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 128043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.; Ma, N.L.; Zhang, W.; Lei, Z.; Su, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; et al. Innovative hydrolysis of corn stover biowaste by modified magnetite laccase immobilized nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, H.; Kadam, A.; Paul, D.; Govindwar, S. A Low-Cost Wheat Bran Medium for Biodegradation of the Benzidine-Based Carcinogenic Dye Trypan Blue Using a Microbial Consortium. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3480–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.S.; Cheung, M.K.; Au, C.H.; Kwan, H.S. A Novel Lentinula edodes Laccase and Its Comparative Enzymology Suggest Guaiacol-Based Laccase Engineering for Bioremediation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Material Name | Laccase Loading Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| MACS-NIL-Cu-Laccase | 47 | [28] |
| LA-Au/PDA@SiO2-MEPCM | 50 | [29] |
| Fe3O4@Chitosan | 32 | [30] |
| A-M-HNTs | 84 | [10] |
| M-PW-αCF-CTA | 73 | [24] |
| M-HNTs–CTA | 92 | [22] |
| Sepharose-linked antibody | 33 | [31] |
| Chitosan microspheres | 8 | [32] |
| PD-GMA-Ca@ABTS beads | 8 | [33] |
| Fe3O4-NIL-DAS@lac | 60 | [34] |
| HNTs-M-chitosan (1%) | 100 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadam, A.A.; Shinde, S.K.; Ghodake, G.S.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Sharma, B.; Hyun, S.; Sung, J.-S. Chitosan-Grafted Halloysite Nanotubes-Fe3O4 Composite for Laccase-Immobilization and Sulfamethoxazole-Degradation. Polymers 2020, 12, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102221
Kadam AA, Shinde SK, Ghodake GS, Saratale GD, Saratale RG, Sharma B, Hyun S, Sung J-S. Chitosan-Grafted Halloysite Nanotubes-Fe3O4 Composite for Laccase-Immobilization and Sulfamethoxazole-Degradation. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102221
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadam, Avinash A., Surendra K. Shinde, Gajanan S. Ghodake, Ganesh D. Saratale, Rijuta G. Saratale, Bharat Sharma, Seunghun Hyun, and Jung-Suk Sung. 2020. "Chitosan-Grafted Halloysite Nanotubes-Fe3O4 Composite for Laccase-Immobilization and Sulfamethoxazole-Degradation" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102221
APA StyleKadam, A. A., Shinde, S. K., Ghodake, G. S., Saratale, G. D., Saratale, R. G., Sharma, B., Hyun, S., & Sung, J.-S. (2020). Chitosan-Grafted Halloysite Nanotubes-Fe3O4 Composite for Laccase-Immobilization and Sulfamethoxazole-Degradation. Polymers, 12(10), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102221